Alphaflexiviridae in Focus: Genomic Signatures, Conserved Elements and Viral-Driven Cellular Remodeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
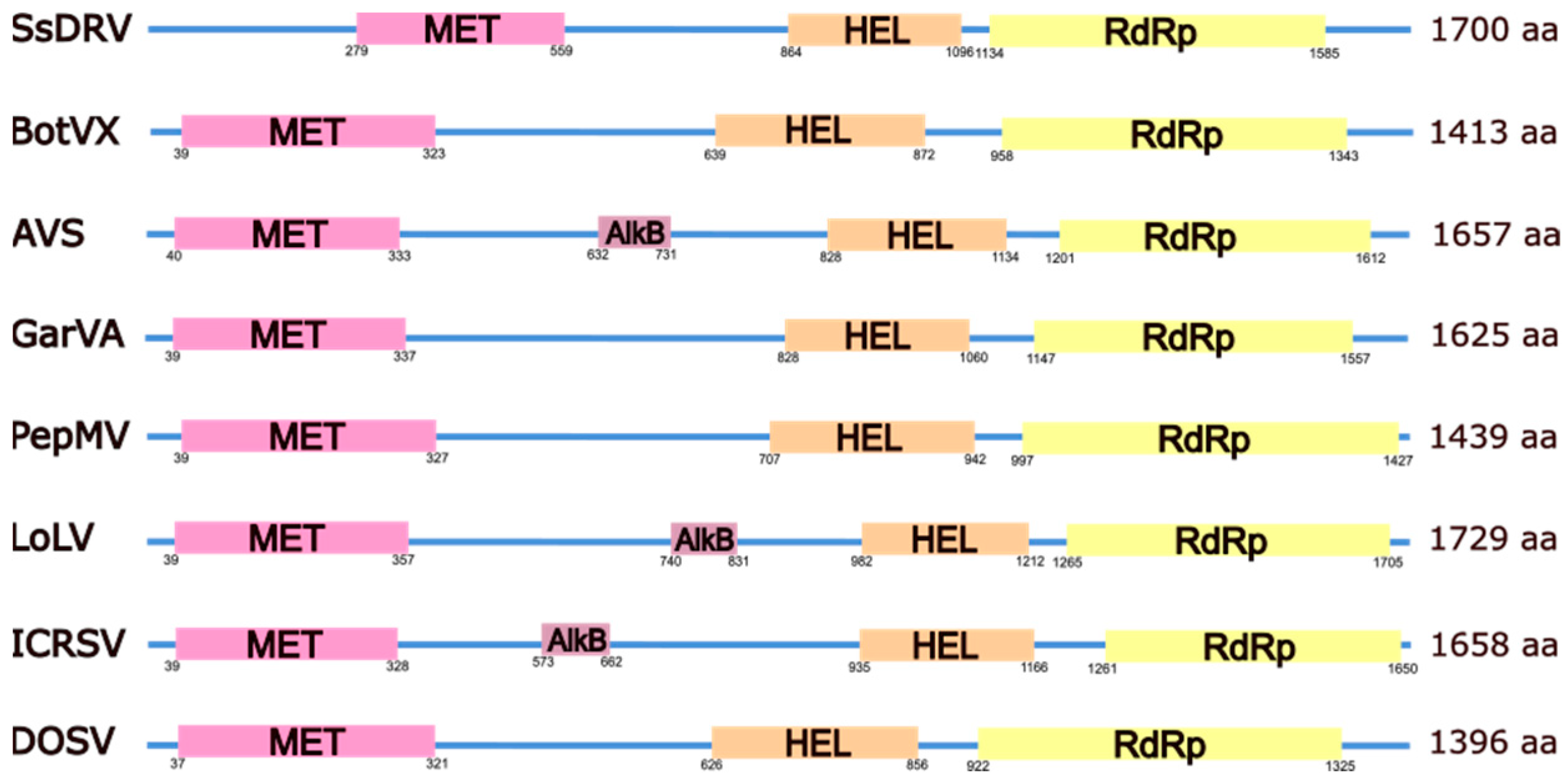
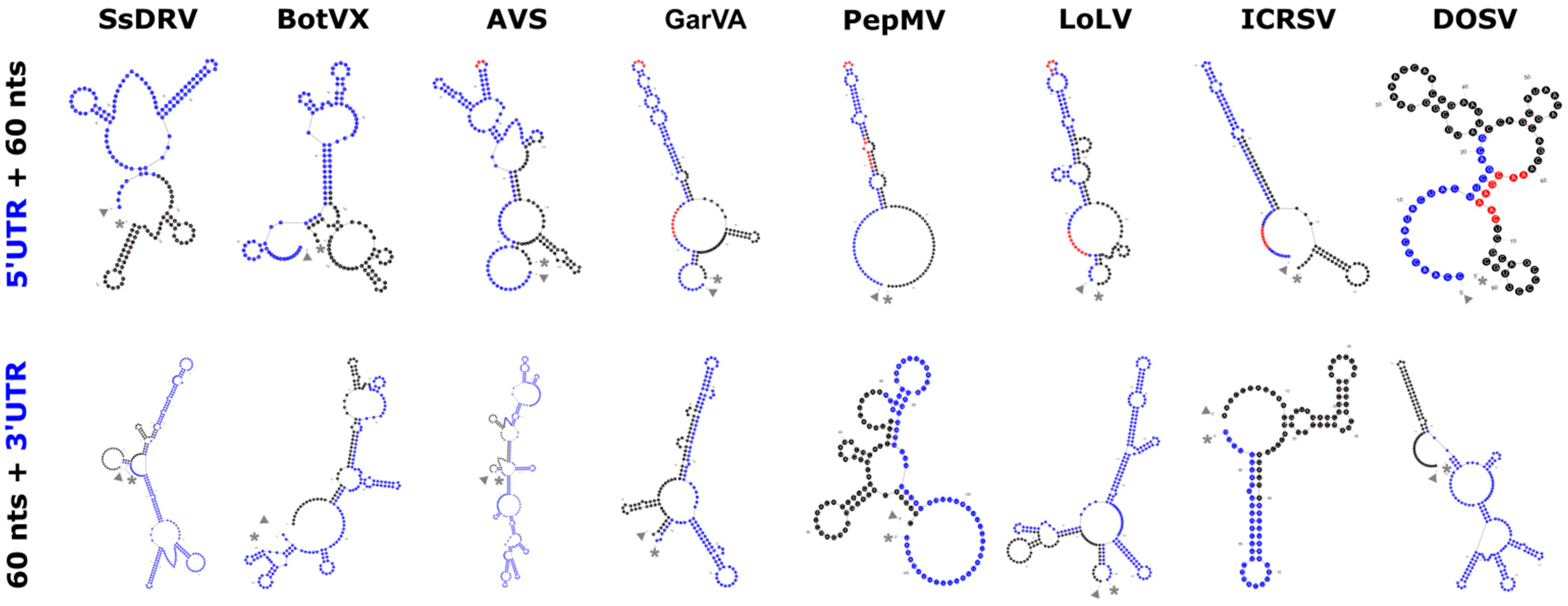
2. The Alphaflexiviridae Genomes
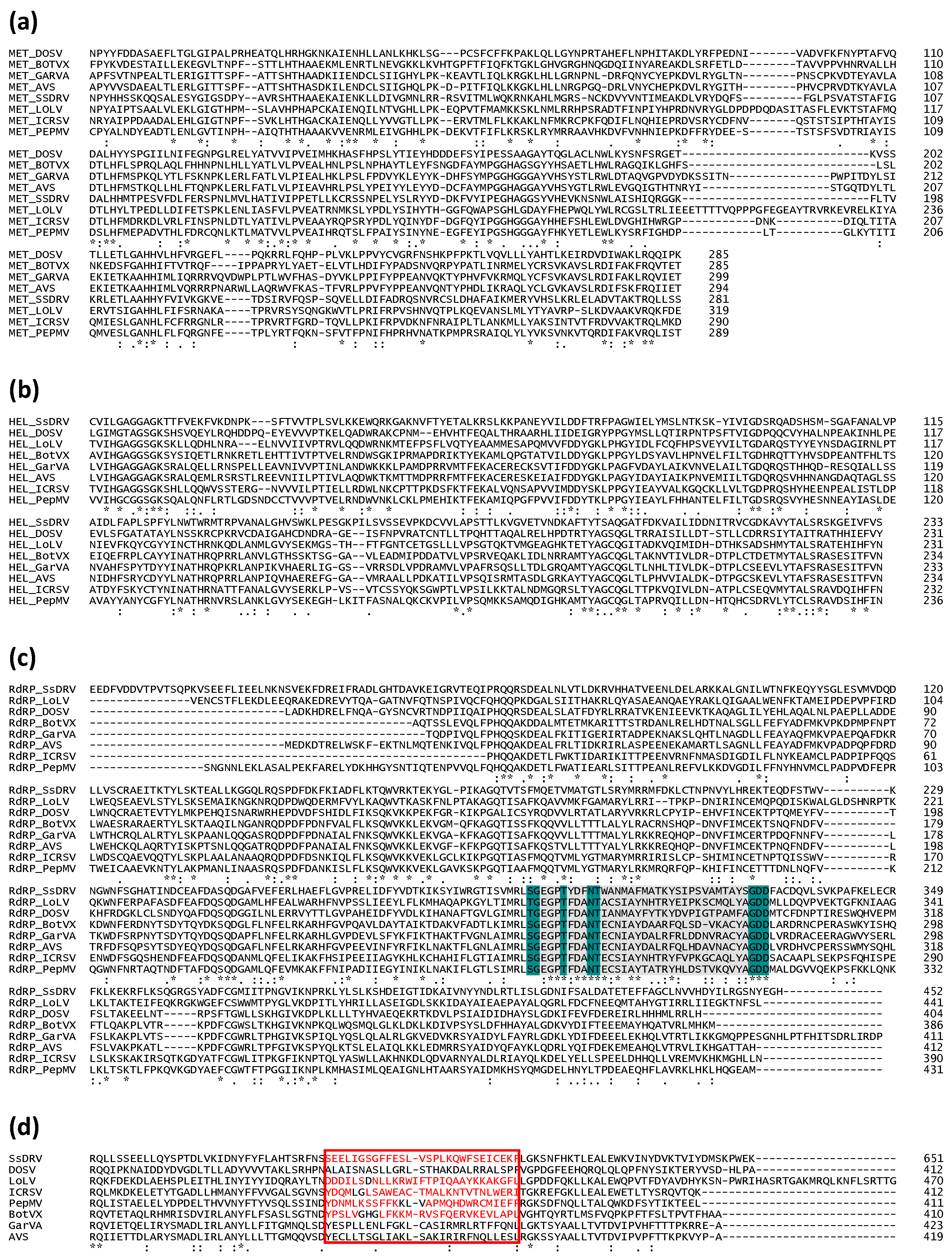
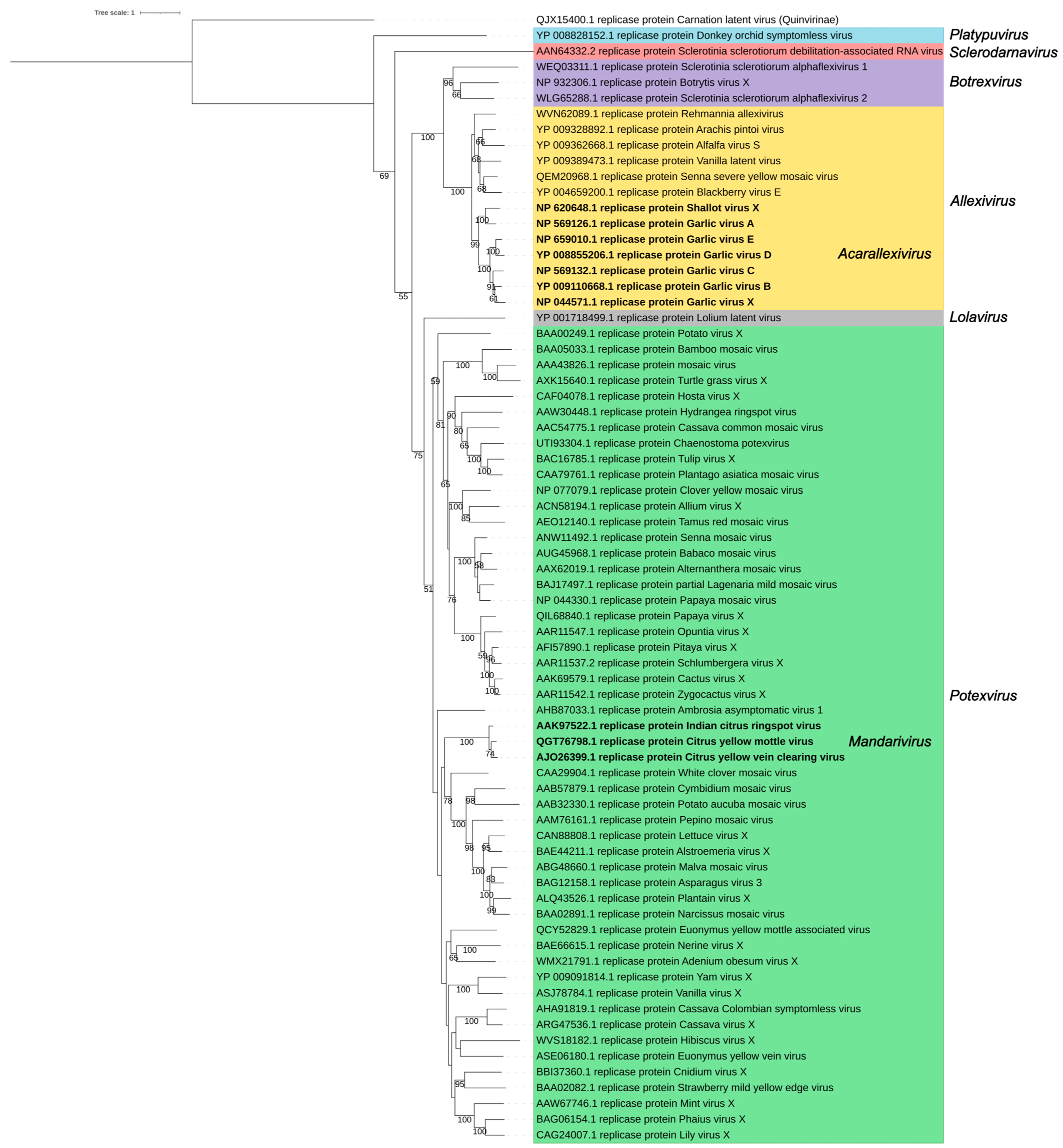
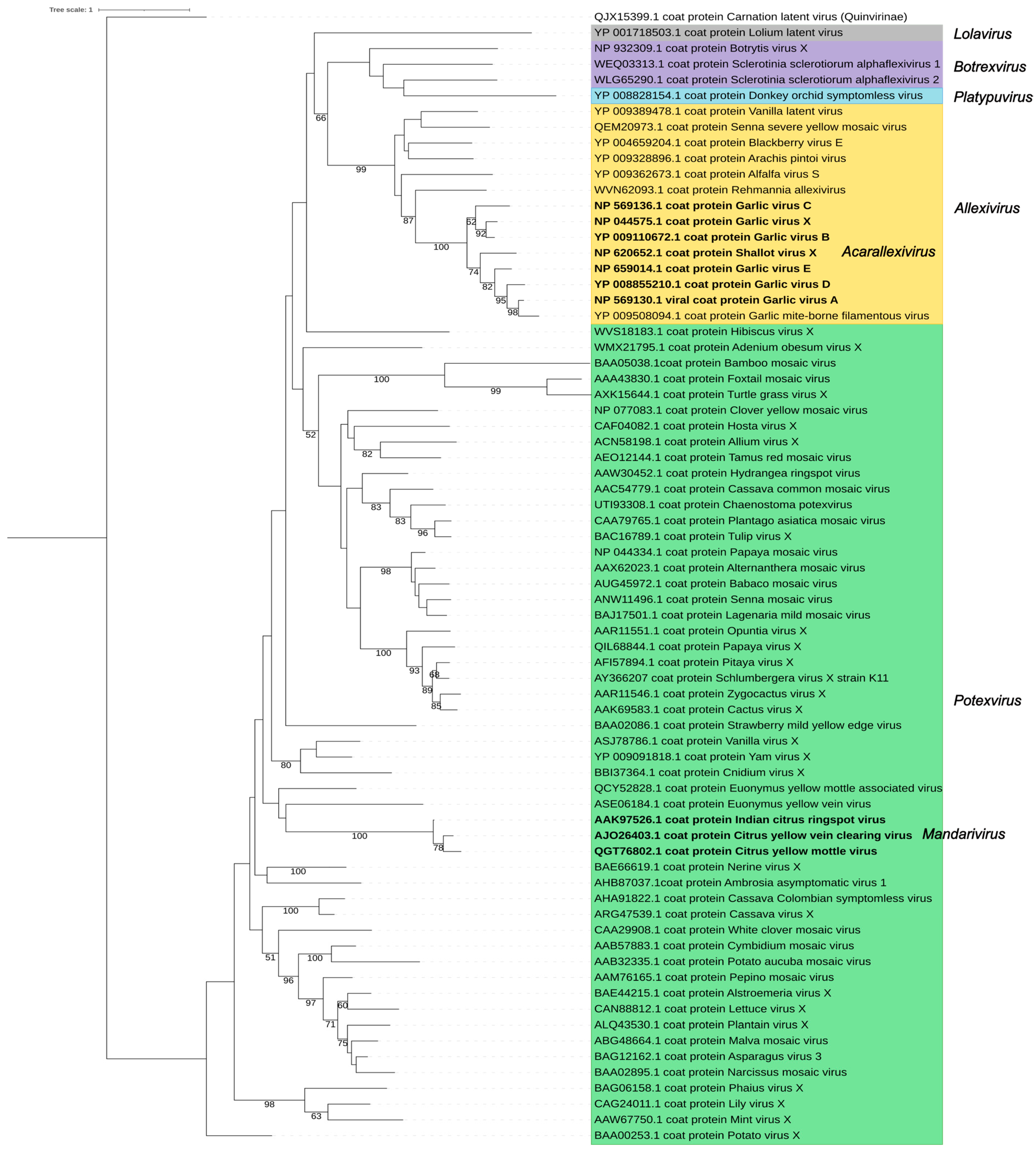
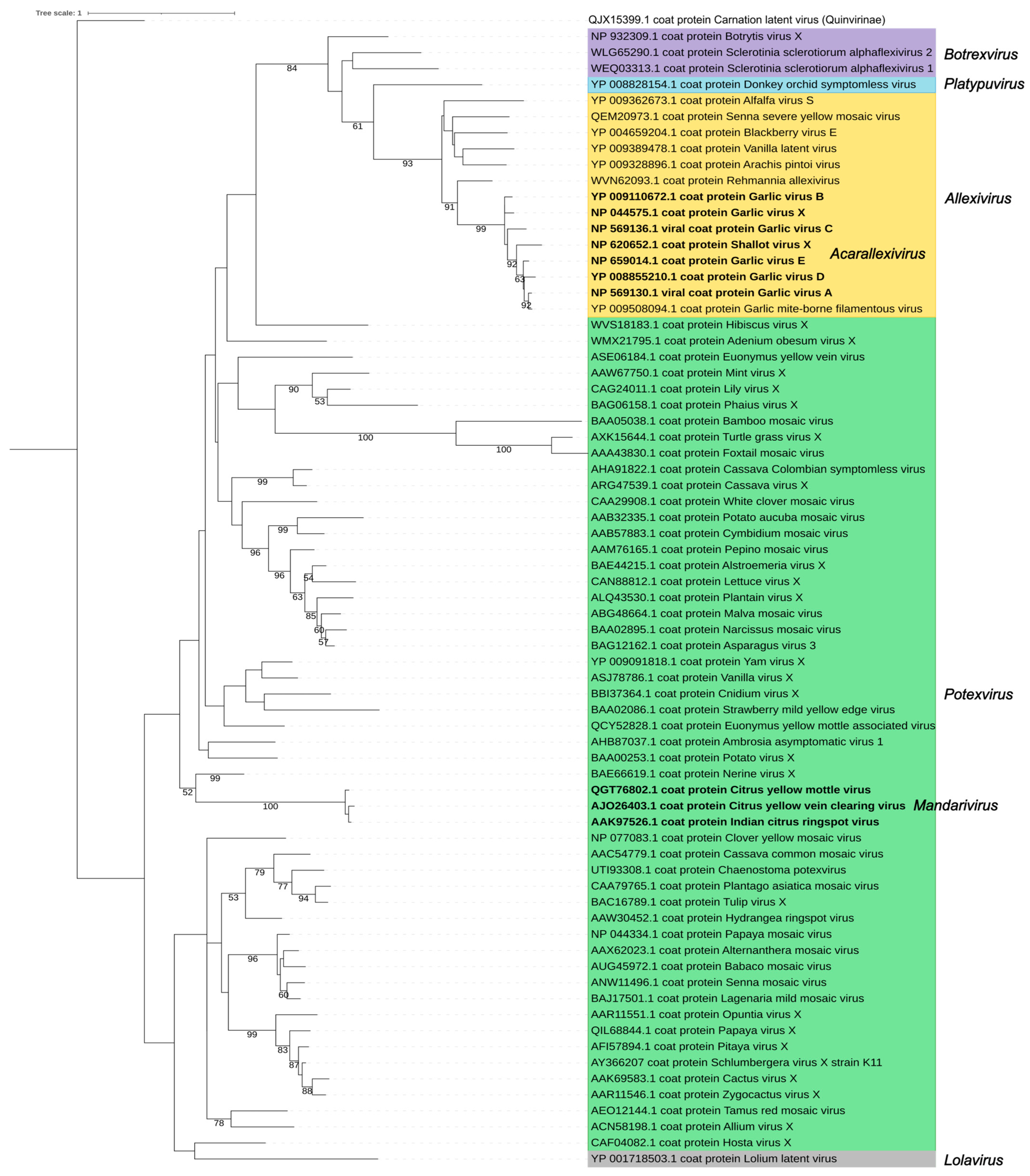
3. The Family Signature: Replicase and Coat Proteins
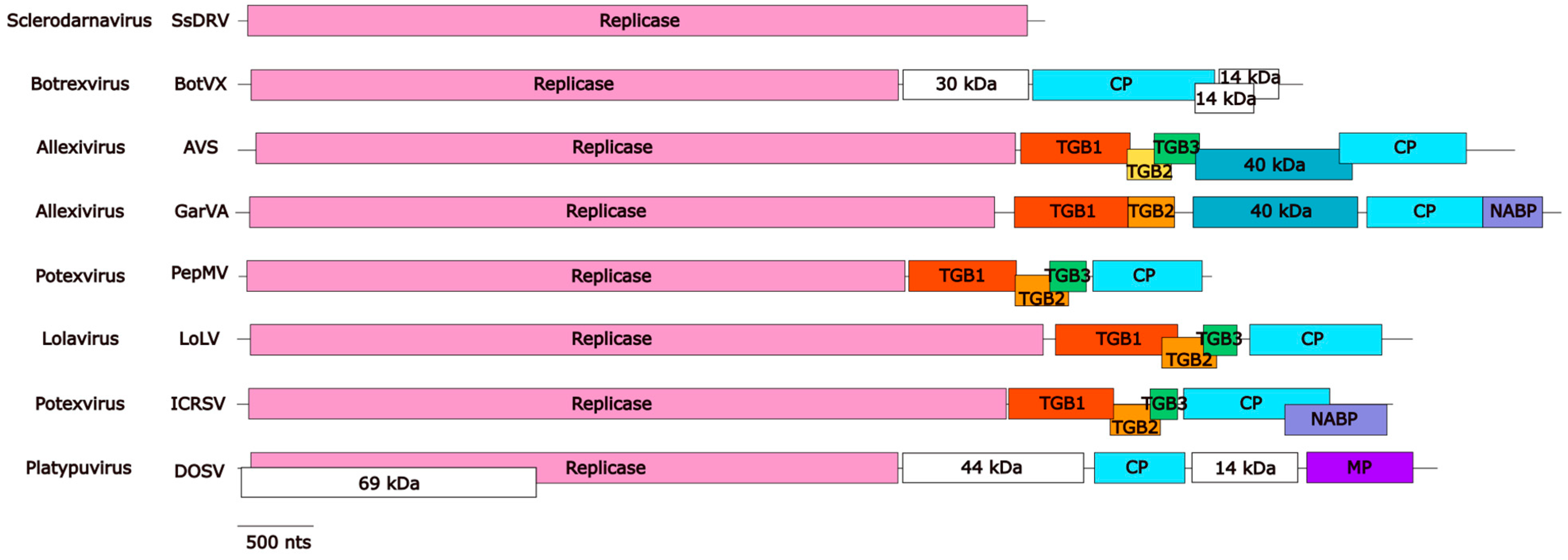
4. The Triple Gene Block (TGB) Proteins Are Conserved Among Plant Alphaflexiviruses with a Few Exceptions
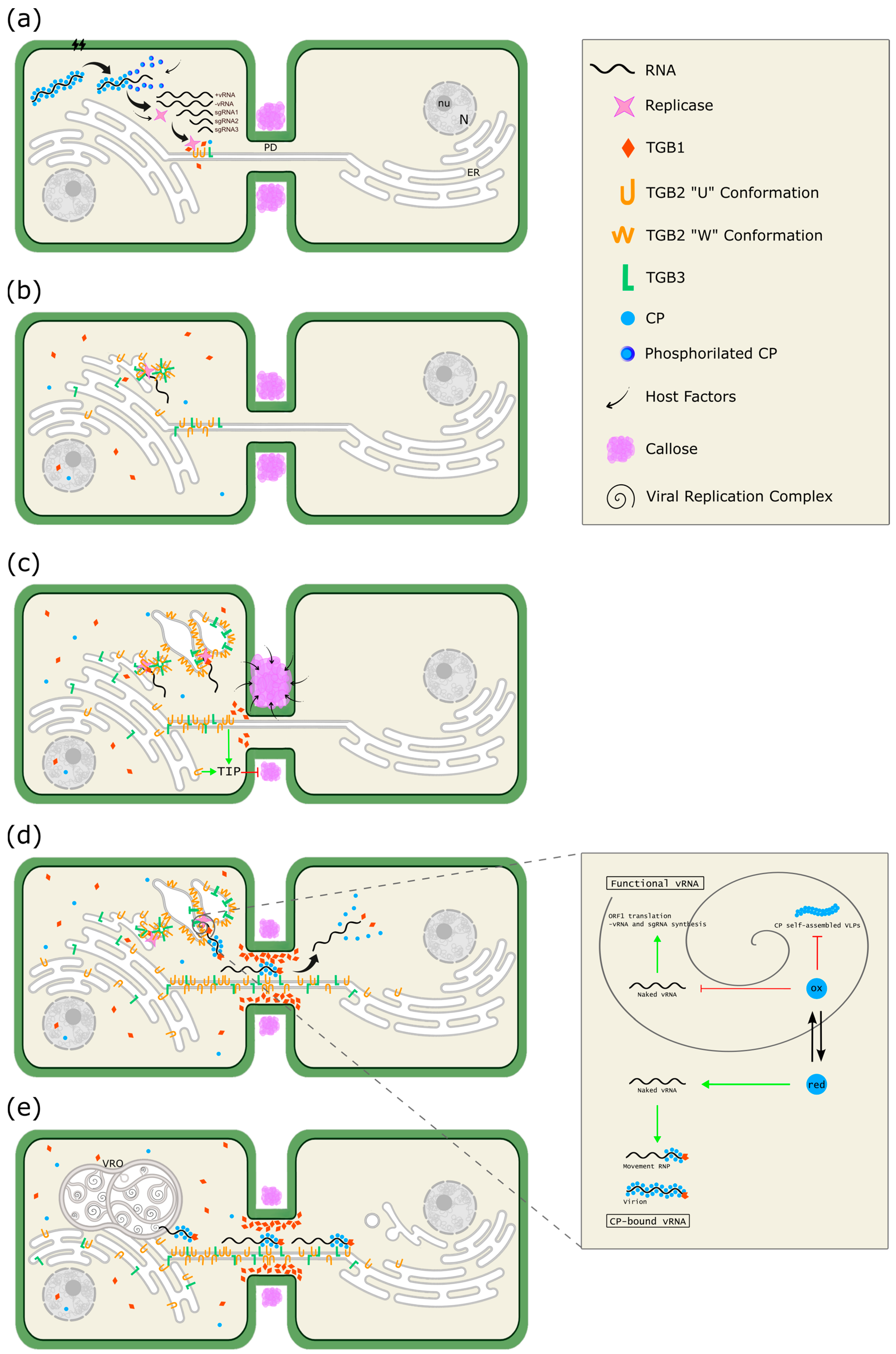
5. A Model for Cellular Remodeling Driven by the Alphaflexiviridae Triple Gene Block (TGB) Proteins
6. 3′-Terminal Nucleic Acid Binding Proteins Appear to Be Accessory in the Alphaflexivirus Genome
7. Conclusions and Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koonin, E.V.; Kuhn, J.H.; Dolja, V.V.; Krupovic, M. Megataxonomy and Global Ecology of the Virosphere. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrad042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholthof, K.-B.G.; Adkins, S.; Czosnek, H.; Palukaitis, P.; Jacquot, E.; Hohn, T.; Hohn, B.; Saunders, K.; Candresse, T.; Ahlquist, P.; et al. Top 10 Plant Viruses in Molecular Plant Pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 938–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verchot, J. Potato Virus X: A Global Potato-Infecting Virus and Type Member of the Potexvirus Genus. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 23, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.D.; Kim, K.-H.; Hemenway, C. Restoration of a Stem-Loop Structure Required for Potato Virus X RNA Accumulation Indicates Selection for a Mismatch and a GNRA Tetraloop. Virology 1999, 260, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.J.; Park, M.R.; Kim, K.W.; Plante, C.A.; Hemenway, C.L.; Kim, K.H. Cis-Acting Sequences Required for Coat Protein Binding and in Vitro Assembly of Potato Virus X. Virology 2005, 334, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.Y.; Cho, W.K.; Kim, K.H. Identification of Tobacco Proteins Associated with the Stem-Loop 1 RNAs of Potato Virus X. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai-Nair, N.; Kim, K.H.; Hemenway, C. Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements in the Potato Virus X 3′ Non-Translated Region Differentially Affect Minus-Strand and Plus-Strand RNA Accumulation. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 326, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Kong, L.R.; Yeh, T.Y.; Cheng, C.P.; Hsu, Y.H.; Lin, N.S. The Conserved 5′ Apical Hairpin Stem Loops of Bamboo Mosaic Virus and Its Satellite RNA Contribute to Replication Competence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4641–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-L.; Meng, M.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Tsai, C.