Antibiotic-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens and COVID-19: The Pandemic beyond the Pandemic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MDR, XDR, PDR and DTR Bacteria
3. Enterobacter spp., A. baumanni, and K. pneumoniae
3.1. The Genus Enterobacter
3.2. A. baumannii
3.3. K. pneumoniae
4. Therapies for Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
5. Co-Infections and Secondary Bacterial Infections in the COVID-19 Outbreak
6. State of the Art in the World
6.1. Asia
6.2. Europe
6.3. Africa
6.4. Australia
6.5. America
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strathdee, S.A.; Davies, S.C.; Marcelin, J.R. Confronting antimicrobial resistance beyond the COVID-19 pandemic and the 2020 US election. Lancet 2020, 396, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2015. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/193736 (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- World Health Organization. One Health Joint Plan of Action (2022–2026): Working Together for the Health of Humans, Animals, Plants and the Environment; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Jesudason, T. A new One Health Joint Action Plan. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Villamañán, A.; San Millán, Á.; Carrilero, L. Tackling AMR from a multidisciplinary perspective: A primer from education and psychology. Int. Microbiol. 2022, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebisi, Y.A.; Ogunkola, I.O. The global antimicrobial resistance response effort must not exclude marginalised populations. Trop. Med. Health 2023, 51, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. 2014. Available online: https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/AMR%20Review%20Paper%20-%20Tackling%20a%20crisis%20for%20the%20health%20and%20wealth%20of%20nations_1.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2016. Available online: https://amrreview.org/sites/default/files/160525_Final%20paper_with%20cover.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Catalano, A. COVID-19: Could irisin become the handyman myokine of the 21st century. Coronaviruses 2020, 1, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G.M.; Glover, R.E.; McQuaid, C.F.; Olaru, I.D.; Gallandat, K.; Leclerc, Q.J.; Fuller, N.M.; Willcocks, S.J.; Hasan, R.; van Kleef, E.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance and COVID-19: Intersections and implications. eLife 2021, 10, e64139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Alzate, L.; Hofstraat, K.; de Vries, D.H. The pandemic beyond the pandemic: A Scoping review on the social relationships between COVID-19 and antimicrobial resistance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, A.R.; Safaee, M.M.; Wuest, W.M.; Furst, A.L. The silent pandemic: Emergent antibacterial resistances following the global response to SARS-CoV-2. iScience 2021, 24, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S. A parallel and silent emerging pandemic: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) amid COVID-19 pandemic. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votta, M.; Cardillo, M. Civil society engagement in the fight against AMR: From the new National Plan in Italy to the AMR patient alliance at the European level. World J. Clin. Med. Images 2022, 1, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rawson, T.M.; Moore, L.S.P.; Castro-Sanchez, E.; Charani, E.; Davies, F.; Satta, G.; Ellington, M.J.; Holmes, A.H. COVID-19 and the potential long-term impact on antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1681–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, H.; Smith, I.; Trivedi, K.; Paulin, S.; Balkhy, H.H. Tackling antimicrobial resistance in the COVID-19 pandemic. Bull. World Health Organ. 2020, 98, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnet, D.L.; Harbarth, S. Will coronavirus disease (COVID-19) have an impact on antimicrobial resistance? Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founou, R.C.; Blocker, A.J.; Noubom, M.; Tsayem, C.; Choukem, S.P.; Van Dongen, M.; Founou, L.L. The COVID-19 pandemic: A threat to antimicrobial resistance containment. Futur. Sci. OA 2021, 7, FSO736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Hays, J.P.; Kemp, A.; Okechukwu, R.; Murugaiyan, J.; Ekwanzala, M.D.; Ruiz Alvarez, M.J.; Paul-Satyaseela, M.; Iwu, C.D.; Balleste-Delpierre, C.; et al. The potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on global antimicrobial and biocide resistance: An AMR Insights global perspective. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlab038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, B.J.; So, M.; Raybardhan, S.; Leung, V.; Soucy, J.-P.R.; Westwood, D.; Daneman, N.; MacFadden, D.R. Antibiotic prescribing in patients with COVID-19: Rapid review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartelli, M. COVID-19 impact on the understanding of infection prevention and control measures. Bangladesh J. Med. Sci. 2021, 20, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Koizumi, R.; Tsuzuki, S.; Asai, Y.; Ishikane, M.; Kusama, Y.; Ohmagari, N. Antimicrobial use fell substantially in Japan in 2020—The COVID-19 pandemic may have played a role. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 119, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; Saturnino, C.; Pellegrino, M.; Mariconda, A.; Longo, P.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Aquaro, S. COVID-19 at a glance: An up-to-date overview on variants, drug design and therapies. Viruses 2022, 14, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulayyim, H.J.A.; Ismail, R.; Hamid, A.A.; Ghafar, N.A. Antibacterial resistance during COVID-19: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Andreu, I.; Mariconda, A.; Saturnino, C.; Giuzio, F.; Longo, P.; Aquaro, S.; Catalano, A. Drugs for COVID-19: An update. Molecules 2022, 27, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.D.; Lohm, D.; Flowers, P.; Whittaker, A. The immune self, hygiene and performative virtue in general public narratives on antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance. Health 2023, 27, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, G.R.; Durayb, B.; King, C.; Rashid, H. Antimicrobial resistance following prolonged use of hand hygiene products: A systematic review. Pharmacy 2022, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinicropi, M.S.; Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; Mariconda, A.; Pellegrino, M.; Saturnino, C.; Longo, P.; Aquaro, S. Triclosan: A small molecule with controversial roles. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacopetta, D.; Catalano, A.; Ceramella, J.; Saturnino, C.; Salvagno, L.; Ielo, I.; Drommi, D.; Scali, E.; Plutino, M.R.; Rosace, G.; et al. The different facets of triclocarban: A review. Molecules 2021, 26, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, S.G.; Ahammad, S.Z. COVID-19 and antimicrobial resistance: A cross-study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicky, P.-H.; Niedermann, M.S.; Timsit, J.-F. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in the era of COVID-19 pandemic: How common and what is the impact? Crit. Care 2021, 25, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Van Boeckel, T.; Frost, I.; Kariuki, S.; Khan, E.A.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Levy-Hara, G.; Mendelson, M.; Outterson, K.; et al. The Lancet infectious diseases commission on antimicrobial resistance: 6 years later. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e51–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, K.; Mendelson, M.; Kang, G.; Venkatasubramanian, R.; Sinha, R.; Vijay, S.; Balaji Veeraraghavan, B.; Basnyat, B.; Rodrigues, C.; Bansal, N.; et al. How can lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic enhance antimicrobial resistance surveillance and stewardship? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopman, J.; Allegranzi, B.; Mehtar, S. Managing COVID-19 in low-and middle-income countries. JAMA 2020, 323, 1549–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobie, T.A.; Roba, A.A.; Booth, J.A.; Kristiansen, K.I.; Aseffa, A.; Skarstad, K.; Bjørås, M. Antimicrobial resistance: A challenge awaiting the post-COVID-19 era. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 111, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukuhor, H.O. The interrelationships between antimicrobial resistance, COVID-19, past, and future pandemics. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejandro, A.L.; Bruce, M.; Leo, C. Parents’ awareness of antimicrobial resistance: A qualitative study utilising the health belief model in Perth, Western Australia. Austral. New Zeal. J. Public Health 2022, 46, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardebili, A.; Izanloo, A.; Rastegar, M. Polymyxin combination therapy for multidrug-resistant, extensively-drug resistant, and difficult-to-treat drug-resistant Gram-negative infections: Is it superior to polymyxin monotherapy? Exp. Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2023, 21, 387–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Scumaci, D.; Giuzio, F.; Saturnino, C.; Aquaro, S.; Rosano, C.; Sinicropi, M.S. Multidrug resistance (MDR): A widespread phenomenon in pharmacological therapies. Molecules 2022, 27, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quraini, M.A.; Jabri, Z.A.; Sami, H.; Mahindroo, J.; Taneja, N.; Muharrmi, Z.A.; Busaidi, I.A.; Rizvi, M. Exploring synergistic combinations in extended and pan-drug resistant (XDR and PDR) whole genome sequenced Acinetobacter Baumannii. Microorg. 2023, 11, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willyard, C. The drug-resistant bacteria that pose the greatest health threats. Nature 2017, 543, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.X.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Wan, Q.Q.; Chen, J.H.; Tay, F.R.; Niu, L.N. Considerations and caveats in combating ESKAPE pathogens against nosocomial infections. Adv. Sci. 2019, 7, 1901872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulani, M.S.; Kamble, E.; Kumkar, S.N.; Tawre, M.S.; Pardesi, K.R. Emerging strategies to combat ESKAPE pathogens in the era of antimicrobial resistance: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial antibacterial resistance: The most critical pathogens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Gonzalez-Avila, L.U.; Martínez-Trejo, A.; Saldaña-Padilla, A.; Hernández-Cortez, C.; Bello-López, J.M.; Castro-Escarpulli, G. ESKAPE and beyond: The burden of coinfections in the COVID-19 pandemic. Pathogens 2023, 12, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, B.J.; Soucy, J.R.; Leung, V.; So, M.; Kwan, A.T.H.; Portnoff, J.S.; Bertagnolio, S.; Raybardhan, S.; MacFadden, D.R.; Daneman, N. Antibacterial resistance associated with the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez Jorge, G.; Rodrigues Dos Santos Goes, I.C.; Gontijo, M.T.P. Les misérables: A parallel between antimicrobial resistance and COVID-19 in underdeveloped and developing countries. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 24, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibacterial Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019 (2019 AR Threats Report). 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest-threats.html (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Kumar, M.; Silori, R.; Mazumder, P.; Shrivastava, V.; Loge, F.; Barceló, D.; Mahlknecht, J. Wars and pandemics: AMR accelerators of the 21st century? Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnano San Lio, R.; Favara, G.; Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Agodi, A. How antimicrobial resistance is linked to climate change: An overview of two intertwined global challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, S.S.; Adjemian, J.; Lai, Y.L.; Spaulding, A.B.; Ricotta, E.; Prevots, D.R.; Palmore, T.N.; Rhee, C.; Klompas, M.; Dekker, J.P.; et al. Difficult-to-treat resistance in Gram-negative bacteremia at 173 US hospitals: Retrospective cohort analysis of prevalence, predictors, and outcome of resistance to all first-line agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F.; Cantón, R. Increasing prevalence of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Europe. Eurosurveillance 2008, 13, 19044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brolund, A. Overview of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae from a Nordic perspective. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2014, 4, 24555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, Y.L.; Chen, H.M.; Hii, M.; Hsueh, P.R. Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales infections: Recent advances in diagnosis and treatment. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 59, 106528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, P.D.; Aitken, S.L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Mathers, A.J.; van Duin, D.; Clancy, C.J. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidance on the treatment of Extended-Spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacterales (ESBL-E), carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with Difficult-to-Treat Resistance (DTR-P. aeruginosa). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO Priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.; Carrara, E.; Retamar, P.; Tängdén, T.; Bitterman, R.; Bonomo, R.A.; de Waele, J.; Daikos, G.L.; Akova, M.; Harbarth, S.; et al. European Society of clinical microbiology and infectious diseases (ESCMID) guidelines for the treatment of infections caused by Multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli (endorsed by ESICM-European Society of intensive care Medicine). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenec, L.; Cain, A.K.; Dawson, C.J.; Liu, Q.; Dinh, H.; Lott, H.; Penesyan, A.; Maharjan, R.; Short, F.L.; Hassan, K.A.; et al. Cross-protection and cross-feeding between Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii promotes their co-existence. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Pezzani, M.D. Public health burden of antimicrobial resistance in Europe. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Bravata-Alcantará, J.C.; Sosa-Hernández, O.; Delgado-Balbuena, L.; León-García, G.; Cortés-Ortíz, I.A.; Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Castro-Escarpulli, G.; et al. Clonal dispersion of Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit designed to patients COVID-19. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2021, 15, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdam, A.J. Enterobacteriaceae? Enterobacterales? What should we call enteric gram-negative bacilli? A micro-comic strip. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01888-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin-Regli, A.; Pagès, J.M. Enterobacter aerogenes and Enterobacter cloacae; versatile bacterial pathogens confronting antibiotic treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davin-Regli, A.; Masi, M.; Bialek, S.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; Pagès, J.-M. Antimicrobial resistance and drug efflux pumps in Enterobacter and Klebsiella. In Efflux-Mediated Drug Resistance in Bacteria: Mechanisms, Regulation and Clinical Implications; Li, X.-Z., Elkins, C.A., Zgurskaya, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel, K.; Chagas, T.P.G.; De-Simone, S.G. Acinetobacter baumannii infections in times of COVID-19 pandemic. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, P.; Doudoroff, M.; Stanier, R.Y. A study of the Moraxella group. II. Oxidative-negative species (genus Acinetobacter). J. Bacteriol. 1968, 95, 1520–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabay, O.; Ekşi, F.; Yıldırım, M.S. Investigation of antibiotic resistance profiles and carbapenemase resistance genes in Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from clinical samples. Eur. J. Ther. 2022, 28, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, G.; De Gaetano, S.; Midiri, A.; Zummo, S.; Biondo, C. The Challenge of overcoming antibiotic resistance in carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: “Attack on Titan”. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.K.; Roop, S.A.; Hospenthal, D.R.; Dooley, D.P.; Wenner, K.; Hammock, J.; Taufen, N.; Gourdine, E. Bacteriology of war wounds at the time of injury. Mil. Med. 2006, 171, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze, T.; Hogardt, M.; Velázquez, E.S.; Hack, D.; Besier, S.; Wichelhaus, T.A.; Rochwalsky, U.; Kempf, V.A.; Reinheimer, C. Molecular surveillance of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in Ukrainian patients, Germany, March to June 2022. Euro. Surveill. 2023, 28, 2200850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteway, C.; Breine, A.; Philippe, C.; Van der Henst, C. Acinetobacter baumannii. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocera, F.P.; De Martino, L. Editorial on the research topic of the Special Issue “Current Status of Acinetobacter infections”. Pathogens 2023, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, P.G.; Hagen, R.M.; Podbielski, A.; Frickmann, H.; Warnke, P. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from war-injured patients from the Eastern Ukraine. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serapide, F.; Quirino, A.; Scaglione, V.; Morrone, H.L.; Longhini, F.; Bruni, A.; Garofalo, E.; Matera, G.; Marascio, N.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; et al. Is the pendulum of antimicrobial drug resistance swinging back after COVID-19? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, R.; Bussini, L.; Gaibani, P.; Bovo, F.; Fornaro, G.; Lombardo, D.; Ambretti, S.; Pensalfine, G.; Appolloni, L.; Bartoletti, M.; et al. Carbapenem-resistant bacteria in an intensive care unit during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A multicenter before-and-after cross-sectional study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2022, 43, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Gavaruzzi, F.; Ceccarelli, G.; Borrazzo, C.; Oliva, A.; Alessandri, F.; Magnanimi, E.; Pugliese, F.; Venditti, M. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in intensive care unit. Infection 2022, 50, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutman, A.; Lerner, A.; Schwartz, D.; Carmeli, Y. Evaluation of carriage and environmental contamination by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 949.e5–949.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doidge, M.; Allworth, A.M.; Woods, M.; Marshall, P.; Terry, M.; O’Brien, K.; Goh, H.M.; George, N.; Nimmo, G.R.; Schembri, M.A.; et al. Control of an outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Australia after introduction of environmental cleaning with a commercial oxidizing disinfectant. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, S.; Innes, G.K.; Walters, M.S.; Mehr, J.; Arias, J.; Greeley, R.; Chew, D. Increase in hospital-acquired carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infection and colonization in an acute care hospital during a surge in COVID-19 admissions—New Jersey, February–July 2020. Morb. Mort. Weekly Rep. 2020, 69, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Hu, C.; Luo, L.; Fang, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Peng, Z.; Pan, H. Clinical features and outcomes of 221 patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafiso, V.; Stracquadanio, S.; Lo Verde, F.; Dovere, V.; Zega, A.; Pigola, G.; Aranda, J.; Stefani, S. COLR Acinetobacter baumannii sRNA signatures: Computational comparative identification and biological targets. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, S.T. Habitat association of Klebsiella species. Infect. Control 1985, 6, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, C.; Thom, K.A.; Masnick, M.; Johnson, J.K.; Harris, A.D.; Morgan, D.J. Frequency of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing and non-KPC-producing Klebsiella species contamination of healthcare workers and the environment. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlander, C. Uber die scizomyceten bei der acuten fibrosen pneumonie. Arch. Pathol. Anat. Physiol. Klin. Med. 1882, 87, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, S.; Camprubi, S.; Alberti, S.; Benedi, V.J.; Tomas, J.M. Mechanisms of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistance to complement-mediated killing. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.M.; Bachman, M.A. Colonization, infection, and the accessory genome of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podschun, R.; Ullmann, U. Klebsiella spp. as nosocomial pathogens: Epidemiology, taxonomy, typing methods, and pathogenicity factors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuling, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, D. Molecular pathogenesis of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Kotb, S.; Lyman, M.; Ismail, G.; El Fattah, M.A.; Girgis, S.A.; Etman, A.; Hafez, S.; El-Kholy, J.; Zaki, M.E.S.; Rashed, H.-A.G.; et al. Epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Egyptian intensive care units using National Healthcare–associated Infections Surveillance Data, 2011–2017. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mędrzycka-Dąbrowska, W.; Lange, S.; Zorena, K.; Dąbrowski, S.; Ozga, D.; Tomaszek, L. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in ICU COVID-19 patients—A scoping review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westblade, L.F.; Simon, M.S.; Satlin, M.J. Bacterial coinfections in Coronavirus Disease 2019. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, T.; Harada, S.; Okamoto, K.; Ishino, S.; Kaneko, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ito, R.; Mizoguchi, M. COVID-19 and fatal sepsis caused by hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae, Japan, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Livias, K.; Pinzas-Acosta, K.; Perez-Abad, L.; Panduro-Correa, V.; Rabaan, A.A.; Pecho-Silva, S.; Dámaso-Mata, B. A multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae outbreak in a Peruvian hospital: Another threat from the COVID-19 pandemic. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2022, 43, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miftode, I.L.; Leca, D.; Miftode, R.S.; Roşu, F.; Plesca, C.; Loghin, I.; Timpau, A.S.; Mitu, I.; Mitituc, T.; Dorneanu, O.; et al. The clash of the titans: COVID-19, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, and first mcr-1-mediated colistin resistance in humans in Romania. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Sharma, L.; Cruz, C.S.D.; Zhang, D. Clinical epidemiology, risk factors, and control strategies of Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 750662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan-Najera, J.C.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Barrios-Camacho, H. Hypervirulence and hypermucoviscosity: Two different but complementary Klebsiella spp. phenotypes? Virulence 2017, 8, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, E.T., Jr.; Zierhut, M. Hypervirulent, multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae–Emergence of a superbug of concern for eye care providers. Ocular Immunol. Inflamm. 2022, 30, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, L.K.; Yeh, K.M.; Lin, J.C.; Fung, C.P.; Chang, F.Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: A new invasive syndrome. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choby, J.E.; Howard-Anderson, J.; Weiss, D.S. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae–clinical and molecular perspectives. J. Int. Med. 2020, 287, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederman, E.R.; Crum, N.F. Pyogenic liver abscess with a focus on Klebsiella pneumoniae as a primary pathogen: An emerging disease with unique clinical characteristics. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struve, C.; Roe, C.C.; Stegger, M.; Stahlhut, S.G.; Hansen, D.S.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Andersen, P.S.; Driebe, E.M.; Keim, P.; Krogfelt, K.A. Mapping the evolution of hypervirulent Kleb. Pneumoniae Mbio. 2015, 6, e00630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shankar, C.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Nabarro, L.E.B.; Ravi, R.; Ragupathi, N.K.D.; Rupali, P. Whole genome analysis of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from community and hospital acquired bloodstream infection. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Du, P.; Xiao, N.; Ji, F.; Russo, T.A.; Guo, J. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae is emerging as an increasingly prevalent K. pneumoniae pathotype responsible for nosocomial and healthcare-associated infections in Beijing, China. Virulence 2020, 11, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafat, C.; Messika, J.; Barnaud, G.; Dufour, N.; Magdoud, F.; Billard-Pomarès, T.; Gaudry, S.; Dreyfuss, D.; Branger, C.; Decré, D.; et al. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae, a 5-year study in a French ICU. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, J.F.; Payne, Z.; Coward, A.; Hopkins, K.L.; Turton, J.A.; Doumith, M.; Woodford, N. Virulence genes in isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae from the UK during 2016, including among carbapenemase gene-positive hypervirulent K1-ST23 and ‘non-hypervirulent’ types ST147, ST15 and ST383. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odouard, C.; Ong, D.; Shah, P.R.; Gin, T.; Allen, P.J.; Downie, J.; Lim, L.; McCluskey, P. Rising trends of endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis in Australia. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 45, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mgbemena, O.; Serota, D.P.; Kumar, S.; Wozniak, J.E.; Weiss, D.S.; Kempker, R.R. Peculiar purulence: Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae causing pyomyositis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, E.; Ranson, E.L.; Tsan, A.T.; Bergmann-Leitner, E.S.; Garner, O.B.; Yang, S. Clinical and genomic characterization of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp) infections via passive surveillance in Southern California, 2020–2022. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1001169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y. A global perspective on the convergence of hypervirulence and carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, A.; Awada, B.; Mocadie, M.; Sherri, N.; Haraoui, L.P.; Baby, V.; Araj, G.F.; Kanj, S.S.; Rizk, N.; Matar, G.M.; et al. An unequivocal superbug: PDR Klebsiella pneumoniae with an arsenal of resistance and virulence factor genes. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschtgen, M.S.; Henriques-Normark, B.; Normark, S. The rise of hyper-virulence. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 336–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antibacterial Resistance Threats in the United States. Centers for Disease Control. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/threats-report/2019-ar-threats-report-508.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- World Health Organization. Global Priority List of Antibacterial Resistance Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics. Available online: https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/WHO-PPL-Short_Summary_25Feb-ET_NM_WHO.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Emerging carbapenemases in Gram-negative aerobes. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2002, 8, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, A.J. Epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative infections globally. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katip, W.; Meechoui, M.; Thawornwittayakom, P.; Chinwong, D.; Oberdorfer, P. Efficacy and safety of high loading dose of colistin in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A prospective cohort study. J. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 4, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammanco, A.; Calà, C.; Fasciana, T.; Dowzicky, M.J. Global assessment of the activity of tigecycline against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens between 2004 and 2014 as part of the tigecycline evaluation and surveillance trial. Msphere 2017, 2, e00310-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novović, K.; Jovčić, B. Colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Molecular mechanisms and epidemiology. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankey, G.A. Tigecycline. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzana, P.; Protonotariou, E.; Kassomenaki, A.; Meletis, G.; Tychala, A.; Keskilidou, E.; Arhonti, M.; Katsanou, C.; Daviti, A.; Vasilaki, O.; et al. In vitro synergistic activity of antimicrobial combinations against carbapenem-and colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collalto, D.; Fortuna, A.; Visca, P.; Imperi, F.; Rampioni, G.; Leoni, L. Synergistic activity of colistin in combination with clofoctol against colistin resistant gram-negative pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04275-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Qin, Z.H.; Yue, H.Y.; Bergen, P.J.; Deng, L.M.; He, W.Y.; Zeng, Z.L.; Peng, X.F.; Liu, J.H. Synergistic effects of capric acid and colistin against colistin-susceptible and colistin-resistant Enterobacterales. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, L.; Kong, J.; Pan, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Yao, Z.; Cao, J. Flufenamic acid, a promising agent for the sensitization of colistin-resistant Gram-negative bacteria to colistin. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04052-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burastero, G.J.; Orlando, G.; Santoro, A.; Menozzi, M.; Franceschini, E.; Bedini, A.; Cervo, A.; Faltoni, M.; Bacca, E.; Biagioni, E.; et al. Ceftazidime/avibactam in ventilator-associated pneumonia due to difficult-to-treat non-fermenter gram-negative bacteria in COVID-19 patients: A case series and review of the literature. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Xu, J.; Bai, N.; Liang, B.; Cai, Y. The efficacy and safety of ceftolozane-tazobactam in the treatment of GNB infections: A meta-analysis of clinical studies. Exp. Rev. Anti-infect. Ther. 2023, 21, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khankhel, Z.S.; Dillon, R.J.; Thosar, M.; Bruno, C.; Puzniak, L. Ceftolozane/tazobactam for the treatment of bacteremia: A systematic literature review (SLR). Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2022, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Hamouche, J.E.; Wang, G.; Smith, M.; Yin, C.; Dhand, A.; Dimitrova, N.; Fallon, J.T. Integrated genome-wide analysis of an isogenic pair of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates with differential antimicrobial resistance to ceftolozane/tazobactam, ceftazidime/avibactam, and piperacillin/tazobactam. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, A.; Del Giacomo, P.; Rossolini, G.M.; Tumbarello, M. Meropenem/vaborbactam: A next generation β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor combination. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.N.; Lodise, T.P. New perspectives on antimicrobial agents: Imipenem-relebactam. Antimicrob. Ag. Chemother. 2022, 66, e00256-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, J.; Dillon, R.; Massello, M.; Ralph, L.; Yang, Z. Cost–effectiveness of imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam for hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia. J. Compar. Eff. Res. 2023, 12, e220113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaeer, K.M.; Zmarlicka, M.T.; Chahine, E.B.; Piccicacco, N.; Cho, J.C. Plazomicin: A next-generation aminoglycoside. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2019, 39, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Burton, C.E. Eravacycline, a newly approved fluorocycline. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong’uti, S.; Czech, M.; Robilotti, E.; Holubar, M. Cefiderocol: A new cephalosporin stratagem against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y. Treatment options for carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, S565–S575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaibani, P.; Giani, T.; Bovo, F.; Lombardo, D.; Amadesi, S.; Lazzarotto, T.; Coppi, M.; Rossolini, G.M.; Ambretti, S. resistance to ceftazidime/avibactam, meropenem/vaborbactam and imipenem/relebactam in Gram-negative MDR bacilli: Molecular mechanisms and susceptibility testing. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ghali, A.; Kunz Coyne, A.J.; Caniff, K.; Bleick, C.; Rybak, M.J. Sulbactam-durlobactam: A Novel β-lactam-β-lactamase inhibitor combination targeting carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections. Pharmacother. J. Human Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2023, 43, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugaiyan, J.; Kumar, P.A.; Rao, G.S.; Iskandar, K.; Hawser, S.; Hays, J.P.; Mohsen, Y.; Adukkadukkam, S.; Awuah, W.A.; Jose, R.A.M.; et al. Progress in alternative strategies to combat antimicrobial resistance: Focus on antibiotics. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Chen, L.-K.; Zhu, T. Phage therapy for secondary bacterial infections with COVID-19. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 52, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, P.; Kose, S.; Dao, S.; Ganbarov, K.; Tanomand, A.; Dal, T.; Aghazadeh, M.; Ghotaslou, R.; Ahangarzadeh Rezaee, M.; Yousefi, B.; et al. How CRISPR-Cas system could be used to combat antimicrobial resistance. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Jia, X.; Yue, C.; Deng, S.; Zhang, X. Non-antibiotic prevention and treatment against Acinetobacter baumannii infection: Are vaccines and adjuvants effective strategies? Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Al-Saryi, N.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Aziz, S.N. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii as an emerging concern in hospitals. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 6987–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hujer, A.M.; Higgins, P.G.; Rudin, S.D.; Buser, G.L.; Marshall, S.H.; Xanthopoulou, K.; Seifert, H.; Rojas, L.J.; Domitrovic, T.N.; Cassidy, P.M.; et al. Nosocomial outbreak of extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates containing blaOXA-237 carried on a plasmid. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00797-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.D.; Fairfield, C.J.; Drake, T.M.; Turtle, L.; Seaton, R.A.; Wootton, D.G.; Sigfrid, L.; Harrison, E.M.; Docherty, A.B.; de Silva, T.I.; et al. Co-infections, secondary infections, and antimicrobial use in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 during the first pandemic wave from the ISARIC WHO CCP-UK study: A multicentre, prospective cohort study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e354–e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segala, F.V.; Bavaro, D.F.; Di Gennaro, F.; Salvati, F.; Marotta, C.; Saracino, A.; Murri, R.; Fantoni, M. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 epidemic on antimicrobial resistance: A literature review. Viruses 2021, 13, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.J.; Loman, N.; Bogaert, D.; O’Grady, J. Co-infections: Potentially lethal and unexplored in COVID-19. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariyawasam, R.M.; Julien, D.A.; Jelinski, D.C.; Larose, S.L.; Rennert-May, E.; Conly, J.M.; Dingle, T.C.; Chen, J.Z.; Tyrrell, G.J.; Ronksley, P.E. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis (November 2019–June 2021). Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2022, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvester, R.; Madhavan, A.; Kokkat, A.; Parolla, A.; Adarsh, B.M.; Harikrishnan, M.; Abdulla, M.H. Global surveillance of antimicrobial resistance and hypervirulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae from LMICs: An in-silico approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, N.; Ciccarese, F.; Balacchi, C.; Rimondi, M.R.; Modolon, C.; Sportoletti, C.; Capozzi, C.; Renzulli, M.; Paccapelo, A.; Castelli, A.; et al. Co-infections and superinfections in COVID-19 critically Ill patients are associated with CT imaging abnormalities and the worst outcomes. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, B.J.; So, M.; Leung, V.; Raybardhan, S.; Lo, J.; Kan, T.; Leung, F.; Westwood, D.; Daneman, N.; MacFadden, D.R.; et al. Predictors and microbiology of respiratory and bloodstream bacterial infection in patients with COVID-19: Living rapid review update and meta-regression. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, B.J.; So, M.; Raybardhan, S.; Leung, V.; Westwood, D.; MacFadden, D.R.; Soucy, J.P.R.; Daneman, N. Bacterial coinfection and secondary infection in patients with COVID-19: A living rapid review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microb. Infect. 2020, 26, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, Q.X.M.; Kong, H.; Chen, H.; Fu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, J. Secondary bacterial infections in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansbury, L.; Lim, B.; Baskaran, V.; Lim, W.S. Coinfections in people with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Hsueh, P.R. Co-infections among patients with COVID-19: The need for combination therapy with non-anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents? J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrinenko, A.; Kolesnichenko, S.; Kadyrova, I.; Turmukhambetova, A.; Akhmaltdinova, L.; Klyuyev, D. Bacterial co-infections and antimicrobial resistance in patients hospitalized with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia in Kazakhstan. Pathogens 2023, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovelli, A.; Oliva, A.; Siccardi, G.; Tramontano, A.; Pellegrino, D.; Mastroianni, C.M.; Venditti, M.; Palange, P. Risk factors and effect on mortality of superinfections in a newly established COVID-19 respiratory sub-intensive care unit at University Hospital in Rome. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floridia, M.; Giuliano, M.; Monaco, M.; Palmieri, L.; Lo Noce, C.; Palamara, A.T.; Pantosti, A.; Brusaferro, S.; Onder, G. Microbiologically confirmed infections and antibiotic-resistance in a national surveillance study of hospitalised patients who died with COVID-19, Italy 2020–2021. Antimicrob. Res. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traglia, G.M.; Pasteran, F.; Escalante, J.; Nishimura, B.; Tuttobene, M.R.; Subils, T.; Nuñez, M.R.; Rivollier, M.G.; Corso, A.; Tolmasky, M.E.; et al. Genomic comparative analysis of two multi-drug resistance (MDR) Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains assigned to international clonal lineage II recovered pre-and post-COVID-19 pandemic. Biology 2023, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh Ahmed, M.; Abdulrahman, Z.F.A.; Taha, Z.M.A. Risk factors of clonally related, multi, and extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in severely Ill COVID-19 patients. Canad. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 2023, 3139270. [Google Scholar]
