Abstract
Systems biology is established as an integrative computational analysis methodology with practical and theoretical applications in clinical cardiology. The integration of genetic and molecular components of a disease produces interacting networks, modules and phenotypes with clinical applications in complex cardiovascular entities. With the holistic principle of systems biology, some of the features of complexity and natural progression of cardiac diseases are approached and explained. Two important interrelated holistic concepts of systems biology are described; the emerging field of personalized medicine and the constraint-based thinking with downward causation. Constraints in cardiovascular diseases embrace three scientific fields related to clinical cardiology: biological and medical constraints; constraints due to limitations of current technology; and constraints of general resources for better medical coverage. Systems healthcare and personalized medicine are connected to the related scientific fields of: ethics and legal status; data integration; taxonomic revisions; policy decisions; and organization of human genomic data.
1. Introduction
The term “constraints” was described in biology in the context of natural selection and organism survival. Biological networks are constrained by a variety of factors such as the biological, environmental and physicochemical. Biological constraints could be self-imposed and produced by regulatory networks while hard constraints are imposed by other factors (e.g., environment) [1]. Constraint-based analysis methods are being used to study genome-scale models and the biological properties of whole organisms. The constraint-based concept is used widely in systems biology (SB) from genomes to clinical phenotypes, and it is related to personalized medicine and clinical guidelines having an impact on current clinical practice and diseases. Cardiologists following patients with complex cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), such as coronary artery disease (CAD) and heart failure (HF), are complying with current clinical practice, but they are also familiarized with the clinical constraints hypothesis incorporated in medical guidelines directions.
Traditional healthcare systems are using a reductionist approach explaining and managing complex diseases as they reduce—through a very simple manner—the medical problem to an isolated organ-problem or biochemical fault [2]. In traditional medicine the term “disease” designates that specific molecular systems or organs of the human body are unnaturally functioning and, therefore, subvert human health [3]. With the reductionist approach significant advances in diagnosis and therapy of CAD were applied in everyday clinical practice, with a decrease of cardiac events and symptoms and an increase in longevity. Despite these successes in clinical management, complex CVDs continue to be the leading cause of mortality and morbidity, while chronic progression of the atherosclerotic process continues. Over the past few years it has become obvious that medical issues from molecular to clinical reasoning necessitate a new scientific approach requiring cooperation between medicine and interrelated sciences. Medicine cannot be considered in isolation from other systemic sciences, and a holistic approach is needed for complex diseases. Chronic complex systemic medical problems should be addressed with the holistic approach as it needs interdisciplinary integration and study of dynamical interactions between organs’ complex networks involving genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors. Many of the medical issues are interconnected with other systemic sciences including SB. The SB approach should be regarded as the science that combines biology with physics, mathematics, medicine and many other sciences like ecology and sociology. Systems healthcare (systems medicine) is the holistic approach to health based on the holistic principle of SB and to current clinical medical practice. Systems healthcare integrates data from molecules to phenotypes and from societies to environment, extending to the disciplines of economics, ethics and law [4].
The present paper discusses the constraint-based concept of SB as it is applicable to clinical cardiology and to the important clinical limitations that are present in the current practice of personalized medicine [5]. Constraints’ application to clinical decisions augments robustness to the unremittingly progressive clinical course of chronic cardiac diseases. In order to overcome some important inherent limitations in contemporary clinical cardiology, the interdisciplinary approach between a constraint-based concept and personalized medicine is underlined. In clinical practice, cardiologists, unknowingly to themselves, are practicing in conformity with the concept of constraints and that is in accordance with current medical guidelines. The concept of constraint-thinking is a significant decision-making clinical tool which constantly and in a timely fashion is revised by medical advances in prophylaxis and clinical management. Complex cardiovascular diseases like CAD and HF are multifarious in clinical presentation revealing, also, a progressively advancing natural clinical course. Cardiovascular diseases are complex biological entities produced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Furthermore, personal reaction to pharmaceutical therapy and drug effectiveness and toxicity are the result of the interactions between genetic profiles and environmental factors [6]. The holistic approach is based on the integration of a network components and functions (e.g., genetic, molecular or environmental) during the different stages of disease progression. Personalized medicine and clinical constraints are considered essential concepts of the holistic principle of SB in following complexity of the disease states and clinical progression.
2. Methodology of Systems Biology
The traditional biological description of the living world is based on the nonlinear interactions of molecular processes without explanation for their functional interconnections [7]. The advances of molecular biology proved successful in studying isolated molecules and some of their interconnections, but were unsuccessful in experimentally predicting complex phenomena such as complex disease progression. Traditional and molecular biology are based on the classical reductionist understanding that differs from the SB holistic perception. Reductionist understanding of the biological phenomena “is mostly understood as a means to explain phenomena generated by systems in terms of the properties of their parts, often when considered in isolation” [7]. With the holistic approach, complex wholes are understood from the properties they possess as “whole systems” and not from the behavior of the isolated parts. The holistic principle analyzes the structural organization and regulation of biological networks, deciphers complex signaling mechanisms and interconnections and discloses positive or negative feedback mechanisms [8]. From cellular mechanisms to phenotypes, functional properties are “emerging” through a self-organized procedure which complies with the foundations of a hierarchical multileveled system. Systems biology is regarded as the science that somehow “replaced” molecular biology with emphasis on the construction and explanation of bigger biological systems such as networks and signaling information [9].
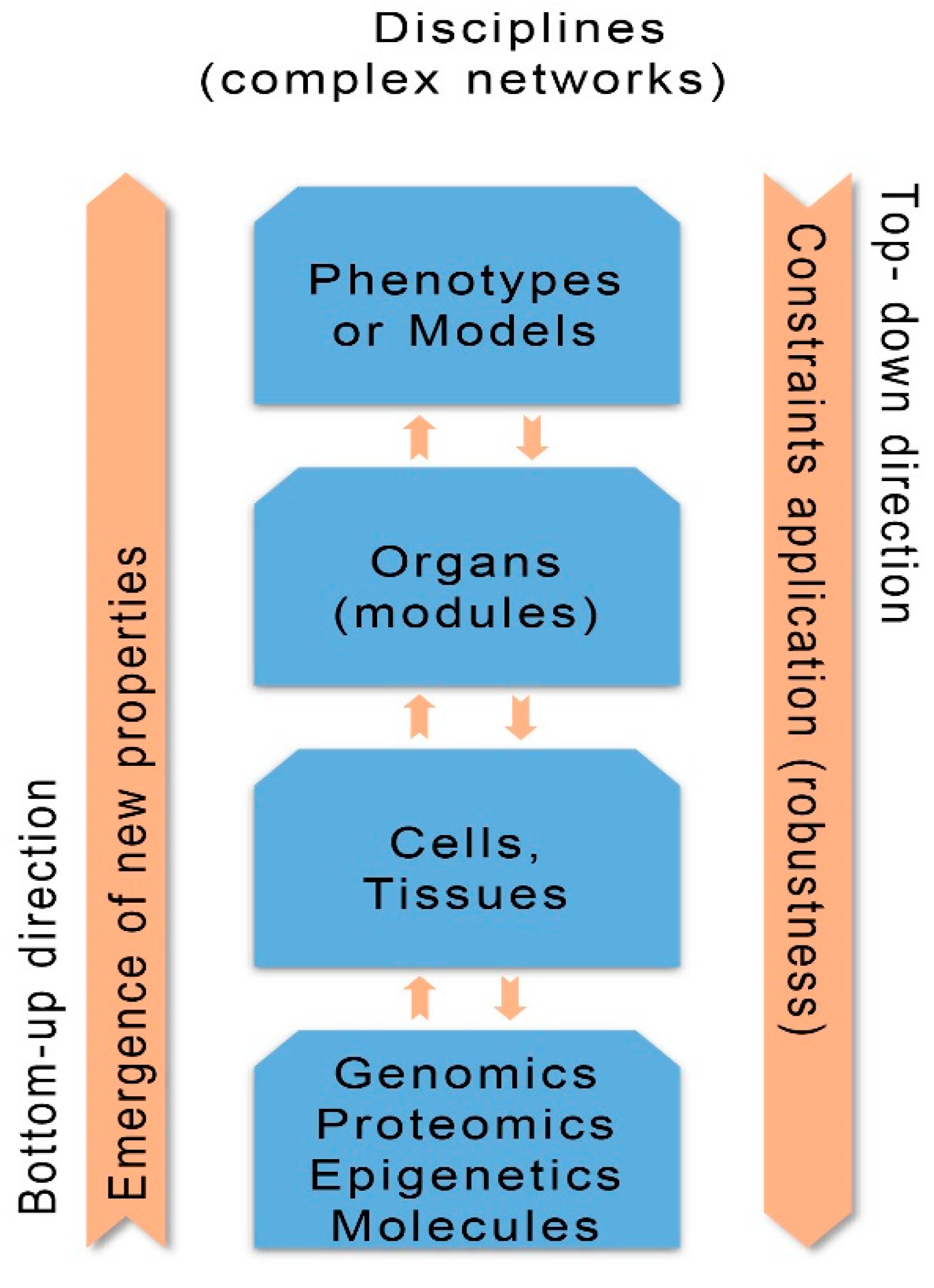
The aim of SB is to ascertain how function and behavior of living organisms are justified by the interaction of their constituents [10]. Thus SB is a scientific discipline that analyses living organisms and biological networks (systems) from the level of genomics and molecules to phenotypes. The biological networks demonstrate hierarchical structuring composed of collaborating biological components (nodes). The complex interactions (detectable or unnoticed) existing between nodes constructs a network system with new emergent properties that reflect health related behaviors or different disease states [11]. Systems biology methodology with its integrative computational analysis constructs interacting and integrating network processes and models of clinical phenotypes having an impact to disease progression and therapy [12]. The SB approach, besides the concept of network construction, uses two potential directions for studying and explaining complex diseases: the bottom-up direction (indicates progression from genes to phenotypes) and the top-down direction (indicates decomposition from phenotypes to genes) [13] (Figure 1).
