Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein Quantification via Spatial Proximity Analyte Reagent Capture Luminescence Assay: Application as Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Serum and Effusions of Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Undergoing GS-441524 Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Samples
2.2. Effusion Samples
2.3. Determination of FCoV Viral RNA Load in Blood and Effusion Samples
2.4. Evaluation of the SPARCLTM AGP Immunoassay
2.5. Time Course of AGP Concentrations in Serum
2.6. Feline Serum Amyloid A (SAA)
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
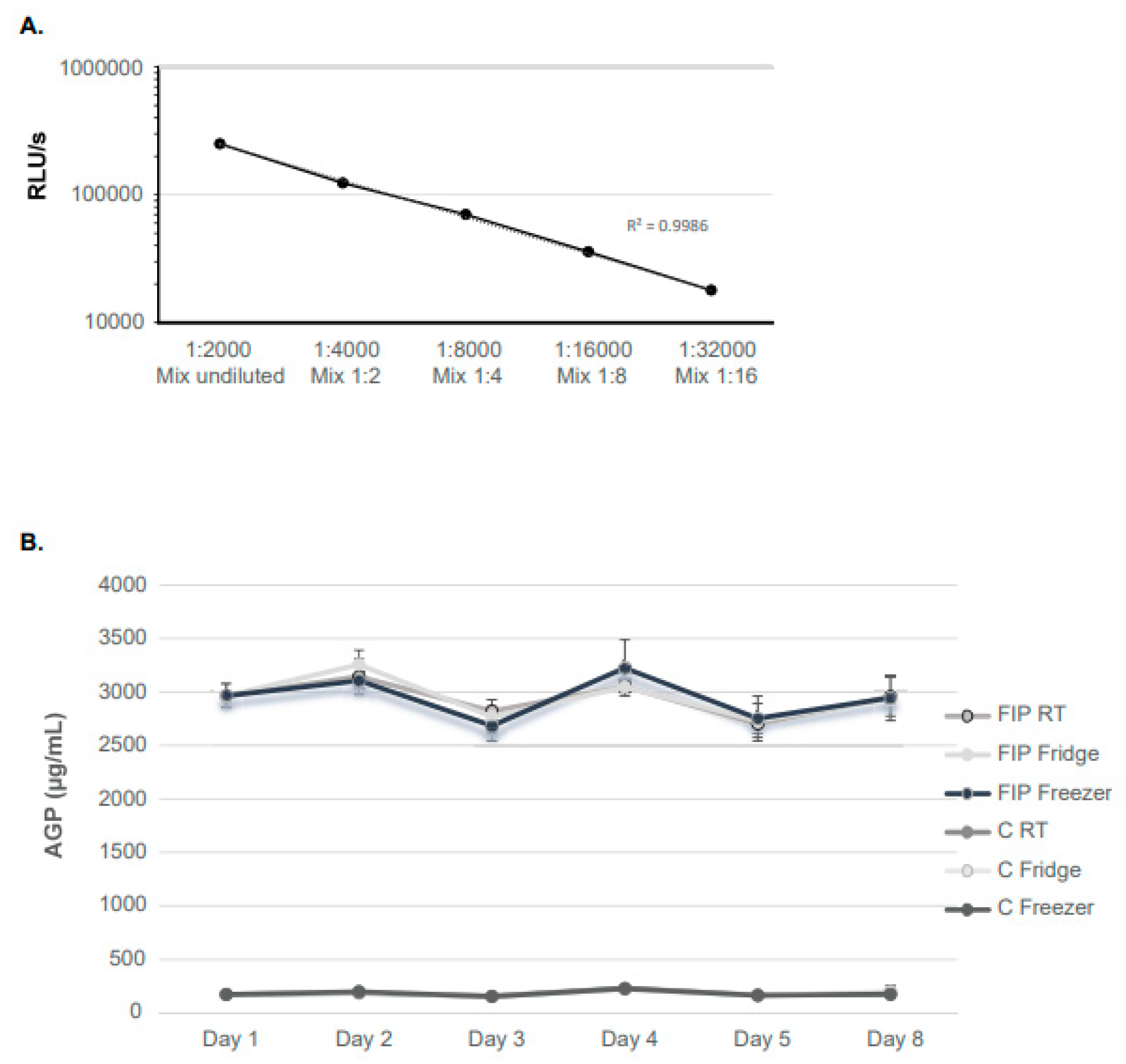
3.1. Establishment and Evaluation of AGP Measurement Using the VetBio-1 SPARCLTM Assay
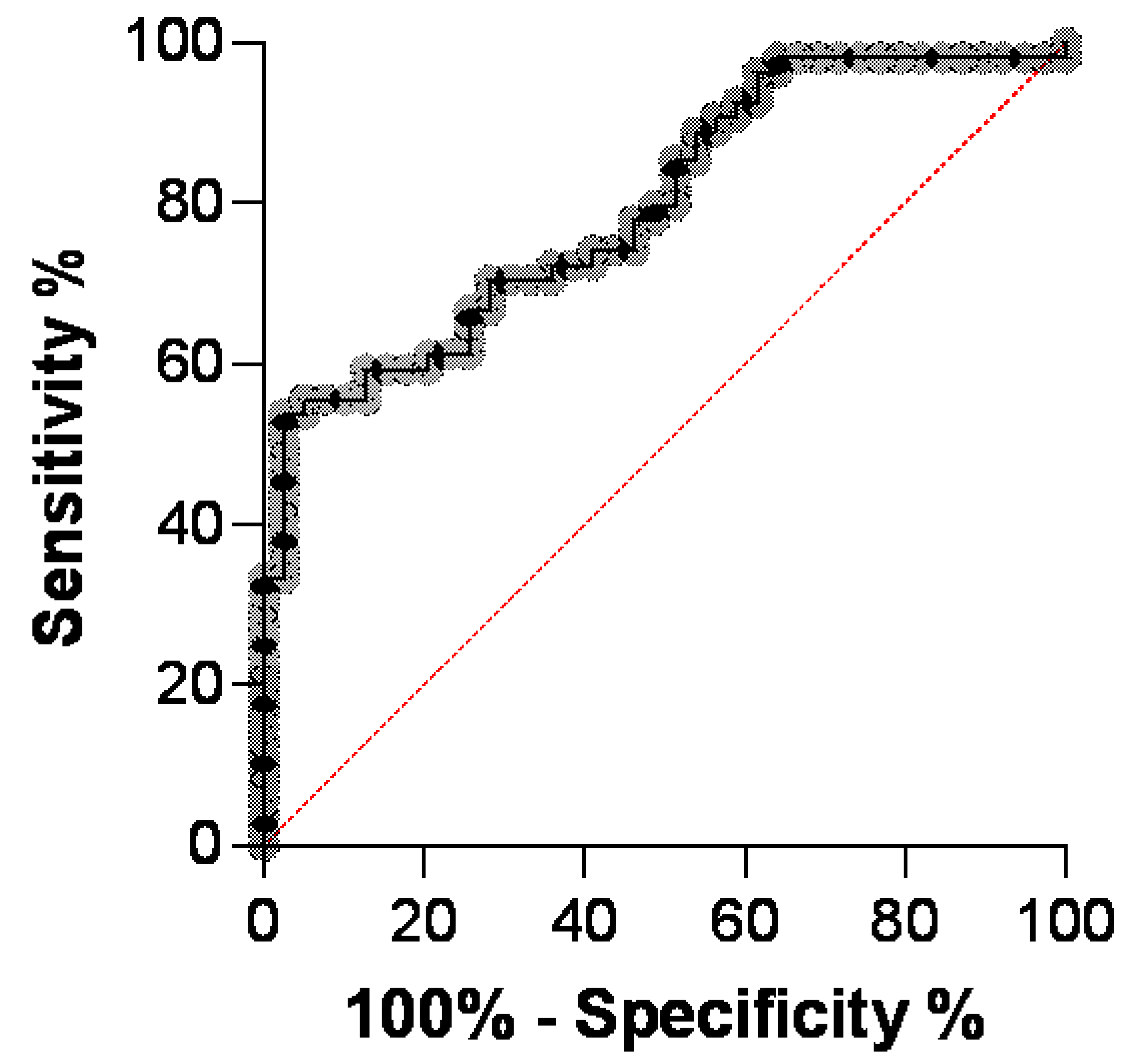
3.2. Comparison of AGP Concentrations in Serum of Cats with FIP, Diseased Cats without FIP and Healthy Cats
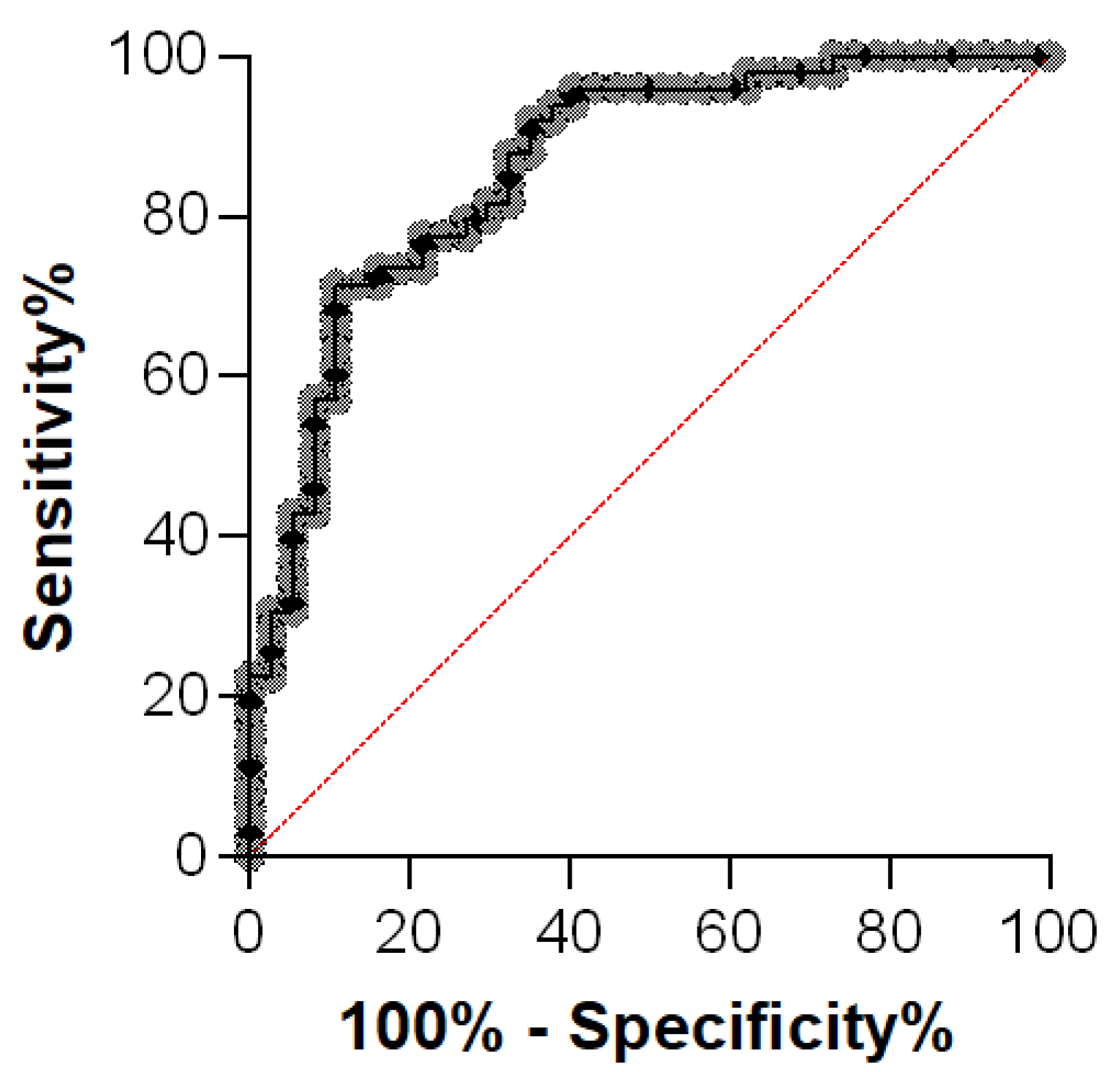
3.3. Comparison of AGP Concentrations in Effusion Samples of Cats with FIP and Diseased Cats without FIP
3.4. AGP Concentrations during GS-441524 Treatment of Cats with FIP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Cat Name 1 | Age (Years) | Sex 2 | AGP 3 | SAA2 4 | BN 5 | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S#001 | 12.5 | mn | 2278 | 99.3 | 1.40 | Mast cell tumor |
| S#002 | 0.7 | mn | 1838 | 105.5 | 1.85 | Femur fracture |
| S#003 | 9.3 | fn | 1734 | 79.1 | 2.84 | Septic effusion |
| S#004 | 0.9 | mn | 1128 | 86.2 | 0.27 | Bite wound |
| S#005 | 13.1 | mn | 1225 | 57.2 | 0.94 | Urinary retention problems |
| S#006 | 1.4 | mn | 1430 | 100.9 | 0.27 | Pancreatitis |
| S#007 | 13.8 | mn | 595 | 58.2 | 0.37 | Cardiomyopathy |
| S#008 | 0.8 | fn | 305 | 23.5 | 0.25 | Wound infection |
| S#009 | 8.1 | mn | 845 | 70.4 | 0.40 | Trauma (car crash) |
| S#010 | 11.5 | mn | 924 | 86.4 | 0.29 | Cachexia, FeLV infection |
| S#011 | 1.5 | mn | 801 | 30.2 | 1.04 | Fibular fracture |
| S#012 | 14.1 | mn | 2062 | 58.1 | 0.34 | Abdominal wall hernia (car crash) |
| S#013 | 13.9 | mn | 1474 | 24.9 | 1.00 | Neoplasia |
| S#014 | 7.2 | fn | 1959 | 62 | 0.94 | Pelvic fracture, abdominal hernia |
| S#015 | 3.0 | mn | 2927 | 95.4 | 3.10 | Head and brain trauma, bite wound |
| S#016 | 6.5 | fn | 1391 | 37.6 | 0.20 | Intestinal foreign body |
| S#017 | 12.0 | mn | 2568 | 38.9 | 0.50 | Gastroenteritis |
| S#018 | 2.5 | mn | 597 | 25.3 | 0.60 | Lower urinary tract disease |
| S#019 | 5.5 | mn | 3449 | 72.6 | 4.17 | Cachexia, renal disease, FeLV infection |
| S#020 | 7.9 | mn | 2668 | 114.5 | 0.21 | Lymphoma |
| S#021 | 2.3 | mn | 590 | 47.3 | 1.04 | Polytrauma |
