NTB-A and 2B4 Natural Killer Cell Receptors Modulate the Capacity of a Cocktail of Non-Neutralizing Antibodies and a Small CD4-Mimetic to Eliminate HIV-1-Infected Cells by Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Cell Lines and Primary Cells
2.3. Plasmids, Antibodies, and Plasma
2.4. Antibody Expression and Purification
2.5. Small Molecules
2.6. Proviral Constructs
2.7. Viral Production and Infection
2.8. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Cell Surface and Intracellular Staining
2.9. FACS-Based ADCC Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
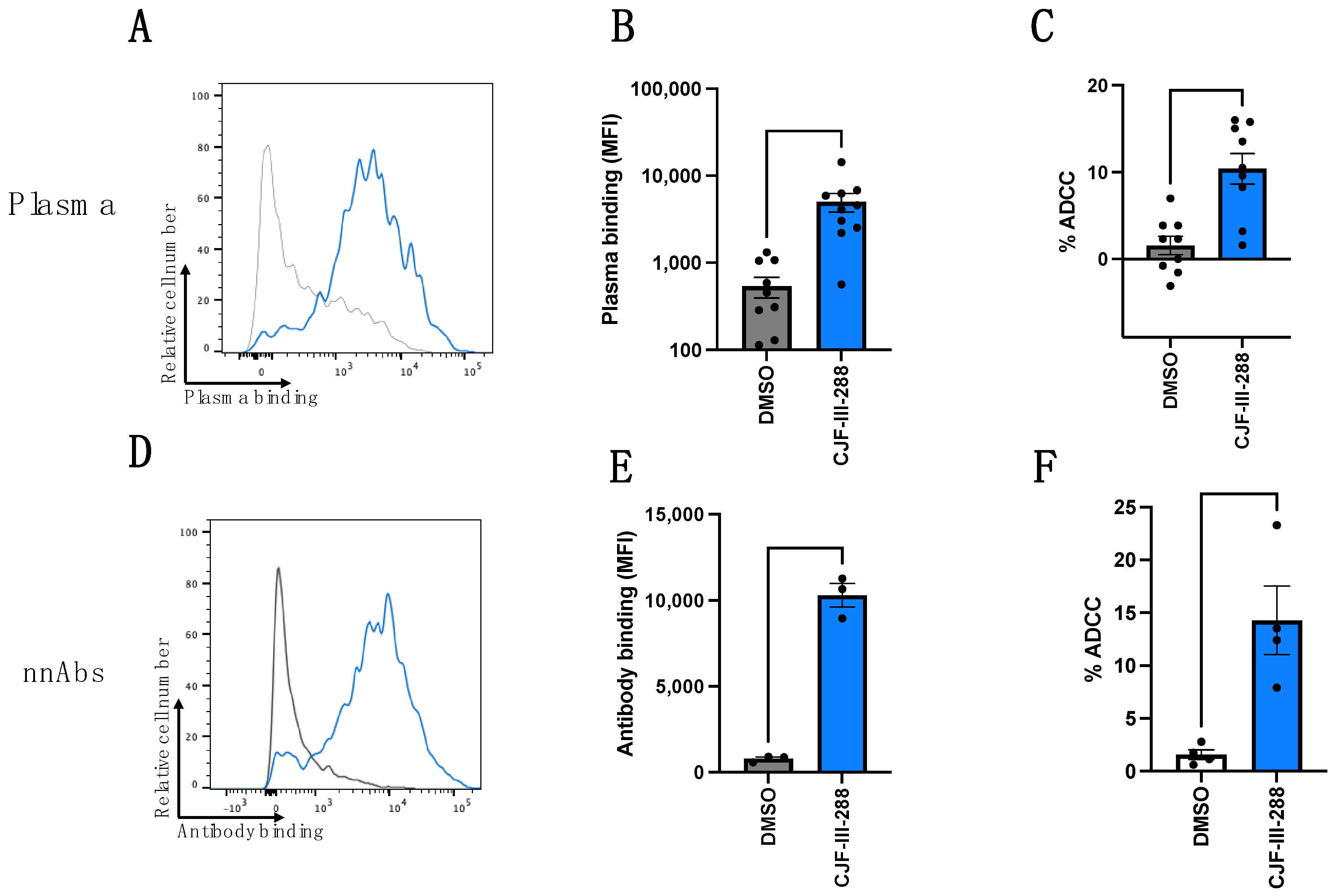
3.1. CD4mc Enables nnAbs to Recognize and Eliminate HIV-1-Infected Cells by ADCC
3.2. NTB-A and 2B4 Contribute to ADCC-Mediated Elimination of HIV-1-Infected Cells by PLWH Plasma or by a Cocktail of nnAbs in Combination with CD4mc CJF-III-288
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forthal, D.N.; Finzi, A. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in HIV infection. AIDS 2018, 32, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Board, N.L.; Moskovljevic, M.; Wu, F.; Siliciano, R.F.; Siliciano, J.D. Engaging innate immunity in HIV-1 cure strategies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajashekar, J.K.; Richard, J.; Beloor, J.; Prevost, J.; Anand, S.P.; Beaudoin-Bussieres, G.; Shan, L.; Herndler-Brandstetter, D.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Medjahed, H.; et al. Modulating HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein conformation to decrease the HIV-1 reservoir. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 904–916.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegaskanda, S.; Weinfurter, J.T.; Friedrich, T.C.; Kent, S.J. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity is associated with control of pandemic H1N1 influenza virus infection of macaques. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5512–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forthal, D.N.; Landucci, G.; Daar, E.S. Antibody from patients with acute human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection inhibits primary strains of HIV type 1 in the presence of natural-killer effector cells. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6953–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borducchi, E.N.; Liu, J.; Nkolola, J.P.; Cadena, A.M.; Yu, W.H.; Fischinger, S.; Broge, T.; Abbink, P.; Mercado, N.B.; Chandrashekar, A.; et al. Publisher Correction: Antibody and TLR7 agonist delay viral rebound in SHIV-infected monkeys. Nature 2018, 564, E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halper-Stromberg, A.; Lu, C.L.; Klein, F.; Horwitz, J.A.; Bournazos, S.; Nogueira, L.; Eisenreich, T.R.; Liu, C.; Gazumyan, A.; Schaefer, U.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies and viral inducers decrease rebound from HIV-1 latent reservoirs in humanized mice. Cell 2014, 158, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldt, B.; Schultz, N.; Dunlop, D.C.; Alpert, M.D.; Harvey, J.D.; Evans, D.T.; Poignard, P.; Hessell, A.J.; Burton, D.R. A panel of IgG1 b12 variants with selectively diminished or enhanced affinity for Fcγ receptors to define the role of effector functions in protection against HIV. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10572–10581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruel, T.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Amraoui, S.; Malbec, M.; Richard, L.; Bourdic, K.; Donahue, D.A.; Lorin, V.; Casartelli, N.; Noel, N.; et al. Elimination of HIV-1-infected cells by broadly neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Robertson, M.W.; Galinha, A.; Mazieres, N.; Spagnoli, R.; Fridman, W.H.; Sautes, C. Affinity of the interaction between Fc γ receptor type III (Fc γRIII) and monomeric human IgG subclasses. Role of Fc γRIII glycosylation. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, L.L.; Ruitenberg, J.J.; Phillips, J.H. Functional and biochemical analysis of CD16 antigen on natural killer cells and granulocytes. J. Immunol. 1988, 141, 3478–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaudoin-Bussieres, G.; Prevost, J.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Melillo, B.; Chen, J.; Smith Iii, A.B.; Pazgier, M.; Finzi, A. Elicitation of Cluster A and Co-Receptor Binding Site Antibodies are Required to Eliminate HIV-1 Infected Cells. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, J.M.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Wei, X.; Wang, S.; Levy, D.N.; Wang, W.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M.; Derdeyn, C.A.; Allen, S.; et al. Antigenic conservation and immunogenicity of the HIV coreceptor binding site. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veillette, M.; Coutu, M.; Richard, J.; Batraville, L.A.; Dagher, O.; Bernard, N.; Tremblay, C.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Roger, M.; Finzi, A. The HIV-1 gp120 CD4-bound conformation is preferentially targeted by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediating antibodies in sera from HIV-1-infected individuals. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veillette, M.; Desormeaux, A.; Medjahed, H.; Gharsallah, N.E.; Coutu, M.; Baalwa, J.; Guan, Y.; Lewis, G.; Ferrari, G.; Hahn, B.H.; et al. Interaction with cellular CD4 exposes HIV-1 envelope epitopes targeted by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2633–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.; Veillette, M.; Brassard, N.; Iyer, S.S.; Roger, M.; Martin, L.; Pazgier, M.; Schon, A.; Freire, E.; Routy, J.P.; et al. CD4 mimetics sensitize HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2687–E2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willey, R.L.; Maldarelli, F.; Martin, M.A.; Strebel, K. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein induces rapid degradation of CD4. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 7193–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magadan, J.G.; Perez-Victoria, F.J.; Sougrat, R.; Ye, Y.; Strebel, K.; Bonifacino, J.S. Multilayered mechanism of CD4 downregulation by HIV-1 Vpu involving distinct ER retention and ERAD targeting steps. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magadan, J.G.; Bonifacino, J.S. Transmembrane domain determinants of CD4 Downregulation by HIV-1 Vpu. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, R.; Skowronski, J. CD4 down-regulation by nef alleles isolated from human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5549–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, J.; Richard, J.; Medjahed, H.; Alexander, A.; Jones, J.; Kappes, J.C.; Ochsenbauer, C.; Finzi, A. Incomplete Downregulation of CD4 Expression Affects HIV-1 Env Conformation and Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Responses. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00484-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, J.; Richard, J.; Ding, S.; Pacheco, B.; Charlebois, R.; Hahn, B.H.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Finzi, A. Envelope glycoproteins sampling states 2/3 are susceptible to ADCC by sera from HIV-1-infected individuals. Virology 2018, 515, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, J.; Anand, S.P.; Rajashekar, J.K.; Zhu, L.; Richard, J.; Goyette, G.; Medjahed, H.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, Y.; et al. HIV-1 Vpu restricts Fc-mediated effector functions in vivo. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsahafi, N.; Bakouche, N.; Kazemi, M.; Richard, J.; Ding, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Das, D.; Anand, S.P.; Prevost, J.; Tolbert, W.D.; et al. An Asymmetric Opening of HIV-1 Envelope Mediates Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 578–587.