Acute Kidney Injury in the Context of COVID-19: An Analysis in Hospitalized Mexican Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
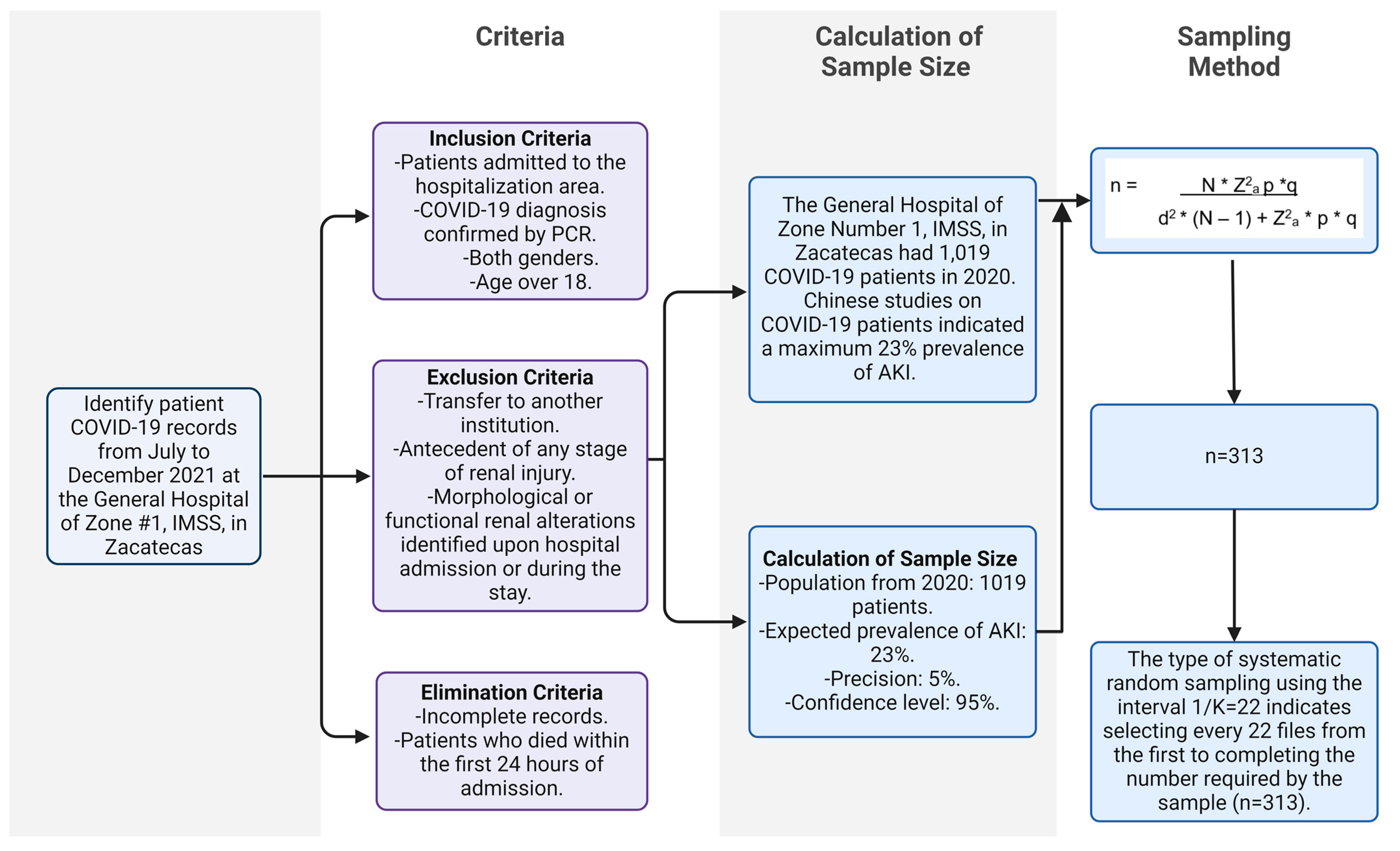
2.2. Study Population and Sample
2.3. Selection and Randomization
2.4. Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Sample Overview
3.2. Comparison of Laboratory Data between Groups with AKI and without AKI
3.3. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics between Groups with AKI and without AKI
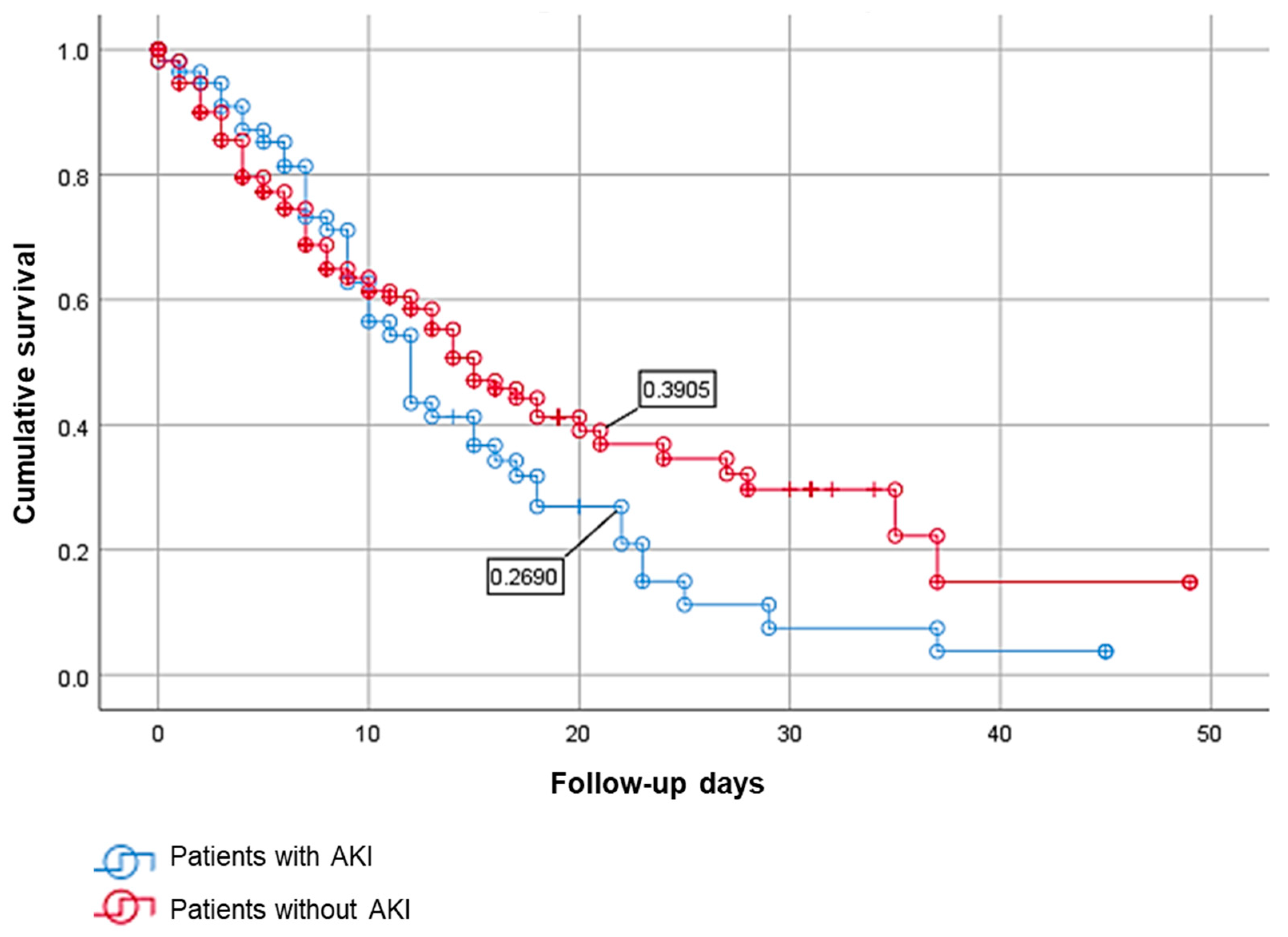
3.4. Survival Analysis between COVID-19 Patients with AKI and without AKI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Bashir et al. (2022) found a 12.7% prevalence in their study, highlighting the lower end of the spectrum [14].
- Morosini et al. (2021) observed a prevalence of 37.14%, demonstrating the higher variability in different patient populations [64].
- Wen et al. (2020) reported a 41% prevalence in a subset of severe and critical patients, which is particularly relevant to our study’s focus on hospitalized patients [65].
