Development of a Rapid Epstein–Barr Virus Detection System Based on Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and a Lateral Flow Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.2.1. Cell DNA Extraction
2.2.2. EBV DNA Extraction
2.3. Construction of Standard EBV Plasmids
2.4. Measurement of Viral DNA Concentration
2.5. PCR for EBV Detection
2.5.1. Primer Screening
2.5.2. Determination of the Test Sample Type
2.5.3. Sensitivity Evaluation
2.6. RPA Method of EBV Detection
2.6.1. Basic RPA System
2.6.2. Optimization of the Reaction Conditions
2.6.3. Sensitivity Evaluation
2.7. RPA-LFA Method of EBV Detection
2.7.1. Basic RPA-LFA System
2.7.2. Optimization of Reaction Conditions
2.7.3. Sensitivity Evaluation
2.8. The Detection of Cell Lines
3. Results
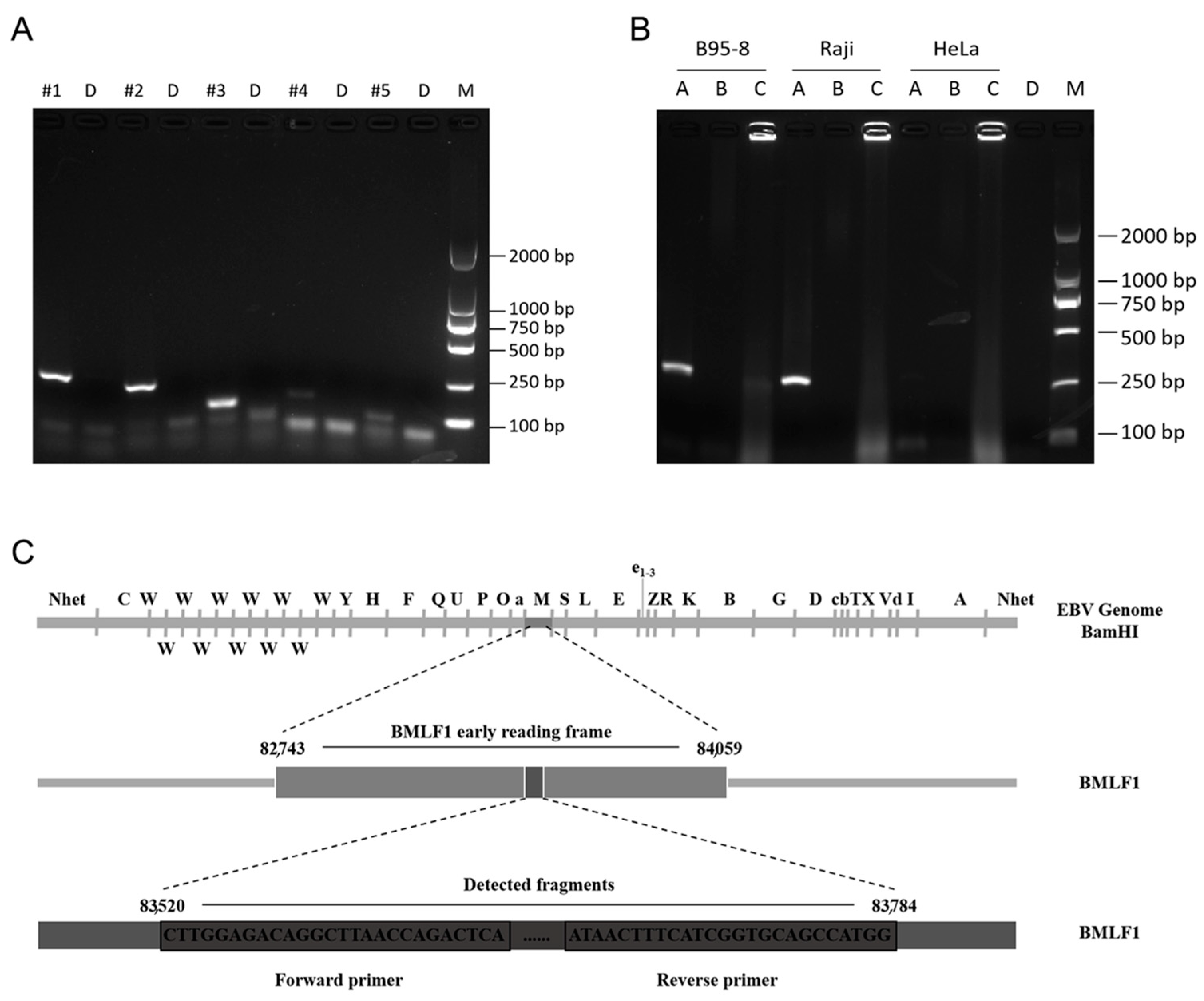
3.1. Screening of Amplification Primers and Sample Types
3.2. Establishment of a Reaction System for EBV Detection by the RPA-LFA System
3.3. Determination of the RPA-LFA Reaction Temperature
3.4. Determination of the RPA-LFA Reaction Time
3.5. Comparison of the Sensitivity of the PCR and RPA-LFA Methods for EBV Detection
3.6. Use of the PCR and RPA Systems to Detect EBV in Different Cell Lines
3.7. RPA-LFA Specificity Evaluation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldi, L.; Hacker, D.L.; Adam, M.; Wurm, F.M. Recombinant protein production by large-scale transient gene expression in mammalian cells: State of the art and future perspectives. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, G. Biopharmaceutical benchmarks 2006. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehring, D.; Gonzalez, R.; Pörtner, R.; Czermak, P. Experimental and modelling study of different process modes for retroviral production in a fixed bed reactor. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 122, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacey, G.N. Cell contamination leads to inaccurate data: We must take action now. Nature 2000, 403, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, P.; Marshall, D.; Reid, Y.; Parkes, H.; Gelber, C. The costs of using unauthenticated, over-passaged cell lines: How much more data do we need? Biotechniques 2007, 43, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, P.W.; Wiebe, M.E.; Leung, J.C.; Hussein, I.T.M.; Keumurian, F.J.; Bouressa, J.; Brussel, A.; Chen, D.; Chong, M.; Dehghani, H.; et al. Viral contamination in biologic manufacture and implications for emerging therapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merten, O.W. Virus contaminations of cell cultures—A biotechnological view. Cytotechnology 2002, 39, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, P.D.; Hounshell, J.; Sherman, L.A.; Godwin, J.; Bennett, C.L. Legal, Financial, and Public Health Consequences of HIV Contamination of Blood and Blood Products in the 1980s and 1990s. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanguy, E.; Béziat, V.; Mogensen, T.H.; Casanova, J.-L.; Tangye, S.G.; Zhang, S.-Y. Human inborn errors of immunity to herpes viruses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 62, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I. Epstein–Barr Virus Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Working Group. Biological Agents: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100, pp. 1–441. [Google Scholar]
- Valent, S.C.; Yasmin, E. Epstein-Barr Virus Infections in Families: The Role of Children with Infectious Mononucleosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 154, 824–850. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.; Lipman, M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damania, B.; Kenney, S.C.; Raab-Traub, N. Epstein-Barr virus: Biology and clinical disease. Cell 2022, 185, 3652–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uphoff, C.C.; Denkmann, S.A.; Steube, K.G.; Drexler, H.G. Detection of EBV, HBV, HCV, HIV-1, HTLV-I and -II, and SMRV in human and other primate cell lines. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 904767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioda, S.; Kasai, F.; Watanabe, K.; Kawakami, K.; Ohtani, A.; Iemura, M.; Ozawa, M.; Arakawa, A.; Hirayama, N.; Kawaguchi, E.; et al. Screening for 15 pathogenic viruses in human cell lines registered at the JCRB Cell Bank: Characterization of in vitro human cells by viral infection. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 172472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, M.; Bozic, M.; Konrad, P.M.; Grohs, K.; Santner, B.I.; Kessler, H.H. Analytical and clinical performance of a new molecular assay for Epstein-Barr virus DNA quantitation. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 212, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Qing, T.Y.; Zhao, L.Q.; Tan, H.; Ding, N.; Ding, Y.X.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, R.Q.; Wang, J.R.; Chen, Z.W. Rapid Internal Control Reference Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assays for EBV and CMV Detection. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 650–655. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, S.; Shibata, Y.; Kawada, J.-I.; Hara, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Morishima, T.; Ihira, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Asano, Y.; Kimura, H. Rapid detection of Epstein–Barr virus DNA by loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. J. Clin. Virol. 2006, 37, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yao, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Cao, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiang, T.; et al. Genome sequencing analysis identifies Epstein-Barr virus subtypes associated with high risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasifoglu, N.; Oz, S.; Dinleyici, E.C.; Us, T.; Bor, O.; Durmaz, G.; Akgun, Y. Comparison of Methods Used for the Diagnosis of Epstein-Barr Virus Infections in Children. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.C.; Lee, L.P. One-step digital plasma separation for molecular diagnostics. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, MicroTAS 2013, Freiburg, Germany, 27–31 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Piepenburg, O.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.L.; Armes, N.A. DNA Detection Using Recombination Proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, Y.; Tsunokawa, Y.; Takebe, N.; Nawa, H.; Nakanishi, S.; Terada, M.; Sugimura, T. Nucleotide sequences of cDNAs for human papillomavirus type 18 transcripts in HeLa cells. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, K.; Li, J.; Broutian, T.R.; Padilla-Nash, H.; Xiao, W.; Jiang, B.; Rocco, J.W.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, B.; Wangsa, D.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of HPV integration in human cancers reveals recurrent, focal genomic instability. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sells, M.A.; Chen, M.L.; Acs, G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, S.R.; Ridpath, J.F.; Black, J.; Macy, M.; Roblin, R. Survey of cell lines in the American Type Culture Collection for bovine viral diarrhea virus. J. Virol. Methods 1994, 48, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattengale, P.; Smith, R.; Gerber, P. Selective transformation of B Lymphocytes by E.B. virus. Lancet 1973, 302, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liao, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Yi, L.; Liu, X.; Shen, H.; Gao, S.; Lu, Q. Duplex On-Site Detection of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Three-Segment Lateral Flow Strips. Biosensors 2021, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeshma, M.; Bhat, A.I.; Jeevalatha, A. Rapid onsite detection of piper yellow mottle virus infecting black pepper by recombinase polymerase amplification-lateral flow assay (RPA-LFA). J. Virol. Methods 2023, 315, 114695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, A.; Ramilo-Fernández, G.; Denis, F.; Oliveira, L.; Shum, P.; Silva, H.; Sotelo, C.G. A New Rapid Method for the Authentication of Common Octopus (Octopus vulgaris) in Seafood Products Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) and Lateral Flow Assay (LFA). Foods 2021, 10, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Tie, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, R.; He, A.; Nie, M.; Fan, G.; Li, F.; Tian, F.; et al. Detection of low-load Epstein-Barr virus in blood samples by enriched recombinase aided amplification assay. AMB Express 2022, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, D.F.; Liu, C.C. On-line cell lysis and DNA extraction on a microfluidic biochip fabricated by microelectromechanical system technology. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 1844–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Joanne, M.; Stetten, F. Review: A comprehensive summary of a decade development of the recombinase polymerase amplification. Analyst 2018, 144, 31–67. [Google Scholar]