-H. Sequences at the 3′ Untranslated Region of Bamboo Mosaic Potexvirus RNA Interact with the Viral RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.; Lin, N.-S. Interfering Satellite RNAs of Bamboo Mosaic Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Hsu, F.-C.; Lee, S.-C.; Lo, Y.-S.; Wang, J.-D.; Shaw, J.; Taliansky, M.; Chang, B.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Lin, N.-S. The Nucleolar Fibrillarin Protein Is Required for Helper Virus-Independent Long-Distance Trafficking of a Subviral Satellite RNA in Plants. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2586–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, S.Y.; Solovyev, A.G. Triple Gene Block: Modular Design of a Multifunctional Machine for Plant Virus Movement. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, G.P.; Adams, M.J.; Kreuze, J.F.; Dolja, V. V Family Flexiviridae: A Case Study in Virion and Genome Plasticity. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2007, 45, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lezzhov, A.A.; Gushchin, V.A.; Lazareva, E.A.; Vishnichenko, V.K.; Morozov, S.Y.; Solovyev, A.G. Translation of the Shallot Virus X TGB3 Gene Depends on Non-AUG Initiation and Leaky Scanning. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 3159–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butkovic, A.; Dolja, V.V.; Koonin, E.V.; Krupovic, M. Plant Virus Movement Proteins Originated from Jelly-Roll Capsid Proteins. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, S.J.; Li, H.; Jones, M.G.K. Donkey Orchid Symptomless Virus: A Viral “Platypus” from Australian Terrestrial Orchids. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-H.; Huang, Y.-W.; Tsai, C.-H. The Functional Roles of the Cis-Acting Elements in Bamboo Mosaic Virus RNA Genome. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Keima, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Hagiwara-Komoda, Y.; Hosoe, N.; Nishida, S.; Nijo, T.; Oshima, K.; Verchot, J.; Namba, S.; et al. Short 5′ Untranslated Region Enables Optimal Translation of Plant Virus Tricistronic RNA via Leaky Scanning. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e02144-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroly, E.; Ferron, F.; Lescar, J.; Canard, B. Conventional and Unconventional Mechanisms for Capping Viral MRNA. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-I.; Chen, Y.-J.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Meng, M. Characterization of the AdoMet-Dependent Guanylyltransferase Activity That Is Associated with the N Terminus of Bamboo Mosaic Virus Replicase. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-L.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Han, Y.-T.; Meng, M. MRNA Guanylation Catalyzed by the S-Adenosylmethionine-Dependent Guanylyltransferase of Bamboo Mosaic Virus. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13153–13162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Yu, C.