A Novel Simian Adenovirus Associating with Human Adenovirus Species G Isolated from Long-Tailed Macaque Feces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monkey Fecal Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. Viral Metagenomics by VIDISCA NGS Analysis
2.3. Nested PCR and RT-PCR
2.4. Virus Isolation
2.5. Viral Protein Identification by Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Whole-Genome Analysis
2.7. Phylogenetic and Recombination Analysis
2.8. Virus Neutralization Assay
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Potential Unknown Viruses by Metagenomics
3.2. Isolation and Whole-Genome Analysis of Potential New Adenovirus from Macaque Feces
3.3. Neutralizing Antibodies against AdV-RBR-6-3 in Long-Tailed Macaques and Humans
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suwannarong, K.; Soonthornworasiri, N.; Maneekan, P.; Balthip, K.; Yimsamran, S.; Maneewatchararangsri, S.; Ponlap, T.; Saengkul, C.; Lantican, C.; Thammasutti, K.; et al. Love or conflict: A qualitative study of the human-long tailed macaque interface in Nakhon Sawan Province, Thailand. Acta Trop. 2023, 240, 106861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greger, M. The human/animal interface: Emergence and resurgence of zoonotic infectious diseases. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 33, 243–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tu, X.; Humphrey, C.; McClure, H.; Jiang, X.; Qin, C.; Glass, R.I.; Jiang, B. Detection of viral agents in fecal specimens of monkeys with diarrhea. J. Med. Primatol. 2007, 36, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Liu, B.; Tao, Y.; Li, C.; Xia, M.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, X.; Liu, H.; Tan, M. Norovirus GII.17 natural infections in rhesus monkeys, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapusinszky, B.; Ardeshir, A.; Mulvaney, U.; Deng, X.; Delwart, E. Case-control comparison of enteric viromes in captive rhesus macaques with acute or idiopathic chronic diarrhea. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00952-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosoltanapiwat, N.; Tongshoob, J.; Ampawong, S.; Reamtong, O.; Prasittichai, L.; Yindee, M.; Tongthainan, D.; Tulayakul, P.; Boonnak, K. Simian adenoviruses: Molecular and serological survey in monkeys and humans in Thailand. One Health 2022, 15, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Taraporewala, Z.F.; Yang, H.; Rao, S.; Yuan, L.; Cao, D.; Hoshino, Y.; Mertens, P.P.; Carner, G.R.; McNeal, M.; et al. Simian rotaviruses possess divergent gene constellations that originated from interspecies transmission and reassortment. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, S.; Seto, J.; Liu, E.B.; Ismail, A.M.; Madupu, R.; Heim, A.; Jones, M.S.; Dyer, D.W.; Chodosh, J.; Seto, D.A. Zoonotic adenoviral human pathogen emerged through genomic recombination among human and nonhuman simian hosts. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00564-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, S.S.; Mazet, J.A.; Woolhouse, M.; Parrish, C.R.; Carroll, D.; Karesh, W.B.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Lipkin, W.I.; Daszak, P. Prediction and prevention of the next pandemic zoonosis. Lancet 2012, 380, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, K. Metagenomic identification of viral pathogens. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greninger, A.L.; Chen, E.C.; Sittler, T.; Scheinerman, A.; Roubinian, N.; Yu, G.; Kim, E.; Pillai, D.R.; Guyard, C.; Mazzulli, T.; et al. A metagenomic analysis of pandemic influenza A (2009 H1N1) infection in patients from North America. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Mbala-Kingebeni, P.; Naccache, S.N.; Thézé, J.; Bouquet, J.; Federman, S.; Somasekar, S.; Yu, G.; Sanchez-San Martin, C.; Achari, A.; et al. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of the 2014 Ebola virus disease outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00827-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, K.; Ye, G.; Wu, W.; Sun, Z.; Liu, F.; Wu, K.; Zhong, B.; et al. RNA based mNGS approach identifies a novel human coronavirus from two individual pneumonia cases in 2019 Wuhan outbreak. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, H.; Asif, A.; Fatima, M.; Rehman, Y. Potential role of viral metagenomics as a surveillance tool for the early detection of emerging novel pathogens. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delwart, E. Animal virus discovery: Improving animal health, understanding zoonoses, and opportunities for vaccine development. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.F.; Anderson, D.E. Viruses in bats and potential spillover to animals and humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.T.; Hou, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J.; He, H.; Si, W.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Xing, G.; et al. Virome characterization of game animals in China reveals a spectrum of emerging pathogens. Cell 2022, 185, 1117–1129.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.R.; Montoya, V.; Gardy, J.L.; Patrick, D.M.; Tang, P. Metagenomics for pathogen detection in public health. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, V.; Eloit, M. Viral metagenomics and blood safety. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2016, 23, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Berkhout, B.; van der Hoek, L. Detection of new viruses by VIDISCA. Virus discovery based on cDNA-amplified fragment length polymorphism. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 454, 73–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella, C.M.; Deijs, M.; van der Hoek, L. Enhanced bioinformatic profiling of VIDISCA libraries for virus detection and discovery. Virus Res. 2019, 263, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Hoek, L.; Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Vermeulen-Oost, W.; Berkhout, R.J.; Wolthers, K.C.; Wertheim-van Dillen, P.M.; Kaandorp, J.; Spaargaren, J.; Berkhout, B. Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edridge, A.W.D.; Deijs, M.; Namazzi, R.; Cristella, C.; Jebbink, M.F.; Maurer, I.; Kootstra, N.A.; Buluma, L.R.; van Woensel, J.B.M.; de Jong, M.D.; et al. Novel orthobunyavirus identified in the cerebrospinal fluid of a Ugandan child with severe encephalopathy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edridge, A.W.D.; Abd-Elfarag, G.; Deijs, M.; Jebbink, M.F.; Boele van Hensbroek, M.; van der Hoek, L. Divergent rhabdovirus discovered in a patient with new-onset nodding syndrome. Viruses 2022, 14, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canuti, M.; Eis-Huebinger, A.M.; Deijs, M.; de Vries, M.; Drexler, J.F.; Oppong, S.K.; Müller, M.A.; Klose, S.M.; Wellinghausen, N.; Cottontail, V.M.; et al. Two novel parvoviruses in frugivorous new and old world bats. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canuti, M.; Williams, C.V.; Sagan, S.M.; Oude Munnink, B.B.; Gadi, S.; Verhoeven, J.T.P.; Kellam, P.; Cotton, M.; Lang, A.S.; Junge, R.E.; et al. Virus discovery reveals frequent infection by diverse novel members of the Flaviviridae in wild lemurs. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boom, R.; Sol, C.J.; Salimans, M.M.; Jansen, C.L.; Wertheim-van Dillen, P.M.; van der Noordaa, J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endoh, D.; Mizutani, T.; Kirisawa, R.; Maki, Y.; Saito, H.; Kon, Y.; Morikawa, S.; Hayashi, M. Species-independent detection of RNA virus by representational difference analysis using non-ribosomal hexanucleotides for reverse transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoltanapiwat, N.; Reamtong, O.; Okabayashi, T.; Ampawong, S.; Rungruengkitkun, A.; Thiangtrongjit, T.; Thippornchai, N.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; Mahittikorn, A.; Mori, H.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based identification and whole-genome characterisation of the first pteropine orthoreovirus isolated from monkey faeces in Thailand. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids. Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes from subtype C-infected seroconverters in India, with evidence of intersubtype recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, H.M.; Ratmann, O.; Boni, M.F. Improved algorithmic complexity for the 3SEQ recombination detection algorithm. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerdsamran, H.; Mungaomklang, A.; Iamsirithaworn, S.; Prasertsopon, J.; Wiriyarat, W.; Saritsiri, S.; Anusorntanawat, R.; Siriyakorn, N.; Intalapaporn, P.; Sirikhetkon, S.; et al. Seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Thai adults during the first three epidemic waves. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.Y.; Li, L.L.; Ao, Y.Y.; Xie, Z.P.; Li, J.S.; Duan, Z.J.; Yu, J.M.; Zhang, B. A novel astrovirus identified in wild rhesus monkey feces in China. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2385–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, Y.Y.; Yu, J.M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Xin, Y.Y.; Li, L.L.; Duan, Z.J. Identification of a novel enterovirus species in rhesus macaque in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malouli, D.; Howell, G.L.; Legasse, A.W.; Kahl, C.; Axthelm, M.K.; Hansen, S.G.; Früh, K. Full genome sequence analysis of a novel adenovirus of rhesus macaque origin indicates a new simian adenovirus type and species. Virol. Rep. 2014, 3–4, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nix, W.A.; Jiang, B.; Maher, K.; Strobert, E.; Oberste, M.S. Identification of enteroviruses in naturally infected captive primates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2874–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, E.A.; Small, C.T.; Freiden, P.; Feeroz, M.M.; Matsen, F.A., 4th; San, S.; Hasan, M.K.; Wang, D.; Jones-Engel, L.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Non-human primates harbor diverse mammalian and avian astroviruses including those associated with human infections. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.C.; Yagi, S.; Kelly, K.R.; Mendoza, S.P.; Tarara, R.P.; Canfield, D.R.; Maninger, N.; Rosenthal, A.; Spinner, A.; Bales, K.L.; et al. Cross-species transmission of a novel adenovirus associated with a fulminant pneumonia outbreak in a new world monkey colony. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.B.; Ferreyra, L.; Fischer, S.L.; Pavan, J.V.; Nates, S.V.; Hudson, N.R.; Tirado, D.; Dyer, D.W.; Chodosh, J.; Seto, D.; et al. Genetic analysis of a novel human adenovirus with a serologically unique hexon and a recombinant fiber gene. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbink, P.; Maxfield, L.F.; Ng'ang'a, D.; Borducchi, E.N.; Iampietro, M.J.; Bricault, C.A.; Teigler, J.E.; Blackmore, S.; Parenteau, L.; Wagh, K.; et al. Construction and evaluation of novel rhesus monkey adenovirus vaccine vectors. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbink, P.; Kirilova, M.; Boyd, M.; Mercado, N.; Li, Z.; Nityanandam, R.; Nanayakkara, O.; Peterson, R.; Larocca, R.A.; Aid, M.; et al. Rapid cloning of novel rhesus adenoviral vaccine vectors. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01924-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkő, M.; Aoki, K.; Arnberg, N.; Davison, A.J.; Echavarría, M.; Hess, M.; Jones, M.S.; Kaján, G.L.; Kajon, A.E.; Mittal, S.K.; et al. Ictv Report Consortium. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Adenoviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.S., 2nd; Harrach, B.; Ganac, R.D.; Gozum, M.M.; Dela Cruz, W.P.; Riedel, B.; Pan, C.; Delwart, E.L.; Schnurr, D.P. New adenovirus species found in a patient presenting with gastroenteritis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5978–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, S.A.; Thackray, L.B.; Zhao, G.; Presti, R.; Miller, A.D.; Droit, L.; Abbink, P.; Maxfield, L.F.; Kambal, A.; Duan, E.; et al. Pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus infection is associated with expansion of the enteric virome. Cell. 2012, 151, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, A.; Ditty, S.E.; Su, J.; McGraw, J.; Hadfield, T.L.; Tibbetts, C.; Seto, D. Genomic and bioinformatics analysis of HAdV-4, a human adenovirus causing acute respiratory disease: Implications for gene therapy and vaccine vector development. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2559–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Ismail, A.M.; Dehghan, S.; Rajaiya, J.; Allard, M.W.; Lim, H.C.; Dyer, D.W.; Chodosh, J.; Seto, D. Genomics-based re-examination of the taxonomy and phylogeny of human and simian Mastadenoviruses: An evolving whole genomes approach, revealing putative zoonosis, anthroponosis, and amphizoonosis. Cladistics 2020, 36, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, I.I.; Pantó, L.; Papp, T.; Harrach, B.; Benkö, M. Genome analysis of four Old World monkey adenoviruses supports the proposed species classification of primate adenoviruses and reveals signs of possible homologous recombination. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Robinson, C.M.; Dehghan, S.; Jones, M.S.; Dyer, D.W.; Seto, D.; Chodosh, J. Homologous recombination in E3 genes of human adenovirus species D. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12481–12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martín, C. Latest insights on adenovirus structure and assembly. Viruses 2012, 4, 847–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.D.; John, L.; Rafie, K.; Strebl, M.; Frängsmyr, L.; Ballmann, M.Z.; Mindler, K.; Havenga, M.; Lemckert, A.; Stehle, T.; et al. Human species D adenovirus hexon capsid protein mediates cell entry through a direct interaction with CD46. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020732118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Sun, X.; Ye, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, X.; Yi, C.; Hao, M.; Wang, Q.; et al. Hexon and fiber of adenovirus type 14 and 55 are major targets of neutralizing antibody but only fiber-specific antibody contributes to cross-neutralizing activity. Virology 2018, 518, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Cun, A.; Yang, W.; Ellenberg, S.; Switzer, W.M.; Kalish, M.L.; Ertl, H.C. Chimpanzee adenovirus antibodies in humans, sub-Saharan Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klann, P.J.; Wang, X.; Elfert, A.; Zhang, W.; Köhler, C.; Güttsches, A.K.; Jacobsen, F.; Weyen, U.; Roos, A.; Ehrke-Schulz, E.; et al. Seroprevalence of binding and neutralizing antibodies against 39 human adenovirus types in patients with neuromuscular disorders. Viruses 2022, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Virus | Primer | PCR Round | Sequence (5′–3′) | Annealing Temp. (°C) | Expected Product Size | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenovirus | Adeno F | First | GCTCGCCATCATTCCAGTTC | 50 | 212 | CR1 |
