Cytokine Response of Natural Killer Cells to Hepatitis B Virus Infection Depends on Monocyte Co-Stimulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. HBV Culture Systems
2.2. Co-Culture with Immune Cells
2.3. HBV DNA Quantification
2.4. HBeAg Detection
2.5. Stimulation of PBMCs Prior to Staining
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Different Cell Lines on HBV Replication and the Effect of Co-Culture with PBMCs
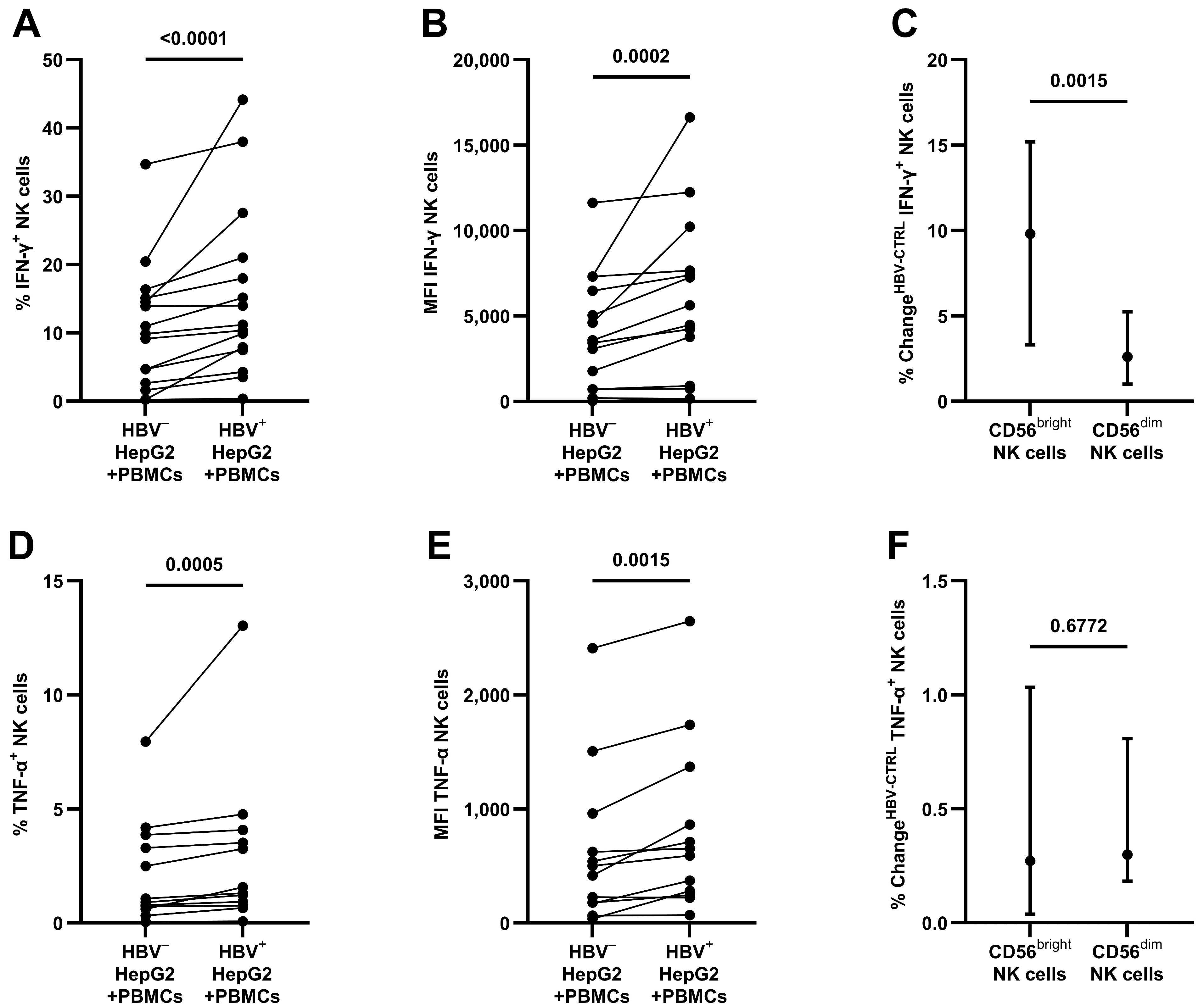
3.2. Production of Antiviral Cytokines by NK Cells after Contact with HBV
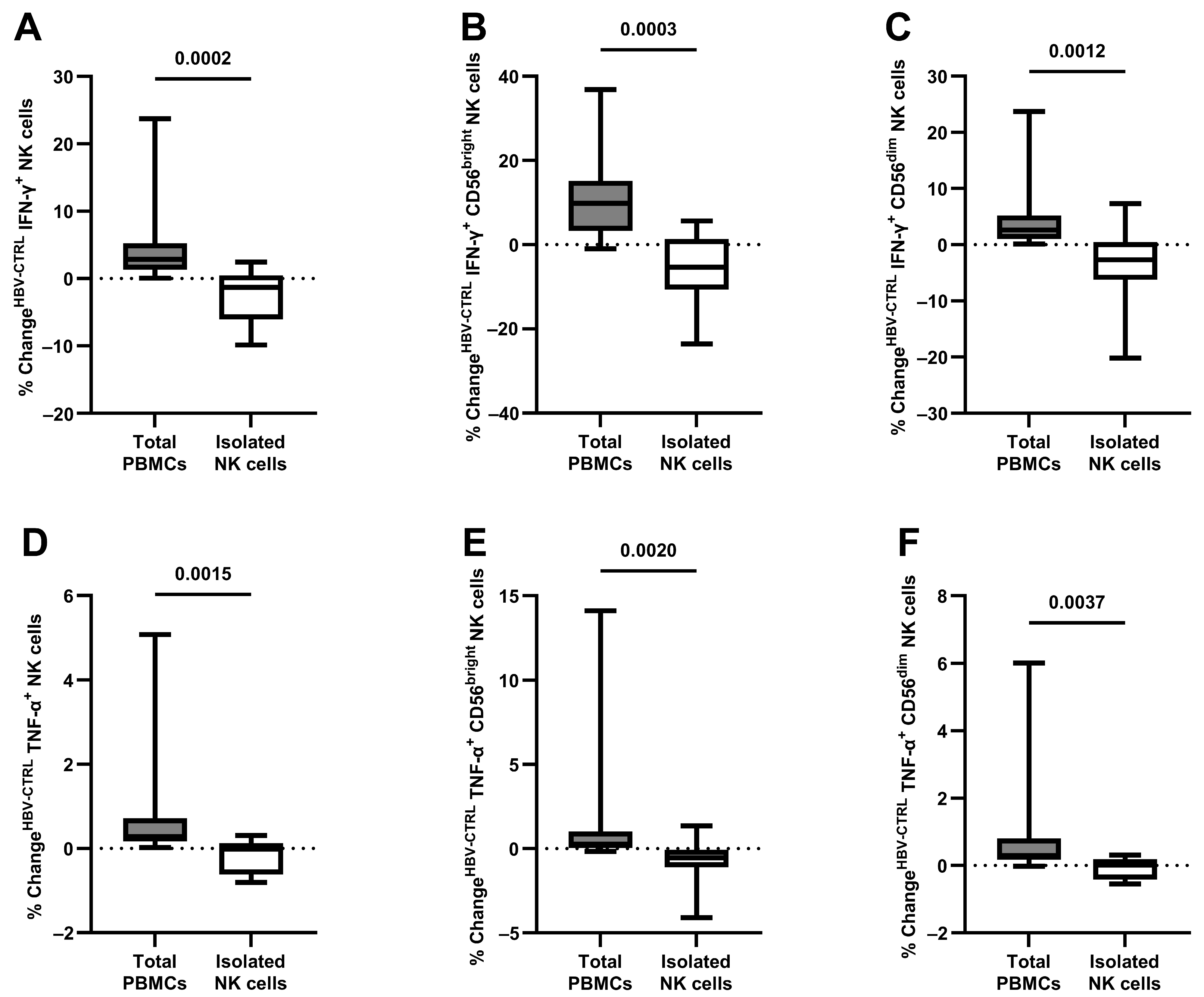
3.3. The Antiviral Capacity of Isolated NK Cells
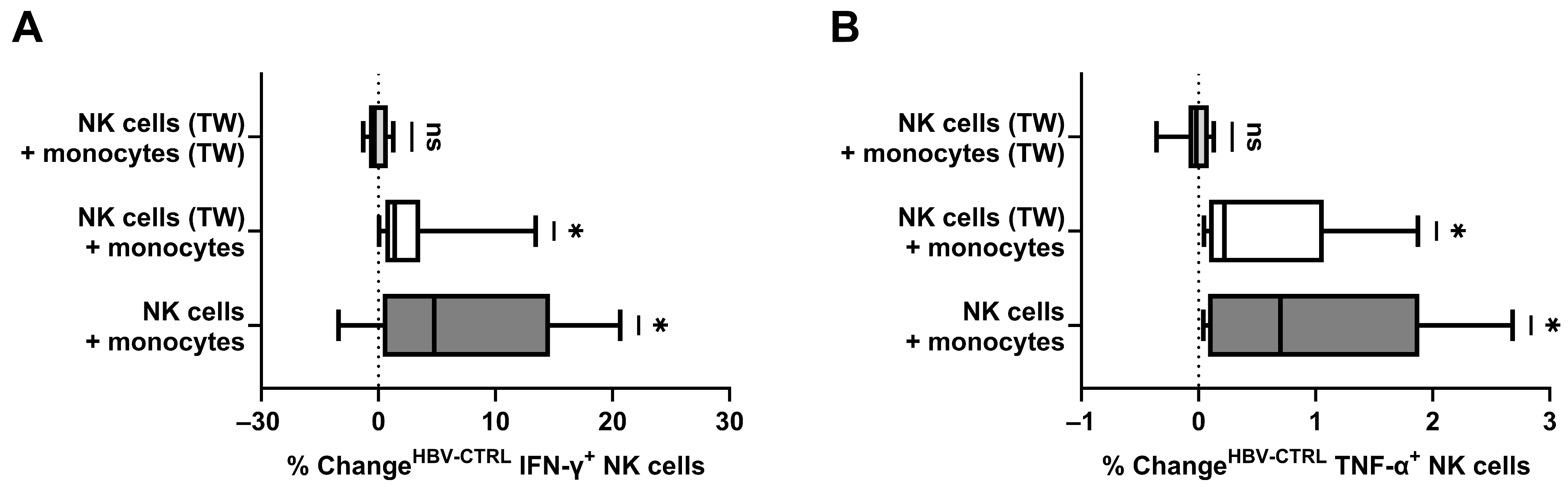
3.4. The Role of Monocytes and Spatial Conditions in NK Cell Stimulation
3.5. Direct Contact between Monocytes, NK Cells, and HBV+ Target Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Europe Hepatitis B & C Collaborators Hepatitis B and C in Europe: An Update from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2023, 8, e701–e716. [CrossRef]
- Dusheiko, G.; Agarwal, K.; Maini, M.K. New Approaches to Chronic Hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, K.; Andreata, F.; Beccaria, C.G.; Iannacone, M. Priming and Maintenance of Adaptive Immunity in the Liver. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 42, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, K.; Katelani, S.; Pappa, M.; Fragkoulis, G.E.; Androutsakos, T. The Role of Interleukins in HBV Infection: A Narrative Review. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Q.; Qudus, M.S.; Yue, Z.; Luo, W.; Zhang, W.; Ouyang, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Innate Immunity, Inflammation, and Intervention in HBV Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Dou, Y.; Wang, Q. Immune Response and Treatment Targets of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1206720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillaire, M.L.B.; Lawrence, P.; Lagrange, B. IFN-γ: A Crucial Player in the Fight Against HBV Infection? Immune Netw. 2023, 23, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehermann, B. Natural Killer Cells in Viral Hepatitis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basílio-Queirós, D.; Mischak-Weissinger, E. Natural Killer Cells- from Innate Cells to the Discovery of Adaptability. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1172437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupke, P.; Adenugba, A.; Schemmerer, M.; Bitterer, F.; Schlitt, H.J.; Geissler, E.K.; Wenzel, J.J.; Werner, J.M. Immunomodulation of Natural Killer Cell Function by Ribavirin Involves TYK-2 Activation and Subsequent Increased IFN-γ Secretion in the Context of In Vitro Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Cells 2023, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Fälth, M.; Stindt, J.; Königer, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D Viruses Exploit Sodium Taurocholate Co-Transporting Polypeptide for Species-Specific Entry into Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wettengel, J.M.; Linden, B.; Esser, K.; Laue, M.; Burwitz, B.J.; Protzer, U. Rapid and Robust Continuous Purification of High-Titer Hepatitis B Virus for In Vitro and In Vivo Applications. Viruses 2021, 13, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.; Chakraborty, A.; Chou, W.-M.; Hasreiter, J.; Wettengel, J.M.; Stadler, D.; Bester, R.; Asen, T.; Zhang, K.; Wisskirchen, K.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Genome Recycling and de Novo Secondary Infection Events Maintain Stable cccDNA Levels. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.S.; Purdy, M.A.; Choi, Y. Cell Culture Systems for Studying Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D Virus Infections. Life Basel Switz. 2023, 13, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Bi, J. Prospects for NK-Based Immunotherapy of Chronic HBV Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1084109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Yan, Z.-H.; Lu, L.; Lu, S.; Zhang, G.; Lin, W. Peripheral Immune Cells Exhaustion and Functional Impairment in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 759292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claus, M.; Greil, J.; Watzl, C. Comprehensive Analysis of NK Cell Function in Whole Blood Samples. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 341, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliviero, B.; Varchetta, S.; Paudice, E.; Michelone, G.; Zaramella, M.; Mavilio, D.; De Filippi, F.; Bruno, S.; Mondelli, M.U. Natural Killer Cell Functional Dichotomy in Chronic Hepatitis B and Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infections. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1151–1160.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Qin, S.; Wei, X.; Liu, X.; Guan, J.; Zhu, H.; Chang, G.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Qian, J.; et al. Highly Activated TRAIL+ CD56bright NK Cells Are Associated with the Liver Damage in HBV-LC Patients. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 232, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhang, S.; Fan, R.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, C.; Shang, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Natural Killer Cells Are Characterized by the Concomitantly Increased Interferon-γ and Cytotoxicity in Acute Resolved Hepatitis B Patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupke, P.; Werner, J.M. Hepatitis E Virus Infection-Immune Responses to an Underestimated Global Threat. Cells 2021, 10, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Jameel, S. Hepatitis E. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2011, 54, 2218–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Gyurova, I.E.; Waggoner, S.N. Mutually Assured Destruction: The Cold War between Viruses and Natural Killer Cells. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freud, A.G.; Mundy-Bosse, B.L.; Yu, J.; Caligiuri, M.A. The Broad Spectrum of Human Natural Killer Cell Diversity. Immunity 2017, 47, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, T.; Hentges, F.; Zimmer, J. Consequences of the Crosstalk between Monocytes/Macrophages and Natural Killer Cells. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth, N.; Gundle, R.; Davies, R.J.O.; Lee, Y.C.G.; McMichael, A.J.; Callan, M.F.C. CD56bright NK Cells Are Enriched at Inflammatory Sites and Can Engage with Monocytes in a Reciprocal Program of Activation. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2004, 173, 6418–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, N.; Ahmad, F.; Hong, H.S.; Eberhard, J.; Lu, I.-N.; Ballmaier, M.; Schmidt, R.E.; Jacobs, R.; Meyer-Olson, D. FcγRIII (CD16)-Mediated ADCC by NK Cells Is Regulated by Monocytes and FcγRII (CD32). Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 3368–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, S.; Kuttruff, S.; Waldhauer, I.; Steinle, A. Mutual Activation of Natural Killer Cells and Monocytes Mediated by NKp80-AICL Interaction. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloss, M.; Decker, P.; Baltz, K.M.; Baessler, T.; Jung, G.; Rammensee, H.-G.; Steinle, A.; Krusch, M.; Salih, H.R. Interaction of Monocytes with NK Cells upon Toll-like Receptor-Induced Expression of the NKG2D Ligand MICA. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2008, 181, 6711–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr, M.; Münzel, T.; Wenzel, P. Interplay of NK Cells and Monocytes in Vascular Inflammation and Myocardial Infarction. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Alvaro, I.; Domínguez-Jiménez, C.; Ortiz, A.M.; Núñez-González, V.; Roda-Navarro, P.; Fernández-Ruiz, E.; Sancho, D.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Interleukin-15 and Interferon-Gamma Participate in the Cross-Talk between Natural Killer and Monocytic Cells Required for Tumour Necrosis Factor Production. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhai, N.; Wang, Z.; Song, H.; Yang, Y.; Cui, A.; Li, T.; Wang, G.; Niu, J.; Crispe, I.N.; et al. Regulatory NK Cells Mediated between Immunosuppressive Monocytes and Dysfunctional T Cells in Chronic HBV Infection. Gut 2018, 67, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serti, E.; Werner, J.M.; Chattergoon, M.; Cox, A.L.; Lohmann, V.; Rehermann, B. Monocytes Activate Natural Killer Cells via Inflammasome-Induced Interleukin 18 in Response to Hepatitis C Virus Replication. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 209–220.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Saha, B.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. IFN-γ Production by Human Natural Killer Cells in Response to HCV-Infected Hepatoma Cells Is Dependent on Accessory Cells. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pollmann, J.; Götz, J.-J.; Rupp, D.; Strauss, O.; Granzin, M.; Grünvogel, O.; Mutz, P.; Kramer, C.; Lasitschka, F.; Lohmann, V.