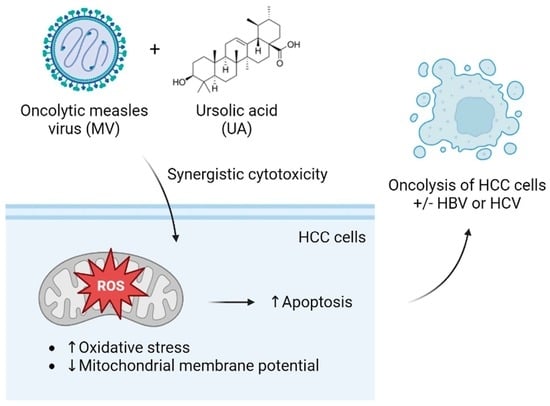
Combination of Oncolytic Measles Virus and Ursolic Acid Synergistically Induces Oncolysis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture, Virus, and Reagents
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Evaluation of Synergistic Effect
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide Double Staining
2.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection by 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein Diacetate (H2DCFDA) Staining
2.7. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) Measurement
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
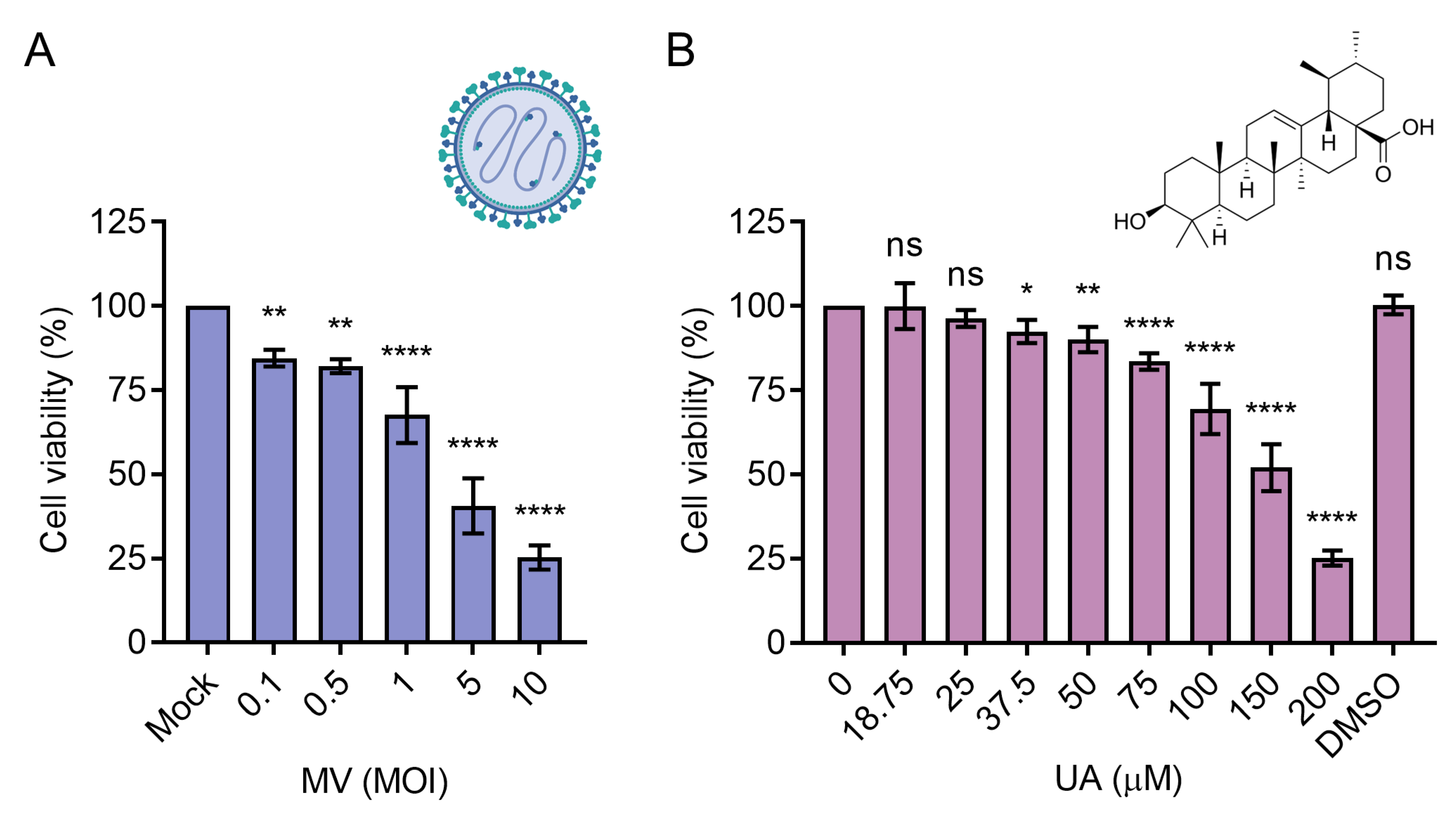
3.1. Cytotoxicity of UA and Oncolytic MV on HCC Cells
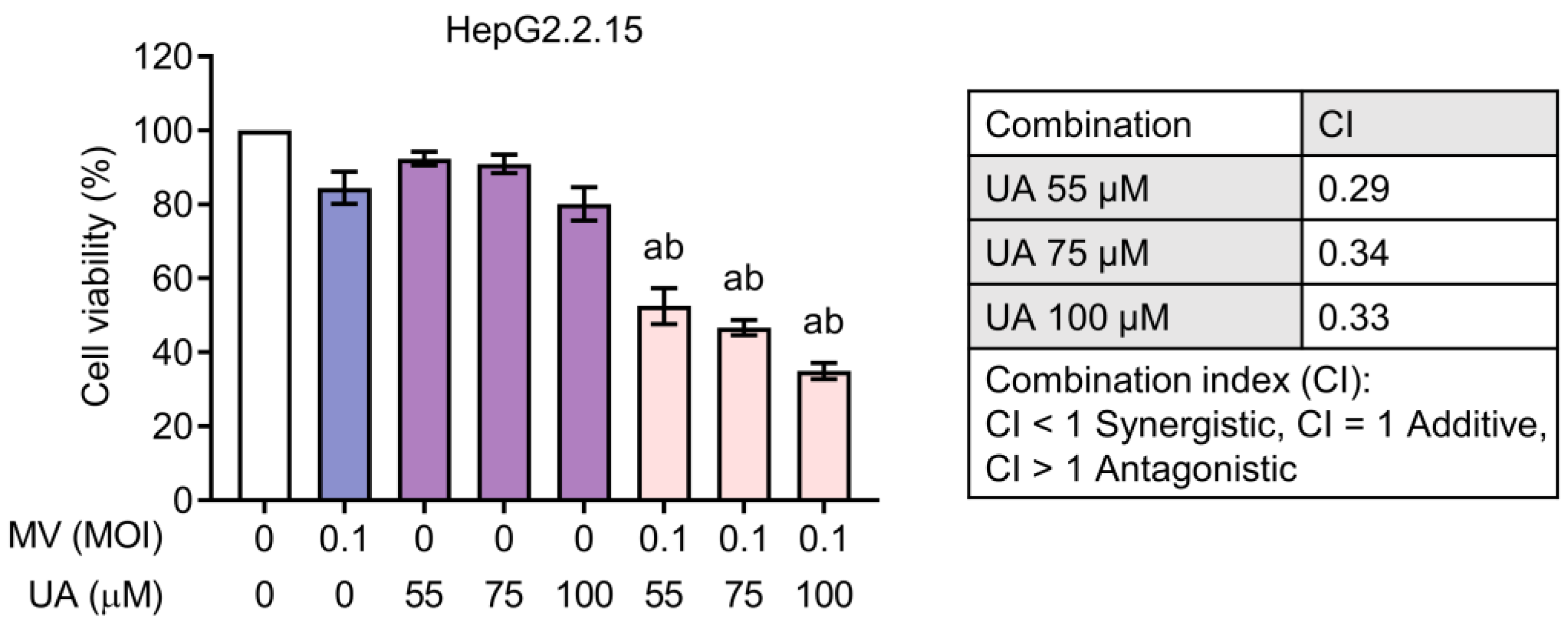
3.2. Combinations of MV and UA Treatment Produce Synergistic Killing Effect
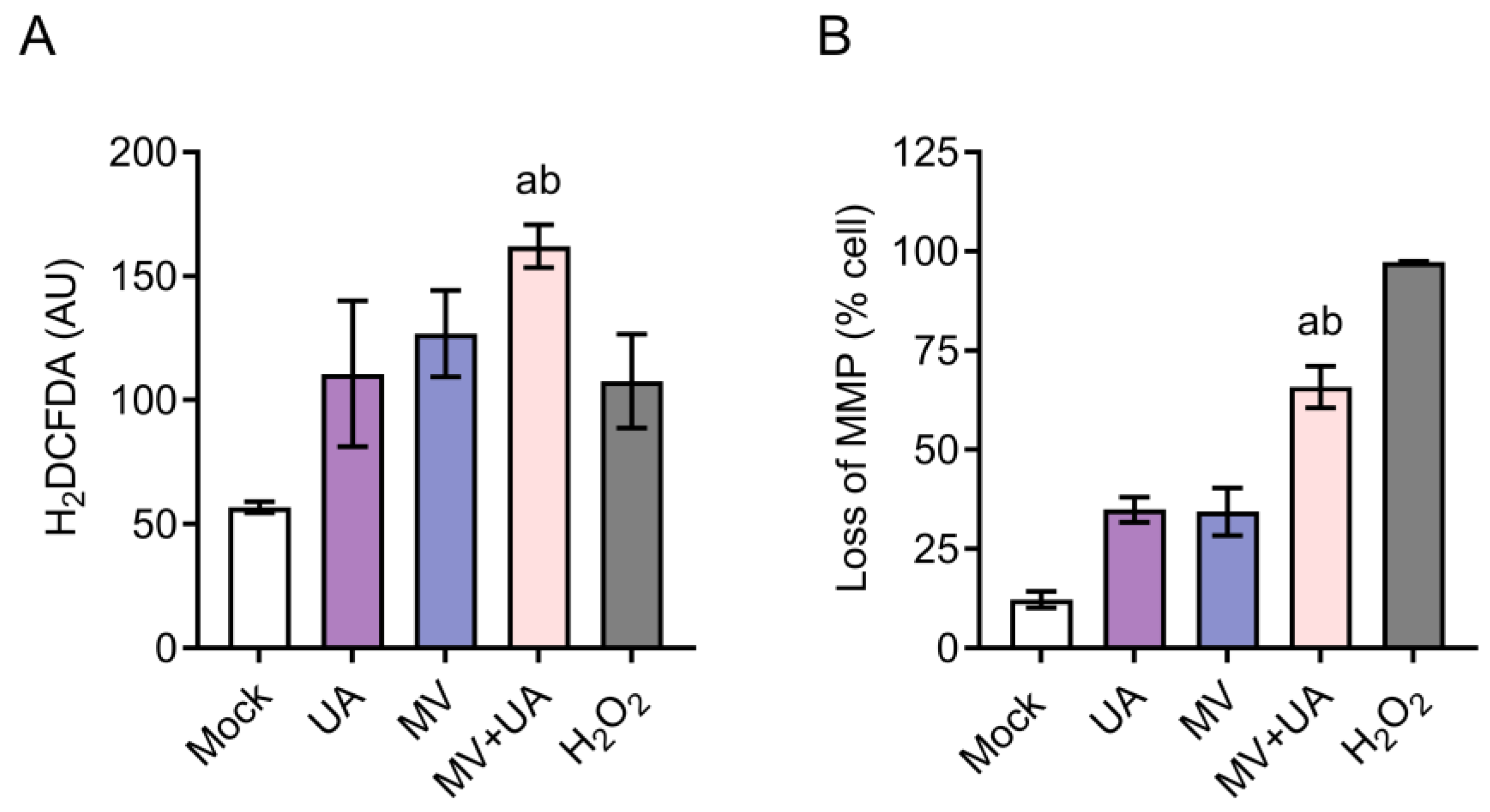
3.3. Combination Treatment of UA and MV Promotes Apoptosis due to Increased Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Damage
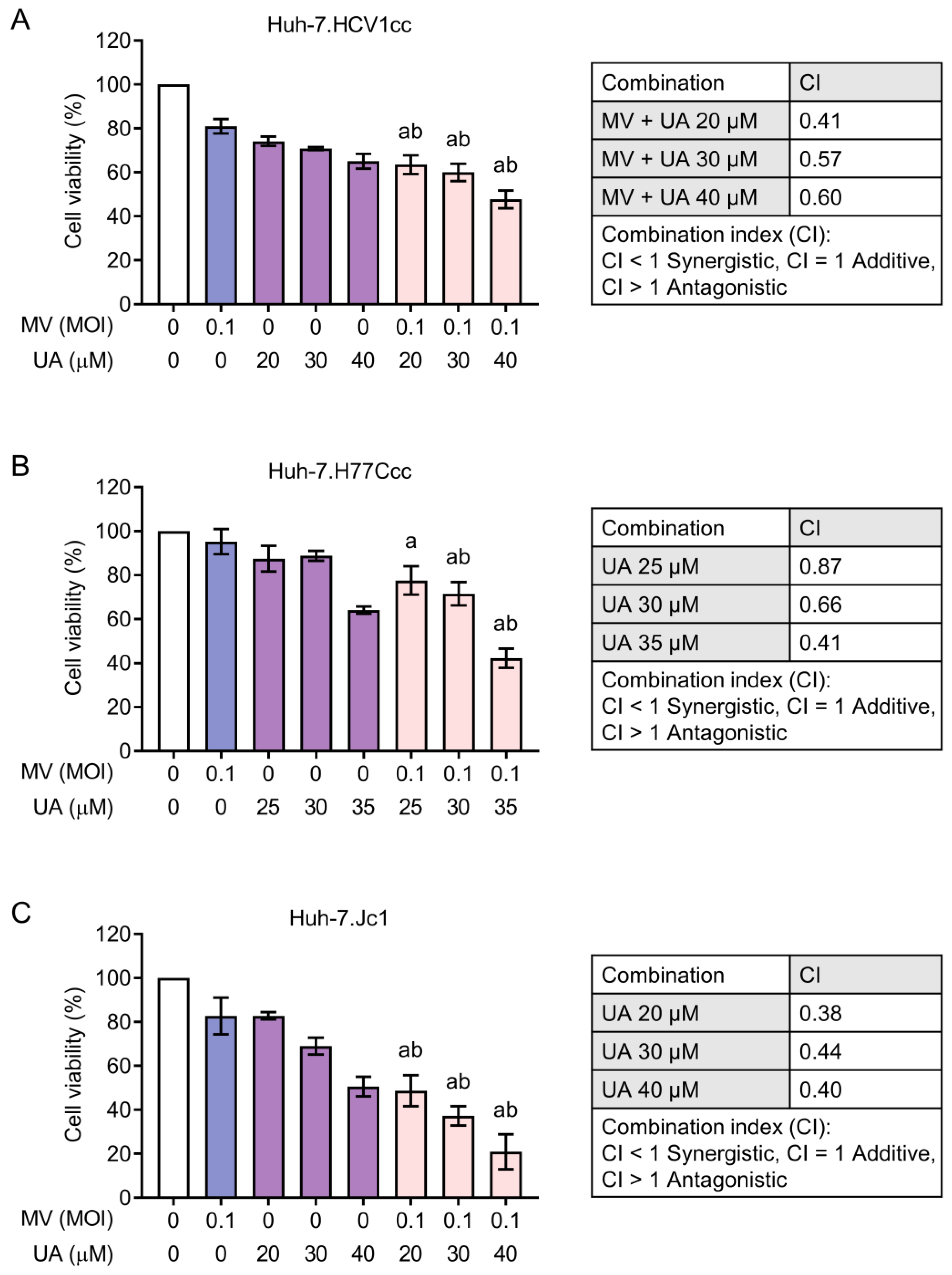
3.4. Synergistic Cytotoxicity of Oncolytic MV and UA Combination on HCC Cells Harboring Replicating Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) or Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumgay, H.; Arnold, M.; Ferlay, J.; Lesi, O.; Cabasag, C.J.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; McGlynn, K.A.; Soerjomataram, I. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Cervantes, A.; Chau, I.; Daniele, B.; Llovet, J.M.; Meyer, T.; Nault, J.C.; Neumann, U.; Ricke, J.; Sangro, B.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv238–iv255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Martinelli, E.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Updated treatment recommendations for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Tong, J. Oncolytic virus-based hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: Current status, intravenous delivery strategies, and emerging combination therapeutic solutions. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 18, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blechacz, B.; Splinter, P.L.; Greiner, S.; Myers, R.; Peng, K.W.; Federspiel, M.J.; Russell, S.J.; LaRusso, N.F. Engineered measles virus as a novel oncolytic viral therapy system for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampe, J.; Bossow, S.; Weiland, T.; Smirnow, I.; Lehmann, R.; Neubert, W.; Bitzer, M.; Lauer, U.M. An armed oncolytic measles vaccine virus eliminates human hepatoma cells independently of apoptosis. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.T.; Federspiel, M.J.; Guo, C.M.; Ooi, L.L.; Russell, S.J.; Peng, K.W.; Hui, K.M. Systemically delivered measles virus-infected mesenchymal stem cells can evade host immunity to inhibit liver cancer growth. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, B.; Berchtold, S.; Venturelli, S.; Burkard, M.; Smirnow, I.; Prenzel, T.; Henning, S.W.; Lauer, U.M. Combination of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor resminostat with oncolytic measles vaccine virus as a new option for epi-virotherapeutic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Ther.-Oncolytics 2015, 2, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.T.; Liu, C.H.; Wong, S.H.; Pan, Y.C.; Lin, L.T. Small molecules baicalein and cinnamaldehyde are potentiators of measles virus-induced breast cancer oncolysis. Phytomedicine 2021, 89, 153611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Wong, S.H.; Tai, C.J.; Tai, C.J.; Pan, Y.C.; Hsu, H.Y.; Richardson, C.D.; Lin, L.T. Ursolic Acid and Its Nanoparticles Are Potentiators of Oncolytic Measles Virotherapy against Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Dai, X.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Ursolic acid in cancer prevention and treatment: Molecular targets, pharmacokinetics and clinical studies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lin, G.; Zheng, R.X.; Huang, F.; Yang, M.S.; Xiao, P.G. Anti-hepatoma activity and mechanism of ursolic acid and its derivatives isolated from Aralia decaisneana. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, M.H.; Kao, T.C.; Yen, G.C. Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid induce apoptosis in HuH7 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through a mitochondrial-dependent pathway and downregulation of XIAP. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6110–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yang, L.; Mei, Y.; Long, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Qimuge, S.; Su, X. Ursolic acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 419343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-M.; Tang, P.M.-K.; Chan, J.Y.-W.; Lam, H.-M.; Au, S.W.-N.; Kong, S.-K.; Tsui, S.K.-W.; Mui-Yee Waye, M.; Mak, T.C.-W.; Fung, K.-P. Anti-Proliferative effect of ursolic acid on multidrug resistant hepatoma cells R-HepG2 by apoptosis induction. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 6, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yie, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tang, Q.; Zheng, F.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Deng, S.; Hann, S.S. Ursolic acid inhibited growth of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through AMPKalpha-mediated reduction of DNA methyltransferase 1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 402, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Ma, H.; Shi, W.; Duan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Lin, J.; Li, S.; Lv, J.; et al. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway by ursolic acid suppresses growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Kan, S.Y.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.; Ko, H.M.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, J.H. Ursolic Acid Suppresses Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exerts Anti-Cancer Effects in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Law, B.Y.K.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, W. Ursolic acid enhances the antitumor effects of sorafenib associated with Mcl-1-related apoptosis and SLC7A11-dependent ferroptosis in human cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.T.; Chung, C.Y.; Hsu, W.C.; Chang, S.P.; Hung, T.C.; Shields, J.; Russell, R.S.; Lin, C.C.; Li, C.F.; Yen, M.H.; et al. Saikosaponin b2 is a naturally occurring terpenoid that efficiently inhibits hepatitis C virus entry. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.P.; Ramirez, S.; Mikkelsen, L.; Bukh, J. Efficient infectious cell culture systems of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) prototype strains HCV-1 and H77. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marukian, S.; Jones, C.T.; Andrus, L.; Evans, M.J.; Ritola, K.D.; Charles, E.D.; Rice, C.M.; Dustin, L.B. Cell culture-produced hepatitis C virus does not infect peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1843–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C.; Martin, N. CompuSyn for Drug Combinations: PC Software and User’s Guide: A Computer Program for Quantitation of Synergism and Antagonism in Drug Combinations, and the Determination of IC50 and ED50 and LD50 Values. Available online: https://www.combosyn.com (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Chou, T.-C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyce, R.S.; Bondre, D.G.; Ha, M.N.; Lin, L.T.; Sisson, G.; Tsao, M.S.; Richardson, C.D. Tumor cell marker PVRL4 (nectin 4) is an epithelial cell receptor for measles virus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esolen, L.M.; Park, S.W.; Hardwick, J.M.; Griffin, D.E. Apoptosis as a cause of death in measles virus-infected cells. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3955–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.M.; Su, X.L. Anticancer effect of ursolic acid via mitochondria-dependent pathways. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4761–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, S.H.; Desnoyers, S.; Ottaviano, Y.; Davidson, N.E.; Poirier, G.G. Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: An early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar]
