Genetic Characterization and Pathogenesis of H5N1 High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus Isolated in South Korea during 2021–2022
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses
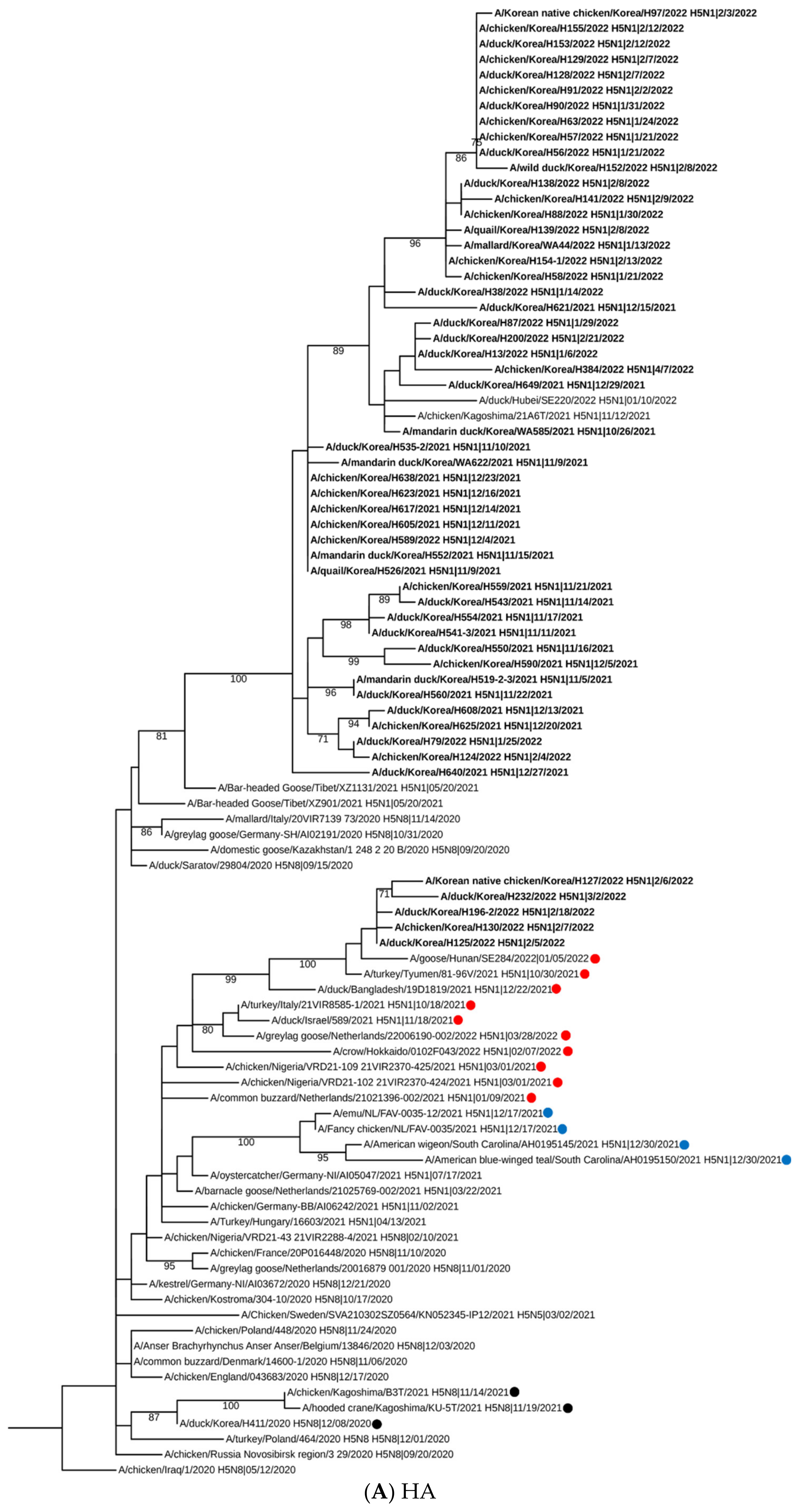
2.2. Sequencing, Phylogenetic Analysis and Genome Constellation
2.3. Animal Experiment
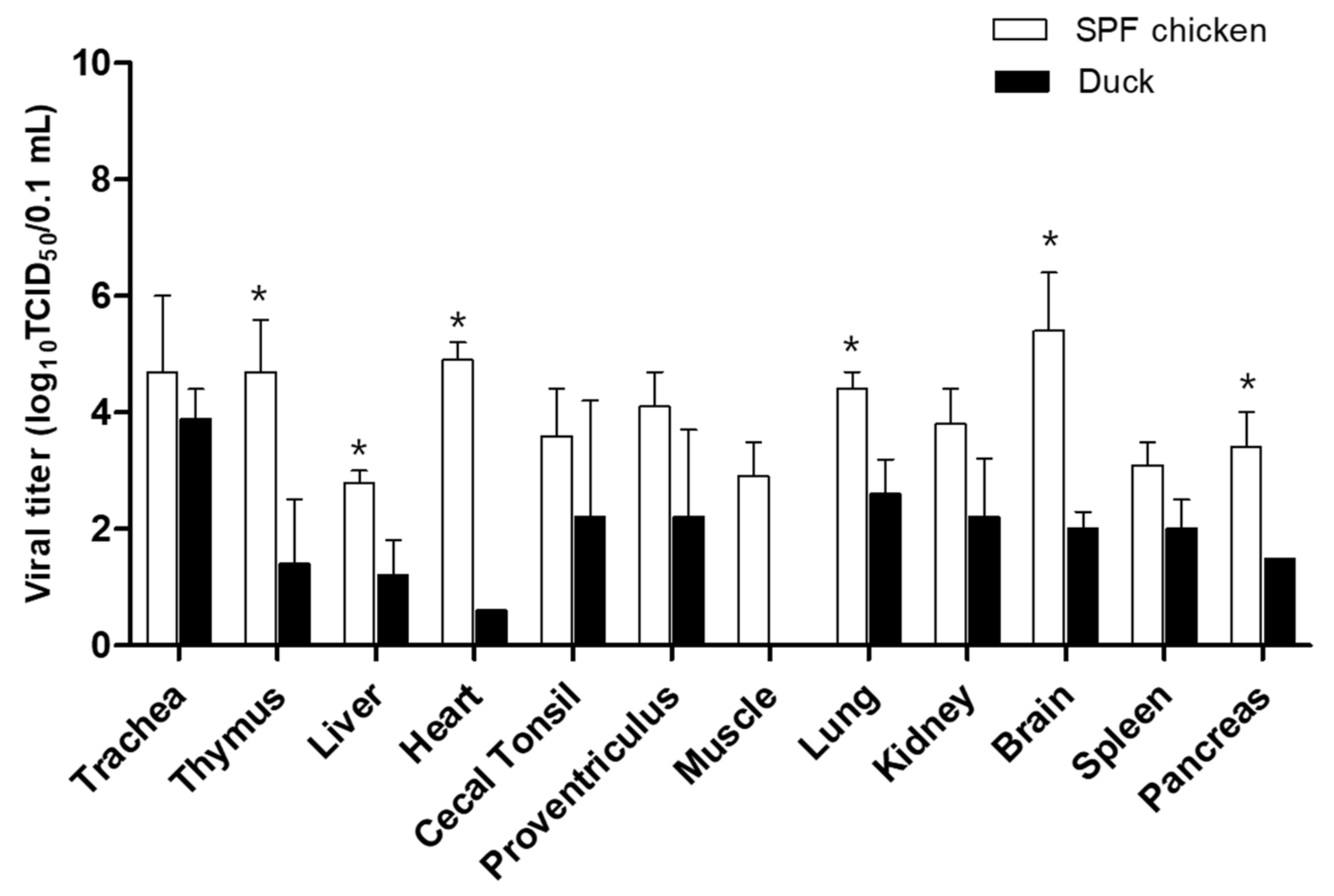
2.4. Viral Shedding, Virus Replication in Organs, and Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI) Test
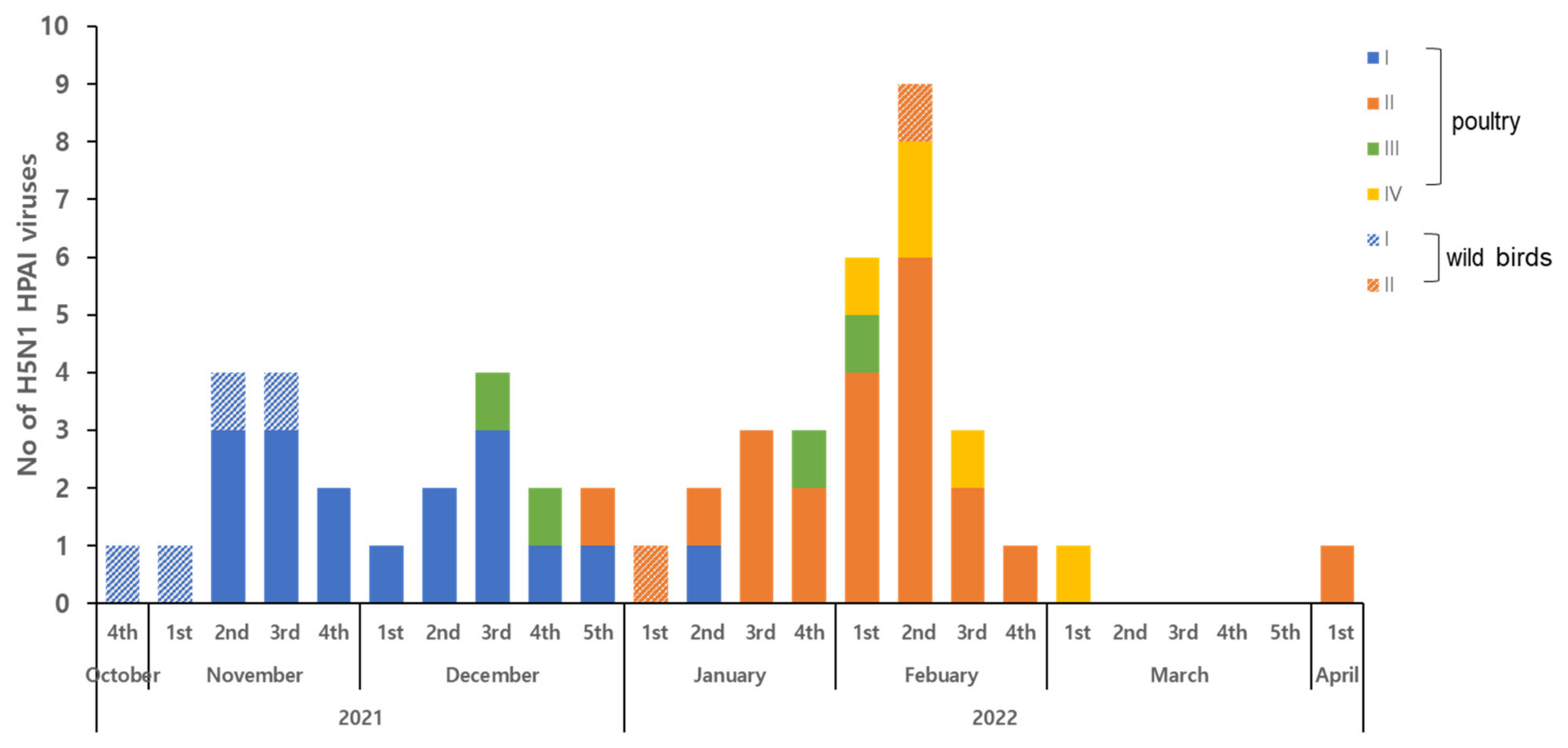
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO/OIE/FAO H5N1 Evolution Working Group. Toward a unified nomenclature system for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N1). Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poovorawan, Y.; Pyungporn, S.; Prachayangprecha, S.; Makkoch, J. Global alert to avian influenza virus infection: From H5N1 to H7N9. Pathog. Glob. Health 2013, 107, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Criado, M.F.; Swayne, D.E. Pathobiological origins and evolutionary history of highly pathogenic avian ifluenza viruses. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caliendo, V.; Lewis, N.S.; Pohlmann, A.; Baillie, S.R.; Banyard, A.C.; Beer, M.; Brown, I.H.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Hansen, R.D.E.; Lameris, T.K.; et al. Transatlantic spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 by wild birds from Europe to North America in 2021. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkie, T.N.; Lopes, S.; Hisanaga, T.; Xu, W.; Suderman, M.; Koziuk, J.; Fisher, M.; Redford, T.; Lung, O.; Joseph, T.; et al. A threat from both sides: Multiple introductions of genetically distinct H5 HPAI viruses into Canada via both East Asia-Australasia/Pacific and Atlantic flyways. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.S.; Banyard, A.C.; Whittard, E.; Karibayev, T.; Al Kafagi, T.; Chvala, I.; Byrne, A.; Meruyert Akberovna, S.; King, J.; Harder, T.; et al. Emergence and spread of novel H5N8, H5N5 and H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic avian influenza in 2020. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlmann, A.; King, J.; Fusaro, A.; Zecchin, B.; Banyard, A.C.; Brown, I.H.; Byrne, A.M.P.; Beerens, N.; Liang, Y.; Heutink, R.; et al. Has epizootic become enzootic? Evidence for a fundamental change in the infection dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza in Europe, 2021. mBio 2022, 13, e0060922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.M.