| S#022 | 3.3 | fn | 967 | 44.9 | 1.08 | Femur fracture |
| S#023 | 14.2 | mn | 2219 | 112 | 0.56 | Abscess |
| S#024 | 7.0 | fn | 618 | 57.7 | 0.86 | Radius ulna fracture |
| S#025 | 9.2 | mn | 2160 | 64.4 | 0.64 | Traumatic abdominal hernia |
| S#026 | 14.2 | fn | 1143 | 42.1 | 1.08 | Traumatic perianal hernia, multiple fractures |
| S#027 | 14.2 | mn | 2494 | 70.5 | 1.63 | Multiple fractures (fall from balcony) |
| S#028 | 0.3 | mn | 2848 | 67.8 | 0.40 | Intestinal foreign body |
| S#029 | 16.3 | fn | 2482 | 128.3 | 0.45 | Lymphoma |
| S#030 | 6.8 | fn | 2375 | 82.4 | 0.96 | Multiple fractures (fall from window) |
| S#031 | 12.2 | mn | 2733 | 23.4 | 3.59 | Septic effusion, pneumothorax |
| S#032 | 1.3 | fn | 647 | 44.9 | 3.73 | Poisoned |
| S#033 | 6.2 | mn | 934 | 63.4 | 1.36 | Trichobezoar in the small intestine |
| S#034 | 2.3 | mn | 1545 | 20.6 | 0.92 | Lymphadenomegaly |
| S#035 | 12.4 | fn | 2297 | 63.7 | 0.42 | Pancreatitis |
| S#036 | 6.7 | mn | 2154 | 73.3 | 1.35 | Septic effusion |
| S#037 | 4.0 | mn | 2889 | 67.7 | 6.62 | Septic effusion |
| S#038 | 7.1 | mn | 2843 | 66.5 | 5.64 | Septic effusion |
| S#039 | 12.2 | fn | 1160 | 98.2 | 0.71 | Pyelonephritis, anemia |
| AGP Cut-Off 1 | Sensitivity % | 95% CI 2 | Specificity % | 95% CI 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 448 | 98.2 | 90.2 to 99.9 | 2.6 | 0.1 to 13.2 |
| 1504 | 88.9 | 77.8 to 94.8 | 46.2 | 31.6 to 61.4 |
| 2531 | 61.1 | 47.8 to 73.0 | 79.5 | 64.5 to 89.2 |
| 2927 | 53.7 | 40.6 to 66.3 | 97.4 | 86.8 to 99.9 |
| Cat Number 1 | Age (Years) | Sex 2 | FCoV RT-qPCR (Ct) 3 | AGP 4 | Diagnosis or Most Likely Differential Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51052938 | 3.7 | fn | 20.3 | 2645 | FIP |
| 51053793 | 0.4 | m | 22.4 | 826 | FIP |
| 51054156 | 0.9 | mn | 22.2 | 717 | FIP |
| 51060583 | 3.4 | mn | 20.7 | 2456 | FIP |
| 51067739 | 0.3 | m | 25.8 | 1104 | FIP |
| 51068738 | 2.7 | mn | 17.5 | 5205 | FIP |
| 51069901 | 0.4 | f | 20.1 | 3023 | FIP/pancreatitis |
| 51070615 | 13.3 | mn | 26.6 | 343 | FIP |
| 51073864 | 2.7 | mn | 21.9 | 2866 | FIP |
| 51078145 | 16.8 | mn | 24.9 | 4702 | FIP |
| 51080287 | 3.1 | mn | 27.6 | 3570 | FIP/FeLV infection |
| 51080288 | 1.0 | mn | 25.7 | 3258 | FIP/FeLV infection |
| 51082265 | 0.9 | mn | 23.7 | 1908 | FIP |
| 51083183 | 9.5 | mn | 19.0 | 4768 | FIP |
| 51083366 | 3.9 | f | 21.8 | 2951 | FIP |
| 51083694 | 1.0 | mn | 18.3 | 2425 | FIP |
| 51084353 | 0.9 | fn | 26.5 | 1871 | FIP |
| 51085752 | 5.1 | mn | 23.6 | 4260 | FIP |
| 51087800 | 1.0 | mn | 20.1 | 4046 | FIP |
| 51088342 | 7.4 | mn | 11.8 | 5443 | FIP |
| 51090502 | 1.1 | m | 31.3 | 1976 | FIP/FeLV infection |
| 51091022 | 4.4 | mn | 29.9 | 2000 | FIP |