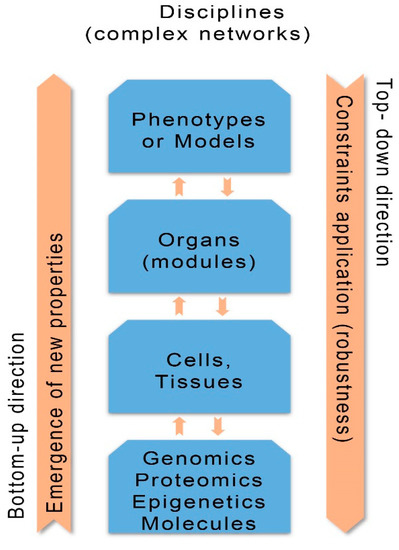
Figure 1.
Concepts of systems biology: bottom-up and top-down directions; disciplines (complex networks); emergence of new properties; constraints application (robustness). (Revised from: [5]).
The bottom-up direction is important to personalized medicine, as upon the emergence of new properties in each level of the disease progression the possibility of exploration for new diagnostic biomarkers and drugs is increased. The top-down direction causes the enforcement of constraints (forcing boundaries) imposed by the higher order phenotypes or modules to the molecular or genomic lower level, independently of lower order changes [14,15].
Dunbar [16] underlines that “causal reasoning in science is not a unitary cognitive process, but a combination of very specific cognitive processes that are coordinated to achieve a causal explanation”. In clinical medicine the causal dependency between stages of disease’s progression and the extraction of useful information in downward direction is recognized. The extracted information is useful to practicing physicians to impose diagnostic and therapeutic constraints. In a downward direction the physician has decreased degrees of freedom, but he selects the most available and clinically suitable diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
During progression of a complex disease, while the genes produce proteins for tissues and organs in a bottom-up direction, it is the disease’s phenotype in a downward causation that determines the kind of proteins that are needed. The downward causation of SB is a holistic principle that objects the classical reductionist position of biology. Based on the holistic principle, behavior of the lower level is regulated by the behavior of the higher level, which in the case of complex CVDs imposes constraints on clinical progression and management. The top-down constraints demonstrate also the impact that the hierarchical higher level of phenotype has on modular clinical level, a fact with significant repercussions for progression and mode of treatment for complex diseases.
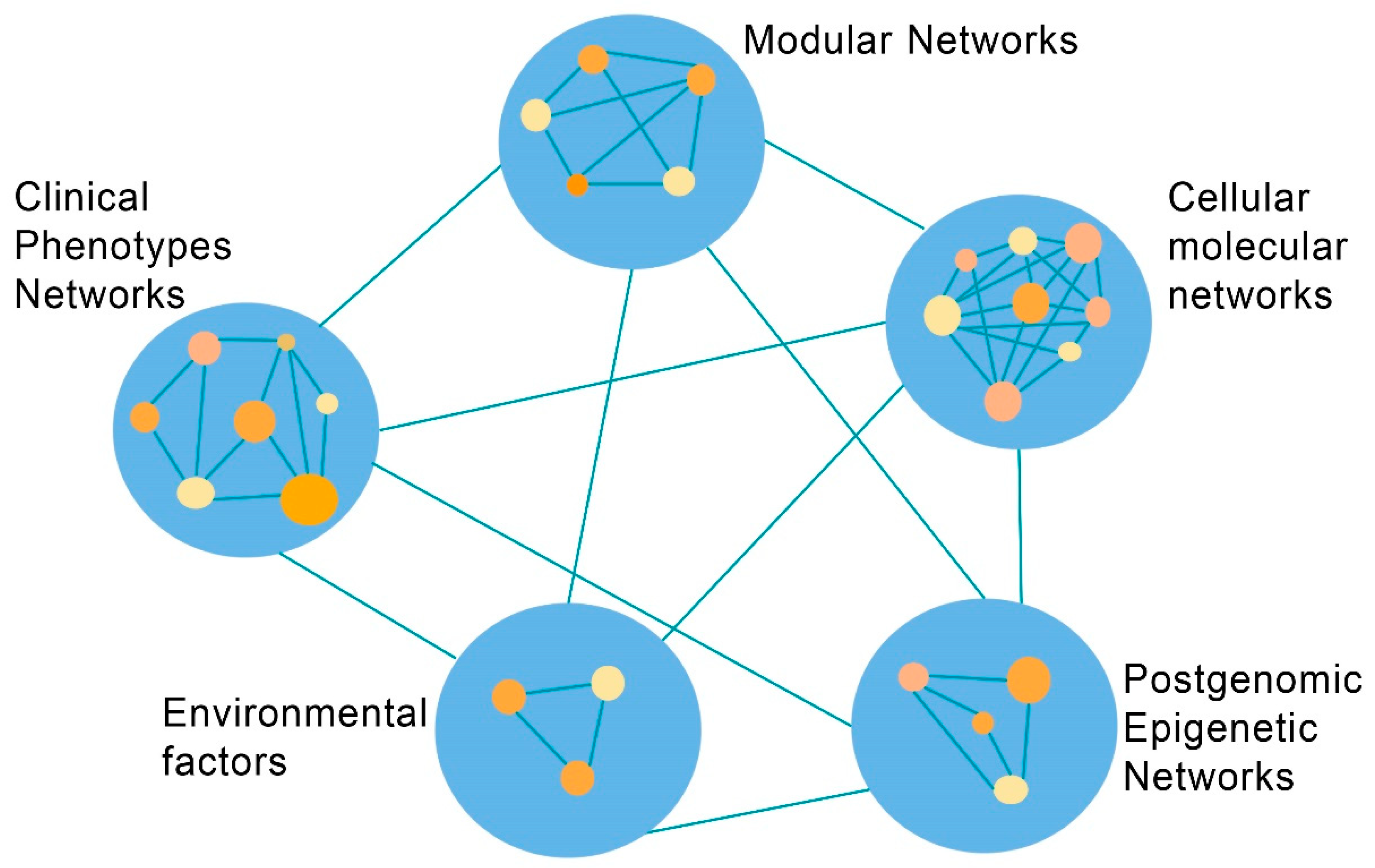
The SB emerges as a discipline to expound the complexities of human physiological status and diseases such as CVDs. From the perspective of clinical phenotype it is essential the construction of appropriate networks in each step of complexity, from the genomic, molecular, modular to phenotypic level (Figure 2).
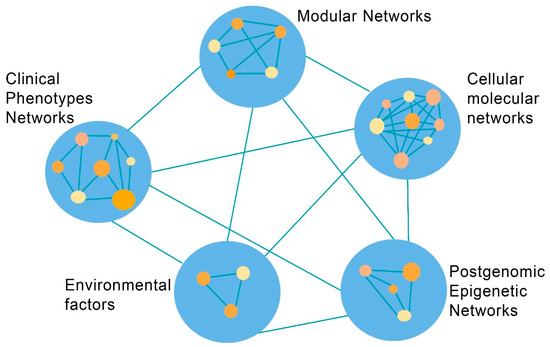
Figure 2.
Coronary artery disease: The network complexity between systems biology discipline levels and environmental factors. (Revised from: [11]).
The specific organizational properties and behavior of each complex biological network should be explored. Networks should be constructed not only separately in each level of complexity of the biological ladder, but also between the successive levels of the complex disease that will facilitate the integration of each molecular component or clinical finding in the “appropriate” network position. This approach will reduce chances for “wrong” positioning of data, and the biomedical research will not be isolated or “indifferent” from the clinical momentum.
The bidirectional transfer of information, together with the system of interconnected networks, increases the possibility of scientific communication and interexchange of ideas between groups of people with diverse talents and scientific fields. The challenge remains to construct that kind of networks by a multidisciplinary participation of researchers and clinicians. In the mind of a clinician this approach of integration of facts from conceptual networks and the simultaneous integration of bidirectional information is more than relevant and clinically fruitful. In reality, the interplay of biological and clinical factors reflects a multileveled system of networks, models and their interrelationships. This approach increases the necessity for SB application in the complex clinical medical field. In order to decipher clinical entities, the interexchange of ideas should be completed by including the concept of network medicine. In the interconnected whole, small networks are lodged or connected to larger networks in order to have a coherent entity. Complex disease does not behave like a well organized biological machine, but should be visualized as a complex network system. In a network system the biological components occupy specific network positions, and the interactions between the components formulate “logical” higher functional networks and models. The recent advent of network medicine as a tool of clinical research gives a new perspective to the “nature” of complex diseases [17]. The network concept is important for translating in a more meaningful way interconnections of collected health and clinical data. Complex disease should be visualized as an aggregate of malfunctioning complex cellular and molecular networks that induce organs’ failure and in the end specific phenotypes. Fiandaca et al. [4] suggest that “the diseased organ… produces a cascade of dysregulated networks, resulting in associated co-morbidities”… while “in the state of wellness, networks are precisely regulated via complex homeostatic mechanisms”; and that specific therapeutic intervention “requires aggregating multi-dimensional datasets…high-performance computation and analytics” while “the goal is to determine interventions that target abnormal networks and promote systems level improvements”.