- Boorgula, S.Y.; Yelamanchili, S.; Kottapalli, P.; Naga, M.D. An update on secondary bacterial and fungal infections and their antimicrobial resistance pattern (AMR) in COVID-19 confirmed patients at a tertiary care hospital. J. Lab. Physicians 2022, 14, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczyk, S.; Taylor, A.; Brown, A.; de Kraker, M.E.A.; El-Saed, A.; Alshamrani, M.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Jacob, M.; Löfmark, S.; Perovic, O.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the surveillance, prevention and control of antimicrobial resistance: A global survey. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 3045–3058. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, A.K. The novel coronavirus COVID-19 outbreak: Global implications for antimicrobial resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; He, S.; Legido-Quigley, H. Antimicrobial resistance research collaborations in Asia: Challenges and opportunities to equitable partnerships. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daria, S.; Islam, M.R. Indiscriminate use of antibiotics for COVID-19 treatment in South Asian Countries is a threat for future pandemics due to antibacterial resistance. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 15, 2632010X221099889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambraki, I.; Chadag, M.; Cousins, M.; Graells, T.; Léger, A.; Henriksson, P.; Troell, M.; Harbarth, S.J.; Wernli, D.; Søgaard Jørgensen, P.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance in South East Asia: A participatory systems modelling approach. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 116, S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, S.; Bansal, N.; Rao, B.K.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Rodrigues, C.; Wattal, C.; Goyal, J.P.; Tadepalli, K.; Mathur, P.; Venkateswaran, R.; et al. Secondary infections in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: Indian experience. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, V.; Jain, C.; Singh, N.; Alsulimani, A.; Gupta, C.; Dar, S.; Haque, S.; Das, S. Paradigm shift in antimicrobial resistance pattern of bacterial isolates during the COVID-19 pandemic. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Khan, M.; Saleem, W.; Karobari, M.I.; Mohamed, R.N.; Heboyan, A.; Rabaan, A.A.; Mutair, A.A.; Alhumaid, S.; Alsadiq, S.A. Evaluation of bi-lateral co-infections and antibacterial resistance rates among COVID-19 patients. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD; ECDC. Antimicrobial Resistance—Tackling the Burden in the European Union—Briefing Note for EU/EEA Countries. 2019. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/health/health-systems/AMR-Tackling-the-Burden-in-the-EU-OECD-ECDC-Briefing-Note-2019.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2023).
- Khaznadar, O.; Khaznadar, F.; Petrovic, A.; Kuna, L.; Loncar, A.; Kolaric, T.O.; Mihaljevic, V.; Tabll, A.A.; Smolic, R.; Smolic, M. Antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial stewardship: Before, during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 727–740. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2022–2020 Data; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Gysin, M.; Acevedo, C.T.; Haldimann, K.; Bodendoerfer, E.; Imkamp, F.; Bulut, K.; Buehler, P.K.; Brugger, S.D.; Becker, K.; Hobbie, S.N. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of respiratory Gram-negative bacterial isolates from COVID-19 patients in Switzerland. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Cogliati Dezza, F.; Arcari, G.; Alessi, F.; Valeri, S.; Curtolo, A.; Sacco, F.; Ceccarelli, G.; Raponi, G.; Alessandri, F.; Mastroianni, C.M.; et al. Clinical impact of COVID-19 on multi-drug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli bloodstream infections in an intensive care unit setting: Two pandemics compared. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 926. [Google Scholar]
- Falcone, M.; Tiseo, G.; Arcari, G.; Leonildi, A.; Giordano, C.; Tempini, S.; Bibbolino, G.; Mozzo, R.; Barnini, S.; Carattoli, A.; et al. Spread of hypervirulent multidrug-resistant ST147 Klebsiella pneumoniae in patients with severe COVID-19: An observational study from Italy, 2020–2021. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Mbow, M.; Lell, B.; Jochems, S.P.; Cisse, B.; Mboup, S.; Dewals, B.G.; Jaye, A.; Dieye, A.; Yazdanbakhsh, M. COVID-19 in Africa: Dampening the storm? Science 2020, 369, 624–626. [Google Scholar]
- Gutema, G.; Homa, G. Cropping up crisis at the nexus between COVID-19 and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Africa: A scoping review and synthesis of early evidence. Cureus 2022, 14, e21035. [Google Scholar]
- Harant, A. Assessing transparency and accountability of national action plans on antimicrobial resistance in 15 african countries. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Mutua, J.M.; Njeru, J.M.; Musyoki, A.M. Multidrug resistant bacterial infections in severely ill COVID-19 patients admitted in a national referral and teaching hospital, Kenya. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 877. [Google Scholar]
- Adebisi, Y.A.; Jimoh, N.D.; Ogunkola, I.O.; Uwizeyimana, T.; Olayemi, A.H.; Ukor, N.A.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E., 3rd. The use of antibiotics in COVID-19 management: A rapid review of national treatment guidelines in 10 African countries. Trop. Med. Health 2021, 49, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Tull, F.; Bamert, R.S.; Smith, L.; Goodwin, D.; Lambert, K. Identifying and prioritising behaviours to slow antimicrobial resistance. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 949. [Google Scholar]
- Merlino, J.; Siarakas, S. Antibiotic prescribing and antimicrobial resistance from an Australian perspective. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 536–538. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Government Department of Health. 2019 Influenza Season in Australia. A Summary from the National Influenza Surveillance Committee. 2021. Available online: https://www1.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/7610377A5BEB1D25CA25874B007D9DD2/%24File/2019-Influenza-Season-Summary.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Basseal, J.M.; Bennett, C.M.; Collignon, P.; Currie, B.J.; Durrheim, D.N.; Leask, J.; McBryde, E.S.; McIntyre, P.; Russell, F.M.; Smith, D.W.; et al. Key lessons from the COVID-19 public health response in Australia. Lancet Reg. Health—West. Pac. 2022, 30, 100616. [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren, M.; Jorgensen, B. Podcasting and constructive journalism in health stories about antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Media Int. Australia 2023, 187, 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, K.A.; Puzniak, L.A.; Yu, K.C.; Klinker, K.P.; Watts, J.A.; Moise, P.A.; Finelii, L.; Ai, C.; Gupta, V. A multicenter comparison of prevalence and predictors of antimicrobial resistance in hospitalized patients before and during the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pandemic. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2022; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.; Sridhar, D. The pandemic legacy of antimicrobial resistance in the USA. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e726–e727. [Google Scholar]
