High-Yield and Quantitative Purification Method for HIV Which Minimizes Forces Applied to Virions Utilized to Investigate Maturation of HIV-1 via Cryo-Electron Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Plating and Transfections
2.2. pNL4.3 Plasmid Preps and Mutagenesis
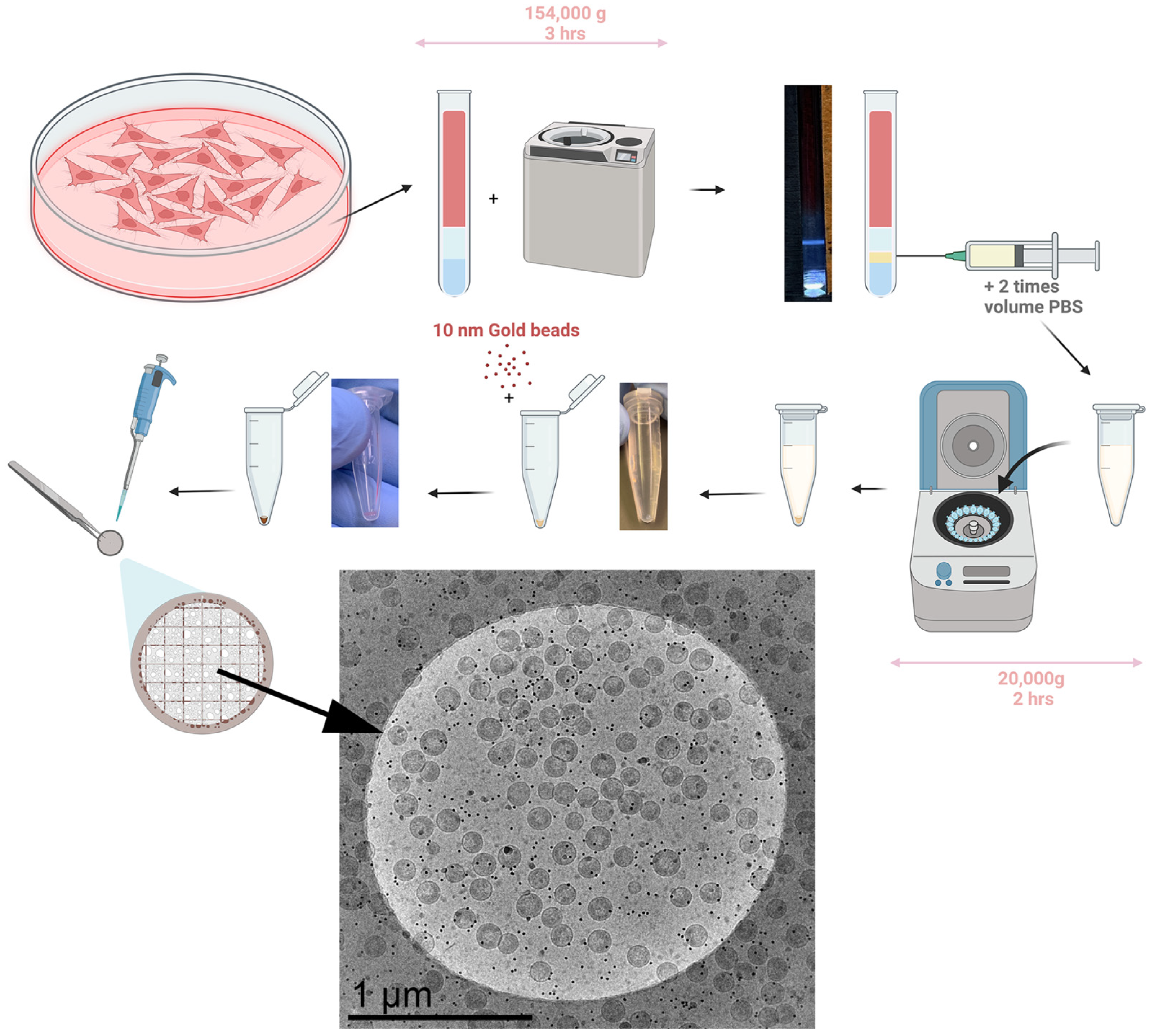
2.3. Preparation of OptiPrep™—Iodixanol Step Gradients
2.4. Preparation of 10X 20 nm Gold Beads
2.5. Freezing of Virions on EM Grids
2.6. Cryo-Electron Tomography of Viral Particles Embedded in Vitreous Ice
2.7. Data Analysis and Tomogram Reconstruction
2.8. Measurement of Virion Retention on Blotted Grids
3. Results
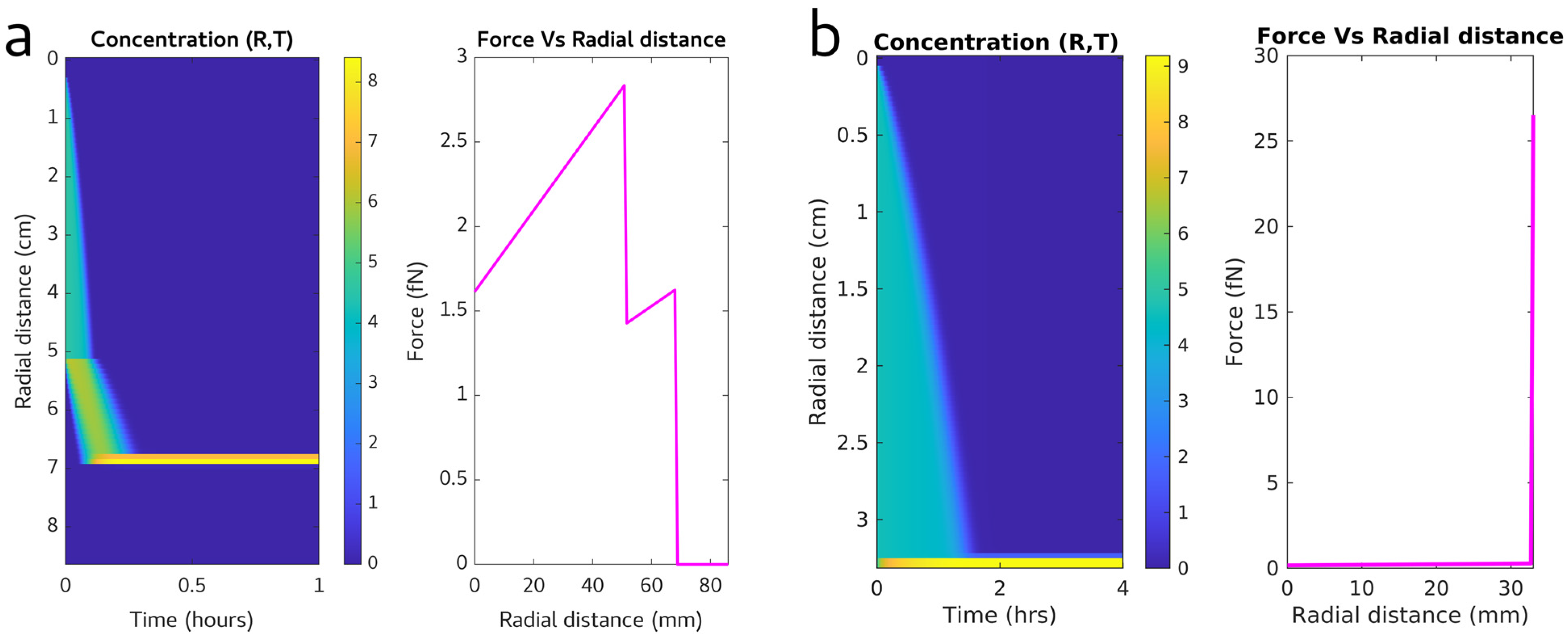
3.1. Calculating an Efficient Purification Protocol for HIV Virions
3.2. Developing the Experimental Method for Virion Purification
3.3. Measuring the Virion Yield in the Purification Protocol
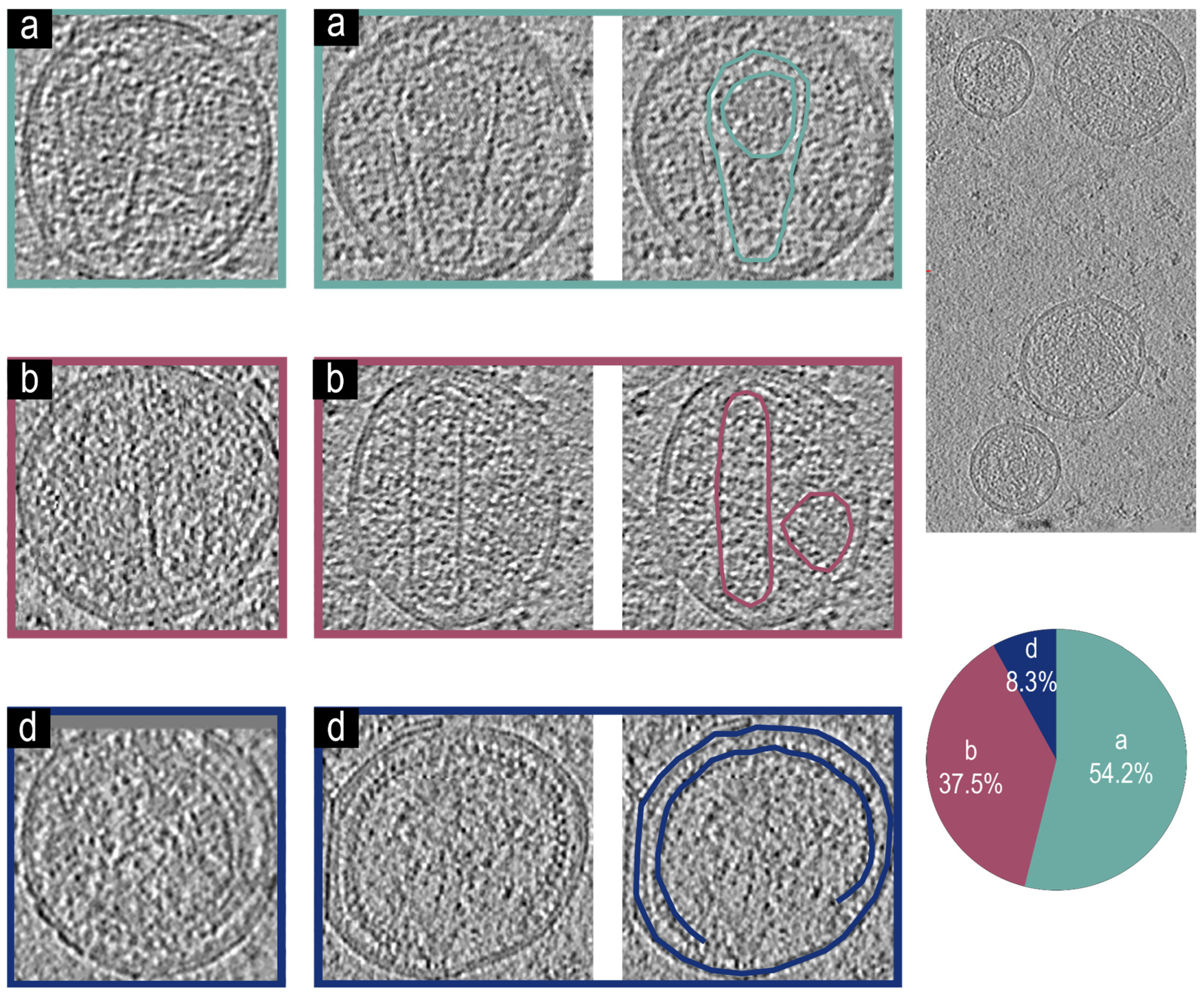
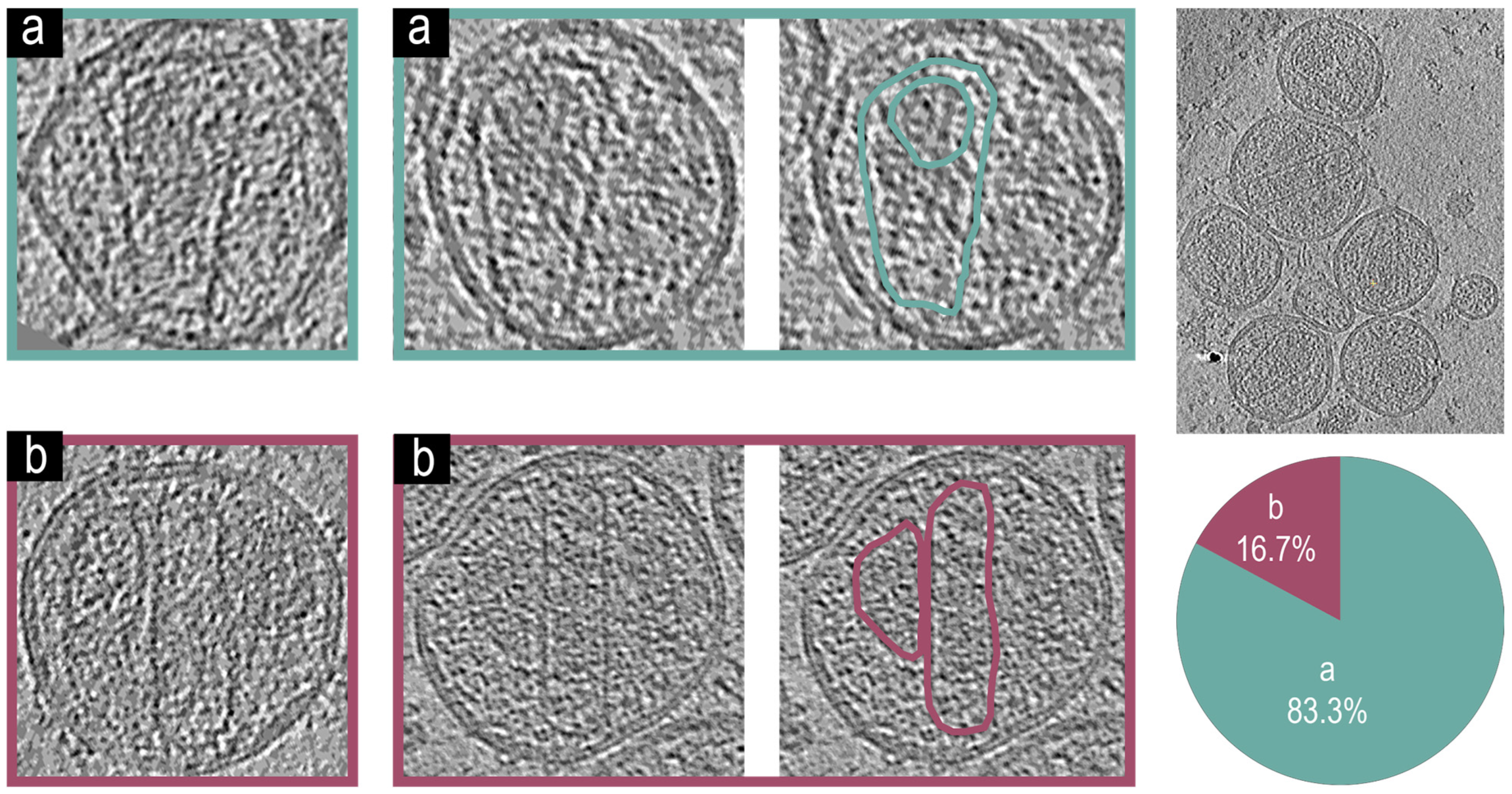
3.4. Cryo-Electron Tomographic Reconstruction of NL4.3:Env(506SEKS509) Virions
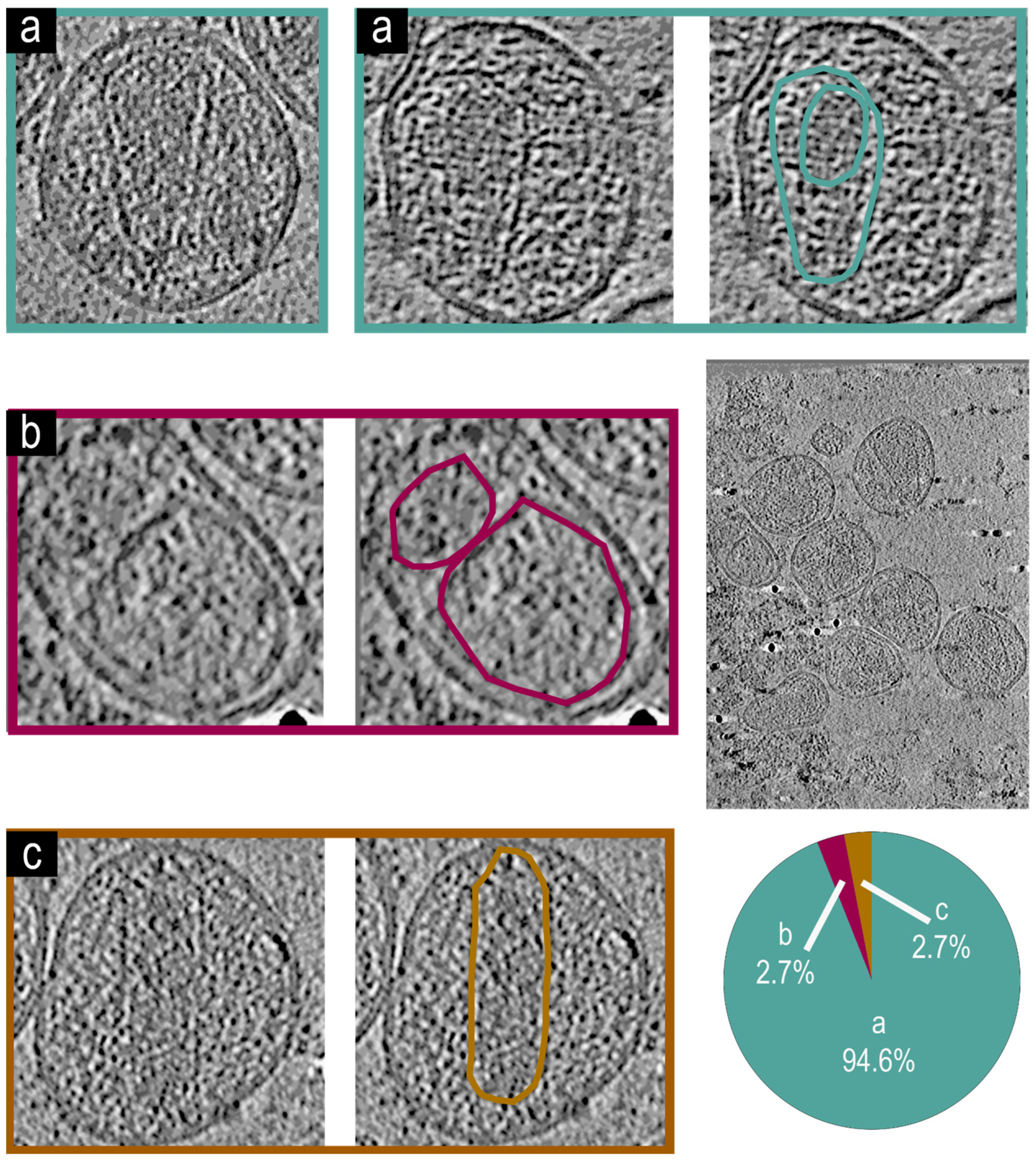
3.5. Cryo-Electron Tomographic Reconstruction of NL4.3() Virions
3.6. Cryo-Electron Tomographic Reconstruction of pNL4-3(RT:D185A&D186A)(Env(506SEKS509)) Virions
3.7. Cryo-Electron Tomographic Reconstruction of NL4.3(IN: V165A&R166A)(Env(506SEKS509) Virions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, F.; Bailes, E.; Robertson, D.L.; Chen, Y.; Rodenburg, C.M.; Michael, S.F.; Cummins, L.B.; Arthur, L.O.; Peeters, M.; Shaw, G.M.; et al. Origin of HIV-1 in the Chimpanzee Pan Troglodytes Troglodytes. Nature 1999, 397, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipe, D.M.; Howley, P.M.; Griffin, D.E.; Lamb, R.A.; Martin, M.A.; Roizman, B.; Straus, S.E. (Eds.) Field’s Virology, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago, M.L.; Range, F.; Keele, B.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Bailes, E.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Fruteau, C.; Noë, R.; Peeters, M.; Brookfield, J.F.Y.; et al. Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection in Free-Ranging Sooty Mangabeys (Cercocebus Atys Atys) from the Taï Forest, Côte d’Ivoire: Implications for the Origin of Epidemic Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 2. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12515–12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, J.M.; Hughes, S.H.; Varmus, H. (Eds.) Retroviruses; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Plainview, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-87969-571-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, L.; Sun, D.; Ning, J.; Liu, J.; Kotecha, A.; Olek, M.; Frosio, T.; Fu, X.; Himes, B.A.; Kleinpeter, A.B.; et al. CryoET Structures of Immature HIV Gag Reveal Six-Helix Bundle. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettenhofer, M.; Yu, X.-F. Highly Purified Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Reveals a Virtual Absence of Vif in Virions. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinpeter, A.B.; Zhu, Y.; Mallery, D.L.; Ablan, S.D.; Chen, L.; Hardenbrook, N.; Saiardi, A.; James, L.C.; Zhang, P.; Freed, E.O. The Effect of Inositol Hexakisphosphate on HIV-1 Particle Production and Infectivity Can Be Modulated by Mutations That Affect the Stability of the Immature Gag Lattice. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 168037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talledge, N.; Yang, H.; Shi, K.; Coray, R.; Yu, G.; Arndt, W.G.; Meng, S.; Baxter, G.C.; Mendonça, L.M.; Castaño-Díez, D.; et al. HIV-2 Immature Particle Morphology Provides Insights into Gag Lattice Stability and Virus Maturation. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 168143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldini, L.; Blömer, U.; Gallay, P.; Ory, D.; Mulligan, R.; Gage, F.H.; Verma, I.M.; Trono, D. In Vivo Gene Delivery and Stable Transduction of Nondividing Cells by a Lentiviral Vector. Science 1996, 272, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldi, M.; Sergi Sergi, L.; Unali, G.; Kerzel, T.; Cuccovillo, I.; Capasso, P.; Annoni, A.; Biffi, M.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; Cantore, A.; et al. Laboratory-Scale Lentiviral Vector Production and Purification for Enhanced Ex Vivo and In Vivo Genetic Engineering. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 19, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.R.; Schooler, J.B.; Ding, H.J.; Kieffer, C.; Fillmore, C.; Sundquist, W.I.; Jensen, G.J. Electron Cryotomography of Immature HIV-1 Virions Reveals the Structure of the CA and SP1 Gag Shells. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 2218–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, J.A.G.; Riches, J.D.; Glass, B.; Bartonova, V.; Zanetti, G.; Kräusslich, H.-G. Structure and Assembly of Immature HIV. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11090–11095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganser, B.K.; Li, S.; Klishko, V.Y.; Finch, J.T.; Sundquist, W.I. Assembly and Analysis of Conical Models for the HIV-1 Core. Science 1999, 283, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, J.A.G.; Wilk, T.; Welker, R.; Kräusslich, H.-G.; Fuller, S.D. Structural Organization of Authentic, Mature HIV-1 Virions and Cores. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schur, F.K.M.; Obr, M.; Hagen, W.J.H.; Wan, W.; Jakobi, A.J.; Kirkpatrick, J.M.; Sachse, C.; Kräusslich, H.