| 51093347 | 0.9 | mn | 38.1 | 2315 | FIP |
| 51096786 | 1.5 | fn | 22.9 | 1599 | FIP |
| 51098401 | 1.3 | fn | 22.5 | 2458 | FIP |
| 51100616 | 10.4 | fn | 19.0 | 4409 | FIP |
| 51101074 | 0.8 | fn | 19.7 | 1847 | FIP/FCV |
| 51102326 | 0.9 | mn | 24.0 | 971 | FIP |
| 51103629 | 0.4 | m | 18.7 | 5611 | FIP |
| 51111636 | 0.6 | f | 30.3 | 4356 | FIP |
| 51113343 | 15.0 | fn | 17.8 | 5374 | FIP |
| 51113346 | 0.9 | f | 19.7 | 3609 | FIP/FeLV infection |
| 51114606 | 12.7 | fn | 18.9 | 3715 | FIP |
| 51118745 | 1.2 | mn | 19.4 | 1424 | FIP |
| 51121069 | 1.9 | mn | 23.0 | 459 | FIP |
| 51121714 | 4.4 | mn | 21.8 | 1125 | FIP |
| 51125665 | 12.4 | mn | 22.5 | 1816 | FIP |
| Cat Number 1 | Age (Years) | Sex 2 | FCoV RT-qPCR (Ct) 3 | AGP 4 | Diagnosis or Most Likely Differential Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51051793 | 13.3 | m | negative | 214 | Suspicion of tumor |
| 51052859 | 11.7 | fn | negative | 218 | Carcinoma in the pericardium |
| 51054322 | 2.0 | f | negative | 152 | Paralytic ileus |
| 51055437 | 9.8 | mn | negative | 450 | Encephalopathy |
| 51057024 | 14.6 | mn | negative | 1598 | IBD, chronic enteropathy |
| 51061233 | 1.5 | mn | negative | 1345 | Fever and effusion of unknown etiology |
| 51061244 | 11.0 | mn | negative | 1329 | Triaditis with pot. obstructive cholestasis |
| 51071148 | 12.9 | mn | negative | 560 | Triaditis, cardiomyopathy |
| 51072682 | 15.8 | fn | negative | 159 | Neoplasia |
| 51073972 | 11.0 | fn | negative | 1630 | Chylothorax |
| 51074362 | 16.6 | fn | negative | 1659 | Hepatopathy, suspicion of tumor |
| 51074741 | 0.9 | f | negative | 1565 | Fever and effusion of unknown etiology |
| 51083736 | 12.1 | fn | negative | 308 | Chylothorax neoplastic |
| 51085698 | 1.5 | f | negative | 114 | Ovariectomy |
| 51088349 | 6.0 | mn | negative | 459 | Pulmonary thrombose |
| 51089415 | 8.3 | mn | negative | 468 | Gastrointestinal bleeding |
| 51091461 | 4.9 | fn | negative | 2685 | Renal empyema, nephrectomy |
| 51101065 | 14.7 | fn | negative | 1226 | Carcinoma |
| 51101301 | 12.3 | mn | negative | 1147 | Carcinoma |
| 51102634 | 8.9 | fn | negative | 404 | Neoplasia |
| 51104521 | 0.5 | m | negative | 170 | Cardiovascular disease |
| 51106980 | 1.9 | mn | negative | 417 | Phlebitis |
| 51107291 | 11.8 | fn | negative | 83 | Cardiomyopathy, pulmonary hypertension |
| 51108712 | 0.9 | fn | negative | 599 | Immune-mediated pancytopenia, aplastic anemia |
| 51109370 | 13.5 | fn | negative | 116 | Bronchial pneumonia |
| 51111000 | 13.3 | fn | negative | 480 | Chylothorax |
| 51111246 | 11.3 | mn | negative | 214 | Thymoma |