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, E.K.; Jung, J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, Y.J. Pathogenicity of H5N8 virus in chickens from Korea in 2014. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 16, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.K.; Song, B.M.; Kang, H.M.; Woo, S.H.; Heo, G.B.; Jung, S.C.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.H. Experimental infection of SPF and Korean native chickens with highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N8). Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.K.; Lee, Y.N.; Kye, S.J.; Lewis, N.S.; Brown, I.H.; Sagong, M.; Heo, G.B.; Kang, Y.M.; Cho, H.K.; Kang, H.M.; et al. Characterization of a novel reassortant H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus clade 2.3.4.4 in Korea, 2017. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.C.; Song, B.M.; Lee, Y.N.; Lee, E.K.; Heo, G.B.; Kye, S.J.; Lee, K.H.; Bae, Y.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, B. Pathogenicity of clade 2.3.4.4 H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in three chicken breeds from South Korea in 2016/2017. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 20, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.G.; Lee, Y.N.; Lee, D.H.; Shin, J.I.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, D.H.; Lee, E.K.; Heo, G.B.; Sagong, M.; Kye, S.J.; et al. Multiple Reassortants of H5N8 clade 2.3.4.4b highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses detected in South Korea during the winter of 2020–2021. Viruses 2021, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Cha, R.M.; Kye, S.J.; Lee, Y.N.; Kim, N.Y.; Baek, Y.G.; Heo, G.B.; Sagong, M.; Lee, K.N.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. Pathogenicity of H5N8 high pathogenicity avian influenza virus in chickens and ducks from South Korea in 2020–2021. Viruses 2021, 13, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; European Union Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza; Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, E.; Staubach, C.; et al. Avian influenza overview December 2021–March 2022. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07289. [Google Scholar]
