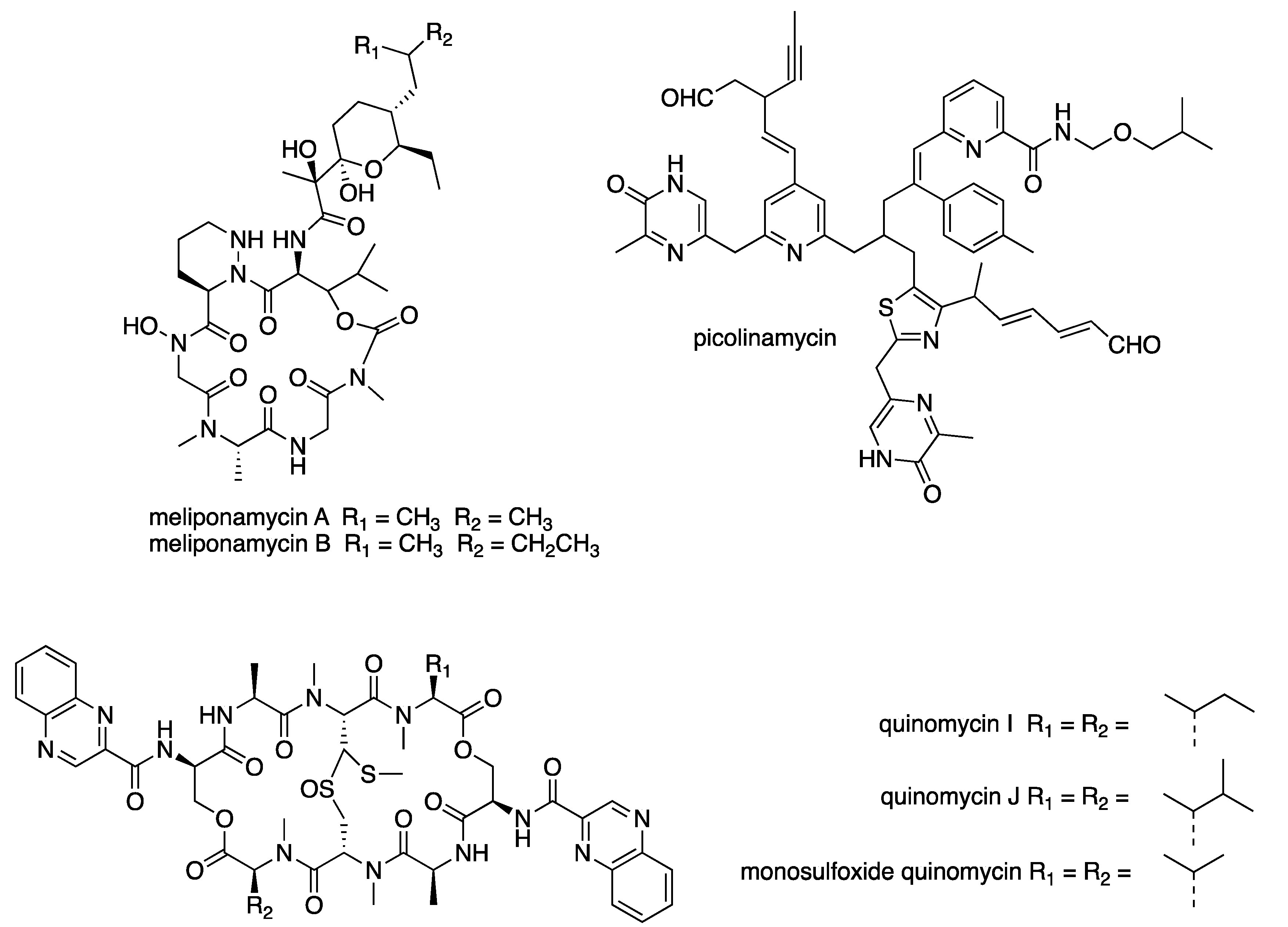
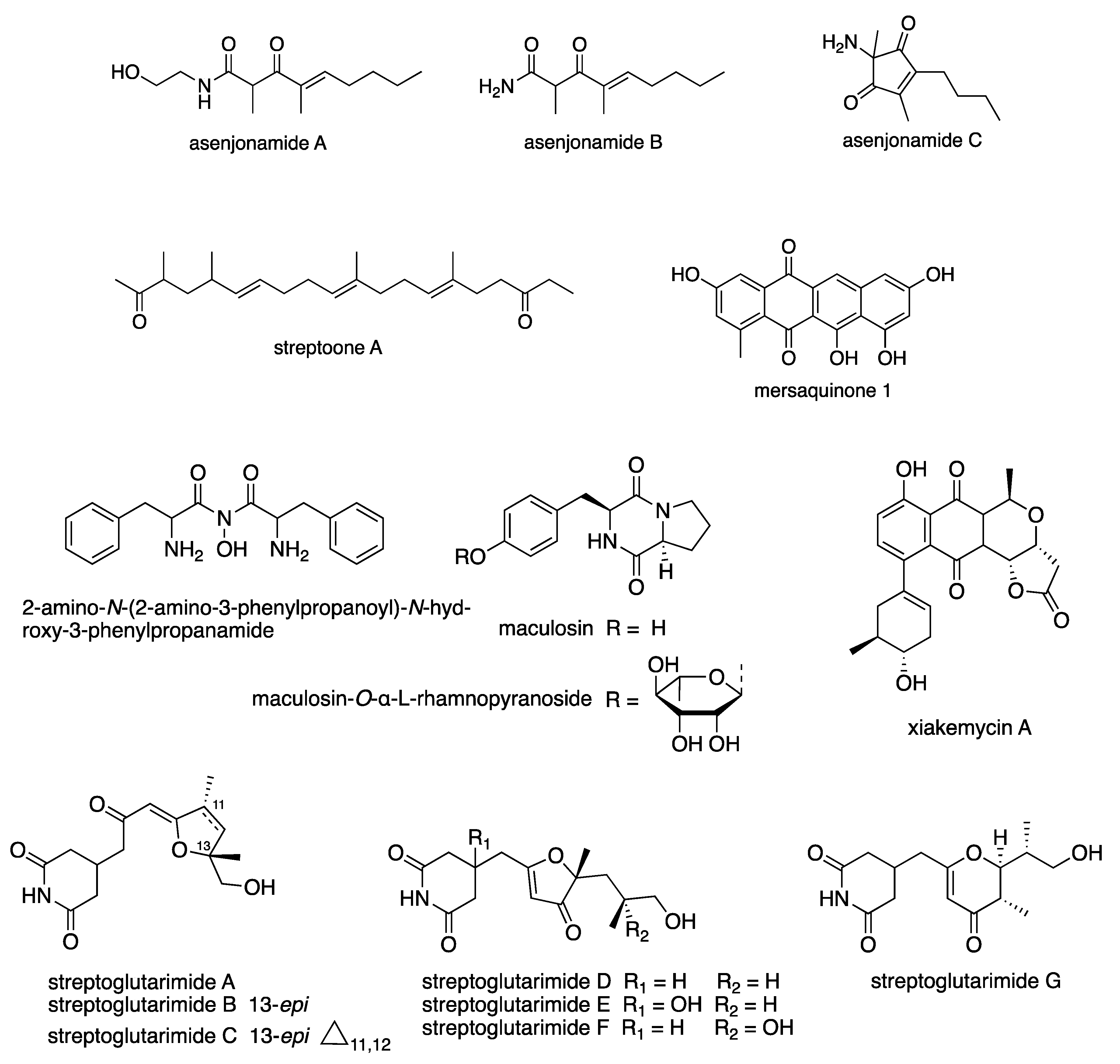
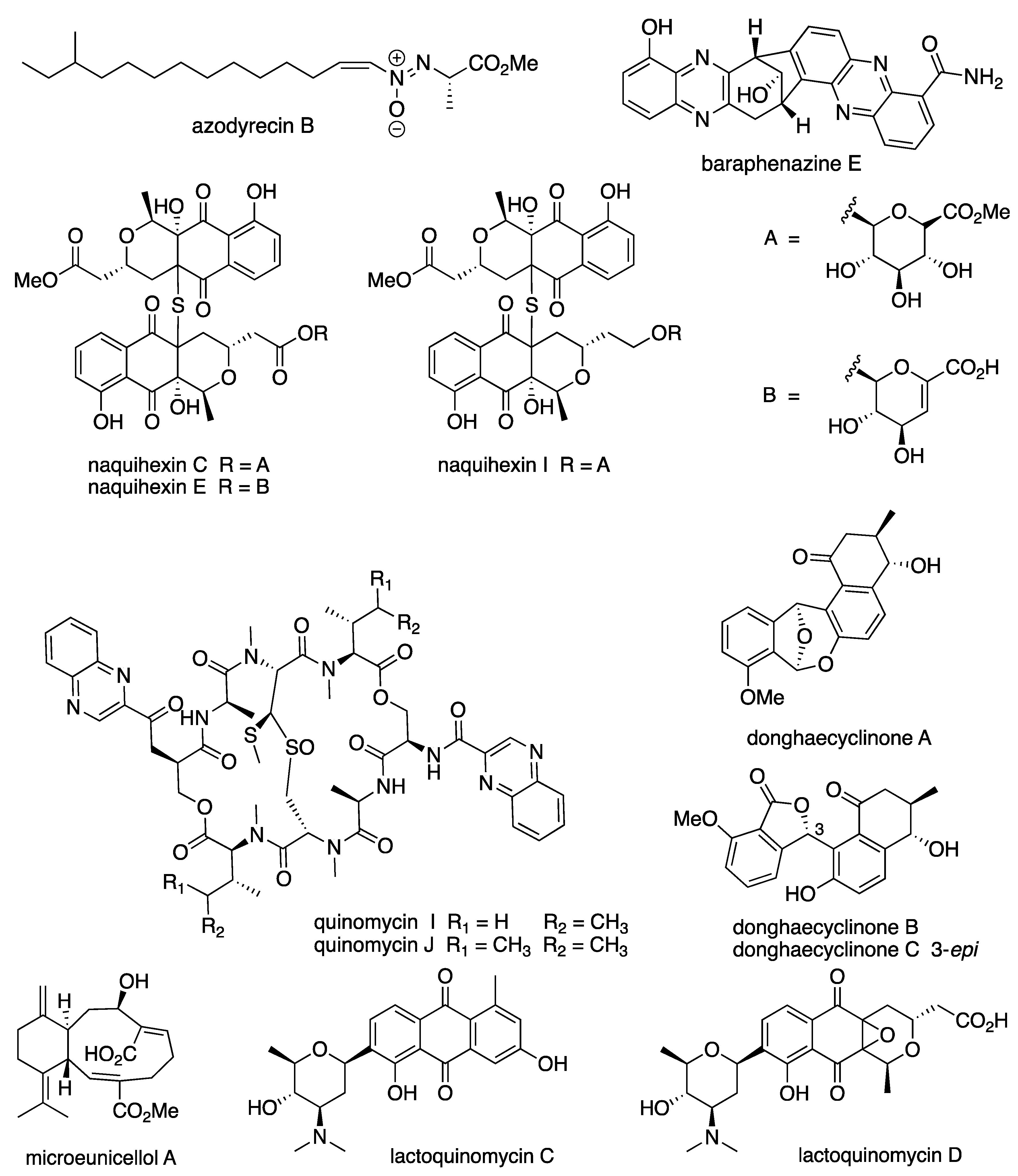
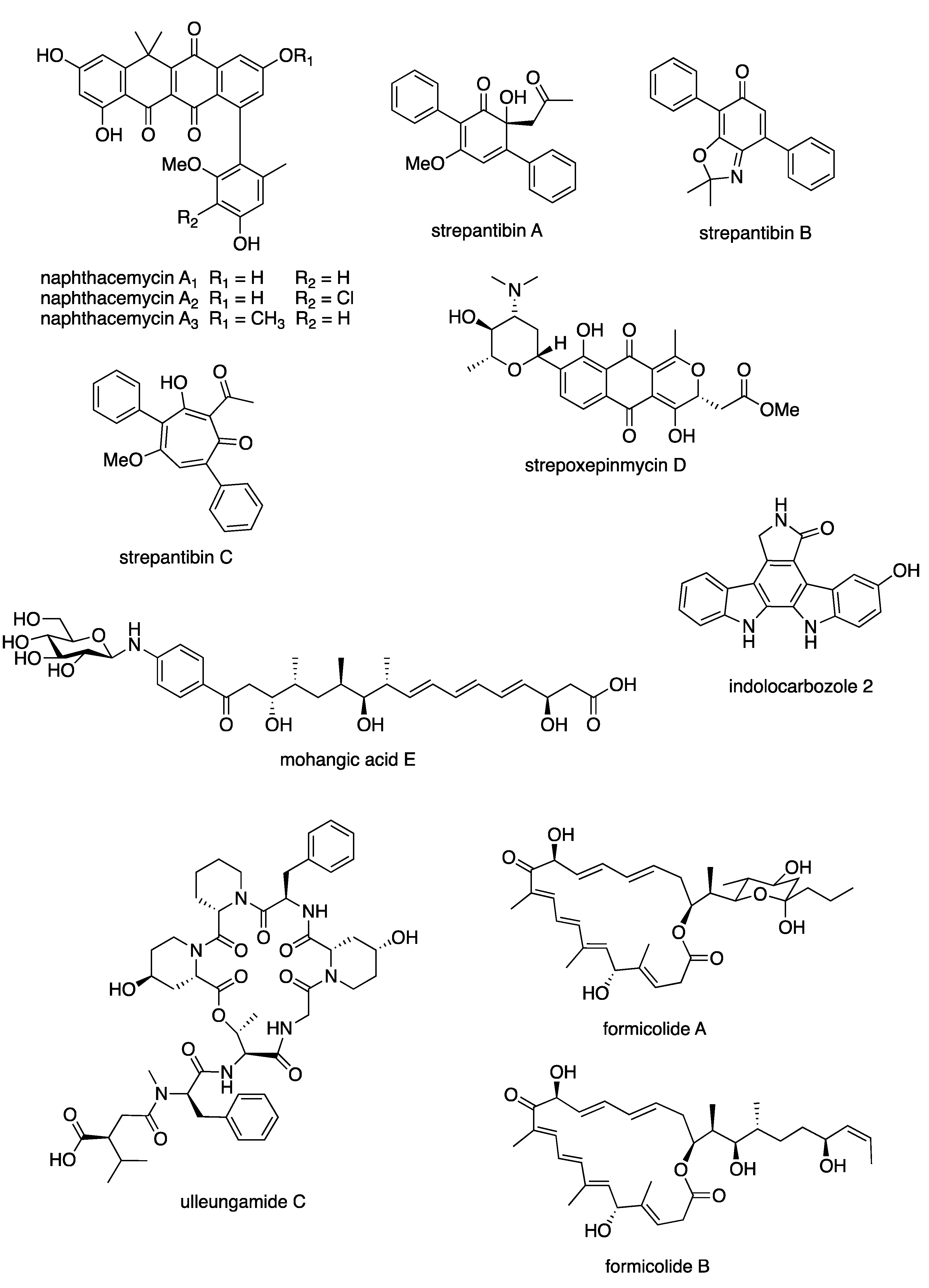
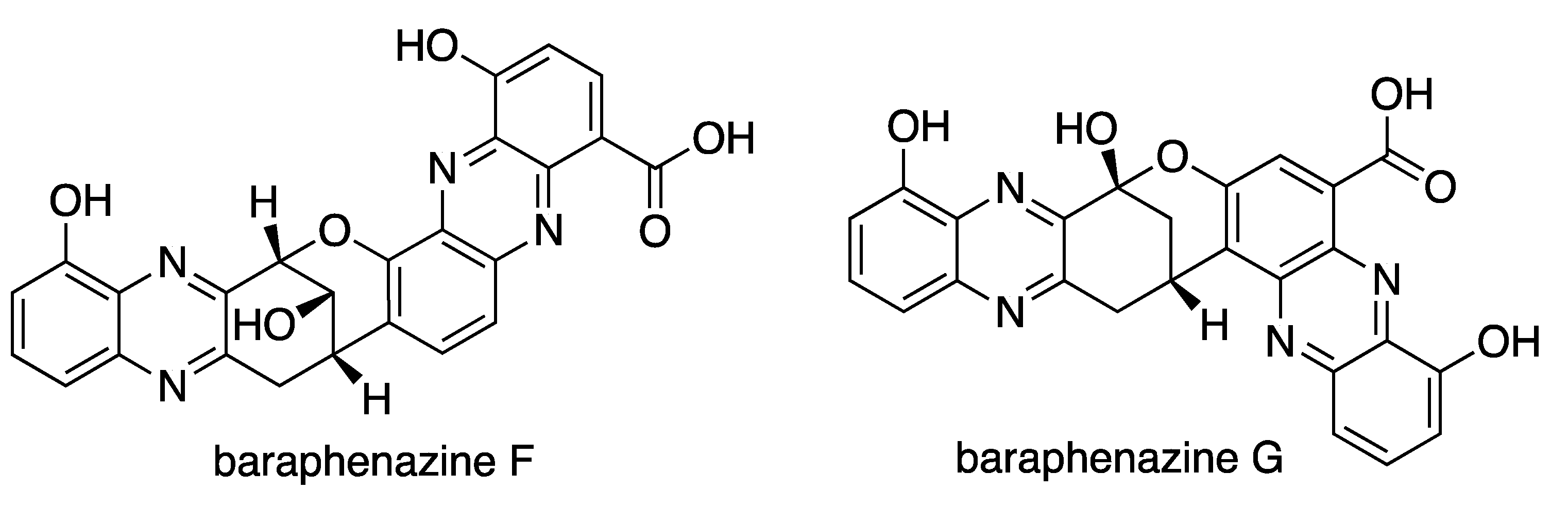
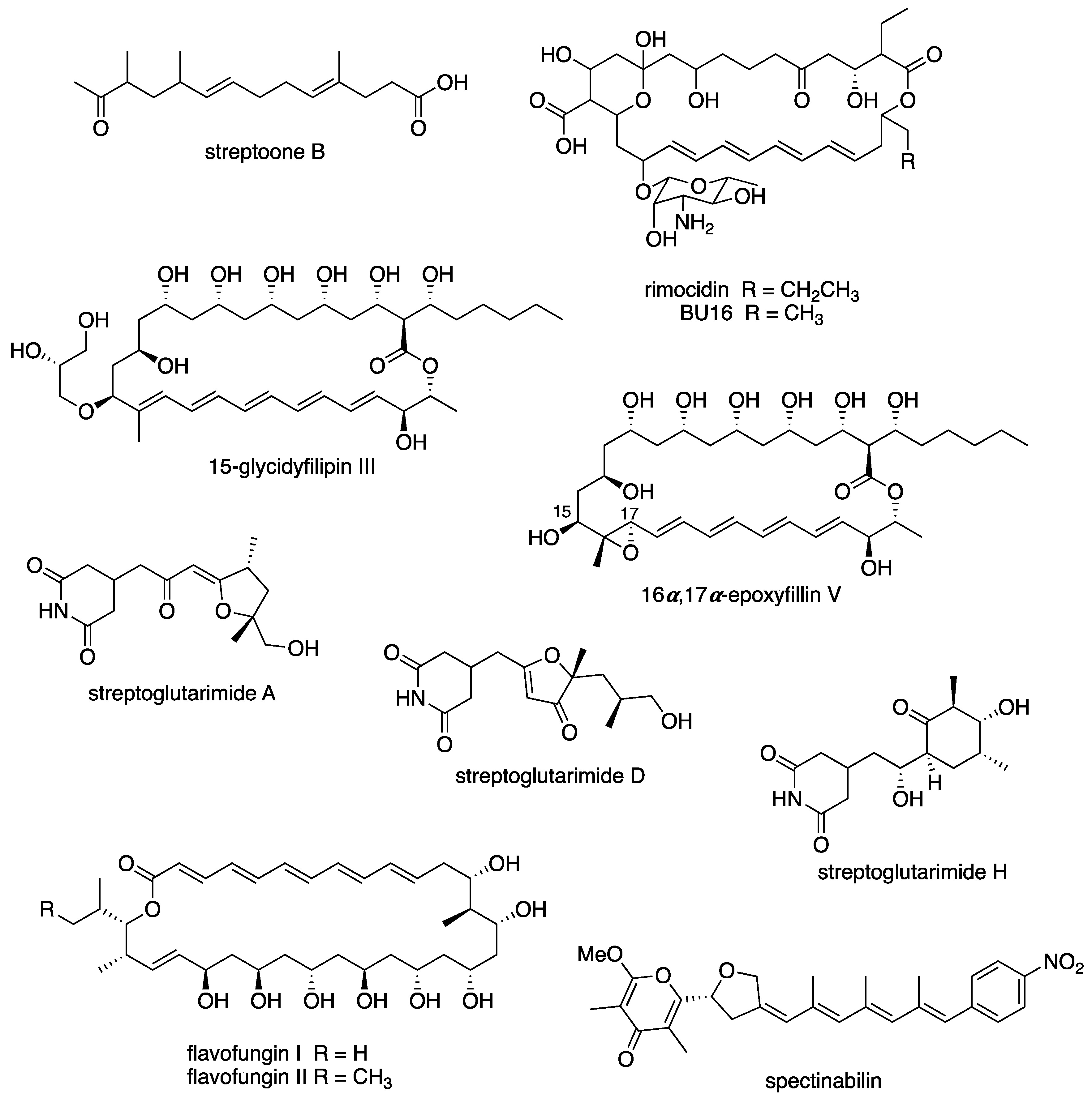
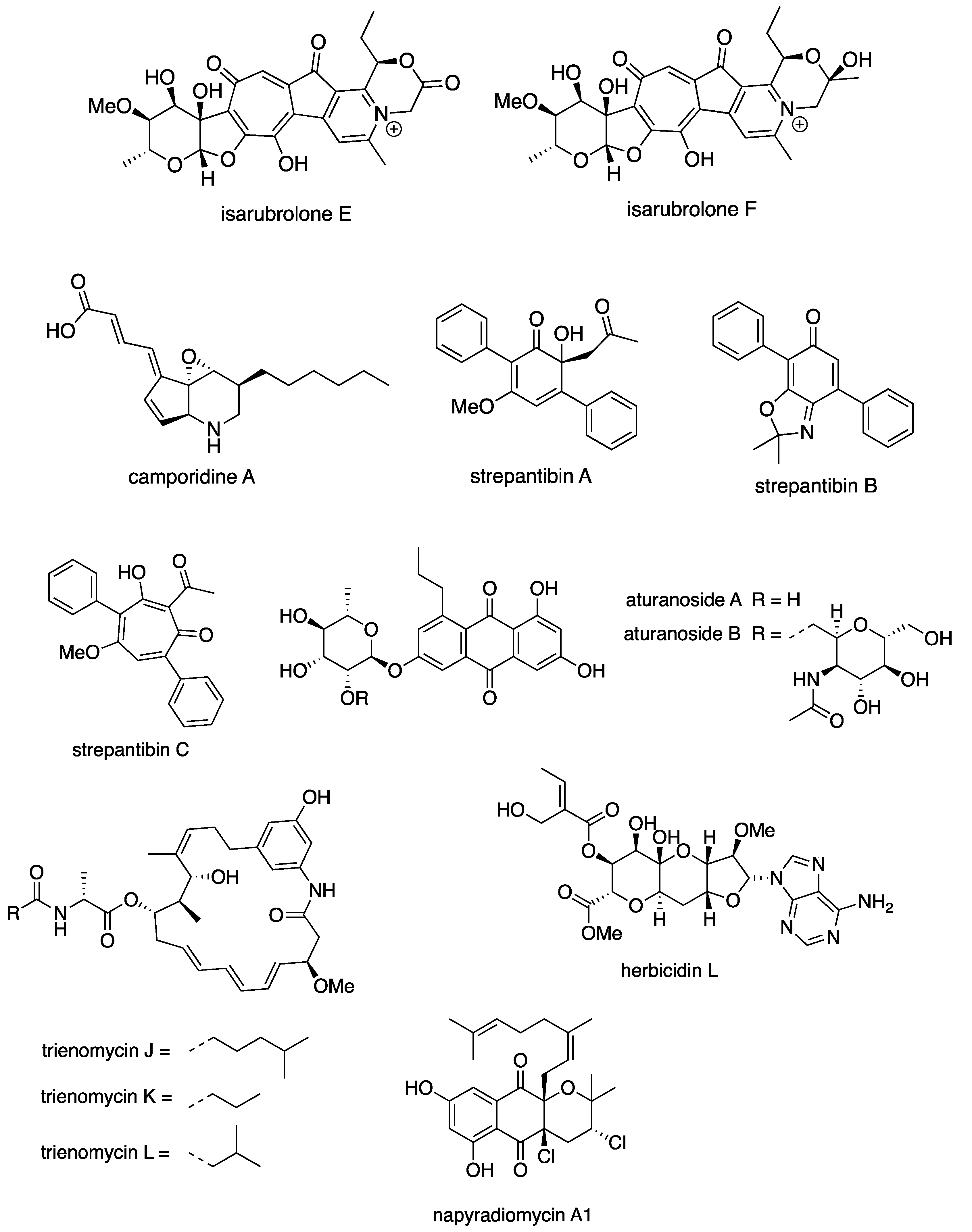
Abstract
There is a real consensus that new antibiotics are urgently needed and are the best chance for combating antibiotic resistance. The phylum Actinobacteria is one of the main producers of new antibiotics, with a recent paradigm shift whereby rare actinomycetes have been increasingly targeted as a source of new secondary metabolites for the discovery of new antibiotics. However, this review shows that the genus Streptomyces is still the largest current producer of new and innovative secondary metabolites. Between January 2015 and December 2020, a significantly high number of novel Streptomyces spp. have been isolated from different environments, including extreme environments, symbionts, terrestrial soils, sediments and also from marine environments, mainly from marine invertebrates and marine sediments. This review highlights 135 new species of Streptomyces during this 6-year period with 108 new species of Streptomyces from the terrestrial environment and 27 new species from marine sources. A brief summary of the different pre-treatment methods used for the successful isolation of some of the new species of Streptomyces is also discussed, as well as the biological activities of the isolated secondary metabolites. A total of 279 new secondary metabolites have been recorded from 121 species of Streptomyces which exhibit diverse biological activity. The greatest number of new secondary metabolites originated from the terrestrial-sourced Streptomyces spp.
