Sensorless Control Method of High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Discrete Current Error
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Rotor Position Estimation Method and Angle Error Analysis Based on Sliding Mode Observer
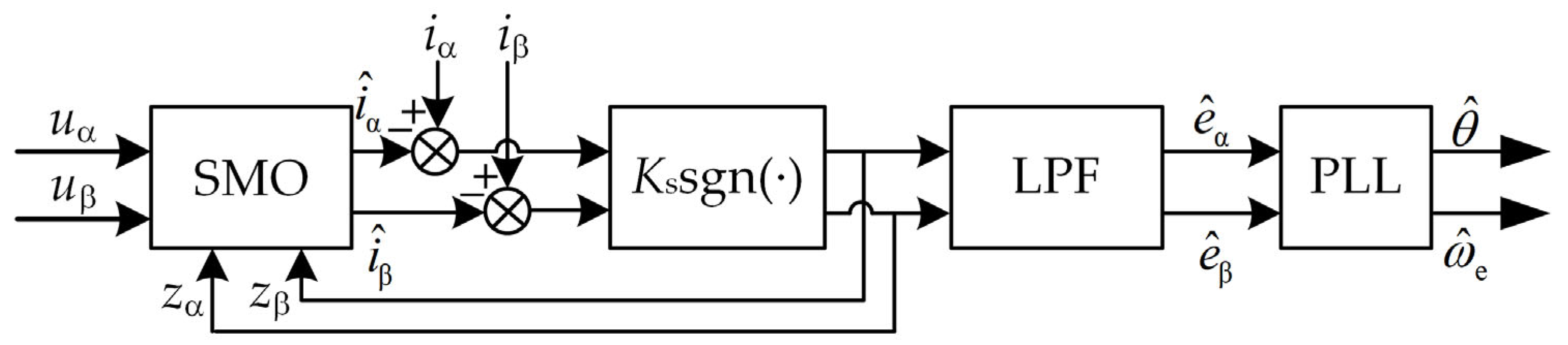