3. Constraints in Medicine and Clinical Cardiology
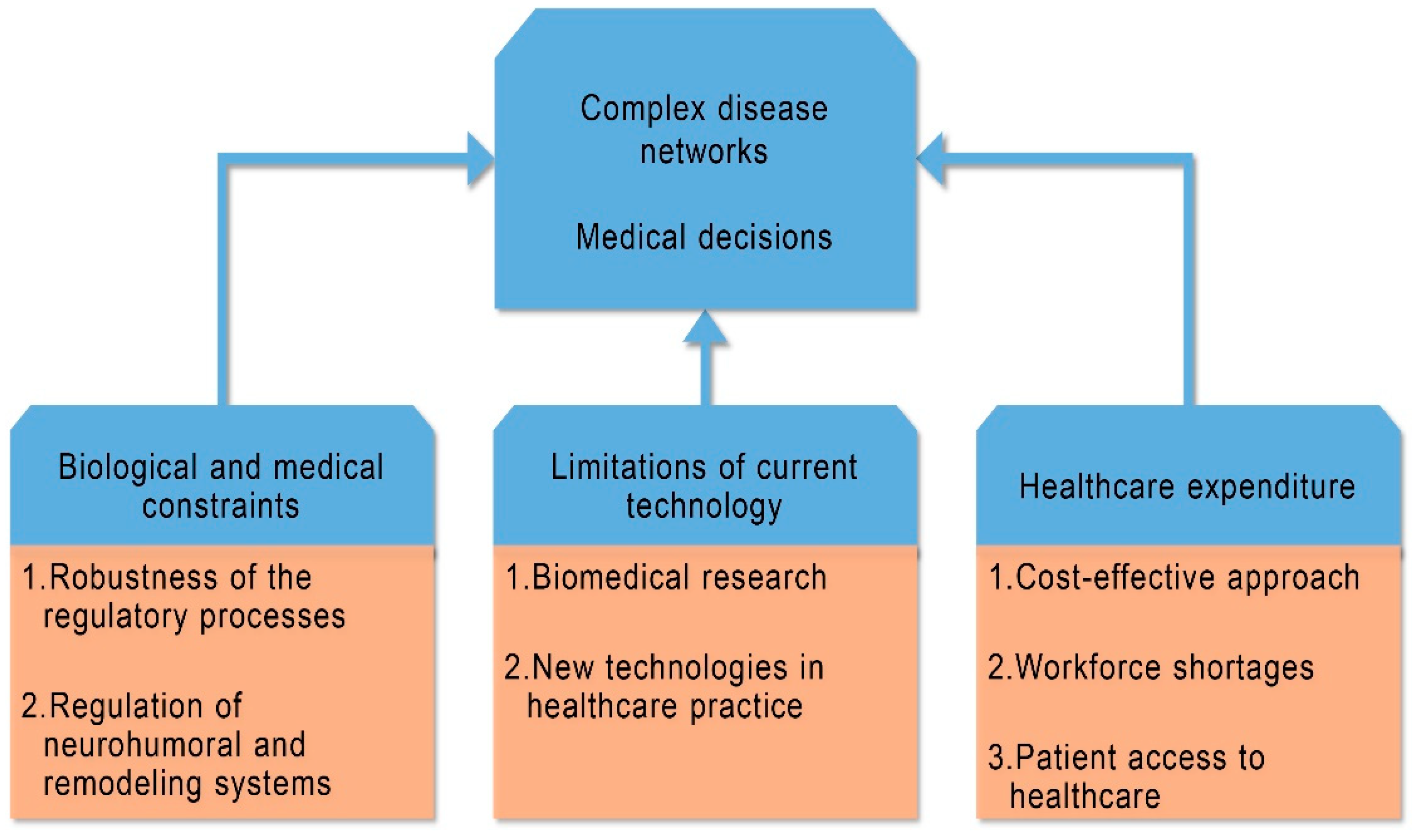
The application of constraints in medicine and clinical cardiology presumes that the constraint-based hypothesis, as it is implemented in biological and medical domains, should reflect a systems’ robustness. Also, the concept of constraints should be considered as a regulatory mechanism not only for molecular or other biological networks but also it is a decisive factor for medical decisions. Based on these assumptions the application of constraints encompasses three fields related to clinical cardiology: biological and medical constraints applied to cardiovascular diseases; constraints due to limitations of current technology; constraints of general resources for better medical coverage (Table 1).

Table 1.
Constraints and personalized medicine in cardiovascular diseases.
3.1. Biological and Medical Constraints
The constraint-based thinking constitutes a holistic concept with downward causation interpreting many complex features of biology and diseases. In biology the term “constraints” is referred to antagonistic biological processes addressed to every evolutionary change in order to strengthen natural selection. Also, the constraint-based reasoning was applied to experimental biology to strengthen robustness of some experimental biological models [18].
Green and Jones [19] believe that the constraint-based interpretation of biological entities differs from mechanistic thinking of “change-relating causal features”, while the “constraint-based explanations emphasize formal dependencies and generic organizational features that are relatively independent of lower-level changes in causal details”. Furthermore, SB evaluates functional properties of living organisms and explores structured biological entities of genetic regulatory and metabolic networks, and the dynamics of enlarged networks in the form of modules (discrete functional regulatory networks) and phenotypes [13]. It seems that the term “constraints” implies the presence of scale-dependency and close connection between biological systems functioning at different levels with strong downward causation (top-down effect). The top-down direction is crucial at first for information extraction from the lower levels and secondly for the capacity of the higher level to enforce constraints to lower levels with decreased degrees of freedom. The downward causation is interpreted as a regulatory constraining process that modifies and, in the end, determines behavior of lower level variables. The applied constraints limit some behaviors at the lower stage and simultaneously allow or “authorize” alternative behaviors to be released [14,15,20].
For example, the boundary of cardiac cell geometrical structure generates both cellular membrane potential and cardiac rhythm. The imposed constraints of cellular membrane boundary structure and the triggered cardiac action potential through downward causation are responsible for the appearance and maintenance of cardiac rhythm [15]. The above example indicates the limits of the reductionist position as cellular membrane, action potential and cardiac rhythm do not related directly to the genetic scale. The whole cellular membrane construction and function belong to a higher level of cardiac cellular construction.
Multileveled complex CVDs progression can be translated as a staged (leveled) structure with downward causation and constraints application from the top (phenotype) to the lower step (genome) of the disease. The top-down constraints’ application actually represents downward causation “imposing” some “biological behavior” or “order” to the lower level of the disease (pathological, diagnostic or therapeutic). The concept of constraint-based reasoning is proposed as a significant scientific tool for cardiovascular questioning and clinical research organization. Implementation of constraints in clinical cardiology has an impact to explain some properties of disease complexity and, also, to elucidate the unrelenting progression towards final disease stages. In fact, medical guidelines are founded on the constraint-based concept having downward causation. The cardiologist has decreased degrees of freedom, as only specific diagnostic tests and therapeutic procedures are available. In a way, the cardiologist “selects” the appropriate methodology according to current clinical guidelines using diagnostic and therapeutic constraints in a downward direction. In the realm of SB thinking, the applied constraints increase robustness of the regulatory processes for the stability of the unsteady metabolic networks and, also, for the variability of clinical complex entities [5,21,22].
In this paper, it is proposed that the constraint-based thinking could be used not only as a concept for metabolic networks, but also as a fundamental clinical tool deciphering progressiveness of a disease’s clinical course. Both cardiac atherosclerotic process and CVDs are considered complex entities that follow a downward direction and causation in pathogenesis or in clinical management [11]. For example, the size of a myocardial infarction and particularly the location and the importance of the myocardial area involved would induce a post-infarction myocardial dysfunction alongside of some compensatory mechanisms such as myocardial remodeling and growth of local coronary collaterals. According to SB approach, the size of myocardial infarction (phenotype) will impose constraints with downward direction on the degree of myocardial compensation and will dictate the most suitable medical and/or coronary invasive therapy, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or bypass surgery.
In another example, patients with cardiac ischemic high-risk features are recommended for clinically indicated PCI and treated with dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) in the post-PCI period according to 2017 DAPT guidelines [23]. Some patients demonstrated an increased number of ischemic and bleeding episodes following PCI which influenced the decision for intensity and duration of the DAPT in the post-PCI period. Therefore, pre-PCI constraints should be used in some of these patients with high-risk features if the invasive procedure is unavoidable or the DAPT regimen should be revised. A more personal approach with constraints in medical decisions and DAPT application is obligatory to some of these patients.
