Detection of Dengue Virus 1 and Mammalian Orthoreovirus 3, with Novel Reassortments, in a South African Family Returning from Thailand, 2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation, Virus Isolation and Sequencing
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Case Presentation
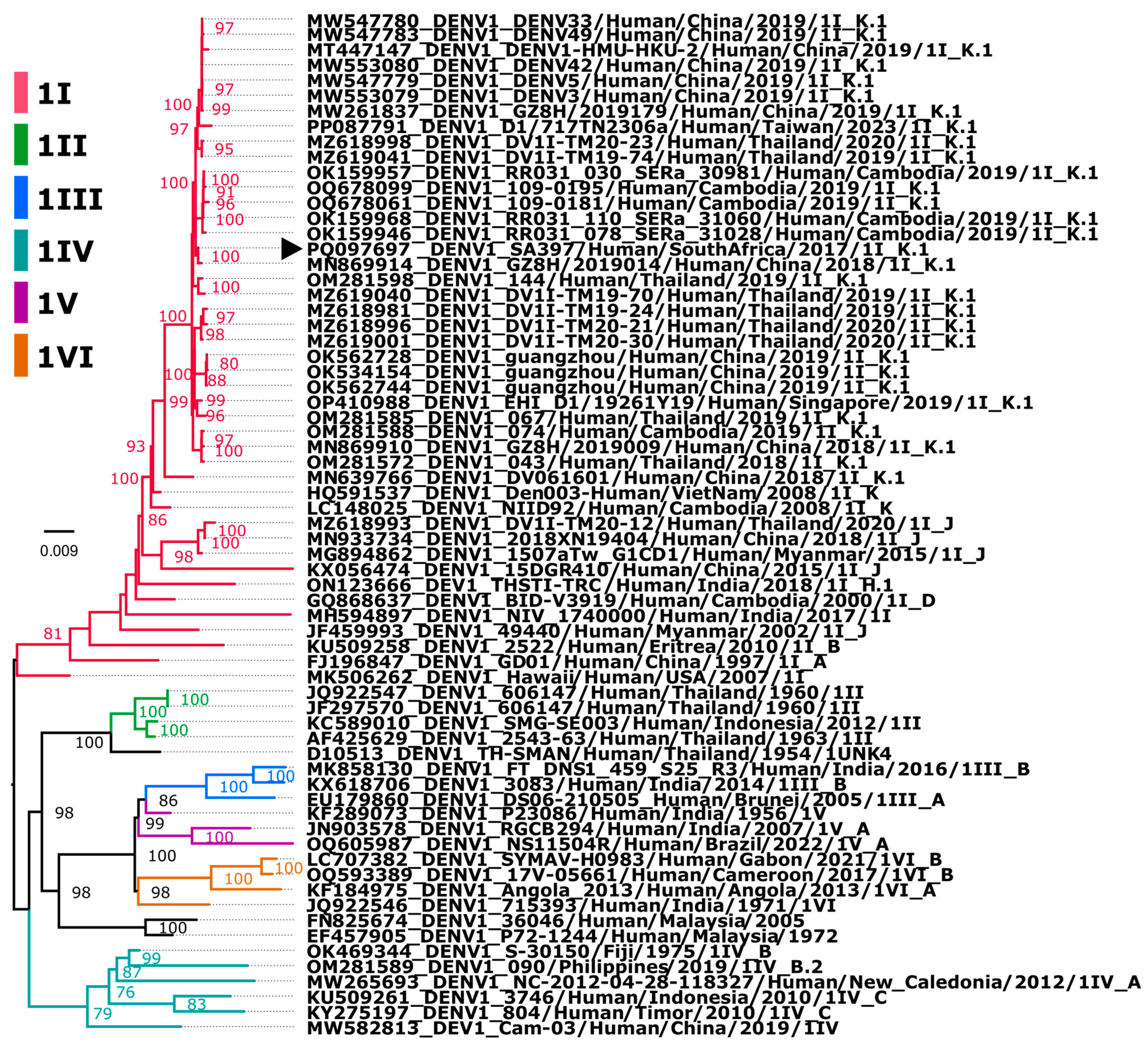
3.2. Assembly and Phylogenetic Position of Imported DENV-1 Genome
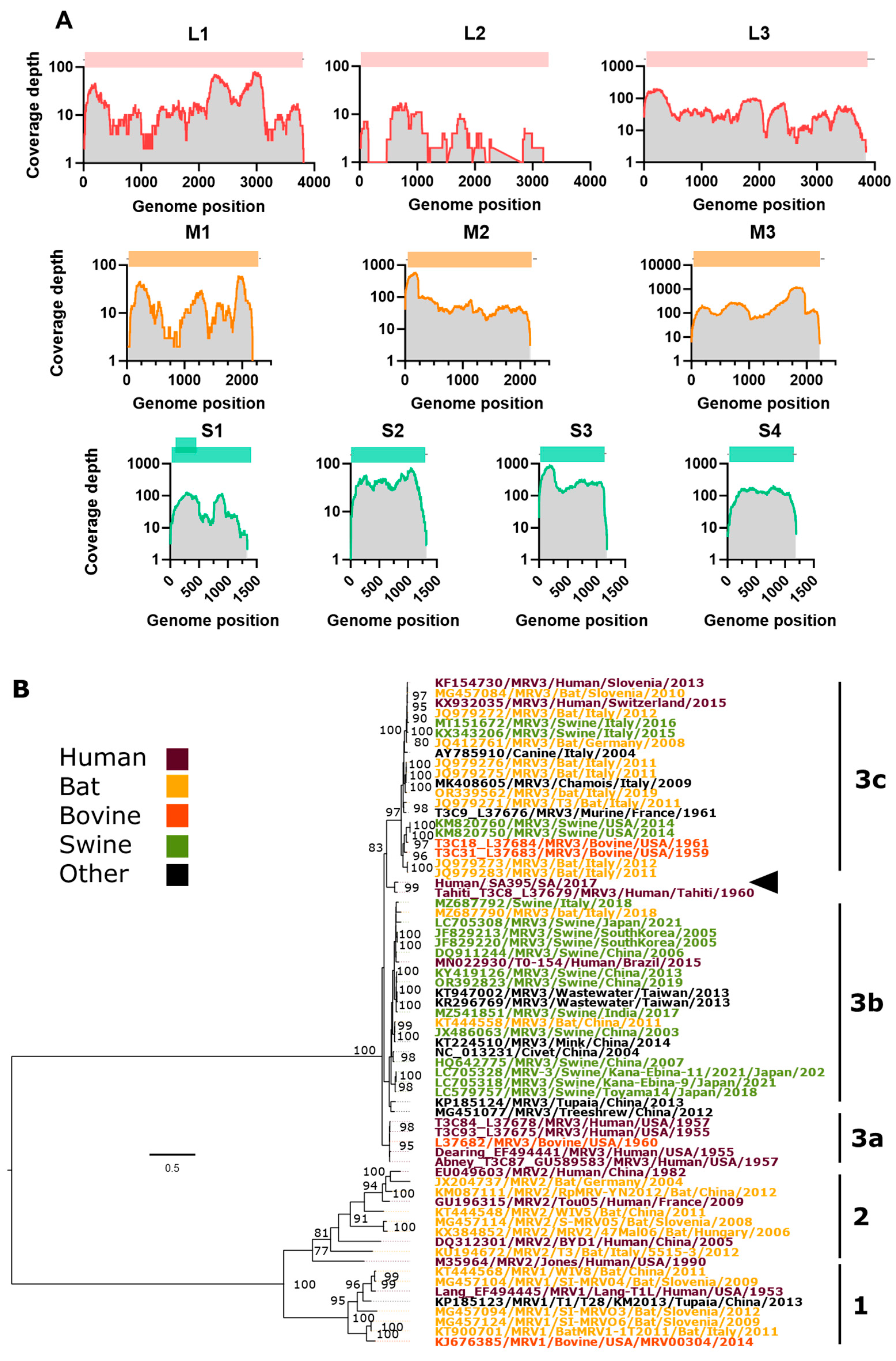
3.3. Assembly and Phylogenetic Position of MRV Genome
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhan, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Cheng, S. Global, regional, and national dengue burden from 1990 to 2017: A systematic analysis based on the global burden of disease study 2017. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 32, 100712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, K.; Saito, M.; Mapua, C.A.; Natividad, F.F. Dengue illness: Clinical features and pathogenesis. J. Infect. Chemother. 2007, 13, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, J.G.; Ong, A.; Tan, L.K.; Chaterji, S.; Chow, A.; Lim, W.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Chua, R.; Chua, C.R.; Tan, S.W.; et al. The early clinical features of dengue in adults: Challenges for early clinical diagnosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, M.U.; Sinka, M.E.; Duda, K.A.; Mylne, A.Q.; Shearer, F.M.; Barker, C.M.; Moore, C.G.; Carvalho, R.G.; Coelho, G.E.; Van Bortel, W.; et al. The global distribution of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus. eLife 2015, 4, e08347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msimang, V.; Kemp, A.; van Vuren, P.J.; Weyer, J.; Paweska, J.T. Increased Importation of Dengue Cases into South Africa: A Risk for Establishment of Local Endemicity? NICD The National Institute for Communicable Diseases: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2018; pp. 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Attoui, H.; Banyai, K.; Brussaard, C.P.D.; Danthi, P.; Del Vas, M.; Dermody, T.S.; Duncan, R.; Fang, Q.; Johne, R.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Spinareoviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attoui, H.; Biagini, P.; Stirling, J.; Mertens, P.P.; Cantaloube, J.F.; Meyer, A.; de Micco, P.; de Lamballerie, X. Sequence characterization of Ndelle virus genome segments 1, 5, 7, 8, and 10: Evidence for reassignment to the genus Orthoreovirus, family Reoviridae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 287, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooms, L.S.; Kobayashi, T.; Dermody, T.S.; Chappell, J.D. A post-entry step in the mammalian orthoreovirus replication cycle is a determinant of cell tropism. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 41604–41613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, A.; Katayama, M.; Lai, H.; Wataru, S.; Takenaka-Uema, A.; Horimoto, T.; Murakami, S. Isolation and genetic characterization of a mammalian orthoreovirus from Vespertilio sinensis in Japan. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.C.; Wang, Y.F.; Huang, S.W.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, J.R. High Incidence of Mammalian Orthoreovirus Identified by Environmental Surveillance in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmak, G.; Bina, D.; Macdonald, J.; Couillard, L. Nine-year study of the occurrence of culturable viruses in source water for two drinking water treatment plants and the influent and effluent of a Wastewater Treatment Plant in Milwaukee, Wisconsin (August 1994 through July 2003). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vuren, P.J.; Wiley, M.; Palacios, G.; Storm, N.; McCulloch, S.; Markotter, W.; Birkhead, M.; Kemp, A.; Paweska, J.T. Isolation of a Novel Fusogenic Orthoreovirus from Eucampsipoda africana Bat Flies in South Africa. Viruses 2016, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, K.B.; Voon, K.; Crameri, G.; Tan, H.S.; Rosli, J.; McEachern, J.A.; Suluraju, S.; Yu, M.; Wang, L.F. Identification and characterization of a new orthoreovirus from patients with acute respiratory infections. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, K.B.; Voon, K.; Yu, M.; Keniscope, C.; Rasid, K.A.; Wang, L.F. Investigation of a potential zoonotic transmission of orthoreovirus associated with acute influenza-like illness in an adult patient. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, M.O.; Martinez, L.C.; Isa, M.B.; Ferreyra, L.J.; Canna, F.; Pavan, J.V.; Paez, M.; Notario, R.; Nates, S.V. Twenty year study of the occurrence of reovirus infection in hospitalized children with acute gastroenteritis in Argentina. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2002, 21, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikuletic, T.; Steyer, A.; Kotar, T.; Zorec, T.M.; Poljak, M. A novel reassortant mammalian orthoreovirus with a divergent S1 genome segment identified in a traveler with diarrhea. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 73, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, U.A.; Ribeiro, G.O.; Villanova, F.; Luchs, A.; Milagres, F.A.P.; Komninakis, S.V.; Tahmasebi, R.; Lobato, M.; Brustulin, R.; Chagas, R.T.D.; et al. First identification of mammalian orthoreovirus type 3 by gut virome analysis in diarrheic child in Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyer, A.; Gutierrez-Aguire, I.; Kolenc, M.; Koren, S.; Kutnjak, D.; Pokorn, M.; Poljsak-Prijatelj, M.; Racki, N.; Ravnikar, M.; Sagadin, M.; et al. High similarity of novel orthoreovirus detected in a child hospitalized with acute gastroenteritis to mammalian orthoreoviruses found in bats in Europe. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3818–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska, D.W.; Capaul, R.; Prader, S.; Zagordi, O.; Geissberger, F.D.; Kugler, M.; Knorr, M.; Berger, C.; Gungor, T.; Reichenbach, J.; et al. Persistent mammalian orthoreovirus, coxsackievirus and adenovirus co-infection in a child with a primary immunodeficiency detected by metagenomic sequencing: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, L.A.; Barin, F.; Barthez, M.A.; Bonnaud, B.; Roingeard, P.; Goudeau, A.; Castelnau, P.; Vernet, G.; Paranhos-Baccala, G.; Komurian-Pradel, F. Novel human reovirus isolated from children with acute necrotizing encephalopathy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, K.L.; Barton, E.S.; Ibach, M.L.; Robinson, C.; Campbell, J.A.; O’Donnell, S.M.; Valyi-Nagy, T.; Clarke, P.; Wetzel, J.D.; Dermody, T.S. Isolation and molecular characterization of a novel type 3 reovirus from a child with meningitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelli, D.; Beato, M.S.; Cavicchio, L.; Lavazza, A.; Chiapponi, C.; Leopardi, S.; Baioni, L.; De Benedictis, P.; Moreno, A. First identification of mammalian orthoreovirus type 3 in diarrheic pigs in Europe. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naglic, T.; Rihtaric, D.; Hostnik, P.; Toplak, N.; Koren, S.; Kuhar, U.; Jamnikar-Ciglenecki, U.; Kutnjak, D.; Steyer, A. Identification of novel reassortant mammalian orthoreoviruses from bats in Slovenia. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, C.; Lesnik, R.; Brinkmann, A.; Ebinger, A.; Radonic, A.; Nitsche, A.; Muhldorfer, K.; Wibbelt, G.; Kurth, A. Isolation and characterization of three mammalian orthoreoviruses from European bats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombino, E.; Lelli, D.; Canziani, S.; Quaranta, G.; Guidetti, C.; Leopardi, S.; Robetto, S.; De Benedictis, P.; Orusa, R.; von Degerfeld, M.M.; et al. Main causes of death of free-ranging bats in Turin province (North-Western Italy): Gross and histological findings and emergent virus surveillance. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, P.; Li, H.; Wang, J.W.; Wang, B.; Xie, R.H.; Xu, H.; Zhao, L.Y.; Li, L.; Pan, Y.; Song, Y.; et al. Genetic and pathogenic characterization of a novel reassortant mammalian orthoreovirus 3 (MRV3) from a diarrheic piglet and seroepidemiological survey of MRV3 in diarrheic pigs from east China. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 208, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanappa, A.T.; Sooryanarain, H.; Deventhiran, J.; Cao, D.; Venkatachalam, B.A.; Kambiranda, D.; LeRoith, T.; Heffron, C.L.; Lindstrom, N.; Hall, K.; et al. A novel pathogenic Mammalian orthoreovirus from diarrheic pigs and Swine blood meal in the United States. mBio 2015, 6, e00593-15. [Google Scholar]