| 51113179 | 17.4 | fn | negative | 837 | High-grade enteropathy with secondary peritonitis |
| 51113895 | 14.2 | m | negative | 2101 | Lymphoma |
| 51114398 | 0.9 | mn | negative | 3950 | Pyothorax |
| 51120616 | 8.7 | mn | negative | 1005 | Carcinomatosis |
| 51121032 | 1.9 | f | negative | 647 | Gastroenterocolopathy |
| 51123075 | 14.5 | mn | negative | 383 | Mediastinal neoplasia |
| 51124448 | 1.0 | mn | negative | 3336 | Pancreatitis, gastroenteritis |
| 51126811 | 12.4 | f | negative | 532 | Carcinomatosis |
| 51128014 | 10.3 | fn | negative | 564 | Carcinomatosis |
| 51128383 | 14.6 | mn | negative | 756 | Neoplasia |
References
- Pedersen, N.C. A review of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection: 1963–2008. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Allen, C.E.; Lyons, L.A. Pathogenesis of feline enteric coronavirus infection. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.E.; Poland, A.; Carlson, J.; Pedersen, N.C. Risk factors for feline infectious peritonitis among cats in multiple-cat environments with endemic feline enteric coronavirus. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1997, 210, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addie, D.; Belak, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Egberink, H.; Frymus, T.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Hartmann, K.; Hosie, M.J.; Lloret, A.; Lutz, H.; et al. Feline infectious peritonitis. ABCD guidelines on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, S.; Addie, D.D.; Egberink, H.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hosie, M.J.; Truyen, U.; Belak, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Frymus, T.; Lloret, A.; et al. Feline Infectious Peritonitis: European Advisory Board on Cat Diseases Guidelines. Viruses 2023, 15, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennema, H.; Poland, A.; Foley, J.; Pedersen, N.C. Feline infectious peritonitis viruses arise by mutation from endemic feline enteric coronaviruses. Virology 1998, 243, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewerchin, H.L.; Cornelissen, E.; Nauwynck, H.J. Replication of feline coronaviruses in peripheral blood monocytes. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 2483–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipar, A.; Meli, M.L. Feline infectious peritonitis: Still an enigma? Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbon, A.J.; Michalopoulou, E.; Meli, M.L.; Barker, E.N.; Tasker, S.; Baptiste, K.; Kipar, A. Colony Stimulating Factors in Early Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Infection of Monocytes and in End Stage Feline Infectious Peritonitis; A Combined In Vivo And In Vitro Approach. Pathogens 2020, 9, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddart, C.A.; Scott, F.W. Intrinsic resistance of feline peritoneal macrophages to coronavirus infection correlates with in vivo virulence. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, S.; Egberink, H.; Hartmann, K. Effect of feline interferon-omega on the survival time and quality of life of cats with feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, Y.; Ritz, S.; Weber, K.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Hartmann, K. Randomized, placebo controlled study of the effect of propentofylline on survival time and quality of life of cats with feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaplace, M.; Huet, H.; Gambino, A.; Le Poder, S. Feline Coronavirus Antivirals: A Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, P.J.; Bannasch, M.; Thomasy, S.M.; Murthy, V.D.; Vernau, K.M.; Liepnieks, M.; Montgomery, E.; Knickelbein, K.E.; Murphy, B.; Pedersen, N.C. Antiviral treatment using the adenosine nucleoside analogue GS-441524 in cats with clinically diagnosed neurological feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.G.; Perron, M.; Murakami, E.; Bauer, K.; Park, Y.; Eckstrand, C.; Liepnieks, M.; Pedersen, N.C. The nucleoside analog GS-441524 strongly inhibits feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) virus in tissue culture and experimental cat infection studies. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krentz, D.; Zenger, K.; Alberer, M.; Felten, S.; Bergmann, M.; Dorsch, R.; Matiasek, K.; Kolberg, L.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Meli, M.L.; et al. Curing Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis with an Oral Multi-Component Drug Containing GS-441524. Viruses 2021, 13, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicklbauer, K.; Krentz, D.; Bergmann, M.; Felten, S.; Dorsch, R.; Fischer, A.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Meli, M.L.; Spiri, A.M.; Alberer, M.; et al. Long-term follow-up of cats in complete remission after treatment of feline infectious peritonitis with oral GS-441524. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2023, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthie, S.; Eckersall, P.D.; Addie, D.D.; Lawrence, C.E.; Jarrett, O. Value of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein in the diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Rec. 1997, 141, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, J.J.; Eckersall, P.D.; Martynez-Subiela, S. Acute phase proteins in dogs and cats: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 34, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazuchova, K.; Held, S.; Neiger, R. Usefulness of acute phase proteins in differentiating between feline infectious peritonitis and other diseases in cats with body cavity effusions. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 19, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Spagnolo, V.; Colombo, A.; Paltrinieri, S. Changes in some acute phase protein and immunoglobulin concentrations in cats affected by feline infectious peritonitis or exposed to feline coronavirus infection. Vet. J. 2004, 167, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paltrinieri, S.; Giordano, A.; Tranquillo, V.; Guazzetti, S. Critical assessment of the diagnostic value of feline alpha1-acid glycoprotein for feline infectious peritonitis using the likelihood ratios approach. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2007, 19, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giori, L.; Giordano, A.; Giudice, C.; Grieco, V.; Paltrinieri, S. Performances of different diagnostic tests for feline infectious peritonitis in challenging clinical cases. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 52, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paltrinieri, S.; Metzger, C.; Battilani, M.; Pocacqua, V.; Gelain, M.E.; Giordano, A. Serum alpha1-acid glycoprotein (AGP) concentration in non-symptomatic cats with feline coronavirus (FCoV) infection. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2007, 9, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addie, D.D.; Silveira, C.; Aston, C.; Brauckmann, P.; Covell-Ritchie, J.; Felstead, C.; Fosbery, M.; Gibbins, C.; Macaulay, K.; McMurrough, J.; et al. Alpha-1 Acid Glycoprotein Reduction Differentiated Recovery from Remission in a Small Cohort of Cats Treated for Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Viruses 2022, 14, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan-Tafti, H.; Binger, D.G.; Blackwood, J.J.; Chen, Y.; Creager, R.S.; de Silva, R.; Eickholt, R.A.; Gaibor, J.E.; Handley, R.S.; Kapsner, K.P.; et al. A homogeneous chemiluminescent immunoassay method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4191–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanelli, P.; Bertazzolo, W.; Prisciandaro, A.; Leone, A.; Bonfanti, U.; Paltrinieri, S. Measurement of Feline Alpha-1 Acid Glycoprotein in Serum and Effusion Using an ELISA Method: Analytical Validation and Diagnostic Role for Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Pathogens 2024, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gut, M.