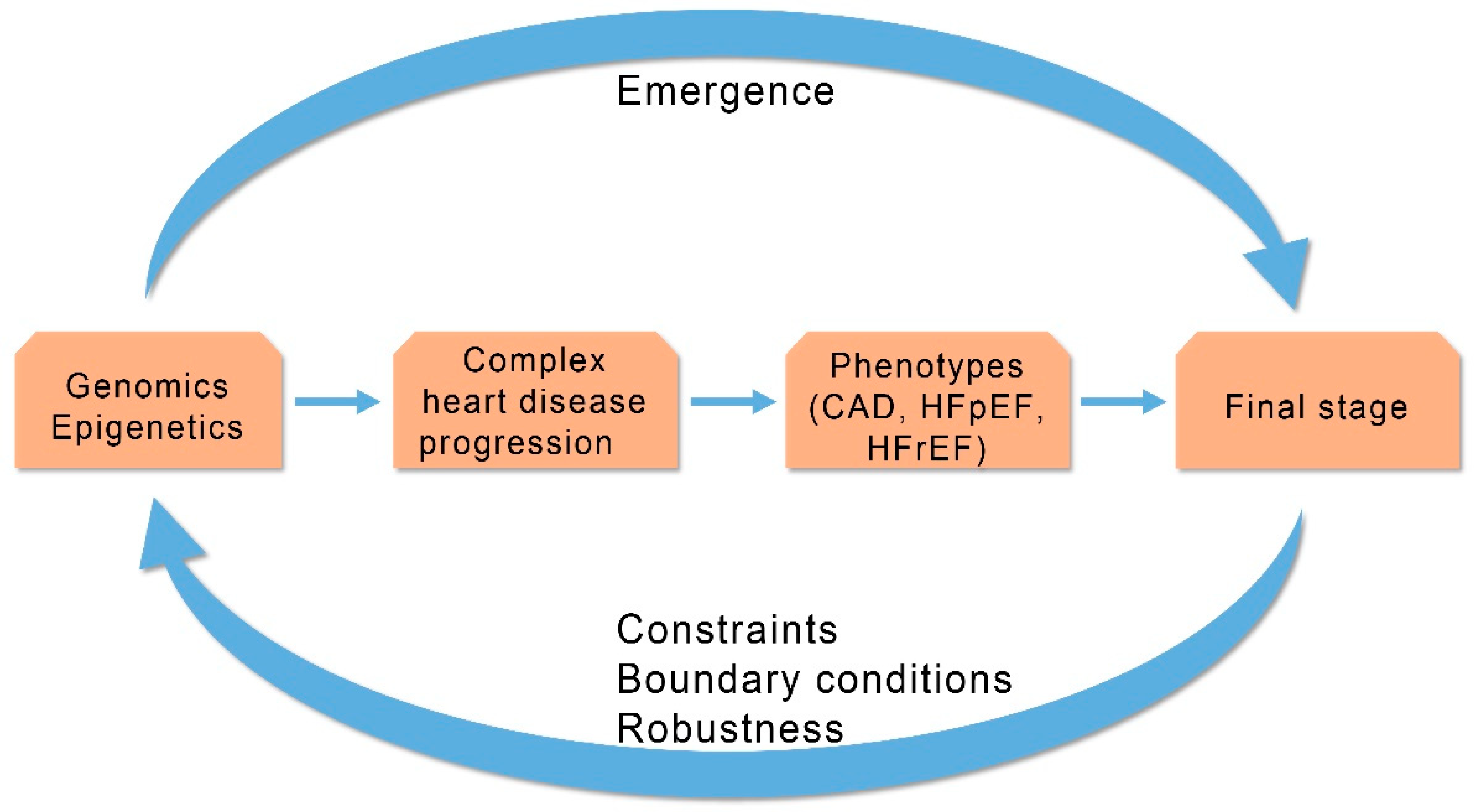
Human HF is a complex cardiac disease characterized by chronic clinical progression that involves participation of intrinsic compensatory or regulatory mechanisms [13]. The SB methodology, to unravel potential causes of HF progression from early stages of myocardial dysfunction to more advanced phases of myocardial failure, integrates genes, epigenetic mechanisms and molecules, deciphers molecular networks or modular functional elements, and clarifies the interconnection of myocardial mechanical dysfunction with cardiac remodeling and other compensatory mechanisms [24]. Heart failure should be addressed as a biological complex entity that is unstable, adaptive and self organized through its regulatory mechanisms (Figure 3).
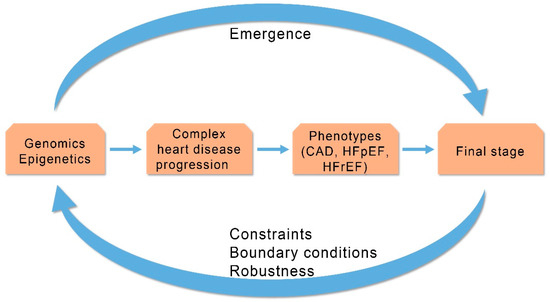
Figure 3.
Progression of complex heart diseases: Relationship between emergent properties and constraints outlines progression of complex heart diseases. CAD (Coronary Artery Disease), HFpEF (Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction), HFrEF (Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction). (Revised from: [5]).
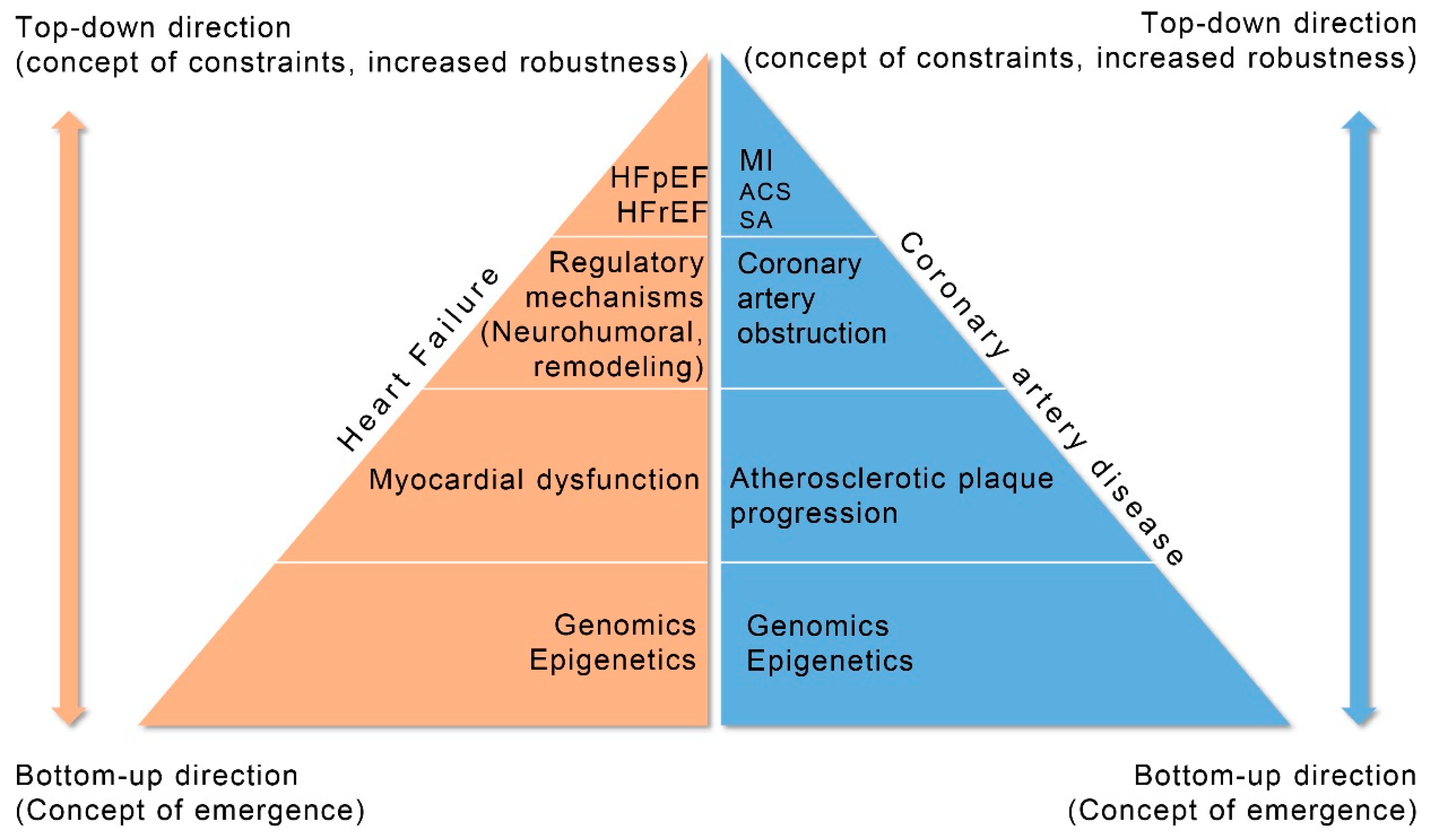
The regulatory mechanisms incorporate neurohumoral and remodeling systems that intend to compensate failing myocardium and change the unstable clinical equilibrium to a more stable clinical equilibrium status. The size of myocardial dysfunction in HF patients is related to the degree of compensation by the regulatory mechanisms. Thus, activation of the compensatory mechanisms (neurohumoral and remodeling) represents a constraint-based control (downward causation) of the degree of the compensation from the higher level (HF phenotype) to lower level (regulatory mechanisms). However, the activation of the regulatory mechanisms is often the cause of unwanted effects (symptoms) and clinical deterioration needing specific treatment to improve clinical status. The degree of clinical deterioration (by the regulatory mechanisms) in each stage of a disease’s progression dictates appropriate personalized treatment. Information and communication technologies could help through collection of related clinical data mined from published papers to improve management of HF patients. This could be achieved by the identification of the related biological networks that connect data in each level of HF progression and, after monitoring, the activated compensatory regulatory mechanisms from genome to clinical phenotypes can be clarified (Figure 4).