2.1. Principle of Estimating Rotor Position Based on Sliding Mode Algorithm
2.2. Analysis of Estimation Angle Error in the State of High-Speed and Low Carrier Wave Ratio
2.2.1. The Delay of the Sensorless Algorithm
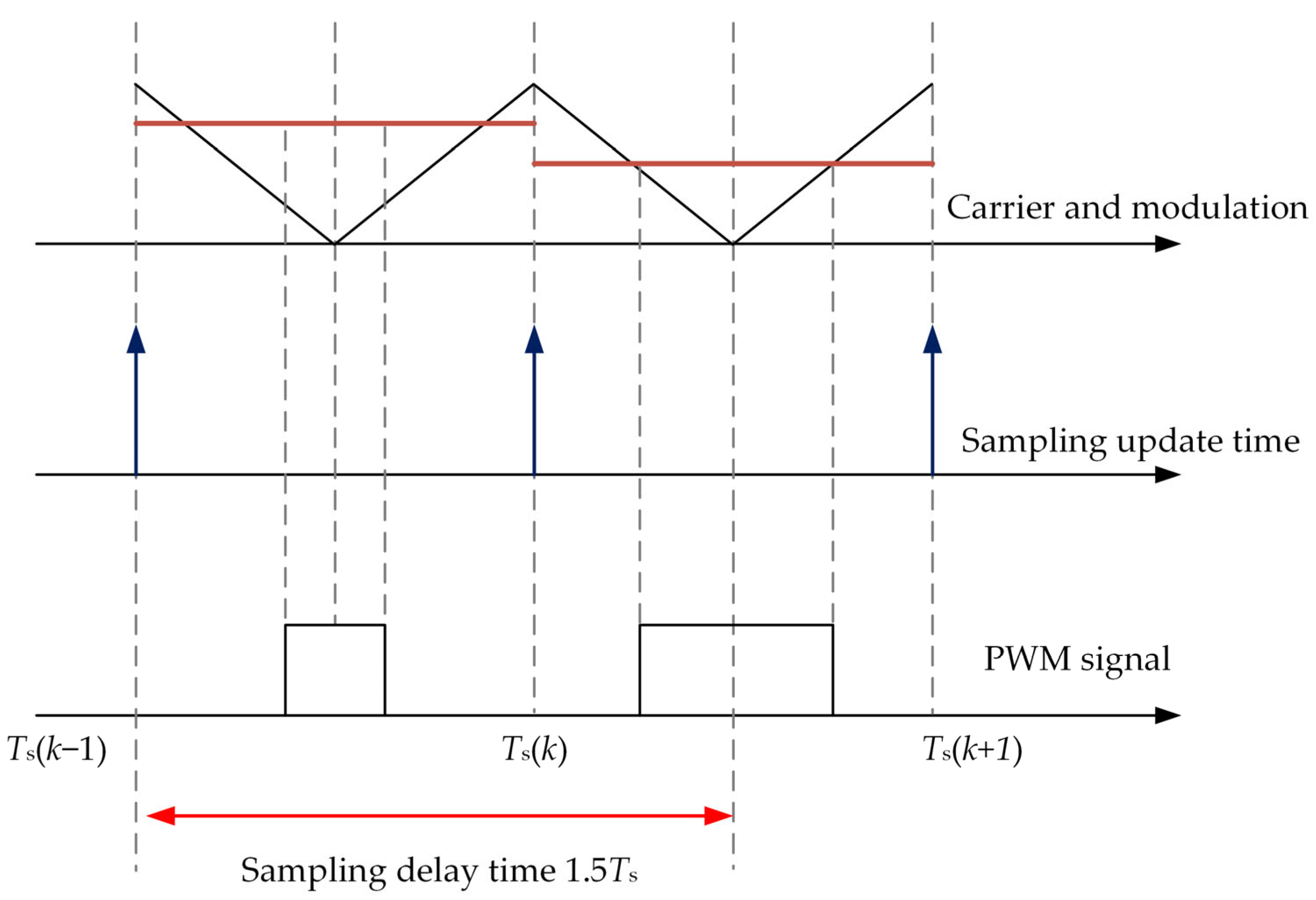
2.2.2. Digital Control Delay
2.2.3. Other Delay Issues
