Detections of Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus 2 (RHDV2) Following the 2020 Outbreak in Wild Lagomorphs across the Western United States
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
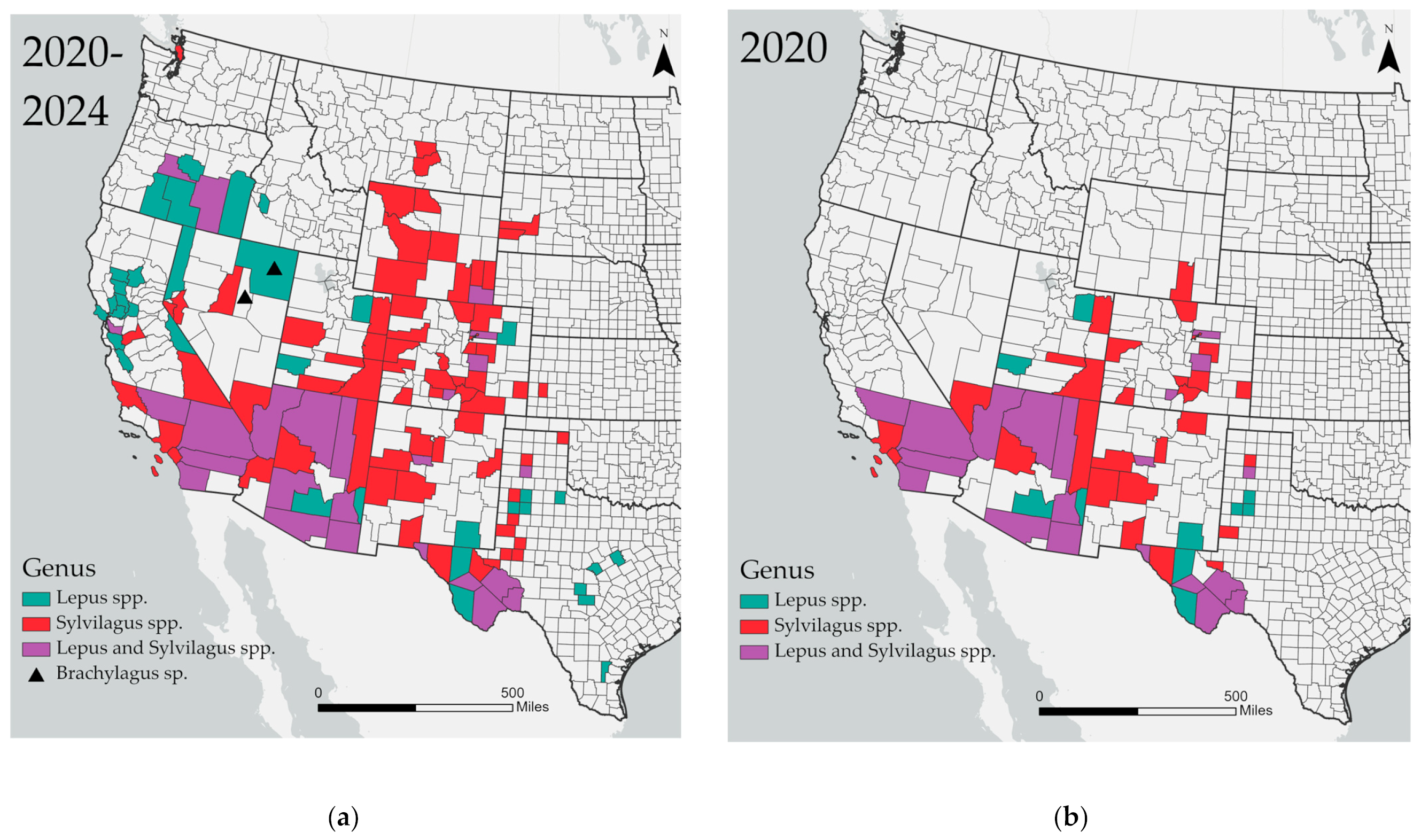
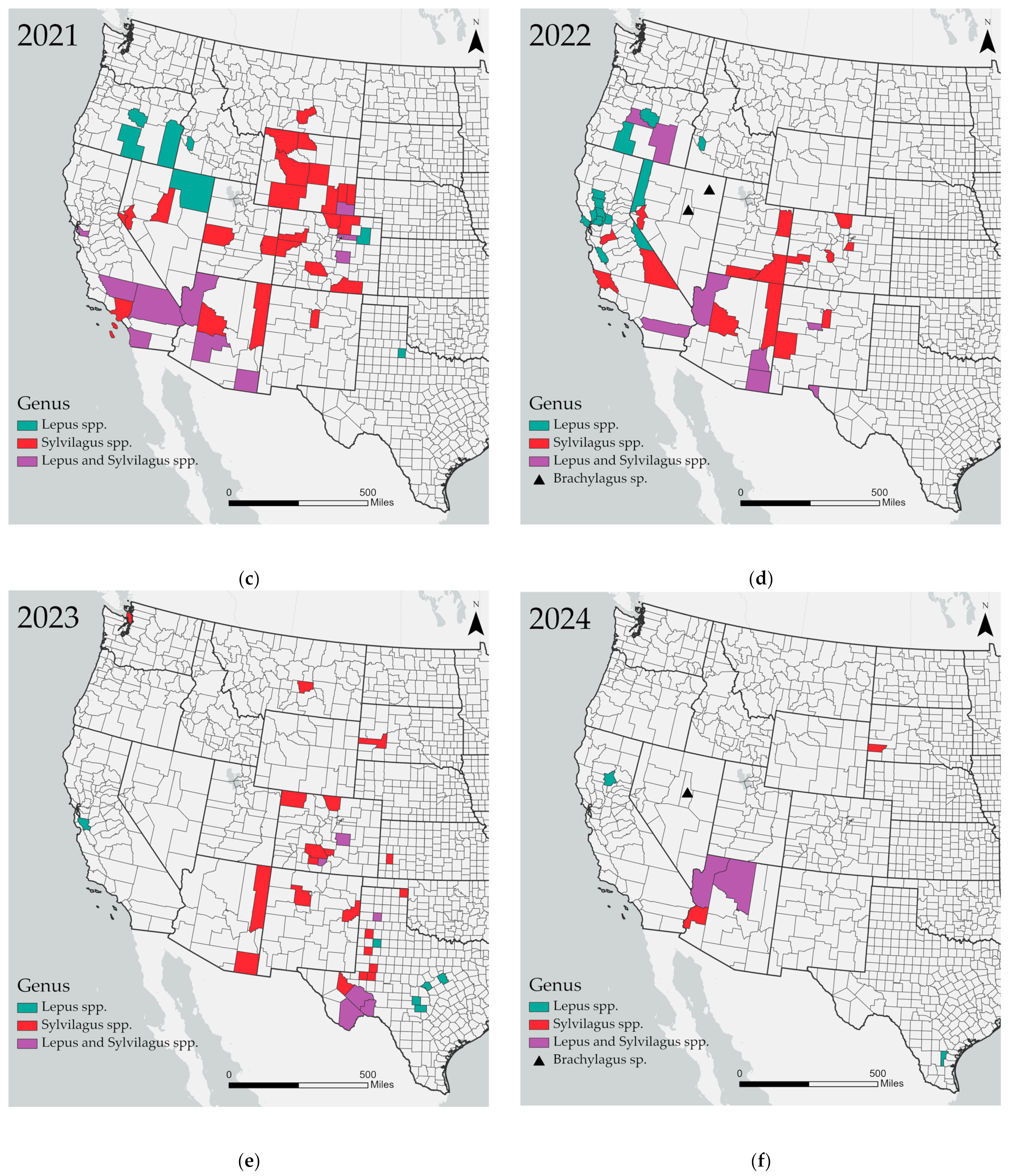
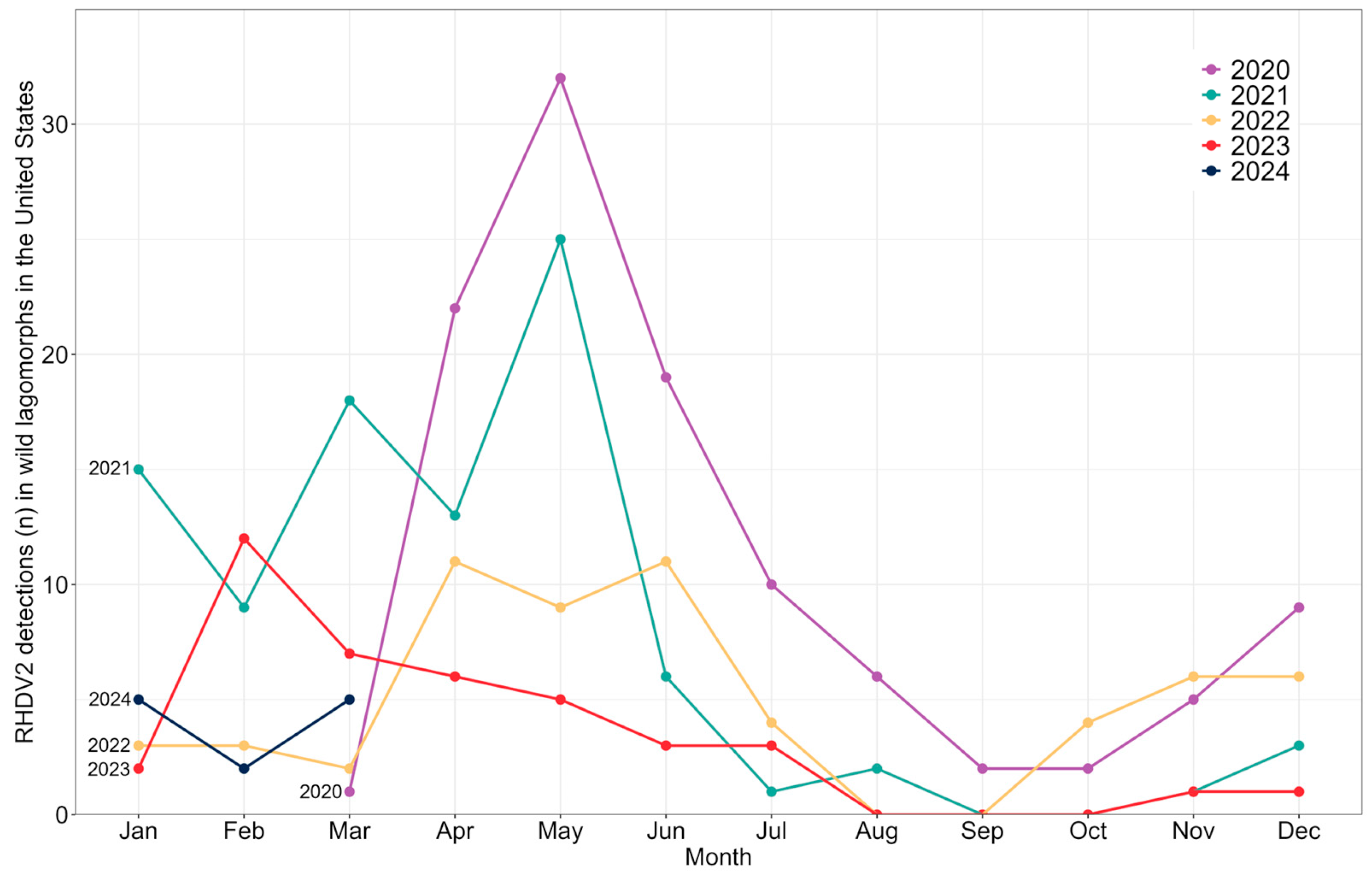
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Pendu, J.; Abrantes, J.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guitton, J.S.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lopes, A.M.; Marchandeau, S.; Alda, F.; Almeida, T.; Célio, A.P.; et al. Proposal for a unified classification system and nomenclature of lagoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, A.W.; Marnell, F.; Barrett, D.; Reid, N.; Hanna, R.E.B.; McElroy, M.C.; Casey, M. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus 2 (RHDV2; GI.2) in Ireland focusing on wild Irish hares (Lepus timidus hibernicus): An overview of the first outbreaks and contextual review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarda, A.; Pugliese, N.; Cavadini, P.; Circella, E.; Capucci, L.; Caroli, A.; Legretto, M.; Mallia, E.; Lavazza, A. Detection of the new emerging rabbit haemorrhagic disease type 2 virus (RHDV2) in Sicily from rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) and Italian hare (Lepus corsicanus). Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neimanis, A.S.; Ahola, H.; Larsson Pettersson, U.; Lopes, A.M.; Abrantes, J.; Zohari, S.; Esteves, P.J.; Gavier-Widén, D. Overcoming species barriers: An outbreak of lagovirus Europaeus GI.2/RHDV2 in an isolated population of mountain hares (Lepus timidus). BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puggioni, G.; Cavadini, P.; Maestrale, C.; Scivoli, R.; Botti, G.; Ligios, C.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lavazza, A.; Capucci, L. The new French 2010 rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus causes an RHD-like disease in the Sardinian Cape hare (Lepus capensis mediterraneus). Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velarde, R.; Cavadini, P.; Neimanis, A.; Cabezón, O.; Chiari, M.; Gaffuri, A.; Lavín, S.; Grilli, G.; Gavier-Widén, D.; Lavazza, A.; et al. Spillover events of infection of brown hares (Lepus europaeus) with rabbit haemorrhagic disease type 2 virus (RHDV2) caused sporadic cases of an European brown hare syndrome-like disease in Italy and Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, R.; Abrantes, J.; Lopes, A.M.; Estruch, J.; Côrte-Real, J.V.; Esteves, P.J.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Ruiz-Olmo, J.; Rouco, C. Spillover event of recombinant lagovirus Europaeus/GI.2 into the Iberian hare (Lepus granatensis) in Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 3187–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, K.P.; Nicieza, I.; Balseiro, A.; Muguerza, M.A.; Rosell, J.M.; Casais, R.; Álvarez, Á.L.; Parra, F. Variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus in young rabbits, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capucci, L.; Cavadini, P.; Schiavitto, M.; Lombardi, G.; Lavazza, A. Increased pathogenicity in rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus type 2 (RHDV2). Vet. Rec. 2017, 180, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.B.A.; Edmonds, S.E.; Kerr, S.R.; Broughton-Neiswanger, L.E.; Snekvik, K.R. Clinical and pathologic findings in an outbreak in rabbits of natural infection by rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus 2 in the northwestern United States. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.N.; King, T.; O’Connor, T.; Read, A.J.; Arrow, J.; Trought, K.; Duckworth, J.; Piper, M.; Strive, T. Age and infectious dose significantly affect disease progression after RHDV2 infection in naïve domestic rabbits. Viruses 2021, 13, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Boucher, S.; Le Normand, B.; Plassiart, G.; Portejoie, Y.; Decors, A.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guérin, J.-L.; Marchandeau, S. Detection of a new variant of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in France. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.E.; Dusek, R.J.; Prevost, S.; Clifford, D.L.; Moriarty, M.E.; Takahashi, F. Modeling the response of an endangered rabbit population to RHDV2 and vaccination. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2024, 6, e13072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, J.; van der Loo, W.; Le Pendu, J.; Esteves, P.J. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease (RHD) and rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV): A review. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouco, C.; Abrantes, J.; Serronha, A.; Lopes, A.M.; Maio, E.; Magalhães, M.J.; Blanco, E.; Bárcena, J.; Esteves, P.J.; Santos, N.; et al. Epidemiology of RHDV2 (Lagovirus europaeus/GI.2) in free-living wild European rabbits in Portugal. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e373–e382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.T.; Johnston, C.H.; Alves, P.C.; Hacklander, K. Lagomorphs: Pikas, Rabbits, and Hares of the World; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 67–220. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Conservation Online System. Available online: https://ecos.fws.gov/ecp0/reports/ad-hoc-species-report?kingdom=V&kingdom=I&status=E&status=T&status=EmE&status=EmT&status=EXPE&status=EXPN&status=SAE&status=SAT&mapstatus=3&fcrithab=on&fstatus=on&fspecrule=on&finvpop=on&fgroup=on&header=Listed+Animals (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Smith, A.T.; Ruedas, L.A. Sylvilagus cognatus (errata version published in 2020). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T41309A165117485. 2016. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41309/165117485 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Barry, R.; Lanier, H.C. Sylvilagus obscurus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41301A45192437. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41301/45192437 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Ruedas, L.A.; Smith, A.T. Sylvilagus robustus (Errata Version Published in 2020). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41310A165116781. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41310/165116781 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Litvaitis, J.; Lanier, H.C. Sylvilagus transitionalis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T21212A45181534. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/21212/45181534 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Brown, D.E.; Smith, A.T. Lepus townsendii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41288A45189364. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41288/45189364 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Lanier, H.; Hik, D. Ochotona collaris. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T41257A45182533. 2016. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41257/45182533 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Lanier, H.C.; Nielsen, C. Sylvilagus aquaticus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41296A45190578. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41296/45190578 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Nielsen, C.; Lanier, H.C. Sylvilagus floridanus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41299A45191626. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41299/45191626 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- McCleery, R.; Lanier, H.C. Sylvilagus palustris. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41303A45192995. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41303/45192995 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Capucci, L.; Brown, D.E. Lepus alleni. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41272A45185265. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41272/45185265 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Smith, A.T.; Johnston, C.H. Lepus othus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T11795A45178124. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/11795/45178124 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Rachlow, J.; Becker, P.A.; Shipley, L. Brachylagus idahoensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T2963A45176206. 2016. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/2963/45176206 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Smith, A.T.; Beever, E. Ochotona princeps. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T41267A45184315. 2016. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41267/45184315 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Smith, A.T.; Brown, D.E. Sylvilagus audubonii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41297A45190821. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41297/45190821 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Smith, A.T.; Brown, D.E. Sylvilagus nuttallii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41300A45192243. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41300/45192243 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Brown, D.E.; Lorenzo, C.; Álvarez-Castañeda, S.T. Lepus californicus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41276A45186309. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41276/45186309 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Brown, D.E.; Smith, A.T. Lepus callotis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T11792A45177499. 2019. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/11792/45177499 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Hansen, D.L.; Bedrosian, G.; Beatty, G. Biology of cottontail rabbits (Sylvilagus spp.) as prey of golden eagles (Aquila chrysaetos) in the western United States. Unpublished report prepared by the Western Golden Eagle Team, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. 2017. Available online: https://ecos.fws.gov/ServCat/Reference/Profile/87137 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Delibes-Mateos, M.; Delibes, M.; Ferreras, P.; Villafuerte, R. Key role of European rabbits in the conservation of the Western Mediterranean Basin hotspot. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.E.; Beatty, G.; Brown, J.E.; Smith, A.T. History, status, and population trends of cottontail rabbits and jackrabbits in the western United States. West. Wildl. 2018, 5, 16–42. Available online: https://wwjournal.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/9/2021/05/Brown_etal_WW_2018.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Bębnowska, D.; Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P. Characteristics of a new variant of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus–RHDV2. Acta Biol. 2019, 26, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monterroso, P.; Garrote, G.; Serronha, A.; Santos, E.; Delibes-Mateos, M.; Abrantes, J.; Perez de Ayala, R.; Silvestre, F.; Carvalho, J.; Vasco, I.; et al. Disease-mediated bottom-up regulation: An emergent virus affects a keystone prey, and alters the dynamics of trophic webs. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Calzada, J. Lynx pardinus (Errata Version Published in 2020). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015: e.T12520A174111773. 2015. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/12520/174111773 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- BirdLife International. Aquila adalberti. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021: e.T22696042A205085721. 2021. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22696042/205085721 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- USGS National Wildlife Health Center. Diagnostic Case Submission Guidelines for Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease. Available online: https://d9-wret.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/assets/palladium/production/s3fs-public/atoms/files/USGS_NWHC_RHDV2_submission_guidelines.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Weyna, A.A.W.; Andreasen, V.A.; Burrell, C.E.; Kunkel, M.R.; Radisic, R.; Goodwin, C.C.; Fenton, H.; Dugovich, B.S.; Poulson, R.L.; Ruder, M.G.; et al. Causes of morbidity and mortality in wild cottontail rabbits in the eastern United States, 2013–2022. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asin, J.; Moriarty, M.E.; Mikolon, A.B.; Clifford, D.L.; Rejmanek, D.; Uzal, F.A.; Crossley, B.M. An RT-qPCR Assay from rectal swabs for the detection of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus 2 in natural cases. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2023, 2023, e1869692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.D.; Carvalho, C.L.; Barros, S.C.; Henriques, A.M.; Ramos, F.; Fagulha, T.; Luís, T.; Duarte, E.L.; Fevereiro, M. A real time Taqman RT-PCR for the detection of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus 2 (RHDV2). J. Virol. Methods 2015, 219, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simes, M.T.; Longshore, K.M.; Nussear, K.E.; Beatty, G.L.; Brown, D.E.; Esque, T.C. Black-tailed and white-tailed jackrabbits in the American west: History, ecology, ecological significance, and survey methods. West. N. Am. Nat. 2015, 75, 491–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.; Gidlewski, T.; Berninger, M.L.; Petrowski, H.M.; Bracht, A.J.; de Rueda, C.B.; Barrette, R.W.; Grady, M.; O’Hearn, E.S.; Lewis, C.E.; et al. Comparative susceptibility of eastern cottontails and New Zealand white rabbits to classical rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) and RHDV2. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e968–e978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, S.; Tur, A. Conservation strategy for the New England cottontail (Sylvilagus transitionalis). Available online: https://youngforest.org/sites/default/files/2023-08/conservation-strategy-for-new-england-cottontail_0.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Gallie, J.; Hayes, G. Columbia Basin Pygmy Rabbit Reintroduction and Genetic Management Plan 2019. Available online: https://wdfw.wa.gov/sites/default/files/publications/02211/wdfw02211.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Williams, D.F.; Kelly, P.A.; Hamilton, L.P. Controlled Propagation and Reintroduction Plan for the Riparian Brush Rabbit (Sylvilagus bachmani riparius). Available online: https://esrp.csustan.edu/publications/pdf/rbr_prop_plan_final-official.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. South Florida Multi-Species Recovery Plan. 1999. Available online: https://www.fws.gov/verobeach/MSRPPDFs/LowerKeysRabbit.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Crowell, M.; LaHue, N.; Heath, E.; Shoemaker, K.; Matocq, M. Detection of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus 2 in the pygmy rabbit (Brachylagus idahoensis) in Nevada, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2023, 59, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; An, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, H. Epidemiological characterization and risk assessment of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus 2 (RHDV2/b/GI.2) in the world. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, C.; Mendoza, M.; Sarto, M.P.; de Bagüés, M.P.J.; Luján, L.; Molín, J.; Calvo, A.J.; Monroy, F.; Calvo, J.H. Detection of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus GI.2/RHDV2/b in the Mediterranean pine vole (Microtus duodecimcostatus) and white-toothed shrew (Crocidura russula). J. Wild Dis. 2019, 55, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, P.L.; Hall, R.N.; Cox, T.E.; Kovaliski, J.; McLeod, S.R.; Strive, T. Changes in virus transmission dynamics following the emergence of RHDV2 shed light on its competitive advantage over previously circulating variants. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.L. Breeding of the cottontail rabbit in southern Michigan. Am. Midl. Nat. 1938, 20, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, B.T.; Leopold, B.D.; Burger, L.W.; Godwin, K.D. Movements and home range dynamics of cottontail rabbits in Mississippi. J. Wildl. Manag. 2001, 65, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asin, J.; Rejmanek, D.; Clifford, D.L.; Mikolon, A.B.; Henderson, E.E.; Nyaoke, A.C.; Macías-Rioseco, M.; Streitenberger, N.; Beingesser, J.; Woods, L.W.; et al. Early circulation of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus type 2 in domestic and wild lagomorphs in southern California, USA (2020–2021). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e394–e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahar, J.E.; Hall, R.N.; Peacock, D.; Kovaliski, J.; Piper, M.; Mourant, R.; Huang, N.; Campbell, S.; Gu, X.; Read, A.; et al. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus 2 (RHDV2; GI.2) is replacing endemic strains of RHDV in the Australian landscape within 18 months of its arrival. Virol. J. 2018, 92, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root, J.J.; Gidlewski, T. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease. In Wildlife Disease and Health in Conservation; Jessup, D.A., Radcliffe, R.W., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Di Profio, F.; Melegari, I.; Sarchese, V.; Robetto, S.; Bermudez Sanchez, S.; Carella, E.; Orusa, R.; Cavadini, P.; Lavazza, A.; Marsilio, F.; et al. Potential role of wolf (Canis lupus) as passive carrier of European brown hare syndrome virus (EBHSV). Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 117, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiari, M.; Molinari, S.; Cavadini, P.; Bertasi, B.; Zanoni, M.; Capucci, L.; Lavazza, A. Red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) feeding brown hares (Lepus europaeus) infected by European brown hare syndrome virus (EBHSv) might be involved in the spread of the virus. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2016, 62, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchán, T.; Rocha, G.; Alda, F.; Silva, E.; Thompson, G.; de Trucios, S.H.; Pagés, A. Detection of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) in nonspecific vertebrate hosts sympatric to the European wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, C.; Estrada, R.; Villafuerte, R.; Osácar, J.J.; Lucientes, J. Epidemiology of viral haemorrhagic disease and myxomatosis in a free-living population of wild rabbits. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, F.A.A.; Pinto, A.; Burgoyne, T.; Dalton, K.P.; Carvalho, C.L.; Ramilo, D.W.; Carneiro, C.; Carvalho, T.; Peleteiro, M.C.; Parra, F.; et al. Spillover events of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus 2 (Recombinant GI.4P-GI.2) from Lagomorpha to Eurasian Badger. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 69, 1030–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, B.D. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease: Field epidemiology and the management of wild rabbit populations. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2002, 21, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutze, G.; Bird, P.; Kovaliski, J.; Peacock, D.; Jennings, S.; Cooke, B. Emerging epidemiological patterns in rabbit haemorrhagic disease, its interaction with myxomatosis, and their effects on rabbit populations in South Australia. Wildl. Res. 2002, 29, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, J.S.; Twigg, L.E.; Gray, G.S. The epidemiology of rabbit haemorrhagic disease, and its impact on rabbit populations, in south-western Australia. Wildl. Res. 2004, 31, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lark, T.J.; Spawn, S.A.; Bougie, M.; Gibbs, H.K. Cropland expansion in the United States produces marginal yields at high costs to wildlife. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringenberg, J.M. Ecology of Eastern Cottontail Rabbits in a Fragmented Agricultural Landscape. Master’s Thesis, University of Nebraska Kearney, Kearney, NE, USA, 19 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, M.J.; Hughes, P.T.; Hines, J.E.; Nichols, J.D. Testing metapopulation concepts: Effects of patch characteristics and neighborhood occupancy on the dynamics of an endangered lagomorph. Oikos 2014, 123, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forys, E.A.; Humphrey, S.R. Home range and movements of the Lower Keys marsh rabbit in a highly fragmented habitat. J. Mammal. 1996, 77, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, J.M.; Wachocki, B.; Wright, M.; Zeveloff, S.I.; Skopec, M.M. Habitat selection by the pygmy rabbit (Brachylagus idahoensis) in Northeastern Utah. West. N. Am. Nat. 2014, 74, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, V.K.; Xu, L.; Moran, K.; Mohamed, F.; Boston, T.; Pauszek, S.J.; Vierra, D.A.; Faburay, B.; Dodd, K.A.; Barrette, R.W. Coding-complete genome sequences of emerging rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus type 2 isolates detected in 2020 in the United States. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medgene, RHDV2 Conditional License–State Permissions. Available online: https://medgenelabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/RHDV2-Conditional-License-State-Permissions-16Jan24.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Cominsky, B.; Porter, S.; Root, J.J.; Schueler, A.; Anderson, G.; VanderWal, S.; Benson, A. A novel vaccine candidate against rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus 2 (RHDV2) confers protection in domestic rabbits. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 83, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Factsheet. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/sites/default/files/fs-rhdv2.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2024).