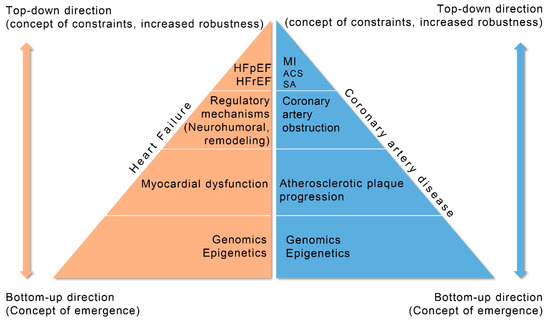
Figure 4.
Progression of coronary artery disease (CAD) and heart failure (HF) explained by systems biology approach. HFpEF (Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction), HFrEF (Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction), MI (Myocardial Infarction), ACS (Acute Coronary Syndromes), SA (Stable Angina).
3.2. Constraints Due to Limitations of Current Technology
In clinical practice, constraints may arise for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions due to limited facilities of current technological status.
New technologies require “cost effectiveness studies in the presence of health care input constraints” and crucial adjustments of conventional incremental cost effectiveness ratios (ICERs), because “without such adjustments the cost effectiveness analysis might lead to health losses” [25] (Figure 5).
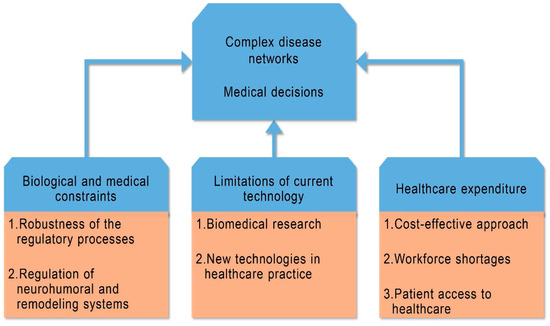
Figure 5.
Constraints in three fields related to clinical cardiology; they behave as regulatory mechanisms for complex disease networks and medical decisions.
For example, novel techniques based on computer simulation, a process of mathematical modeling, are designed to predict atherosclerotic changes in coronary arteries. Such techniques are: positron emission tomography (PET), with the use of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose, can label metabolically active areas in the myocardium and arteries; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can produce a molecular imaging of the cardiovascular system; cardiac computed tomography (CT) or CT angiography can be used for coronary calcium scoring and to measure subclinical or asymptomatic obstructive CAD; optical coherence tomography (OCT) for atherosclerotic plaque composition and stability.
In coronary artery areas with bifurcations or curbs there seems to exist a strong connection between concentrations of circulating plasma low density lipoprotein and turbulent flow with the development of atherosclerosis. Digitized images of coronary arterial post-mortem segments were analyzed with a computational fluid dynamic analysis, and the critical role of the local low wall static pressure was underlined for coronary wall thickening as a precipitating factor in the pathogenesis of coronary atherosclerosis [26]. Another example of new technology is the Heart Flow Analysis, a system based on cloud services that offers non-invasively detailed information of coronary arteries and is used instead of an invasive cardiac procedure. The Heart Flow Analysis is scheduled to support the functional evaluation of CAD. It produces a personalized 3D model of coronary arteries using computed tomography (CT) images constructing a fluid dynamic model of the coronary blood flow. It identifies and calculates the size of coronary obstruction and advises cardiologists for further management. All new technologies have a positive cost-effective value for health care systems as they diminish current constraints for medical risks, and also reduce the high cost on health spending.
Digital health technologies aim to increase health care decision-making and improve health management. They represent actually “a broad spectrum of measurement technologies that include personal wearable devices and internal devices as well as sensors…but the current state of technology development and deployment requires… a cautionary note” [27]. Also, digital health technology can “identify health risks and assist with diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of health and disease conditions” [28]. To some of the patients, digital health applications can offer new diagnoses and chances for novel treatment, but worldwide use of new digital health devices will need clinical trials to prove their usefulness [28]. Therefore, the existent constraints for the full value of digital health technologies will be retracted when the new technologies become standardized and interoperable during clinical trials, and when new clinical guidelines have incorporated digital health devices [27].
Gaveikaite et al. [29] suggest that telehealth services can increase the “quality of health services for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) management” and in those patients “complex interactions between multiple variables influence the adoption of telehealth services” for COPD by different healthcare professionals. Moreover, some constraints remain as “key variables were identified that require attention to ensure success of telehealth services” but “there is no consensus where self-management services should be positioned in the COPD care pathway” [29]. Thus, medical practitioners or researchers from other fields, such as pulmonary diseases’ practitioners, computer science and network science researchers, can contribute their expertise to a common cause to explore further complex and interrelated human disease conditions.
Significant constraints are raised when the genetic base of chronic atherosclerotic disease is explored with modern genetic technologies. In complex cardiovascular atherosclerotic disorder the importance of genetics is elusive, as the disease is multifaceted and is not explained by single-gene mutations. In reality, the diverse phenotypes of CAD represent integrated clinical wholes with clinical behavior continuously changing due to the progressive nature of atherosclerotic process. Current understanding of genetics and genomics, as well as genome-wide association studies (GWAS), are inadequate alone to explain the natural course of cardiac atherosclerosis. It seems that “the genetic risk variants of atherosclerosis are activated concurrently with functionally active specific environmental risk factors” and that cardiac atherosclerosis could be studied only as a unified complex entity [11]. The GWAS approach was expected to trace statistically significant interrelationships between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and atherosclerosis. It was expected that SNPs related to atherosclerosis to be more frequently present in CAD patients than in control individuals, but, in contrast, a variety of genomic DNA markers were detected in individuals without CAD. Also, it was found that genomic technologies as SNP array, gene expression microarray and micro-RNA array were unable to demonstrate accurately the genetic atherosclerotic profile of CAD people. With the GWAS approach, it was found that only 10.6% of individuals with atherosclerosis possessed a probable heritable genetic factor. More important was that large-scale association analysis identified new risk loci for CAD, and that DNA methylation-mediated epigenetic downregulations and histone modifications triggered by lifestyle features play a vital role in atherosclerosis [30,31,32]. The GWAS approach, based only on genetic variability, does not identify and clarify the vessel wall pathological changes or the clinical progressive nature of CAD phenotypes [21].
The World Health Organization determines that a biomarker is “any substance, structure, or process that can be measured in the body or its products and influence or predict the incidence of outcome or disease” [33]. The role of genetic biomarkers is limited and the genetic variation is of uncertain significance in clinical “whole exome sequencing” (WES), requiring continuous revision when clinical interpretation is demanded [34,35]. Moreover, WES technologies are evolving using new diagnostic tools and medical clinicians and laboratory scientists can increase further their knowledge for complex diseases and tailor unique therapies for individual patients. Timmerman [34] stresses the importance of standardization in laboratory research and argues that “the match between phenotype and genotype is circumscribed by the team’s reliance on specific standards”. As an example, he describes how a “clinical exome sequencing team” elects the time when to trust standards and a clinical exome sequencing technology will make “the transition from a laboratory research tool to a routine clinical technique used to diagnose patients”.
Emerging technologies are developing for “multi-omics studies and an increasing shift toward proteomics-going straight to the heart of biology that represents actual disease state and progression” and “to gain insight into the pathophysiology of disease and to identify proteins that are causally associated with disease, providing new targets for effective drug development” [36]. Regardless of the advances in metabolomic methodologies that succeeded to produce thousands of molecules or biomarkers—some of those related to cardiology—many more are needed to give a new description of clinical phenotypes. It seems that more imaginative holistic approaches and new methodologies are needed to define novel clinical cardiac phenotypes. New multimodal systems of “omics”, metabolic pathways, environmental impacts and sophisticated disease-related networks are required to be integrated and provide a new holistic and realistic picture.
3.3. Constraints on Healthcare Budget
Health economic evaluations and the results of cost-effectiveness analyses studies are helpful for decision makers to confront the main economic constraint, the health care budget. In reality, besides the health care budget, there are “multiple other resource constraints that are involved relating, for instance, to health care inputs such as a shortage of skilled labor” [25]. There are, also, other constraints involved, “consisting of supply-side (e.g., workforce shortages), demand-side (e.g., obstacles of access to healthcare) and healthcare system constraints (e.g., regulatory constraints)” [25]. Complex CVDs swiftly increase their complexity changing pathology and course while clinical stages are overlapping. Moreover, alterations of the clinical course are approached differently in each phase of the disease. Clinical approach is modified in each step of the disease guided by current clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic constraints. Both, health system and practicing cardiologists are responsible for the wise use of the available resources and, also, to increase patients’ longevity. In view of the chronic and progressive course of the CVDs and in order to eliminate health disparities between underserved communities health authorities should define specific medical strategies and remove imposed constraints [37].
