Molecular Detection of Respiratory Tract Viruses in Chickens at the Point of Need by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
Abstract
1. Introduction
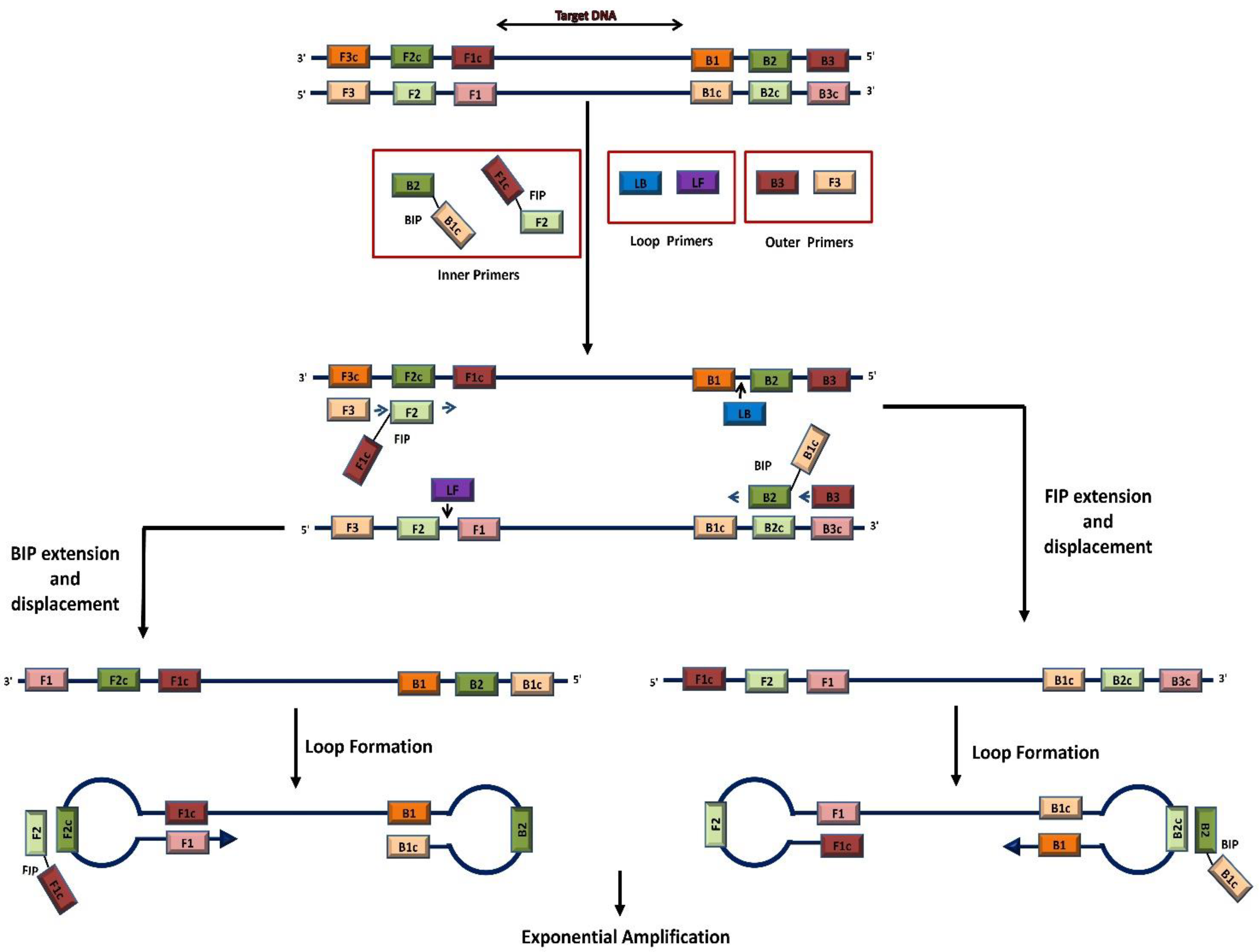
2. Standalone LAMP Method
2.1. LAMP Primers
2.2. LAMP Incubation
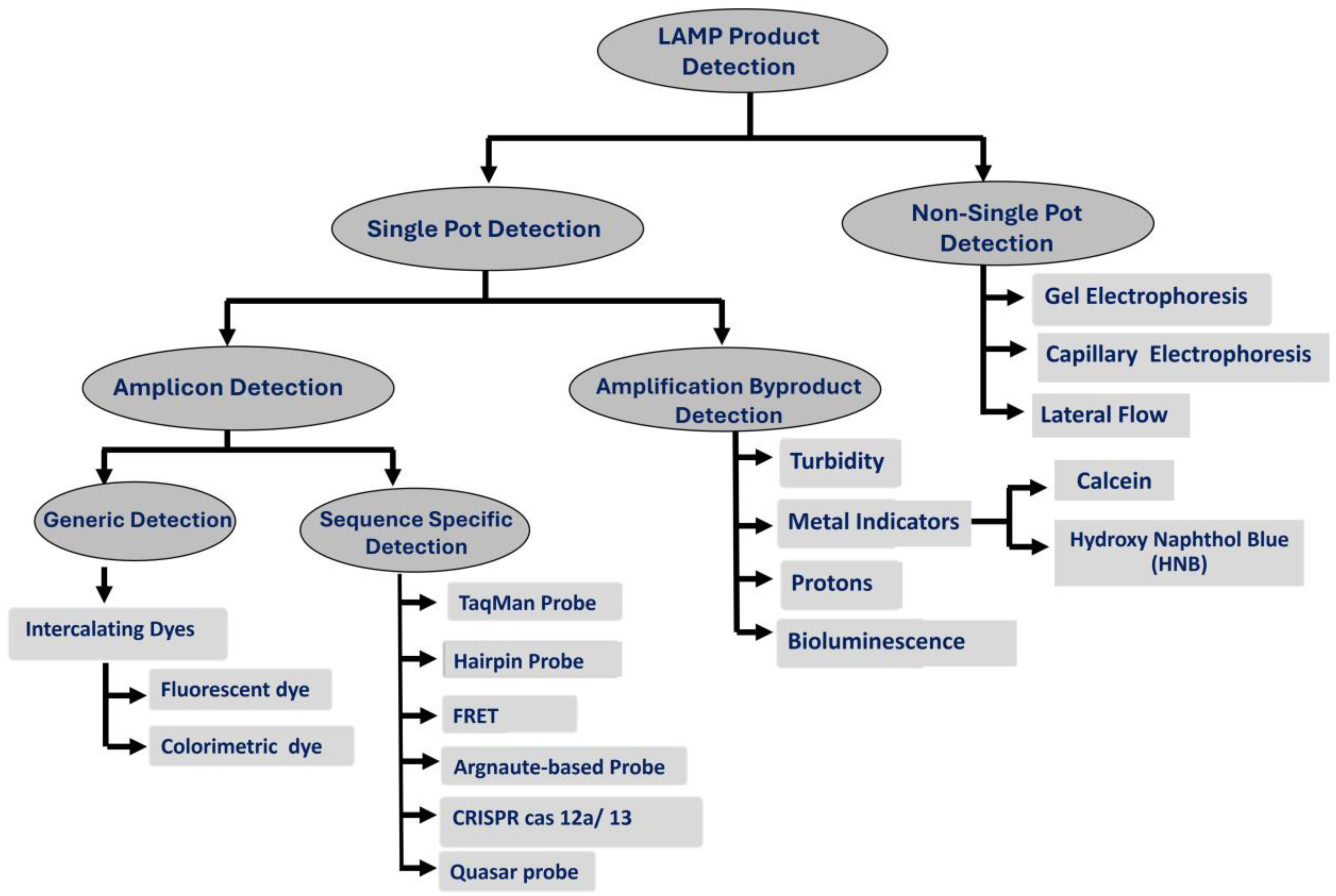
2.3. LAMP Product Detection
2.3.1. Single-Pot Detection
- A.
- Amplicon Detection
- A.1.
- Generic Amplicon Detection
- A.2.
- Specific Amplicon Detection
- A.2.1.
- TaqMan Probe
- A.2.2.
- Hairpin Probe
- A.2.3.
- Fluorescent Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
- A.2.4.
- Argonaute-Based Probes
- A.2.5.
- CRISPR Cas 12a/13
- A.2.6.
- Quasar probes
- B.
- Detection of amplification byproducts
- B.1.
- Turbidity-based detection
- B.2.
- Metal indicators
- B.2.1.
- Calcein (Fluorexon, C30H26N2O13)
- B.2.2.
- Hydroxy naphthol blue (HNB)
- B.3.
- Protons
- B.4.
- Bioluminescence
2.3.2. Post-Amplification Detection
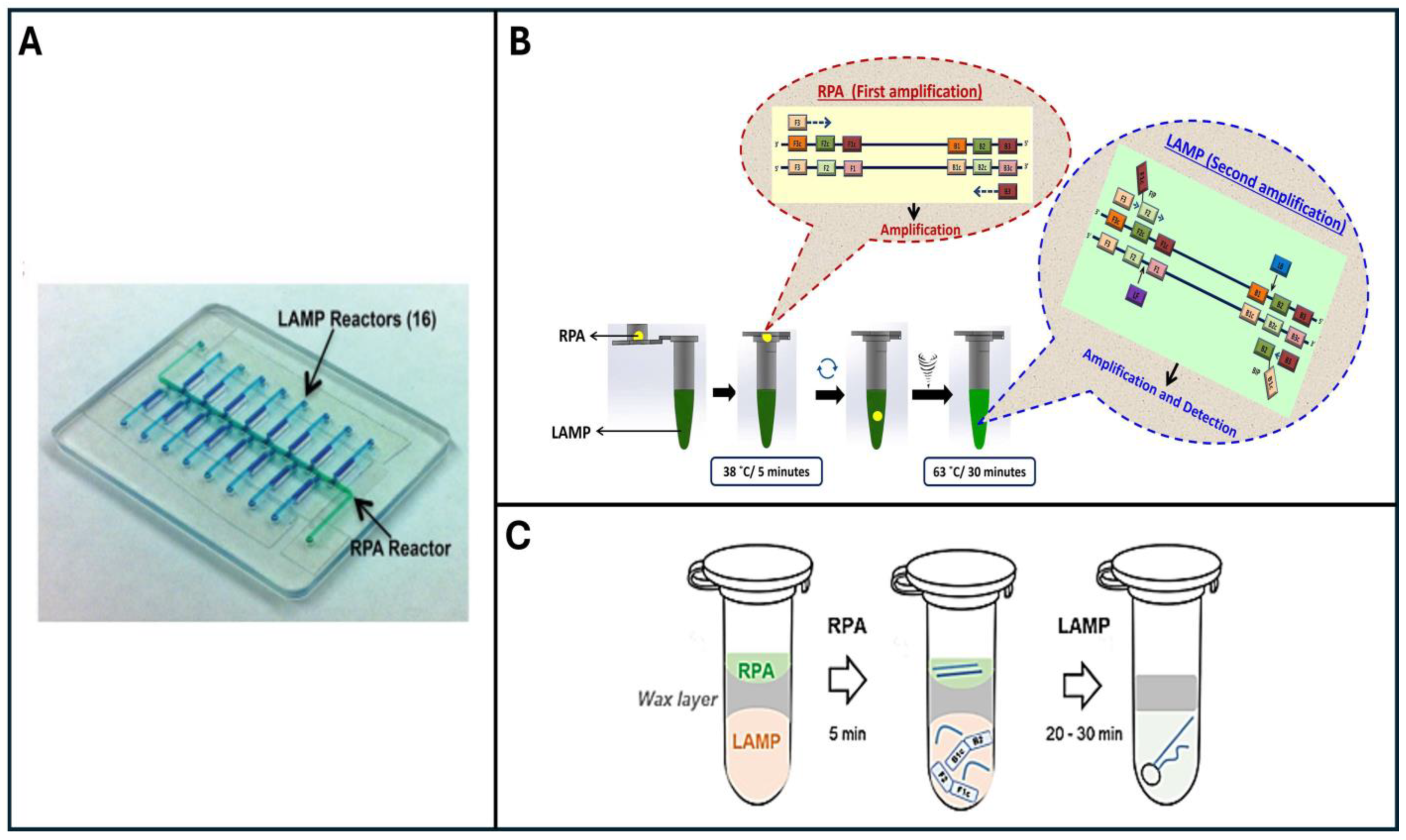
3. Two-Stage Penn-RAMP Technique
4. Detection of Respiratory Tract Viruses in Broiler Chickens with LAMP
4.1. DNA Virus
Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus (ILTV)
4.2. RNA Viruses
4.2.1. Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV)
4.2.2. Avian Influenza Virus (AIV)
4.2.3. Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV)
4.2.4. Avian Metapneumovirus (aMPV)
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yehia, N.; Salem, H.M.; Mahmmod, Y.; Said, D.; Samir, M.; Mawgod, S.A.; Sorour, H.K.; AbdelRahman, M.A.A.; Selim, S.; Saad, A.M.; et al. Common viral and bacterial avian respiratory infections: An updated review. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferragamo, M. What Is Avian Flu? Council on Foreign Relations. Available online: https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/what-avian-flu#:~:text=The%20ongoing%20avian%20flu%20outbreak,of%20the%20disease%20in%202024 (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Villegas, P. Viral diseases of the respiratory system. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 1143–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.J.; Niemi, J.; Christensen, J.P.; Tranter, R.B.; Bennett, R.M. A review of the financial impact of production diseases in poultry production systems. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2018, 59, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, S.; Guerin, J.L.; Ducatez, M.F. Low pathogenic avian influenza and coinfecting pathogens: A review of experimental infections in avian models. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusch, E.; Suarez, D. The multifaceted zoonotic risk of H9N2 avian influenza. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, P.R. Sensitivity and specificity of the fluorescent antibody technique for detection of infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Can. J. Comp. Med. 1978, 42, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.K.; Brown, A.J.; Bracewell, C.D. Comparison of the haemagglutination inhibition test and the serum neutralisation test in tracheal organ cultures for typing infectious bronchitis virus strains. Avian Pathol. 1987, 16, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, M.W.; Kemp, D.J.; Sheppard, M.; Fahey, K.J. Detection of DNA from infectious laryngotracheitis virus by colourimetric analyses of polymerase chain reactions. J. Virol. Methods 1990, 30, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humberd, J.; García, M.; Riblet, S.M.; Resurreccion, R.S.; Brown, T.P. Detection of infectious laryngotracheitis virus in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues by nested polymerase chain reaction. Avian Dis. 2002, 46, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callison, S.A.; Hilt, D.A.; Boynton, T.O.; Sample, B.F.; Robison, R.; Swayne, D.E.; Jackwood, M.W. Development and evaluation of a real-time Taqman RT-PCR assay for the detection of infectious bronchitis virus from infected chickens. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 138, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudian, A.; Kirkpatrick, N.C.; Coppo, M.; Lee, S.W.; Devlin, J.M.; Markham, P.F.; Browning, G.F.; Noormohammadi, A.H. Development of a SYBR Green quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for rapid detection and quantification of infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Kong, C.; Cui, X.; Cui, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S.; Hao, L.; Wang, Y. Detection of infectious laryngotracheitis virus by real-time PCR in naturally and experimentally infected chickens. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Benitez, J.F.; Martínez-Bautista, R.; Ríos-Cambre, F.; Ramírez-Mendoza, H. Molecular detection and isolation of avian metapneumovirus in Mexico. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellahi, S.; El Harrak, M.; Kuhn, J.H.; Sebbar, G.; Bouaiti, E.A.; Khataby, K.; Fihri, O.F.; El Houadfi, M.; Ennaji, M.M. Comparison of SYBR green I real-time RT-PCR with conventional agarose gel-based RT-PCR for the diagnosis of infectious bronchitis virus infection in chickens in Morocco. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvin, R.; Kabiraj, C.K.; Hossain, I.; Hassan, A.; Begum, J.A.; Nooruzzaman, M.; Islam, M.T.; Chowdhury, E.H. Investigation of respiratory disease outbreaks of poultry in Bangladesh using two real-time PCR-based simultaneous detection assays. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1036757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.M.; Nakajima, C.; Ohashi, K.; Onuma, M. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid detection of Newcastle disease virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.T.; Zhang, J.; Sun, D.H.; Ma, L.N.; Liu, X.T.; Cai, X.P.; Liu, Y.S. Development of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid detection of H9 avian influenza virus. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 151, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xue, C.; Qin, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, F.; Bi, Y.; Cao, Y. An improved reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for sensitive and specific detection of Newcastle disease virus. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.P.; Ma, L.N.; Ding, Y.Z.; Liu, X.T.; Cai, X.P.; Ma, L.Q.; Zhang, Y.G.; Liu, Y.S. Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the rapid detection of infectious bronchitis virus in infected chicken tissues. Mol. Cell. Probes 2010, 24, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tholoth, M.; Mauk, M.G.; Anis, E.; Bau, H.H. A closed-tube, single-step, real time, reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for infectious bronchitis virus detection in chickens. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 284, 113940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, K.; Hase, T.; Notomi, T. Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2002, 16, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, H.; Kawana, T.; Fukushima, E.; Suzutani, T. Tolerance of loop-mediated isothermal amplification to a culture medium and biological substances. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-C.; Peng, J.; Mauk, M.G.; Awasthi, S.; Song, J.; Friedman, H.; Bau, H.H.; Liu, C. Smart cup: A minimally-instrumented, smartphone-based point-of-care molecular diagnostic device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, H.H.; Liu, C.; Mauk, M.; Song, J. Is instrumentation-free molecular detection possible? Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic method for infectious diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2009, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, P.A.; Ziros, P.G.; Bellou, M.; Vantarakis, A. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for the detection of Salmonella in food. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, M.; Dominguez, D.C.; Li, X.; Sanchez, J.; Scott, G. A versatile PDMS/paper hybrid microfluidic platform for sensitive infectious disease diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7978–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, M.; Sanchez, J.; Tavakoli, H.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Sun, J.; Dien Bard, J.; Li, X. A low-cost microfluidic platform for rapid and instrument-free detection of whooping cough. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1065, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zapatero-Rodriguez, J.; Estrela, P.; O’Kennedy, R. Point-of-care diagnostics in low resource settings: Present status and future role of microfluidics. Biosensors 2015, 5, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.M.; Augustine, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Nara, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Microfluidics Based Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, Y.; Yin, Q.; Li, R.; Mauk, M.G.; Bai, H.; Bau, H.H. Manually-Operated, Slider Cassette for Multiplexed Molecular Detection at the Point of Care. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 369, 132353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, C.S.; Light, Y.K.; Koh, C.Y.; Wheeler, S.S.; Coffey, L.L.; Meagher, R.J. Quenching of Unincorporated Amplification Signal Reporters in Reverse-Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Enabling Bright, Single-Step, Closed-Tube, and Multiplexed Detection of RNA Viruses. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3562–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Liu, C.; Mauk, M.G.; Rankin, S.C.; Lok, J.B.; Greenberg, R.M.; Bau, H.H. Two-Stage Isothermal Enzymatic Amplification for Concurrent Multiplex Molecular Detection. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Zhou, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, D.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Huang, J.; Liu, T.; Zhao, P.; Xu, H.; et al. Argonaute-integrated isothermal amplification for rapid, portable, multiplex detection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 207, 114169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Tholoth, M.; Anis, E.; Bau, H.H. Two stage, nested isothermal amplification in a single tube. Analyst 2021, 146, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchai, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomi, T.; Mori, Y.; Tomita, N.; Kanda, H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Principle, features, and future prospects. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özay, B.; McCalla, S.E. A review of reaction enhancement strategies for isothermal nucleic acid amplification reactions. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2021, 3, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borer, P.N.; Dengler, B.; Tinoco, I., Jr.; Uhlenbeck, O.C. Stability of ribonucleic acid double-stranded helices. J. Mol. Biol. 1974, 86, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lowe, S.B.; Gooding, J.J. Brief review of monitoring methods for loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) Biosens. Bioelectron 2014, 61, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandelman, O.A.; Church, V.L.; Moore, C.A.; Kiddle, G.; Carne, C.A.; Parmar, S.; Jalal, H.; Tisi, L.C.; Murray, J.A. Novel bioluminescent quantitative detection of nucleic acid amplification in real-time. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiddle, G.; Hardinge, P.; Buttigieg, N.; Gandelman, O.; Pereira, C.; McElgunn, C.J.; Rizzoli, M.; Jackson, R.; Appleton, N.; Moore, C.; et al. GMO detection using a bioluminescent real time reporter (BART) of loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) suitable for field use. BMC Biotechnol. 2012, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Domesle, K.J.; Wang, F.; Ge, B. Rapid detection of Salmonella in food and feed by coupling loop-mediated isothermal amplification with bioluminescent assay in real-time. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, R.; Shi, R.; Han, Q.; Sun, J.; Yuan, W. A real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of Lawsonia intracellularis in porcine fecal samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 151, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Liu, C.; Mauk, M.G.; Peng, J.; Schoenfeld, T.; Bau, H.H. A multifunctional reactor with dry-stored reagents for enzymatic amplification of nucleic acids. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Pandian, V.; Mauk, M.G.; Bau, H.H.; Cherry, S.; Tisi, L.C.; Liu, C. Smartphone-based mobile detection platform for molecular diagnostics and spatiotemporal disease mapping. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4823–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowski, Y.; Gurung, M.K.; Larsen, A.N. Characterization and engineering of a DNA polymerase reveals a single amino-acid substitution in the fingers subdomain to increase strand-displacement activity of A-family prokaryotic DNA polymerases. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, W.B. The Thermodynamics and Kinetics of ”HeaterMeals”: An Exercise in Undergraduate Inorganic Chemistry. J. Chem. Educ. 2000, 77, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.J.; Mauk, M.G.; Seok, Y.; Bau, H.H. Electricity-free chemical heater for isothermal nucleic acid amplification with applications in COVID-19 home testing. Analyst 2021, 146, 4212–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Mauk, M.G.; Hackett, B.A.; Cherry, S.; Bau, H.H.; Liu, C. Instrument-Free Point-of-Care Molecular Detection of Zika Virus. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7289–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W. Principles and applications of loop-mediated isothermal amplification to point-of-care tests. Biosensors 2022, 12, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, N.; Ahmad, F.J.; Kar, S. Recent advances in loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid and efficient detection of pathogens. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eischeid, A.C. SYTO dyes and EvaGreen outperform SYBR Green in real-time PCR. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fothergill, S.M.; Joyce, C.; Xie, F. Metal enhanced fluorescence biosensing: From ultra-violet towards second near-infrared window. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 20914–20929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Sano, S.; Takahashi, K.; Jikihara, T. Method for colorimetric detection of double-stranded nucleic acid using leuco triphenylmethane dyes. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 473, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkad, S.D.; Nimse, S.B.; Song, K.S.; Kim, T. HCV Detection, Discrimination, and Genotyping Technologies. Sensors 2018, 18, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; El-Tholoth, M.; Li, Y.; Graham-Wooten, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Weiss, S.R.; Collman, R.G.; Bau, H.H. Single- and Two-Stage, Closed-Tube, Point-of-Care, Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13063–13071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Li, R.; Ma, Z.; Han, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, Y. Development and evaluation of a novel loop mediated isothermal amplification coupled with TaqMan probe assay for detection of genetically modified organism with NOS terminator. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Ahn, J.K.; Lee, C.Y.; Park, H.G. A hairpin probe-mediated isothermal amplification method to detect target nucleic acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1114, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Teng, P.H.; Chen, C.L.; Lee, P.Y. Real-time target-specific detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification for white spot syndrome virus using fluorescence energy transfer-based probes. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 173, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, R.B.; Periasamy, A. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscopy imaging of live cell protein localizations. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; He, R.; Chen, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; et al. A programmable omnipotent Argonaute nuclease from mesophilic bacteria kurthia massiliensis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegge, J.W.; Swarts, D.C.; Chandradoss, S.D.; Cui, T.J.; Kneppers, J.; Jinek, M.; Joo, C.; van der Oost, J. DNA-guided DNA cleavage at moderate temperatures by clostridium butyricum Argonaute. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 5809–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, M.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Tong, Y.; et al. A versatile biosensing platform coupling CRISPR–Cas12a and aptamers for detection of diverse analytes. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Kellner, M.J.; Joung, J.; Collins, J.J.; Zhang, F. Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid detection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6. Science 2018, 360, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, R.; Li, J. CRISPR/cas systems redefine nucleic acid detection: Principles and methods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, K.; Najib, M.A.; Khalid, M.F.; Mohamad, S.; Palaz, F.; Ozsoz, M.; Aziah, I. RT-LAMP CRISPR-Cas12/13-Based SARS-CoV-2 Detection Methods. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Li, Y.; Kou, J.; Liao, D.; Zhang, W.; Yin, L.; Man, S.; Ma, L. Novel non-nucleic acid targets detection strategies based on CRISPR/Cas toolboxes: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 215, 114559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Wan, Z.; Lu, R.; Yang, X.; Yu, G.; Reboud, J.; Cooper, J.M.; Tian, Z.; et al. Multiplex, Real-Time, Point-of-care RT-LAMP for SARS-CoV-2 Detection Using the HFman Probe. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.S.; Park, S.; Bae, J.H.; Yoon, S.Y.; Lim, C.S.; Cho, M.C. Development of a multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) for the diagnosis of bacterial periprosthetic joint infection. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmand, N.; Karhanek, M.; Persson, H.H.; Webb, C.D.; Lee, T.H.; Zahradníková, A.; Davis, R.W. Direct electrical detection of DNA synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6466–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal-Maldonado, D.; Drogalis Beckham, L.; Wood, R.D.; Doublié, S. When DNA Polymerases Multitask: Functions Beyond Nucleotidyl Transfer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 8, 815845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Chandar, N.B.; Chourey, S.; Agarwalla, H.; Ganguly, B.; Das, A. Role of metal ion in specific recognition of pyrophosphate ion under physiological conditions and hydrolysis of the phosphoester linkage by alkaline phosphatase. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 11034–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Nagamine, K.; Tomita, N.; Notomi, T. Detection of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Reaction by Turbidity Derived from Magnesium Pyrophosphate Formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirato, K. Detecting amplicons of loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 63, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, M.; Honda, E.; Ogura, A.; Nomoto, A.; Hanaki, K. Colorimetric detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by using hydroxy naphthol blue. Biotechniques 2009, 46, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, G.; Buss, J.; Barry, A.J.; Patton, G.C.; Tanner, N.A. Enhancing colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification speed and sensitivity with guanidine chloride. Biotechniques 2020, 69, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshani, A.; Zare, H.; Sadeghian, H.; Safdari, H.; Riahi-Zanjani, B.; Aryan, E. A Comparative Study on Visual Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Closed Tube Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification: Shedding Light on the Use of Eriochrome Black T. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C., Jr. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. Biotechniques 2015, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroka, M.; Wasowicz, B.; Rymaszewska, A. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): The Better Sibling of PCR? Cells 2012, 10, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, Y.; Yin, Q.; Bai, H.; Bau, H.H. Sensitive, Single-Pot, Two-Stage Assay for Hepatitis Viruses. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.J.; Eberle, R.; Hayward, G.S.; Mcgeoch, D.J.; Minson, A.C.; Pellet, P.E.; Roizman, B.; Studdert, M.J.; Thiry, E. The order herpesvirales. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.; Spatz, S.J.; Guy, J.S. Infectious laryngotracheitis. In Diseases of Poultry, 13th ed.; Swayne, D.E., Glisson, J.R., McDougald, L.R., Nolan, L.K., Suarez, D.L., Nair, V., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2013; pp. 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Menendez, K.R.; García, M.; Spatz, S.; Tablante, N.L. Molecular epidemiology of infectious laryngotracheitis: A review. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.; Volkening, J.; Riblet, S.; Spatz, S. Genomic sequence analysis of the United States infectious laryngotracheitis vaccine strains chicken embryo origin (CEO) and tissue culture origin (TCO). Virology 2013, 440, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.M.; Ji, J.; Pickens, T.T.; Du, L.Q.; Cao, Y.C.; Li, H.M.; Wang, L.G.; Ma, J.Y.; Bi, Y.Z. Rapid detection of infectious laryngotracheitis virus isolates by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 165, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Xie, J.; Cao, Y.; Kang, R.; Lin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liao, D.; Li, X.; Ye, Y.; Pan, M.; et al. A modified loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detecting avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tholoth, M.; Ba, H.; Mauk, M.G.; Anis, E.; Bau, H.H. Molecular Detection of Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus in Chickens with a Microfluidic Chip. Animals 2021, 11, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Cook, J.K.A.; Van der Heijden, H.M.J. Infectious bronchitis virus variants: A review of the history, current situation and control measures. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.A.; Jackwood, M.; Jones, R.C. The long view: 40 years of infectious bronchitis research. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valastro, V.; Holmes, E.C.; Britton, P.; Fusaro, A.; Jackwood, M.W.; Cattoli, G.; Monne, I. S1 gene-based phylogeny of infectious bronchitis virus: An attempt to harmonize virus classification. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 39, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D. Coronaviruses in poultry and other birds. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D. Coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackwood, M.W.; de Wit, S. Infectious bronchitis. In Diseases of Poultry, 13th ed.; Swayne, D.E., Glisson, J.R., McDougald, L.R., Nolan, L.K., Suarez, D.L., Nair, V., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2013; pp. 139–160. [Google Scholar]
- Gelb, J., Jr.; Ladman, B.S.; Pope, C.R.; Ruano, J.M.; Brannick, E.M.; Bautista, D.A.; Coughlin, C.M.; Preskenis, L.A. Characterization of nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus DMV/1639/11 recovered from Delmarva broiler chickens in 2011. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leghari, R.A.; Fan, B.; Wang, H.; Bai, J.; Zhang, L.; Abro, S.H.; Jiang, P. Full-length genome sequencing analysis of avian infectious bronchitis virus isolate associated with nephropathogenic infection. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2921–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, A.; Raja, A.; Dhinakar Raj, G.; Thangavelu, A.; Kumanan, K. Rapid detection of avian infectious bronchitis virus by reverse transcriptase-loop mediated isothermal amplification. Proc. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B 2015, 85, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, Z.; Zhai, X.; Zuo, L.; Mei, X.; Xiang, R.; Kang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H. Simultaneous and visual detection of infectious bronchitis virus and Newcastle disease virus by multiple LAMP and lateral flow dipstick. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5401–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.J.D.; Donis, R.O. Continued evolution of highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1): Updated nomenclature. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2012, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.H.; Criado, M.F.; Swayne, D.E. Pathobiological Origins and Evolutionary History of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, I.A.; Ross, T.M. A Review of H5Nx Avian Influenza Viruses. In Therapeutic Advances in Vaccines and Immunotherapy; SAGE Publications Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 7, p. 2515135518821625. [Google Scholar]
- Swayne, D.E.; Suarez, D.L.; Sims, L. Influenza. In Diseases of Poultry; Swayne, D.E., Boulianne, M., Logue, C., McDougald, L.D., Nair, V., Suarez, D.L., Eds.; Wiley: Ames, IA, USA, 2020; pp. 210–256. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tefsen, B.; Shi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Bat-derived influenza-like viruses H17N10 and H18N11. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Ninomiya, A.; Minekawa, H.; Notomi, T.; Ishizaki, T.; Tashiro, M.; Odagiri, T. Development of H5-RT-LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification) system for rapid diagnosis of H5 avian influenza virus infection. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6679–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Ninomiya, A.; Minekawa, H.; Notomi, T.; Ishizaki, T.; Van Tu, P.; Tien, N.T.K.; Tashiro, M.; Odagiri, T. Rapid diagnosis of H5N1 avian influenza virus infection by newly developed influenza H5 hemagglutinin gene-specific loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 141, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postel, A.; Letzel, T.; Frischmann, S.; Grund, C.; Beer, M.; Harder, T. Evaluation of Two Commercial Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays for Detection of Avian Influenza H5 and H7 Hemagglutinin Genes. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Yu, X.-W.; Yao, W.; Yu, B.-L.; He, L.-K.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Tian, G.-B.; Ping, J.-H.; Wang, X.-R. Development of a reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay to detect avian influenza viruses in clinical specimens. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, H. Development of a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the rapid detection of avian influenza virus subtype H7. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 179, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakauchi, M.; Takayama, I.; Takahashi, H.; Tashiro, M.; Kageyama, T. Development of a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the rapid diagnosis of avian influenza A (H7N9) virus infection. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 204, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, T. A hitherto unrecorded disease of fowls due to filter passing virus. J. Comp. Pathol. Therap. 1927, 48, 144–169. [Google Scholar]
- Mayo, M.A. Virus Taxonomy—Houston 2002. Arch. Virol. 2002, 147, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Czeglédi, A.; Ujvári, D.; Somogyi, E.; Wehmann, E.; Werner, O.; Lomniczi, B. Third genome size category of avian paramyxovirus serotype 1 (Newcastle disease virus) and evolutionary implications. Virus Res. 2006, 120, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.J. Newcastle disease and other avian paramyxoviruses. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2000, 19, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, M.S.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, Y.N.; Park, J.K.; Yuk, S.S.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, I.S.; et al. Exchange of Newcastle disease viruses in Korea: The relatedness of isolates between wild birds, live bird markets, poultry farms and neighboring countries. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.M.; King, D.J.; Suarez, D.L.; Wong, C.W.; Afonso, C.L. Characterization of class I newcastle disease virus isolates from Hong Kong live bird markets and detection using real-time reverse transcription-PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.J.; Haddas, R.; Simanov, L.; Lublin, A.; Rehmani, S.F.; Wajid, A.; Bibi, T.; Khan, T.A.; Yaqub, T.; Setiyaningsih, S. Identification of new sub-genotypes of virulent Newcastle disease virus with potential panzootic features. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 29, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, O.S.; Koch, G.; Hartog, L.; Ravenshorst, N.; Peeters, B.P.H. Virulence of Newcastle disease virus is determined by the cleavage site of the fusion protein and by both the stem region and globular head of the haemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirunda, H.; Thekisoe, O.; Kasaija, P.; Kerfua, S.; Nasinyama, G.; OpudaAsibo, J.; Inoue, N. Use of reverse transcriptase loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for field detection of Newcastle disease virus using less invasive samples. Vet. World 2012, 5, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kwon, Y.-K.; Kim, H.-R. The Development of Novel Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays for the Detection and Differentiation of Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.C. Avian pneumovirus infection: Questions still unanswered. Avian Pathol. 1996, 25, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussan, D.A.; Haddad, R.; Khawaldeh, G. Molecular survey of avian respiratory pathogens in commercial broiler chicken flocks with respiratory diseases in Jordan. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catelli, E.; Lupini, C.; Cecchinato, M.; Ricchizzi, E.; Brown, P.; Naylor, C.J. Field avian metapneumovirus evolution avoiding vaccine induced immunity. Vaccine 2010, 28, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, C.R. Virus taxonomy–San Diego 1998. Arch.Virol. 