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsahafi, N.; Ding, S.; Richard, J.; Markle, T.; Brassard, N.; Walker, B.; Lewis, G.K.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Brockman, M.A.; Finzi, A. Nef Proteins from HIV-1 Elite Controllers Are Inefficient at Preventing Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.; Sannier, G.; Zhu, L.; Prevost, J.; Marchitto, L.; Benlarbi, M.; Beaudoin-Bussieres, G.; Hongil, K.; Sun, Y.; Chatterjee, D.A.; et al. CD4 downregulation precedes Env expression and protects HIV-1-infected cells from ADCC mediated by non-neutralizing antibodies. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, J.B.; Gorman, J.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Z.; Arthos, J.; Burton, D.R.; Koff, W.C.; Courter, J.R.; Smith, A.B., III; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Conformational dynamics of single HIV-1 envelope trimers on the surface of native virions. Science 2014, 346, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruel, T.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Lorin, V.; Lortat-Jacob, H.; Baleux, F.; Bourdic, K.; Noel, N.; Lambotte, O.; Mouquet, H.; Schwartz, O. Lack of ADCC Breadth of Human Nonneutralizing Anti-HIV-1 Antibodies. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02440-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bredow, B.; Arias, J.F.; Heyer, L.N.; Moldt, B.; Le, K.; Robinson, J.E.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Burton, D.R.; Evans, D.T. Comparison of Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity and Virus Neutralization by HIV-1 Env-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6127–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neil, S.J.; Zang, T.; Bieniasz, P.D. Tetherin inhibits retrovirus release and is antagonized by HIV-1 Vpu. Nature 2008, 451, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, J.F.; Heyer, L.N.; von Bredow, B.; Weisgrau, K.L.; Moldt, B.; Burton, D.R.; Rakasz, E.G.; Evans, D.T. Tetherin antagonism by Vpu protects HIV-infected cells from antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6425–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.A.; Hamlin, R.E.; Monroe, A.; Moldt, B.; Hotta, M.T.; Rodriguez Caprio, G.; Fierer, D.S.; Simon, V.; Chen, B.K. HIV-1 Vpu antagonism of tetherin inhibits antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic responses by natural killer cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6031–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, N.; Goff, D.; Katsura, C.; Jorgenson, R.L.; Mitchell, R.; Johnson, M.C.; Stephens, E.B.; Guatelli, J. The interferon-induced protein BST-2 restricts HIV-1 release and is downregulated from the cell surface by the viral Vpu protein. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerboni, C.; Neri, F.; Casartelli, N.; Zingoni, A.; Cosman, D.; Rossi, P.; Santoni, A.; Doria, M. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Nef protein downmodulates the ligands of the activating receptor NKG2D and inhibits natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusali, G.; Potesta, M.; Santoni, A.; Cerboni, C.; Doria, M. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef and Vpu proteins downregulate the natural killer cell-activating ligand PVR. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4496–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, J.; Pickering, S.; Mumby, M.J.; Medjahed, H.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Delgado, G.G.; Dirk, B.S.; Dikeakos, J.D.; Sturzel, C.M.; Sauter, D.; et al. Upregulation of BST-2 by Type I Interferons Reduces the Capacity of Vpu To Protect HIV-1-Infected Cells from NK Cell Responses. mBio 2019, 10, e01113–e01119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.H.; Sowrirajan, B.; Davis, Z.B.; Ward, J.P.; Campbell, E.M.; Planelles, V.; Barker, E. Degranulation of natural killer cells following interaction with HIV-1-infected cells is hindered by downmodulation of NTB-A by Vpu. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.; Bonaparte, M.; Sacks, J.; Guterman, J.; Fogli, M.; Mavilio, D.; Barker, E. HIV modulates the expression of ligands important in triggering natural killer cell cytotoxic responses on infected primary T-cell blasts. Blood 2007, 110, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchitto, L.; Benlarbi, M.; Prevost, J.; Laumaea, A.; Descoteaux-Dinelle, J.; Medjahed, H.; Bourassa, C.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Kirchhoff, F.; Sauter, D.; et al. Impact of HIV-1 Vpu-mediated downregulation of CD48 on NK-cell-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. mBio 2023, 14, e0078923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.; Pacheco, B.; Gohain, N.; Veillette, M.; Ding, S.; Alsahafi, N.; Tolbert, W.D.; Prevost, J.; Chapleau, J.P.; Coutu, M.; et al. Co-receptor Binding Site Antibodies Enable CD4-Mimetics to Expose Conserved Anti-cluster A ADCC Epitopes on HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins. EBioMedicine 2016, 12, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.; Prevost, J.; von Bredow, B.; Ding, S.; Brassard, N.; Medjahed, H.; Coutu, M.; Melillo, B.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Hahn, B.H.; et al. BST-2 Expression Modulates Small CD4-Mimetic Sensitization of HIV-1-Infected Cells to Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00219-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.P.; Prevost, J.; Baril, S.; Richard, J.; Medjahed, H.; Chapleau, J.P.; Tolbert, W.D.; Kirk, S.; Smith, A.B., III; Wines, B.D.; et al. Two Families of Env Antibodies Efficiently Engage Fc-γ Receptors and Eliminate HIV-1-Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01823-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchitto, L.; Richard, J.; Prevost, J.; Tauzin, A.; Yang, D.; Chiu, T.-J.; Chen, H.-C.; Diaz-Salinas, M.A.; Nayrac, M.; Benlarbi, M.; et al. The combination of three CD4-induced antibodies targeting highly conserved Env regions with a small CD4-mimetic achieves potent ADCC activity. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryceson, Y.T.; March, M.E.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Long, E.O. Synergy among receptors on resting NK cells for the activation of natural cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion. Blood 2006, 107, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryceson, Y.T.; March, M.E.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Long, E.O. Activation, coactivation, and costimulation of resting human natural killer cells. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 214, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsahafi, N.; Richard, J.; Prevost, J.; Coutu, M.; Brassard, N.; Parsons, M.S.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Brockman, M.; Finzi, A. Impaired Downregulation of NKG2D Ligands by Nef Proteins from Elite Controllers Sensitizes HIV-1-Infected Cells to Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00109–e00117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.S.; Richard, J.; Lee, W.S.; Vanderven, H.; Grant, M.D.; Finzi, A.; Kent, S.J. NKG2D Acts as a Co-Receptor for Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Anti-HIV-1 Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2016, 32, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biassoni, R. Human natural killer receptors, co-receptors, and their ligands. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2009, 14, 14.10.1–14.10.40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaig, R.M.; Stark, S.; Watzl, C. Cutting edge: NTB-A activates NK cells via homophilic interaction. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6524–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staunton, D.E.; Fisher, R.C.; LeBeau, M.M.; Lawrence, J.B.; Barton, D.E.; Francke, U.; Dustin, M.