The pre-hospital management strategy for patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) is a strong example from a medical or ethical point of view that requires coherent relations among patients and cardiologists. Patients with chest pain need immediate medical attention in an emergency cardiology department for further management that includes probable admission in acute coronary unit and PCI. However, there are worldwide limitations to further management of these patients due to restricted resources and insufficient organization (constraints). Patient’s transfer to the nearer medical center should be imperative following standard procedures and avoiding unnecessary bureaucratic retardations. Invasive procedures such as PCI and bypass surgery vary on their outcome from medical institution to another due to differences in expertise and resources. Thus, local medical circumstances can limit (constrain) medical decisions and practices diverging from current medical guidelines.
4. Personalized Medicine-Complex Cardiac Diseases
Systems biology was followed by a new concept termed “systems medicine”, a global and holistic approach that collects diverse longitudinal data for each individual [38]. The collected data can be used to explain the complexity of human biology and disease after evaluation of both genetic and environmental determinants [38]. Price et al. [39] comment on to the above data “as personal, dense, dynamic data clouds: personal, because each data cloud is unique to an individual; dense, because of the high number of measurements; and dynamic, because we monitor longitudinally” and these “data clouds embody the essence of precision medicine” [39].
The Hundred Person Wellness Project (HPWP) is a 10-month pilot study of 100 “well” individuals and it is focused on “optimizing wellness through longitudinal data collection, integration and mining of individual data clouds” and to “identify markers for wellness to early disease transitions for most common diseases” [40]. The term “personalized medicine” (precision medicine in USA) “describes the ability to tailor diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy-ideally to individual patients, but at the very least to stratified patient groups” [41]. The National Institutes of Health (USA) defines precision medicine as “an emerging approach for disease treatment and prevention that takes into account individual variability in genes, environment, and lifestyle for each person” [42].
The term of personalized medicine refers to the holistic principle for a tailored and exclusive medical care approach for refined personalized therapy and superior drug safety and efficacy. The SB concept aimed to an extensive cognitive change and a reappraisal of human diseases, and, also, contributed to evolution of novel technologies with more sophisticated explanation of human complexity that motivated the emergence of individualized medicine [43]. In personalized medicine patients are examined as “persons” and not only for symptoms and clinical signs. Cardiologists are not concentrated to angina only as a symptom but they are inquiring about personal or family medical history as well as patients’ preferences for their mode of treatment. Consequently, personalized medicine and medical guidelines are not equivalent conceptions in clinical thinking and practicing, especially for chronic CVDs. Guidelines are addressed to a specific group of patients as an ensemble of persons but disregard the “individual” patient with his personal or family medical history and his preferences for further disease management. Preferences for invasive or noninvasive therapy and variations in therapeutic effectiveness of pharmacologic agents are medical aspects to be decided between practicing cardiologist and patient.
Personalized medicine, clinical guidelines and constraints are considered interrelated scientific fields for management and follow-up. Patients with chronic CVDs progressively deteriorate and need specific management in each stage of the disease. It is mandatory for a cross-disciplinary collaboration between scientists and clinical experts from the biomedical and clinical research fields in order to interexchange knowledge and skills and answer the multiple questions for unmet medical needs encountered by clinicians. Aboab et al. [44], proposed a model of data analysis to increase the reliability of published biomedical and clinical research. That is an important and welcome step for health care and research. The integrating, inter-professional and interdisciplinary collaboration of scientists with clinical experts, for meticulous analysis of health data, is a step forward to a more effective use of clinical and research findings. Complex diseases are chronic processes with an extended interplay of variables and reliable ideas [45].
However, in the field of complex diseases or complex clinical situations, there remains the problem of clinical application for biomedical research findings, and the cooperation between researchers and non-researchers is more complicated. That involves the design of a complex disease modeling with a methodology that translates research findings and connects different pieces of knowledge and compares evidence. It is common knowledge that complex diseases are incomplete and inconclusive in their conception.
The constraints’ concept is relevant to health services and medical technology, and available management procedures should be implemented accurately in all stages of CVDs knowing their chronic progressive nature as well as advances on the technological availability [46]. The field of digital medicine is promising but requires continuous validation based on large randomized clinical trials. In patients with CVDs, clinical evaluation using telemedicine with external sensors application to track-down important clinical data should be further assessed [47]. Constraints should be applied to clinical approval for digital medical information obtained from outpatients having a complex clinical picture. Digital medical information without further verification with well controlled randomized clinical trials should not be accepted. Medical guidelines are based on large randomized clinical trials (RCTS), but to establish effectiveness of procedural cardiac interventions precise restrictions (constraints) are implemented in the designed trials [48]. Furthermore, in everyday clinical practice, literal interpretation of the results of RCTS could be hazardous, with high risk, if medical proficiency and local technical support are not appropriate [49].
4.1. Personalized Medicine-Ethics and Legal Status
Systemic medical approach requires different national health policy in accord with national laws and international consensus. A new policy includes the use of new cost-effective technology and data collection, while mandatory is patients’ cooperation. The “individualistic autonomy” notion is the dominant thinking in clinical practice and research, as well as between patients, medical practitioners and health authorities. With this term it is acknowledged that patient’s absolute prerogative is the choice of his medical management. This assumption is medically inappropriate considering complexities and constraints involved in medical management of patients with diverse cardiac clinical phenotypes. Medical guidelines and common sense support the notion that medical practitioners are strongly “related” to medical decisions and, thus, a more realistic position would be the “relational autonomy” of a patient’s decision [50]. The “relational autonomy” position is associated with the concept of constraints proposing restrictions to the individualistic approach while encourages patient-medical practitioner cooperation. Furthermore, the psychology to implicate guidelines and modern technology to clinical practice requires common sense from both patients and medical practitioners, while at the same time evaluates risks and benefits [51,52]. Sometimes, an unreasonable attitude from both patients and doctors who doubt and enquire negatively the value of modern medicine has consequences to rational application of constraints in clinical decisions. If the medical knowledge that is related to scientific data and technologies is shared between clinicians and patients, then ethical transparency for disease’s detection and treatment will improve [53].
In personalized medicine a lot of ethical and moral arguments are raised by both worried and anxious patients and medical authorities [54]. It is understandable that new genome editing technologies which have the capability to introduce targeted genomic sequence changes can transfer them to next human generations [55]. These technologies not only can transform biological research and develop novel molecular therapeutics for human diseases, but they also produce ethical problems. Genome editing is a personal decision, but some ethical problems arise in the society for unwanted accidental gene mutations, and for the cost of genetic testing. The new editing technologies should secure the highest standards of research, data collection and applicability ethics.
4.2. Personalized Medicine-Data Integration
Numerous national healthcare organizations are implicated to collect, store, analyze and interpret human genomic data for biomedical research and medical application. However, in top-quality digitized health care systems deviations are observed in coding and collecting data due to different regional clinical practices. Collection and management of human genomic data give rise to some concerns about ethical, privacy and legal problems, or for unauthorized access or misuse of data [56,57]. Constraints emerge when private information and sensitive healthcare data are unprotected due to deficient measures taken for privacy and security [58]. The use of advanced technology for the prediction of future individual healthcare requirements needs data protection as inadequate security can affect a large number of people [59]. Electronic health records, sensors and servers contain a growing volume of digital data for use in healthcare and disease management [60]. The extensive use of big data on healthcare organizations are “ranging from single-physician offices and multi-provider groups to large hospital networks and care organizations” [61]. Bossen et al. [62] argue “that useful data require encounters between people, technologies, and data… routed in particular places and particular times and require effort on the part of the people involved”. To harness emerging disease data, a committee from the National Academies of Science [63] suggested a framework for an information system called a Knowledge Network of disease that “integrates the rapidly expanding range of information on the causes of disease” enabling researchers, medical practitioners and the public to get knowledge of the produced information. The Knowledge Network will help researchers to conceive disease mechanisms, and medical practitioners to initiate new treatments based on distinctive disease characteristics and adapted to each patient [63].
Under the definition of personalized medicine, large number of data are gathered and integrated from different sources namely sequencing genomes, molecular banks, accumulated “omics” data, and references from clinical studies, bioinformatics and current guidelines. In patients with complex CVDs, data for comorbidities, environmental parameters, socioeconomic status nutrition and social habits are assembled, integrated and conceived as a whole [64].
The SB approach is used in current medical research to reveal hidden biological pathways and also identify unseen biomarkers and design novel drugs. Moreover, SB is helpful to comprehend disease progressiveness and complexity, and clarify drug safety profiles and efficacy [65]. It is argued that novel therapies are nevertheless in early stages due to “limited accessibility of robust and affordable molecular systems biology platforms” [65]. In future, general public health and current clinical medicine will change with the application of specific preventive and therapeutic programs focused on the individual patient [66]. This approach would be successful through interconnection of the available electronic medical records with new discoveries in the fields of biomarkers and pharmacotherapy [5].
A bioinformatics team (Biochemical Pharmacology Discussion Group, BPDG) scheduled a robust biomarker strategy to identify disease-related biomarkers and provide drug candidates [67]. The BPDG reported two main methods for designing pharmaceutical drugs: the traditional drug discovery (TDD) and the phenotypic drug discovery (PDD) [67]. Thus, for drug discovery, biomarker-based mechanisms are targeted (TDD method) or biological compounds are tested until final improvement of the phenotype became evident without considering the responsible molecular mechanisms (PDD method).