| Adeno R | First | CTGAGTAGAGTTTGGGAGTTG | ||||
| Adeno FN | Nested | CCAGTTCTTTACTTAGCCTTGC | 50 | 171 | CR1 | |
| Adeno RN | Nested | ACGTTTAGTTCCTACTTGAGC | ||||
| Enterovirus | Entero F | First | ACACATCGTGAAACACACTG | 55 | 312 | Protease |
| Entero R | First | GTTGTACCAATCGTGATGTTC | ||||
| Entero FN | Nested | ATCCATTGTATCTCCCCTTG | 55 | 185 | Protease | |
| Entero RN | Nested | GTGGAAAGCCCACCCATAGA | ||||
| Astrovirus | Astro F | First | TGCCAATTATGCGGCTTCTC | 50 | 312 | Capsid |
| Astro R | First | GTGATGGTAAATGTTCTAGAC | ||||
| Astro FN | Nested | TACTAAGACACTGGCTATTGC | 50 | 98 | Capsid | |
| Astro RN | Nested | TTCCGCCATACTGAGATTTC |
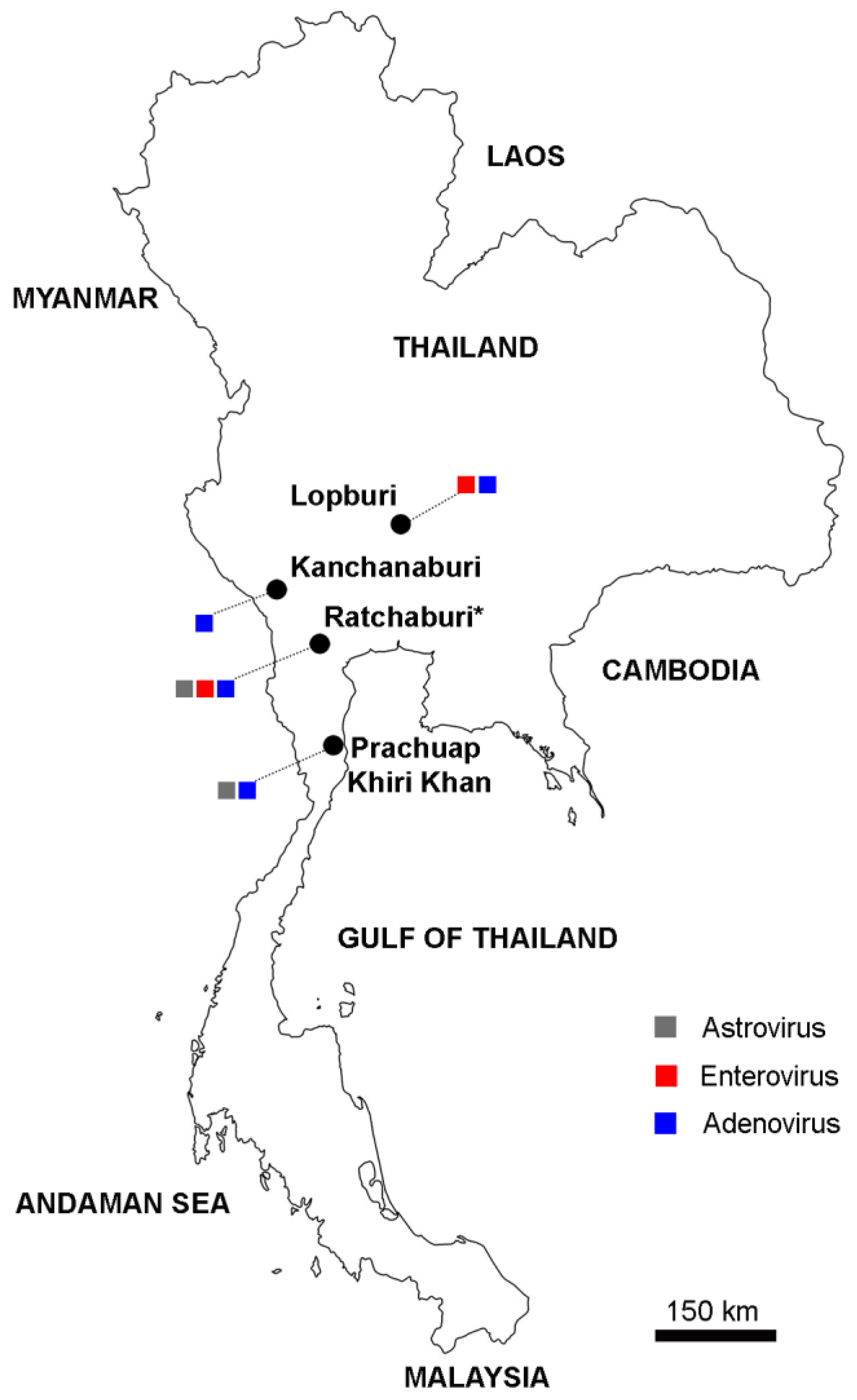
| Site | Sample Type | Collection Year | No. of Samples | No. of Positives (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AstV | EV | AdV | ||||
| Ratchaburi | Feces | 2018–2019 | 39 * | 4 (10.3%) | 5 (12.8%) | 5 (12.8%) |
| Kanchanaburi | Feces | 2018–2019 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 2 (16.7%) |
| Lopburi | Feces | 2013 | 46 | 0 | 9 (19.6%) | 1 (2.2%) |
| Prachuap Khiri Khan | Rectal swab | 2017 | 90 | 2 (2.2%) | 0 | 1 (1.1%) |
| Total | 187 | 6 (3.2%) | 14 (7.5%) | 9 (4.8%) | ||
| Gene | Transcription Class | Sequence Coverage | % Identity | Most Identical AdV | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA polymerase | E2B | 100% | 98.7% | Rhesus AdV 53 | KM591903.1 |
| III (penton base) | L2 | 100% | 99.3% | Rhesus AdV 53 | KM591903.1 |
| II (hexon) | L3 | 100% | 91.6% | Rhesus AdV 52 | KM591902.1 |
| Protease | L3 | 100% | 98.9% | Rhesus AdV 53 | KM591903.1 |
| Fiber-1 | L5 | 98% | 71.9% | Rhesus AdV 55 | MF198449.1 |
| Fiber-2 | L5 | 100% | 95.3% | Rhesus AdV 55 | MF198449.1 |
| CR1-α | E3 | 100% | 83.6% | Simian AdV 11 | KP329562.1 |
| CR1-β | E3 | 99% | 85.0% | Simian AdV 11 | KP329562.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosoltanapiwat, N.; van der Hoek, L.; Kinsella, C.M.; Tongshoob, J.; Prasittichai, L.; Klein, M.; Jebbink, M.F.; Deijs, M.; Reamtong, O.; Boonnak, K.; et al. A Novel Simian Adenovirus Associating with Human Adenovirus Species G Isolated from Long-Tailed Macaque Feces. Viruses 2023, 15, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061371
Kosoltanapiwat N, van der Hoek L, Kinsella CM, Tongshoob J, Prasittichai L, Klein M, Jebbink MF, Deijs M, Reamtong O, Boonnak K, et al. A Novel Simian Adenovirus Associating with Human Adenovirus Species G Isolated from Long-Tailed Macaque Feces. Viruses. 2023; 15(6):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061371
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosoltanapiwat, Nathamon, Lia van der Hoek, Cormac M. Kinsella, Jarinee Tongshoob, Luxsana Prasittichai, Michelle Klein, Maarten F. Jebbink, Martin Deijs, Onrapak Reamtong, Kobporn Boonnak, and et al. 2023. "A Novel Simian Adenovirus Associating with Human Adenovirus Species G Isolated from Long-Tailed Macaque Feces" Viruses 15, no. 6: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061371
APA StyleKosoltanapiwat, N., van der Hoek, L., Kinsella, C. M., Tongshoob, J., Prasittichai, L., Klein, M., Jebbink, M. F., Deijs, M., Reamtong, O., Boonnak, K., Khongsiri, W., Phadungsombat, J., Tongthainan, D., Tulayakul, P., & Yindee, M. (2023). A Novel Simian Adenovirus Associating with Human Adenovirus Species G Isolated from Long-Tailed Macaque Feces. Viruses, 15(6), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061371