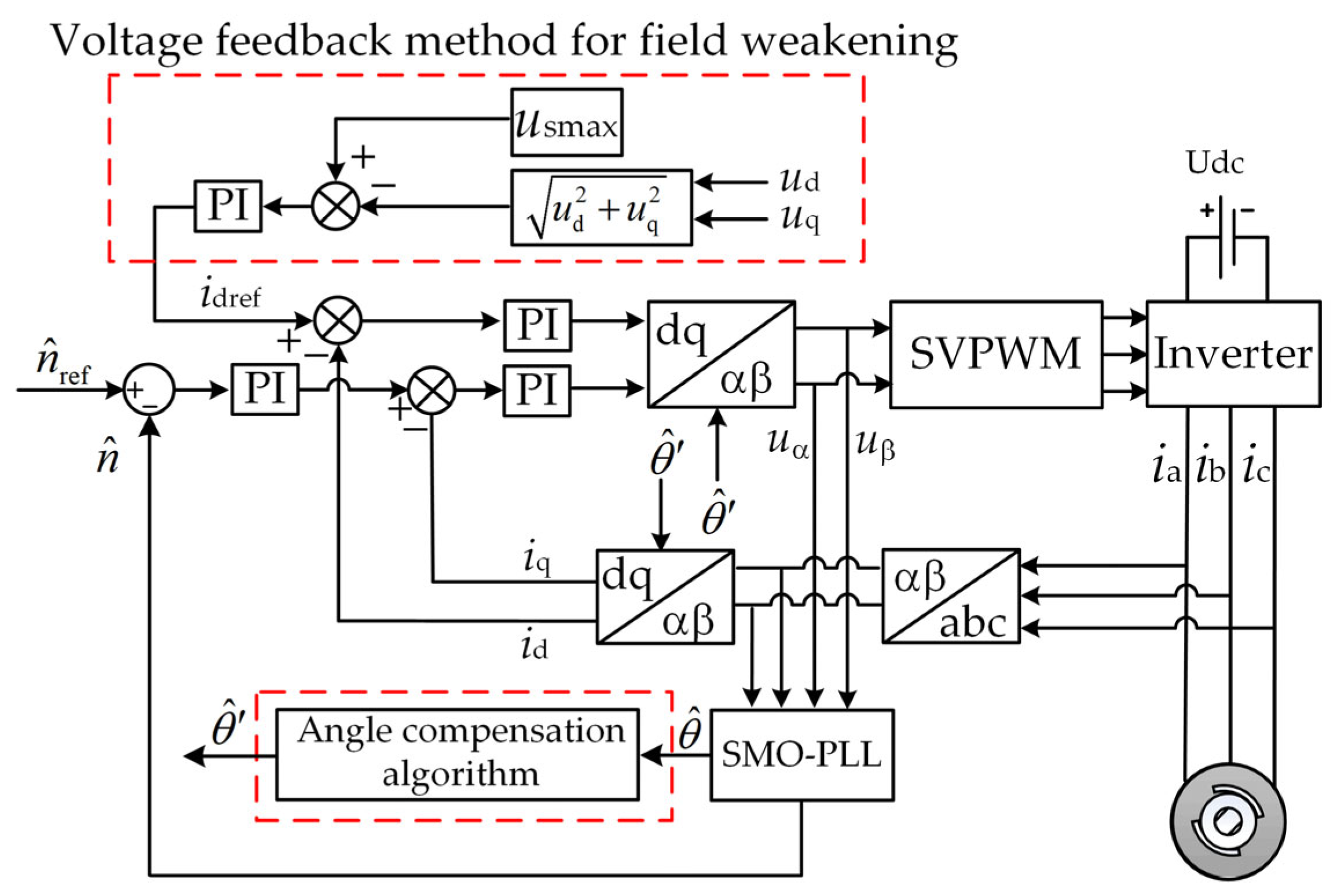
3. Angle Compensation Method Based on Discrete Current Error
3.1. Analysis of Angle Error Judgment Basis
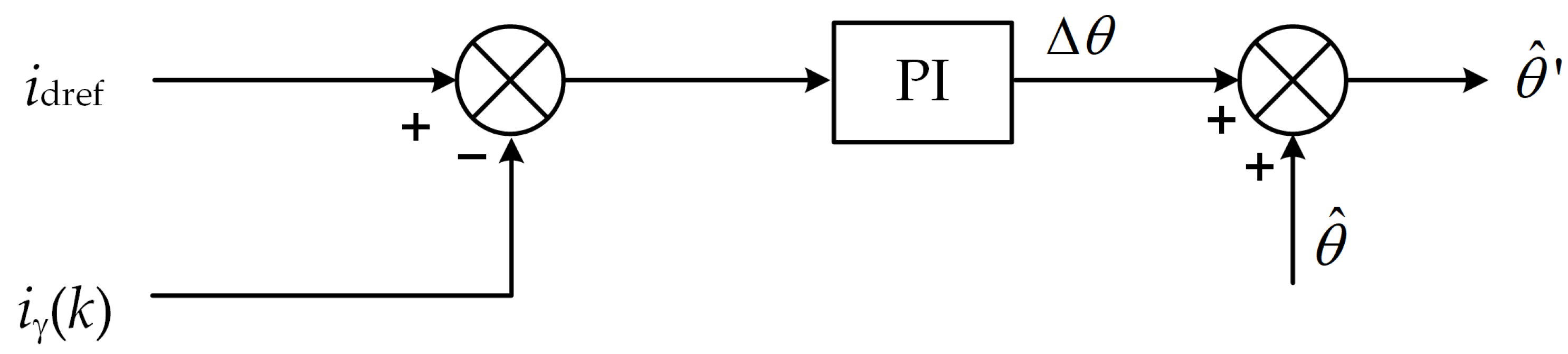
3.2. Principle of Angle Compensation Method Based on Discrete Current Error
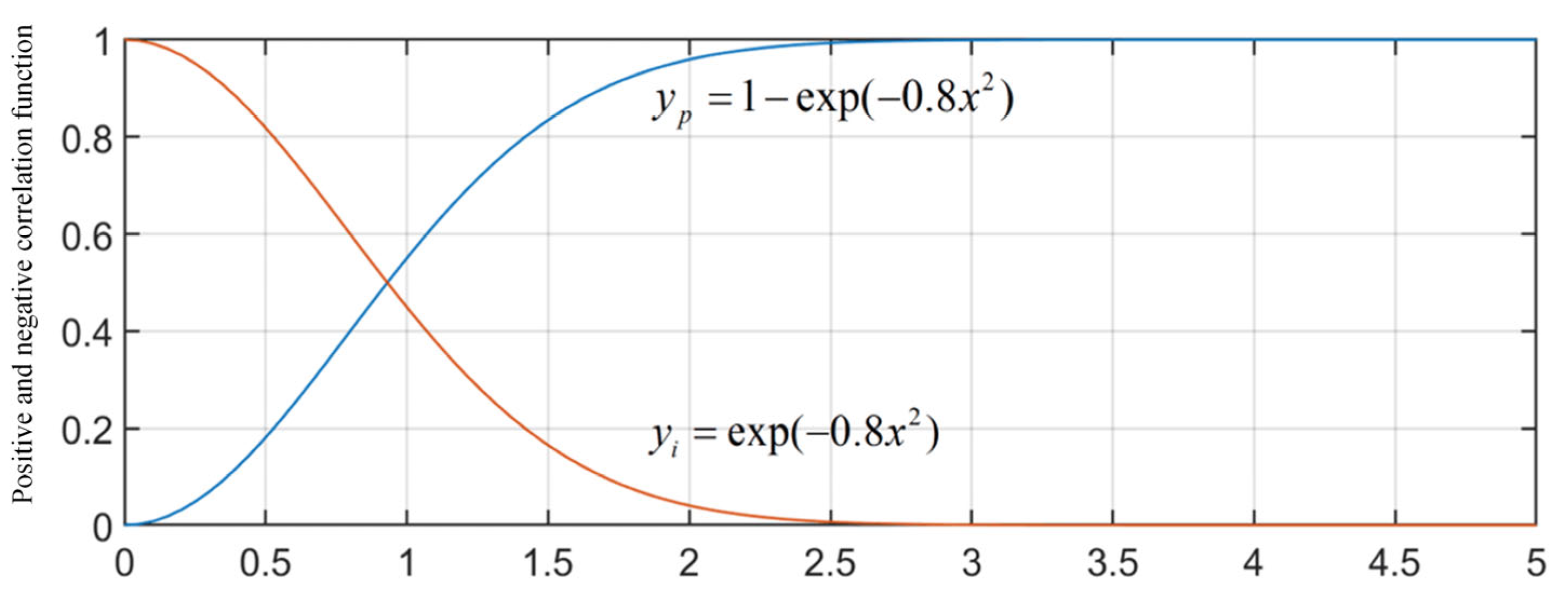
