Protoporphyrin IX-Dependent Antiviral Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid against Feline Coronavirus Type II
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures and Viruses
2.2. Compounds
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Antiviral Effects of Compounds
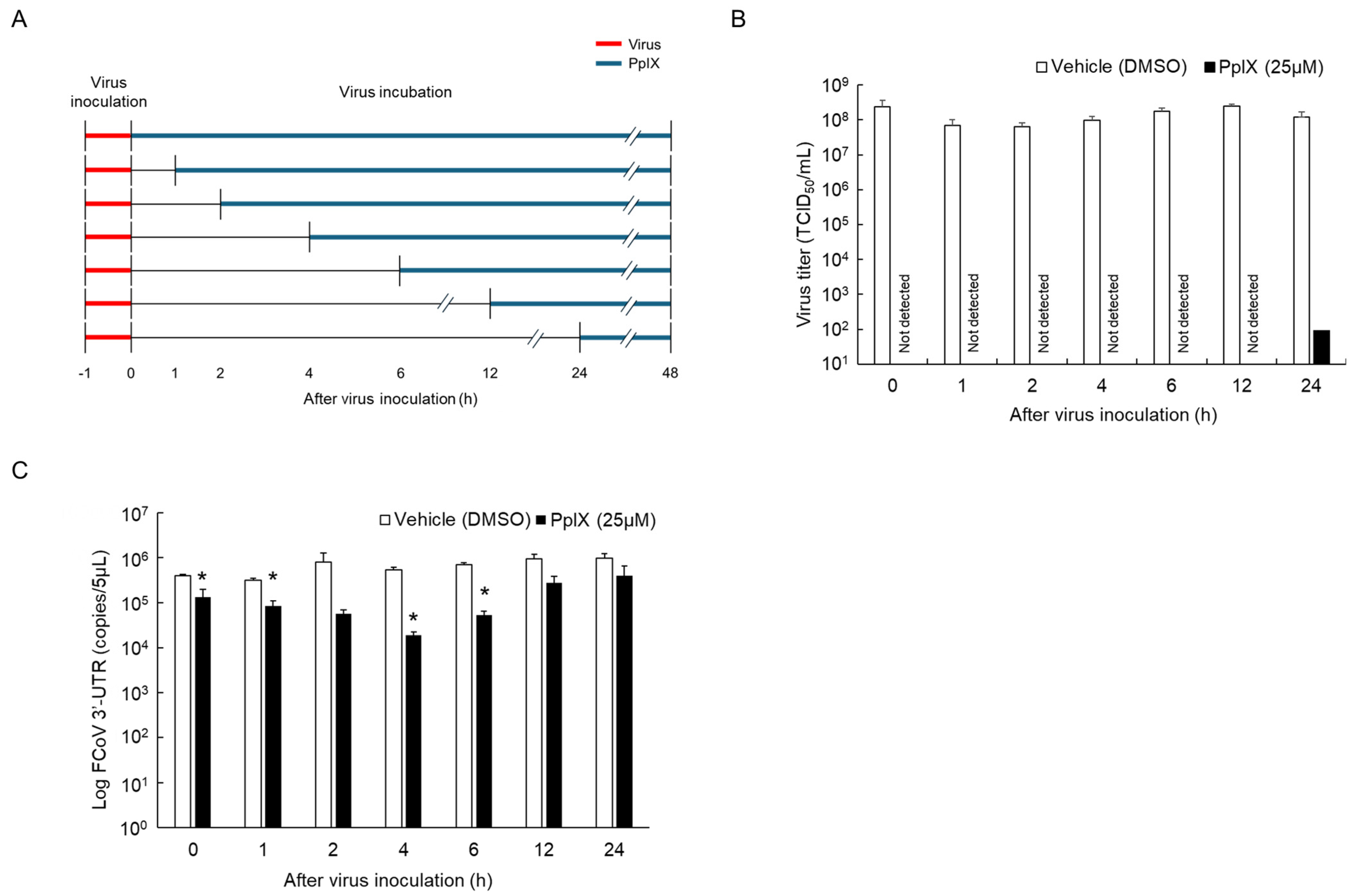
2.5. Time of Addition Assay for PpIX
2.6. RNA Isolation
2.7. Quantification of FCoV 3′-UTR
2.8. Measurement of Feline HO-1 Gene Expression
2.9. Direct Antiviral Effects of PpIX
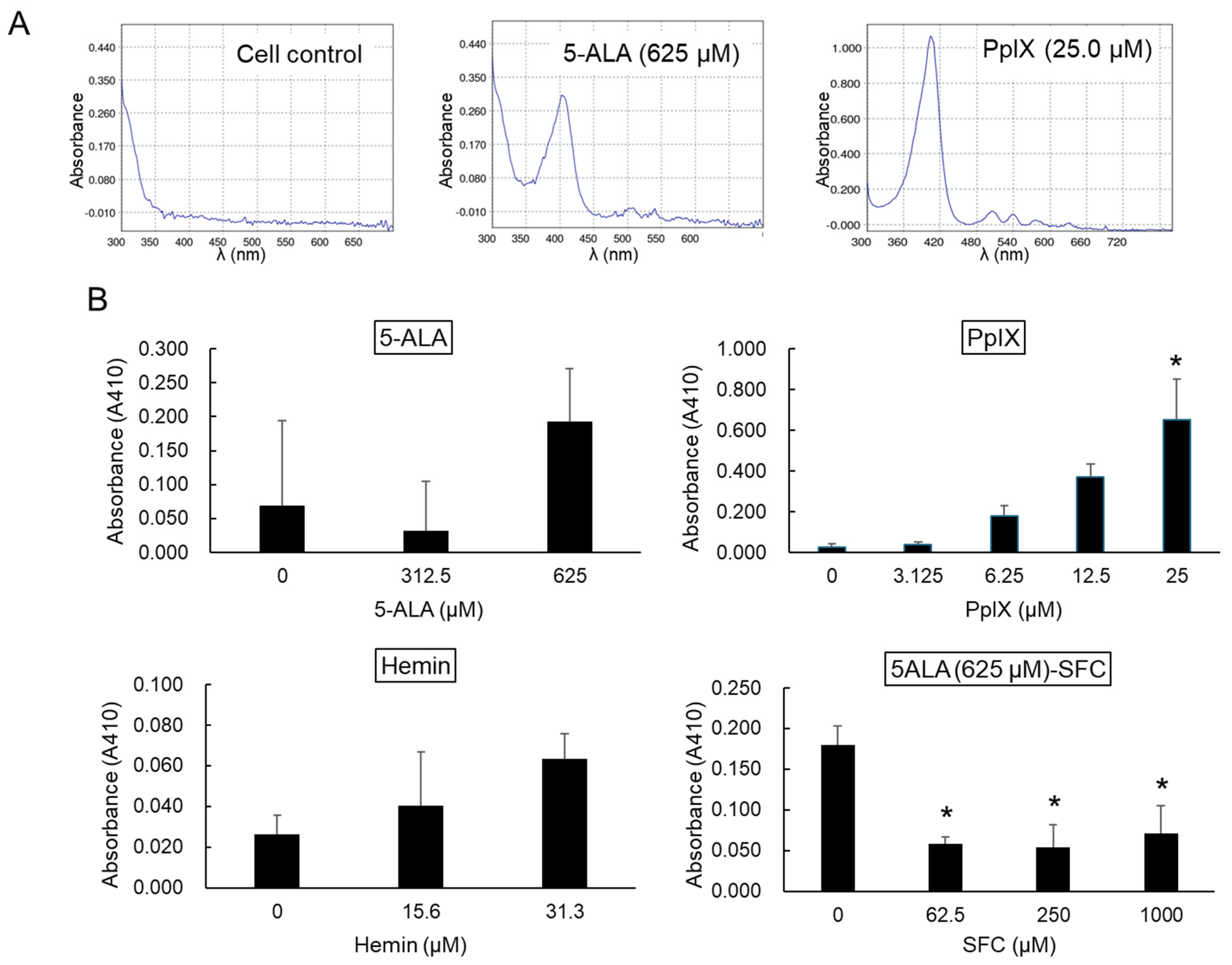
2.10. Measurement of Intracellular PpIX Levels
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
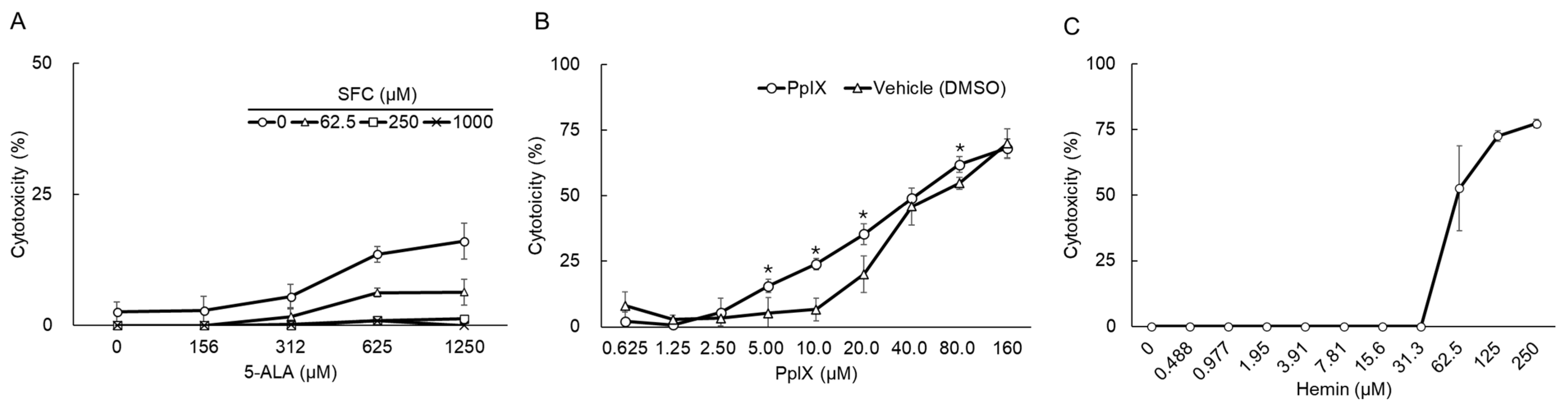
3.1. Cytotoxic Effects of Compounds
3.2. Antiviral Effects of 5-ALA against FCoV
3.3. Antiviral Effects of PpIX against FCoV
3.4. Antiviral Effects of Hemin against FCoV
3.5. Impact of SFC on Antiviral Effects Induced by 5-ALA
3.6. Effects of Treatment with Each Compound on the Intracellular Level of PpIX
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taxon Details|ICTV. Available online: https://ictv.global/taxonomy/taxondetails?taxnode_id=202301849&taxon_name=Alphacoronavirus%20suis (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Tekes, G.; Thiel, H.J. Feline Coronaviruses: Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. In Advances in Virus Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 96, pp. 193–218. ISBN 9780128047361. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, C.S.; Porter, E.; Matthews, D.; Kipar, A.; Tasker, S.; Helps, C.R.; Siddell, S.G. Genotyping Coronaviruses Associated with Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes, J.A.; Whittaker, G.R. Feline Coronavirus: Insights into Viral Pathogenesis Based on the Spike Protein Structure and Function. Virology 2018, 517, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohdatsu, T.; Okada, S.; Koyama, H. Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Type II and Antigenic Relationship between Feline, Porcine, and Canine Coronaviruses. Arch. Virol. 1991, 117, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Black, J.W.; Boyle, J.F.; Evermann, J.F.; McKeirnan, A.J.; Ott, R.L. Pathogenic Differences between Various Feline Coronavirus Isolates. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1984, 173, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Allen, C.E.; Lyons, L.A. Pathogenesis of Feline Enteric Coronavirus Infection. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipar, A.; Meli, M.L.; Baptiste, K.E.; Bowker, L.J.; Lutz, H. Sites of Feline Coronavirus Persistence in Healthy Cats. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, L.; Van Der Lubben, M.; Te Lintelo, E.G.; Bekker, C.P.J.; Geerts, T.; Schuijff, L.S.; Grinwis, G.C.M.; Egberink, H.F.; Rottier, P.J.M. Pathogenic Characteristics of Persistent Feline Enteric Coronavirus Infection in Cats. Vet. Res. 2010, 41, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C. An Update on Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Virology and Immunopathogenesis. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C. An Update on Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, B.N.; Millet, J.K.; Regan, A.D.; Hamilton, B.S.; Rinaldi, V.D.; Duhamel, G.E.; Whittaker, G.R. Mutation in Spike Protein Cleavage Site and Pathogenesis of Feline Coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Egberink, H.F.; Halpin, R.; Spiro, D.J.; Rottie, P.J.M. Spike Protein Fusion Peptide and Feline Coronavirus Virulence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meli, M.L.; Spiri, A.M.; Zwicklbauer, K.; Krentz, D.; Felten, S.; Bergmann, M.; Dorsch, R.; Matiasek, K.; Alberer, M.; Kolberg, L.; et al. Fecal Feline Coronavirus RNA Shedding and Spike Gene Mutations in Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Treated with GS-441524. Viruses 2022, 14, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jähne, S.; Felten, S.; Bergmann, M.; Erber, K.; Matiasek, K.; Meli, M.L.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hartmann, K. Detection of Feline Coronavirus Variants in Cats without Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Viruses 2022, 14, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.G.; Perron, M.; Murakami, E.; Bauer, K.; Park, Y.; Eckstrand, C.; Liepnieks, M.; Pedersen, N.C. The Nucleoside Analog GS-441524 Strongly Inhibits Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP) Virus in Tissue Culture and Experimental Cat Infection Studies. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Perron, M.; Bannasch, M.; Montgomery, E.; Murakami, E.; Liepnieks, M.; Liu, H. Efficacy and Safety of the Nucleoside Analog GS-441524 for Treatment of Cats with Naturally Occurring Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, H.; Ji, W.; Liu, J.; Liao, X.; Li, J.; Hu, C. A Retrospective Study of Clinical and Laboratory Features and Treatment on Cats Highly Suspected of Feline Infectious Peritonitis in Wuhan, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lovell, S.; Tiew, K.-C.; Mandadapu, S.R.; Alliston, K.R.; Battaile, K.P.; Groutas, W.C.; Chang, K.-O. Broad-Spectrum Antivirals against 3C or 3C-like Proteases of Picornaviruses, Noroviruses, and Coronaviruses. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11754–11762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Jacque, N.; Novicoff, W.; Li, E.; Negash, R.; Evans, S.J.M. Unlicensed Molnupiravir Is an Effective Rescue Treatment Following Failure of Unlicensed GS-441524-like Therapy for Cats with Suspected Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, V.; Gogolski, S.; Felten, S.; Hartmann, K.; Kennedy, M.; Olah, G.A. 2022 AAFP/EveryCat Feline Infectious Peritonitis Diagnosis Guidelines. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 905–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Satoh, K.; Doki, T. Possible Antiviral Activity of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid in Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus (Feline Coronavirus) Infection. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 647189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, O.; Grimm, B. New Insights in the Topology of the Biosynthesis of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid. Plant Signal Behav. 2013, 8, e23124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belot, A.; Puy, H.; Hamza, I.; Bonkovsky, H.L. Update on Heme Biosynthesis, Tissue-Specific Regulation, Heme Transport, Relation to Iron Metabolism and Cellular Energy. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 2235–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, S.; Isoda, N.; Huynh, L.T.; Kim, T.; Yoshimoto, K.; Tanaka, T.; Inui, K.; Hiono, T.; Sakoda, Y. Antiviral Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Phosphate against Classical Swine Fever Virus: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Pathogens 2022, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, Z.; Malik, Z.; Orenstein, A.; Mendelson, E.; Ben-Hur, E. Treatment of Viral Infections With 5-Aminolevulinic