-G.; Briggs, J.A.G. An Atomic Model of HIV-1 Capsid-SP1 Reveals Structures Regulating Assembly and Maturation. Science 2016, 353, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, J.S.; Miller, J.; Tai, J.; Kim, A.; Ghanam, R.H.; Summers, M.F. Structural Basis for Targeting HIV-1 Gag Proteins to the Plasma Membrane for Virus Assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11364–11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Ablan, S.D.; Lockett, S.J.; Nagashima, K.; Freed, E.O. Phosphatidylinositol (4,5) Bisphosphate Regulates HIV-1 Gag Targeting to the Plasma Membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14889–14894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favard, C.; Chojnacki, J.; Merida, P.; Yandrapalli, N.; Mak, J.; Eggeling, C.; Muriaux, D. HIV-1 Gag Specifically Restricts PI(4,5)P2 and Cholesterol Mobility in Living Cells Creating a Nanodomain Platform for Virus Assembly. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Gonçalves-Carneiro, D.; Zang, T.M.; Bieniasz, P.D. Initiation of HIV-1 Gag Lattice Assembly Is Required for Recognition of the Viral Genome Packaging Signal. eLife 2023, 12, e83548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchon, A.; Santos, S.; Chen, J.; Brown, M.; Nikolaitchik, O.A.; Tai, S.; Chao, J.A.; Freed, E.O.; Pathak, V.K.; Hu, W.S.; et al. Plasma Membrane Anchoring and Gag:Gag Multimerization on Viral RNA Are Critical Properties of HIV-1 Gag Required To Mediate Efficient Genome Packaging. mBio 2021, 12, e0325421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieniasz, P.; Telesnitsky, A. Multiple, Switchable Protein:RNA Interactions Regulate Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Assembly. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarni, S.; Biswas, B.; Liu, S.; Olson, E.D.; Kitzrow, J.P.; Rein, A.; Wysocki, V.H.; Musier-Forsyth, K. HIV-1 Gag Protein with or without P6 Specifically Dimerizes on the Viral RNA Packaging Signal. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14391–14401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, P.-I.; Miller, A.K.; Ballew, J.; Sandrin, V.; Adler, F.R.; Saffarian, S. Identification of Pauses during Formation of HIV-1 Virus Like Particles. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouvenet, N.; Simon, S.M.; Bieniasz, P.D. Visualizing HIV-1 Assembly. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 410, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouvenet, N.; Simon, S.M.; Bieniasz, P.D. Imaging the Interaction of HIV-1 Genomes and Gag during Assembly of Individual Viral Particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19114–19119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundquist, W.I.; Kräusslich, H.