- Crannell, Z.A.; Rohrman, B.; Richards-Kortum, R. Equipment-free incubation of recombinase polymerase amplification reactions using body heat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 112146–112153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davi, S.D.; Kissenkötter, J.; Faye, M.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Stahl-Hennig, C.; Faye, O.; Faye, O.; Sall, A.A.; Weidmann, M.; Ademowo, O.G.; et al. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Monkeypox virus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 95, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, G.; Yin, W.; Wu, X.; Lin, Y.; Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Sun, T.; Wei, X. Rapid detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) by recombinase polymerase amplification. J. Virol. Methods 2022, 300, 114362–114368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, C.K.; Kamle, S.; Sinha, R.P.; Bhatnagar, R.K.; Kachru, D.N. Development of nanocolloidal gold based immunochromatographic assay for rapid detection of transgenic vegetative insecticidal protein in genetically modified crops. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Río, J.S.d.; Adly, N.Y.; Acero-Sánchez, J.L. Electrochemical detection of Francisella tularensis genomic DNA using solid-phase recombinase polymerase amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 674–678. [Google Scholar]






| Genebank | Nucleotide Positions | Primer | Sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| V01555 | 83,520 | PCR-FP1 | CTTGGAGACAGGCTTAACCAGACTCA |
| −83,784 | PCR-RP1 | CCATGGCTGCACCGATGAAAGTTAT | |
| 82,507 | PCR-FP2 | GTGCCTCCTCAAATGTTCCAGAAGT | |
| −82,737 | PCR-RP2 | TAAACTGAATCTCCACCTGTGTAACCTCA | |
| 165,806 | PCR-FP3 | CTACCTGTGCCGCATGAAACTGGGCGAGACCGA | |
| −165,904 | PCR-RP3 | CATGTCACAGTAAGGACAGAGAAGTCTGGG | |
| 82,339 | PCR-FP4 | AGTTAGCATTGGCGTCGG | |
| −82,497 | PCR-RP4 | GGAACGGTGATTAGGCACTG | |
| 4683 | PCR-FP5 | CCTGGTCATCCTTTGCCA | |
| −4777 | PCR-RP5 | TGCTTCGTTATAGCCGTAGT |
| Genebank | Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| V01555 | RPA-FP1 | [FITC]CTTGGAGACAGGCTTAACCAGACTCA |
| RPA-FP2 | CTTGGAGACAGGCTTAACCAGACTCA | |
| RPA-RP | [BIOTIN]CCATGGCTGCACCGATGAAAGTTAT | |
| RPA-Probe | [FITC]TGCCGGCCCCTCGAGATTCTGACCGGGGACC[THF]CTGGTTGCTCTGTTG[C3-Spacer] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Tang, D.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Shen, C. Development of a Rapid Epstein–Barr Virus Detection System Based on Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and a Lateral Flow Assay. Viruses 2024, 16, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010106
Sun Y, Tang D, Li N, Wang Y, Yang M, Shen C. Development of a Rapid Epstein–Barr Virus Detection System Based on Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and a Lateral Flow Assay. Viruses. 2024; 16(1):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010106
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yidan, Danni Tang, Nan Li, Yudong Wang, Meimei Yang, and Chao Shen. 2024. "Development of a Rapid Epstein–Barr Virus Detection System Based on Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and a Lateral Flow Assay" Viruses 16, no. 1: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010106
APA StyleSun, Y., Tang, D., Li, N., Wang, Y., Yang, M., & Shen, C. (2024). Development of a Rapid Epstein–Barr Virus Detection System Based on Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and a Lateral Flow Assay. Viruses, 16(1), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010106