References
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Krynytska, I.; Marushchak, M.; Birchenko, I.; Dovgalyuk, A.; Tokarskyy, O. COVID-19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome versus Classical Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (a Narrative Review). Iran. J. Microbiol. 2021, 13, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molani, S.; Hernandez, P.V.; Roper, R.T.; Duvvuri, V.R.; Baumgartner, A.M.; Goldman, J.D.; Ertekin-Taner, N.; Funk, C.C.; Price, N.D.; Rappaport, N.; et al. Risk Factors for Severe COVID-19 Differ by Age for Hospitalized Adults. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; et al. Human Kidney Is a Target for Novel Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głowacka, M.; Lipka, S.; Młynarska, E.; Franczyk, B.; Rysz, J. Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, A.; Hatfield, K.M.; Arons, M.; James, A.; Taylor, J.; Spicer, K.; Bardossy, A.C.; Oakley, L.P.; Tanwar, S.; Chisty, Z.; et al. Asymptomatic and Presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Residents of a Long-Term Care Skilled Nursing Facility-King County, Washington, March 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panitchote, A.; Mehkri, O.; Hastings, A.; Hanane, T.; Demirjian, S.; Torbic, H.; Mireles-Cabodevila, E.; Krishnan, S.; Duggal, A. Factors Associated with Acute Kidney Injury in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, E.L.; Janse, R.J.; de Jong, Y.; van der Endt, V.H.W.; Milders, J.; van der Willik, E.M.; de Rooij, E.N.M.; Dekkers, O.M.; Rotmans, J.I.; van Diepen, M. Acute Kidney Injury and Kidney Replacement Therapy in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukland, E.A.; Klepstad, P.; Aukland, S.M.; Ghavidel, F.Z.; Buanes, E.A. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with COVID-19 in the Intensive Care Unit: Evaluation of Risk Factors and Mortality in a National Cohort. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaubroeck, H.; Vandenberghe, W.; Boer, W.; Boonen, E.; Dewulf, B.; Bourgeois, C.; Dubois, J.; Dumoulin, A.; Fivez, T.; Gunst, J.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Critical COVID-19: A Multicenter Cohort Analysis in Seven Large Hospitals in Belgium. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumlertgul, N.; Pirondini, L.; Cooney, E.; Kok, W.; Gregson, J.; Camporota, L.; Lane, K.; Leach, R.; Ostermann, M. Acute Kidney Injury Prevalence, Progression and Long-Term Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.M.; Mukhtar, M.S.; Mohamed, Y.G.; Cetinkaya, O.; Fiidow, O.A. Prevalence of Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19 Patients- Retrospective Single-Center Study. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney Disease Is Associated with In-Hospital Death of Patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, J.S.; Ng, J.H.; Ross, D.W.; Sharma, P.; Shah, H.H.; Barnett, R.L.; Hazzan, A.D.; Fishbane, S.; Jhaveri, K.D. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, G.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Yu, C.; Ma, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yao, Y.; et al. Renal Involvement and Early Prognosis in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.M.B.; Lukitsch, I.; Torres-Ortiz, A.E.; Walker, J.B.; Varghese, V.; Hernandez-Arroyo, C.F.; Alqudsi, M.; LeDoux, J.R.; Velez, J.C.Q. Acute Kidney Injury Associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Urban New Orleans. Kidney360 2020, 1, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caution on Kidney Dysfunctions of COVID-19 Patients|medRxiv. Available online: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.08.20021212v2 (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Cai, Y.; Tang, C.; Song, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Lei, Y.; Li, F.; et al. Duration of Acute Kidney Injury and In-Hospital Mortality in Elder Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Biomed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9929038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.-Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, B.-C. Acute Kidney Injury in the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease. Kidney Dis. (Basel) 2020, 6, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; Tian, T.; Luo, J.; Yang, Y. Acute Kidney Injury Is Associated with Severe Infection and Fatality in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 40 Studies and 24,527 Patients. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadi, A.; Farrokhpour, H.; Rashedi, S.; Kafan, S.; Sotoudehnia, M.; Rahimzadeh, H.; Tabatabaei, S.; Razeghi, E.; Aghsaeifard, Z. Long-Term Impact of the COVID-19 Associated AKI: The Relationship between Kidney Recovery and Mortality in a 10-Month Follow-Up Cohort Study. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2022, 47, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nlandu, Y.; Mafuta, D.; Sakaji, J.; Brecknell, M.; Engole, Y.; Abatha, J.; Nkumu, J.-R.; Nkodila, A.; Mboliassa, M.-F.; Tuyinama, O.; et al. Predictors of Mortality in COVID-19 Patients at Kinshasa Medical Center and a Survival Analysis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez-Íñiguez, J.S.; Madero, M. Global Perspectives in Acute Kidney Injury: Mexico. Kidney360 2022, 3, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Martínez, I.; Ochoa Salmorán, H.; Enríquez Barajas, A.; Teniza Frías, E.; Vargas González, K.; Padilla Pérez, F.J.; Díaz Greene, E.J.; Esponda Prado, J.G. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with COVID-19 in the Intensive Care Unit of the Hospital Ángeles Pedregal. Acta Médica Grupo Ángeles 2021, 19, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas-Aparicio, G.A.; León-Rodríguez, I.; la Barrera, C.A.; González-Navarro, M.; Peralta-Prado, A.B.; Luna-Villalobos, Y.; Velasco-Morales, A.; Calderón-Dávila, N.; Ormsby, C.E.; Ávila-Ríos, S. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Severe COVID-19 in Mexico. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez Requena, L.I.; Rodríguez Zarate, C.; Sánchez Calzada, A.; Chaires Gutiérrez, R.; Aguirre Sánchez, J.S. Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Replacement Therapy in Severe Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 under Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Med. Crítica (Col. Mex. Med. Crítica) 2022, 36, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Echavarría, A.I.; Yáñez-Morales, M.; Camarillo-Cisneros, J.; Ramos-Luján, F.A.; Saad-Manzanera, M.I.; Contreras-Pacheco, A.E.; Solís-Valdez, J.; González-Cristóbal, S.C.; Enríquez-Sánchez, L.B. Acute kidney injury as a predictor of hospital discharge in COVID-19 patients. Med. Interna Mex. 2021, 721–727. [Google Scholar]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.; Chaudhary, K.; Saha, A.; Chauhan, K.; Vaid, A.; Zhao, S.; Paranjpe, I.; Somani, S.; Richter, F.; Miotto, R.; et al. AKI in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Hernández, W.M.; Soto, L.F.; Del Rosario-Trinidad, M.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; Martínez-Mier, G.; Osuna-Ramos, J.F.; Bastida-González, F.; Bernal-Dolores, V.; del Ángel, R.M.; et al. Leukocyte Glucose Index as a Novel Biomarker for COVID-19 Severity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna-Ramos, J.F.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Ochoa-Ramírez, L.A.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; Ramos-Payán, R.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; Romero-Utrilla, A.; Ríos-Burgueño, E.R.; Rodríguez-Millán, J.; del Ángel, R.M.; et al. The Usefulness of Peripheral Blood Cell Counts to Distinguish COVID-19 from Dengue during Acute Infection. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, D.; Soler, M.J.; Sparks, M.A.; Hiremath, S.; South, A.M.; Welling, P.A.; Swaminathan, S.; on behalf of the COVID-19 and ACE2 in Cardiovascular, L. Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19: Emerging Evidence of a Distinct Pathophysiology. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, M.; Bell, S.; Forni, L.; Joannidis, M.; Koyner, J.L.; Liu, K.; Cantaluppi, V. Pathophysiology of COVID-19-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelayo, J.; Lo, K.B.; Bhargav, R.; Gul, F.; Peterson, E.; DeJoy, R., III; Salacup, G.F.; Albano, J.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Azmaiparashvili, Z.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Community- and Hospital-Acquired Acute Kidney Injury with COVID-19 in a US Inner City Hospital System. Cardiorenal Med. 2020, 10, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamyshnyi, A.; Krynytska, I.; Matskevych, V.; Marushchak, M.; Lushchak, O. Arterial Hypertension as a Risk Comorbidity Associated with COVID-19 Pathology. Int. J. Hypertens. 