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. Blast-1 possesses a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) membrane anchor, is related to LFA-3 and OX-45, and maps to chromosome 1q21-23. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 169, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Staunton, D.; Fisher, R.; Amiot, M.; Fortin, J.J.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. Expression of the Blast-1 activation/adhesion molecule and its identification as CD48. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 2192–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogli, M.; Mavilio, D.; Brunetta, E.; Varchetta, S.; Ata, K.; Roby, G.; Kovacs, C.; Follmann, D.; Pende, D.; Ward, J.; et al. Lysis of endogenously infected CD4+ T cell blasts by rIL-2 activated autologous natural killer cells from HIV-infected viremic individuals. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavilio, D.; Benjamin, J.; Daucher, M.; Lombardo, G.; Kottilil, S.; Planta, M.A.; Marcenaro, E.; Bottino, C.; Moretta, L.; Moretta, A.; et al. Natural killer cells in HIV-1 infection: Dichotomous effects of viremia on inhibitory and activating receptors and their functional correlates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15011–15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolting, A.; Dugast, A.S.; Rihn, S.; Luteijn, R.; Carrington, M.F.; Kane, K.; Jost, S.; Toth, I.; Nagami, E.; Faetkenheuer, G.; et al. MHC class I chain-related protein A shedding in chronic HIV-1 infection is associated with profound NK cell dysfunction. Virology 2010, 406, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.F.; Hu, H.Y.; Xu, X.Q.; Fu, G.F. Changes in NK Cell Subsets and Receptor Expressions in HIV-1 Infected Chronic Patients and HIV Controllers. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 792775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Y.; Gorny, M.K.; Palker, T.; Karwowska, S.; Zolla-Pazner, S. Epitope mapping of two immunodominant domains of gp41, the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, using ten human monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4832–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritschi, C.J.; Anang, S.; Gong, Z.; Mohammadi, M.; Richard, J.; Bourassa, C.; Severino, K.T.; Richter, H.; Yang, D.; Chen, H.C.; et al. Indoline CD4-mimetic compounds mediate potent and broad HIV-1 inhibition and sensitization to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2222073120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emi, N.; Friedmann, T.; Yee, J.K. Pseudotype formation of murine leukemia virus with the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Salazar, M.G.; Keele, B.F.; Learn, G.H.; Giorgi, E.E.; Li, H.; Decker, J.M.; Wang, S.; Baalwa, J.; Kraus, M.H.; et al. Genetic identity, biological phenotype, and evolutionary pathways of transmitted/founder viruses in acute and early HIV-1 infection. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1273–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsenbauer, C.; Edmonds, T.G.; Ding, H.; Keele, B.F.; Decker, J.; Salazar, M.G.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Shattock, R.; Haynes, B.F.; Shaw, G.M.; et al. Generation of Transmitted/Founder HIV-1 Infectious Molecular Clones and Characterization of Their Replication Capacity in CD4 T Lymphocytes and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2715–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.; Prevost, J.; Baxter, A.E.; von Bredow, B.; Ding, S.; Medjahed, H.; Delgado, G.G.; Brassard, N.; Sturzel, C.M.; Kirchhoff, F.; et al. Uninfected Bystander Cells Impact the Measurement of HIV-Specific Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Responses. mBio 2018, 9, e00358-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumaea, A.; Smith, A.B., III; Sodroski, J.; Finzi, A. Opening the HIV envelope: Potential of CD4 mimics as multifunctional HIV entry inhibitors. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2020, 15, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauzin, A.; Marchitto, L.; Belanger, E.; Benlarbi, M.; Beaudoin-Bussieres, G.; Prevost, J.; Yang, D.; Chiu, T.-J.; Chen, H.-C.; Bourassa, C.; et al. Three families of CD4-induced antibodies are associated with the capacity of plasma from people living with HIV to mediate ADCC in presence of CD4-mimetics. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.L.; Murakowski, D.K.; Bournazos, S.; Schoofs, T.; Sarkar, D.; Halper-Stromberg, A.; Horwitz, J.A.; Nogueira, L.; Golijanin, J.; Gazumyan, A.; et al. Enhanced clearance of HIV-1-infected cells by broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1 in vivo. Science 2016, 352, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Nogueira, L.; Stoffel, E.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Breton, G.; Millard, K.G.; Turroja, M.; Butler, A.; Ramos, V.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Prolonged viral suppression with anti-HIV-1 antibody therapy. Nature 2022, 606, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| All Samples | Chronic Infected | ART-Treated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of plasma samples | 9 | 4 | 5 |
| Median age | 34 | 34 | 36 |
| (IQR) | (28–56) | (28–40) | (33–56) |
| Sex | Male (8) | Male (4) | Male (4) |
| Female (1) | Female (0) | Female (1) | |
| Median days since | 1143 | 1158 | 1018 |
| Infection (IQR) | (792–5166) | (856–1194) | (792–5166) |
| Median viral load | 50 | 35,341 | 50 |
| (Copies/mL, IQR) | (40–809,600) | (29,234–809,600) | (40–50) |
| Median CD4 T cell count | 570 | 416 | 600 |
| (Cells/mm3, IQR) | (200–1149) | (200–691) | (570–1149) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marchitto, L.; Tauzin, A.; Benlarbi, M.; Beaudoin-Bussières, G.; Dionne, K.; Bélanger, É.; Chatterjee, D.; Bourassa, C.; Medjahed, H.; Yang, D.; et al. NTB-A and 2B4 Natural Killer Cell Receptors Modulate the Capacity of a Cocktail of Non-Neutralizing Antibodies and a Small CD4-Mimetic to Eliminate HIV-1-Infected Cells by Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. Viruses 2024, 16, 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071167
Marchitto L, Tauzin A, Benlarbi M, Beaudoin-Bussières G, Dionne K, Bélanger É, Chatterjee D, Bourassa C, Medjahed H, Yang D, et al. NTB-A and 2B4 Natural Killer Cell Receptors Modulate the Capacity of a Cocktail of Non-Neutralizing Antibodies and a Small CD4-Mimetic to Eliminate HIV-1-Infected Cells by Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. Viruses. 2024; 16(7):1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071167
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarchitto, Lorie, Alexandra Tauzin, Mehdi Benlarbi, Guillaume Beaudoin-Bussières, Katrina Dionne, Étienne Bélanger, Debashree Chatterjee, Catherine Bourassa, Halima Medjahed, Derek Yang, and et al. 2024. "NTB-A and 2B4 Natural Killer Cell Receptors Modulate the Capacity of a Cocktail of Non-Neutralizing Antibodies and a Small CD4-Mimetic to Eliminate HIV-1-Infected Cells by Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity" Viruses 16, no. 7: 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071167
APA StyleMarchitto, L., Tauzin, A., Benlarbi, M., Beaudoin-Bussières, G., Dionne, K., Bélanger, É., Chatterjee, D., Bourassa, C., Medjahed, H., Yang, D., Chiu, T.-J., Chen, H.-C., III, A. B. S., Richard, J., & Finzi, A. (2024). NTB-A and 2B4 Natural Killer Cell Receptors Modulate the Capacity of a Cocktail of Non-Neutralizing Antibodies and a Small CD4-Mimetic to Eliminate HIV-1-Infected Cells by Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. Viruses, 16(7), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071167