1998, 143, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banet-Noach, C.; Simanov, L.; Perk, S. Characterization of Israeli avian metapneumovirus strains in turkeys and chickens. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.A. Avian pneumovirus infections of turkeys and chickens. Vet. J. 2000, 160, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirjis, F.F.; Noll, S.L.; Halvorson, D.A.; Nagaraja, K.V.; Martin, F.; Shaw, D.P. Effects of bacterial coinfection on the pathogenesis of avian pneumovirus infection in turkeys. Avian Dis. 2004, 48, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, L.Y.; Brandao, P.E.; Chacon, J.L.; Assayag, M.S.; Maiorka, P.C.; Raffi, P.; Saidenberg, A.B.; Jones, R.C.; Ferreira, A.J. Orchitis in roosters with reduced fertility associated with avian infectious bronchitis virus and avian metapneumovirus infections. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cea, P.; Arca, S.; Gomez-Lucia, E.; Domenech, A.; Biarnes, M.; Blanco, A.; Benitez, L.; Madrid, R. Development of a Fast and Affordable Diagnostic System for RNA Viruses Using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification and DNA-Nanoprobe Detection. Authorea Prepr. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Technique | Working Principle | Advantages | Disadvantages | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intercalating Dyes | 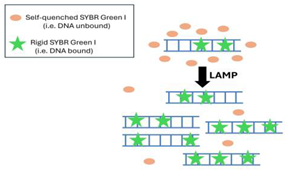 |
|
| [53,54,57] |
| 2 | TaqMan Probe | 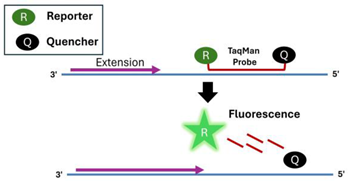 |
|
| [57,59] |
| 3 | Hairpin Probe |  |
|
| [60] |
| 4 | Fluorescent Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) |  |
|
| [61,62]. |
| 5 | Argonaute (PfAgo)-Based Signal Amplification | 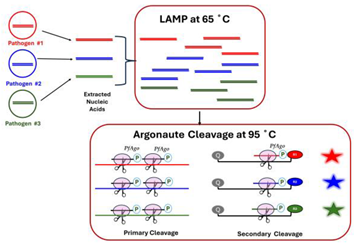 |
|
| [35,63,64,65] |
| 6 | CRISPR Cas 12a/13 |  |
|
| [66,67,68,69] |
| 7 | Quasar Probes | 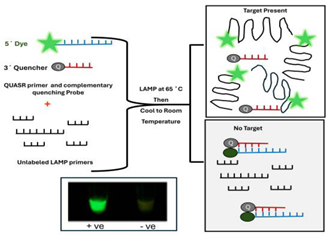 |
|
| [33] |
| 8 | Turbidity-Based Detection | 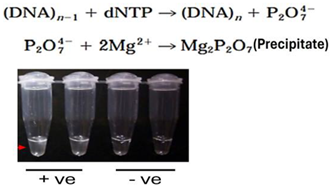 |
|
| [75,76] |
| 9 | Calcein (Fluorexon, C30H26N2O13) |  |
|
| [52,77,78,79] |
| 10 | HNB (Hydroxy Naphthol Blue) |  |
|
| [52,77,78,79] |
| 11 | Protons |  |
|
| [52,58,80] |
| 12 | Bioluminescence | 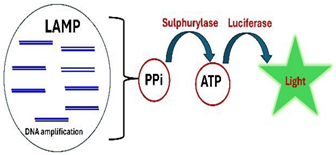 |
|
| [42,43,47] |
| 13 | Lateral-Flow-Assay | 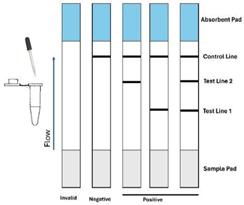 |
|
| [52] |
| 14 | Gel Electrophoresis/CE | 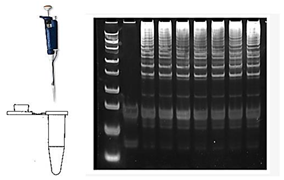 |
| [52] |
| Features | LAMP | Penn-RAMP (RPA + LAMP) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | ~63 °C | 37 °C + 63 °C |
| Sensitivity | High (102–10 genomic copies/reaction) | Very High (1 Copy/reaction) 10-fold better |
| Specificity | High | High |
| Multiplexing | ≤3 | ~16 |
| Viruses | LAMP Limit of Detection | Penn-RAMP Limit of Detection |
|---|---|---|
| Infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) | 50 copies/µL [87] 353 copies/µL [88] 416 genomic copies/µL [36] | 41 genomic copies/µL [36] |
| Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV) | 1 EID50/mL [21] 666 genomic copies/µL [36] 2 × 102 EID50/mL [20,98] | 66 genomic copies/µL [36] |
| Avian influenza virus (AIV) | 0.1 PFU/µL (H5) [106] 0.01 PFU/µL (H7) [109] 10 copies/µL (H9) [18] | NA |
| Newcastle Disease virus (NDV) | 103 EID50/mL [117] 5 genome copies/µL [99] 4.5 × 104 copies/µL [17] | NA |
| Avian metapneumovirus (aMPV) | 10 copies/µL [129] | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Tholoth, M.; Bau, H.H. Molecular Detection of Respiratory Tract Viruses in Chickens at the Point of Need by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). Viruses 2024, 16, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081248
El-Tholoth M, Bau HH. Molecular Detection of Respiratory Tract Viruses in Chickens at the Point of Need by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). Viruses. 2024; 16(8):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081248
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Tholoth, Mohamed, and Haim H. Bau. 2024. "Molecular Detection of Respiratory Tract Viruses in Chickens at the Point of Need by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)" Viruses 16, no. 8: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081248
APA StyleEl-Tholoth, M., & Bau, H. H. (2024). Molecular Detection of Respiratory Tract Viruses in Chickens at the Point of Need by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). Viruses, 16(8), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081248