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Meng, M. Functional Analysis of the Conserved Histidine Residue of Bamboo Mosaic Virus Capping Enzyme in the Activity for the Formation of the Covalent Enzyme–M7 GMP Intermediate. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-I.; Shih, T.-W.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Han, Y.-T.; Huang, Y.-L.; Meng, M. The Helicase-Like Domain of Plant Potexvirus Replicase Participates in Formation of RNA 5′ Cap Structure by Exhibiting RNA 5′-Triphosphatase Activity. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 12114–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Lee, C.-C. Function and Structural Organization of the Replication Protein of Bamboo Mosaic Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Morris, T.J. Evolution and Taxonomy of Positive-Strand RNA Viruses: Implications of Comparative Analysis of Amino Acid Sequences. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1993, 28, 375–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, T.A.M.; Olsthoorn, R.C.L.; Livieratos, I.C. Role of the Pepino Mosaic Virus 3′-Untranslated Region Elements in Negative-Strand RNA Synthesis in Vitro. Virus Res. 2014, 190, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-C.; Desprez, A.; Olsthoorn, R.C.L. Structural Homology between Bamboo Mosaic Virus and Its Satellite RNAs in the 5’untranslated Region. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Born, E.; Omelchenko, M.V.; Bekkelund, A.; Leihne, V.; Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Falnes, P.O. Viral AlkB Proteins Repair RNA Damage by Oxidative Demethylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5451–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Meng, B. Prediction of the Molecular Boundary and Functionality of Novel Viral AlkB Domains Using Homology Modelling and Principal Component Analysis. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, K.; Sasaki, N.; Yoshida, T.; Suzuki, K.; Masujima, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Watanabe, S.; Tochio, N.; Kigawa, T.; Yamaji, Y.; et al. Identification of a Proline-Kinked Amphipathic α-Helix Downstream from the Methyltransferase Domain of a Potexvirus Replicase and Its Role in Virus Replication and Perinuclear Complex Formation. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaira, A.M.; Lim, H.-S.; Bauchan, G.R.; Owens, R.A.; Natilla, A.; Dienelt, M.M.; Reinsel, M.D.; Hammond, J. Lolium Latent Virus (Alphaflexiviridae) Coat Proteins: Expression and Functions in Infected Plant Tissue. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaira, A.M.; Lim, H.S.; Bauchan, G.; Gulbronson, C.J.; Miozzi, L.; Vinals, N.; Natilla, A.; Hammond, J. The Interaction of Lolium Latent Virus Major Coat Protein with Ankyrin Repeat Protein NbANKr Redirects It to Chloroplasts and Modulates Virus Infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Lu, S.; Wen, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, F.; et al. Genomic Characterization and Molecular Detection of Rehmannia Allexivirus Virus, a Novel Allexivirus Infecting Rehmannia Glutinosa. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirrezabala, X.; Méndez-López, E.; Lasso, G.; Sánchez-Pina, M.A.; Aranda, M.A.; Valle, M. The Near-Atomic CryoEM Structure of a Flexible Filamentous Plant Virus Shows Homology of Its Coat Protein with Nucleoproteins of Animal Viruses. Elife 2015, 4, e11795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, T.; Bohon, J.; Gagné, M.-È.L.; Bolduc, M.; Leclerc, D.; Li, H. Crystal Structure of the Coat Protein of the Flexible Filamentous Papaya Mosaic Virus. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 422, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMaio, F.; Chen, C.-C.; Yu, X.; Frenz, B.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Lin, N.-S.; Egelman, E.H. The Molecular Basis for Flexibility in the Flexible Filamentous Plant Viruses. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinzato, A.; Kandiah, E.; Lico, C.; Betti, C.; Baschieri, S.; Zanotti, G. Atomic Structure of Potato Virus X, the Prototype of the Alphaflexiviridae Family. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuenemann, E.C.; Byrne, M.J.; Peyret, H.; Saunders, K.; Castells-Graells, R.; Ferriol, I.; Santoni, M.; Steele, J.F.C.; Ranson, N.A.; Avesani, L.; et al. A Replicating Viral Vector Greatly Enhances Accumulation of Helical Virus-Like Particles in Plants. Viruses 2021, 13, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-López, E.; Aranda, M.A. A Regulatory Role for the Redox Status of the Pepino Mosaic Virus Coat Protein. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-R.; Seo, J.-K.; Kim, K.-H. Viral and Nonviral Elements in Potexvirus Replication and Movement and in Antiviral Responses. Adv. Virus Res. 2013, 87, 75–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, A.M.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Morel, B.; Stamatakis, A. RAxML-NG: A Fast, Scalable and User-Friendly Tool for Maximum Likelihood Phylogenetic Inference. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4453–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, S.Y.; Solovyev, A.G. Phylogenetic Relationship of Some “Accessory” Helicases of Plant Positive-Stranded RNA Viruses: Toward Understanding the Evolution of Triple Gene Block. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verchot-Lubicz, J.; Torrance, L.; Solovyev, A.G.; Morozov, S.Y.; Jackson, A.O.; Gilmer, D. Varied Movement Strategies Employed by Triple Gene Block–Encoding Viruses. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 1231–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verchot, J.; Angell, S.M.; Baulcombe, D.C. In Vivo Translation of the Triple Gene Block of Potato Virus X Requires Two Subgenomic MRNAs. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8316–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, N.O.; Rakitina, D.V.; Solovyev, A.G.; Schiemann, J.; Morozov, S.Y. RNA Helicase Activity of the Plant Virus Movement Proteins Encoded by the First Gene of the Triple Gene Block. Virology 2002, 296, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshchiner, A.D.; Solovyev, A.G.; Morozov, S.Y.; Kalinina, N.O. A Minimal Region in the NTPase/Helicase Domain of the TGBp1 Plant Virus Movement Protein Is Responsible for ATPase Activity and Cooperative RNA Binding. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3087–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-K.; Chang, B.-Y.; Liao, J.-T.; Lin, N.-S.; Hsu, Y.-H. Arg-16 and Arg-21 in the N-Terminal Region of the Triple-Gene-Block Protein 1 of Bamboo Mosaic Virus Are Essential for Virus Movement. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, D.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Wung, C.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; Lin, N.-S.; Chang, B.-Y. Functional Analyses and Identification of Two Arginine Residues Essential to the ATP-Utilizing Activity of the Triple Gene Block Protein 1 of Bamboo Mosaic Potexvirus. Virology 2000, 277, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouleau, M.; Smith, R.J.; Bancroft, J.B.; Mackie, G.A. Purification, Properties, and Subcellular Localization of Foxtail Mosaic Potexvirus 26-KDa Protein. Virology 1994, 204, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wung, C.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Liou, D.Y.; Huang, W.C.; Lin, N.S.; Chang, B.Y. Identification of the RNA-Binding Sites of the Triple Gene Block Protein 1 of Bamboo Mosaic Potexvirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinnet, O.; Lederer, C.; Baulcombe, D.C. A Viral Movement Protein Prevents Spread of the Gene Silencing Signal in Nicotiana Benthamiana. Cell 2000, 103, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senshu, H.; Ozeki, J.; Komatsu, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Hatada, K.; Aoyama, M.; Kagiwada, S.; Yamaji, Y.; Namba, S. Variability in the Level of RNA Silencing Suppression Caused by Triple Gene Block Protein 1 (TGBp1) from Various Potexviruses during Infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaubert, M.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mello, A.F.S.; Perry, K.L.; Moffett, P. ARGONAUTE2 Mediates RNA-Silencing Antiviral Defenses against Potato Virus Xin Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, E.H.; Rakitina, D.V.; Morozov, S.Y.; Baulcombe, D.C. Cell-to-Cell Movement of Potato Potexvirus X Is Dependent on Suppression of RNA Silencing. Plant J. 2005, 44, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.-S.; Vaira, A.M.; Domier, L.L.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, H.G.; Hammond, J. Efficiency of VIGS and Gene Expression in a Novel Bipartite Potexvirus Vector Delivery System as a Function of Strength of TGB1 Silencing Suppression. Virology 2010, 402, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.-S.; Vaira, A.M.; Reinsel, M.D.; Bae, H.; Bailey, B.A.; Dornier, L.L.; Hammond, J. Pathogenicity of Alternanthera Mosaic Virus Is Affected by Determinants in RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase and by Reduced Efficacy of Silencing Suppression in a Movement-Competent TGB1. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Módena, N.A.; Zelada, A.M.; Conte, F.; Mentaberry, A. Phosphorylation of the TGBp1 Movement Protein of Potato Virus X by a Nicotiana Tabacum CK2-like Activity. Virus Res. 2008, 137, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-C.; Chen, I.-H.; Hou, P.-Y.; Wang, L.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Cheng, C.-P. The Phosphorylation of the Movement Protein TGBp1 Regulates the Accumulation of the Bamboo Mosaic Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2024, 105, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilsner, J.; Linnik, O.; Wright, K.M.; Bell, K.; Roberts, A.G.; Lacomme, C.; Santa Cruz, S.; Oparka, K.J.; Linnik, O.; Santa Cruz, S.; et al. The TGB1 Movement Protein of Potato Virus X Reorganizes Actin and Endomembranes into the X-Body, a Viral Replication Factory. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-T.; Chou, Y.-L.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, T.-M.; Lin, N.-S.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chang, B.-Y. Topological Properties of the Triple Gene Block Protein 2 of Bamboo Mosaic Virus. Virology 2008, 379, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Chai, M.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, A.; Cheng, X. The Potato Virus X TGBp2 Protein Plays Dual Functional Roles in Viral Replication and Movement. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01635-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazareva, E.A.; Lezzhov, A.A.; Chergintsev, D.A.; Golyshev, S.A.; Dolja, V.V.; Morozov, S.Y.; Heinlein, M.; Solovyev, A.G. Reticulon-like Properties of a Plant Virus-encoded Movement Protein. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.J.; Samuels, T.D.; Wang, Y.S.; Blancaflor, E.; Payton, M.; Mitra, R.; Krishnamurthy, K.; Nelson, R.S.; Verchot-Lubicz, J. The Potato Virus X TGBp2 Movement Protein Associates with Endoplasmic Reticulum-Derived Vesicles during Virus Infection. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 1877–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilsner, J.; Linnik, O.; Louveaux, M.; Roberts, I.M.; Chapman, S.N.; Oparka, K.J. Replication and Trafficking of a Plant Virus Are Coupled at the Entrances of Plasmodesmata. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, A.; Meshi, T. Cell-to-Cell Movement of Potato Virus X: The Role of P12 and P8 Encoded by the Second and Third Open Reading Frames of the Triple Gene Block. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2001, 14, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A.R.; Heppler, M.L.; Ju, H.J.; Krishnamurthy, K.; Payton, M.E.; Verchot-Lubicz, J. Potato Virus X TGBp1 Induces Plasmodesmata Gating and Moves between Cells in Several Host Species Whereas CP Moves Only in N. Benthamiana Leaves. Virology 2004, 328, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.-L.; Hung, Y.