3.3. Variable Proportional Integral Coefficient PI Regulator
3.4. Parameter Robustness Analysis of the Proposed Method
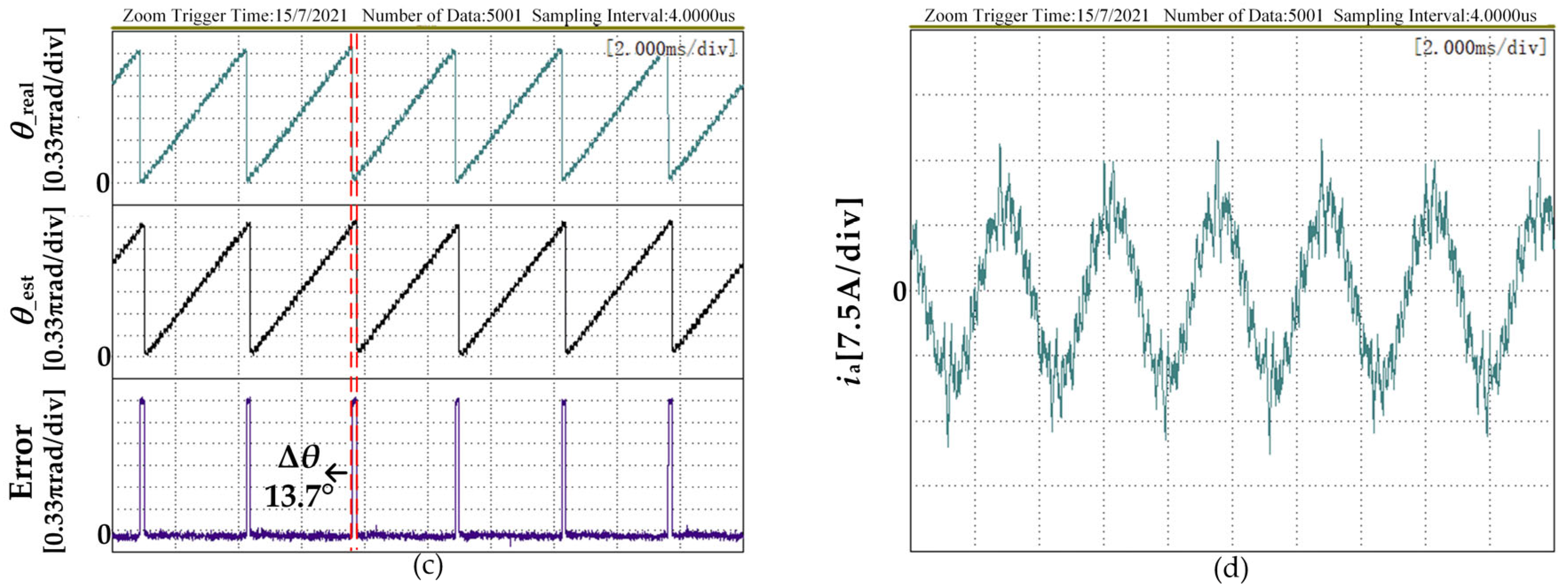
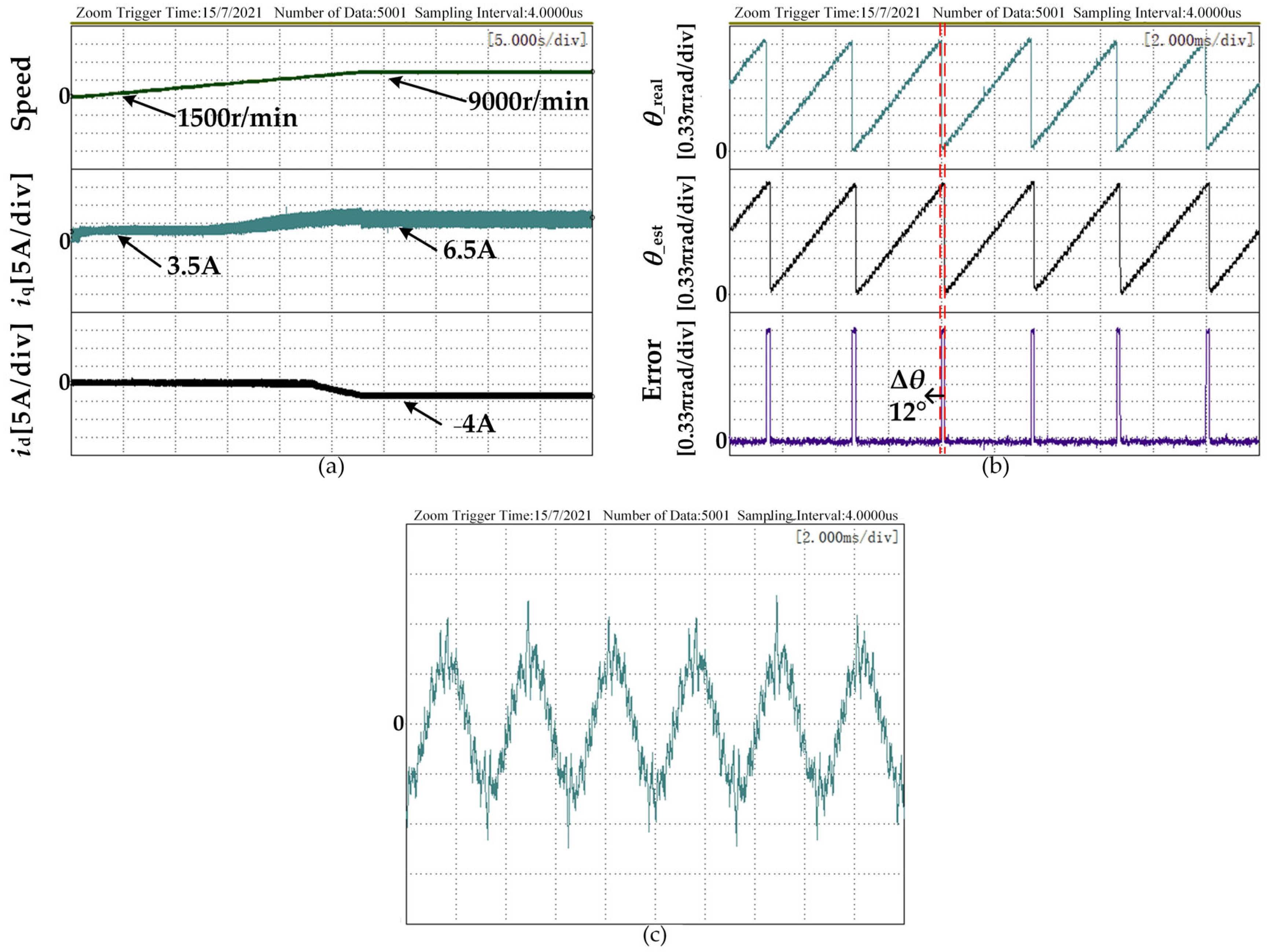
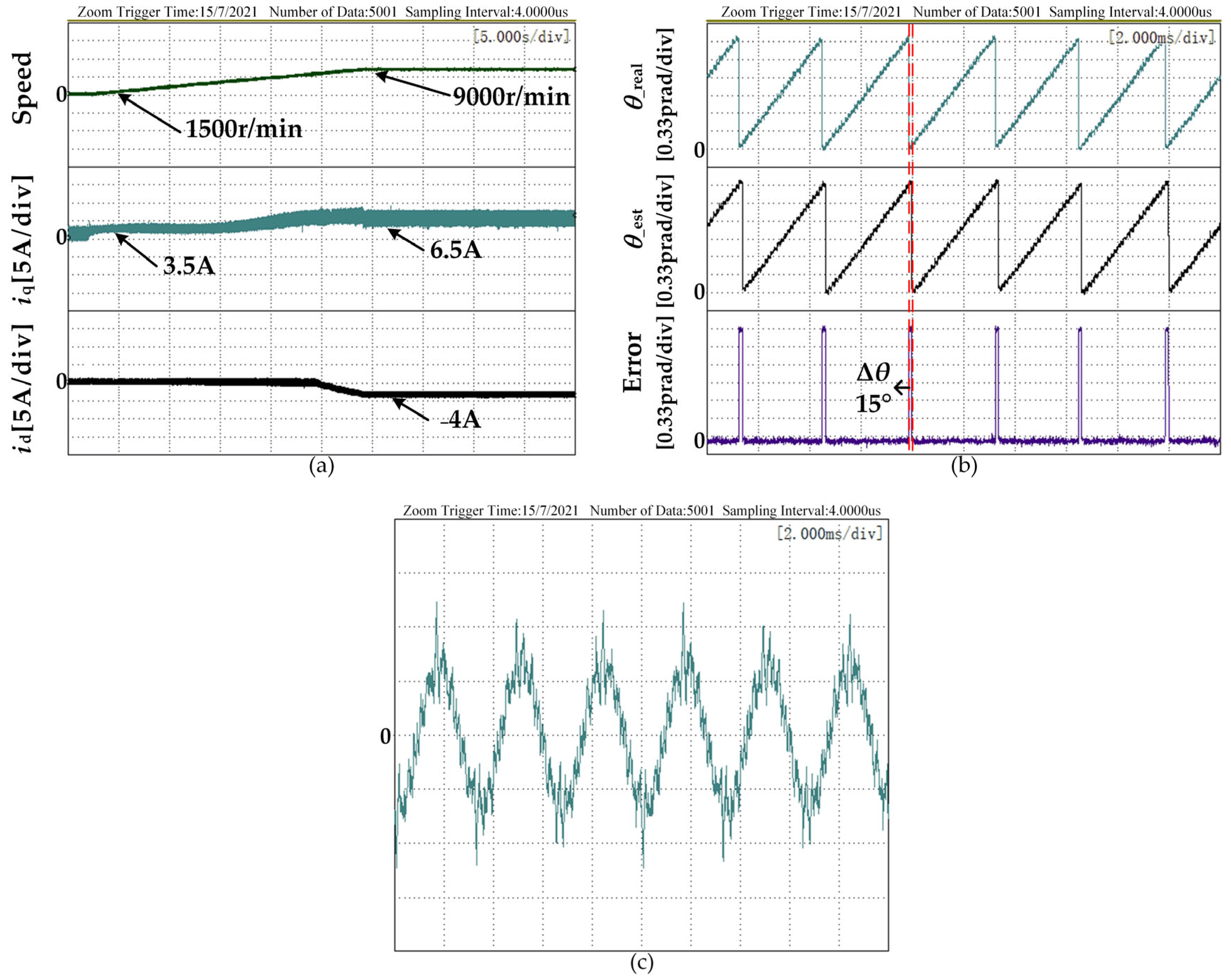
4. Experimental Verification and Result Analysis