1. Introduction
Indiscriminate use of antibiotics has led to a rise in antimicrobial resistance [1]. This dramatically increases the demands for research and discovery of new drugs and antibiotics. Natural products isolated from microorganisms as well as their semi-synthetic derivatives and synthetic analogues have historically been one of the most important sources of antibiotics [2]. Nature includes a large number of microbial species including at least 1.5 million fungi and as many as 5 × 1012 distinct microbial species [1]. However, only a small fraction of about 250,000 to 300,000 living species, mainly in oceans and rainforests, have been identified and documented [1,3]. Worryingly, over the past few decades, there has been a significant decrease in the discovery of new natural product-derived medicines from 20 to 30 approved drugs per decade to only 3 to 4 newly marketed drugs, which has triggered many uncertainties in the medical industries [1]. This decline in translation from discovery to the clinic seems to be due to a decrease in screening efforts rather than a lack of new compounds [1]. For example, of the 18 largest pharmaceutical companies, 15 have withdrawn from antibiotic research [4]. Therefore, the need to produce new antibiotics has driven researchers to put more effort into finding new and novel natural products from untouched and under-explored habitats [5].
The phylum Actinobacteria is one of the main producers of biologically active products with medical, industrial and agricultural applications [6]. This phylum constitutes one of the largest of the 30 major phyla classified in the Domain Bacteria. There are 6 classes, 18 orders, 14 suborders, 63 families and 374 genera recorded in this phylum, with Streptomyces as the largest genus of this phylum [7]. Similar to other genera of Actinobacteria, Streptomyces are Gram-positive bacteria with a GC content of 69–78% [8] and with physiologically characteristics that resemble those of many fungal species [9]. They belong to the family Streptomycetaceae and the order Streptomycetales [10]. Approximately 39% of Actinobacteria have been sources of new natural products, of which around 80% are from the genus Streptomyces [11].
The genus Streptomyces was first discovered as a widespread source of antibiotics in 1943. Subsequently, more than 800 Streptomyces spp. with validly published names have been registered so far [7]. Rediscovery of known secondary metabolites from Streptomyces species has redirected scientists to the discovery of rare actinomycetes with claims that Streptomyces species are no longer an important biological resource for new antibiotics [12,13]. Environmental conditions and different habitats strongly contribute to the diversity and production of natural bioactive compounds [14]. In this review paper, “Streptomycetes” is used to refer to soil and marine microorganisms classified as Streptomyces spp. from the phylum Actinobacteria in the order Actinomycetales and the family Streptomycetaceae [7]. Streptomycetes are ubiquitous in terrestrial and marine environments with the highest recorded diversity in terrestrial habitats [15]. Whatever the habitats, the natural products produced by Streptomycetes under normal and extreme conditions exhibit great structural diversity and significant biological activity [16,17]. Since techniques for the isolation of Streptomycetes are well understood, this genus has been frequently isolated. Consequently, genus Streptomyces produces the highest number of natural products compared to other genera of Actinobacteria.
An interesting recent study by Laskaris et al. (2021) on “Streptomyces, Greek Habitats and Novel Pharmaceuticals: A Promising Challenge” did an excellent job of reporting compounds from Greek Streptomyces including antibiotics, antitumor compounds, biofilm inhibitors, antiparasitics, bacterial toxin production inhibitors and antioxidants [18]. Their work showed that Streptomyces is still a large current producer of bioactive compounds.
In this review, we support their conclusion and present practical ideas, and encouraging results to help researchers meet challenges preventing progress to find novel antibiotics from natural environment. Here, we summarize new Streptomyces species and natural bioactive compounds from various sources and from 2015 to 2020. We describe culture conditions and molecular biology protocols to help in their isolation and characterization.
2. Hidden Potential of Streptomyces: Metagenomic Insights and Evidence
Metagenomics studies have shown that a high number of Streptomyces spp. and other genera of Actinobacteria from environmental samples remain unculturable under normal laboratory condition [19]. These are referred to as viable but not culturable (VBNC) [12]. Even the potential of cultured Streptomyces spp. to produce bioactive secondary metabolites is not fully realized as environmental factors (pH, temperature, incubation time) have profound effects on antibiotic production [20]. The development of genome sequencing methods and in silico genome mining tools have revolutionized the bioactive screening approach in Actinobacteria [21]. Genome mining showed that one Streptomyces strain possessed 25–70 Biosynthetic Gene Clusters (BGCs), most of which are cryptic (Silent BGC) and were not expressed under normal laboratory conditions [22,23]. This suggests that the chemical abilities possessed by a single bacterium to combat pathogens is poorly studied. Guerrero-Garzon et al. (2020) reported that 10 strains of Streptomyces spp. isolated from the marine sponge Antho dichotoma has limited bioactivity, however, using draft genomes, pronounced biosynthetic gene clusters were recorded of which all the strains harbor between 7.1 Mb to 10 Mb which encodes at least 28 to 36 BGCs per genome [24]. Additionally, genome quality and genome completeness remain vital for accurate analyses in genome mining and in silico identification of BGCs [25,26]. A study by Belknap et al. (2020) stated that genome mining not only revealed the potential novel secondary metabolite BGCs but also show that Streptomyces strains that are considered the same species can have high variation in the BGCs with potential derivatives of natural products [27]. Liu et al. (2020) also used a genome mining approach on Streptomyces strain YINM00001 and reported fifty-two putative secondary metabolites biosynthetic gene clusters which included cycloheximide, dynactin, warkmycin, and anthramycin biosynthetic gene clusters that are responsible for the strong antifungal and antibacterial activity of the strain [28]. Genome mining also reveals that Streptomyces spp. can harbor resistance genes to pathogens which is useful to combat the escalating issue of drug resistant pathogens and these resistance genes can easily be transferred between Streptomyces spp. [29]. Current perspectives of genome mining unveil the unimaginable amount of cryptic smBGCs (secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters) in Streptomyces spp. genomes [30]. Further, securing a high-quality and close Streptomyces genome sequence is essential to precisely predict their smBGCs and their functional annotation [25,26]. When exploring the evolutionary dynamics of smBGCs from lineage divergence of Streptomyces sister taxa, it was revealed that the sister taxa strains contain 310 distinct smBGCs belonging to 22 different gene cluster classes [31]. Moreover, genome mining enables the engineering of genes by integrating regulatory genes and codons which can optimize the production of secondary metabolites and deletion of negative regulatory gene [32]. Thus, the full potential of Streptomyces spp. as a source of bioactive secondary metabolites is yet to be explored.
In terms of activating these silent cryptic genes in vitro, researchers should be made aware that a single BGC can lead to one or more secondary metabolites [33]. In addition, as secondary metabolites have different roles from primary metabolites, they are mainly produced under stressed, unusual or extreme conditions [31]. Understanding these concepts may help researchers in designing culture-based conditions that help them overcome challenges that impede progress in the search for new antibiotics from natural and extreme environments.
This review summarizes these culture-based methods by reviewing a large number of Streptomycetes studies from various environments.
3. Novel Streptomyces Species Isolated from Terrestrial Environments
Streptomyces can be found in a variety of terrestrial habitats, including extreme environments, gastrointestinal commensals with insects, and living in symbiosis with plants, fungi, and animals [34]. They are also highly abundant in soils and sediments [11,35].
3.1. Isolation Methods
Streptomycetes are ubiquitous in nature and have colonized a wide range of ecologically important terrestrial habitats. To isolate Streptomycete species from environmental samples, sophisticated research techniques and correlated studies are needed to mimic the native environmental conditions. A diverse suite of isolation methods has been used to successfully isolate new strains of Streptomycetes [36]. These include different methods of pre-treatment, the use of specific selective media under specific laboratory conditions, the use of supplements, and modification of the incubation time and temperature [37,38,39,40]. In particular, it is important to understand the physiological and biochemical conditions of the sampled environment. However, some bacterial cells cannot be cultured using culture-dependent methods or modern laboratory techniques and are referred to as “viable but not culturable” (VBNC) [41]. For this, high throughput sequencing metagenomic studies have shown that a large number of microbial communities remain unculturable from environmental samples [42].
3.2. Extreme Environments
Extreme environments are characterized by high salinity, high or low pH, arid conditions, low nutrient and oxygen content, high or low temperatures, and high exposure to UV rays, and which would be detrimental to “normal” conditions as required for human survival [43]. In recent years, researchers have focused more on the extreme environment as a potent source of new species of Streptomycetes with biological activity [44]. This group of bacteria has the ability to survive under multiple such conditions (polyextremophilic) because they possess distinctive adaptive characteristics such as the production of specific enzymes, switching between different metabolic modes (i.e., heterotrophy and autotrophy) and antibiosis [39].
Thirty-six new strains of Streptomyces were reported from various extreme environments between 2015 and 2020 (Table 1). In order to isolate new strains of Streptomycetes from these samples collected from these environments, it is essential to consider various factors such as pH, temperature, nutrients required, as well as the use of pre-treatments. Culturing Streptomyces from samples collected from these environments does not necessarily require extreme conditions to obtain new Streptomyces spp. [45]. The pretreatments applied activate the endospores, which grow on the isolation media [46,47].
The culture media is supplemented with nutrients and other supplements to support bacterial growth. The isolation of Streptomyces spp. from an extreme environment is effective when different carbon sources (glycerol, soluble starch, glucose, trehalose, carboxy-methylcellulose, humic acid and dextrose) are supplemented with culture media for the successful isolation of novel Streptomyces spp. [37,40,48,49,50,51,52,53,54] as indicated in Table 1. Carbon–nitrogen sources can also be added to the isolation media; casein [55,56], peptone [8,57], malt extract [58] and yeast extract [53,58,59]. The isolation media can be supplemented by K2Cr2O7 [54,60,61,62,63,64], nalidixic acid, nystatin, cycloheximide, rifampicin, and tetracycline [37,38,40,49,51,53,55,56,58,59,65,66,67,68,69] to inhibit the growth of unwanted bacteria and fungi (See Table 1 and Supplementary Table S1).
Selective pretreatment is carried out to eliminate Gram-negative, fastidious bacteria and unwanted microorganisms [12]. There are different pre-treatment methods used for environmental samples, including chemical pretreatment, physical pretreatment, and heating. Samples from extreme environments are subjected to various chemical pretreatments, including the addition of chemicals to the samples and dilution with deionized water. Physical treatments have also been applied to samples, which involves shaking the sample on a rotary shaker or a tumble shaker and heat treatment of the sample involving wet heat treatment or dry heat treatment. Streptomyces spores are very resistant to exogenous chemicals and temperature extremes due to the complex chemical compositions of their cell wall [70]. This is advantageous when performing pretreatments to selectively isolate Streptomyces spp. Some of the commonly used pretreatments for the isolation of Streptomyces from an extreme terrestrial environment include distilled water with added NaCl [38,52,71,72], air-drying [53,64,68] pretreatment by ultrasound [56,69] and agitation on a rotary stirrer [37,40,54,57,66,69]. Dry heat treatment and wet heat treatment are the most frequently used pretreatments. Notably, a combination of physical and chemical treatment [66] or two different physical treatment methods [69] have been shown to be significant and effectively isolate strains of Streptomyces. On the other hand, there are samples from extreme environments, which are not subjected to any pretreatment [51,54,60,61,65,73].

Table 1.
Novel Streptomyces spp. reported from extreme environments between 2015 and 2020.
Table 1.
Novel Streptomyces spp. reported from extreme environments between 2015 and 2020.
| Strain | Nature of the Sample | Isolation Medium | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomyces boncukensis sp. nov. | Saltern soil | Starch Casein agar, pH 7.0–7.2, supplemented with filter-sterilized cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1) and 3% NaCl | Turkey | [38] |
| Streptomyces taklimakanensis sp. nov. | Desert | Gauze’s No. 1 medium 1 supplemented with Nystatin (100 mg mL−1) and nalidixic acid (50 mg mL−1) | North-West China | [40] |
| Streptomyces alkaliterrae sp. nov. | Alkaline soil close to Soda lake | Starch casein agar adjusted to pH 8.5 with 1N NaOH and supplemented with 5% (w/v) sodium chloride and cycloheximide and nystatin (each at 50 μg mL−1) | India | [37] |
| Streptomyces cahuitamycinicus sp. nov | Desert soil | Minimal medium supplemented with cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1) and nalidixic acid (10 μg mL−1) | Turkmenistan | [53] |
| Streptomyces acidicola sp. nov. | Soil from peat swamp forest | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1) and nystatin (50 μg mL−1) | Thailand | [51] |
| Streptomyces harenosi sp. nov. | Sand dunes | Actinomycete isolation agar (HiMedia), pH 7.3 | Indonesia | [74] |
| Streptomyces tibetensis sp. nov. | Acid sandy soil sample | ISP medium 7 adjusted to pH 7.3 at 25 °C supplemented with an inhibitor solution containing K2Cr2O7 (25 mg mL−1), calcium propionate (30 mg mL−1) and cycloheximide (50 mg mL−1) | China | [66] |
| Streptomyces abyssomicinicus sp. nov. | Rock soil sample | Humic acid vitamin agar | Mexico | [50] |
| Streptomyces altiplanensis sp. nov. | Arid soil samples | Starch Casein Agar within the pH range of 7.0–7.2, supplemented with 50 μg mL−1 nyastatin and 50 μg mL−1 cycloheximide | Chile | [65] |
| Streptomyces cyaneochromogenes sp. nov. | Soil sampled at a manganese contaminated area | Gause’s synthetic medium 1, supplemented with 0.04 g K2Cr2O7 | China | [64] |
| Streptomyces huasconensis sp. nov. | Arid soil samples | Starch Casein agar within the pH range of 7.0–7.2 | Chile | [48] |
| Streptomyces cadmiisoli sp. nov. | Cadmium-contaminated soil | Modified proline agar medium, supplemented with 2.0–3.0 mL solution (1.775 g L−1) in a 100 mL medium + Gause’s synthetic agar medium no.1 | China | [61] |
| Streptomyces fodineus sp. nov. | Acidic mine area soil | Acidified (pH 5) starch-Casein Agar supplemented with cycloheximide and nystatin, each at 50 μg mL−1 | Korea | [49] |
| Streptomyces dengpaensis sp. nov | Desert soil | ISP 7 medium (HiMedia) supplemented with inhibitor solution containing (25 mg mL−1), calcium propionate (30 mg mL−1) and cycloheximide (50 mg mL−1) | China | [67] |
| Streptomyces durbertensis sp. nov. | Saline–alkali soil | CMKA medium 1 supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | North-East China | [69] |
| Streptomyces polaris sp. nov. | Frozen soil | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with (50 mg L−1) | High Arctic | [60] |
| Streptomyces septentrionalis sp. nov. | ||||
| Streptomyces desertarenae sp. nov. | Desert Soil | Reasoner’s 2A (R2A; BD) agar adjusted to pH 7.0. | China | [57] |
| Streptomyces manganisoli sp. nov. | Manganese-polluted soil | Modified proline agar medium, supplemented with 2.0–3.0 mL solution (1.775 g L−1) in a 100 mL medium | China | [63] |
| Streptomyces salilacus sp. nov. | Salt lake sediment | ISP (International Streptomyces Project) medium 4 supplemented with 1.5% (w/v) NaCl | China | [52] |
| Streptomyces sediminis sp. nov. | Crater lake sediments | ISP 2 medium supplemented with 10 mg L−1 tetracycline with (50 μg mL−1) of nystatin and (5 μg mL−1) of rifampicin | Turkey | [58] |
| Streptomyces asenjonii sp. nov. | Hyper-arid Atacama desert soils | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar | Chile, Peru, South America | [73] |
| Streptomyces aridus sp. nov. | Subsurface soil of Atacama desert | Glucose-yeast extract agar (HiMedia) supplemented with cycloheximide and nystatin (each at 25 μg mL−1) | Chile, Peru, South America | [59] |
| Streptomyces jeddahensis sp. nov. | Desert soil | Mineral salt medium (MSM) | Saudi Arabia | [71] |
| Streptomyces caldifontis sp. nov. | Hot water spring sediment | Starch casein agar medium supplemented with 25 μg mL−1 nystatin | Pakistan | [55] |
| Streptomyces daqingensis sp. nov. | Saline–alkaline soil | CMKA medium 2 supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | North-East China | [56] |
| Streptomyces actinomycinicus sp. nov. | Soil of a peat swamp forest | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with nalidixic acid (25 mg mL−1) and cycloheximide (50 mg mL−1) | Thailand | [68] |
| Streptomyces luozhongensis sp. nov. | Desert soil | Gauze’s No. 1 medium 2 pH 7.2, supplemented with 2.0–3.0 mL of solution (1.775 g L−1) in a 100 mL medium at pH 7.2 | Lop Nur, Xinjiang, North-West China | [54] |
| Streptomyces xiangtanensis sp. nov. | Soil near Xiangtan Manganese mine | Gauze’s synthetic medium 1 adjusted to pH 7.2, supplemented with 2.0–3.0 mL of K2Cr2O7 solution (1.775 g/L) in a 100 mL medium | Central-South China | [62] |
| Streptomyces arcticus sp. nov. | Frozen soil | Mineral agar 1 Gause medium supplemented with (50 mg L−1) | Arctic | [75] |
| Streptomyces canalis sp. nov. | Hypersaline soilsample | B7 medium supplemented with 1.5% (w/v) NaCl | China | [72] |
| Streptomyces alkaliphilus sp. nov. | Saline lake sediment | Solid basal medium, Horikoshi 1 supplemented with 100 mL of sterilized 10% Na2CO3 | Kenya | [76] |
| Streptomyces lonarensis sp. nov. | Lake sediments (alkaline salt water meteorite lake) | Medium for the isolation of alkalophilic actinomycetes at pH 10.0 or 11.0 (after autoclaving) , or NaOH were separately sterilized and used for adjusting the pH | India | [8] |
Refer to Supplementary Table S1 for the composition of each media. The superscript (1,2) on some media indicates slight changes in the amount of ingredients used.
