Urea/Creatinine Ratio’s Correlation with Creatine Kinase Normalization in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients with Myositis: Evaluating Prognostic and Predictive Value
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Enrollment
2.2. Clinical Management Pathway
2.3. Acquisitions Dataset
2.3.1. Primary Outcome
2.3.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Clinical Features
3.3. Laboratory Findings
3.4. Treatment and Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marino, A.; Munafò, A.; Augello, E.; Bellanca, C.M.; Bonomo, C.; Ceccarelli, M.; Musso, N.; Cantarella, G.; Cacopardo, B.; Bernardini, R. Sarilumab Administration in COVID-19 Patients: Literature Review and Considerations. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vito, A.; Geremia, N.; Fiore, V.; Princic, E.; Babudieri, S.; Madeddu, G. Clinical Features, Laboratory Findings and Predictors of Death in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in Sardinia, Italy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 7861–7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaira, L.A.; De Vito, A.; Deiana, G.; Pes, C.; Giovanditto, F.; Fiore, V.; Lechien, J.R.; Saussez, S.; Policicchio, D.; Boccaletti, R.; et al. Systemic Inflammatory Markers and Psychophysical Olfactory Scores in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: Is There Any Correlation? J. Laryngol. Otol. 2021, 135, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; De Vito, A.; Scano, V.; Paliogiannis, P.; Fiore, V.; Madeddu, G.; Maida, I.; Zinellu, E.; Mangoni, A.A.; Arru, L.B.; et al. The PaO2/FiO2 Ratio on Admission Is Independently Associated with Prolonged Hospitalization in COVID-19 Patients. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2021, 15, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanella, E.; Marino, A.; Ceccarelli, M.; Gussio, M.; Cosentino, F.; Moscatt, V.; Micali, C.; Nunnari, G.; Celesia, B.M.; Cacopardo, B. Pain Crisis Management in a Patient with Sickle Cell Disease during SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report and Literature Review. World Acad. Sci. J. 2022, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Pampaloni, A.; Scuderi, D.; Cosentino, F.; Moscatt, V.; Ceccarelli, M.; Gussio, M.; Celesia, B.M.; Bruno, R.; Borraccino, S.; et al. High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygenation and Tocilizumab Administration in Patients Critically Ill with COVID-19: A Report of Three Cases and a Literature Review. World Acad. Sci. J. 2020, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckholz, A.P.; Kaplan, A.; Rosenblatt, R.E.; Wan, D. Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis, and Outcomes of 6 Patients with COVID-19 Infection and Rhabdomyolysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 2557–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Tong, Q. Rhabdomyolysis as Potential Late Complication Associated with COVID-19. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1618–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosla, S.G.; Nylen, E.S.; Khosla, R. Rhabdomyolysis in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Infection: Five Case Series. J. Investig. Med. High Impact. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2324709620984603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegada, S.; Muppidi, V.; Wilkinson, D.C.; Siddamreddy, S.; Katta, S.K. Coronavirus Disease 2019-Induced Rhabdomyolysis. Cureus 2020, 12, e10123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-García, S.; Bernal, J.; Bachiller-Corral, J. Rhabdomyolysis as the Main Manifestation of Coronavirus Disease 2019. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2174–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, A.K.; Maurer, L.R.; Christensen, M.A.; El Moheb, M.; Naar, L.; Alser, O.; Gaitanidis, A.; Langeveld, K.; Kapoen, C.; Breen, K.; et al. Rhabdomyolysis in Severe COVID-19: Male Sex, High BMI, and Prone Positioning Confer High Risk. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 266, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughal, M.S.; Kaur, I.P.; Alhashemi, R.; Rehman, R.; Du, D. Acute Viral Myositis Complicated by Rhabdomyolysis: A Sole Manifestation of COVID-19 Infection. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect 2021, 11, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solís, J.G.; Pineda, A.E.; Minutti, P.A.; Sánchez, A.A. Case Report: Rhabdomyolysis in a Patient with COVID-19: A Proposed Diagnostic-Therapeutic Algorithm. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroun, M.W.; Dieiev, V.; Kang, J.; Barbi, M.; Marashi Nia, S.F.; Gabr, M.; Eman, G.; Kajita, G.; Swedish, K. Rhabdomyolysis in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study. Cureus 2021, 13, e12552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, P.K.; Sigoli, E.; Bragança, L.J.G.; Cornachione, A.S. The Musculoskeletal Involvement after Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Infection. Front. Mater. 2022, 13, 813924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Campanella, E.; Ceccarelli, M.; Larocca, L.; Bonomo, C.; Micali, C.; Munafò, A.; Celesia, B.M.; Nunnari, G.; Cacopardo, B. Sarilumab Administration in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Report of Four Cases and a Literature Review. World Acad. Sci. J. 2022, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, M.; Libra, A.; Ciancio, N.; Sambataro, G.; Sciacca, E.; Muscato, G.; Marino, A.; Vancheri, C.; Spicuzza, L. Use of Remdesivir in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19 Pneumonia: Effect on the Hypoxic and Inflammatory State. Viruses 2023, 15, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Mukerji, S.S.; Collens, S.I.; Padera, R.F.; Pinkus, G.S.; Amato, A.A.; Solomon, I.H. Skeletal Muscle and Peripheral Nerve Histopathology in COVID-19. Neurology 2021, 97, E849–E858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, A.M.; Palumbo, N.; Nathan, S.K.; Singer, P.S.; Castellanos-Reyes, L.J.; Sethna, C.B. Pediatric COVID-19-Associated Rhabdomyolysis: A Case Report. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tram, N.; Chiodini, B.; Montesinos, I.; Vicinanza, A.; Beretta-Piccoli, X.; Gubbelmans, N.; Demey, M.; Genis, N.; Tilmanne, A.; Smeesters, P.R.; et al. Rhabdomyolysis and Acute Kidney Injury as Leading COVID-19 Presentation in an Adolescent. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, E314–E315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilpin, S.; Byers, M.; Byrd, A.; Cull, J.; Peterson, D.; Thomas, B.; Jacobson, P. Rhabdomyolysis as the Initial Presentation of SARS-CoV-2 in an Adolescent. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e2020019273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, F.; Moscatt, V.; Marino, A.; Pampaloni, A.; Scuderi, D.; Ceccarelli, M.; Benanti, F.; Gussio, M.; Larocca, L.; Boscia, V.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Predictors of Death among Hospitalized Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Sicily, Italy: A Retrospective Observational Study. Biomed Rep. 2022, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, M.K.; Higgins, V.; Adeli, K. CALIPER Paediatric Reference Intervals for the Urea Creatinine Ratio in Healthy Children & Adolescents. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 76, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaianese, F.; Costantino, A.; Benucci, C.; Lasagni, D.; Trapani, S. Benign Acute Children Myositis: 5 Years Experience in a Tertiary Care Pediatric Hospital. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 4341–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szenborn, L.; Toczek-Kubicka, K.; Zaryczański, J.; Marchewka-Kowalik, M.; Miśkiewicz, K.; Kuchar, E. Benign Acute Childhood Myositis during Influenza B Outbreak. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1039, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Azevedo, A.; Costa e Silva, A.; Juliana Silva, C.; Poço Miranda, S.; Costa, M.; Martinho, I. Benign Acute Childhood Myositis: A 5-Year Retrospective Study. Arch. Pédiatr. 2022, 29, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murala, S.; Ram, A.; Vijayakumar, R.; Nagarajan, E. Infectious Myositis. RRNMF Neuromuscul. J. 2021, 2, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, A.; Naveen, R.; Aggarwal, R.; Gupta, L. COVID-19 and Myositis: What We Know So Far. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudo, C.; Fichera, G.; Pilati, L.; Cortinovis, A.L.; Cavallin, C.; Bertin, S.; Zuliani, M.; Cecchin, D. COVID-19 Musculoskeletal Involvement in Children. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1200877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, J.R.; Ali, S.S.; Nagra, D.; Adas, M.A.; Buazon, A.D.; Galloway, J.B.; Gordon, P.A. Skeletal Muscles and COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Rhabdomyolysis and Myositis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisca, G.; Mariani, M.; Pirlo, D.; Romanengo, M.; Pistorio, A.; Gaiero, A.; Panicucci, C.; Piccotti, E.; Bruno, C. Management and Outcome of Benign Acute Childhood Myositis in Pediatric Emergency Department. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, J.; Macartney, K.; Britton, P.N. Influenza-Associated Myositis: A Single-Centre, 5-Year Retrospective Study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, N.C.; Chi, H.; Tai, Y.L.; Peng, C.C.; Tseng, C.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Tan, B.F.; Lin, C.Y. Impact of Wearing Masks, Hand Hygiene, and Social Distancing on Influenza, Enterovirus, and All-Cause Pneumonia during the Coronavirus Pandemic: Retrospective National Epidemiological Surveillance Study. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e21257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrano, R.; Villani, A.; Berrettini, S.; Caione, P.; Chiara, A.; Costantino, A.; Formigari, R.; Franzoni, E.; Gattinara, G.C.; Giustardi, A.; et al. Point of View of the Italians Pediatric Scientific Societies about the Pediatric Care during the COVID-19 Lockdown: What Has Changed and Future Prospects for Restarting. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2020, 46, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaude, M.; Mori, M.; Tjäder, I.; Gustafsson, T.; Wernerman, J.; Rooyackers, O. Protein Metabolism and Gene Expression in Skeletal Muscle of Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerapornratana, S.; Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Gómez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Acute Kidney Injury from Sepsis: Current Concepts, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Prevention and Treatment. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



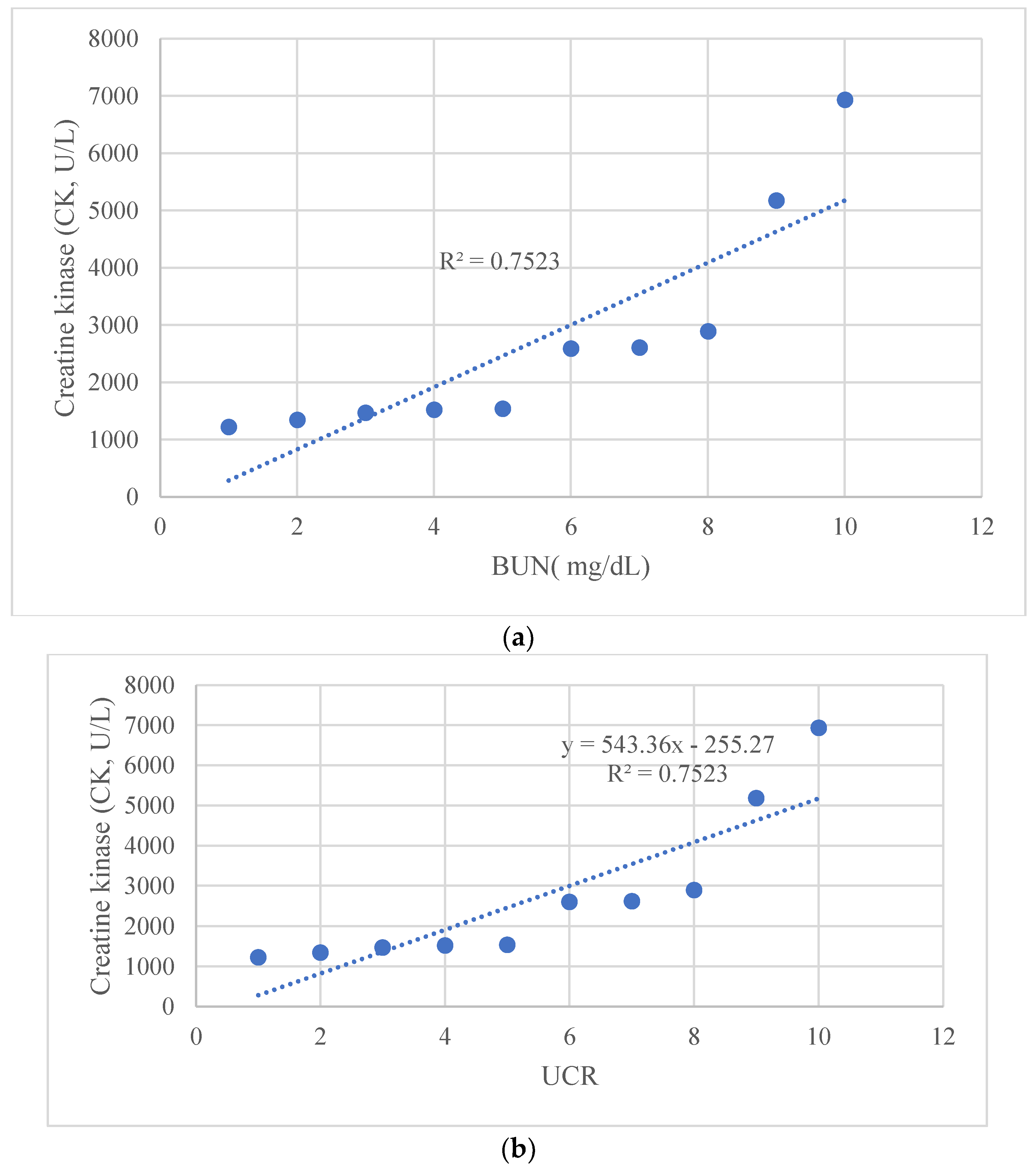
| Patient Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Age (years) | 7 | 5 | 6 | 12 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 5 |
| Sex | M | M | M | F | M | M | M | M | F | F |
| White blood cell count (cells /µL) | 7220 | 5450 | 5710 | 7220 | 6170 | 4220 | 6940 | 4567 | 5620 | 8650 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13 | 12.5 | 11.6 | 13 | 13.7 | 112 | 14 | 13.5 | 13.9 | 12.3 |
| Platelet count (×103/µL) | 350 | 178 | 277 | 250 | 250 | 227 | 121 | 231 | 201 | 231 |
| Creatine kinase (CK, U/L) | 1225 | 1346 | 1475 | 1524 | 1543 | 2596 | 2614 | 2892 | 5180 | 6937 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (BUN, mg/dL) | 6 | 8.64 | 9.74 | 10.85 | 13.8 | 16.28 | 19 | 22.29 | 26 | 35.75 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.45 | 0.55 |