Acid and Light. Lasers Surg. Med. 1997, 21, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Ngwe Tun, M.M.; Kurosaki, Y.; Sakura, T.; Inaoka, D.K.; Fujine, K.; Kita, K.; Morita, K.; Yasuda, J. 5-Amino Levulinic Acid Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 545, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doki, T.; Toda, M.; Hasegawa, N.; Hohdatsu, T.; Takano, T. Therapeutic Effect of an Anti-Human-TNF-Alpha Antibody and Itraconazole on Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gut, M.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Huder, J.B.; Pedersen, N.C.; Lutz, H. One-tube fluorogenic reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction for the quantitation of feline coronaviruses. J. Virol. Methods 1999, 77, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Pan, X.; Chen, D.; Xie, X.; Wu, Y.; Shang, W.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Y.; Fan, S.; He, J. Broad-Spectrum Antivirals of Protoporphyrins Inhibit the Entry of Highly Pathogenic Emerging Viruses. Bioorg Chem. 2021, 107, 104619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Ota, U.; Hatta, S.; Ichikawa, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Okitsu, Y.; Fukuhara, N.; Onishi, Y.; Ishizuka, M.; et al. Dynamics of Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 11, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Konduru, K.; Solovena, V.; Zhou, Z.-H.; Kumari, N.; Takeda, K.; Nekhai, S.; Bavari, S.; Kaplan, G.G.; Yamada, K.M.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of the Heme Oxygenase-1 Inducer Hemin against Ebola Virus Infection. Curr. Trends Immunol. 2016, 17, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, C.; Ni, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.; et al. Heme Oxygenase-1 Acts as an Antiviral Factor for Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Infection and over-Expression Inhibits Virus Replication in Vitro. Antivir. Res. 2014, 110, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Gao, K.; Song, M.; Liu, Q. The Spectroscopy Analyses of PpIX by Ultrasound Irradiation and Its Sonotoxicity in Vitro. Ultrasonics 2013, 53, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Schuetz, J.D. The Role of ABCG2 and ABCB6 in Porphyrin Metabolism and Cell Survival. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, H.Q.; Li, Y.F.; Hu, J.; Jiang, J.D.; Li, Y.H. Heme Oxygenase-1 Agonist CoPP Suppresses Influenza Virus Replication through IRF3-Mediated Generation of IFN-α/β. Virology 2019, 528, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Ahn, H.S.; Go, H.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Song, C.S.; Lee, S.W.; Do Ha, S.; et al. Hemin as a Novel Candidate for Treating COVID-19 via Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Target | Orientation | Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feline GAPDH | For | 5′-GCCGTGGAATTTGCCGT-3′ | XM_003989222 |
| Rev | 5′-GCCATCAATGACCCCTTCAT-3′ | ||
| Probe | 5′6-FAM-CTCAACTAC-ZEN-ATGGTCTACATGTTCCAGTATGATTCCA-3′IABkFQ | ||
| FCoV 3′-UTR | For | 5′-GATTTGATTTGGCAATGCTAGATTT-3′ | [29] |
| Rev | 5′-AACAATCACTAGATCCAGACGTTAGCT-3′ | ||
| Probe | FAM-5’-TCCATTGTTGGCTCGTCATAGCGGA -3’BHQ1 |
| Target | Orientation | Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feline GAPDH | For | 5′-GCCGTGGAATTTGCCGT-3′ | XM_003989222 |
| Rev | 5′-GCCATCAATGACCCCTTCAT-3′ | ||
| Feline HO-1 | For | 5′-GGTGACCCGGAAAGGATTTA-3′ | NM_001009307 |
| Rev | 5′-TTGTTGCGCTCGATCTGT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doki, T.; Shimada, J.; Tokunaga, M.; To, K.; Orino, K.; Takano, T. Protoporphyrin IX-Dependent Antiviral Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid against Feline Coronavirus Type II. Viruses 2024, 16, 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101595
Doki T, Shimada J, Tokunaga M, To K, Orino K, Takano T. Protoporphyrin IX-Dependent Antiviral Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid against Feline Coronavirus Type II. Viruses. 2024; 16(10):1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101595
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoki, Tomoyoshi, Junna Shimada, Misa Tokunaga, Kaito To, Koichi Orino, and Tomomi Takano. 2024. "Protoporphyrin IX-Dependent Antiviral Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid against Feline Coronavirus Type II" Viruses 16, no. 10: 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101595
APA StyleDoki, T., Shimada, J., Tokunaga, M., To, K., Orino, K., & Takano, T. (2024). Protoporphyrin IX-Dependent Antiviral Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid against Feline Coronavirus Type II. Viruses, 16(10), 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101595