3.3. Symbionts
Microorganisms are the most common symbiotic partners of eukaryotes. They live either in mutualism with the host organism or may be parasitic to the host organism [77]. Streptomycetes are not only free species, but have also evolved to live in symbiosis with other animals, fungi and plants [78]. Similar to extreme conditions, Streptomyces have developed specific adaptive strategies and it is therefore very important to have knowledge of the sample environment to successfully isolate them [78]. In addition, it is important to know the different environmental factors such as pH, temperature, specific nutrients necessary for the preparation of isolation media [12].
Different parts of plants are sampled for the isolation of Streptomycetes, including tree bark [79], leaf litter [80], bulbil [81], roots [82,83,84], stem [85,86,87], fruits [88], seeds [89] and phylloplane [90] (Table 2). Mosses have also been recorded as a source of novel Streptomyces spp. [91]. Studies have proven that Streptomyces are very important for the growth and development of plants as they play an important role in nutrient uptake, have high absorption of tropospheric di-hydrogen and they also play an important role in forests by actively participating in biodegradation of biopolymers, which increases the fertility of forests soil [92].
Humic acid vitamin agar is typically used to isolate new Streptomyces spp. from plant samples [70,77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. There are also other isolation media that have been used for isolation, including potato dextrose agar [93] and vitamin arginine agar [88] (Table 2). Different carbon sources have been used in these isolation media, including humic acid, glucose, dextrose, methanol and starch. The main sources of carbon–nitrogen in isolation media are beef or yeast extracts. Additionally, supplements such as nalidixic acid and cycloheximide may be added to the medium to reduce fungal and fastidious bacterial growth as shown in (Table 2).
Plant samples are often pretreated using a range of chemical, physical and thermal methods. Chemical pretreatment includes different concentrations of NaCl [82,88], sodium hypochlorite [89], Lodewyckx pretreatment [81] and hydrogen peroxide [81]. The only heat treatment applied is air-drying, which involves spreading the sample evenly on clean sheets and leaving it at room temperature to remove moisture from the sample [79,83]. This pretreatment is effective because desiccation selectively kills other common bacteria and fungi and activates Streptomyces spores [94]. In addition, sonic oscillation can also be applied [80].
Additionally, fungi and lichens are also a source of new Streptomycetes. For example, symbiotic Streptomycetes that reside on fungus farming ants are beneficial because they protect the fungal garden and ants against pathogenic fungi [78]. Streptomycetes have also been shown to suppress phytopathogenic fungi [95]. Streptomycetes are mutually important for fungi because they promote mycorrhizal symbiosis [96], which indirectly benefits plants. For successful isolation of Streptomycetes from fungal samples, vitamin arginine agar [97] and potato dextrose agar [98] (Table 2) were used. No pretreatment was applied to isolate the new Streptomycetes from fungi from the data reviewed.

Table 2.
Novel Streptomyces spp. reported from plants and Fungi between 2015 and 2020.
Table 2.
Novel Streptomyces spp. reported from plants and Fungi between 2015 and 2020.
| Strain | Nature of Sample | Isolation Medium | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomyces bauhiniae sp. nov. | Tree bark of Bauhinia variegata Linn | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1) and nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1) | Thailand | [79] |
| Streptomyces fuscigenes sp. nov. | Bamboo (Sasa borealis) litter | Bennett’s Agar adjusted to pH 7.3 with NaOH and supplemented with cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1) and nalidixic acid (20 μg mL−1) at pH 5.5 | Republic of Korea | [80] |
| Streptomyces dioscori sp. nov. | Bulbil of Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (25 mg L−1) | South-West China | [81] |
| Streptomyces carminius sp. nov. | Roots of Sophora alopecuroides | Gauze’s No. 1 medium 3 at pH 7.5 | North-West China | [84] |
| Streptomyces geranii sp. nov. | Root of Geranium carolinianum Linn | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with nystatin (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [83] |
| Streptomyces populi sp. nov. | Stem of Populus adenopoda | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with nalidixic acid (25 mg L−1) and cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) | China | [87] |
| Streptomyces lichenis sp. nov. | Lichen sample | Arginine-vitamin (AV) agar | Thailand | [97] |
| Streptomyces roietensis sp. nov. | Surface-sterilized stem of jasmine rice, Oryza sativa KDML 105 | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar | Thailand | [85] |
| Streptomyces capparidis sp. nov. | Fruits of Capparis spinosa | Tap water-yeast extract (TWYE) witin the pH range of 7.0–7.2 supplemented with 3% (w/v) NaCl | China | [88] |
| Streptomyces ginkgonis sp. nov. | Aril of a seed of Ginkgo biloba | Gause’s Synthetic agar medium 2 supplemented with streptomycin sulphate (10 μg mL−1) and actidione (50 μg mL−1) | Yangling, China | [89] |
| Streptomyces tremellae sp. nov. | Culture of mushroom Tremella fuciformis | Potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium (200 gpotato tissue, 20 g glucose, 20 g agar and 1000 mL deionized water, pH 5.6); cycloheximide (100 μg mL−1) | China | [98] |
| Streptomyces polygonati sp. nov. | Root of Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) | Humic acid-vitamin agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [82] |
| Streptomyces pini sp. nov. | Phylloplane of pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) needle-like leaves | Ammonium mineral salts medium amended with 0.5% (v/v) methanol as carbon source and cycloheximide (10 μg mL−1) | India | [90] |
| Streptomyces phyllanthi sp. nov. | Stem of Phyllanthus amarus | Yeast extract-malt extract medium (ISP2 medium) supplemented with 10 μg L−1 tetracycline | Thailand | [86] |
| Streptomyces bryophytorum sp. nov. | Moss (Bryophyta) | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | North China | [91] |
Refer to Supplementary Table S1 for the composition of each media. The superscript (2,3) on some media indicates slight changes in the amount of ingredients used.
Furthermore, several studies have shown that insects are also an important host of Streptomyces. They are beneficial for the insect microbiome because they influence the production of metabolites and the biosynthetic potential to inhibit and resist pathogens [99]. The main areas of insects that studies generally focus on are the intestinal region [100,101], the cuticle [102], and the head region [93,103,104,105,106] (Table 3). Studies have shown that Streptomycetes live in symbiosis with insects and strengthen their defensive mechanism by producing chemicals for ecological adaptation [99]. For example, endosymbiotic Streptomyces live in the antennal glands of female solitary wasps, where they are secreted as a white matter that the larvae absorb and wrap around their cocoon as a defense mechanism [107].
As with other samples, to isolate Streptomycetes from insects, different carbon sources (humic acid, starch, methylcellulose and oats) can be added to the isolation media [93,100,102,106] as well as cycloheximide and nalidixic acid have been the main supplements in isolation settings [102,103,104,105,106]. Unlike samples from plants and extreme environments, only two different pretreatment procedures have been applied to insect-derived samples from the data collected, which include physical pretreatment where the sample was shaken in a rotary shaker at 180 r.p.m. at 28 °C for 30 min [102,103,104,105,106], or a chemical pre-treatment where samples were surface sterilized in 70% ethanol [100].

Table 3.
Novel Streptomyces spp. reported from insects and other animals between 2015 and 2020.
Table 3.
Novel Streptomyces spp. reported from insects and other animals between 2015 and 2020.
| Strain | Nature of Sample | Isolation Medium | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomyces smaragdinus sp. nov. | Gut of the fungus-farming termite Macrotermes natalensis | Chitin agar supplemented with 0.05 g L−1 cycloheximide | South Africa | [101] |
| Streptomyces buecherae sp. nov. | Femaloe cave myotis bat (Myotis velifer) | ISP 2 Medium | New Mexico | [108] |
| Streptomyces corynorhini sp. nov. | Male Townsend’s big-eared bat | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1), nalidixic acid (50 mg L−1), trimethoprim (50 mg L−1) | New Mexico | [109] |
| Streptomyces capitiformicae sp. nov. | Head of an ant (Camponotus japonicus Mayr) | Sodium succinate-asparagine agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid 20 mg L−1 | China | [104] |
| Streptomyces lasiicapitis sp. nov. | Head of an ant(Lasius fuliginosus L.) | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [106] |
| Streptomyces camponoti sp. nov. | Cuticle of Camponotus japonicus Mayr | Gause’s synthetic agar no. 1 1 adjusted to pH 7.2 supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | Harbin, Heilongjiang, China | [102] |
| Streptomyces cuticulae sp. nov. | ||||
| Streptomyces amphotericinicus sp. nov. | Head of an ant | Sodium succinate-asparagine agar pH 7.2, supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | Harbin, Heilongjiang, China | [103] |
| Streptomyces kronopolitis sp. nov. | Millipede (Kronopolites svenhedind Verhoeff) | Gause’s Synthetic Agar No. 1 1 supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [110] |
| Streptomyces camponoticapitis sp. nov. | Head of an ant (Camponotus japonicus Mayr) | Tap Water Yeast Extract Agar (TWYE)2 supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [105] |
| Streptomyces formicae sp. nov. | Head of Camponotus japonicus Mayr ant | Gause’s synthetic agar no. 1 1 supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [93] |
| Streptomyces fractus sp. nov. | Gut of a South African termite | Medium II at pH 7, supplemented with μg mL−1 cycloheximide and 10 μg mL−1 nalidixic acid | South Africa | [100] |
Refer to Supplementary Table S1 for the composition of each media. The superscript (1) on some media indicates slight changes in the amount of ingredients used.
3.4. Soil and Sediments
Actinomycetes represent up to 50% of the total population of Actinobacteria found in the soil (varies on different soil) [111]. They play a major role in the soil by biodegrading biopolymers such as lignocellulose, cellulose and hemicellulose [112,113,114]. Streptomyces also play an important role in biogeochemical cycles due to their high ability to produce the enzyme hydrogenase, which actively participates in the hydrogen cycle [92]. In addition, Streptomyces also influence the structure of soil microbial communities [115]; they are involved in the decomposition of plant litter and the formation of organic matter in the soil [116], as well as weathering of rocks [117]. New strains of Streptomycetes have been isolated from different soil samples, including rhizospheric soil [118,119,120], free soil [121,122,123], forest soil [124,125,126], wetland soil [127], and the sediments and the soil of the savannah. There were 16 new Streptomyces spp. isolated and reported from the rhizosphere (Table 4), which underlines the importance of Streptomyces spp. to plants. Streptomyces in the rhizosphere are essential for plant growth and development as they enhance root and shoot growth, biological nitrogen fixation, mineral solubilization, and they also serve as biological control agents against insects, pests and pathogens [10].
For the preferential isolation of Streptomycetes from soil, a number of isolation methods have been reported to enhance the growth of Streptomyces. Different isolation agars that could selectively isolate Streptomyces spp. have been used. Humic acid vitamin agar is prolific in the isolation of novel Streptomyces spp. isolates (Table 4). Other commonly used isolation media include starch casein agar and Gauze synthetic agar (Table 4).

Table 4.
Novel Streptomyces spp. reported from terrestrial soil samples between 2015 and 2020.
Table 4.
Novel Streptomyces spp. reported from terrestrial soil samples between 2015 and 2020.
| Strain | Nature of Sample | Isolation Medium | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomyces triticiradicis sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) | cellulose-proline agar (CPA) supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | Central China | [128] |
| Streptomyces coryli sp. nov | Soil from a commercial hazelnutorchard | Stevenson’s medium no. 3 adjusted to pH 7.0 and supplemented with cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1), nalidixic acid (10 μg mL−1), nystatin (50 μg mL−1) and novobiocin (10 μg mL−1) | Turkey | [129] |
| Streptomyces paludis sp. nov. | Alpine wetland soil | Gause’s synthetic agar medium 2 adjusted pH 7.2 | China | [130] |
| Streptomyces boluensis sp. nov. | Lake sediment | M1 agar supplemented with filter-sterilized cycloheximide (50 mg mL−1) and rifampicin (5 mg mL−1) | Turkey | [131] |
| Streptomyces roseicoloratus sp. nov. | Soil in cotton fields | GJ medium adjusted to pH 7.0–7.5 | North-WestChina | [132] |
| Streptomyces soli sp. nov. | Birch forest soil | Streptomyces Project 2 (ISP2) medium (yeast extract–malt extract agar) adjusted to pH 7.2 supplemented with 10 mg L−1 tetracycline | China | [133] |
| Streptomyces albicerus sp. nov. | River sediment | Glycerol-arginine medium adjusted to pH 7.5 and supplemented with 100 μL of 50 mg mL−1 K2Cr2O7 in a 100 mL medium to reduce fungal contamination | China | [134] |
| Streptomyces inhibens sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | North-East China. | [118] |
| Streptomyces dangxiongensis sp. nov. | Grass soil | Gause’s synthetic agar medium 2 adjusted to pH 7.2 and supplemented with nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1) | China | [135] |
| Streptomyces rhizosphaericola sp. nov. | Brazilian Cerrado biome (wheat rhizosphere) | Glucose Yeast Extract Agar (GYEA) –HiMedia | Brazil | [119] |
| Streptomyces sporangiiformans sp. nov. | Soil collected from Mount Song | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [136] |
| Streptomyces monticola sp. nov. | Soil from Mount Song | Sodium succinate-asparagine agar adjusted to pH 7.2 and supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [137] |
| Streptomyces tritici sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 μg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 μg L−1) | Central China | [120] |
| Streptomyces venetus sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil of an oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) | Starch casein agar (SCA) adjusted to pH 7.0–7.2 supplemented with nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1) and cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1) | Thailand | [138] |
| Streptomyces xiangluensis sp. nov. | Soil from Xianglu Mountain | Sodium succinate-asparagine agar adjusted to pH 7.2 and supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [139] |
| Streptomyces urticae sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soilof Urtica urens L. | Cellulose proline agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | northeast China | [140] |
| Streptomyces tunisialbus sp. nov. | Tunisian rhizosphere soil of Lavandula officinalis | Glucose yeast-malt extract agar (DSMZ medium 65) | Tunisia (North America) | [141] |
| Streptomyces flavalbus sp. nov. | Rhizosphere of maize (Zea mays L.) | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with nystatin (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | North-East China | [142] |
| Streptomyces lutosisoli sp. nov. | Muddy soil from stream | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | North-East China | [143] |
| Streptomyces boninensis sp. nov. | Soil | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented benlate (final conc. 25 μg mL−1 (w/v)) and nalidixic acid (final conc. 25 μg mL−1 (w/v)) | Japan | [123] |
| Streptomyces triticisoli sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil of wheat | Gause’s Synthetic Agar No. 1 2 adjusted to pH 7.2 supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [144] |
| Streptomyces cerasinus sp. nov. | Soil | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1) and nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1) | Thailand | [121] |
| Streptomyces solisilvae sp. nov. | Tropical forest soil | Starch–casein–nitrate agar within the pH range of 7.0–7.2 and supplemented with cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1), nystatin (50 μg mL−1) and nalidixic acid (20 μg mL−1) | China | [126] |
| Streptomyces thermoalkaliphilus sp. nov. | Soil of a tropical rainforest | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar | China | [145] |
| Streptomyces swartbergensis sp. nov. | Soil collected from the banks of the Gamka river | MC agar pH 7.4 | South Africa | [146] |
| Streptomyces luteus sp. nov. | Soil | Mannitol-casein acid hydrolysis (GW1) medium prepared with 5% (w/v) NaCl | SouthernChina | [122] |
| Streptomyces xylanilyticus sp. nov. | Soil | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1) and nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1) | Thailand | [147] |
| Streptomyces odonnellii sp. nov. | Soil savanna | Malt extract–yeast extract–glucose-agar medium pH 7.0 | Brazil | [148] |
| Streptomyces fuscichromogenes sp. nov. | Soil from a tropical rain forest | Yeast extract-malt extract agar (ISP 2) supplemented with 10 mg L−1 tetracycline | China | [149] |
| Streptomyces krungchingensis sp. nov. | Soil collected from Krung Ching Waterfall National Park | Starch casein nitrate agar within the pH range of 7.0–7.2 and supplemented with nystatin (25 mg L−1) and tetracycline (10 mg L−1) | Thailand | [150] |
| Streptomyces rhizosphaerihabitans sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil and humus layer from bamboo forest | Starch casein agar at pH 5.5 adjusted with HCl | Korea | [151] |
| Streptomyces adustus sp. nov. | ||||
| Streptomyces indoligenes sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil of Populus euphratica | Gause’s synthetic agar medium 2 adjusted to pH 7.2 | China | [152] |
| Streptomyces yangpuensis sp. nov. | Soil | Gause’s synthetic agar medium 2 adjusted to pH 7.2 | China | [116] |
| Streptomyces xinjiangensis sp. nov. | Soil | Reasoner’s 2A (R2A) agar medium at pH 7.2; adjust with crystalline before adding agar | China | [153] |
| Streptomyces alfalfae sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil in an alfalfa field | International Streptomyces Project 2 (ISP2) supplemented with 10 mg L−1 tetracycline | China | [154] |
| Streptomyces palmae sp. nov. | Oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) rhizosphere soil | Starch casein agar (SCA) within the pH range of 7.0–7.2 supplemented with nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1) and cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1) | Thailand | [155] |
| Streptomyces gamaensis sp. nov. | Tropical soil | Gause’s synthetic agar No. 1 adjusted to pH 7.2 and supplemented with nystatin (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | Gama, Chad | [156] |
| Streptomyces andamanensis sp. nov. | Soil | Starch casein nitrate agar plates (HiMedia) supplemented with 25 mg mL−1 nystatin | Thailand | [157] |
| Streptomyces lacrimifluminis sp. nov. | Soil from river bank | Gause’s synthetic agar medium 3 adjusted to pH 7.2 supplemented with nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1) | China | [158] |
| Streptomyces olivicoloratus sp. nov. | Forest soil | HV agar adjusted to pH 7.2 and supplemented with 50 mg mL−1 filter-sterilized cycloheximide, 50 mg mL−1 nystatin and 0.5 mg mL−1 rifampicin | Korea | [159] |
| Streptomonospora halotolerans sp. nov. | Muddy soil | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | China | [160] |
| Streptomyces tyrosinilyticus sp. nov. | River sediment | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | North China | [161] |
| Streptomyces albiflavescens sp. nov. | Rainforest soil | ISP 2 medium with 10 mg L−1 tetracycline | South-West China | [124] |
| Streptomyces polymachus sp. nov. | Forest soil | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar | South Korea | [125] |
| Streptomyces maoxianensis sp. nov. | Pine forest soil | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar supplemented with cycloheximide (50 mg L−1) and nalidixic acid (20 mg L−1) | South-West China | [162] |
| Streptomyces rubrisoli sp. nov. | Red soil | Modified mineral-medium agar containing 0.5% sorbitol supplemented with cycloheximide, nystatin, nalidixic acid (each at 50 μg mL−1), and novobiocin (at 25 μg mL−1) | China | [163] |
| Streptomyces gilvifuscus sp. nov. | Forest soil | Humic acid vitamin (HV) agar | Republic of Korea | [164] |
| Streptomyces lushanensis sp. nov. | Soil from mount Lushan | ISP media | China | [165] |
| Streptomyces bambusae sp. nov. | Bamboo rhizosphere soil | Humic acid vitamin agar (HV agar) adjusted to pH 7.2 and supplemented with filter-sterilized cycloheximide (50 μg mL−1), nystatin (50 μg mL−1), and rifampicin (0.5 μg mL−1) | Republic of Korea | [166] |
| Streptomyces sasae sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil of bamboo (Sasa borealis) | Starch casein agar adjusted to pH 8.5 | Republic of Korea | [167] |
Refer to Supplementary Table S1 for the composition of each media. The superscript (2,3) on some media indicates slight changes in the amount of ingredients used.
Different pretreatment techniques have also been applied to samples, such as ultrasonic treatment [140], orbital shaking [166] and water bath sonication [163], and are crucial to activate Streptomycete spores and inhibit the growth of unwanted microbes [168] (Table 5). Subjecting the sample to heat treatment for 1 h at 120 [146] is an important pre-treatment because actinomycete spores, including Streptomycetes, are more resistant to desiccation than other facultative and Gram–negative anaerobic bacteria [94]. In addition, the selective isolation of actinobacteria by suspending the sample in 1.5% phenol for 30 min is a chemical pretreatment used [138] that disrupts the cell wall of other common bacteria and fungi and improves the growth of Streptomyces [94]. Furthermore, treatment of samples by air-drying for a week [121,130,147] or two [129,136] is a commonly used pretreatment method (Table 5). Moreover, different carbon sources (cellulose, glucose, chitin, starch, dextrose, mannitol and proteose) and combined nitrogen-carbon sources (casein, yeast extract, malt extract, tryptone and peptone) have been added to the media for successful isolation of Streptomycetes [128,129,133,136] from soil sediments (see Table 4 and Supplementary Notes on Supplementary Table S1). Highlighted data shows that soil and sediment are the main source of new Streptomyces spp. in the terrestrial environment (Figure 1), followed by the extreme environment and other symbionts.