- Sagong, M.; Lee, Y.N.; Song, S.; Cha, R.M.; Lee, E.K.; Kang, Y.M.; Cho, H.K.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, K.N. Emergence of clade 2.3.4.4b novel reassortant H5N1 high pathogenicity avian influenza virus in South Korea during late 2021. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e3255–e3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, H.M.; Jeong, O.M.; Kim, M.C.; Kwon, J.S.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, C.B.; Lee, J.B.; et al. DNA barcoding techniques for avian influenza virus surveillance in migratory bird habitats. J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OIE Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. Available online: https://www.oie.int/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/3.03.04_AI.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs of Republic of Korea. Special Animal Disease Section (Korean). 2022. Available online: www.mafra.go.kr/FMD-AI2 (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Baek, Y.G.; Lee, Y.N.; Park, Y.R.; Chung, D.H.; Kwon, J.H.; Si, Y.J.; Heo, G.B.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, E.K. Evolution, transmission, and pathogenicity of high pathogenicity avian influenza virus A (H5N8) clade 2.3.4.4, South Korea, 2014–2016. Front. Vet. Sci 2022, 9, 906944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isoda, N.; Onuma, M.; Hiono, T.; Sobolev, I.; Lim, H.Y.; Nabeshima, K.; Honjyo, H.; Yokoyama, M.; Shestopalov, A.; Sakoda, Y. Detection of new H5N1 high pathogenicity avian influenza viruses in winter 2021–2022 in the far east, which are genetically close to those in Europe. Viruses 2022, 14, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuya, K.; Mine, J.; Tokorozaki, K.; Kojima, I.; Esaki, M.; Miyazawa, K.; Tsunekuni, R.; Sakuma, S.; Kumagai, A.; Takadate, Y.; et al. Genetically diverse highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1/H5N8) viruses among wild waterfowl and domestic piultry, Japan, 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, P.; Shi, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, X.; Kong, H.; Yan, C.; Zeng, X.; Liu, L.; Tian, G.; et al. Global dissemination of H5N1 influenza viruses bearing the clade 2.3.4.4b HA gene and biologic analysis of the ones detected in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; European Union Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza; Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, E.; Staubach, C.; et al. Avian influenza overview March–June 2022. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07415. [Google Scholar]