- Beaty, B.J.; Calisher, C.H.; Shope, R.E. Arboviruses. In Diagnostic Procedures for Viral, Rickettsial, and Chlamydial Infections, 7th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 189–212. [Google Scholar]
- van Vuren, P.J.; Parry, R.; Khromykh, A.A.; Paweska, J.T. A 1958 Isolate of Kedougou Virus (KEDV) from Ndumu, South Africa, Expands the Geographic and Temporal Range of KEDV in Africa. Viruses 2021, 13, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djikeng, A.; Halpin, R.; Kuzmickas, R.; Depasse, J.; Feldblyum, J.; Sengamalay, N.; Afonso, C.; Zhang, X.; Anderson, N.G.; Ghedin, E.; et al. Viral genome sequencing by random priming methods. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, R.; James, M.E.; Asgari, S. Uncovering the Worldwide Diversity and Evolution of the Virome of the Mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, V.; Cleemput, S.; Fonseca, V.; Tegally, H.; Brito, A.F.; Gifford, R.; Tran, V.T.; Kien, D.T.H.; Huynh, T.; Yacoub, S.; et al. A new lineage nomenclature to aid genomic surveillance of dengue virus. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilsker, M.; Moosa, Y.; Nooij, S.; Fonseca, V.; Ghysens, Y.; Dumon, K.; Pauwels, R.; Alcantara, L.C.; Vanden Eynden, E.; Vandamme, A.M.; et al. Genome Detective: An automated system for virus identification from high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, V.; Libin, P.J.K.; Theys, K.; Faria, N.R.; Nunes, M.R.T.; Restovic, M.I.; Freire, M.; Giovanetti, M.; Cuypers, L.; Nowe, A.; et al. A computational method for the identification of Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya virus species and genotypes. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siew, Z.Y.; Loh, A.; Segeran, S.; Leong, P.P.; Voon, K. Oncolytic Reoviruses: Can These Emerging Zoonotic Reoviruses Be Tamed and Utilized? DNA Cell Biol. 2023, 42, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohl, J.A.; Lay, S.; Chea, S.; Ahyong, V.; Parker, D.M.; Gallagher, S.; Fintzi, J.; Man, S.; Ponce, A.; Sreng, S.; et al. Discovering disease-causing pathogens in resource-scarce Southeast Asia using a global metagenomic pathogen monitoring system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2115285119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poltep, K.; Phadungsombat, J.; Nakayama, E.E.; Kosoltanapiwat, N.; Hanboonkunupakarn, B.; Wiriyarat, W.; Shioda, T.; Leaungwutiwong, P. Genetic Diversity of Dengue Virus in Clinical Specimens from Bangkok, Thailand, during 2018–2020: Co-Circulation of All Four Serotypes with Multiple Genotypes and/or Clades. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermody, T.S.; Nibert, M.L.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Fields, B.N. Sequence diversity in S1 genes and S1 translation products of 11 serotype 3 reovirus strains. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4842–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XiaoMing, H.; HuoChun, Y.; HongBiao, Z.; Tao, L.; ShiShan, Y.; JinXue, L.; Chan, D. Isolation and identification of a strain of porcine reovirus serotype 1 in China. CABI Databases 2013, 43, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Fu, S.; Cao, L.; Lei, W.; Cao, Y.; Song, J.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; et al. Isolation and identification of a natural reassortant mammalian orthoreovirus from least horseshoe bat in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, V.T.; Yoon, S.W.; Noh, J.Y.; Jang, S.S.; Na, W.; Song, D.; Jeong, D.G.; Kim, H.K. Characterization of replication and variations in genome segments of a bat reovirus, BatMRV/B19-02, by RNA-seq in infected Vero-E6 cells. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, L.; Hovis, J.F.; Mastrota, F.M.; Bell, J.A.; Huebner, R.J. Observations on a newly recognized virus (Abney) of the reovirus family. Am. J. Hyg. 1960, 71, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hrdy, D.B.; Rosen, L.; Fields, B.N. Polymorphism of the migration of double-stranded RNA genome segments of reovirus isolates from humans, cattle, and mice. J. Virol. 1979, 31, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, F.; Tu, X.; Chen, Q.; et al. Emergence and Autochthonous Transmission of Dengue Virus Type I in a Low-Epidemic Region in Southeast China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 638785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, A.; Jupp, P.G. Potential for dengue in South Africa: Mosquito ecology with particular reference to Aedes aegypti. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1991, 7, 574–583. [Google Scholar]
- Jupp, P.G.; Kemp, A. The potential for dengue in South Africa: Vector competence tests with dengue 1 and 2 viruses and 6 mosquito species. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 87, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Date of Blood Collection | Case Number | Age | Sex | Symptoms | Clinical Features and Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 July 2017 | SA395 | 46 | M | Onset (date not recorded): Fever (38.7 °C) without rash, headache, severe body aches | No blood hematology test results were reported. The patients were not hospitalized. No previous history of dengue or yellow fever vaccination. All patients reported mosquito bites. |