Table 5.
Different pre-treatments employed for the isolation of novel Streptomyces spp. terrestrial samples between 2015 and 2020.
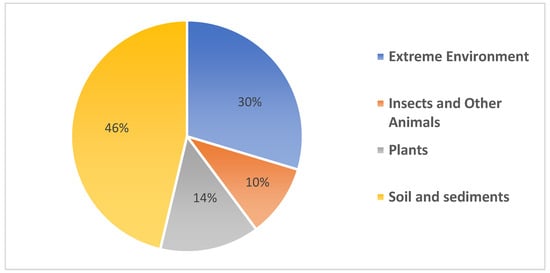
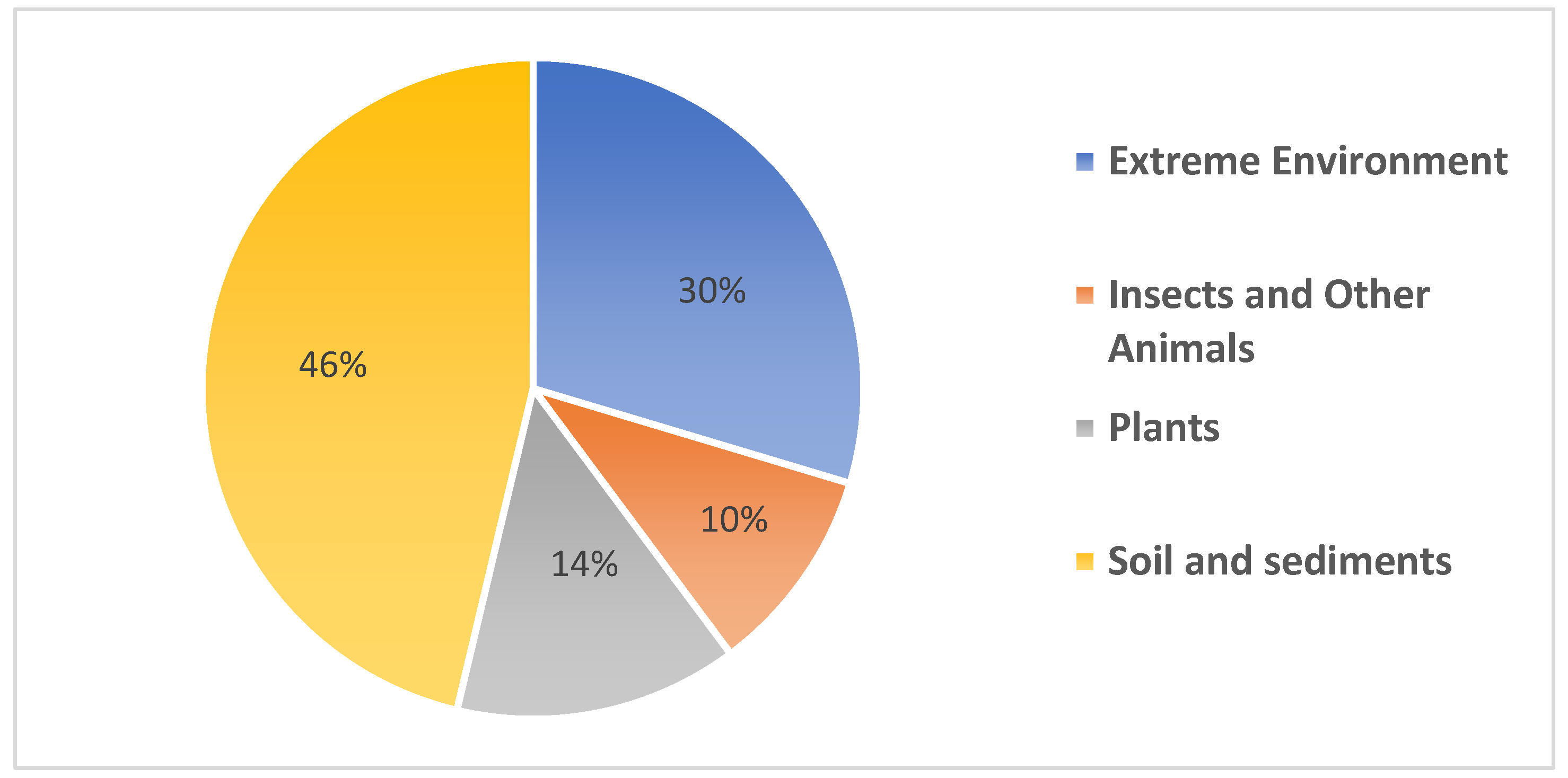
Figure 1.
Distribution of new Streptomyces spp. sampled from different terrestrial sources. Soils and sediments sources provide 46% of the new Streptomyces spp., 30% from extreme environments, 14% from plants and 10% originated from insects.
To summarize, the data collected have shown that soil and sediments are prominent sources of novel Streptomyces spp. from the terrestrial environment as shown in Figure 1 below, followed by extreme environments and other symbionts.
4. Novel Streptomycetes Species Isolated from Marine Environments
Despite the fact that marine Actinobacteria are less studied than terrestrial Actinobacteria, studies have revealed that marine sources of Actinomycetes harbor some of the most important bioactive metabolites for industrial and medical applications [12,169]. However, it is still not clear whether these organisms, in particular Streptomyces spp., are also present in terrestrial sources or exclusive to marine environments [170,171]. Several studies have found that actinobacterial spores are generally dormant and wash away from terrestrial ecosystems in runoff and rivers to the ocean floor and remain dormant [171]. There, at the bottom of the ocean, they will often be exposed to harsh conditions such as high pressure, high salinity and nutrient deficiency. As a result, they will evolve genetically over time and produce a secondary metabolite profile distinct from terrestrial actinobacteria [171]. However, to date, knowledge about the chemistry, distribution and biodiversity of marine Streptomyces and other genera of marine Actinobacteria is still limited [172]. In addition, marine ecosystems are extremely dynamic and it is very difficult to access varying ocean depths for sampling [173]. However, after the development of SCUBA, microbial ocean studies accelerated for the discovery of new drugs [173]. Marine Streptomyces are not only found in seawater and sediments, but also in a wide range of biological sources, including sponges, algae, corals, fish, jellyfish and mangroves [174]. In this review, only two marine sources were reported as sources of new Streptomyces spp. namely marine invertebrates and sediments.
4.1. Isolation Methods
Actinobacteria adapt well and successfully colonize different marine ecosystems where they exhibit a wide range of morphologically, physiologically and metabolic diversity. Marine Streptomyces may require special growth conditions, which require knowledge and experience to prepare isolation media. To mimic such marine environments, researchers must have in-depth knowledge of the different abiotic factors in the sampled environment to successfully isolate new marine Streptomycetes. Since marine habitats are halophilic environments, salt supplements are important ingredients that are added to the isolation medium to provide osmotic values similar to seawater [175]. In addition, the NaCl added to the medium serves to protect the halophilic bacterial cells from changes in osmotic pressure between the external and internal environment of the bacteria [176]. Similar to the terrestrial environment, culture independent studies using high throughput sequencing are used to study marine microbial communities that are not culturable in the laboratory. At the same time, the knowledge gained over time from these culture independent studies on the morphological and physical characteristics of marine Streptomycetes has led to better strategies for growth and culture media to recover these previously uncultured Streptomyces [36,177].
4.2. Invertebrates
About 89% of organisms living in the marine environment are invertebrates [178]. This is clearly reflected by the high number of microbial symbionts associated with this group. These microbial symbionts have produced medically important natural products and studies have shown that Actinomycetes are the most prolific producers of marine novel antibiotics with about 80% of reported compounds from marines’ microorganisms originating from actinomycetes [178]. This can be seen by the great diversity of actinobacteria colonizing marine habitats. Streptomyces are also known to be abundant in marine habitats [167,173]. For successful isolation of marine Streptomyces, different concentrations of sodium salts were added to the medium of different marine samples. Some of the isolation media supplemented, 50% (v/v) sea water [179,180], 3% NaCl [181,182] and even up to 70% seawater can be added to the growth media [183]. In addition, isolation media are made specifically to isolate Streptomycetes spp. from marine samples [182]. In addition to humic acid isolation agar [179,184], other isolation agars such as actinomycete isolation agar [181], inorganic salt-starch agar [183] and starch and casein [180] have also been used to isolate new Streptomycetes from the marine environment. In comparison, humic acid and starch are the only two sources of carbon supplemented reported for us for the isolation of marine invertebrate Streptomyces [179,181,182]. Among these supplements, casein is the main source of carbon-nitrogen [180,181,182]. Other isolation media have been summarized in Table 6. Notably, a sample underwent chemical pretreatment using 3% NaCl [184]. Three percent NaCl has proven to be the optimum concentration that supports actinobacterial growth compared to concentrations lower or higher than 3% [185]. Moreover, the addition of NaCl to the medium selectively inhibits other fastidious microbes by altering the ionic strength of the medium, thus generating an osmotic shock for the microbes resulting in dehydration and growth retardation resulting in cell death [186,187]. Furthermore, NaCl addition also disrupts the solubility of oxygen by disrupting enzymatic functions, thus reducing the growth rate of fastidious bacteria and fungi [188].

Table 6.
Novel Streptomyces spp. reported from marine vertebrates and invertebrates between 2015 and 2020.
4.3. Sediments
Marine sediments represent 63.5% of the Earth’s surface [190], constituting inorganic and organic products from erosion of landmasses, volcanic activities and biochemical activities in the ocean [191]. Apparently, this ecosystem is the most under-sampled marine habitat [192], presumably due to the inaccessibility of the deep-sea floor. Marine sediments have a remarkable diversity of microbial communities constituting approximately 0.18–3.6% of the Earth’s total living biomass [193,194].
In this context, sediments refer to shallow- [195] to deep-water sediments [196], sandy beaches [197] and mangrove sediments [34,198,199] (Table 7). Reports have suggested that these habitats harbor a great number of microbial species, which are still under-explored [12,172]. This is clearly reflected from the data collected at the time of writing where deep-sea sediments are the least sampled for Streptomyces (Table 7) compared to sediments from mangrove forests. A total of 20 new Streptomyces species were isolated from marine sediments between 2015 and 2020 (Table 7) Microorganisms in seawater play an important role in the marine food chain by recycling and breaking down organic matter and other biochemical processes [200]. From this study, 11 out of 20 new Streptomycetes spp. from marine sediments were isolated from mangrove habitats (Table 7).
Streptomycetes from marine sediment samples were isolated using several isolation media. One of the most widely used media is the International Streptomyces Project (ISP2) media [34,201,202,203,204] (Table 7). As seen with marine invertebrate-derived samples, NaCl is also an important ingredient in the isolation medium of marine sediments. These sodium sources include both fresh and aged seawater [196,199] or NaCl solution [205,206] to give the medium an ionic strength similar to that of the sampled environment. In addition, different carbon sources (chitin, dextrose, glucose and soluble starch) combined with carbon-nitrogen sources (casein, peptone, malt extract, yeast extract and tryptone) were added to the medium to successfully isolate them. Furthermore, the media were also supplemented with nystatin and cycloheximide [196,197,199,204,207,208,209,210].

Table 7.
Novel Streptomyces spp. from marine sediments between 2015 and 2020.
Table 7.
Novel Streptomyces spp. from marine sediments between 2015 and 2020.
| Strain | Nature of Sample | Isolation Medium | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomyces marianii sp. | Subtidal marine sediment | Gause’s inorganic agar media (pH 7.2–7.4) supplemented with 75 mg mL−1 of cycloheximide and 25 mg mL−1 of nystatin | India | [196] |
| Streptomyces otsuchiensis sp. nov. | Marine sediment | Bushnell–Haas medium for 5 hrs and 3.0% (w/v) NaCl | Japan | [205] |
| Streptomyces nigra sp. nov. | Rhizosphere soil Avicennia marina | Modified ZoBell 2216E agar plates (HiMedia) | China | [211] |
| Streptomyces caeni sp. nov. | Mangrove mud | that had been made with 70% aged seawater in distilled water (instead of pure distilled water), and supplemented with cycloheximide (25 mg mL−1), potassium dichromate (50 mg mL−1) and nystatin (50 mg mL−1) | China | [199] |
| Streptomyces qaidamensis sp. nov. | Sand | Gause’s synthetic agar medium 2 at pH 7.2 supplemented with nalidixic acid (25 μg mL−1) | China | [197] |
| Streptomyces monashensis sp. nov. | Mangrove soil | ISP2 agar | Malaysia | [34] |
| Streptomyces euryhalinus sp. nov. | Sediment in a mangrove forest | Enrichment medium at pH 7.5 | India | [198] |
| Streptomyces colonosanans sp. nov. | Sediment in mangrove soil | g mL−1) and nalidixic (20 μg mL−1) | Malaysia | [201] |
| Streptomyces kalpinensis sp. nov. | Salt water beach | GW1 medium | China | [195] |
| Streptomyces humi sp. nov. | Mangrove soil | g mL−1) and nystatin (10 μg mL−1) | Malaysia | [206] |
| Streptomyces litoralis sp. nov. | Salt water beach | GW1 medium prepared with 5% (w/v) NaCl | China | [212] |
| Streptomyces ovatisporus sp. nov. | Marine sediments collected at a depth of 42 m | Non-sporulating medium within the pH range of 7.2–7.4 and supplemented with filter-sterilized rifampicin (5 μg mL−1g mL−1) | Turkey | [204] |
| Streptomyces chitinivorans sp. nov. | Brackish sediment of a fish dumping yard in Chilika lake | Colloidal Chitin agar (CCA) medium supplemented with nystatin (50 mg L−1) | India | [208] |
| Streptomyces verrucosisporus sp. nov. | Marine sediments | Seawater– proline −1−1) | Thailand | [207] |
| Streptomyces antioxidans sp. nov. | Mangrove forest soil | g mL−1) | Malaysia | [213] |
| Streptomyces malaysiense sp. nov. | Mangrove soil | g mL−1) | Malaysia | [202] |
| Streptomyces lonarensis sp. nov. | Lake sediment | Beef extract-yeast extract-glucose agar medium adjusted to a pH between 8 and 10 with addition of an appropriate amount of 10% sterile Na2CO3 solution | India | [8] |
| Streptomyces gilvigriseus sp. nov. | Mangrove sediments | mL−1) | Malaysia | [203] |
| Streptomyces mangrovisoli sp. nov. | Mangrove sediments | g mL−1) | Malaysia | [209] |
| Streptomyces mangrovi sp. nov. | Mangrove sediments | SM3 agar (Gauze’s medium) 2 g mL−1).] supplemented with sterile seawater (3.3%, w/v) | Egypt | [210] |
Refer to Supplementary Table S1 for the composition of each media. The superscript (2) on some media indicates slight changes in the amount of ingredients used.
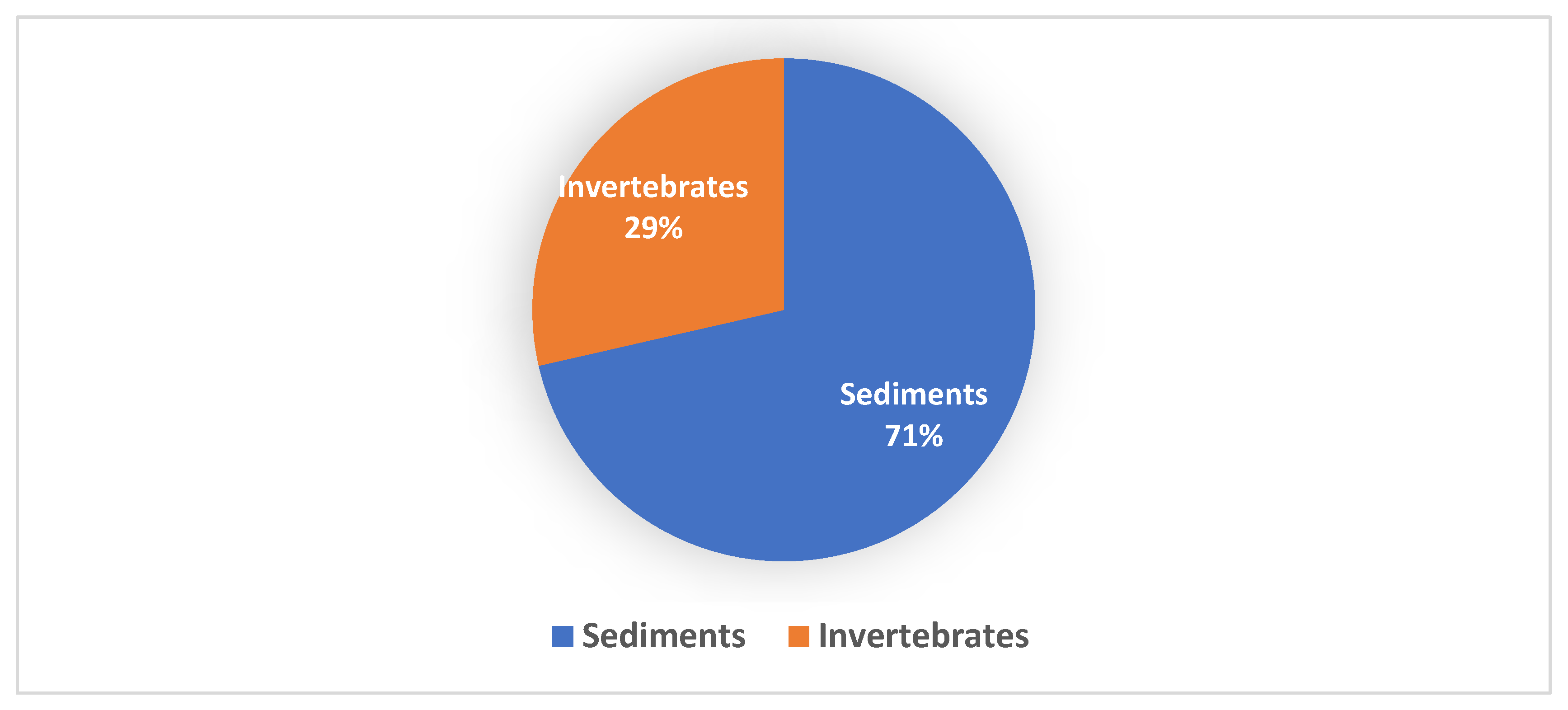
More than 70% of the new Streptomyces spp. were isolated from marine sediments and only 7 (29%) of the new Streptomyces spp. from the marine environment were isolated from marine invertebrates (Figure 2).
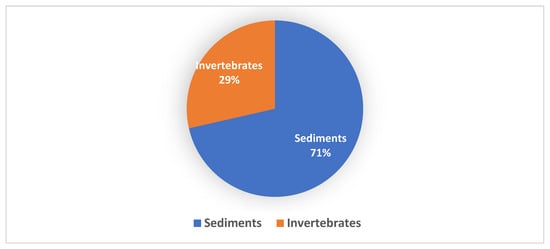
Figure 2.
Marine sources of novel Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020 shows 71% of the total novel Streptomyces spp. originated from sediments and 29% were isolated from marine invertebrates.
The pre-treatment of samples is also an important procedure for marine sediments, with heat being the most commonly applied pre-treatment (Table 8). Of the 27 novel Streptomyces spp. isolated from marine samples, less than half of the samples, constituting only 11 new Streptomyces spp., have undergone some form of pre-treatment. The pre-treatments carried out were either treatment by the wet method [201,208,213] or by dry heat [199,207]. Chemical pre-treatment is used when a source of sodium is added such as 3% NaCl [205] or 3.3% seawater [210]. Sodium modifies the tonicity of the isolation medium and thus selectively inhibits the growth of unwanted microbes [186].

Table 8.
Pretreatment Method for isolation of novel Streptomyces spp. From marine sources between 2015–2020.