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Huder, J.B.; Pedersen, N.C.; Lutz, H. One-tube fluorogenic reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction for the quantitation of feline coronaviruses. J. Virol. 1999, 77, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, M.L.; Spiri, A.M.; Zwicklbauer, K.; Krentz, D.; Felten, S.; Bergmann, M.; Dorsch, R.; Matiasek, K.; Alberer, M.; Kolberg, L.; et al. Fecal Feline Coronavirus RNA Shedding and Spike Gene Mutations in Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Treated with GS-441524. Viruses 2022, 14, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.E.; Camus, M.S.; Freeman, K.P.; Giori, L.; Hooijberg, E.H.; Jeffery, U.; Korchia, J.; Meindel, M.J.; Moore, A.R.; Sisson, S.C.; et al. ASVCP Guidelines: Principles of Quality Assurance and Standards for Veterinary Clinical Pathology (version 3.0): Developed by the American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology’s (ASVCP) Quality Assurance and Laboratory Standards (QALS) Committee. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 48, 542–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.E.; Schaap, M.K.; Kjelgaard-Hansen, M. Evaluation of a commercially available human serum amyloid A (SAA) turbidimetric immunoassay for determination of feline SAA concentration. Vet. Res. Commun. 2006, 30, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kules, J.; Horvatic, A.; Guillemin, N.; Ferreira, R.F.; Mischke, R.; Mrljak, V.; Chadwick, C.C.; Eckersall, P.D. The plasma proteome and the acute phase protein response in canine pyometra. J. Proteom. 2020, 223, 103817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stranieri, A.; Giordano, A.; Paltrinieri, S.; Giudice, C.; Cannito, V.; Lauzi, S. Comparison of the performance of laboratory tests in the diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, I.A. Tutorials in Clinical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, S.; Wada, H.; Tamura, M.; Koide, T.; Higaki, M.; Mikura, S.I.; Yasutake, T.; Hirao, S.; Nakamura, M.; Honda, K.; et al. Kinetics of c-reactive protein (CRP) and serum amyloid A protein (SAA) in patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), as presented with biologic half-life times. Biomarkers 2011, 16, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

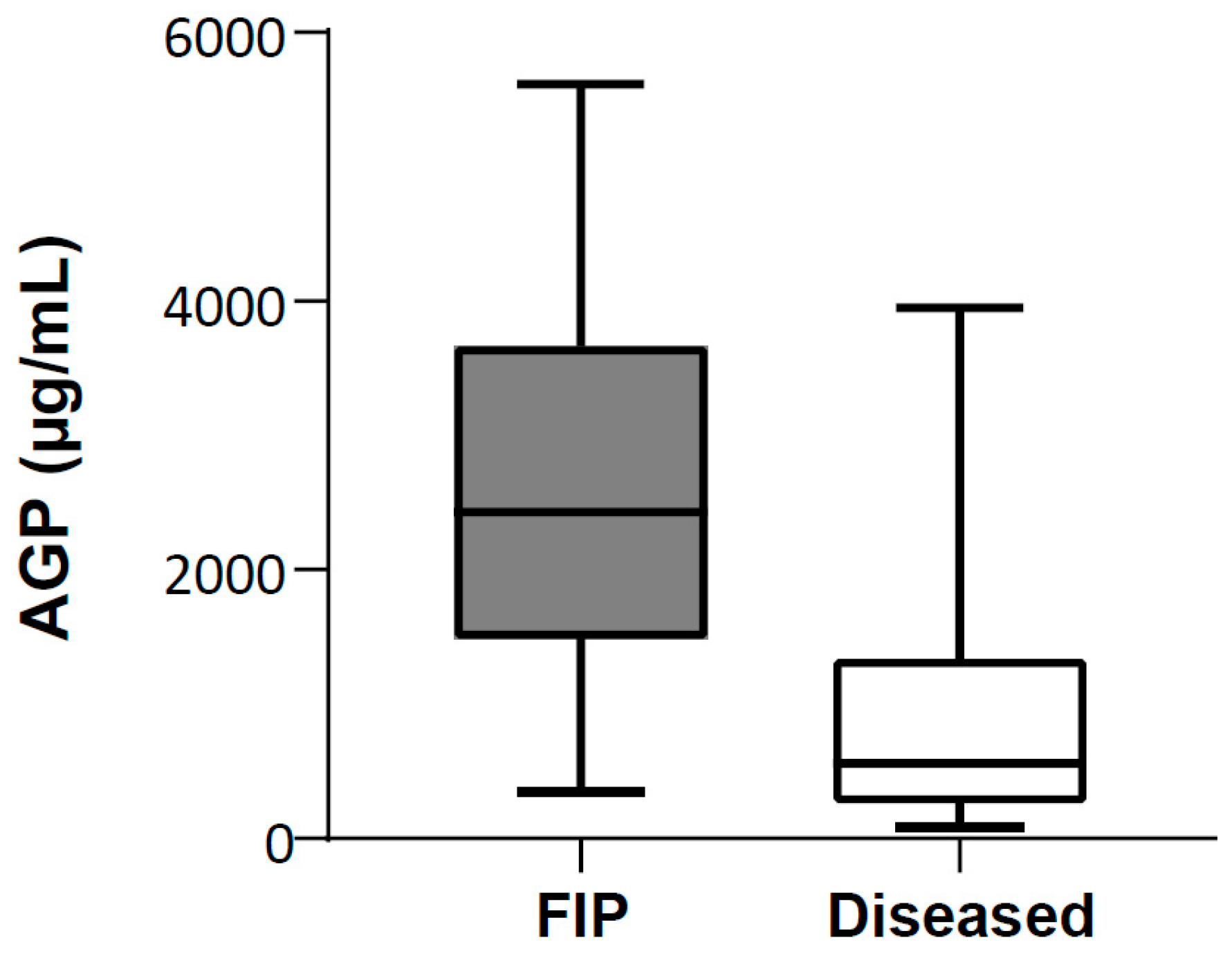
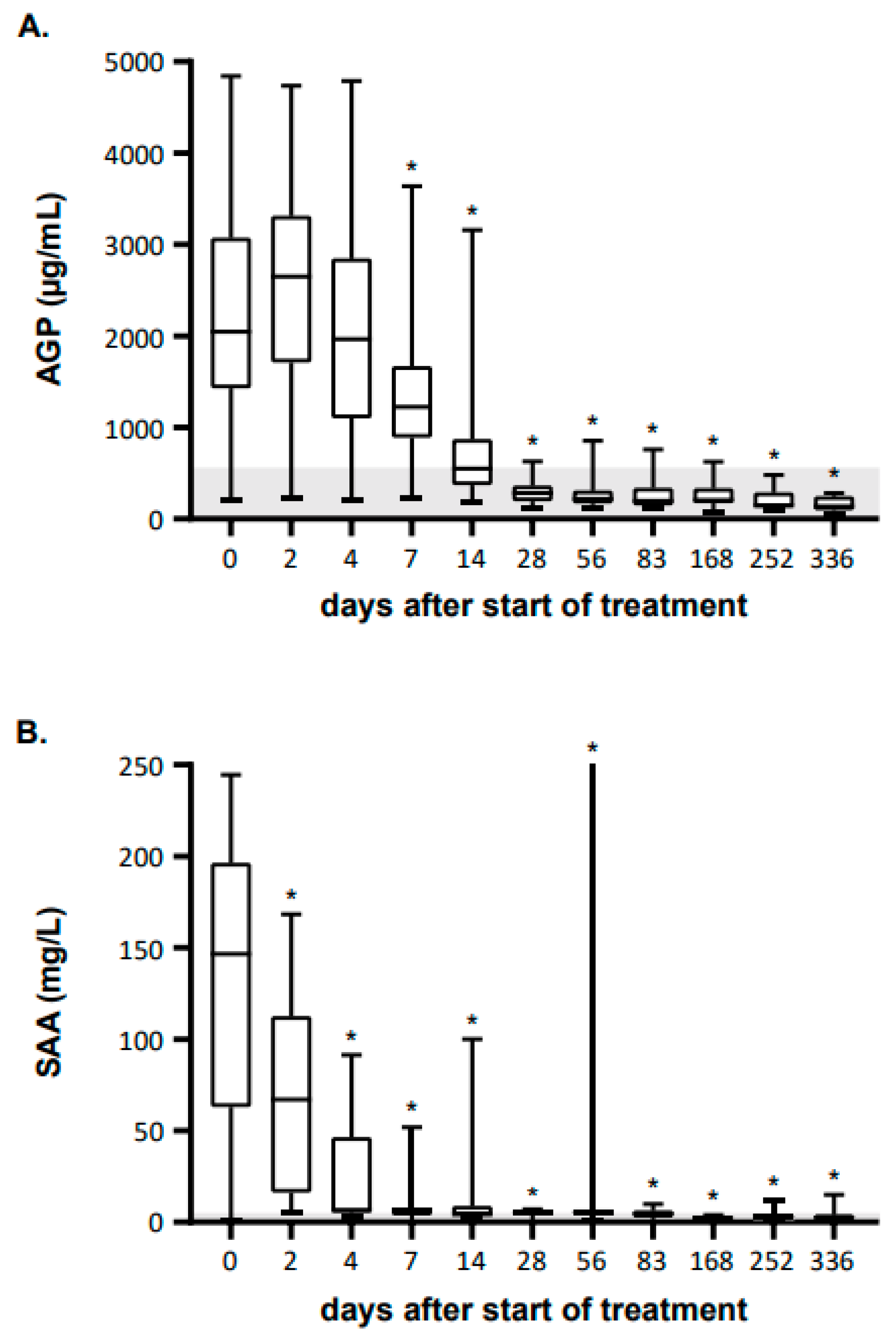
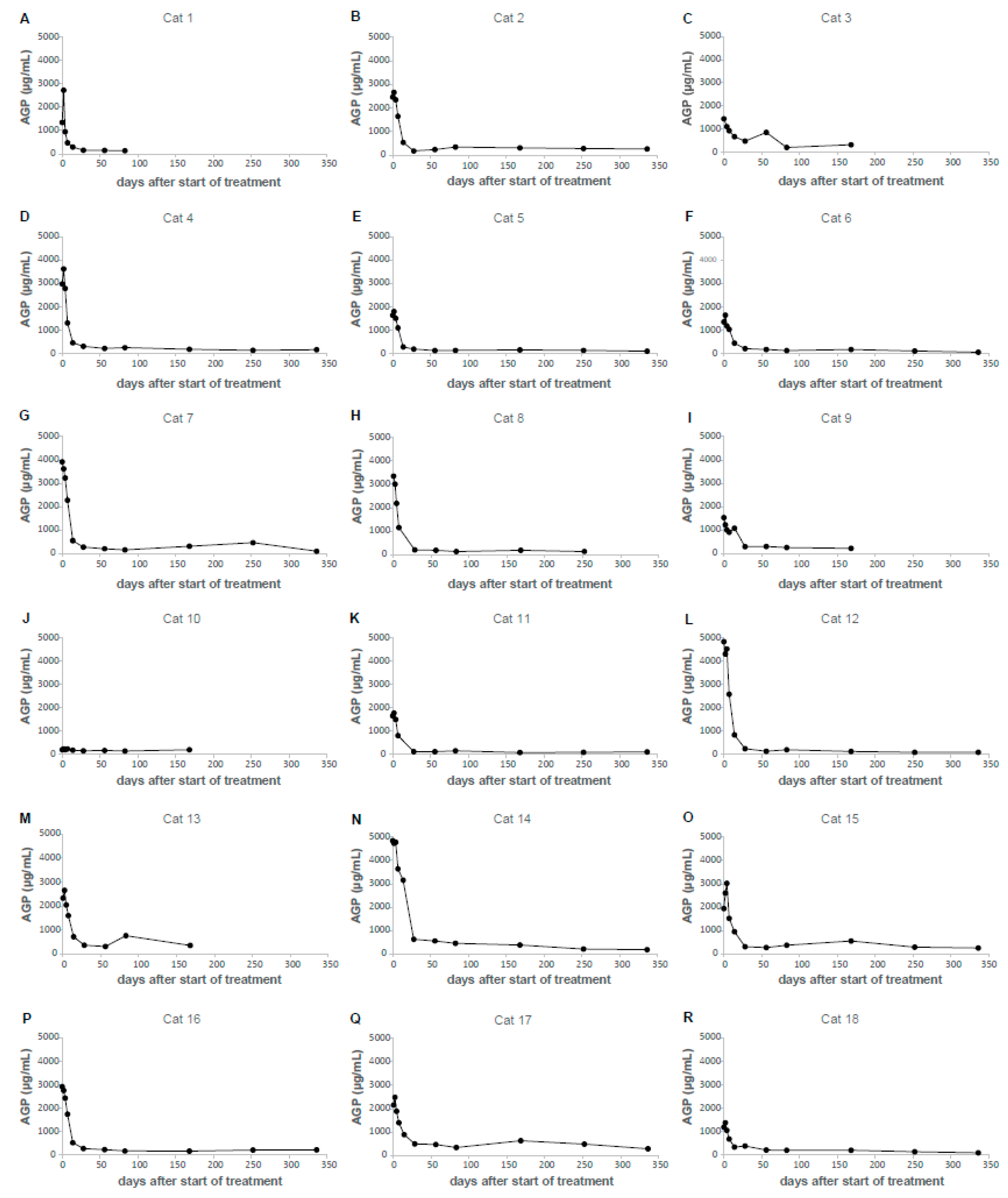
| Group | N | Q1 (µg/mL) | Median (µg/mL) | Q3 (µg/mL) | IQR (µg/mL) | Range (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIP | 54 | 1997 | 2954 | 3755 | 1759 | 200–5861 |
| Diseased without FIP | 39 | 950 | 1734 | 2428 | 1478 | 305–3449 |