- Sells, M.A.; Chen, M.L.; Acs, G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Khan, K.; Hafeez, A.; Irfan, M.; Armaghan, M.; Rahman, A.U.; Gurer, E.S.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Butnariu, M.; Bagiu, I.C.; et al. Ursolic acid: A natural modulator of signaling networks in different cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lin, P.-Y.; Chuang, W.-L. Ursolic acid-induced apoptosis via regulation of the PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways in Huh-7 cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beishline, K.; Azizkhan-Clifford, J. Sp1 and the ‘hallmarks of cancer’. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 224–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.N.; Ullevig, S.L.; Short, J.D.; Wang, L.; Ahn, Y.J.; Asmis, R. Ursolic Acid and Related Analogues: Triterpenoids with Broad Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.R.; Meng, R.Y.; Rah, S.Y.; Jin, H.; Ray, N.; Kim, S.H.; Park, B.H.; Kim, S.M. Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Autophagy by Ursolic Acid Inhibits Growth and Metastasis of Esophageal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, L.; Nayak, V. Ursolic acid disturbs ROS homeostasis and regulates survival-associated gene expression to induce apoptosis in intestinal cancer cells. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-F.; Hsieh, C.-P.; Chueh, P.-J.; Chen, Y.-L. Combined use of zoledronic acid augments ursolic acid-induced apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells through enhanced oxidative stress and autophagy. Molecules 2016, 21, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reczek, C.R.; Chandel, N.S. The Two Faces of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2017, 1, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, T.P.; Wedd, J.P. The optimal timing and management of hepatitis B and C in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-Y.; Chang, C.-I.; Lin, B.-W.; Yu, F.-L.; Lin, P.-Y.; Hsu, J.-L.; Yen, C.-H.; Liao, M.-H.; Shih, W.-L. Suppression of hepatitis B virus X protein-mediated tumorigenic effects by ursolic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, S.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, R.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Fang, X. Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid: Novel hepatitis C virus antivirals that inhibit NS5B activity. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cheng, P. Improving antitumor efficacy via combinatorial regimens of oncolytic virotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeland, C.E.; Ungerechts, G. Measles Virus as an Oncolytic Immunotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivelu, L.; Liu, C.H.; Lin, L.T. Immunogenic cell death: The cornerstone of oncolytic viro-immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1038226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Petell, C.A.; Paraskevakou, G.; Zollman, P.J.; Schroeder, M.; Carlson, B.; Decker, P.A.; Wu, W.; James, C.D.; et al. Combination of measles virus virotherapy and radiation therapy has synergistic activity in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7155–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, C.J.; Liu, C.H.; Pan, Y.C.; Wong, S.H.; Tai, C.J.; Richardson, C.D.; Lin, L.T. Chemovirotherapeutic Treatment Using Camptothecin Enhances Oncolytic Measles Virus-Mediated Killing of Breast Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Jacobson, B.A.; Belgum, H.; Raza, A.; Sadiq, A.; Drees, J.; Wang, H.; Jay-Dixon, J.; Etchison, R.; Federspiel, M.J.; et al. Measles vaccine strains for virotherapy of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, V.; Berchtold, S.; Berger, A.; Venturelli, S.; Burkard, M.; Leischner, C.; Malek, N.P.; Lauer, U.M. Chemovirotherapy for pancreatic cancer: Gemcitabine plus oncolytic measles vaccine virus. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5534–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, G.; Rajala, M.S. Combination of Oncolytic Measles Virus Armed With BNiP3, a Pro-apoptotic Gene and Paclitaxel Induces Breast Cancer Cell Death. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toan, N.L.; Hang, N.T.; Luu, N.K.; Van Mao, C.; Van Ba, N.; Xuan, N.T.; Cam, T.D.; Yamamoto, N.; Van Tong, H.; Son, H.A. Combination of Vaccine Strain Measles Virus and Nimotuzumab in the Treatment of Laryngeal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3727–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaraman, S.; Canjuga, D.; Ghosh, M.; Codrea, M.C.; Sieger, R.; Wedekink, F.; Tatagiba, M.; Koch, M.; Lauer, U.M.; Nahnsen, S.; et al. Measles Virus-Based Treatments Trigger a Pro-inflammatory Cascade and a Distinctive Immunopeptidome in Glioblastoma. Mol. Ther.