- Takadate, Y.; Tsunekuni, R.; Kumagai, A.; Mine, J.; Kikutani, Y.; Sakuma, S.; Miyazawa, K.; Uchida, Y. Different infectivity and transmissibility of H5N8 and H5N1 high pathogenicity avian influenza viruses isolated from chickens in Japan in the 2021/2022 season. Viruses 2023, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Song, B.M.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, E.K.; Hanna, A.; Gilbert, M.; Brown, I.H.; Pybus, O.G. Wild waterfowl migration and domestic duck density shape the epidemiology of highly pathogenic H5N8 influenza in the Republic of Korea. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 34, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Bahl, J.; Swayne, D.E.; Lee, Y.N.; Lee, Y.J.; Song, C.S.; Lee, D.H. Domestic ducks play a major role in the maintenance and spread of H5N8 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in South Korea. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerens, N.; Germeraad, E.A.; Venema, S.; Verheij, E.; Pritz-Verschuren, S.B.E.; Gonzales, J.L. Comparative pathogenicity and environmental transmission of recent highly pathogenic avian influenza H5 viruses. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; McCauley, J. GISAIF: From vision to reality. EuroSurveillance 2017, 22, 30494. [Google Scholar]


| Virus Name | Subtype | Reassortant | Genotype | Phylogenetic Group within Each Gene Segment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB2 | PB1 | PA | HA | NP | NA | MP | NS | ||||
| 21WA585 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21WA622 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22WA44 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H519-2-3 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H526 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H535-2 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H541-3 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H543 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H550 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H552 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H554 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H559 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H560 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H589 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H590 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H605 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H608 | H5N1 | ACB5C1AA | III | A | C | B | 5 | C | 1 | A | A |