5. Summary
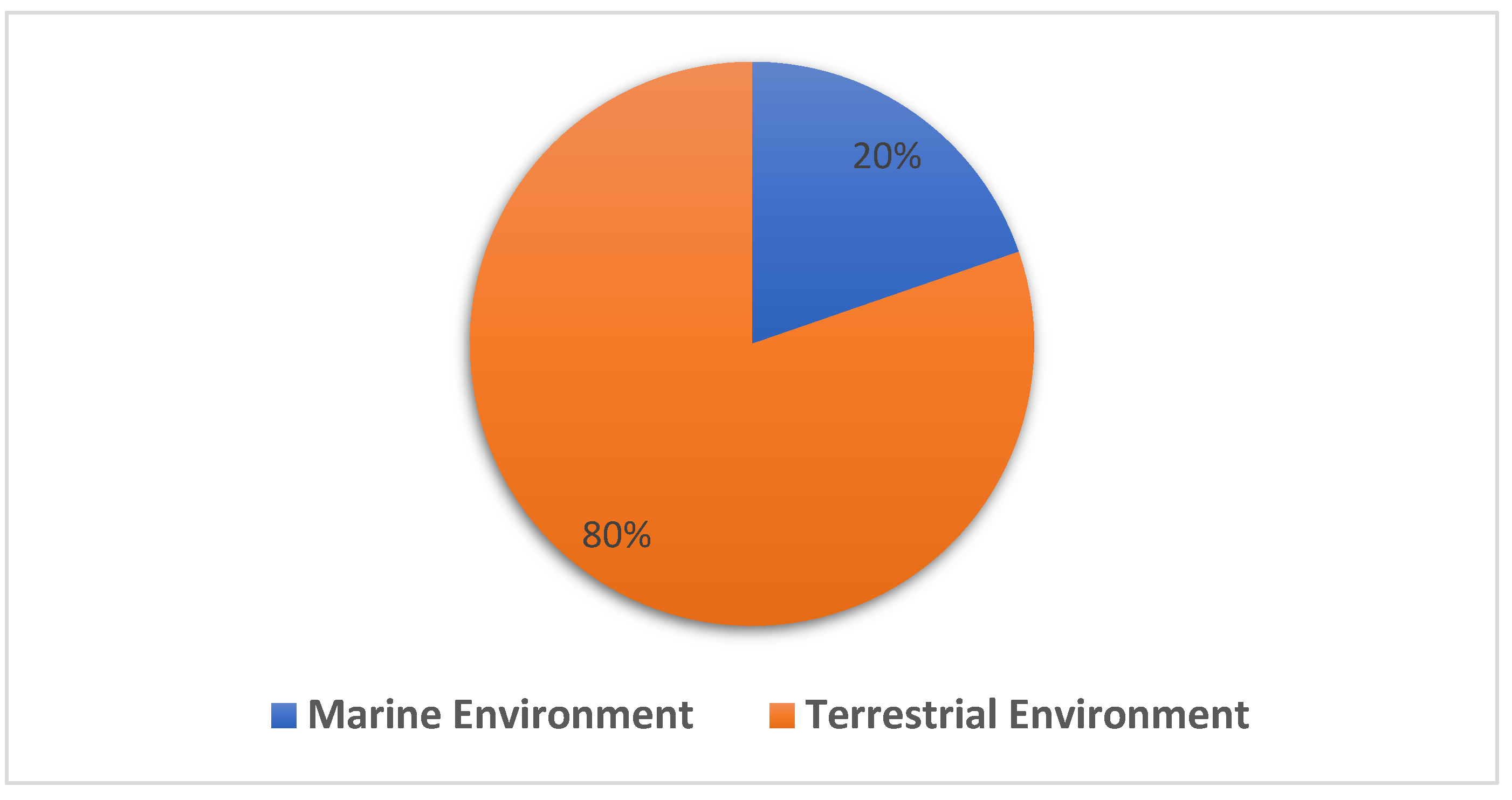
In summary, the data collected have shown that terrestrial environment has been the source of a higher number of novel Streptomyces spp. (80%) compared to the marine environment (20%) as shown in Figure 3.
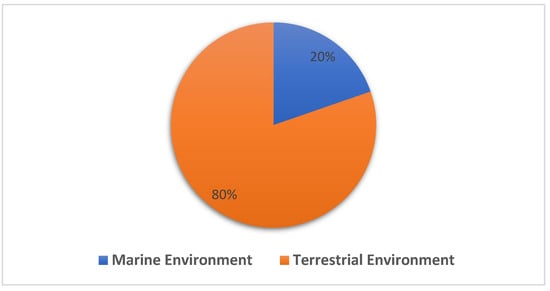
Figure 3.
Distribution of novel Streptomyces spp. recorded in terrestrial and marine environment between 2015 and 2020, with 80% sourced from terrestrial environments and 20% reported from the marine environment.
6. Streptomyces as Source of Antibiotics
Streptomyces spp. have the genetic capacity to produce an average of 30 secondary metabolites [99], making them the most prolific producers of antibiotics. This genus produces about 80% of the total antibiotics sourced from the phylum Actinobacteria [11,16] and produces two thirds of the antibiotics from natural sources that are currently available for public use [7]. The production of secondary metabolites by Streptomycetes is abundant; when resources are limited, they produce aerial hyphae, which divide into spores that can withstand adverse conditions [214]. This is an important factor for successful colonization by Streptomycetes in normal and extreme environments. Strepomycete secondary metabolites protect the vegetative bacterial cell by sequestering heavy metals such as iron, protecting against UV rays, inhibiting other competitors and playing a major role in quorum sensing [15,99].
The discovery of Streptomycetes as a source of antibiotics began in 1940 when the antibiotic actinomycin, commonly used as chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of a variety of cancers, was discovered, filling the void left by penicillin that was ineffective against tuberculosis and certain Gram–negative pathogens [215]. Two years later, streptothricin was isolated from Streptomyces lavendulae [216] followed by streptomycin from Streptomyces griseus [217]. Approximately 12,400 bioactive compounds used clinically and in agriculture were produced by the genus Streptomyces throughout the years, such as the immunosuppressive tacrolimus produced by S. tsukubaensis, the anti-tumor platenolides were obtained from S. platensis, and the insecticide avermectin, as a few examples [6,218]. However, there was a sharp decline in the discovery of such bioactive compounds from 1985 to 2006 [2]. In addition, in the past 30 years, only two Streptomyces-sourced antibiotics have been approved for clinical treatment of systemic infections [16]. This has led researchers to focus their attention on the production of bioactive compounds from other genera of actinobacteria, commonly referred to as “rare Actinomycetes” [219]. A recent study has shown that Streptomyces spp. are no longer considered a potential source of new antibiotics given that no compound isolated from Streptomycetes underwent clinical trials between 2007 and mid-2013 [12], while three compounds isolated from rare marine Actinomycetes are currently undergoing clinical trials [12]. However, data collected from 2015 to 2020 show that a high number of new secondary metabolites were isolated from Streptomycete species. A total of 279 new natural products with diverse bioactivities were discovered from 121 Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020.
6.1. Terrestial Streptomyces as a Source of Antibiotics
Actinomycetes from terrestrial environments produce a large number of bioactive compounds. The data collected showed that despite the decrease in bioactive compounds isolated from Streptomycetes in terrestrial samples, a high number of new secondary metabolites are still isolated from this environment. Seventy-three terrestrial Streptomyces spp. were isolated between 2015 and 2020 as sources of 173 new bioactive compounds, the majority of which show significant antibiotic bioactivity.
6.2. Marine Streptomyces as a Source of Antibiotics
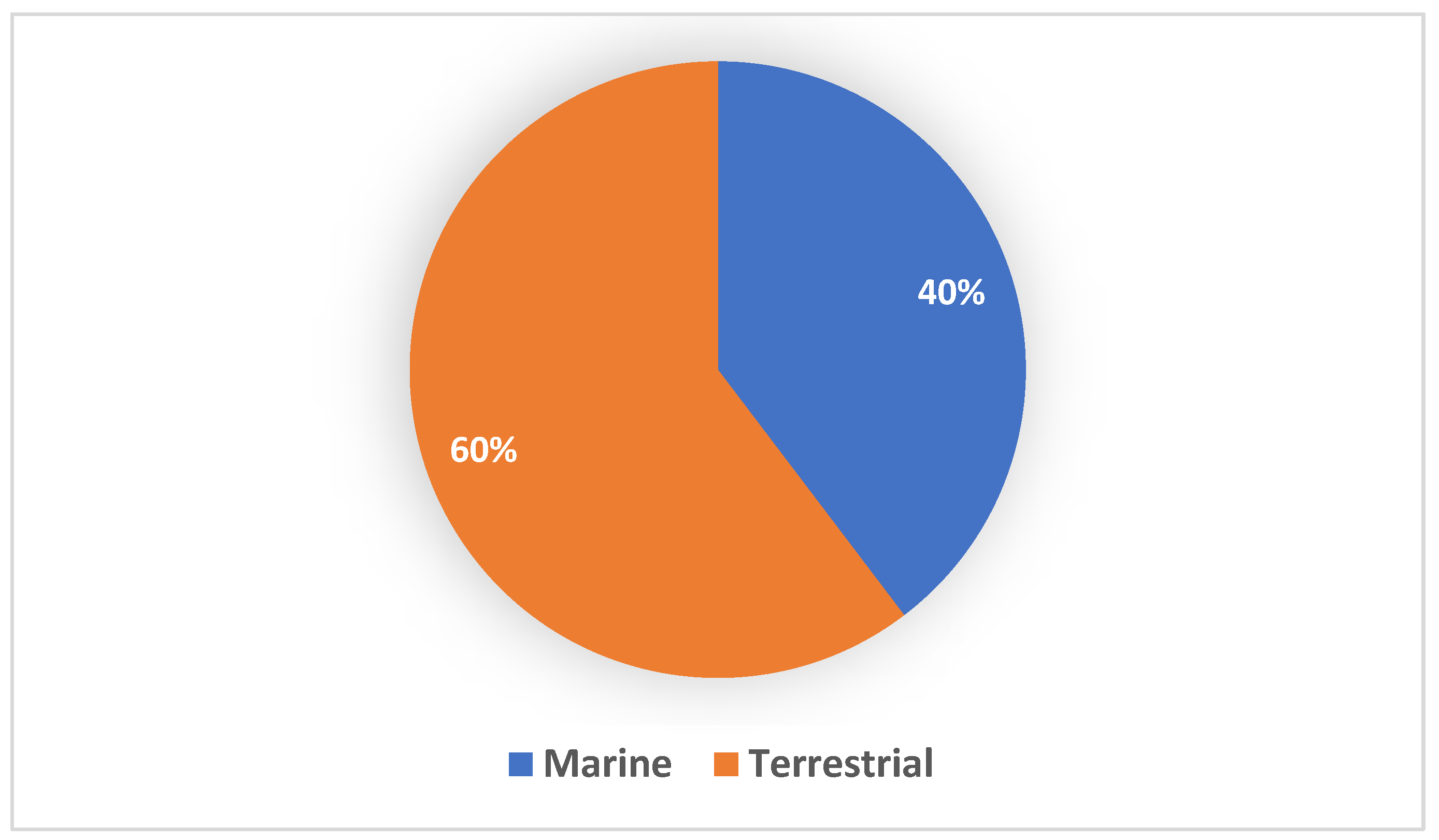
Marine natural products (MNPs) are also a prolific source of novel antibiotics [220]. Actinomycete sources alone account for approximately 80% of novel antibiotics derived from the marine environment [178]. Studies targeting specific and understudied marine microbial phyla can result in a greater likelihood of finding specific marine compounds, since most compounds isolated from marine microorganisms are closely related to compounds isolated from terrestrial microorganisms [221]. Unfortunately, the marine environment is one of the most under-explored environments, but still holds as a promising source of new and innovative natural products [220], which is clearly illustrated in Figure 4. Nair et al. (2020), highlighting the urgent need to explore marine habitats for new microbial bioactive compounds [220]. A total of 106 new bioactive compounds have been discovered from 48 Streptomyces spp. sourced from the marine environment between 2015 and 2020.
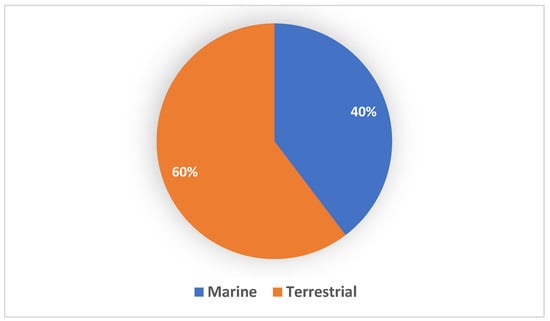
Figure 4.
Distribution of Streptomyces spp. with novel/new natural products from terrestrial and marine environment between 2015 and 2020. The terrestrial Streptomyces spp. were the source of 60% of novel/new natural products while marine Streptomyces spp. were sources of only 40% of novel/new natural products.
6.3. New Compounds from Streptomyces spp. with Bioactivity
All new compounds from Streptomyces spp. as reported between 2015 and 2020 are reviewed below. Despite the fact that a high number of new compounds were reported during the timeframe covered by this review, only a selection of the structures with significant biological activity as stated in their respective articles are presented.
6.4. Antibacterial Activity
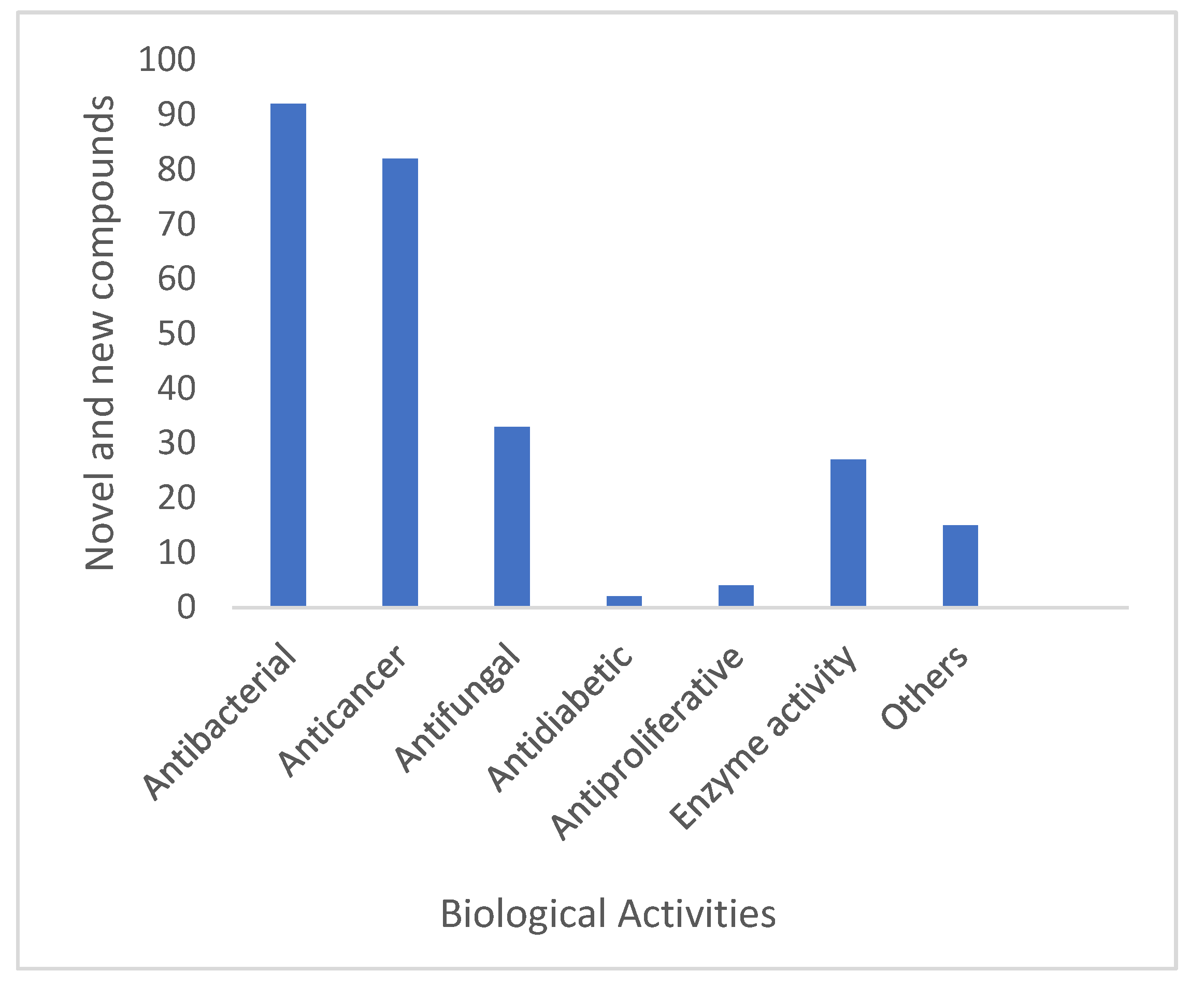
Infections by pathogenic bacteria are a leading cause of death worldwide. Unfortunately, the resistance to antibiotics acquired by pathogenic bacteria has led to an increasing number of untreatable bacterial diseases [220]. Thus, the need to scour natural habitats for new antibacterial compounds has increased. Between 2015 and 2020, 92 new compounds were reported from 39 Streptomyces spp. with antibacterial activity against a wide range of bacterial pathogens, including two of the multidrug-resistant pathogens (Table 9). This shows that Streptomyces spp. are undoubtedly still the current leading producer of antibacterial agents. Figure 5 showed some examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. with significant antibacterial activity.

Table 9.
Novel/new antibacterial bioactive compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020.
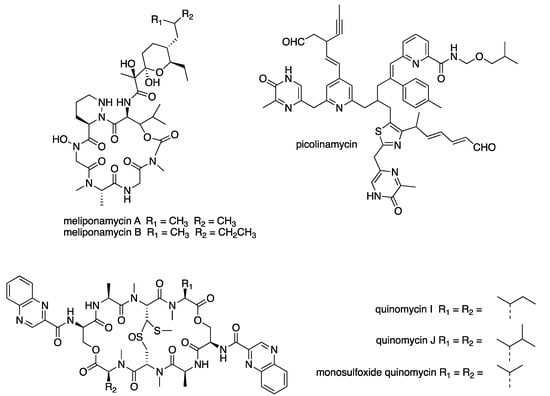
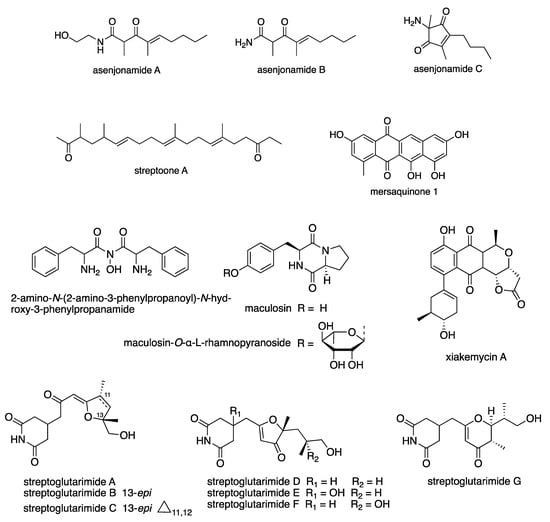
Figure 5.
Examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020 with antibacterial activity.
6.5. Anticancer Activity
Cancer is a major health crisis and is also a major cause of death globally [246]. Scientific fields devoted to treating cancer have developed rapidly and discoveries in therapeutic methods such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiotherapy and surgery offer effective treatments for cancerous tumors [260]. Natural resources have a high potential in the production of anticancer compounds. A suitable source of anticancer compounds is from Streptomyces spp. [260]. During the study period of this review, a total of 82 new anticancer compounds were isolated from 38 Streptomyces spp. (Table 10). Figure 6 showed some examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. with significant anticancer activity.

Table 10.
Novel/new anticancer bioactive compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020.
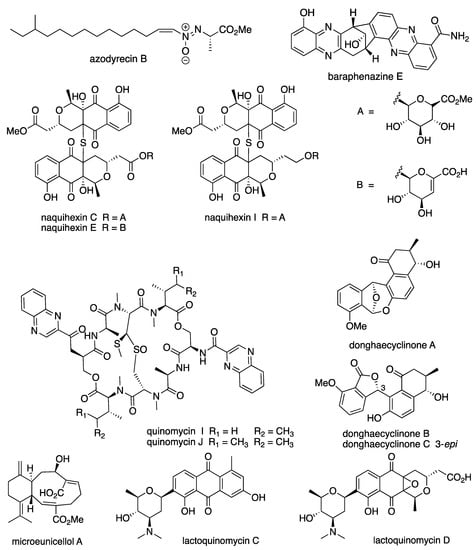
Figure 6.
Examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020 with anticancer activity.
6.6. Enzyme Inhibitor/Inducer Activity
Streptomycetes also produce metabolites with enzyme modulatory activity. There were 27 new compounds derived from 11 Streptomyces spp. during the period of study and these compounds exhibit both enzymes inducing and/or inhibitory activity (Table 11).

Table 11.
Novel/new compounds with enzyme modulatory activity isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020.
Figure 7 showed some examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. with significant enzyme modulatory activity.
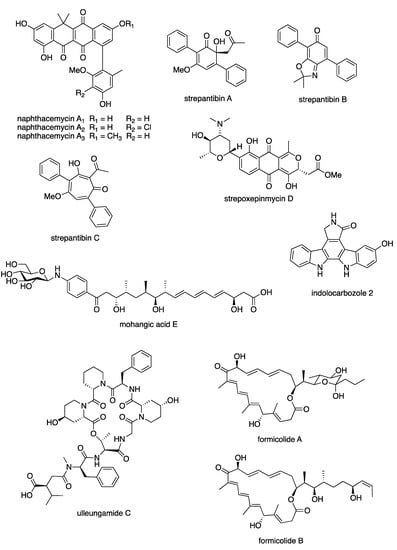
Figure 7.
Examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020 with enzyme modulatory activity.
6.7. Antifungal
New antifungal drugs are urgently needed to alleviate infectious diseases caused by pathogenic fungi. At present, drug resistant fungi are evolving continuously, so the need to find new antifungal drugs is increasing. For example, the multi-drug resistant fungi Candida albicans, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida glabrata have all been shown to be resistant to azole drugs after their drug binding sites mutated, thereby reducing binding affinity. In addition, other therapeutic antifungal drugs were also ineffective against these multi-drug resistant species. [293,294,295,296]. Interestingly, several compounds obtained from Streptomyces spp. have antifungal properties that could be utilized in fighting against drug-resistant and fungal pathogens. 33 new antifungal compounds were reported from nine Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020 (Table 12). Figure 8 showed some examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. with significant antifungal activity.

Table 12.
Novel/new antifungal therapeutic compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020.