4.1. Experimental Platform Parameters
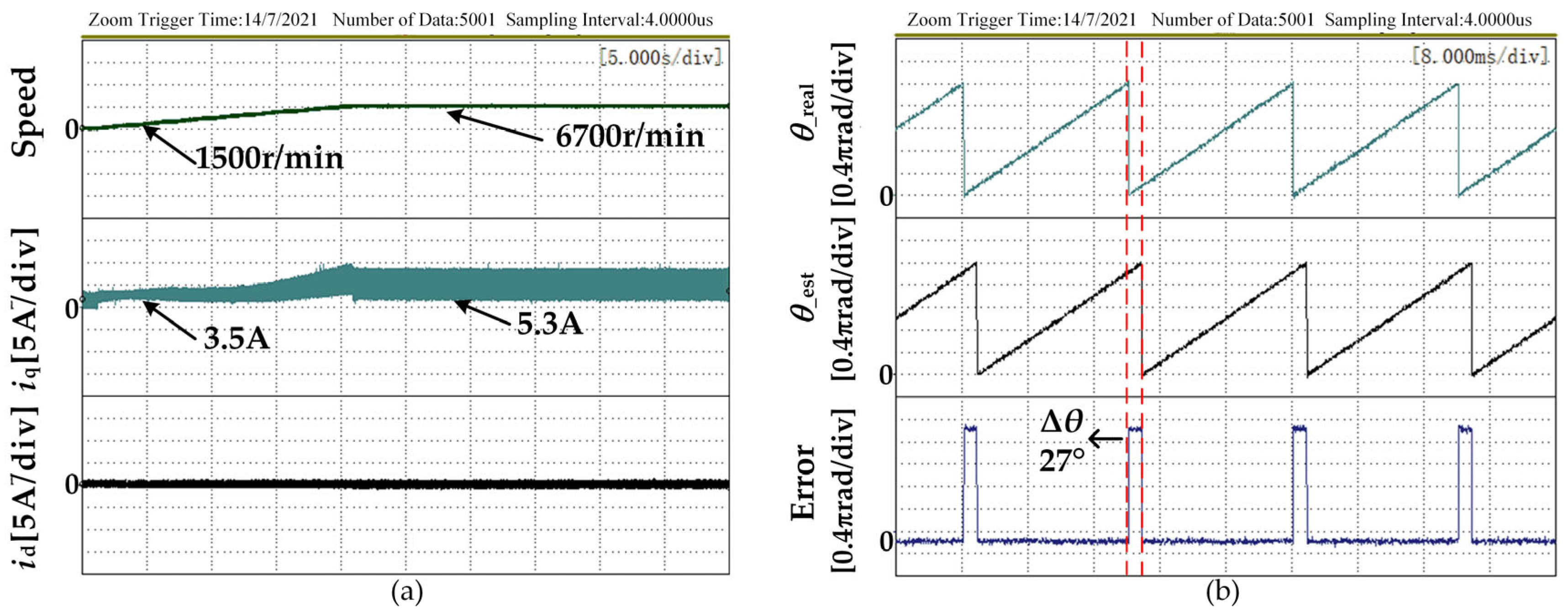
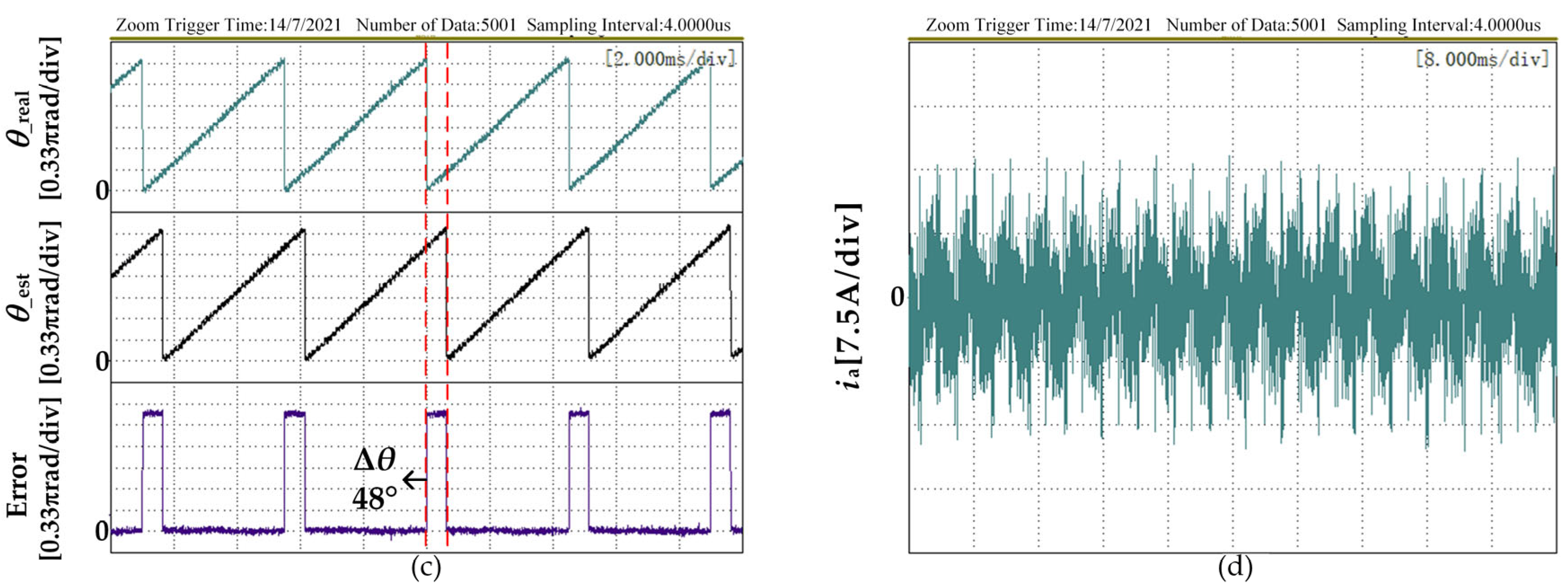
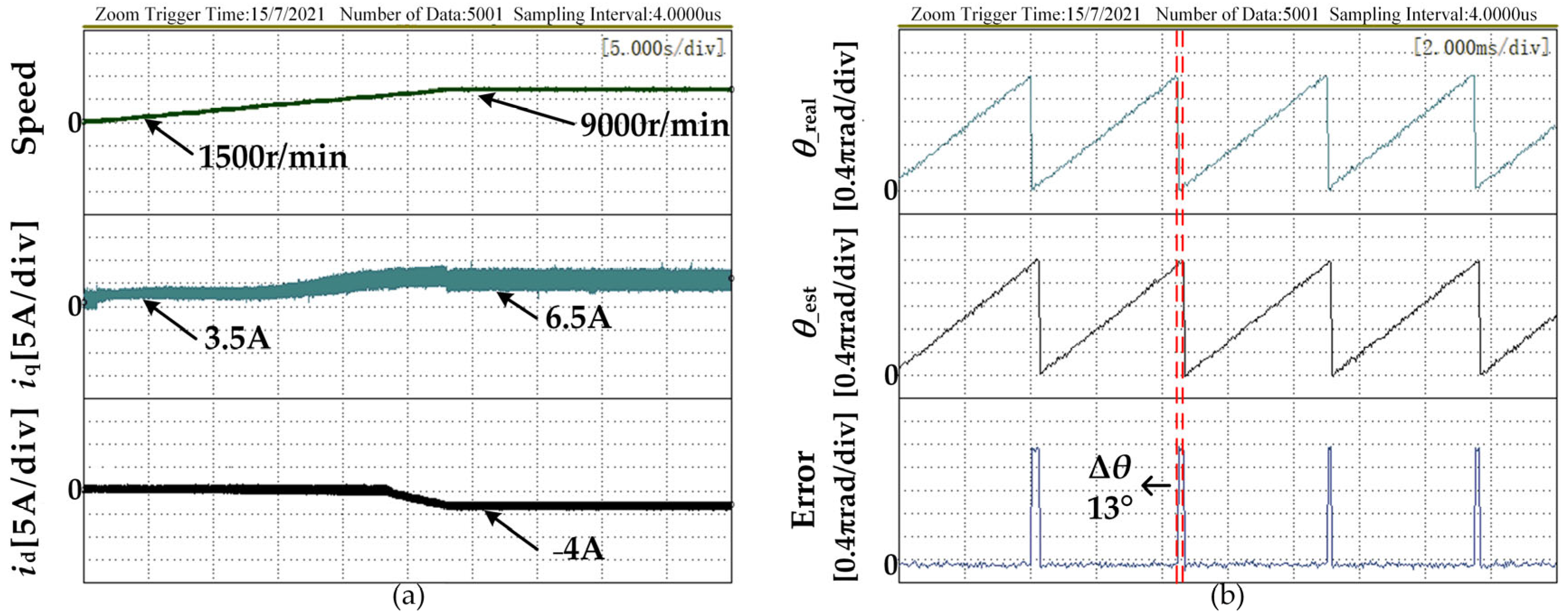
4.2. Experimental Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed method uses the static difference of the d-axis current discretized by Euler’s approximation method as the basis for judging whether there is an angle estimation error, that is when there is an angle estimation error, there is a static difference between the actual value of the d-axis current and the reference value, and otherwise, there is no error.