-G. HIV-1 Assembly, Budding, and Maturation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a015420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, E.O. HIV-1 Assembly, Release and Maturation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Potempa, M.; Swanstrom, R. The Choreography of HIV-1 Proteolytic Processing and Virion Assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40867–40874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdick, R.C.; Li, C.; Munshi, M.; Rawson, J.M.O.; Nagashima, K.; Hu, W.-S.; Pathak, V.K. HIV-1 Uncoats in the Nucleus near Sites of Integration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5486–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharan, A.; Bachmann, N.; Talley, S.; Zwikelmaier, V.; Campbell, E.M. Nuclear Pore Blockade Reveals That HIV-1 Completes Reverse Transcription and Uncoating in the Nucleus. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinpeter, A.B.; Freed, E.O. HIV-1 Maturation: Lessons Learned from Inhibitors. Viruses 2020, 12, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundquist, W.I.; Krug, R.M. Assemble, Replicate, Remodel and Evade. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, a006924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenhorn, W.; Göttlinger, H. Essential Ingredients for HIV-1 Budding. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieniasz, P.D. The Cell Biology of HIV-1 Virion Genesis. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulky, A.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Jia, Y.; Arnold, E.; Kappes, J.C. Identification of Amino Acid Residues in the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Reverse Transcriptase Tryptophan-Repeat Motif That Are Required for Subunit Interaction Using Infectious Virions. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 349, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fricke, T. Diaz-Griffero Felipe Inhibition of Reverse Transcriptase Activity Increases Stability of the HIV-1 Core. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschbach Jenna, E.; Puray-Chavez, M.; Mohammed, S.; Wang, Q.K.; Xia, M.; Huang, L.C.; Shan, L.; Kutluay Sebla, B. HIV-1 Capsid Stability and Reverse Transcription Are Finely Balanced to Minimize Sensing of Reverse Transcription Products via the cGAS-STING Pathway. mBio 2024, 15, e0034824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankovic, S.; Deshpande, A.; Harel, S.; Aiken, C. Rousso Itay HIV-1 Uncoating Occurs via a Series of Rapid Biomechanical Changes in the Core Related to Individual Stages of Reverse Transcription. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, A.; Englund, G.; Orenstein, J.M.; Martin, M.A.; Craigie, R. Multiple Effects of Mutations in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Integrase on Viral Replication. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, K.A.; Wang, H.; Slaughter, A.; Feng, L.; Kessl, J.J.; Koh, Y.; Wang, W.; Ballandras-Colas, A.; Patel, P.A.; Fuchs, J.R.; et al. Allosteric Integrase Inhibitor Potency Is Determined through the Inhibition of HIV-1 Particle Maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8690–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, A.; Gottlinger, H.; Haseltine, W.; Sodroski, J. Identification of a Sequence Required for Efficient Packaging of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 RNA into Virions. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 4085–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luban, J.; Goff, S.P. Binding of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) RNA to Recombinant HIV-1 Gag Polyprotein. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 3203–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, E.M.; Lever, A.M. Location of Cis-Acting Signals Important for RNA Encapsidation in the Leader Sequence of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 2. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4133–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, G.K.; De Guzman, R.N.; Turner, R.B.; Chancellor, K.J.; Wu, Z.R.; Summers, M.F. NMR Structure of the HIV-1 Nucleocapsid Protein Bound to Stem-Loop SL2 of the Ψ-RNA Packaging Signal. Implications for Genome Recognition 11Edited by P. Wright. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 301, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, S.C.; Heng, X.; Lu, K.; Kharytonchyk, S.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Carter, G.; Barton, S.; Hosic, A.; Florwick, A.; Santos, J.; et al. Structure of the HIV-1 RNA Packaging Signal. Science 2015, 348, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Heng, X.; Garyu, L.; Monti, S.; Garcia, E.L.; Kharytonchyk, S.; Dorjsuren, B.; Kulandaivel, G.; Jones, S.; Hiremath, A.; et al. NMR Detection of Structures in the HIV-1 5′-Leader RNA That Regulate Genome Packaging. Science 2011, 334, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutluay, S.B.; Zang, T.; Blanco-Melo, D.; Powell, C.; Jannain, D.; Errando, M.; Bieniasz, P.D. Global Changes in the RNA Binding Specificity of HIV-1 Gag Regulate Virion Genesis. Cell 2014, 159, 1096–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulli, S.J.; Hibbert, C.S.; Mirro, J.; Pederson, T.; Biswal, S.; Rein, A. Selective and Nonselective Packaging of Cellular RNAs in Retrovirus Particles. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriaux, D.; Mirro, J.; Harvin, D.; Rein, A. RNA Is a Structural Element in Retrovirus Particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessl, J.J.; Kutluay, S.B.; Townsend, D.; Rebensburg, S.; Slaughter, A.; Larue, R.C.; Shkriabai, N.; Bakouche, N.; Fuchs, J.R.; Bieniasz, P.D.; et al. HIV-1 Integrase Binds the Viral RNA Genome and Is Essential during Virion Morphogenesis. Cell 2016, 166, 1257–1268.