- El Omeiri, N.; Beith, A.; Bruinsma, N.; Caipo, M.; Barcos, L.; Mesplet, M.; del Barrio, L.; Minassian, M.; Arias, I.C.; Vásquez, G.; et al. Driving multisectoral antimicrobial resistance action in South America: Lessons learned from implementing an enhanced tripartite AMR country self-assessment tool. One Health 2022, 16, 100474. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.L.; Mortimer, T.D.; Grad, Y.H. Machine learning models for Neisseria gonorrhoeae antimicrobial susceptibility tests. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2023, 1520, 74–88. [Google Scholar]
- Coen, M.E.; Williford, S.L.; Muvva, R.; Genberg, B.; Greenbaum, A.; Schumacher, C.M. Characteristics of reported gonorrhea diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic compared with pre–COVID-19 pandemic, Baltimore City, Maryland. Sex. Transmit. Dis. 2023, 50, 215. [Google Scholar]
- López-Jácome, L.E.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Franco-Cendejas, R.; Camacho-Ortiz, A.; Morfin-Otero, M.D.R.; Rodríguez-Noriega, E.; Ponce-de-León, A.; Ortiz-Brizuela, E.; Rojas-Larios, F.; Velázquez-Acosta, M.D.C.; et al. Increment antimicrobial resistance during the COVID-19 pandemic: Results from the Invifar Network. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Gandra, S.; Alvarez-Uria, G.; Stwalley, D.; Nickel, K.B.; Reske, K.A.; Kwon, J.H.; Dubberke, E.R.; Olsen, M.A.; Burnham, J.P. Microbiology clinical culture diagnostic yields and antimicrobial resistance proportions before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in an Indian Community Hospital and two US Community Hospitals. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 537. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.R.; Corso, A.; Pasteran, F.; Shal, J.; Sosa, A.; Pillonetto, M.; de Souza Peral, R.T.; Hormazabal, J.C.; Araya, P.; Saavedra, S.Y.; et al. Increased detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales bacteria in Latin America and the Caribbean during the COVID-19 pandemic. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, G.H.D.A.; de Oliveira, A.R.; dos Santos Barbosa, M.; Rossato, L.; da Silva Barbosa, K.; Simionatto, S. Multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in patients with COVID-19: An epidemiological and clinical study. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Acronym | Resistant to: |
|---|---|---|
| Pan-drug-resistant | PDR | All antibiotics. even including colistin and tegacyclin |
| Difficult-to-treat drug-resistant | DTR | All first-line agents, including all β-lactams (carbapenems and β-lactamase inhibitor combinations) and fluoroquinolones |
| Extensively drug-resistant | XDR | All drugs except for colistin and tegacyclin |
| Multidrug-resistant | MDR | Three or even more antimicrobial agents |
| Carbapenems-resistant | CR | Carbapenems |
| Extended-spectrum β-lactamase | ESBL | Extended-spectrum β-lactamase, including penicillins, cephalosporins (also the third generation), and the monobactam aztreonam |
| Enterobacterales | |
| Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales | CRE |
| Extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing Enterobacterales | EPE |
| Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales | CPE |
| A. baumannii | |
| Carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii | CR-Ab |
| Extensively drug-resistant A. baumannii | XDR-Ab |
| Multidrug-resistant A. baumannii | MDR-Ab |
| P. aeruginosa | |
| Difficult-to-treat drug-resistant P. aeruginosa | DTR-Pa |
| Carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa | CR-Pa |
| Extensively drug-resistant P. aeruginosa | XDR-Pa |
| K. pneumoniae | |
| Carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae | CR-Kp |
| Structure | Name | Class |
|---|---|---|
| Doripenem | 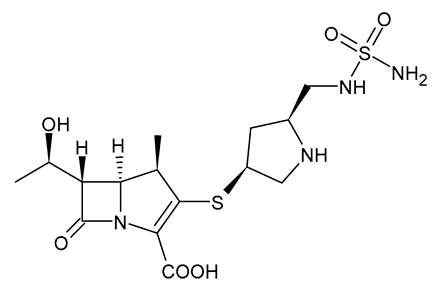 | Carbapenem |
| Ertapenem | 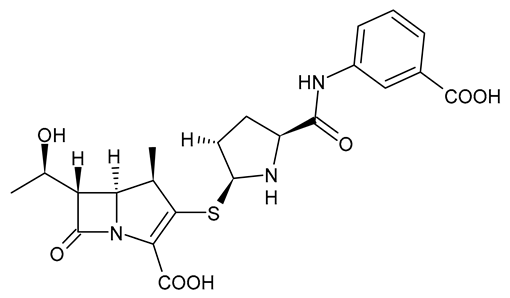 | Carbapenem |
| Imipenem | 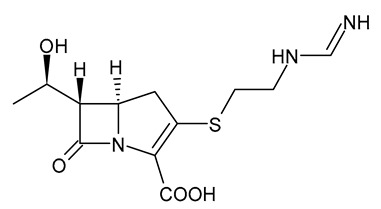 | Carbapenem |
| Meropenem | 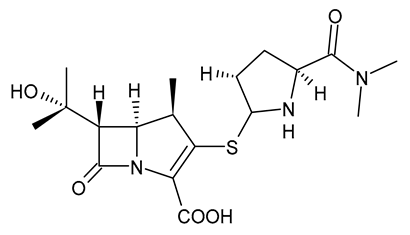 | Carbapenem |
| Tigecycline | 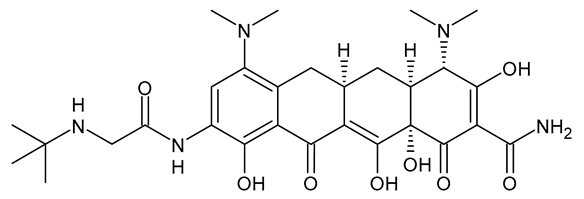 | Glycylcycline Antibiotic |
| Ceftazidime | 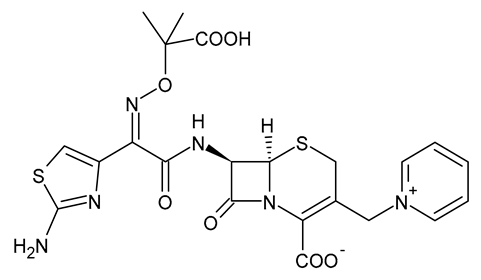 | β-Lactam Antibiotic (Cephalosporin) |
| Cefiderocol | 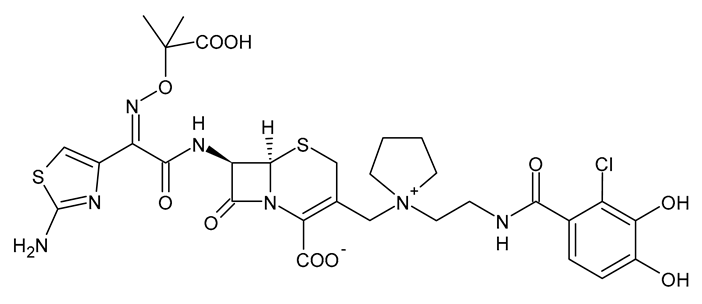 | β-Lactam Antibiotic (Cephalosporin) |
| Ceftolozane | 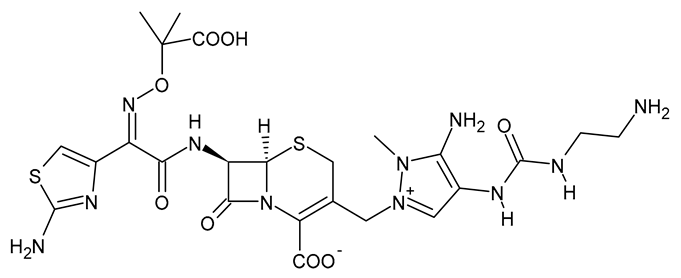 | β-Lactam Antibiotic (Cephalosporin) |
| Avibactam |  | β-Lactamase Inhibitor |
| Tazobactam |  | β-Lactamase Inhibitor |
| Vaborbactam | 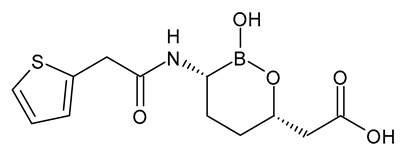 | β-Lactamase Inhibitor |
| Durlobactam | 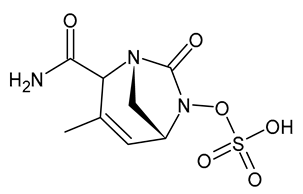 | β-Lactamase Inhibitor |
| Plazomicin |  | Aminoglycoside Antibiotic |
| Eravacycline | 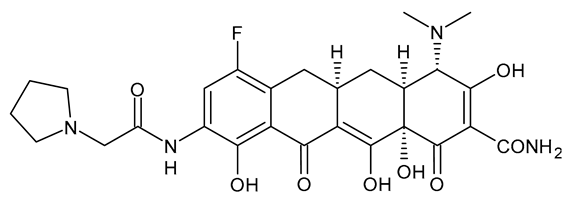 | Fluorocycline Antibiotic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Catalano, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Pellegrino, M.; Giuzio, F.; Marra, M.; Rosano, C.; Saturnino, C.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Aquaro, S. Antibiotic-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens and COVID-19: The Pandemic beyond the Pandemic. Viruses 2023, 15, 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091843
Catalano A, Iacopetta D, Ceramella J, Pellegrino M, Giuzio F, Marra M, Rosano C, Saturnino C, Sinicropi MS, Aquaro S. Antibiotic-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens and COVID-19: The Pandemic beyond the Pandemic. Viruses. 2023; 15(9):1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091843
Chicago/Turabian StyleCatalano, Alessia, Domenico Iacopetta, Jessica Ceramella, Michele Pellegrino, Federica Giuzio, Maria Marra, Camillo Rosano, Carmela Saturnino, Maria Stefania Sinicropi, and Stefano Aquaro. 2023. "Antibiotic-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens and COVID-19: The Pandemic beyond the Pandemic" Viruses 15, no. 9: 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091843
APA StyleCatalano, A., Iacopetta, D., Ceramella, J., Pellegrino, M., Giuzio, F., Marra, M., Rosano, C., Saturnino, C., Sinicropi, M. S., & Aquaro, S. (2023). Antibiotic-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens and COVID-19: The Pandemic beyond the Pandemic. Viruses, 15(9), 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091843













