Low Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Farmed and Free-Ranging White-Tailed Deer in Florida
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. WTD Specimen Collection
2.1.1. Farmed WTD
2.1.2. Free-Ranging WTD
2.2. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.3. Genomic Sequencing and Lineage Classification
2.4. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection
2.4.1. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection by Indirect ELISA
2.4.2. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection by sVNT
2.4.3. Virus Neutralizing Antibodies
2.5. Data Analyses
2.5.1. Statistical Analysis
2.5.2. Human Data Source
2.5.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
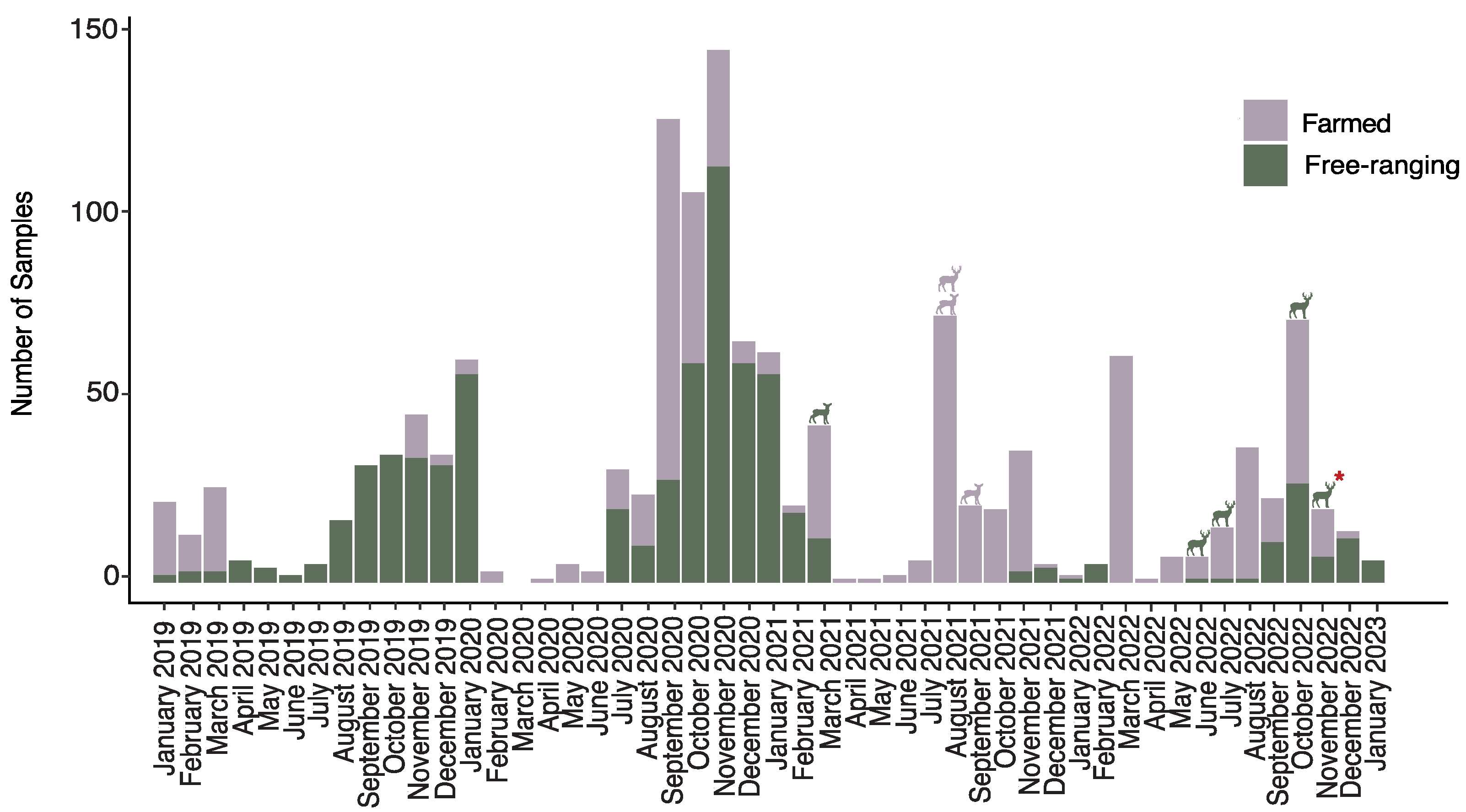
3.1. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Farmed and Free-Ranging WTD
3.2. Little Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity in Florida WTD
3.3. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Prevalence in Farmed and Free-Ranging WTD in Northern Florida
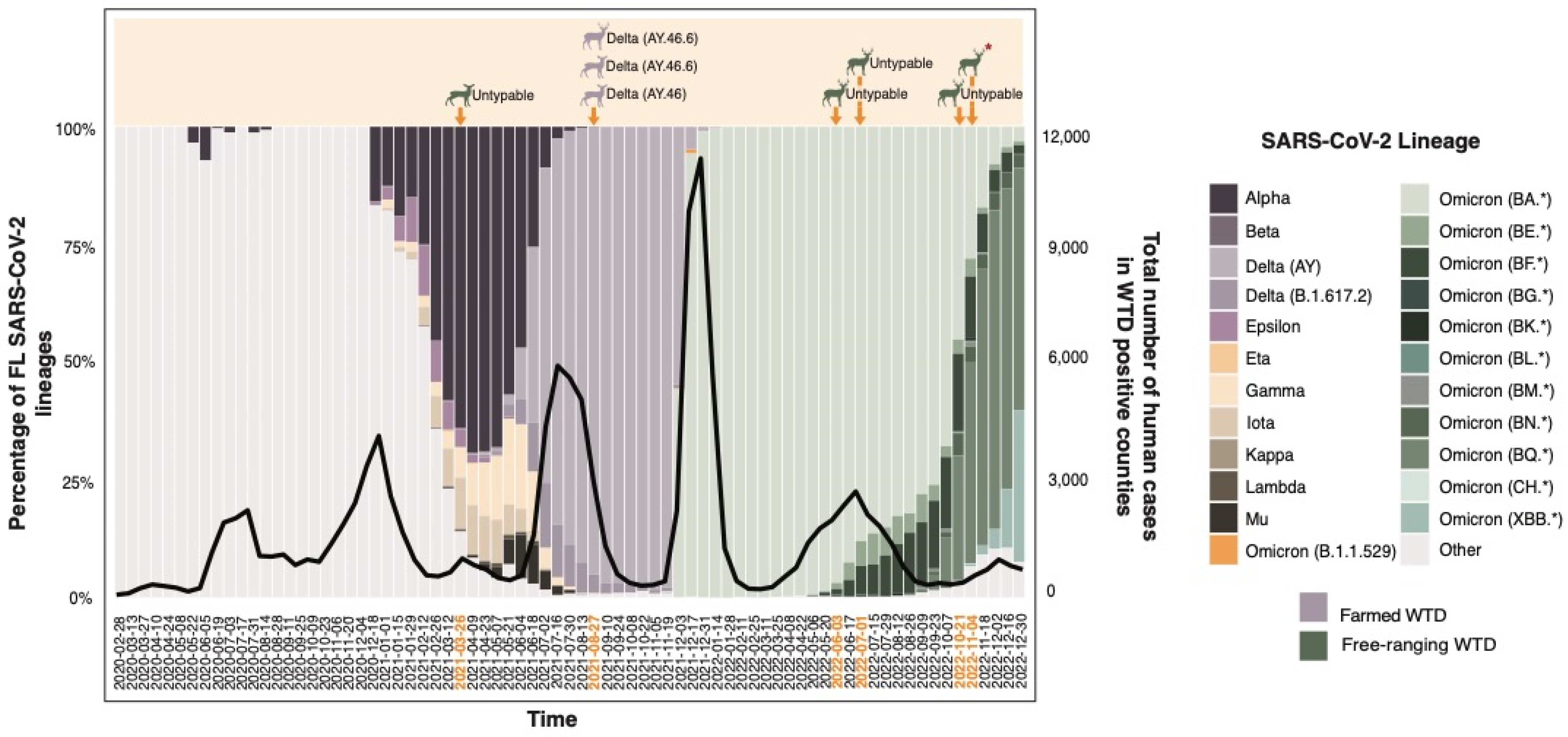
3.4. Timing of Infection and SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Florida’s Humans and WTD
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandler, J.C.; Bevins, S.N.; Ellis, J.W.; Linder, T.J.; Tell, R.M.; Jenkins-Moore, M.; Root, J.J.; Lenoch, J.B.; Robbe-Austerman, S.; DeLiberto, T.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 exposure in wild white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2114828118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.V.; Martins, M.; Falkenberg, S.; Buckley, A.; Caserta, L.C.; Mitchell, P.K.; Cassmann, E.D.; Rollins, A.; Zylich, N.C.; Renshaw, R.W.; et al. Susceptibility of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) to SARS-CoV-2. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00083-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.M.; Hartwig, A.E.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Marano, J.M.; Root, J.J.; Bosco-Lauth, A.M. Experimental infection of elk (Cervus canadensis) and mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) with SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boggiatto, P.M.; Buckley, A.; Cassmann, E.D.; Seger, H.; Olsen, S.C.; Palmer, M.V. Persistence of viral RNA in North American elk experimentally infected with an ancestral strain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, A.R.; Langwig, K.E.; Brown, K.L.; Marano, J.M.; Rai, P.; King, K.M.; Sharp, A.K.; Ceci, A.; Kailing, C.D.; Kailing, M.J.; et al. Widespread exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in wildlife communities. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damas, J.; Hughes, G.M.; Keough, K.C.; Painter, C.A.; Persky, N.S.; Corbo, M.; Hiller, M.; Koepfli, K.