-Oncolytics 2019, 12, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Erlichman, C.; McDonald, C.J.; Ingle, J.N.; Zollman, P.; Iankov, I.; Russell, S.J.; Galanis, E. Heat shock protein inhibitors increase the efficacy of measles virotherapy. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellerhoff, T.P.; Berchtold, S.; Venturelli, S.; Burkard, M.; Smirnow, I.; Wulff, T.; Lauer, U.M. Novel epi-virotherapeutic treatment of pancreatic cancer combining the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor resminostat with oncolytic measles vaccine virus. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1931–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-H.; Tai, C.-J.; Kuo, Y.-T.; Chang, S.-S.; Lin, L.-T. Combination of Oncolytic Measles Virus and Ursolic Acid Synergistically Induces Oncolysis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Viruses 2023, 15, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061294
Liu C-H, Tai C-J, Kuo Y-T, Chang S-S, Lin L-T. Combination of Oncolytic Measles Virus and Ursolic Acid Synergistically Induces Oncolysis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Viruses. 2023; 15(6):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061294
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ching-Hsuan, Chen-Jei Tai, Yu-Ting Kuo, Shen-Shong Chang, and Liang-Tzung Lin. 2023. "Combination of Oncolytic Measles Virus and Ursolic Acid Synergistically Induces Oncolysis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells" Viruses 15, no. 6: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061294
APA StyleLiu, C.-H., Tai, C.-J., Kuo, Y.-T., Chang, S.-S., & Lin, L.-T. (2023). Combination of Oncolytic Measles Virus and Ursolic Acid Synergistically Induces Oncolysis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Viruses, 15(6), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061294