| UCR | 23 | 27 | 28.7 | 31 | 30.5 | 35.4 | 50 | 45.5 | 58.7 | 65 |
| Normalization of CK (day) | 7 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, U/L) | 46 | 112 | 58 | 53 | 76 | 35 | 55 | 65 | 89 | 150 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, U/L) | 35 | 25 | 19 | 20 | 23 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 29 | 34 |
| C-reactive protein (CRP, mg/dL) | 2.41 | 2.36 | 4.77 | 4.53 | 5.29 | 3.19 | 5.83 | 9.74 | 7.11 | 6.59 |
| Serum sodium (mmol/L) | 138 | 137 | 139 | 140 | 141 | 145 | 137 | 144 | 142 | 143 |
| Serum potassium (mmol/L) | 4.5 | 4.2 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 4.4 | 4.2 |
| Urea Creatinine Ratio (SI Units) | BUN Creatinine Ratio (CON Units) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assay | Age Partition | n | Lower Reference Limit | Upper Reference Limit | Lower Reference Limit | Upper Reference Limit |
| Creatinine (enzymatic) | 0 to <15 days | 51 | 21 | 162 | 5 | 40 |
| 15 days to <1 year | 126 | 49 | 438 | 12 | 108 | |
| 1 to <3 years | 59 | 127 | 419 | 31 | 1 | |
| 3 to <5 years | 89 | 130 | 299 | 32 | 74 | |
| 5 to <8 years | 115 | 87 | 246 | 22 | 61 | |
| 8 to <10 years Female | 57 | 69 | 177 | 17 | 44 | |
| 8 to <10 years Male | 41 | 83 | 189 | 21 | 47 | |
| 10 to <15 years | 272 | 50 | 146 | 12 | 36 | |
| 15 to <19 years | 228 | 44 | 107 | 11 | 26 | |
| Creatinine (Jaffe) | 0 to <15 days | 74 | 26 | 121 | 6 | 30 |
| 15 days to <1 year | 120 | 35 | 156 | 9 | 39 | |
| 1 to <5 years | 148 | 70 | 198 | 17 | 49 | |
| 5 to <8 years | 113 | 69 | 160 | 17 | 40 | |
| 8 to <10 years Female | 57 | 57 | 131 | 14 | 32 | |
| 8 to <10 years Male | 42 | 66 | 156 | 16 | 39 | |
| 10 to <15 years Female | 147 | 42 | 111 | 10 | 27 | |
| 10 to <15 years Male | 130 | 50 | 134 | 12 | 33 | |
| 15 to <19 years | 229 | 42 | 99 | 10 | 25 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pizzo, F.; Marino, A.; Di Nora, A.; Spampinato, S.; Cacciaguerra, G.; Costanza, G.; Scarlata, F.; Biasco, A.; Consentino, M.C.; Lubrano, R.; et al. Urea/Creatinine Ratio’s Correlation with Creatine Kinase Normalization in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients with Myositis: Evaluating Prognostic and Predictive Value. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16, 13-25. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16010002
Pizzo F, Marino A, Di Nora A, Spampinato S, Cacciaguerra G, Costanza G, Scarlata F, Biasco A, Consentino MC, Lubrano R, et al. Urea/Creatinine Ratio’s Correlation with Creatine Kinase Normalization in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients with Myositis: Evaluating Prognostic and Predictive Value. Infectious Disease Reports. 2024; 16(1):13-25. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16010002
Chicago/Turabian StylePizzo, Francesco, Andrea Marino, Alessandra Di Nora, Serena Spampinato, Giovanni Cacciaguerra, Giuseppe Costanza, Federica Scarlata, Arturo Biasco, Maria Chiara Consentino, Riccardo Lubrano, and et al. 2024. "Urea/Creatinine Ratio’s Correlation with Creatine Kinase Normalization in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients with Myositis: Evaluating Prognostic and Predictive Value" Infectious Disease Reports 16, no. 1: 13-25. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16010002
APA StylePizzo, F., Marino, A., Di Nora, A., Spampinato, S., Cacciaguerra, G., Costanza, G., Scarlata, F., Biasco, A., Consentino, M. C., Lubrano, R., Cacopardo, B., Nunnari, G., Ruggieri, M., & Pavone, P. (2024). Urea/Creatinine Ratio’s Correlation with Creatine Kinase Normalization in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients with Myositis: Evaluating Prognostic and Predictive Value. Infectious Disease Reports, 16(1), 13-25. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16010002