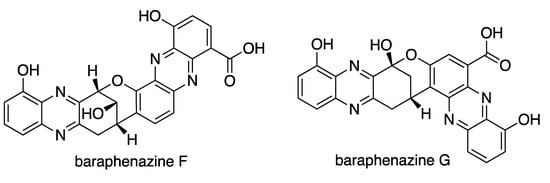
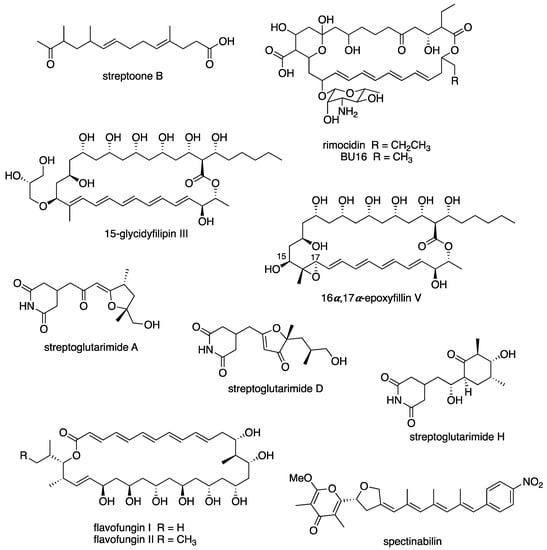
Figure 8.
Examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020 with antifungal activity.
6.8. Other Biological Activity
There were also new natural products from Streptomycetes, which show other biological activities as described in Table 13 below. A total of 18 different bioactivities were recorded from 23 Streptomyces spp., which produced 45 bioactive compounds in total between 2015 and 2020 (Table 13). Figure 9 showed some examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. with other biological activity.

Table 13.
Other biological activity from novel/new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020.
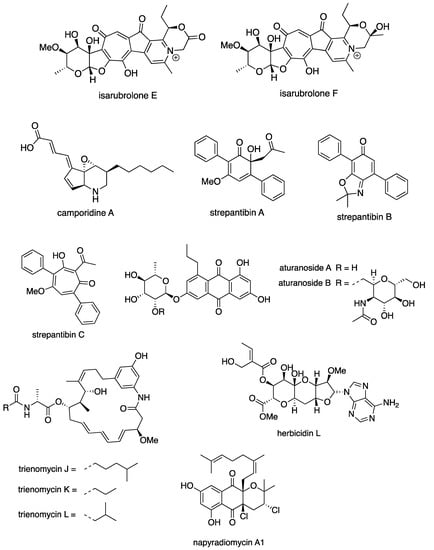
Figure 9.
Examples of new compounds isolated from Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020 with other biological activity.
Streptomyces spp. are still a potential source of new and interesting secondary metabolites with diverse bioactivities. The significant biological activity of new secondary metabolites obtained from the genus Streptomycetes is dominated by antibacterial activity, followed by anticancer, antifungal and enzyme modulatory activities as shown in Figure 10.
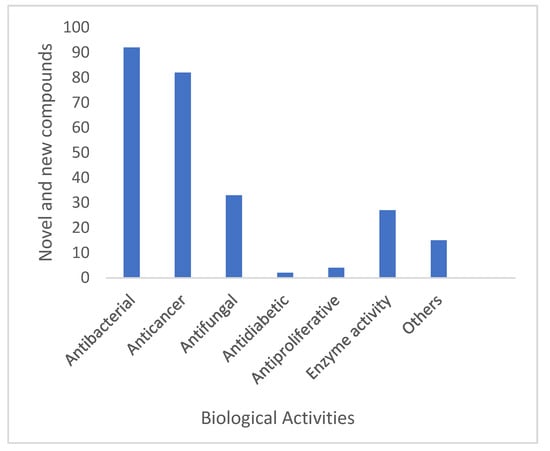
Figure 10.
Biological activities exhibited by novel and new secondary metabolites reported from terrestrial and marine Streptomyces spp. between 2015 and 2020.
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
During the six years of study (January 2015 to December 2020), a high number of new Streptomyces spp. were isolated from terrestrial and marine environments using different isolation procedures. This includes different pre-treatment methods such as chemical, physical and thermal treatments that were used with various selective isolation media to promote the isolation of a total of 135 new Streptomycetes. From this total, 108 new Streptomyces spp. (80%) were sourced from terrestrial habitats and 27 (20%) from marine habitats. Additionally, a total of 279 new natural products have been isolated from 121 Streptomyces spp. with diverse biological activities. A high number (91) of the new natural products shows antibacterial activity followed by anticancer and antifungal effects.
Streptomyces species are undoubtedly a potential source of pharmaceutically important drugs. Despite the tireless efforts of Scientists to discover bioactive metabolites from other prokaryotic sources, including rare actinomycetes, and synthetic drug production, species of the genus Streptomyces are still recognized as a major producer of microbial metabolites. A thorough knowledge and understanding of microbial physiology and metabolism is essential for the successful isolation of novel Streptomyces spp. Culture independent studies have also shown that there are large numbers of Streptomycetes and new natural products that are remain undiscovered under typical laboratory conditions [14,157]. This should be a guide for the future selective isolation procedure to target these Streptomyces spp. and activate their silent biosynthetic gene clusters, which are not expressed under typical laboratory conditions, for new drug discovery. In addition, more effort should be invested in the marine environment for the discovery of new Streptomyces spp. and their associated bioactivities.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microbiolres13030031/s1, Table S1: Isolation media compositions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.D., A.P. and R.S.; Writing—original draft preparation, L.D., A.P. and R.S.; Writing—review and editing, L.D., A.P. and T.T.; Supervision, A.P. and T.T.; Critically evaluated and edited the manuscript, J.O. and R.A.K. Sadly R.S. tragically died in an accident in 2021. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Robert A. Keyzers has provided funding for open access publication fees.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The lead author L.D would like to thank the University of the South Pacific for funding her studies and Robert A. Keyzers for providing open access publication fees. All the authors would like to thank their respective departments for their support and cooperation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Berdy, J. Thoughts and facts about antibiotics: Where we are now and where we are heading. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demain, A.L.; Fang, A. The natural functions of secondary metabolites. In History of Modern Biotechnology; Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 69, pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Locey, K.J.; Lennon, J.T. Scaling laws predict global microbial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5970–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, J.G.; Gilbert, D.N.; Spellberg, B. Seven ways to preserve the miracle of antibiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genilloud, O. Actinomycetes: Still a source of novel antibiotics. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 1203–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manteca, A.; Yague, P. Streptomyces as a Source of Antimicrobials: Novel Approaches to Activate Cryptic Secondary Metabolite Pathways. In Antimicrobials, Antibiotic Resistance, Antibiofilm Strategies and Activity Methods; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Parte, A.C.; Sardà Carbasse, J.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Reimer, L.C.; Göker, M. List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5607–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.K.; Mawlankar, R.; Sonalkar, V.V.; Shinde, V.K.; Zhan, J.; Li, W.J.; Rele, M.V.; Dastager, S.G.; Kumar, L.S. Streptomyces lonarensis sp. nov., isolated from Lonar Lake, a meteorite salt water lake in India. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2016, 109, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, S.; Lu, Q.; Zheng, H.; Osterman, I.A.; Lukyanov, D.A.; Sergiev, P.V.; Dontsova, O.A.; Liu, S.; Ye, J.; et al. Studies on Antibacterial Activity and Diversity of Cultivable Actinobacteria Isolated from Mangrove Soil in Futian and Maoweihai of China. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 3476567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Srinivas, V.; Prasanna, S.L. Streptomyces. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Grasso, L.; Chillura-Martino, D.; Alduina, R. Production of Antibacterial Compounds from Actinomycetes. In Actinobacteria—Basics and Biotechnological Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Subramani, R.; Sipkema, D. Marine Rare Actinomycetes: A Promising Source of Structurally Diverse and Unique Novel Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, H.B. Selman A. Waksman, winner of the 1952 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Frankowski, J.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. The influence of weather conditions on bioactive compound content in sorghum grain. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 246, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, G.A.; Banat, A.M.; Abdelhameed, A.M.; Banat, I.M. Streptomyces from traditional medicine: Sources of new innovations in antibiotic discovery. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procopio, R.E.; Silva, I.R.; Martins, M.K.; Azevedo, J.L.; Araujo, J.M. Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, D. Bioactive Molecules from Extreme Environments. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskaris, P.; Karagouni, A.D. Streptomyces, Greek Habitats and Novel Pharmaceuticals: A Promising Challenge. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.; Epstein, S.; D’onofrio, A.; Ling, L.L. Uncultured microorganisms as a source of secondary metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Jeong, Y.T.; Ryu, Y.J.; Song, C.H.; Lee, Y.S. Isolation, identification and optimal culture conditions of Streptomyces albidoflavus C247 producing antifungal agents against Rhizoctonia solani AG2-2. Mycobiology 2009, 37, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzotto, E.; Weber, T. Omics and multi-omics approaches to study the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in microorganisms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroghazi, J.R.; Metcalf, W.W. Comparative genomics of actinomycetes with a focus on natural product biosynthetic genes. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meij, A.; Worsley, S.F.; Hutchings, M.I.; van Wezel, G.P. Chemical ecology of antibiotic production by actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 392–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Garzón, J.F.; Zehl, M.; Schneider, O.; Rückert, C.; Busche, T.; Kalinowski, J.; Bredholt, H.; Zotchev, S.B. Streptomyces spp. from the marine sponge Antho dichotoma: Analyses of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters and some of their products. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Hwang, S.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Palsson, B.; Cho, B.-K. Mini review: Genome mining approaches for the identification of secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters in Streptomyces. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Hwang, S.; Kim, W.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.; Kim, H.U.; Yoon, Y.J.; Oh, M.-K.; Palsson, B.O.; et al. Systems and synthetic biology to elucidate secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters encoded in Streptomyces genomes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 1330–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belknap, K.C.; Park, C.J.; Barth, B.M.; Andam, C.P. Genome mining of biosynthetic and chemotherapeutic gene clusters in Streptomyces bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Ren, Z.; Chunyu, W.-X.; Li, G.-D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.-T.-L.; Sun, H.-B.; Wang, M.; Xie, T.-P.; Wang, M.; et al. Exploration of Diverse Secondary Metabolites From Streptomyces sp. YINM00001, Using Genome Mining and One Strain Many Compounds Approach. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 831174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomy, D.; Culp, E.; Adamek, M.; Cheng, E.Y.; Ziemert, N.; Wright, G.D.; Sass, P.; Brötz-Oesterhelt, H. The ADEP biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces hawaiiensis NRRL 15010 reveals an accessory clpP gene as a novel antibiotic resistance factor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01292-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Kim, W.; Hwang, S.; Lee, Y.; Cho, S.; Palsson, B.; Cho, B.-K. Thirty complete Streptomyces genome sequences for mining novel secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudoir, M.J.; Pepe-Ranney, C.; Buckley, D.H. Diversification of secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters coincides with lineage divergence in Streptomyces. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Gao, G.; Lü, J.; Long, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, M.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Z.; et al. Engineered Streptomyces lividans strains for optimal identification and expression of cryptic biosynthetic gene clusters. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.A.; Passari, A.K.; Jajoo, A.; Bhasin, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Hashem, A.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Abd Allah, E.F. Tapping into Actinobacterial genomes for natural product discovery. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.; Ser, H.L.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Saokaew, S.; Duangjai, A.; Khan, T.M.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Streptomyces monashensis sp. nov., a novel mangrove soil actinobacterium from East Malaysia with antioxidative potential. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Li, W.-J.; Dastager, S.G.; Hozzein, W.N. Actinobacteria in special and extreme habitats: Diversity, function roles, and environmental adaptations. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeberlein, T.; Lewis, K.; Epstein, S.S. Isolating “uncultivable” microorganisms in pure culture in a simulated natural environment. Science 2002, 296, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiecimska, M.; Golinska, P.; Nouioui, I.; Wypij, M.; Rai, M.; Sangal, V.; Goodfellow, M. Streptomyces alkaliterrae sp. nov., isolated from an alkaline soil, and emended descriptions of Streptomyces alkaliphilus, Streptomyces calidiresistens and Streptomyces durbertensis. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatar, D.; Veyisoglu, A.; Saygin, H.; Sahin, N. Streptomyces boncukensis sp. nov., isolated from saltern soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivlata, L.; Satyanarayana, T. Thermophilic and alkaliphilic Actinobacteria: Biology and potential applications. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.L.; Zhang, L.L.; Luo, X.X.; Xia, Z.F.; Sun, B.B.; Zeng, H. Streptomyces taklimakanensis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from the Taklimakan desert. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, J.; Park, D.J.; Kim, C.J.; Hozzein, W.N.; Wadaan, M.A.; Shu, W.S.; Ding, L.X.; Li, W.J. Gordonia jinhuaensis sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium, isolated from a VBNC (viable but non-culturable) state in pharmaceutical wastewater. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIver, L.J.; Abu-Ali, G.; Franzosa, E.A.; Schwager, R.; Morgan, X.C.; Waldron, L.; Segata, N.; Huttenhower, C. bioBakery: A meta’omic analysis environment. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenova, G.M.; Manucharova, N.A.; Zvyagintsev, D.G. Extremophilic and extremotolerant actinomycetes in different soil types. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2011, 44, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, P.; Hong, K.; Pote, J.; Prabakar, K. Extreme Environment Streptomyces: Potential Sources for New Antibacterial and Anticancer Drug Leads? Int. J. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 5283948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, R.K. Culturability and secondary metabolite diversity of extreme microbes: Expanding contribution of deep sea and deep-sea vent microbes to natural product discovery. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, C. Morphological Identification of Actinobacteria. In Actinobacteria—Basics and Biotechnological Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitushkin, V.D.; Demina, G.R.; Kaprelyants, A.S. Rpf Proteins Are the Factors of Reactivation of the Dormant Forms of Actinobacteria. Biochemistry 2016, 81, 1719–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Albayay, C.; Dorador, C.; Schumann, P.; Andrews, B.; Asenjo, J.; Nouioui, I. Streptomyces huasconensis sp. nov., an haloalkalitolerant actinobacterium isolated from a high altitude saline wetland at the Chilean Altiplano. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2315–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.K.; Kang, H.J.; Roh, S.G.; Park, J.S.; Kim, S.B. Streptomyces fodineus sp. nov., an actinobacterium with antifungal activity isolated from mine area soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaki, H.; Sakurai, K.; Hosoyama, A.; Kimura, A.; Trujilo, M.E.; Igarashi, Y.; Tamura, T. Diversity of PKS and NRPS gene clusters between Streptomyces abyssomicinicus sp. nov. and its taxonomic neighbor. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipun, K.; Chantavorakit, T.; Mingma, R.; Duangmal, K. Streptomyces acidicola sp. nov., isolated from a peat swamp forest in Thailand. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.X.; Gao, G.B.; Xia, Z.F.; Chen, Z.J.; Wan, C.X.; Zhang, L.L. Streptomyces salilacus sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from a salt lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygin, H.; Ay, H.; Guven, K.; Cetin, D.; Sahin, N. Streptomyces cahuitamycinicus sp. nov., isolated from desert soil and reclassification of Streptomyces galilaeus as a later heterotypic synonym of Streptomyces bobili. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2750–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Han, X.; Xia, Z.; Luo, X.; Wan, C.; Zhang, L. Streptomyces luozhongensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete with antifungal activity and antibacterial activity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Ahmed, I.; Khalid, N.; Osman, G.; Khan, I.U.; Xiao, M.; Li, W.J. Streptomyces caldifontis sp. nov., isolated from a hot water spring of Tatta Pani, Kotli, Pakistan. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; He, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces daqingensis sp. nov., isolated from saline-alkaline soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.Y.; Yang, Z.W.; Asem, M.D.; Fang, B.Z.; Salam, N.; Alkhalifah, D.H.M.; Hozzein, W.N.; Nie, G.X.; Li, W.J. Streptomyces desertarenae sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from a desert sample. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, H.; Nouioui, I.; Del Carmen Montero-Calasanz, M.; Klenk, H.P.; Isik, K.; Cetin, D.; Sahin, N. Streptomyces sediminis sp. nov. isolated from crater lake sediment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, H.; Labeda, D.P.; Nouioui, I.; Castro, J.F.; Del Carmen Montero-Calasanz, M.; Bull, A.T.; Asenjo, J.A.; Goodfellow, M. Streptomyces aridus sp. nov., isolated from a high altitude Atacama Desert soil and emended description of Streptomyces noboritoensis Isono et al. 1957. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kamjam, M.; Nopnakorn, P.; Zhang, L.; Peng, F.; Deng, Z.; Hong, K. Streptomyces polaris sp. nov. and Streptomyces septentrionalis sp. nov., isolated from frozen soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Tang, X.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.; Tang, Y.; Gao, J. Streptomyces cadmiisoli sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from cadmium-contaminated soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, P.; Yu, Y.Z.; Zhao, J.R.; Gao, J. Streptomyces xiangtanensis sp. nov., isolated from a manganese-contaminated soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, P.; Zhao, J.; Li, K.; Tang, X.; Gao, J. Streptomyces manganisoli sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from manganese-contaminated soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, K.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Gao, J. Streptomyces cyaneochromogenes sp. nov., a blue pigment-producing actinomycete from manganese-contaminated soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2202–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Albayay, C.; Dorador, C.; Schumann, P.; Schniete, J.K.; Herron, P.; Andrews, B.; Asenjo, J.; Nouioui, I. Streptomyces altiplanensis sp. nov., an alkalitolerant species isolated from Chilean Altiplano soil, and emended description of Streptomyces chryseus (Krasil’nikov et al. 1965) Pridham 1970. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, L.; Ye, Z.; Lu, L.; Li, Y. Streptomyces tibetensis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from the Tibetan Plateau. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.W.; Bao, J. Streptomyces dengpaensis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from desert soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3322–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanasupawat, S.; Phongsopitanun, W.; Suwanborirux, K.; Ohkuma, M.; Kudo, T. Streptomyces actinomycinicus sp. nov., isolated from soil of a peat swamp forest. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Guo, X.; Yan, R.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces durbertensis sp. nov., isolated from saline-alkali soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3635–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobek, J.; Smidova, K.; Cihak, M. A Waking Review: Old and Novel Insights into the Spore Germination in Streptomyces. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottig, A.; Atasayar, E.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Sproer, C.; Schumann, P.; Schauer, J.; Steinbuchel, A. Streptomyces jeddahensis sp. nov., an oleaginous bacterium isolated from desert soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.X.; Han, X.X.; Luo, X.X.; Xia, Z.F.; Wan, C.X.; Zhang, L.L. Streptomyces canalis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from an alkali-removing canal. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3219–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, M.; Busarakam, K.; Idris, H.; Labeda, D.P.; Nouioui, I.; Brown, R.; Kim, B.Y.; Del Carmen Montero-Calasanz, M.; Andrews, B.A.; Bull, A.T. Streptomyces asenjonii sp. nov., isolated from hyper-arid Atacama Desert soils and emended description of Streptomyces viridosporus Pridham et al. 1958. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, A.B.; Nouioui, I.; Klenk, H.P.; Goodfellow, M. Streptomyces harenosi sp. nov., a home for a gifted strain isolated from Indonesian sand dune soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 4874–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ruan, C.; Peng, F.; Deng, Z.; Hong, K. Streptomyces arcticus sp. nov., isolated from frozen soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhwale, J.K.; Goker, M.; Rohde, M.; Sproer, C.; Schumann, P.; Klenk, H.P.; Boga, H.I. Streptomyces alkaliphilus sp. nov., isolated from sediments of Lake Elmenteita in the Kenyan Rift Valley. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnani, N.; Rajski, S.R.; Bugni, T.S. Symbiosis-inspired approaches to antibiotic discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 784–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seipke, R.F.; Barke, J.; Brearley, C.; Hill, L.; Yu, D.W.; Goss, R.J.; Hutchings, M.I. A single Streptomyces symbiont makes multiple antifungals to support the fungus farming ant Acromyrmex octospinosus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchanasin, P.; Yuki, M.; Kudo, T.; Ohkuma, M.; Kuncharoen, N.; Phongsopitanun, W.; Tanasupawat, S. Streptomyces bauhiniae sp. nov., isolated from tree bark of Bauhinia variegata Linn. in Thailand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Whang, K.S. Streptomyces fuscigenes sp. nov., isolated from bamboo (Sasa borealis) litter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tian, J.; Li, X.; Gan, L.; He, L.; Chu, Y.; Tian, Y. Streptomyces dioscori sp. nov., a Novel Endophytic Actinobacterium Isolated from Bulbil of Dioscorea bulbifera L. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Guan, X.; Guo, L.; Jia, F.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces polygonati sp. nov., an endophytic actinomycete isolated from a root of Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lai, X.; Gan, L.; Long, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y. Streptomyces geranii sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinobacterium isolated from root of Geranium carolinianum L. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2562–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wan, C.; Luo, X.; Zhang, L. Streptomyces carminius sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from Sophora alopecuroides in Xinjiang, China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewkla, O.; Franco, C.M.M. Streptomyces roietensis sp. nov., an endophytic actinobacterium isolated from the surface-sterilized stem of jasmine rice, Oryza sativa KDML 105. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4868–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klykleung, N.; Phongsopitanun, W.; Pittayakhajonwut, P.; Ohkuma, M.; Kudo, T.; Tanasupawat, S. Streptomyces phyllanthi sp. nov., isolated from the stem of Phyllanthus amarus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3923–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Li, X.; Gan, L.; Long, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y. Streptomyces populi sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinobacterium isolated from stem of Populus adenopoda Maxim. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.F.; Li, Q.L.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, Y.G.; Zhou, X.K.; Narsing Rao, M.P.; Duan, Y.Q.; Li, W.J. Streptomyces capparidis sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinobacterium isolated from fruits of Capparis spinosa L. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.L. Streptomyces ginkgonis sp. nov., an endophyte from Ginkgo biloba. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhaiyan, M.; Poonguzhali, S.; Saravanan, V.S.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Pragatheswari, D.; Santhanakrishnan, P.; Kim, S.J.; Weon, H.Y.; Kwon, S.W. Streptomyces pini sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from phylloplane of pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) needle-like leaves. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4204–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jin, P.; Liu, C.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces bryophytorum sp. nov., an endophytic actinomycete isolated from moss (Bryophyta). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2016, 109, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constant, P.; Poissant, L.; Villemur, R. Isolation of Streptomyces sp. PCB7, the first microorganism demonstrating high-affinity uptake of tropospheric H2. ISME J. 2008, 2, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Liu, C.; Guo, L.; Piao, C.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Jia, F.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces formicae sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from the head of Camponotus japonicus Mayr. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2016, 109, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Kajiura, T.; Nonomura, H. New methods for the highly selective Isolation of Streptosporangium and Dactylosporangium from soil. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1991, 72, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quecine, M.C.; Araujo, W.L.; Marcon, J.; Gai, C.S.; Azevedo, J.L.; Pizzirani-Kleiner, A.A. Chitinolytic activity of endophytic Streptomyces and potential for biocontrol. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 47, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey-Klett, P.; Garbaye, J.; Tarkka, M. The mycorrhiza helper bacteria revisited. New Phytol. 2007, 176, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeng-In, P.; Phongsopitanun, W.; Savarajara, A.; Tanasupawat, S. Streptomyces lichenis sp. nov., isolated from lichen. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3641–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.Q.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Li, B.B.; Li, C.H.; Huang, Q.H.; Zhang, Q.H.; Dai, W.H.; Jiang, Y.J. Streptomyces tremellae sp. nov., isolated from a culture of the mushroom Tremella fuciformis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5028–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrette, M.G.; Carlson, C.M.; Ortega, H.E.; Thomas, C.; Ananiev, G.E.; Barns, K.J.; Book, A.J.; Cagnazzo, J.; Carlos, C.; Flanigan, W.; et al. The antimicrobial potential of Streptomyces from insect microbiomes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohland, J.; Meyers, P.R. Streptomyces fractus sp. nov., a novel streptomycete isolated from the gut of a South African termite. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitalla, J.W.; Benndorf, R.; Martin, K.; Vollmers, J.; Kaster, A.K.; de Beer, Z.W.; Poulsen, M.; Beemelmanns, C. Streptomyces smaragdinus sp. nov., isolated from the gut of the fungus growing-termite Macrotermes natalensis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5806–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, C.; Zheng, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Jin, L.; Song, W.; Yan, K.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Two new species of the genus Streptomyces: Streptomyces camponoti sp. nov. and Streptomyces cuticulae sp. nov. isolated from the cuticle of Camponotus japonicus Mayr. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Mu, S.; Lu, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, D.; Yan, K.; Xiang, W.; Liu, C. Streptomyces amphotericinicus sp. nov., an amphotericin-producing actinomycete isolated from the head of an ant (Camponotus japonicus Mayr). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4967–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Piao, C.; Yu, Y.; Cao, P.; Li, C.; Yang, F.; Li, M.; Xiang, W.; Liu, C. Streptomyces capitiformicae sp. nov., a novel actinomycete producing angucyclinone antibiotics isolated from the head of Camponotus japonicus Mayr. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Z.; Yan, K.; Xiang, W.; Liu, C. Streptomyces camponoticapitis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from the head of an ant (Camponotus japonicus Mayr). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3855–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, K.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W.; Liu, C. Streptomyces lasiicapitis sp. nov., an actinomycete that produces kanchanamycin, isolated from the head of an ant (Lasius fuliginosus L.). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, M.; Oh, D.C.; Clardy, J.; Currie, C.R. Chemical analyses of wasp-associated Streptomyces bacteria reveal a prolific potential for natural products discovery. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamm, P.S.; Dunlap, C.A.; Mullowney, M.W.; Caimi, N.A.; Kelleher, N.L.; Thomson, R.J.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Northup, D.E. Streptomyces buecherae sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from multiple bat species. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamm, P.S.; Caimi, N.A.; Northup, D.E.; Valdez, E.W.; Buecher, D.C.; Dunlap, C.A.; Labeda, D.P.; Porras-Alfaro, A. Streptomyces corynorhini sp. nov., isolated from Townsend’s big-eared bats (Corynorhinus townsendii). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ye, L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, H.; Yan, K.; Xiang, W.; Wang, X. Streptomyces kronopolitis sp. nov., an actinomycete that produces phoslactomycins isolated from a millipede (Kronopolites svenhedind Verhoeff). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5352–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, O.S.; Babalola, O.O. Streptomyces: Implications and interactions in plant growth promotion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.S.; Jordan, M.S.; Adams, S.M.; Suen, G.; Goodwin, L.A.; Davenport, K.W.; Currie, C.R.; Raffa, K.F. Cellulose-degrading bacteria associated with the invasive woodwasp Sirex noctilio. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amore, A.; Pepe, O.; Ventorino, V.; Birolo, L.; Giangrande, C.; Vincenza, F. Cloning and recombinant expression of a cellulase from the cellulytic strain Streptomyces sp. G12 isolated from compost. Microb. Cell Factories 2012, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, E.; Zhu, Y.; Teng, C.; Sun, B.; Song, H.; Yang, R. A typical endo-xylanase from Streptomyces rameus L2001 and its unique characteristics in xylooligosaccharide production. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 359, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontemps, C.; Toussaint, M.; Revol, P.V.; Hotel, L.; Jeanbille, M.; Uroz, S.; Turpault, M.P.; Blaudez, D.; Leblond, P. Taxonomic and functional diversity of Streptomyces in a forest soil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 342, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhi, X.; Yang, L.; Cen, X.; Zhao, G.; Ding, X. Streptomyces yangpuensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulla, H. Bioweathering and biotransformation of granitic rock minerals by actinomycetes. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Song, W.; Duan, L.; Jiang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces inhibens sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from rhizosphere soil of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas Hoyos, H.A.; Nobre Santos, S.; Da Silva, L.J.; Paulino Silva, F.S.; Bonaldo Genuario, D.; Domingues Zucchi, T.; Melo, I.S. Streptomyces rhizosphaericola sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from the wheat rhizosphere. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, L.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, W.; Wang, X. Streptomyces tritici sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from rhizosphere soil of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchanasin, P.; Moonmangmee, D.; Phongsopitanun, W.; Tanasupawat, S.; Moonmangmee, S. Streptomyces cerasinus sp. nov., isolated from soil in Thailand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 3854–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.X.; Kai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wan, C.X.; Zhang, L.L. Streptomyces luteus sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Take, A.; Inahashi, Y.; Omura, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Matsumoto, A. Streptomyces boninensis sp. nov., isolated from soil from a limestone cave in the Ogasawara Islands. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zheng, J.; Xin, D.; Xin, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J. Streptomyces albiflavescens sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65 Pt 5, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Kim, J. Antifungal and antibacterial activities of Streptomyces polymachus sp. nov. isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2385–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yang, X.; Huang, D.; Huang, X. Streptomyces solisilvae sp. nov., isolated from tropical forest soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 3553–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.L.; Wang, H.; Xue, Z.L.; Li, J.S.; Qi, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.D.; Xiang, W.S. Two new glutarimide antibiotics from Streptomyces sp. HS-NF-780. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Han, C.; Yu, B.; Zhao, J.; Yan, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, C.; Xiang, W. Taxonomic Characterization, and Secondary Metabolite Analysis of Streptomyces triticiradicis sp. nov.: A Novel Actinomycete with Antifungal Activity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saygin, H.; Veyisoglu, A.; Tatar, D.; Nigiz, C.; Tokatli, A.; Sahin, N. Streptomyces coryli sp. nov., isolated from hazelnut orchard soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 4791–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tang, X.; Li, K.; Guo, Y.; Feng, M.; Gao, J. Streptomyces paludis sp. nov., isolated from an alpine wetland soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatli, A.; Idil, O.; Veyisoglu, A.; Saygin, H.; Guven, K.; Cetin, D.; Sahin, N. Streptomyces boluensis sp. nov., isolated from lake sediment. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Liu, C.F.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Z.F.; Huang, Y.J.; Luo, X.X. Streptomyces roseicoloratus sp. nov., isolated from cotton soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Jiang, X.; Kong, D.; Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Han, X.; Ma, Q.; Tan, H.; Ruan, Z. Streptomyces soli sp. nov., isolated from birch forest soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Yuan, L.; Xia, Z.; Wan, C.; Zhang, L. Streptomyces albicerus sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from the sediments of the Tailan River in Xinjiang, China. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, S.; Yang, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Chen, T.; Liu, G.; Dyson, P. Streptomyces dangxiongensis sp. nov., isolated from soil of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2729–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Han, L.; Yu, M.; Cao, P.; Li, D.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Characterization of Streptomyces sporangiiformans sp. nov., a Novel Soil Actinomycete with Antibacterial Activity against Ralstonia solanacearum. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Han, L.; Zhao, J.; Ju, H.; Jiang, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces monticola sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sujarit, K.; Kudo, T.; Ohkuma, M.; Pathom-Aree, W.; Lumyong, S. Streptomyces venetus sp. nov., an actinomycete with a blue aerial mycelium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3333–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Jiang, H.; Han, L.; Jiang, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces xiangluensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 2249–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, C.; Ling, L.; Zhao, J.; Jin, L.; Jiang, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces urticae sp. nov., isolated from rhizosphere soil of Urtica urens L. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayed, A.; Slama, N.; Mankai, H.; Bachkouel, S.; El Kahoui, S.; Tabbene, O.; Limam, F. Streptomyces tunisialbus sp. nov., a novel Streptomyces species with antimicrobial activity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Jin, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces flavalbus sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from rhizosphere of maize (Zea mays L.). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Sun, T.; Jiang, S.; Mu, S.; Li, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces lutosisoli sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from muddy soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Han, C.; Zhao, J.; Shi, H.; Hu, J.; Jiang, S.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces triticisoli sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from rhizosphere soil of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, B.; Ou, X.; Pan, S.; Shao, Y.; Huang, F. Streptomyces thermoalkaliphilus sp. nov., an alkaline cellulase producing thermophilic actinomycete isolated from tropical rainforest soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Roes-Hill, M.; Prins, A.; Meyers, P.R. Streptomyces swartbergensis sp. nov., a novel tyrosinase and antibiotic producing actinobacterium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonmangmee, D.; Kanchanasin, P.; Phongsopitanun, W.; Tanasupawat, S.; Moonmangmee, S. Streptomyces xylanilyticus sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4189–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, P.H.F.; Macrae, A.; Reinert, F.; de Souza, R.F.; Coelho, R.R.R.; Potter, G.; Klenk, H.P.; Labeda, D.P. Streptomyces odonnellii sp. nov., a proteolytic streptomycete isolated from soil under cerrado (savanna) vegetation cover. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 5211–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhuang, J.; Xin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J. Streptomyces fuscichromogenes sp. nov., an actinomycete from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripreechasak, P.; Phongsopitanun, W.; Tamura, T.; Tanasupawat, S. Streptomyces krungchingensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Whang, K.S. Streptomyces rhizosphaerihabitans sp. nov. and Streptomyces adustus sp. nov., isolated from bamboo forest soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3573–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Sun, Y.; Xie, S.; Wan, C.; Zhang, L. Streptomyces indoligenes sp. nov., isolated from rhizosphere soil of Populus euphratica. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, Y.Q.; Asem, M.D.; Lu, C.Y.; Shi, X.H.; Chu, X.; Zhang, W.Q.; Di An, D.; Li, W.J. Streptomyces xinjiangensis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from Lop Nur region. Arch. Microbiol. 2016, 198, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, W.; Sun, Z.; Yi, L.; Zhao, S.; Liang, Y. Streptomyces alfalfae sp. nov. and comparisons with its closest taxa Streptomyces silaceus, Streptomyces flavofungini and Streptomyces intermedius. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujarit, K.; Kudo, T.; Ohkuma, M.; Pathom-Aree, W.; Lumyong, S. Streptomyces palmae sp. nov., isolated from oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) rhizosphere soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Ye, L.; Liu, C.; Abagana, A.Y.; Zheng, W.; Sun, P.; Li, J.; Xiang, W.; Wang, X. Streptomyces gamaensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete with antifungal activity isolated from soil in Gama, Chad. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sripreechasak, P.; Tamura, T.; Shibata, C.; Suwanborirux, K.; Tanasupawat, S. Streptomyces andamanensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 2030–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G.; Chen, T.; Li, S.; Dyson, P. Streptomyces lacrimifluminis sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium that produces antibacterial compounds, isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4981–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Kim, J. Streptomyces olivicoloratus sp. nov., an antibiotic-producing bacterium isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3262–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, L.; Liu, C.; Sun, P.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Xiang, W.; Wang, X. Streptomonospora halotolerans sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3183–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, L.; Liu, C.; Bai, L.; Han, C.; Li, J.; Xiang, W.; Wang, X. Streptomyces tyrosinilyticus sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from river sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3091–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Fang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Jin, P.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Streptomyces maoxianensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from soil in Maoxian, China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Ruan, J.; Huang, Y. Streptomyces rubrisoli sp. nov., neutrotolerant acidophilic actinomycetes isolated from red soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3103–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Kim, J. Streptomyces gilvifuscus sp. nov., an actinomycete that produces antibacterial compounds isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3493–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.H.; Cheng, J.; Chen, W.; Li, H.Q.; Yang, J.Y.; Park, D.J.; Kim, C.J.; Shen, R.; Duan, Y.Q.; Li, W.J. Streptomyces lushanensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete with anti-cyanobacterial activity. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Kim, J. Streptomyces bambusae sp. nov., Showing Antifungal and Antibacterial Activities, Isolated from Bamboo (Bambuseae) Rhizosphere Soil Using a Modified Culture Method. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Whang, K.S. Streptomyces sasae sp. nov., isolated from bamboo (Sasa borealis) rhizosphere soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3547–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.T.; Shameemullah, M.; Watson, E.T.; Mayfield, C.I. Studies on the ecology of actinomycetes in soil—VI. The influence of moisture tension on growth and survival. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmaraj, S.; Ashokkumar, B.; Dhevendaran, K. Isolation of marine Streptomyces and the evaluation of its bioactive molecules. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 240–248. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Bayer, K.; Hentschel, U. Diversity, abundance and natural products of marine sponge-associated actinomycetes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.A.; Rutherford, L.T.; Hodson, R.E. Evidence for indegenous Streptomyces population in a marine environment determined with a 16S rRNA probe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 3695–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Gupta, R.K. Diversity and isolation of rare actinomycetes: An overview. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 39, 256–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawsar, S. Scuba Diving for Marine Microbiologists. Available online: https://www.biotecharticles.com/Careers-Article/Scuba-Diving-For-Marine-Microbiologists-1400.html (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Dharmaraj, S. Marine Streptomyces as a novel source of bioactive substances. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 2123–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, L.A.; Fenical, W.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.A.; Mincer, T.J.; Ward, A.C.; Bull, A.T.; Goodfellow, M. Salinispora arenicola gen. nov., sp. nov. and Salinispora tropica sp. nov., obligate marine actinomycetes belonging to the family Micromonosporaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55 Pt 5, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudryk, Z.; Donderski, W. Effect of sodium chloride on the metabolic activity of halophillic bacteria isolated from the lake Gardno estuary. Estuaries 1991, 14, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, E.A.; Vatsa, P.; Sanchez, L.; Gaveau-Vaillant, N.; Jacquard, C.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Klenk, H.P.; Clement, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; van Wezel, G.P. Taxonomy, Physiology, and Natural Products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blockley, A.; Elliott, D.; Roberts, A.; Sweet, M. Symbiotic Microbes from Marine Invertebrates: Driving a New Era of Natural Product Drug Discovery. Diversity 2017, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kong, F.; Zhou, S.; Huang, D.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, W. Streptomyces tirandamycinicus sp. nov., a Novel Marine Sponge-Derived Actinobacterium with Antibacterial Potential against Streptococcus agalactiae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhou, S.; Huang, D.; Chen, J.; Zhu, W. Streptomyces spongiicola sp. nov., an actinomycete derived from marine sponge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dhaneesha, M.; Hasin, O.; Sivakumar, K.C.; Ravinesh, R.; Naman, C.B.; Carmeli, S.; Sajeevan, T.P. DNA Binding and Molecular Dynamic Studies of Polycyclic Tetramate Macrolactams (PTM) with Potential Anticancer Activity Isolated from a Sponge-Associated Streptomyces zhaozhouensis subsp. mycale subsp. nov. Mar. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, H.W.; Lu, Y.H. Streptomyces reniochalinae sp. nov. and Streptomyces diacarni sp. nov., from marine sponges. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harunari, E.; Hamada, M.; Shibata, C.; Tamura, T.; Komaki, H.; Imada, C.; Igarashi, Y. Streptomyces hyaluromycini sp. nov., isolated from a tunicate (Molgula manhattensis). J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.S.; Souza, D.T.; Zucchi, T.D.; Pansa, C.C.; de Figueiredo Vasconcellos, R.L.; Crevelin, E.J.; de Moraes, L.A.; Melo, I.S. Streptomyces atlanticus sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from marine sponge Aplysina fulva (Pallas, 1766). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2016, 109, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.K.; Hodson, M.P.; Hewavitharana, A.K.; Bose, U.; Shaw, P.N.; Fuerst, J.A. Effects of salinity on antibiotic production in sponge-derived Salinispora actinobacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.M.; Taylor, T.M.; Schmidt, S.E. Chemical Preservatives and Natural Antimicrobial Compounds. In Food Microbiology: Fundamentals and Frontiers, 4th ed.; American Society for Microbiology Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 765–801. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.; Xin, X.; He, J.; Cui, B.; Guo, D.; Liu, S.; Yan, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Nan, J. Effect of NaCl Concentration on Microbiological Properties in NaCl Assistant Anaerobic Fermentation: Hydrolase Activity and Microbial Community Distribution. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipley, J.R. Sodium Benzoate and Benzoic Acid. In Antimicrobials in Food; Davidson, P.M., Sofos, J.N., Branen, A.L., Eds.; Tailor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 11–48. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.Q.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, D.F.; Yu, S.Y.; Khieu, T.N.; Son, C.K.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, J.C.; Li, W.J. Streptomyces bohaiensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from Scomberomorus niphonius in the Bohai Sea. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stach, J.E.; Maldonado, L.A.; Masson, D.G.; Ward, A.C.; Goodfellow, M.; Bull, A.T. Statistical approaches for estimating actinobacterial diversity in marine sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6189–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamelander, T.; Spilling, K.; Winder, M. Organic matter export to the seafloor in the Baltic Sea: Drivers of change and future projections. Ambio 2017, 46, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snelgrove, P.V.R. Getting to the bottom of Marine biodiversity: Sedimentary habitats. BioScience 1999, 49, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Doi, H.; Uramoto, G.I.; Wormer, L.; Adhikari, R.R.; Xiao, N.; Morono, Y.; D’Hondt, S.; Hinrichs, K.U.; Inagaki, F. Global diversity of microbial communities in marine sediment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 27587–27597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallmeyer, J.; Pockalny, R.; Adhikari, R.R.; Smith, D.C.; D’Hondt, S. Global distribution of microbial abundance and biomass in subseafloor sediment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16213–16216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.Q.; Xia, Z.F.; Wan, C.X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.X.; Zhang, L.L. Streptomyces kalpinensis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from a salt water beach. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4892–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iniyan, A.M.; Wink, J.; Landwehr, W.; Ramprasad, E.V.V.; Sasikala, C.; Ramana, C.V.; Schumann, P.; Sproer, C.; Bunk, B.; Joseph, F.R.S.; et al. Streptomyces marianii sp. nov., a novel marine actinomycete from southern coast of India. J. Antibiot. 2021, 74, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, W.; Chen, T.; Liu, G.; Li, S.; Dos Santos, L.T.; Castro, H.C.; et al. Streptomyces qaidamensis sp. nov., isolated from sand in the Qaidam Basin, China. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Choudhury, J.D.; Mahansaria, R.; Saha, M.; Mukherjee, J. Streptomyces euryhalinus sp. nov., a new actinomycete isolated from a mangrove forest. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, M.; Zhong, W.; Mo, K.; Zhu, J.; Zou, X.; Hu, Y.; Bao, S. Streptomyces caeni sp. nov., isolated from mangrove mud. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3080–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Mangwani, N. Ocean acidification and marine microorganisms: Responses and consequences. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.; Ser, H.L.; Duangjai, A.; Saokaew, S.; Bukhari, S.I.; Khan, T.M.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Streptomyces colonosanans sp. nov., A Novel Actinobacterium Isolated from Malaysia Mangrove Soil Exhibiting Antioxidative Activity and Cytotoxic Potential against Human Colon Cancer Cell Lines. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ser, H.L.; Palanisamy, U.D.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Streptomyces malaysiense sp. nov.: A novel Malaysian mangrove soil actinobacterium with antioxidative activity and cytotoxic potential against human cancer cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ser, H.L.; Zainal, N.; Palanisamy, U.D.; Goh, B.H.