Pharmaceutical companies helped by one or more AI-based (Artificial Intelligence) drug development companies were able to give priority for interaction to some of the hundreds of implicated proteins. In CVDs, the target is more than one protein, a network of interacting proteins is needed. In this aspect, AI plays a significant role as it matches the properties of thousands of molecules having pharmaceutical potential to the properties of proteins involved in a complex medical disorder, thus disclosing molecules able to bind to a protein-target.
4.3. Personalized Medicine-Taxonomic Revision
A new conception of disease taxonomy with patients’ stratification based on precise individual biological status is needed. Revision of current disease taxonomy to a personalized oriented medicine is a difficult task and requires important changes to structure and management of the whole healthcare system that implicates organizational and political issues. Personalized medicine to be established needs to overcome significant constraints implemented in different fields of clinical medicine and public health system. At the same moment, existing medical knowledge and practices should be revised with new data related to diagnostic biomarkers (innovating disease causation), phenotypic categorization, treatment revision and reorganization of healthcare system. Medical and social determinants that a personalized approach would include, needs a multi-disciplinary contribution. Some of the constraints and regulatory challenges are analyzed below and should be embraced by both the society and medical health system. Personalized medicine provides further rationalization to current guidelines-based clinical medicine. With personalized medicine it is expected that there will be an overhaul to some of the constraints present inside guidelines and to propose reorganization of existent disease classification with a new taxonomy.
In an important “expert consensus report” a committee of experts appointed by the National Academies of Science [63], emphasized that “a new data network that integrates emerging research on the molecular makeup of diseases with clinical data on individual patients could drive the development of a more accurate classification of disease”. Also, in the above report was stressed that biomedical research data will help to develop a “New Taxonomy” which will define disease “based on underlying molecular and environmental causes, rather than on physical signs and symptoms” [63]. Furthermore, together with improvement of health status the biomedical research will advance because of the access to the patient’s information “through electronic health records, while still protecting patient rights” [63].
A new taxonomy of human complex CVDs could restructure diseases’ diagnosis, therapy, mode of progression, and critical clinical directions towards to more individualized management.
Green et al. [68], mentioning personalized medicine argue for “an urgent need for finer-grained disease categories and faster taxonomic revision, through integration of genomic and phenotypic data” while their analysis is associated with the Danish National Genome Center and its endeavor “to bring Denmark to the forefront of personalized medicine”. They mention, also, “how persistent tensions in medicine between variation and standardization, and between change and continuity, remain obstacles for the production as well as the evaluation of genomics-based taxonomies of difference” [68]. Green et al. [68], delineated how “the new taxonomy is supposed to be developed” and have proposed a meta-taxonomy of taxonomy revisions as a basis for discussions. In this meta-taxonomy field they included four new, “fine-grained disease categories” based on: (a) stratification into subgroups of diseases; (b) reclassification of previous categories, “merging previously distinct categories according to shared molecular characteristics”; (c) clustering of disease and risk groups, “based on a network of risk factors and observed co-morbidities”; (d) expansion of current disease categories.
4.4. Personalized Medicine-Policy Decisions
To explore new disease taxonomy will inevitably trigger some constraints of acceptance by the political and academic systems due to prevalent and deep-rooted problems. Change of disease taxonomy needs modifications to the entire health care system, a difficult problem for countries having fewer centralized and digitalized facilities. National personalized medical projects have been developed aiming to upgrade diagnosis and therapies, particularly for chronic complex diseases, giving rise to ethical and administrative problems. Persuasive national strategies for personalized medicine are those of the 100,000 Genomes Project in the UK and the All of Us Research Program in the USA [69,70].
These national strategies include: data accumulation, creation of infrastructure, and organizing interexchange of data with physicians, nurses and genetic counselors [71]. Policy strategies by health authorities and implementation of personalized medicine in clinical practice are promising ambitions. Political, economic and scientific interests for personalized medicine are challenged by the shortage or absence of convincing evidence for wide clinical application of genomic data. It appears that not enough data have been collected yet and there are some uncertainties for clinical application [35]. It is acknowledged the urge for new health technologies and the additional investment to tackle the constraints in healthcare systems. These healthcare constraints include “a shortage of health workers, ineffective supply chains, or inadequate information systems, or organizational constraints such as weak incentives and poor service integration” [72].
4.5. Personalized Medicine-Organization of Human Genomic Data
The committee of experts appointed by the National Academies of Science (USA) outlined a course of action for the construction of a Knowledge Network of disease with the potential to develop a New Taxonomy defining disease [63]. A Knowledge Network based on a centralized database “continuously revises and validates new disease categories” after the integration of genomic and health data, but “integrating data… are very challenging due to the existence of diverse practices for diagnosis and coding” and needs “regulatory amendments, such as data standardization” [68].
In a recent Comment about “better governance of human genomic data” it was argued that for “the collection, storage and curation of human genomic data for biomedical research”, some “genomic data repositories and consortia have adopted governance frameworks to both enable wide access and protect against possible harms” [73]. The authors of this important Comment explain, also, that purpose of this document is “the identification of the functions that governance of genomic data should fulfill”, and also to demonstrate the governance frameworks of six large-scale international genomic projects [73]. The information presented through the six genomic projects is intended primarily to demonstrate the identified governance functions and describe the differences in transparency concerning the information they produce about their governance approaches. There are constraints when access to genomic data is required for biomedical research. There is limited access to health resources or “unequal opportunities for researchers to access and analyze data… because of limitations in human capital, fiscal resources and technological sophistication” [73]. Constraints are applied when genomic data between groups are interpreted, as there are differences in the capacity to benefit from generating genomic data. For example, in the GWAS, which comprise the main source of information for genetic reference databases, 88% (2017) of the genomes still belong to people of European descent with 72% of participants recruited from three countries (USA, UK, Iceland) [74].
The governance frameworks have been initiated to assist biomedical research but systems’ persistent inequalities obscure “the contributions and the important role of different data providers” [75]. It is recommended that “governance of science becomes more transparent, representative and responsive to the voices of many constituencies by conducting public consultations about data-sharing” [75]. An example of effective governance framework is the Human Heredity and Health in Africa (H3Africa) Initiative (https://h3africa.org/ accessed on 9 February 2021) that underlines the genomic research that benefits African populations [73]. The H3Africa promotes research of genomics and environmental factors of common diseases, with the objective to improve the health status of African populations, generating new data [73].
5. Conclusions
Coronary artery disease and heart failure are complex and self-organized chronic and progressive entities. Human disease complexity can be explored with the holistic principle of systems biology. Two important interrelated holistic concepts are described, the emerging field of personalized medicine and the constraint-based thinking with downward causation from the phenotype to molecules and genomes. Constraints (limitations) in cardiovascular diseases include limitations to the biological and medical field, constraints to the use of current technology and constraints in health expenditures. A more aggressive healthcare cost-effective approach is required that integrates into the system any economic-based constraints for new technologies. Personalized medicine requires taxonomic revision, data integration and policy decisions concerning ethics and legal status in social regulations and economic issues. There is an evidence-based reality for personalized medicine, but this requires a determined decision-making medical and political personnel.