2020, 2020, e8019360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, G.; Calvez, V.; Savoia, C. Hypertension and COVID-19: Current Evidence and Perspectives. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2022, 29, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podzolkov, V.I.; Bragina, A.E.; Tarzimanova, A.I.; Vasilyeva, L.V.; Ogibenina, E.S.; Bykova, E.E.; Shvedov, I.I.; Ivannikov, A.A.; Druzhinina, N.A. Arterial Hypertension and Severe COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients: Data from a Cohort Study. Ration. Pharmacother. Cardiol. 2023, 19, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Nonato, I.; Hernández-Barrera, L.; Oviedo-Solís, C.; Ramírez-Villalobos, D.; Hernández-Prado, B.; Barquera, S. Epidemiología de La Hipertensión Arterial En Adultos Mexicanos: Diagnóstico, Control y Tendencias. Ensanut 2020. Salud Publica Mex 2021, 63, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gameiro, J.; Fonseca, J.A.; Oliveira, J.; Marques, F.; Bernardo, J.; Costa, C.; Carreiro, C.; Braz, S.; Lopes, J.A. Acute Kidney Injury in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Portuguese Cohort. Nefrología 2021, 41, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Kovalic, A.J.; Graber, C.J. Prognostic Value of Leukocytosis and Lymphopenia for Coronavirus Disease Severity. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1839–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Wakabayashi, M.; Yamaji, T.; Chopra, N.; Mikami, T.; Miyashita, H.; Miyashita, S. Value of Leukocytosis and Elevated C-Reactive Protein in Predicting Severe Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 509, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Li, R.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Zheng, Z.; Zeng, S.; Ding, X.; Nie, H. Clinical Features in 52 Patients with COVID-19 Who Have Increased Leukocyte Count: A Retrospective Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Feng, X.; Jiang, C.; Mi, S.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Correlation between White Blood Cell Count at Admission and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küçükceran, K.; Ayrancı, M.K.; Girişgin, A.S.; Koçak, S.; Dündar, Z.D. The Role of the BUN/Albumin Ratio in Predicting Mortality in COVID-19 Patients in the Emergency Department. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 48, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.; Deng, H.; Zhao, H.; Liang, J.; Ke, L.; Li, W. Association between an Increase in Blood Urea Nitrogen at 24 h and Worse Outcomes in COVID-19 Pneumonia. Ren Fail 2021, 43, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, J.S.S.; Moguel, K.G.P.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Nieto, O.R.P.; Martínez, D.E.; López, E.I.Z.; Sánchez, M.V.C. The ∆Pv-aCO2/∆Ca-vO2 Ratio as a Predictor of Mortality in Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Related to COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Position Statement of the ESC Council on Hypertension on ACE-Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers. Available online: https://www.escardio.org/Councils/Council-on-Hypertension-(CHT)/News/position-statement-of-the-esc-council-on-hypertension-on-ace-inhibitors-and-ang (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Sánchez, J.M.R.; del C. de H. Alonso, M.; Barrientos, R.R. Mantenimiento de Tratamientos Crónicos En Pacientes Afectados de COVID-19. FMC-Form. Médica Contin. Atención Primaria 2021, 28, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.C.; Heran, B.S.; Wright, J.M. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors versus Angiotensin Receptor Blockers for Primary Hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD009096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, M.L.G.; Lombardelli, L.; Colombi, D.; Bignami, E.G.; Pergolotti, B.; Repetti, F.; Villani, M.; Bellini, V.; Rossi, T.; Halasz, G.; et al. Prediction of 28-Day Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: Development and Internal Validation of a Clinical Prediction Model. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Zou, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Yuan, Y.; Qi, H.; Fu, S.; et al. Clinical Course and Predictors of 60-Day Mortality in 239 Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Multicenter Retrospective Study from Wuhan, China. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, C.L.; Forero, A.C.P.; Ángel, D.C.V.; López, P.M.R.; Diaz, L.V.G.; Aguilar, D.K.N.; Yate, H.C.M. Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19. J. Bras. Nefrol. 2024, 46, e20230056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavezzi, A.; Troiani, E.; Corrao, S. COVID-19: Hemoglobin, Iron, and Hypoxia beyond Inflammation. A Narrative Review. Clin. Pract. 2020, 10, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.F.; Anwar, S. Management of Hemoglobin Disorders During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesús-González, L.A.; del Ángel, R.M.; Palacios-Rápalo, S.N.; Cordero-Rivera, C.D.; Rodríguez-Carlos, A.; Trujillo-Paez, J.V.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; Osuna-Ramos, J.F.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Rivas-Santiago, B.; et al. A Dual Pharmacological Strategy against COVID-19: The Therapeutic Potential of Metformin and Atorvastatin. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuna-Ramos, J.F.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; Cordero-Rivera, C.D.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Hurtado-Monzón, A.M.; Palacios-Rápalo, S.N.; Jiménez-Camacho, R.; Meraz-Ríos, M.A.; Del Ángel, R.M. Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs as Potential Antivirals: A Repurposing Approach against Flavivirus Infections. Viruses 2023, 15, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Rápalo, S.N.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; Cordero-Rivera, C.D.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Meraz-Ríos, M.A.; Del Ángel, R.M. An Ivermectin – Atorvastatin Combination Impairs Nuclear Transport Inhibiting Dengue Infection in Vitro and in Vivo. iScience 2023, 26, 108294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Rápalo, S.N.; Hernández-Castillo, J.; Cordero-Rivera, C.D.; Benítez-Vega, M.L.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; Osuna-Ramos, J.F.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, A.M.; Cruz, R.; et al. Protocol to Evaluate the Antiviral Effect of FDA-Approved Drugs against Dengue Virus in Huh7 Cells and AG129 Mice. STAR Protoc. 2024, 5, 102992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorathia, N.; Al-Rubaye, H.; Zal, B. The Effect of Statins on the Functionality of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ Regulatory T-Cells in Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials in Asian Populations. Eur. Cardiol. 2019, 14, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessler, M.B. Regulation of Adaptive Immunity in Health and Disease by Cholesterol Metabolism. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, A.; Wheeler-Jones, C.P.D.; Gage, M.C. The Immunomodulatory Effects of Statins on Macrophages. Immuno 2022, 2, 317–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosini, U.M.; Rosso, G.; Merlotti, G.; Colombatto, A.; Nappo, A.; Quaglia, M.; Guglielmetti, G.; Azzolina, D.; Marengo, M.; Castellano, G.; et al. Mo380increased Prevalence of Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2021, 36, gfab082.0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Yali, Q.; Zirui, G.; Shuo, L.; Chaoyang, L.; Wenjuan, X.; Qian, Z.; Ning, H.; Ruijun, G. Prevalence of Acute Kidney Injury in Severe and Critical COVID-19 Patients in Wuhan, China 2020. SSRN Electron. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Sample Total (n = 313) | Presence of AKI (n = 54) | Absence of AKI (n = 259) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age + | 0.004 * | |||
| (mean years) | 60.13 (±14.84) | 65.39 (±14.51) | 59.03 (±14.7) | |
| Gender ° | 0.710 | |||
| Female | 132 (42.17%) | 24 (44.44%) | 108 (41.7%) | |
| Male | 181 (57.83%) | 30 (55.56%) | 151 (58.3%) | |
| Presence of obesity ° | 65 (20.77%) | 12 (22.22%) | 53 (20.46%) | 0.772 |
| Zacatecas area ° | 0.050 * | |||
| Center | 272 (86.9%) | 45 (83.33%) | 227 (87.64%) | |
| Northeast | 1 (0.32%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.39%) | |
| North | 1 (0.32%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.39%) | |
| West | 2 (0.64%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (0.77%) | |
| South | 6 (1.92%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (2.32%) | |
| Southeast | 31 (9.9%) | 9 (16.67%) | 22 (8.49%) |