-P.; Pfenning, A.R.; Zhao, H.; et al. Broad host range of SARS-CoV-2 predicted by comparative and structural analysis of ACE2 in vertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22311–22322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cool, K.; Gaudreault, N.N.; Morozov, I.; Trujillo, J.D.; Meekins, D.A.; McDowell, C.; Carossino, M.; Bold, D.; Mitzel, D.; Kwon, T.; et al. Infection and transmission of ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and its alpha variant in pregnant white-tailed deer. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martins, M.; Boggiatto, P.M.; Buckley, A.; Cassmann, E.D.; Falkenberg, S.; Caserta, L.C.; Fernandes, M.H.V.; Kanipe, C.; Lager, K.; Palmer, M.V.; et al. From Deer-to-Deer: SARS-CoV-2 is efficiently transmitted and presents broad tissue tropism and replication sites in white-tailed deer. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hale, V.L.; Dennis, P.M.; McBride, D.S.; Nolting, J.M.; Madden, C.; Huey, D.; Ehrlich, M.; Grieser, J.; Winston, J.; Lombardi, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in free-ranging white-tailed deer. Nature 2022, 602, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kuchipudi, S.V.; Surendran-Nair, M.; Ruden, R.M.; Yon, M.; Nissly, R.H.; Vandegrift, K.J.; Nelli, R.K.; Li, L.; Jayarao, B.M.; Maranas, C.D.; et al. Multiple spillovers from humans and onward transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in white-tailed deer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2121644119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pickering, B.; Lung, O.; Maguire, F.; Kruczkiewicz, P.; Kotwa, J.D.; Buchanan, T.; Gagnier, M.; Guthrie, J.L.; Jardine, C.M.; Marchand-Austin, A.; et al. Divergent SARS-CoV-2 variant emerges in white-tailed deer with deer-to-human transmission. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 2011–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandegrift, K.J.; Yon, M.; Surendran, N.M.; Gontu, A.; Ramasamy, S.; Amirthalingam, S.; Neerukonda, S.; Nissly, R.H.; Chothe, S.K.; Jakka, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) Infection of Wild White-Tailed Deer in New York City. Viruses 2022, 14, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Palermo, P.M.; Orbegozo, J.; Watts, D.M.; Morrill, J.C. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies in White-Tailed Deer from Texas. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 22, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Feng, A.; Bevins, S.; Chandler, J.; DeLiberto, T.J.; Ghai, R.; Lantz, K.; Lenoch, J.; Retchless, A.; Shriner, S.; Tang, C.Y.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in free-ranging white-tailed deer in the United States. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwa, J.D.; Lobb, B.; Massé, A.; Gagnier, M.; Aftanas, P.; Banerjee, A.; Banete, A.; Blais-Savoie, J.; Bowman, J.; Buchanan, T.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic characterization of delta SARS-CoV-2 infection in free-ranging white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). iScience 2023, 26, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.D.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Everett, J.K.; Adhikari, H.; Reddy, S.; Ellis, J.C.; Zeliff, H.; Greening, S.S.; Cannuscio, C.C.; Strelau, K.M.; et al. Multiple introductions of SARS-CoV-2 alpha and delta variants into white-tailed deer in Pennsylvania. mBio 2022, 13, e0210122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caserta, L.C.; Martins, M.; Butt, S.L.; Hollingshead, N.A.; Covaleda, L.M.; Ahmed, S.; Everts, M.R.R.; Schuler, K.L.; Diel, D.G. White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) may serve as a wildlife reservoir for nearly extinct SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2215067120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hearst, S.; Palermo, P.M.; Watts, D.M.; Campbell, K.; Ivey, R.; Young, C.; Yarbrough, W.; Facundus, E.; Spears, J.; Mills, S.; et al. Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody in Mississippi White-Tailed Deer. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2024, 24, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevins, S.N.; Chipman, R.B.; Beckerman, S.F.; Bergman, D.L.; Collins, D.T.; Deliberto, T.J.; Deliberto, T.J.; Eckery, J.P.; Ellis, J.W.; Gosser, A.L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 occurrence in white-tailed deer throughout their range in the conterminous United States. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstrand, C.D.; Baldwin, T.J.; Rood, K.A.; Clayton, M.J.; Lott, J.K.; Wolking, R.M.; Bradway, D.S.; Baszler, T. An outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 with high mortality in mink (Neovison vison) on multiple Utah farms. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Larsen, C.S.; Paludan, S.R. Corona’s new coat: SARS-CoV-2 in Danish minks and implications for travel medicine. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 38, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- North American Deer Farmers Association (NADeFA). Available online: https://nadefa.org/about-us/#mission (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- Cauvin, A.; Dinh, E.T.; Orange, J.P.; Shuman, R.M.; Blackburn, J.K.; Wisely, S.M. Antibodies to epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV) in farmed and wild Florida white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, S.; Newbolt, C.H.; Ditchkoff, S.S.; Johnson, C.; Zohdy, S.; Smith, R.; Wang, C. Absence of SARS-CoV-2 in a captive white-tailed deer population in Alabama, USA. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roundy, C.M.; Nunez, C.M.; Thomas, L.F.; Auckland, L.D.; Tang, W.; Richison, J.J.; Green, B.R.; Hilton, C.D.; Cherry, M.J.; Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; et al. High Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in White-Tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus) at One of Three Captive Cervid Facilities in Texas. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0057622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- CDC 2019-Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Real-Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/134922/download (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Lednicky, J.A.; Lauzard, M.; Fan, Z.H.; Jutla, A.S.; Tilly, T.B.; Gangwar, M.; Usmani, M.; Shankar, S.N.; Mohamed, K.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; et al. Viable SARS-CoV-2 in the air of a hospital room with COVID-19 patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 100, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsunemitsu, H.; El-Kanawati, Z.R.; Smith, D.R.; Reed, H.H.; Saif, L.J. Isolation of coronaviruses antigenically indistinguishable from bovine coronavirus from wild ruminants with diarrhea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 3264–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Trujillo, J.D.; Carossino, M.; Meekins, D.A.; Morozov, I.; Madden, D.W.; Indran, S.V.; Bold, D.; Balaraman, V.; Kwon, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection, disease and transmission in domestic cats. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sheward, D.J.; Kim, C.; Ehling, R.A.; Pankow, A.; Dopico, X.C.; Dyrdak, R.; Martin, D.P.; Reddy, S.T.; Dillner, J.; Hedestam, G.B.K.; et al. Neutralisation sensitivity of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) variant: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florida Health Charts. Available online: https://www.flhealthcharts.gov/ChartsDashboards/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, M.J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Kashyap, B.; Taw, M.J.; Li, W.-H.; Mukherjee, A.K.; Khan, M.R. Genome analysis of SARS-CoV-2 isolates from a population reveals the rapid selective sweep of a haplotype carrying many pre-existing and new mutations. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID Data Tracker; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Hamer, S.A.; Nunez, C.; Roundy, C.M.; Tang, W.; Thomas, L.; Richison, J.; Benn, J.S.; Auckland, L.D.; Hensley, T.; Cook, W.E.; et al. Persistence of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies longer than 13 months in naturally infected, captive white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus), Texas. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 2112–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosenblatt, E.; Cook, J.D.; DiRenzo, G.V.; Grant, E.H.C.; Arce, F.; Pepin, K.M.; Rudolph, F.J.; Runge, M.C.; Shriner, S.; Walsh, D.P.; et al. Epidemiological modeling of SARS-CoV-2 in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) reveals conditions for introduction and widespread transmission. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1012263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ID | County | Range Status | Sampling Time | In-House ELISA | Genscript sVNT | VNT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ⍺ RBD | Δ RBD | ⍺ N | Δ N | % Inhibition | Titer Ratio | ||||
| OV_71 | Gadsden, FL | Farmed | 24 April 2018 | + | + | − | − | 0 | <1:8 |
| OV_1551 | Gadsden, FL | Farmed | 30 August 2021 | − | + | − | − | 0 | <1:8 |
| OV_709 | Gadsden, FL | Farmed | 21 March 2022 | + | + | − | − | 0 | <1:8 |
| OV_1746 | Jackson, FL | Farmed | 22 October 2022 | − | + | − | − | 0 | <1:8 |
| WOV_43 | Putnam, FL | Free-ranging | 14 November 2022 | + | + | − | − | 89.60 | 1:32 WA1, 1:64 Delta |
| WOV_56 | Putnam, FL | Free-ranging | 4 January 2023 | + | + | − | − | 0 | <1:8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grace, S.G.; Wilson, K.N.; Dorleans, R.; White, Z.S.; Pu, R.; Gaudreault, N.N.; Cool, K.; Campos Krauer, J.M.; Franklin, L.E.; Clemons, B.C.; et al. Low Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Farmed and Free-Ranging White-Tailed Deer in Florida. Viruses 2024, 16, 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121886
Grace SG, Wilson KN, Dorleans R, White ZS, Pu R, Gaudreault NN, Cool K, Campos Krauer JM, Franklin LE, Clemons BC, et al. Low Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Farmed and Free-Ranging White-Tailed Deer in Florida. Viruses. 2024; 16(12):1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121886
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrace, Savannah G., Kristen N. Wilson, Rayann Dorleans, Zoe S. White, Ruiyu Pu, Natasha N. Gaudreault, Konner Cool, Juan M. Campos Krauer, Laura E. Franklin, Bambi C. Clemons, and et al. 2024. "Low Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Farmed and Free-Ranging White-Tailed Deer in Florida" Viruses 16, no. 12: 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121886
APA StyleGrace, S. G., Wilson, K. N., Dorleans, R., White, Z. S., Pu, R., Gaudreault, N. N., Cool, K., Campos Krauer, J. M., Franklin, L. E., Clemons, B. C., Subramaniam, K., Richt, J. A., Lednicky, J. A., Long, M. T., & Wisely, S. M. (2024). Low Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Farmed and Free-Ranging White-Tailed Deer in Florida. Viruses, 16(12), 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121886