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, A.; Gendelman, H.E.; Koenig, S.; Folks, T.; Willey, R.; Rabson, A.; Martin, M.A. Production of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome-Associated Retrovirus in Human and Nonhuman Cells Transfected with an Infectious Molecular Clone. J. Virol. 1986, 59, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefiori, D.C. Measuring HIV Neutralization in a Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay. In HIV Protocols; Prasad, V.R., Kalpana, G.V., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 395–405. ISBN 978-1-59745-170-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ana, L.; Eric, D.; Richard, L.; Ghory Hina, Z.; Silver Pamela, A. Engelman Alan Nuclear Localization of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Preintegration Complexes (PICs): V165A and R166A Are Pleiotropic Integrase Mutants Primarily Defective for Integration, Not PIC Nuclear Import. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10598–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancera, M.; Wyatt, R. Selective Recognition of Oligomeric HIV-1 Primary Isolate Envelope Glycoproteins by Potently Neutralizing Ligands Requires Efficient Precursor Cleavage. Virology 2005, 332, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastronarde, D.N. Automated Electron Microscope Tomography Using Robust Prediction of Specimen Movements. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 152, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrigg, A.; Wilkinson, G.W.G.; Angliss, S.; Greenaway, P.J. HIV-1 Indicator Cell Lines. AIDS 1991, 5, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttlinger, H.G.; Sodroski, J.G.; Haseltine, W.A. Role of Capsid Precursor Processing and Myristoylation in Morphogenesis and Infectivity of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5781–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusert, P.; Fischer, M.; Joos, B.; Leemann, C.; Kuster, H.; Flepp, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Günthard, H.F.; Trkola, A. Quantification of Infectious HIV-1 Plasma Viral Load Using a Boosted in Vitro Infection Protocol. Virology 2004, 326, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimpton, J.; Emerman, M. Detection of Replication-Competent and Pseudotyped Human Immunodeficiency Virus with a Sensitive Cell Line on the Basis of Activation of an Integrated Beta-Galactosidase Gene. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2232–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdelier, M.; Swain, J.; Arone, C.; Mouttou, A.; Bracquemond, D.; Merida, P.; Saffarian, S.; Lyonnais, S.; Favard, C.; Muriaux, D. Optimized Production and Fluorescent Labeling of SARS-CoV-2 Virus-like Particles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swann, H.; Sharma, A.; Preece, B.; Peterson, A.; Eldridge, C.; Belnap, D.M.; Vershinin, M.; Saffarian, S. Minimal System for Assembly of SARS-CoV-2 Virus like Particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atemin, A.; Ivanova, A.; Peppel, W.; Stamatov, R.; Gallegos, R.; Durden, H.; Uzunova, S.; Vershinin, M.D.; Saffarian, S.; Stoynov, S.S. Kinetic Landscape of Single Virus-like Particles Highlights the Efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 Internalization. Viruses 2024, 16, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Preece, B.; Swann, H.; Fan, X.; McKenney, R.J.; Ori-McKenney, K.M.; Saffarian, S.; Vershinin, M.D. Structural Stability of SARS-CoV-2 Virus like Particles Degrades with Temperature. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 534, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrus, J.E.; von Schwedler, U.K.; Pornillos, O.W.; Morham, S.G.; Zavitz, K.H.; Wang, H.E.; Wettstein, D.A.; Stray, K.M.; Côté, M.; Rich, R.L.; et al. Tsg101 and the Vacuolar Protein Sorting Pathway Are Essential for HIV-1 Budding. Cell 2001, 107, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Bromley, J.; Saffarian, S. High-Speed Imaging of ESCRT Recruitment and Dynamics during HIV Virus like Particle Budding. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Bendjennat, M.; Saffarian, S. Abrogating ALIX Interactions Results in Stuttering of the ESCRT Machinery. Viruses 2020, 12, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartel, V.; Ivanchenko, S.; Dupont, A.; Sergeev, M.; Wiseman, P.W.; Krausslich, H.-G.; Brauchle, C.; Muller, B.; Lamb, D.C. Live-Cell Visualization of Dynamics of HIV Budding Site Interactions with an ESCRT Component. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirov, D.G.; Orenstein, J.M.; Freed, E.O. The Late Domain of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 P6 Promotes Virus Release in a Cell Type-Dependent Manner. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VerPlank, L.; Bouamr, F.; LaGrassa, T.J.; Agresta, B.; Kikonyogo, A.; Leis, J.; Carter, C.A. Tsg101, a Homologue of Ubiquitin-Conjugating (E2) Enzymes, Binds the L Domain in HIV Type 1 Pr55Gag. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7724–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Serrano, J.; Yaravoy, A.; Perez-Caballero, D.; Bieniasz, P.D. Divergent Retroviral Late-Budding Domains Recruit Vacuolar Protein Sorting Factors by Using Alternative Adaptor Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12414–12419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Miranda, P.; Becker, J.T.; Benner, B.E.; Blume, A.; Sherer, N.M.; Butcher, S.E. Stability of HIV Frameshift Site RNA Correlates with Frameshift Efficiency and Decreased Virus Infectivity. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6906–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kräusslich, H.G. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Proteinase Dimer as Component of the Viral Polyprotein Prevents Particle Assembly and Viral Infectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 3213–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendjennat, M.; Saffarian, S. The Race against Protease Activation Defines the Role of ESCRTs in HIV Budding. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietmair, S.; Hodson, M.P.; Quek, L.-E.; Timmins, N.E.; Gray, P.; Nielsen, L.K. A Multi-Omics Analysis of Recombinant Protein Production in Hek293 Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benner, B.E.; Bruce, J.W.; Kentala, J.R.; Murray, M.; Becker, J.T.; Garcia-Miranda, P.; Ahlquist, P.; Butcher, S.E.; Sherer, N.M. Perturbing HIV-1 Ribosomal Frameshifting Frequency Reveals a Cis Preference for Gag-Pol Incorporation into Assembling Virions. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0134921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Preece, B.; Peppel, W.; Gallegos, R.; Ysassi, G.; Clinger, G.; Bohn, N.; Adhikary, B.; Mendonça, L.; Belnap, D.; Vershinin, M.; et al. High-Yield and Quantitative Purification Method for HIV Which Minimizes Forces Applied to Virions Utilized to Investigate Maturation of HIV-1 via Cryo-Electron Tomography. Viruses 2025, 17, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030364
Preece B, Peppel W, Gallegos R, Ysassi G, Clinger G, Bohn N, Adhikary B, Mendonça L, Belnap D, Vershinin M, et al. High-Yield and Quantitative Purification Method for HIV Which Minimizes Forces Applied to Virions Utilized to Investigate Maturation of HIV-1 via Cryo-Electron Tomography. Viruses. 2025; 17(3):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030364
Chicago/Turabian StylePreece, Benjamin, Wiley Peppel, Rodrigo Gallegos, Gillian Ysassi, Gabriel Clinger, Nicole Bohn, Broti Adhikary, Luiza Mendonça, David Belnap, Michael Vershinin, and et al. 2025. "High-Yield and Quantitative Purification Method for HIV Which Minimizes Forces Applied to Virions Utilized to Investigate Maturation of HIV-1 via Cryo-Electron Tomography" Viruses 17, no. 3: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030364
APA StylePreece, B., Peppel, W., Gallegos, R., Ysassi, G., Clinger, G., Bohn, N., Adhikary, B., Mendonça, L., Belnap, D., Vershinin, M., & Saffarian, S. (2025). High-Yield and Quantitative Purification Method for HIV Which Minimizes Forces Applied to Virions Utilized to Investigate Maturation of HIV-1 via Cryo-Electron Tomography. Viruses, 17(3), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030364