| Variable | Sample Total (n = 313) | Presence of AKI (n = 54) | Absence of AKI (n = 259) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smoker | 30 (9.58%) | 5 (9.26%) | 25 (9.65%) | 0.929 |
| Arterial Hypertension | 141 (45.05%) | 32 (59.26%) | 109 (42.08%) | 0.021 * |
| Diabetes | 105 (33.55%) | 18 (33.33%) | 87 (33.59%) | 0.907 |
| COPD | 22 (7.03%) | 7 (12.96%) | 15 (5.79%) | 0.061 |
| Asthma | 5 (1.6%) | 2 (3.7%) | 3 (1.16%) | 0.050 * |
| Immunosuppression | 8 (2.56%) | 3 (5.56%) | 5 (1.93%) | 0.175 |
| HIV | 1 (0.32%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.39%) | 0.125 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 17 (5.43%) | 4 (7.41%) | 13 (5.02%) | 0.647 |
| SARS-CoV-2 vaccine | 54 (17.25%) | 10 (18.52%) | 44 (16.99%) | 0.787 |
| Variable | Sample Total (n = 313) | Presence of AKI (n = 54) | Absence of AKI (259) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin g/dL | 0.055 | |||
| (mean) + | 14.53 (±2.27) | 13.99 (±2.4) | 14.64 (±2.23) | |
| Leukocytes upon admission Cells/mL | 0.030 * | |||
| (mean) + | 10.97 (±5.25) | 12.38 (±4.85) | 10.68 (±5.29) | |
| Leukocytes Cells/mL during hospitalization | 0.000 * | |||
| (mean) + | 16.46 (±8.9) | 22.02 (±11.12) | 15.03 (±7.64) | |
| White blood cell count | 0.003 * | |||
| Leukocytosis ° | 118 (37.7%) | 23 (42.59%) | 95 (36.68%) | |
| Leukopenia ° | 144 (46.01%) | 23 (42.59%) | 121 (46.72%) | |
| Normal ° | 51 (16.29%) | 8 (14.81%) | 43 (16.6%) | |
| Creatinine nmol/L | 0.009 * | |||
| (mean) + | 1.18 (±1.16) | 1.56 (±1.68) | 1.11 (±1) | |
| BUN nmol/L | 0.000 * | |||
| (mean) + | 26.32 (±18.41) | 37.32 (±25.7) | 24.02 (±15.61) | |
| C-reactive protein | 0.002 * | |||
| (mean) + | 144 (±111.36) | 186.24 (±122.65) | 135.2 (±107.03) |
| Variable | Sample Total | Presence of AKI | Absence of AKI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE-i | 26 (8.31%) | 7 (12.96%) | 19 (7.34%) | 0.173 |
| Statins | 6 (1.92%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (2.32%) | 0.259 |
| ARAs | 117 (37.38%) | 25 (46.3%) | 92 (35.52%) | 0.137 |
| NSAIDs (Before hospitalization) | 39 (12.46%) | 7 (12.96%) | 32 (12.36%) | 0.902 |
| Endotracheal intubation | 64 (20.45%) | 27 (50%) | 37 (14.29%) | 0.000 * |
| Clinical Diagnosis of Pneumonia | 43 (13.74%) | 24 (44.44%) | 19 (7.34%) | 0.000 * |
| Pneumonia (X-ray) | 42 (13.42%) | 23 (42.59%) | 19 (7.34%) | 0.000 * |
| Death | 143 (45.69%) | 40 (74.07%) | 103 (39.77%) | 0.000 * |
| DHS | 0.003 * | |||
| (mean) | 9.25 (±8) | 12.2 (±8.9) | 8.7 (±7) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borrego-Moreno, J.C.; Cárdenas-de Luna, M.J.; Márquez-Castillo, J.C.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Osuna-Ramos, J.F.; León-Juárez, M.; del Ángel, R.M.; Rodríguez-Carlos, A.; Rivas-Santiago, B.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in the Context of COVID-19: An Analysis in Hospitalized Mexican Patients. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16, 458-471. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16030034
Borrego-Moreno JC, Cárdenas-de Luna MJ, Márquez-Castillo JC, Reyes-Ruiz JM, Osuna-Ramos JF, León-Juárez M, del Ángel RM, Rodríguez-Carlos A, Rivas-Santiago B, Farfan-Morales CN, et al. Acute Kidney Injury in the Context of COVID-19: An Analysis in Hospitalized Mexican Patients. Infectious Disease Reports. 2024; 16(3):458-471. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorrego-Moreno, Juan Carlos, María Julieta Cárdenas-de Luna, José Carlos Márquez-Castillo, José Manuel Reyes-Ruiz, Juan Fidel Osuna-Ramos, Moisés León-Juárez, Rosa María del Ángel, Adrián Rodríguez-Carlos, Bruno Rivas-Santiago, Carlos Noe Farfan-Morales, and et al. 2024. "Acute Kidney Injury in the Context of COVID-19: An Analysis in Hospitalized Mexican Patients" Infectious Disease Reports 16, no. 3: 458-471. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16030034
APA StyleBorrego-Moreno, J. C., Cárdenas-de Luna, M. J., Márquez-Castillo, J. C., Reyes-Ruiz, J. M., Osuna-Ramos, J. F., León-Juárez, M., del Ángel, R. M., Rodríguez-Carlos, A., Rivas-Santiago, B., Farfan-Morales, C. N., García-Herrera, A. C., & De Jesús-González, L. A. (2024). Acute Kidney Injury in the Context of COVID-19: An Analysis in Hospitalized Mexican Patients. Infectious Disease Reports, 16(3), 458-471. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr16030034