| Common Name | Scientific Name | IUCN Red List Classification (Population Trend) | USFWS Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collared pika | Ochotona collaris | LC 1 (Unknown) | NL 5 |
| American pika | Ochotona princeps | LC (Decreasing) | NL |
| Pygmy rabbit | Brachylagus idahoensis | LC (Unknown) | EN— Columbia Basin DPS 6 |
| Swamp rabbit | Sylvilagus aquaticus | LC (Decreasing) | NL |
| Desert cottontail | Sylvilagus audubonii | LC (Decreasing) | NL |
| Brush rabbit | Sylvilagus bachmani | LC (Stable) | EN— S. b. riparius |
| Manzano mountain cottontail | Sylvilagus cognatus | EN 2 (Unknown) | NL |
| Eastern cottontail | Sylvilagus floridanus | LC (Unknown) | NL |
| Mountain cottontail | Sylvilagus nuttallii | LC (Decreasing) | NL |
| Appalachian cottontail | Sylvilagus obscurus | NT 3 (Decreasing) | NL |
| Marsh rabbit | Sylvilagus palustris | LC (Unknown) | EN— S. p. hefneri |
| Davis Mountains cottontail | Sylvilagus robustus | VU 4 (Decreasing) | NL |
| New England cottontail | Sylvilagus transitionalis | VU (Decreasing) | EN |
| Antelope jackrabbit | Lepus alleni | LC (Unknown) | NL |
| Snowshoe hare | Lepus americanus | LC (Stable) | NL |
| Black-tailed jackrabbit | Lepus californicus | LC (Decreasing) | NL |
| White-sided jackrabbit | Lepus callotis | VU (Decreasing) | NL |
| Alaskan hare | Lepus othus | LC (Unknown) | NL |
| White-tailed jackrabbit | Lepus townsendii | LC (Decreasing) | NL |
| Genus | Species | Tested 1 | Positives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brachylagus | Pygmy rabbit | 8 | 7 |
| Lepus | Antelope jackrabbit | 3 | 3 |
| Black-tailed jackrabbit | 106 | 77 | |
| Snowshoe hare | 6 | 0 | |
| White-tailed jackrabbit | 3 | 0 | |
| Lepus (unidentified) | 9 | 8 | |
| Total Lepus | 127 | 88 | |
| Sylvilagus | Brush rabbit | 35 | 1 |
| Desert cottontail | 236 | 121 | |
| Eastern cottontail | 260 | 9 | |
| Marsh rabbit | 11 | 0 | |
| Mountain cottontail | 15 | 6 | |
| New England cottontail | 4 | 0 | |
| Riparian brush rabbit | 28 | 4 | |
| Swamp rabbit | 11 | 0 | |
| Sylvilagus (unidentified) | 181 | 77 | |
| Total Sylvilagus | 781 | 218 | |
| All species | 916 | 313 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ringenberg, J.M.; Weir, K.; Linder, T.; Lenoch, J. Detections of Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus 2 (RHDV2) Following the 2020 Outbreak in Wild Lagomorphs across the Western United States. Viruses 2024, 16, 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071106
Ringenberg JM, Weir K, Linder T, Lenoch J. Detections of Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus 2 (RHDV2) Following the 2020 Outbreak in Wild Lagomorphs across the Western United States. Viruses. 2024; 16(7):1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071106
Chicago/Turabian StyleRingenberg, Jourdan M., Kelsey Weir, Timothy Linder, and Julianna Lenoch. 2024. "Detections of Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus 2 (RHDV2) Following the 2020 Outbreak in Wild Lagomorphs across the Western United States" Viruses 16, no. 7: 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071106
APA StyleRingenberg, J. M., Weir, K., Linder, T., & Lenoch, J. (2024). Detections of Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus 2 (RHDV2) Following the 2020 Outbreak in Wild Lagomorphs across the Western United States. Viruses, 16(7), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071106