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Streptomyces gilvigriseus sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from mangrove forest soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyisoglu, A.; Cetin, D.; Inan Bektas, K.; Guven, K.; Sahin, N. Streptomyces ovatisporus sp. nov., isolated from deep marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4856–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terahara, T.; Naemura, T.; Nampo, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Imada, C.; Hamada, M.; Tamura, T. Streptomyces otsuchiensis sp. nov., a biosurfactant-producing actinobacterium isolated from marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3740–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, N.; Ser, H.L.; Yin, W.F.; Tee, K.K.; Lee, L.H.; Chan, K.G. Streptomyces humi sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from soil of a mangrove forest. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2016, 109, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongsopitanun, W.; Kudo, T.; Ohkuma, M.; Pittayakhajonwut, P.; Suwanborirux, K.; Tanasupawat, S. Streptomyces verrucosisporus sp. nov., isolated from marine sediments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3607–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, L.; Mishra, S.R.; Panda, A.N.; Das, S.; Rastogi, G.; Pattanaik, A.K.; Adhya, T.K.; Suar, M.; Raina, V. Streptomyces chitinivorans sp. nov., a chitinolytic strain isolated from estuarine lake sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3241–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ser, H.L.; Palanisamy, U.D.; Yin, W.F.; Abd Malek, S.N.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Presence of antioxidative agent, Pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro- in newly isolated Streptomyces mangrovisoli sp. nov. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousif, G.; Busarakam, K.; Kim, B.Y.; Goodfellow, M. Streptomyces mangrovi sp. nov., isolated from mangrove forest sediment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 108, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ye, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Debnath, S.C.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, M. Streptomyces nigra sp. nov. Is a Novel Actinobacterium Isolated From Mangrove Soil and Exerts a Potent Antitumor Activity In Vitro. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.Q.; Xia, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, C.X.; Luo, X.X.; Zhang, L.L. Streptomyces litoralis sp. nov., isolated from a salt water beach. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5051–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ser, H.L.; Tan, L.T.; Palanisamy, U.D.; Abd Malek, S.N.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Streptomyces antioxidans sp. nov., a Novel Mangrove Soil Actinobacterium with Antioxidative and Neuroprotective Potentials. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chater, K.F. Recent advances in understanding Streptomyces. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, S.A.; Woodruff, H.B. Bacteriostatic and Bactericidal Substances Produced by a Soil Actinomyces. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1940, 45, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, S.A.; Woodruff, H.B. Selective antibiotic action of various substances of microbial origin. J. Bacteriol. 1942, 44, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, A.; Waksman, S.S. Effect of Streptomycin and Other Antibiotic Substances upon Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Related Organisms. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 57, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manteca, A.; Sanchez, J. Streptomyces development in colonies and soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2920–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Gupta, R.K. Rare actinomycetes: A potential storehouse for novel antibiotics. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 108–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.; Abraham, J. Natural Products from Actinobacteria for Drug Discovery. In Advances in Pharmaceutical Biotechnology; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 333–363. [Google Scholar]
- Voser, T.M.; Campell, M.D.; Carroll, A.R. How diffrent are rare marine microbial natural products compared to their terrestrial counterparts. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hu, X.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Yu, L.; You, X.; Jiang, B.; et al. 1-hydroxy-7-oxolavanducyanin and Delta(7″,8″)-6″-hydroxynaphthomevalin from Streptomyces sp. CPCC 203577. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Bonilla, M.; Oves-Costales, D.; Gonzalez, I.; de la Cruz, M.; Martin, J.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F. Krisynomycins, Imipenem Potentiators against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Produced by Streptomyces canus. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2597–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menegatti, C.; Lourenzon, V.B.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, D.; da Paixao Melo, W.G.; Ferreira, L.L.G.; Andricopulo, A.D.; do Nascimento, F.S.; Pupo, M.T. Meliponamycins: Antimicrobials from Stingless Bee-Associated Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, P.K.; Das, S.; Sahoo, P.; Mandal, S. Streptomyces sp. SM01 isolated from Indian soil produces a novel antibiotic picolinamycin effective against multi drug resistant bacterial strains. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Elshahawi, S.I.; Ponomareva, L.V.; Ye, Q.; Liu, Y.; Copley, G.C.; Hower, J.C.; Hatcher, B.E.; Kharel, M.K.; Van Lanen, S.G.; et al. Structure Determination, Functional Characterization, and Biosynthetic Implications of Nybomycin Metabolites from a Mining Reclamation Site-Associated Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3469–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaweewan, I.; Hemmi, H.; Komaki, H.; Kodani, S. Isolation and structure determination of a new antibacterial peptide pentaminomycin C from Streptomyces cacaoi subsp. cacaoi. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Kumar, S.; Satti, N.K.; Ali, A.; Gupta, P.; Katoch, M. A strain of Streptomyces sp. isolated from rhizospheric soil of Crataegus oxycantha producing nalidixic acid, a synthetic antibiotic. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shao, L.; Wang, M.; Rao, M.; Ge, M.; Xu, Y. Two novel quinomycins discovered by UPLC-MS from Streptomyces sp. HCCB11876. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Elshahawi, S.I.; Wang, X.; Ponomareva, L.V.; Sajid, I.; Shaaban, K.A.; Thorson, J.S. Puromycins B-E, Naturally Occurring Amino-Nucleosides Produced by the Himalayan Isolate Streptomyces sp. PU-14G. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Elshahawi, S.I.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ponomareva, L.V.; Chen, X.; Copley, G.C.; Hower, J.C.; Zhan, C.G.; Parkin, S.; et al. Bi- and Tetracyclic Spirotetronates from the Coal Mine Fire Isolate Streptomyces sp. LC-6-2. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Shafi, J.; Ji, M.; Bi, Y.; Yu, Z. Antimicrobial Metabolites from Streptomyces sp. SN0280. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, M.S.A.; Philippon, T.; Asenjo, J.A.; Bull, A.T.; Goodfellow, M.; Ebel, R.; Jaspars, M.; Rateb, M.E. Asenjonamides A-C, antibacterial metabolites isolated from Streptomyces asenjonii strain KNN 42.f from an extreme-hyper arid Atacama Desert soil. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.B.; Park, J.S.; Lee, S.I.; Shin, B.; Oh, D.C.; Kwon, H.C. Gordonic Acid, a Polyketide Glycoside Derived from Bacterial Coculture of Streptomyces and Gordonia Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2542–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Hong, Y.S.; Jang, M.; Heo, K.T.; Lee, B.; Jang, J.P.; Kim, J.W.; Ryoo, I.J.; Kim, W.G.; Ko, S.K.; et al. Genomics-Driven Discovery of Chlorinated Cyclic Hexapeptides Ulleungmycins A and B from a Streptomyces Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Du, C.; Ichinose, K.; Choi, Y.H.; van Wezel, G.P. Discovery of C-Glycosylpyranonaphthoquinones in Streptomyces sp. MBT76 by a Combined NMR-Based Metabolomics and Bioinformatics Workflow. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wang, X.; Elshahawi, S.I.; Ponomareva, L.V.; Liu, X.; McErlean, M.R.; Cui, Z.; Arlinghaus, A.L.; Thorson, J.S.; Van Lanen, S.G. Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Actinomycins Y6-Y9 and Zp from Streptomyces sp. Strain Go-GS12. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekkour, A.; Meklat, A.; Bijani, C.; Toumatia, O.; Errakhi, R.; Lebrihi, A.; Mathieu, F.; Zitouni, A.; Sabaou, N. A novel hydroxamic acid-containing antibiotic produced by a Saharan soil-living Streptomyces strain. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 60, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Rateb, M.E.; Teng, Q.; Yang, D.; Rudolf, J.D.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Angucyclines and Angucyclinones from Streptomyces sp. CB01913 Featuring C-Ring Cleavage and Expansion. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noomnual, S.; Thasana, N.; Sungkeeree, P.; Mongkolsuk, S.; Loprasert, S. Streptanoate, a new anticancer butanoate from Streptomyces sp. DC3. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.K.; Guo, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.W.; Zhang, L.; Dai, S.J.; He, Q.Y.; You, X.F.; Hu, X.X.; Tuo, L.; et al. Xiakemycin A, a novel pyranonaphthoquinone antibiotic, produced by the Streptomyces sp. CC8-201 from the soil of a karst cave. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Lam, P.W.; Shahab, S.; Santosa, D.A.; Proteau, P.J.; Zabriskie, T.M.; Mahmud, T. Identification of Elaiophylin Skeletal Variants from the Indonesian Streptomyces sp. ICBB 9297. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2768–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Du, C.; Gubbens, J.; Choi, Y.H.; van Wezel, G.P. Metabolomics-Driven Discovery of a Prenylated Isatin Antibiotic Produced by Streptomyces Species MBT28. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.C.; Cullum, R.; Hebishy, A.M.S.; Mohamed, H.A.; Faraag, A.H.I.; Salah, N.M.; Abdelfattah, M.S.; Fenical, W. Mersaquinone, A New Tetracene Derivative from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. EG1 Exhibiting Activity against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Antibiotics 2020, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wong, N.K.; Ju, J. Chlorinated bis-indole alkaloids from deep-sea derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 11791 with antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yi, W.; Ge, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, B. Bioactive Streptoglutarimides A–J from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. ZZ741. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, D.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lian, X.Y. A rare diketopiperazine glycoside from marine-sourced Streptomyces sp. ZZ446. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Zhang, D.S.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, J.Q.; Ding, W.J.; Xu, C.D.; Ma, Z.J. Medermycin-Type Naphthoquinones from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. XMA39. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, J.; Hao, X.; Duan, Y.; Guan, Y.; Shang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Identification and Proposed Relative and Absolute Configurations of Niphimycins C-E from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. IMB7-145 by Genomic Analysis. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitani, S.; Ueguchi, T.; Igarashi, Y.; Leetanasaksakul, K.; Thamchaipenet, A.; Nihira, T. Rakicidin F, a new antibacterial cyclic depsipeptide from a marine sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. J. Antibiot. 2017, 71, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iniyan, A.M.; Sudarman, E.; Wink, J.; Kannan, R.R.; Vincent, S.G.P. Ala-geninthiocin, a new broad spectrum thiopeptide antibiotic, produced by a marine Streptomyces sp. ICN19. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehana, Y.; Umekita, M.; Hatano, M.; Kato, C.; Sawa, R.; Igarashi, M. Fradiamine A, a new siderophore from the deep-sea actinomycete Streptomyces fradiae MM456M-mF7. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brana, A.F.; Sarmiento-Vizcaino, A.; Osset, M.; Perez-Victoria, I.; Martin, J.; de Pedro, N.; de la Cruz, M.; Diaz, C.; Vicente, F.; Reyes, F.; et al. Lobophorin K, a New Natural Product with Cytotoxic Activity Produced by Streptomyces sp. M-207 Associated with the Deep-Sea Coral Lophelia pertusa. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, X.H.; Wei, X.Y.; Qi, S.H. Pteridic acids C-G spirocyclic polyketides from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. SCSGAA 0027. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Tan, Y.; Hu, X.; He, H.; Xiao, C.; You, X.; Wang, Y.; Gan, M. Neo-actinomycins A and B, natural actinomycins bearing the 5H-oxazolo[4,5-b]phenoxazine chromophore, from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. IMB094. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, C.; Rebets, Y.; Tokovenko, B.; Nadmid, S.; Terekhova, L.P.; Myronovskyi, M.; Zotchev, S.B.; Ruckert, C.; Braig, S.; Zahler, S.; et al. New natural products identified by combined genomics-metabolomics profiling of marine Streptomyces sp. MP131-18. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Fan, Z.; Huang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Qin, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; et al. Antitubercular Ilamycins from Marine-Derived Streptomyces atratus SCSIO ZH16 DeltailaR. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1646–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H.; Gu, K.B.; Zhang, D.J.; Li, Y.G.; Tian, L. Ghanamycins A and B, two novel gamma-butyrolactones from marine-derived Streptomyces ghanaensis TXC6-16. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Zou, Y.L.; Wang, G.W.; Liao, Z.H.; Chen, M. Two new compounds from a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Ding, R.; Jiang, S.T.; Tang, J.S.; Hu, D.; Chen, G.D.; Lin, F.; Hong, K.; Yao, X.S.; Gao, H. Aldgamycins J–O, 16-Membered Macrolides with a Branched Octose Unit from Streptomycetes sp. and Their Antibacterial Activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, M.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Sassetti, E.; Melchiorsen, J.; Clausen, M.H.; Gram, L.; Ding, L. Azodyrecins A–C: Azoxides from a Soil-Derived Streptomyces Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3519–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Son, S.; Lee, J.K.; Jang, M.; Heo, K.T.; Ko, S.K.; Park, D.J.; Park, C.S.; Kim, C.J.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Isolation of new streptimidone derivatives, glutarimide antibiotics from Streptomyces sp. W3002 using LC-MS-guided screening. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Abbas, M.; Zhang, Y.; Elshahawi, S.I.; Ponomareva, L.V.; Cui, Z.; Van Lanen, S.G.; Sajid, I.; Voss, S.R.; Shaaban, K.A.; et al. Baraphenazines A–G, Divergent Fused Phenazine-Based Metabolites from a Himalayan Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, R.H.; Yang, L.M.; Wang, L.; Guo, D.; Yang, J.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, Y.T.; Huang, S.X. Dimeric Pyranonaphthoquinone Glycosides with Anti-HIV and Cytotoxic Activities from a Soil-Derived Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, C.; Yuan, J.; Mo, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, S.; Gu, Y.C.; Ju, J. Cytotoxic Anthracycline Metabolites from a Recombinant Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Jang, M.; Lee, B.; Hong, Y.S.; Ko, S.K.; Jang, J.H.; Ahn, J.S. Ulleungdin, a Lasso Peptide with Cancer Cell Migration Inhibitory Activity Discovered by the Genome Mining Approach. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, W.Q.; Zhang, H.; Qi, H.; Xiang, W.S.; Wang, J.D.; Wang, X.J. A new anthracycline-type metabolite from Streptomyces sp. NEAU-L3. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.Y.; Qi, H.; Li, J.S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.D.; Xiang, W.S. A new polysubstituted cyclopentene derivative from Streptomyces sp. HS-NF-1046. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Rateb, M.E.; Love, M.S.; Xu, Z.; Yang, D.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.X.; Jiang, Y.; Duan, Y.; et al. Herbicidins from Streptomyces sp. CB01388 Showing Anti-Cryptosporidium Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Xu, M.D.; Zhang, H.; Qi, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, J.D.; Xiang, W.S.; Wang, X.J. New cytotoxic spectinabilin derivative from ant-associated Streptomyces sp. 1H-GS5. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W. 1,19-seco-Avermectin analogues from a DeltaaveCDE mutant Streptomyces avermectinius strain. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, W.; Che, Q.; Li, D. Geranylpyrrol A and Piericidin F from Streptomyces sp. CHQ-64 DeltardmF. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1684–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Shin, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, K.B.; Lee, S.K.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.C. Salternamides A–D from a Halophilic Streptomyces sp. Actinobacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.; An, J.S.; Hong, S.H.; Bae, E.S.; Chung, B.; Kwon, Y.; Hong, S.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Donghaecyclinones A-C: New Cytotoxic Rearranged Angucyclinones from a Volcanic Island-Derived Marine Streptomyces sp. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, C.; Li, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D.; Che, Q. Dimeric Tetrahydroanthracene Regioisomers and Their Monomeric Precursor Produced by Streptomyces fumigatiscleroticus HDN10255. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2797–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.F.; Chen, M.J.; Liang, D.E.; Shi, L.M.; Ying, Y.M.; Shan, W.G.; Li, G.Q.; Zhan, Z.J. Streptomyces albogriseolus SY67903 Produces Eunicellin Diterpenoids Structurally Similar to Terpenes of the Gorgonian Muricella sibogae, the Bacterial Source. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1641–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Nagai, K.; Kanamoto, A.; Tomoda, H. 2-Epi-anthracimycin, a new cytotoxic agent from the marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces sp. OPMA00631. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Jiang, Y.J.; Ji, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Shen, L. Lactoquinomycin C and D, two new medermycin derivatives from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. SS17A. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; She, Z.; et al. Genome Mining of Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 40010 Leads to Cytotoxic New Polycyclic Tetramate Macrolactams. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.; Izumikawa, M.; Kozone, I.; Hashimoto, J.; Kagaya, N.; Koiwai, H.; Komatsu, M.; Fujie, M.; Sato, N.; Ikeda, H.; et al. Neothioviridamide, a Polythioamide Compound Produced by Heterologous Expression of a Streptomyces sp. Cryptic RiPP Biosynthetic Gene Cluster. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chai, W.; Song, T.; Ma, M.; Lian, X.Y.; Zhang, Z. Anti-glioma Natural Products Downregulating Tumor Glycolytic Enzymes from Marine Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. ZZ406. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chai, W.; Wang, W.; Song, T.; Lian, X.Y.; Zhang, Z. Cytotoxic Bagremycins from Mangrove-Derived Streptomyces sp. Q22. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Li, J.Q.; Zhang, H.J.; Ding, W.J.; Ma, Z.J. Cyclizidine-Type Alkaloids from Streptomyces sp. HNA39. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, J.Q.; Ding, W.J.; Ma, Z.J. Bioactive Indolocarbazoles from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. DT-A61. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Che, Q.; Tan, H.; Qi, X.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Liu, M. Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin-proteasome system. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, Q.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T. Structure and absolute configuration of drimentine I, an alkaloid from Streptomyces sp. CHQ-64. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.; Jang, M.; Lee, B.; Jang, J.P.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Ko, S.K.; Jang, J.H.; Ahn, J.S. A pipecolic acid-rich branched cyclic depsipeptide ulleungamide C from a Streptomyces species induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in promyelocytic leukemia cells. J. Antibiot. 2021, 74, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, E.; Ahn, H.; Jang, Y.J.; Shin, B.; Hwang, S.; Shin, J.; Yoon, Y.J.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Formicolides A and B, Antioxidative and Antiangiogenic 20-Membered Macrolides from a Wood Ant Gut Bacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2776–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zheng, H.; Mu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Gao, J.; Lu, X. Naphthacemycins from a Streptomyces sp. as Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase Inhibitors. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.J.; Zheng, H.B.; Peng, A.H.; Ma, J.H.; Lu, D.D.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xie, W.D. Strepantibins A–C: Hexokinase II Inhibitors from a Mud Dauber Wasp Associated Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Mahal, A.; Xue, J.; Xu, L.; Wei, X. Dinghupeptins A–D, Chymotrypsin Inhibitory Cyclodepsipeptides Produced by a Soil-Derived Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.; Moon, K.; Kim, J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.K.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.C. Mohangic Acids A–E, p-Aminoacetophenonic Acids from a Marine-Mudflat-Derived Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, L.E.; Sanglard, D.; Howard, S.J.; Rogers, P.D.; Perlin, D.S. Mechanisms of Antifungal Drug Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 5, a019752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.J.; Kim, J.D.; Han, J.W.; Kim, B.S. Antifungal activity of rimocidin and a new rimocidin derivative BU16 produced by Streptomyces mauvecolor BU16 and their effects on pepper anthracnose. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, C.A. Fungal echinocandin resistance. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2010, 2, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrin, M.; Faramarzi, S. Study of Azole-Resistant and Cyp51a Gene in Aspergillus fumigatus. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Rao, M.; Liang, Y.; Ge, M. Three novel polyene macrolides isolated from cultures of Streptomyces lavenduligriseus. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Song, T.; Chai, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Lian, X.Y.; Zhang, Z. Rare Polyene-polyol Macrolides from Mangrove-derived Streptomyces sp. ZQ4BG. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.X.; Huang, J.P.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Tang, J.; Yu, Z.; Yan, Y.; Kai, G.; Huang, S.X. Benwamycins A–G, Trialkyl-Substituted Benzene Derivatives from a Soil-Derived Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.; Ahn, S.; Noh, M.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.C. Suncheonosides A–D, Benzothioate Glycosides from a Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Liu, L.L.; He, Q.R.; Yan, W.; Li, D.; Gao, J.M. Ansamycins with Antiproliferative and Antineuroinflammatory Activity from Moss-Soil-Derived Streptomyces cacaoi subsp. asoensis H2S5. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1984–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Qi, S.H. Nahuoic Acids B–E, Polyhydroxy Polyketides from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. SCSGAA 0027. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauermeister, A.; Pereira, F.; Grilo, I.R.; Godinho, C.C.; Paulino, M.; Almeida, V.; Gobbo-Neto, L.; Prieto-Davo, A.; Sobral, R.G.; Lopes, N.P.; et al. Intra-clade metabolomic profiling of MAR4 Streptomyces from the Macaronesia Atlantic region reveals a source of anti-biofilm metabolites. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Ban, Y.H.; Byun, W.S.; Kim, D.; Jang, Y.J.; An, J.S.; Shin, B.; Lee, S.K.; Shin, J.; Yoon, Y.J.; et al. Camporidines A and B: Antimetastatic and Anti-inflammatory Polyketide Alkaloids from a Gut Bacterium of Camponotus kiusiuensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, S.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; Liu, H.; You, X.; et al. Isarubrolones Containing a Pyridooxazinium Unit from Streptomyces as Autophagy Activators. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.P.; Hwang, G.J.; Jang, M.; Takahashi, S.; Ko, S.K.; Osada, H.; Jang, J.H.; Ahn, J.S. Aturanosides A and B, Glycosylated Anthraquinones with Antiangiogenic Activity from a Soil-Derived Streptomyces Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2004–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, Y.; Kyoso, T.; Kim, Y.; Oikawa, T. Simamycin (5′-O-geranyluridine): A new prenylated nucleoside from Streptomyces sp. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, K.A.; Saunders, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Tran, T.; Elshahawi, S.I.; Ponomareva, L.V.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Copley, G.C.; Sunkara, M.; et al. Spoxazomicin D and Oxachelin C, Potent Neuroprotective Carboxamides from the Appalachian Coal Fire-Associated Isolate Streptomyces sp. RM-14-6. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, M.S.; Ishikawa, N.; Karmakar, U.K.; Yamaku, K.; Ishibashi, M. New phenazine analogues from Streptomyces sp. IFM 11694 with TRAIL resistance-overcoming activities. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.A.; Koryudzu, K.; Ishibashi, M. Inubosins A, B, and C are acridine alkaloids isolated from a culture of Streptomyces sp. IFM 11440 with Ngn2 promoter activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).