| SA396 | 8 | F | Onset (date not recorded): Fever (38.5 °C) without rash, severe body aches, nausea | ||
| SA397 | 45 | F | Onset (16 July 2017): Fever (39 °C) without rash, severe body aches, nausea |
| Segment Protein | Nucleotide (nt), Amino Acid (aa) Length | Closest Strain, GenBank, (%) | MRV Serotype | Location, Date | Host | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 λ3 protein | 3822 nt 1267 aa | SHR-A JX415466 88.57% | MRV-1 | China, 2011 | Pig | [43] |
| L2 λ2 protein | 2992/3918 nt (76.3%) 993/1299 aa (76.4%) | AP-151 MN022938 93.99% | MRV-3 | Brazil, 2015 | Human | [18] |
| L3 λ1 protein | 3901 nt 1275 aa | RpMRV-YN2012 KM087107 92.72% | MRV-2 | Yunnan province, China, 2012 | Rhinolophus pusillus (bat) | [44] |
| M1 μ2 protein | 2295 nt 736 aa | BatMRV/B19-02 MW582625 96.19% | MRV-1 | Jeju Island, South Korea, 2019 | Miniopterus schreibersii (bat) | [45] |
| M2 μ1 protein | 2203 nt 708 aa | Abney T3C87 GU589581 93.64% | MRV-3 | Washington, DC, USA, 1957 | Human | [46] |
| M3 μNS protein | 2241 nt 721 aa | BatMRV/B19-02 MW582627 96.90% | MRV-1 | Jeju Island, South Korea, 2019 | Miniopterus schreibersii (bat) | [45] |
| S1 σ1/σ1s protein | 1380 nt σ1—455 aa σ1s—120 aa | Tahiti L37679 93.57% | MRV-3 | Tahiti, French Polynesia, 1960 | Human | [42] |
| S2 σ2 protein | 1323 nt 427 aa | Lang L19774 98.11% | MRV-1 | Ohio, USA, 1953 | Human | [47] |
| S3 σNS protein | 1198 nt 366 aa | BatMRV/B19-02 MW582630 96.79% | MRV-1 | Jeju Island, South Korea, 2019 | Miniopterus schreibersii (bat) | [45] |
| S4 σ3 protein | 1196 nt 365 aa | SI-MRV07 MG999585 92.47% | MRV-3 | Slovenia, 2017 * | Human | [17] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jansen van Vuren, P.; Parry, R.H.; Pawęska, J.T. Detection of Dengue Virus 1 and Mammalian Orthoreovirus 3, with Novel Reassortments, in a South African Family Returning from Thailand, 2017. Viruses 2024, 16, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081274
Jansen van Vuren P, Parry RH, Pawęska JT. Detection of Dengue Virus 1 and Mammalian Orthoreovirus 3, with Novel Reassortments, in a South African Family Returning from Thailand, 2017. Viruses. 2024; 16(8):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081274
Chicago/Turabian StyleJansen van Vuren, Petrus, Rhys H. Parry, and Janusz T. Pawęska. 2024. "Detection of Dengue Virus 1 and Mammalian Orthoreovirus 3, with Novel Reassortments, in a South African Family Returning from Thailand, 2017" Viruses 16, no. 8: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081274
APA StyleJansen van Vuren, P., Parry, R. H., & Pawęska, J. T. (2024). Detection of Dengue Virus 1 and Mammalian Orthoreovirus 3, with Novel Reassortments, in a South African Family Returning from Thailand, 2017. Viruses, 16(8), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081274