- (2)
- Since the static difference value of the d-axis current changes with the speed change, a PI controller with variable proportional and integral coefficient is required, that is, the input value of the PI controller is the given value of the d-axis current, and the feedback value is the discretized d-axis current, The output value is the position angle error compensation amount. By using different proportional integral coefficients at different speeds, it is ensured that the position angle can be accurately and quickly estimated using the proposed sensorless control method at different speeds, and the estimation error is unchanged.
- (3)
- Through theoretical analysis and experimental verification, it can be seen that the proposed method can accurately compensate the estimated rotor position in the case of high-speed and low carrier wave ratio, improve the control accuracy, and have strong parameter robustness. In the case of the model, mismatch caused inductance parameter changes, the angle error can still be accurately compensated to ensure the motor performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Miao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Sun, L.; Gao, D.; Lu, H. Current Control Method of Vehicle Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Active Disturbance Rejection Control. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Valla, M.; Solsona, J. Position Sensorless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives—A Review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 5830–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youness, E.M.; Aziz, D.; Abdelaziz, E.G.; Jamal, B.; Najib, E.O.; Othmane, Z.; Khalid, M.; BOSSOUFI, B. Implementation and validation of backstepping control for PMSG wind turbine using dSPACE controller board. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourabit, Y.E.; Derouich, A.; Ghzizal, A.E.; El Ouanjini, N.; Zamzoum, O. Nonlinear backstepping control for PMSG wind turbine used on the real wind profile of the Dakhla-Morocco city. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, 12297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Nie, J.; Wei, H.L.; Chen, L.; Li, X.H.; Lv, M.Y. Switched PI Control Based MRAS for Sensorless Control of PMSM Drives Using Fuzzy-Logic-Controller. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2022, 3, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Shi, P. A Review of Position Sensorless Compound Control for PMSM Drives. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, G.; Hang, M.; Cheng, S.; Li, P. Sensorless Control Strategy of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on an Improved Sliding Mode Observer. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascu, C.; Andreescu, G.D. PLL Position and Speed Observer with Integrated Current Observer for Sensorless PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5990–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y. Robust predictive current control with online disturbance estimation for induction machine drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 4663–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zhou, C.; Su, J.; Xie, M.; Liu, J.; Xie, T. A Permanent Magnet Flux Linkage Estimation Method Based on Luenberger Observer for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, J.; Xu, J.; Chandra, A. Effects of rotor position error in the performance of field-oriented-controlled PMSM drives for electric vehicle traction applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4738–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J. Design of Iterative Sliding Mode Observer for Sensorless PMSM Control. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2013, 21, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, J.S.; Sul, S.K.; Bae, B.H.; Patel, N.R.; Hiti, S. Modified current control schemes for high-performance permanent-magnet AC drives with low sampling to operating frequency ratio. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zuo, S.; Cao, J. Effects of rotor position error on longitudinal vibration of electric wheel system in in-wheel PMSM driven vehicle. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 1314–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Hsu, Y.L.; Chou, P.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Chen, G.R. Digital implementation issues on high speed permanent magnet machine FOC drive under insufficient sample frequency. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 61484–61493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Hu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, L. An Improved Delay-Suppressed Sliding-Mode Observer for Sensorless Vector-Controlled PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 5913–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Deng, Z. Correction of Rotor Position Estimation error for High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Sensorless Drive System Based on Minimum-Current-Tracking Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 8271–8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zou, J. Online multi-parameter identification method for sensorless control of SPMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 10601–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Fang, J.; Han, B.; Zheng, S. Adaptive Compensation Method for High-Speed Surface PMSM Sensorless Drives of EMF-Based Position Estimation Error. Power Electron. IEEE Trans. 2015, 31, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, K.; Chen, K. An Improved Position-Sensorless Control Method at Low Speed for PMSM Based on High-Frequency Signal Injection into a Rotating Reference Frame. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 86510–86521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Shi, Y.; Song, X.; Hong, K.; Mao, K. Initial Rotor Position Detection Method of SPMSM Based on New High Frequency Voltage Injection Method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 3553–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, K.; Huang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Shen, M. Inductance Parameter Identification Method of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on the HF Rotating Square Wave Voltage Injection. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Sul, S.K.; Lee, J. Compensation of Current Measurement Error for Current-Controlled PMSM Drives. Energy Convers. Congr. Expo. IEEE 2012, 50, 3365–3373. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, W.; Rho, M.S.; Park, S.Y. Effective dead-time compensation using a simple vectorial disturbance estimator in PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, G.; Tao, F.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, B.; Xu, W. Stability Analysis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Current Loop Control at High Speed and Low Carrier Ratio. In Proceedings of the CSEE, Rome, Italy, 7–9 April 2019; Volume 39, pp. 7336–7346+7506. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, N.; Fuchs, F.W.; Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Schorder, D. Digital current control in a rotating reference frame-Part l: System modeling and the discrete time-domain current controller with improved decoupling capabilities. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5290–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
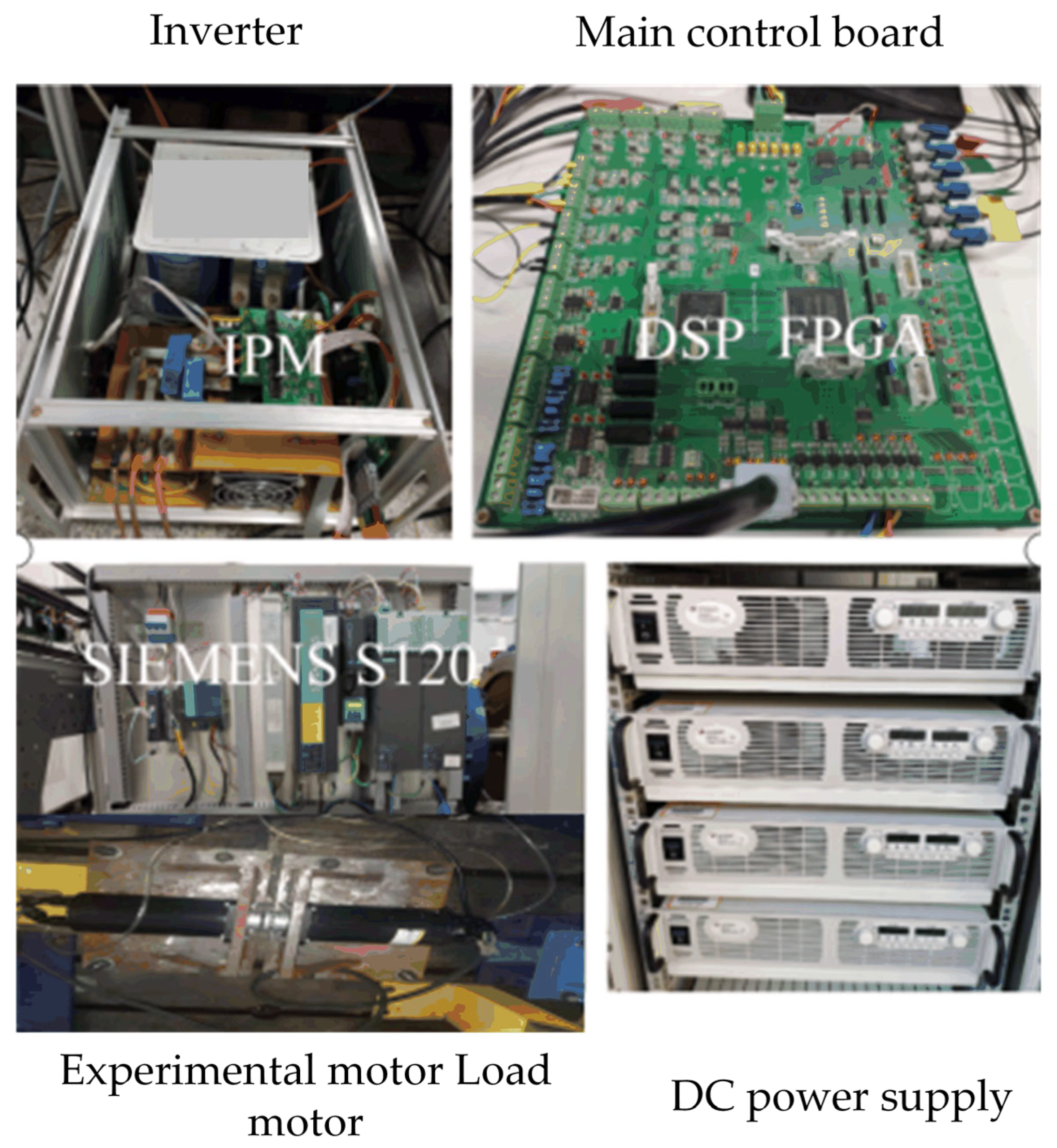



| PN/kW | TN/N·m | ωN/r/min | J/kg·m2 | Ld, Lq /mH | np | Rs/Ω | ψf/Wb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.7 | 11.8 | 3000 | 0.0012 | 3 | 2 | 0.38 | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Du, D.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Guo, L.; Gu, X.; Li, X. Sensorless Control Method of High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Discrete Current Error. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj14030069
Wang Z, Du D, Yu Q, Zhang H, Li C, Guo L, Gu X, Li X. Sensorless Control Method of High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Discrete Current Error. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2023; 14(3):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj14030069
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhiqiang, Dezheng Du, Qi Yu, Haifeng Zhang, Chen Li, Liyan Guo, Xin Gu, and Xinmin Li. 2023. "Sensorless Control Method of High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Discrete Current Error" World Electric Vehicle Journal 14, no. 3: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj14030069
APA StyleWang, Z., Du, D., Yu, Q., Zhang, H., Li, C., Guo, L., Gu, X., & Li, X. (2023). Sensorless Control Method of High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Discrete Current Error. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 14(3), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj14030069