| 21H617 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H621 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H623 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H625 | H5N1 | ACB5C1AA | III | A | C | B | 5 | C | 1 | A | A |
| 21H638 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H640 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 21H649 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H013 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H038 | H5N1 | AAA5A1AA | I | A | A | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H056 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H057 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H058 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H063 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H079 | H5N1 | ACB5C1AA | III | A | C | B | 5 | C | 1 | A | A |
| 22H087 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H088 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H090 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H091 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H097 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H124 | H5N1 | ACB5C1AA | III | A | C | B | 5 | C | 1 | A | A |
| 22H125 | H5N1 | BBA5B1BB | IV | B | B | A | 5 | B | 1 | B | B |
| 22H127 | H5N1 | BBA5B1BB | IV | B | B | A | 5 | B | 1 | B | B |
| 22H128 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H129 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H130 | H5N1 | BBA5B1BB | IV | B | B | A | 5 | B | 1 | B | B |
| 22H138 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H139 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H141 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H152 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H153 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H154-1 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H155 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H196-2 | H5N1 | BBA5B1BB | IV | B | B | A | 5 | B | 1 | B | B |
| 22H200 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| 22H232 | H5N1 | BBA5B1BB | IV | B | B | A | 5 | B | 1 | B | B |
| 22H384 | H5N1 | ADA5A1AA | II | A | D | A | 5 | A | 1 | A | A |
| Bird Species | IVPI | Virus Dose (EID50/0.1 mL) | Mortality (%) | MDT (Day) | HI Titer (log2, Mean ± SD) | LD50 (EID50/0.1 mL) | BID50 (EID50/0.1 mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPF chicken | 2.98 | 106.2 a | 5/5 b (100) | 2.6 | NT | 103.7 | - |
| 105.2 | 5/5 (100) | 4.2 | NT | ||||
| 104.2 | 5/5 (100) | 6.0 | NT | ||||
| 103.2 | 0/5 (0.0) | - | 0/5(0.0) | ||||
| 102.2 | 0/5 (0.0) | - | 0/5(0.0) | ||||
| Contact | 3/3 (100) | 4.6 | NT | ||||
| Duck | - | 106.2 | 0/5 (0.0) | - | 4/4 *(6.5 ± 1.3) | - | 103.2 |
| 104.2 | 0/5 (0.0) | - | 5/5 (5.8 ± 1.1) | ||||
| 102.2 | 0/5 (0.0) | - | 0/5 (0.0) | ||||
| Contact | 0/3 (0.0) | - | 3/3 (5.4 ± 1.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cha, R.M.; Lee, Y.-N.; Park, M.-J.; Baek, Y.-G.; Shin, J.-I.; Jung, C.H.; Sagong, M.; Heo, G.-B.; Kang, Y.-M.; Lee, K.-N.; et al. Genetic Characterization and Pathogenesis of H5N1 High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus Isolated in South Korea during 2021–2022. Viruses 2023, 15, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061403
Cha RM, Lee Y-N, Park M-J, Baek Y-G, Shin J-I, Jung CH, Sagong M, Heo G-B, Kang Y-M, Lee K-N, et al. Genetic Characterization and Pathogenesis of H5N1 High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus Isolated in South Korea during 2021–2022. Viruses. 2023; 15(6):1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061403
Chicago/Turabian StyleCha, Ra Mi, Yu-Na Lee, Min-Ji Park, Yoon-Gi Baek, Jae-In Shin, Chang Hwa Jung, Mingeun Sagong, Gyeong-Beom Heo, Yong-Myung Kang, Kwang-Nyeong Lee, and et al. 2023. "Genetic Characterization and Pathogenesis of H5N1 High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus Isolated in South Korea during 2021–2022" Viruses 15, no. 6: 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061403
APA StyleCha, R. M., Lee, Y.-N., Park, M.-J., Baek, Y.-G., Shin, J.-I., Jung, C. H., Sagong, M., Heo, G.-B., Kang, Y.-M., Lee, K.-N., Lee, Y.-J., & Lee, E.-K. (2023). Genetic Characterization and Pathogenesis of H5N1 High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus Isolated in South Korea during 2021–2022. Viruses, 15(6), 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061403