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Natural Killer Cell Proliferation Involves Monocyte-Derived Cells and the OX40/OX40L Axis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, A.; Tatsumi, T.; Nawa, T.; Suda, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Onishi, Y.; Aono, S.; Shigekawa, M.; Hikita, H.; Sakamori, R.; et al. CD14+ Monocyte-Derived Galectin-9 Induces Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity in Chronic Hepatitis C. Hepatology 2017, 65, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöss, V.; Grünvogel, O.; Wabnitz, G.; Eigenbrod, T.; Ehrhardt, S.; Lasitschka, F.; Lohmann, V.; Dalpke, A.H. Interaction and Mutual Activation of Different Innate Immune Cells Is Necessary to Kill and Clear Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askenase, M.H.; Han, S.-J.; Byrd, A.L.; Morais da Fonseca, D.; Bouladoux, N.; Wilhelm, C.; Konkel, J.E.; Hand, T.W.; Lacerda-Queiroz, N.; Su, X.; et al. Bone-Marrow-Resident NK Cells Prime Monocytes for Regulatory Function during Infection. Immunity 2015, 42, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kupke, P.; Brucker, J.; Wettengel, J.M.; Protzer, U.; Wenzel, J.J.; Schlitt, H.J.; Geissler, E.K.; Werner, J.M. Cytokine Response of Natural Killer Cells to Hepatitis B Virus Infection Depends on Monocyte Co-Stimulation. Viruses 2024, 16, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050741
Kupke P, Brucker J, Wettengel JM, Protzer U, Wenzel JJ, Schlitt HJ, Geissler EK, Werner JM. Cytokine Response of Natural Killer Cells to Hepatitis B Virus Infection Depends on Monocyte Co-Stimulation. Viruses. 2024; 16(5):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050741
Chicago/Turabian StyleKupke, Paul, Johanna Brucker, Jochen M. Wettengel, Ulrike Protzer, Jürgen J. Wenzel, Hans J. Schlitt, Edward K. Geissler, and Jens M. Werner. 2024. "Cytokine Response of Natural Killer Cells to Hepatitis B Virus Infection Depends on Monocyte Co-Stimulation" Viruses 16, no. 5: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050741
APA StyleKupke, P., Brucker, J., Wettengel, J. M., Protzer, U., Wenzel, J. J., Schlitt, H. J., Geissler, E. K., & Werner, J. M. (2024). Cytokine Response of Natural Killer Cells to Hepatitis B Virus Infection Depends on Monocyte Co-Stimulation. Viruses, 16(5), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050741