-J.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Hsu, H.-T.; Yang, J.-Y.; Wung, C.-H.; Lin, N.-S.; Meng, M.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chang, B.-Y. The Stable Association of Virion with the Triple-Gene-Block Protein 3-Based Complex of Bamboo Mosaic Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, S.Y.; Solovyev, A.G. Small Hydrophobic Viral Proteins Involved in Intercellular Movement of Diverse Plant Virus Genomes. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 305–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.M.; Chen, S.; Payton, M.; Dickman, M.B.; Verchot, J. TGBp3 Triggers the Unfolded Protein Response and SKP1-Dependent Programmed Cell Death. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasiów-Jaroszewska, B.; Borodynko, N.; Jackowiak, P.; Figlerowicz, M.; Pospieszny, H. Single Mutation Converts Mild Pathotype of the Pepino Mosaic Virus into Necrotic One. Virus Res. 2011, 159, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabekov, J.G.; Rodionova, N.P.; Karpova, O.V.; Kozlovsky, S.V.; Novikov, V.K.; Arkhipenko, M.V. Translational Activation of Encapsidated Potato Virus X RNA by Coat Protein Phosphorylation. Virology 2001, 286, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Sun, C.I.; Hu, C.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Meng, M.; Lin, N.S.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P.; Hsu, Y.H. A Viral Movement Protein Co-Opts Endoplasmic Reticulum Luminal-Binding Protein and Calreticulin to Promote Intracellular Movement. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 904–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, S.; Cowan, G.H.; Ziegler, A.; Roberts, A.G.; Oparka, K.J.; Torrance, L. Two Plant–Viral Movement Proteins Traffic in the Endocytic Recycling Pathway. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamunusinghe, D.; Hemenway, C.L.; Nelson, R.S.; Sanderfoot, A.A.; Ye, C.M.; Silva, M.A.T.; Payton, M.; Verchot-Lubicz, J. Analysis of Potato Virus X Replicase and TGBp3 Subcellular Locations. Virology 2009, 393, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, C.W. Traffic of a Viral Movement Protein Complex to the Highly Curved Tubules of the Cortical Endoplasmic Reticulum. Traffic 2010, 11, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabekov, J.G.; Rodionova, N.P.; Karpova, O.V.; Kozlovsky, S.V.; Poljakov, V.Y. The Movement Protein-Triggered in Situ Conversion of Potato Virus X Virion RNA from a Nontranslatable into a Translatable Form. Virology 2000, 271, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perraki, A.; Gronnier, J.; Gouguet, P.; Boudsocq, M.; Deroubaix, A.F.; Simon, V.; German-Retana, S.; Legrand, A.; Habenstein, B.; Zipfel, C.; et al. REM1.3’s Phospho-Status Defines Its Plasma Membrane Nanodomain Organization and Activity in Restricting PVX Cell-to-Cell Movement. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridborg, I.; Grainger, J.; Page, A.; Coleman, M.; Findlay, K.; Angell, S. TIP, a Novel Host Factor Linking Callose Degradation with the Cell-to-Cell Movement of Potato Virus X. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnik, O.; Liesche, J.; Tilsner, J.; Oparka, K.J. Unraveling the Structure of Viral Replication Complexes at Super-Resolution. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Boyko, V.P.; Dolja, V.V. Small Cysteine-Rich Proteins of Different Groups of Plant Rna Viruses Are Related to Different Families of Nucleic Acid-Binding Proteins. Virology 1991, 181, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andika, I.B.; Kondo, H.; Nishiguchi, M.; Tamada, T. The Cysteine-Rich Proteins of Beet Necrotic Yellow Vein Virus and Tobacco Rattle Virus Contribute to Efficient Suppression of Silencing in Roots. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kawakubo, S.; Takahashi, H.; Masuta, C. Two Mutually Exclusive Evolutionary Scenarios for Allexiviruses That Overcome Host RNA Silencing and Autophagy by Regulating Viral CRP Expression. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Lu, Y.; Peng, J.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Y.; et al. P15 Encoded by Garlic Virus X Is a Pathogenicity Factor and RNA Silencing Suppressor. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Shimura, H.; Masuta, C. Allexiviruses May Have Acquired Inserted Sequences between the CP and CRP Genes to Change the Translation Reinitiation Strategy of CRP. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ramón, F.; Sempere, R.N.; Méndez-López, E.; Sánchez-Pina, M.A.; Aranda, M.A. Second Generation of Pepino Mosaic Virus Vectors: Improved Stability in Tomato and a Wide Range of Reporter Genes. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roossinck, M.J. Evolutionary and Ecological Links between Plant and Fungal Viruses. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.H.T.; Méndez-López, E.; Wang, C.; Commandeur, U.; Aranda, M.A.; Steinmetz, N.F. Biodistribution of Filamentous Plant Virus Nanoparticles: Pepino Mosaic Virus versus Potato Virus X. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Úbeda, J.R.; Aranda, M.A.; Donaire, L. Alphaflexiviridae in Focus: Genomic Signatures, Conserved Elements and Viral-Driven Cellular Remodeling. Viruses 2025, 17, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050611
Úbeda JR, Aranda MA, Donaire L. Alphaflexiviridae in Focus: Genomic Signatures, Conserved Elements and Viral-Driven Cellular Remodeling. Viruses. 2025; 17(5):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050611
Chicago/Turabian StyleÚbeda, Jesús R., Miguel A. Aranda, and Livia Donaire. 2025. "Alphaflexiviridae in Focus: Genomic Signatures, Conserved Elements and Viral-Driven Cellular Remodeling" Viruses 17, no. 5: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050611
APA StyleÚbeda, J. R., Aranda, M. A., & Donaire, L. (2025). Alphaflexiviridae in Focus: Genomic Signatures, Conserved Elements and Viral-Driven Cellular Remodeling. Viruses, 17(5), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050611