| Healthy | 41 | 157 | 235 | 258 | 100 | 78–616 |
| Group | N | Q1 (µg/mL) | Median (µg/mL) | Q3 (µg/mL) | IQR (µg/mL) | Range (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIP | 49 | 1554 | 2425 | 3609 | 2055 | 343–5611 |
| Diseased without FIP | 37 | 308 | 560 | 1329 | 1021 | 83–3950 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Helfer-Hungerbuehler, A.K.; Spiri, A.M.; Meili, T.; Riond, B.; Krentz, D.; Zwicklbauer, K.; Buchta, K.; Zuzzi-Krebitz, A.-M.; Hartmann, K.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; et al. Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein Quantification via Spatial Proximity Analyte Reagent Capture Luminescence Assay: Application as Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Serum and Effusions of Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Undergoing GS-441524 Therapy. Viruses 2024, 16, 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050791
Helfer-Hungerbuehler AK, Spiri AM, Meili T, Riond B, Krentz D, Zwicklbauer K, Buchta K, Zuzzi-Krebitz A-M, Hartmann K, Hofmann-Lehmann R, et al. Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein Quantification via Spatial Proximity Analyte Reagent Capture Luminescence Assay: Application as Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Serum and Effusions of Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Undergoing GS-441524 Therapy. Viruses. 2024; 16(5):791. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050791
Chicago/Turabian StyleHelfer-Hungerbuehler, A. Katrin, Andrea M. Spiri, Theres Meili, Barbara Riond, Daniela Krentz, Katharina Zwicklbauer, Katharina Buchta, Anna-Maria Zuzzi-Krebitz, Katrin Hartmann, Regina Hofmann-Lehmann, and et al. 2024. "Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein Quantification via Spatial Proximity Analyte Reagent Capture Luminescence Assay: Application as Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Serum and Effusions of Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Undergoing GS-441524 Therapy" Viruses 16, no. 5: 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050791
APA StyleHelfer-Hungerbuehler, A. K., Spiri, A. M., Meili, T., Riond, B., Krentz, D., Zwicklbauer, K., Buchta, K., Zuzzi-Krebitz, A.-M., Hartmann, K., Hofmann-Lehmann, R., & Meli, M. L. (2024). Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein Quantification via Spatial Proximity Analyte Reagent Capture Luminescence Assay: Application as Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Serum and Effusions of Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Undergoing GS-441524 Therapy. Viruses, 16(5), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050791