Author Contributions
Both the authors contributed equally to the preparation and submission of the research. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report that they have no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
References
- Palsson, B.O. Systems Biology; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Federoff, H.J.; Gostin, L.O. Evolving from Reductionism to Holism: Is there a future for systems medicine? JAMA 2009, 302, 994–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boorse, C. A Rebuttal on Health. In What Is Disease? Humber, J.M., Almeder, J.F., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 1–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiandaca, M.S.; Mapstone, M.; Connors, E.; Jacobson, M.; Monuki, E.S.; Malik, S.; Macciardi, F.; Federoff, H.J. Systems healthcare: A holistic paradigm for tomorrow. BMC Syst. Biol. 2017, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. Conceptual Foundations of Systems Biology Explaining Complex Cardiac Diseases. Healthcare 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Wilson, I.D. The challenges of modeling mammalian biocomplexity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boogerd, F.C.; Bruggeman, F.J.; Hofmeyr, J.H.S.; Westerhoff, H.V. (Eds.) Systems Biology, Philosophical Foundations; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, S.; Chen, J.Y. Unraveling human complexity and disease with systems biology and personalized medicine. Pers. Med. 2010, 7, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, E. The evolution of molecular biology. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberghina, L.; Westerhoff, H.V. (Eds.) Systems Biology: Definitions and Perspectives (Topics in Current Genetics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Louridas, G.; Lourida, K. The Complex Cardiac Atherosclerotic Disorder: The Elusive Role of Genetics and the New Consensus of Systems Biology Approach. J. Adv. Ther. Med. Innov. Sci. 2017, 2, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Louridas, G.E.; Kanonidis, I.E.; Lourida, K.G. Systems biology in heart diseases. Hippokratia 2010, 14, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. A conceptual paradigm of heart failure and systems biology approach. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 159, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, G.F.R. Top-down causation and emergence: Some comments on mechanisms. Interface Focus 2011, 2, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, D. A theory of biological relativity: No privileged level of causation. Interface Focus 2011, 2, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, K.N. Understanding the role of cognition in science: The Science as Category framework. In The Cognitive Basis of Science; Carruthers, P., Stich, S., Siegal, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. Heart failure: A complex clinical process interpreted by systems biology approach and network medicine. Anadolu Kardiyol. Derg. 2014, 14, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cui, J.; Zhang, W.; Shen, P. Robustness analysis identifies the plausible model of the Bcl-2 apoptotic switch. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 5143–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.; Jones, N. Constraint-Based Reasoning for Search and Explanation: Strategies for Understanding Variation and Patterns in Biology. Dialectica 2016, 70, 343–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S. Scale Dependency and Downward Causation in Biology. Philos. Sci. 2018, 85, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Biological robustness. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon, U. An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits; Chapman and Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ueki, Y.; Karagiannis, A.; Zanchin, C.; Zanchin, T.; Stortecky, S.; Koskinas, K.C.; Siontis, G.C.; Praz, F.; Otsuka, T.; Hunziker, L.; et al. Validation of High-Risk Features for Stent-Related Ischemic Events as Endorsed by the 2017 DAPT Guidelines. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 12, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. Systems Biology and Biomechanical Model of Heart Failure. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2012, 8, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Baal, P.; Morton, A.; Severens, J.L. Health care input constraints and cost effectiveness analysis decision rules. Soc. Sci. Med. 2018, 200, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoglou, G.; Soulis, J.; Farmakis, T.; Louridas, G. Haemodynamic factors and the important role of local low static pressure in coronary wall thickening. Int. J. Cardiol. 2002, 86, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakslis, E.; Ginsburg, G.S. Digital Health—The Need to Assess Benefits, Risks, and Value. JAMA 2021, 325, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coravos, A.; Goldsack, J.C.; Karlin, D.R.; Nebeker, C.; Perakslis, E.; Zimmerman, N.; Erb, M.K. Digital Medicine: A Primer on Measurement. Digit. Biomark. 2019, 3, 31–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaveikaite, V.; Grundstrom, C.; Lourida, K.; Winter, S.; Priori, R.; Chouvarda, I.; Maglaveras, N. Developing a strategic understanding of telehealth service adoption for COPD care management: A causal loop analysis of healthcare professionals. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloukas, P.; Kanoni, S.; Willenborg, C.; Farrall, M.; Assimes, T.L.; Thompson, J.R.; Ingelsson, E.; Saleheen, D.; Erdmann, J.; The CARDIoGRAMplusC4D Consortium; et al. Large-scale association analysis identifies new risk loci for coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2012, 45, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, A.V.; Emdin, C.A.; Drake, I.; Natarajan, P.; Bick, A.G.; Cook, N.R.; Chasman, D.I.; Baber, U.; Mehran, R.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Genetic Risk, Adherence to a Healthy Lifestyle, and Coronary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Vikram, A.; Hoffman, T.A.; Naqvi, A.; Lewarchik, C.M.; Kim, Y.-R.; Irani, K. Histone and DNA Methylation–Mediated Epigenetic Downregulation of Endothelial Kruppel-Like Factor 2 by Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. International Programme on Chemical Safety, Biomarkers in Risk Assessment: Validity and Validation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans, S. Trust in standards: Transitioning clinical exome sequencing from bench to bedside. Soc. Stud. Sci. 2014, 45, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, S.; Tietbohl, C.; Skaperdas, E. Narrating uncertainty: Variants of uncertain significance (VUS) in clinical exome sequencing. BioSocieties 2017, 12, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimer, J. The Start of a New Proteomics Era. In Advancing Precision Medicine: Current and Future Proteogenomic Strategies for Biomarker Discovery and Development; Science/AAAS: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wesson, D.E.; Lucey, C.R.; Cooper, L.A. Building Trust in Health Systems to Eliminate Health Disparities. JAMA 2019, 322, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.; Flores, M. A personal view on systems medicine and the emergence of proactive P4 medicine: Predictive, preventive, personalized and participatory. New Biotechnol. 2012, 29, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, N.D.; Magis, A.T.; Earls, J.C.; Glusman, G.; Levy, R.; Lausted, C.; McDonald, D.T.; Kusebauch, U.; Moss, C.L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. A wellness study of 108 individuals using personal, dense, dynamic data clouds. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, L.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Price, N.D. Integrating big data and actionable health coaching to optimize wellness. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, S. A Worthwhile Goal. In Advancing Precision Medicine: Current and Future Proteogenomic Strategies for Biomarker Discovery and Development; Science/AAAS: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- National Institutes of Health. What Is Precision Medicine? 2017. Available online: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/primer/precisionmedicine/definition (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Nicholson, J.K. Global systems biology, personalized medicine and molecular epidemiology. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboab, J.; Celi, L.A.; Charlton, P.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Marshall, D.C.; Mayaud, L.; Naumann, T.; McCague, N.; Paik, K.E.; et al. A “datathon” model to support cross-disciplinary collaboration. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 333ps8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscalzo, J.; Kohane, I.; Barabasi, A. Human disease classification in the postgenomic era: A complex systems approach to human pathobiology. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, A.M.; Burton-Houle, T.; Aron, D.C. Applying the Theory of Constraints in Health Care. Qual. Manag. Health Care 2002, 10, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, E.J. A decade of digital medicine innovation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallis, C.J.D.; Detsky, A.S.; Fan, Y. Establishing the Effectiveness of Procedural Interventions: The Limited Role of Randomized Trials. JAMA 2018, 320, 2421–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S. New Technologies Personalize Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2010, 12, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, E.S.; Kelly, S.E.; Lucivero, F.; Machirori, M.; Dheensa, S.; Prainsack, B. Beyond individualism: Is there a place for relational autonomy in clinical practice and research? Clin. Ethics 2017, 12, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avorn, J. The Psychology of Clinical Decision Making—Implications for Medication Use. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D. Thinking, Fast and Slow; Farrar, Straus, and Giroux: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sharrer, G.T. Personalized Medicine: Ethics for Clinical Trials. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2011, 823, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, K.B.; Rothstein, M.A. Ethical, legal and social implications of incorporating personalized medicine into healthcare. Pers. Med. 2015, 12, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, J.D.; Joung, J.K. CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdows, H. The Connected Self. The Ethics and Governance of the Genetic Individual; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M. Genetic Data and the Low. A Critical Perspective on Privacy Protection; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, D. “Big Data” Could Mean Big Problems for People’s Healthcare Privacy. LA Times Online, 11 October 2016. Available online: https://www.latimes.com/business/lazarus/la-fi-lazarus-big-data-healthcare-20161011-snap-story.html (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Schultz, D. As Patients’ Records Go Digital, Theft and Hacking Problems Grow. News KH: KHN, 3 June 2012. Available online: https://khn.org/news/electronic-health-records-theft-hacking/ (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Murdoch, T.B.; Detsky, A.S. The Inevitable Application of Big Data to Health Care. JAMA 2013, 309, 1351–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghupathi, W.; Raghupathi, V. Big data analytics in healthcare: Promise and potential. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2014, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossen, C.; Pine, K.H.; Cabitza, F.; Ellingsen, G.; Piras, E.M. Data work in healthcare: An Introduction. Heal. Inform. J. 2017, 25, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences (NAS). Toward precision medicine: Building a knowledge-network for biomedical research and a new taxonomy of disease. In Committee on A Framework for Developing a New Taxonomy of Disease; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Louridas, G.E.; Louridas, K.G. Systems biology approach for human complexity and personalized cardiology. In Recent Advances in Systems Biology Research; Valente, A.X., Sarkar, A., Gao, Y., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 211–236. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Greef, J.; Hankemeier, T.; McBurney, R.N. Metabolomics-based systems biology and personalized medicine: Moving towards n = 1 clinical trials? Pharmacogenomics 2006, 7, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyner, M.J.; Paneth, N. Seven Questions for Personalized Medicine. JAMA 2015, 314, 999–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The New York Academy of Sciences. Phenotypic and Biomarker-Based Drug Discovery. Academy eBriefing, 12 January 2016. Available online: https://www.nyas.org/ebriefings/phenotypic-and-biomarker-based-drug-discovery/ (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Green, S.; Carusi, A.; Hoeyer, K. Plastic diagnostics: The remaking of disease and evidence in personalized medicine. Soc. Sci. Med. 2019, 112318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genomics England. The 100000 Genomes Project Protocol V3. 2017. Available online: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.4530893.v2 (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- National Institutes of Health. All of US Research Program. Protocol Version v.1.7. 2018. Available online: https://allofus.nih.gov/about/all-us-research-program-protocol (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Minari, J.; Brothers, K.B.; Morrison, M. Tensions in ethics and policy created by National Precision Medicine Programs. Hum. Genom. 2018, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassall, A.; Bozzani, F.; Hanson, K. Considering Health-Systems Constraints in Economic Evaluation in Low- and Middle-Income Settings. Oxf. Res. Encycl. Econ. Financ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Doherty, K.C.; Shabani, M.; Dove, E.S.; Bentzen, H.B.; Borry, P.; Burgess, M.M.; Chalmers, D.; De Vries, J.; Eckstein, L.; Fullerton, S.M.; et al. Toward better governance of human genomic data. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.C.; Rahal, C. A scientometric review of genome-wide association studies. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, J.; Terry, S.F.; Juengst, E.; Coy, S.; Harris, J.R.; Chalmers, D.; Dove, E.S.; Budin-Ljøsne, I.; Adebamowo, C.; Ogbe, E.; et al. Including all voices in international data-sharing governance. Hum. Genom. 2018, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).