Implementation of RT-RAA and CRISPR/Cas13a for an NiV Point-of-Care Test: A Promising Tool for Disease Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of RT-RAA Primers, CRISPR crRNAs, Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Primers and Probes, and RNA Reporters
2.2. Preparation of crRNAs
2.3. Preparation of NiV Single-Strand RNA Template and Viral Genome of Other Swine Diseases
2.4. RT-RAA and Primer Screening
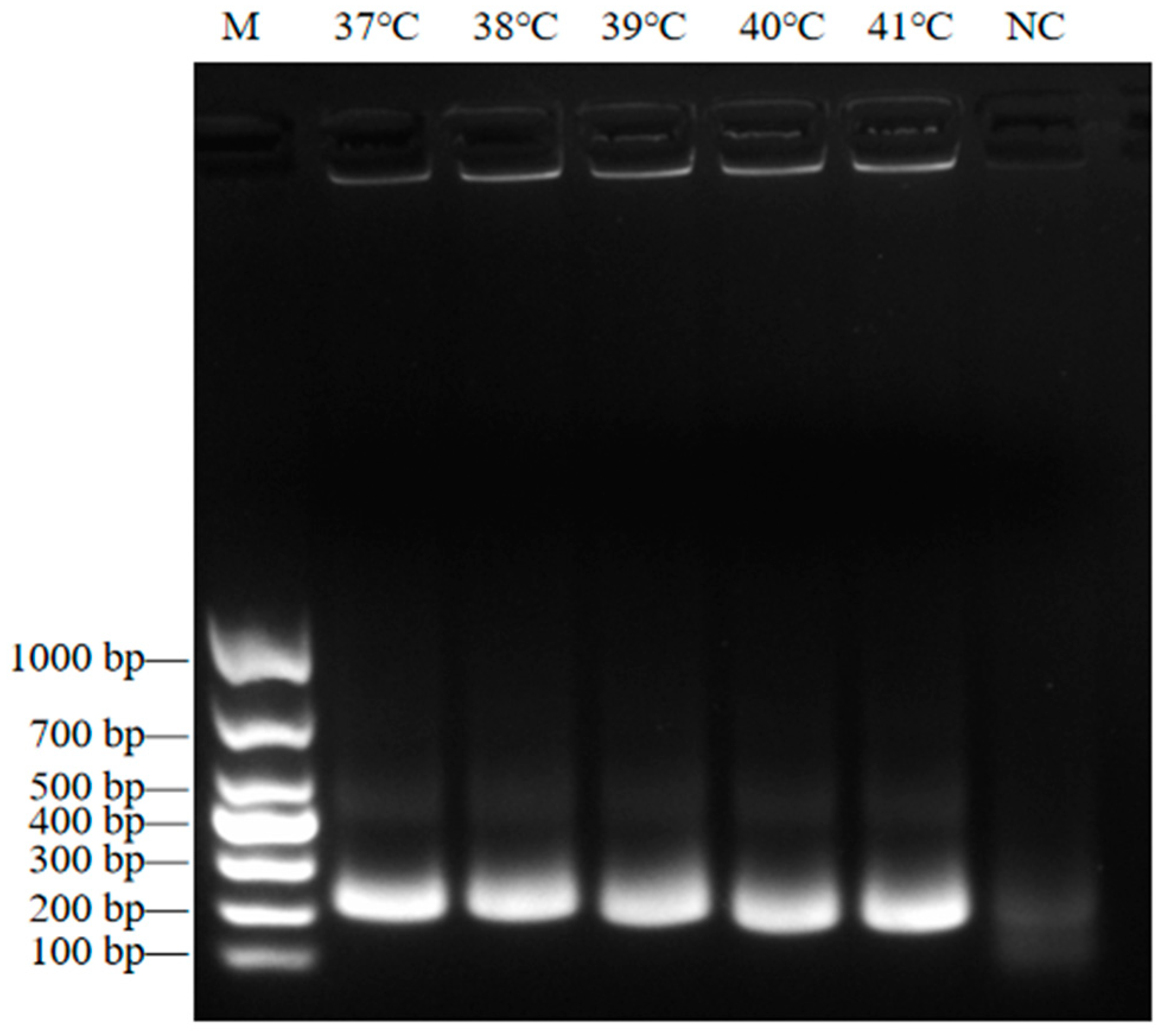
2.5. Determining the Optimal Temperature for RT-RAA
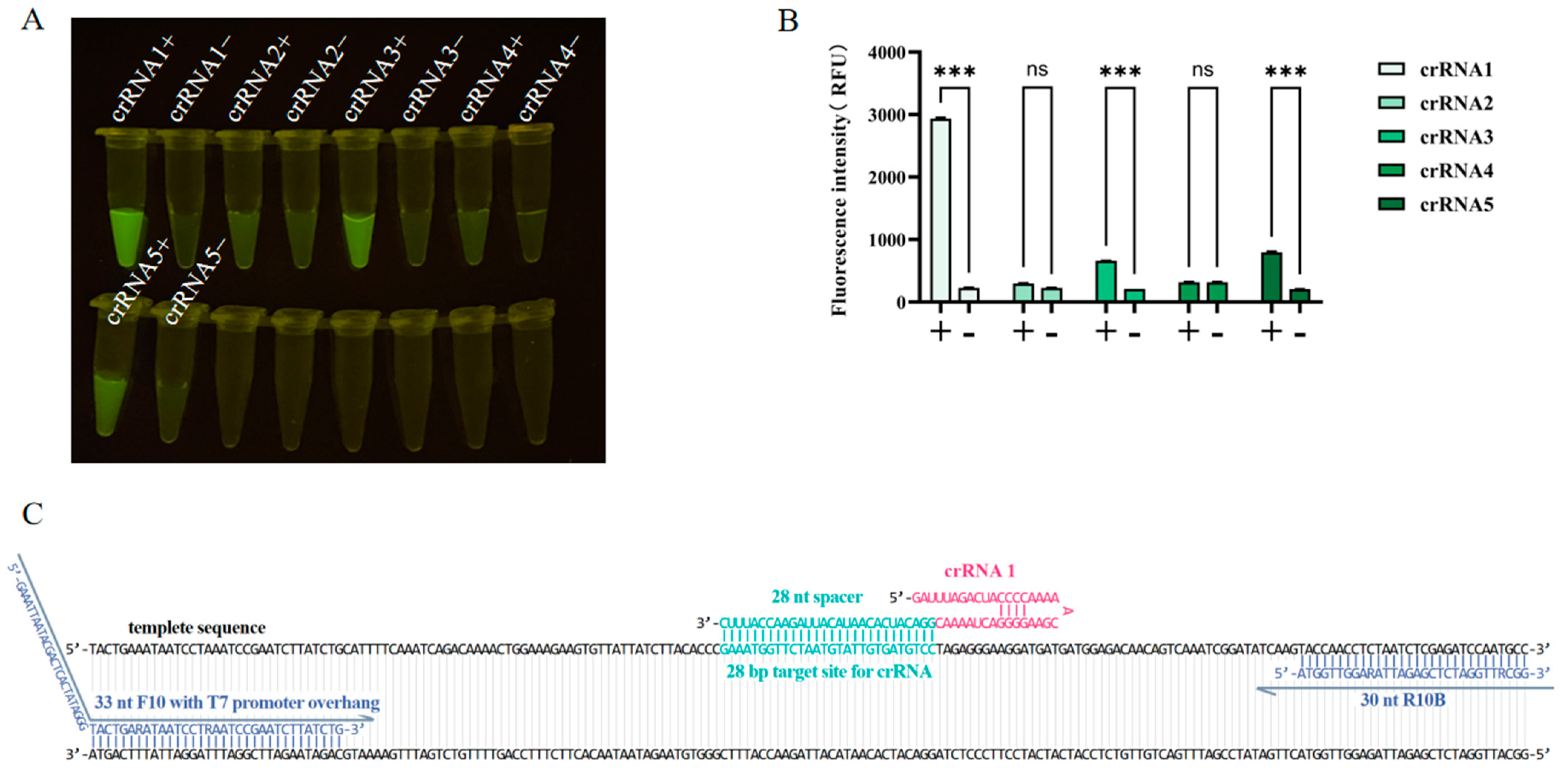
2.6. Screening for crRNAs and CRISPR/Cas13a Detection
2.7. Lateral Flow Assays
2.8. Calibration of the NiV ssRNA Template Copy Number Using ddPCR
2.9. Sensitivity Detection of RT-RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a
2.10. Specificity Detection of RT-RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a
2.11. Detection of RT-RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a Using Simulated NiV Clinical Samples
2.12. Statistics and Reproducibility
3. Results
3.1. Screening of RT-RAA Primers
3.2. Determining the Optimal RT-RAA Reaction Temperature
3.3. Screening of crRNAs
3.4. Sensitivity Detection for RT-RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a
3.5. Specificity of RT-RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a
3.6. Detection of the Application Effect of RT-RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a in Simulated NiV Clinical Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, R.K.; Dhama, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Tiwari, R.; Natesan, S.; Khandia, R.; Munjal, A.; Vora, K.S.; Latheef, S.K.; Karthik, K.; et al. Nipah virus: Epidemiology, pathology, immunobiology and advances in diagnosis, vaccine designing and control strategies—A comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2019, 39, 26–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeletti, S.; Lo Presti, A.; Cella, E.; Ciccozzi, M. Molecular epidemiology and phylogeny of Nipah virus infection: A mini review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luby, S.P. The pandemic potential of Nipah virus. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, R.K.; Graham, S.P. Vaccine development for Nipah virus infection in pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Nipah virus infection—India. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2023-DON490 (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Parashar, U.D.; Sunn, L.M.; Ong, F.; Mounts, A.W.; Arif, M.T.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Kamaluddin, M.A.; Mustafa, A.N.; Kaur, H.; Ding, L.M.; et al. Case-control study of risk factors for human infection with a new zoonotic paramyxovirus, Nipah virus, during a 1998–1999 outbreak of severe encephalitis in Malaysia. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.B.; Bellini, W.J.; Rota, P.A.; Harcourt, B.H.; Tamin, A.; Lam, S.K.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Rollin, P.E.; Zaki, S.R.; Shieh, W.; et al. Nipah virus: A recently emergent deadly paramyxovirus. Science 2000, 288, 1432–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO South-East Asia Regional Strategy for the Prevention and Control of Nipah Virus Infection, 2023–2030; World Health Organization, Regional Office for South-East Asia: New Delhi, India, 2020.
- AbuBakar, S.; Chang, L.Y.; Ali, A.R.; Sharifah, S.H.; Yusoff, K.; Zamrod, Z. Isolation and molecular identification of Nipah virus from pigs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2228–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Khairullah, N.S.; Inoue, S.; Balasubramaniam, V.; Berendam, S.J.; Teh, L.K.; Ibrahim, N.S.; Abdul Rahman, S.; Hassan, S.S.; Hasebe, F.; et al. Serodiagnosis using recombinant nipah virus nucleocapsid protein expressed in Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3134–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, Y.; Noguchi, A.; Marsh, G.A.; Barr, J.A.; Okutani, A.; Hotta, K.; Bazartseren, B.; Fukushi, S.; Broder, C.C.; Yamada, A.; et al. Second generation of pseudotype-based serum neutralization assay for Nipah virus antibodies: Sensitive and high-throughput analysis utilizing secreted alkaline phosphatase. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 179, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Chern, S.W.; Li, Y.; Pallansch, M.A.; Anderson, L.J. Sensitive and broadly reactive reverse transcription-PCR assays to detect novel paramyxoviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2652–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widerspick, L.; Vázquez, C.A.; Niemetz, L.; Heung, M.; Olal, C.; Bencsik, A.; Henkel, C.; Pfister, A.; Brunetti, J.E.; Kucinskaite-Kodze, I.; et al. Inactivation methods for experimental Nipah virus infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Kellner, M.J.; Joung, J.; Collins, J.J.; Zhang, F. Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid detection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6. Science 2018, 360, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makarova, K.S.; Koonin, E.V. Annotation and classification of CRISPR-Cas systems. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1311, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Qiu, M.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Li, J. CRISPR-Cas13a system: A novel tool for molecular diagnostics. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1060947. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Man, S.; Ye, S.; Liu, G.; Ma, L. CRISPR-Cas based virus detection: Recent advances and perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113541. [Google Scholar]
- Kellner, M.J.; Koob, J.G.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Zhang, F. SHERLOCK: Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR nucleases. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2986–3012. [Google Scholar]
- SN/T 3954-2014; Detection of Nipah Virus at Frontier Port by RT-PCR and Real Time Fluorescence RT-PCR. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Shuai, J.; Chen, K.; Han, X.; Zeng, R.; Song, H.; Fu, L.; Zhang, X. Development and validation of a droplet digital PCR assay for Nipah virus quantitation. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 440. [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron, É.; Chiang, C.F.; Lo, M.K.; Karaaslan, E.; Satter, S.M.; Rahman, M.Z.; Hossain, M.E.; Aquib, W.R.; Rahman, D.I.; Sarwar, S.B.; et al. Streamlined detection of Nipah virus antibodies using a split NanoLuc biosensor. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2398640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudayyeh, O.O.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Essletzbichler, P.; Han, S.; Joung, J.; Belanto, J.J.; Verdine, V.; Cox, D.B.T.; Kellner, M.J.; Regev, A.; et al. RNA targeting with CRISPR-Cas13. Nature 2017, 550, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.S.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Guo, T.K.; Azeem, R.M.; Shi, C.W.; Yang, G.L.; Huang, H.B.; Jiang, Y.L.; Wang, J.Z.; et al. CRISPR/Cas13a-based genome editing for establishing the detection method of H9N2 subtype avian influenza virus. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104068. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xia, Q.; Wu, J.; Lin, Y.; Ju, H. A sensitive electrochemical method for rapid detection of dengue virus by CRISPR/Cas13a-assisted catalytic hairpin assembly. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1187, 339131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Bai, L.; Wang, G.; Han, J.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. SATCAS: A CRISPR/Cas13a-based simultaneous amplification and testing platform for one-pot RNA detection and SNPs distinguish in clinical diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 263, 116636. [Google Scholar]



| Name | Sequence (5′—3′) |
|---|---|
| Target sequence | TACTGAAATAATCCTAAATCCGAATCTTATCTGCATTTTCAAATCAGACAAAACTGGAAAGAAGT GTTATTATCTTACACCCGAAATGGTTCTAATGTATTGTGATGTCCTAGAGGGAAGGATGATGATG GAGACAACAGTCAAATCGGATATCAAGTACCAACCTCTAATCTCGAGATCCAATGCC |
| NiV-F1 | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGATTATTTAACATGTACAGATCATATTTCGGA |
| NiV-R1 | TTATGATGGTGTCTCTTAATGTATTGATATCTG |
| NiV-F2 | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAATAATTAATATACATGAGTGTAGGCGATTAGG |
| NiV-R2 | CAGATAAGATTCGGATTTAGGATTATTTCAGTA |
| NiV-F3 | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAATTTCTTTTTACAATTCAGGTATAGATGGAG |
| NiV-R3 | TACTTCAGTAGAATCTGGATTACTATATACTGG |
| NiV-F4 | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGATGTTAAATGAGGCTATGAATTATTTTGATGAC |
| NiV-R4 | TCTTCTGATGTTATTTTTGATGTGATAAAGTTC |
| NiV-F5 | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCTAAAACAATTAAAAATATCACAGCAAGGACTA |
| NiV-R5 | ATCATGATGAGATAATCTAGAAACTAACTTTGG |
| NiV-F6 | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAATCATAAATATAGAAGGATAGGTCTCAACT |
| NiV-R6 | ATCTCCATCTATACCTGAATTGTAAAAAGAAAT |
| NiV-F7 | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTTAATCACAGAATTTCTAATAGTTGATCCTGAA |
| NiV-R7 | GAATTTCAAAGGCCCATTTTATTGATATAGATT |
| NiV-F8 | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAAGAGTCTATACATATTAAGACAATCCAAACAG |
| NiV-R8 | ATCTCTTCTATCTTGAGTTATGAGATTTCTAGT |
| NiV-F9 | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGACTCTTTTAATAAGGTTAAATCTGCTCTCAATA |
| NiV-R9 | GTATTGTCTGATTTATAGTGATTGTGAGGATTA |
| NiV-F10 | TACTGARATAATCCTRAATCCGAATCTTATCTG |
| NiV-R10A | GAATGGATAAAAGATCATCAATAAACATAGACC |
| NiV-R10B | GGCRTTGGATCTCGAGATTARAGGTTGGTA |
| T7-crRNA-F | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGG |
| crRNA-R1 | GATTTAGACTACCCCAAAAACGAAGGGGACTAAAACGGACATCACAATACATTAGAACCATTTC |
| crRNA-R2 | TAGAGGTTGGTACTTGATATCCGATTTGGTTTTAGTCCCCTTCGTTTTTGGGGTAGTCTAAATCCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTAATTTC |
| crRNA-R3 | TAGCCCCCAGAGGGCATTGGATCTCGAGGTTTTAGTCCCCTTCGTTTTTGGGGTAGTCTAAATCCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTAATTTC |
| crRNA-R4 | TATCATAGACACTATATTGTAAATTCTGGTTTTAGTCCCCTTCGTTTTTGGGGTAGTCTAAATCCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTAATTTC |
| crRNA-R5 | CAGGATCCTAGCCTCATCCTTGAGTTGGGTTTTAGTCCCCTTCGTTTTTGGGGTAGTCTAAATCCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTAATTTC |
| ddPCR-F | GATGATGGAGACAACAGTCAAATC |
| ddPCR-R | GACAGGGAACAAGGGATCAA |
| ddPCR-probe | ACCTCTAATCTCGAGATCCAATGCCCT |
| Fluorescence RNA Reporter | 5′-FAM/UUUUUUUUUUU/BHQ1-3′ |
| LFS RNA Reporter | 5′-FAM/UUUUUUUUUUU/biotin-3′ |
| Method | The Number of Positive Samples | The Number of Negative Samples | Total | Positivity Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-qPCR | 10 | 10 | 20 | 50% |
| NiV RT-RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a fluorescence | 10 | 10 | 20 | 50% |
| NiV RT-RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a lateral flow assays | 10 | 10 | 20 | 50% |
| Coincidence rate | 100% | 100% | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Cui, J.; Zheng, H.; Guo, T.; Wei, R.; Sha, Z.; Gu, S.; Ni, B. Implementation of RT-RAA and CRISPR/Cas13a for an NiV Point-of-Care Test: A Promising Tool for Disease Control. Viruses 2025, 17, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040483
Yin J, Cui J, Zheng H, Guo T, Wei R, Sha Z, Gu S, Ni B. Implementation of RT-RAA and CRISPR/Cas13a for an NiV Point-of-Care Test: A Promising Tool for Disease Control. Viruses. 2025; 17(4):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040483
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jingqi, Jin Cui, Hui Zheng, Tingting Guo, Rong Wei, Zhou Sha, Shaopeng Gu, and Bo Ni. 2025. "Implementation of RT-RAA and CRISPR/Cas13a for an NiV Point-of-Care Test: A Promising Tool for Disease Control" Viruses 17, no. 4: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040483
APA StyleYin, J., Cui, J., Zheng, H., Guo, T., Wei, R., Sha, Z., Gu, S., & Ni, B. (2025). Implementation of RT-RAA and CRISPR/Cas13a for an NiV Point-of-Care Test: A Promising Tool for Disease Control. Viruses, 17(4), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040483






