Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Garlic Peel Extract and Their Antibacterial Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Garlic Peel Extract
2.2. Synthesis of Phytonanoparticles
2.3. UV–Visible Spectroscopy and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.6. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activity of Biosynthesized ZnO NPs
2.7. In Silico Analysis
2.7.1. Subtractive Proteomic Analysis
2.7.2. Molecular Docking Simulation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs Using Garlic Peel
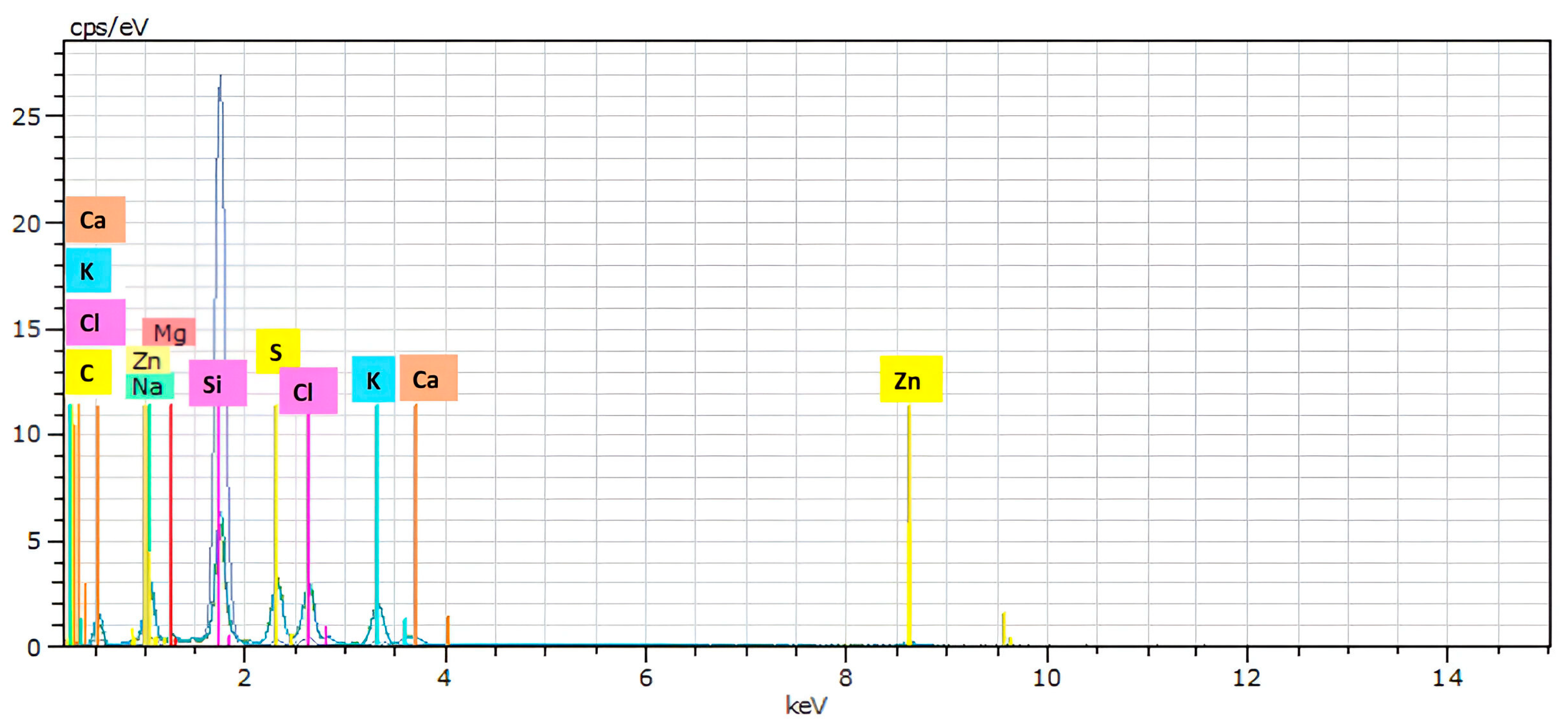
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
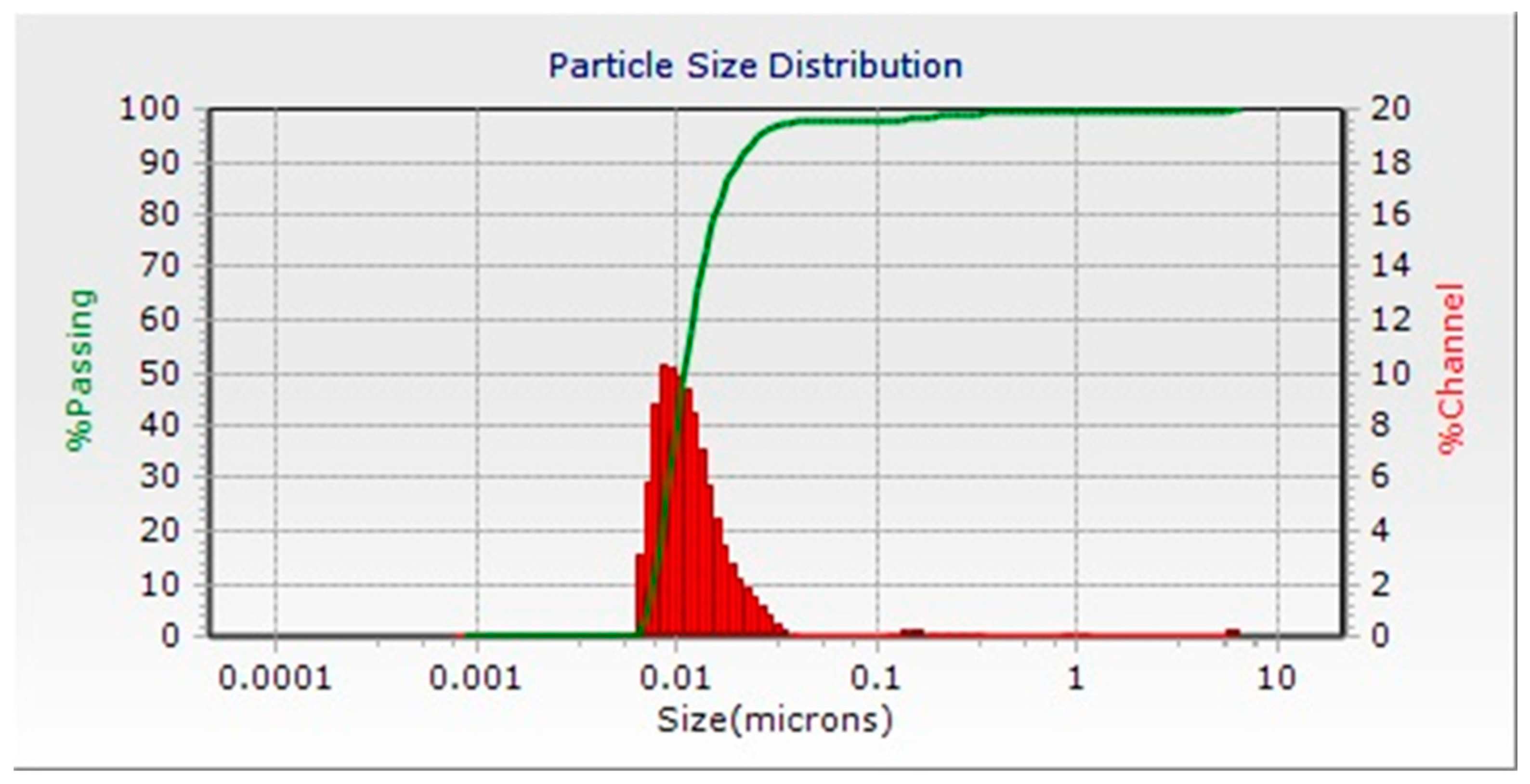
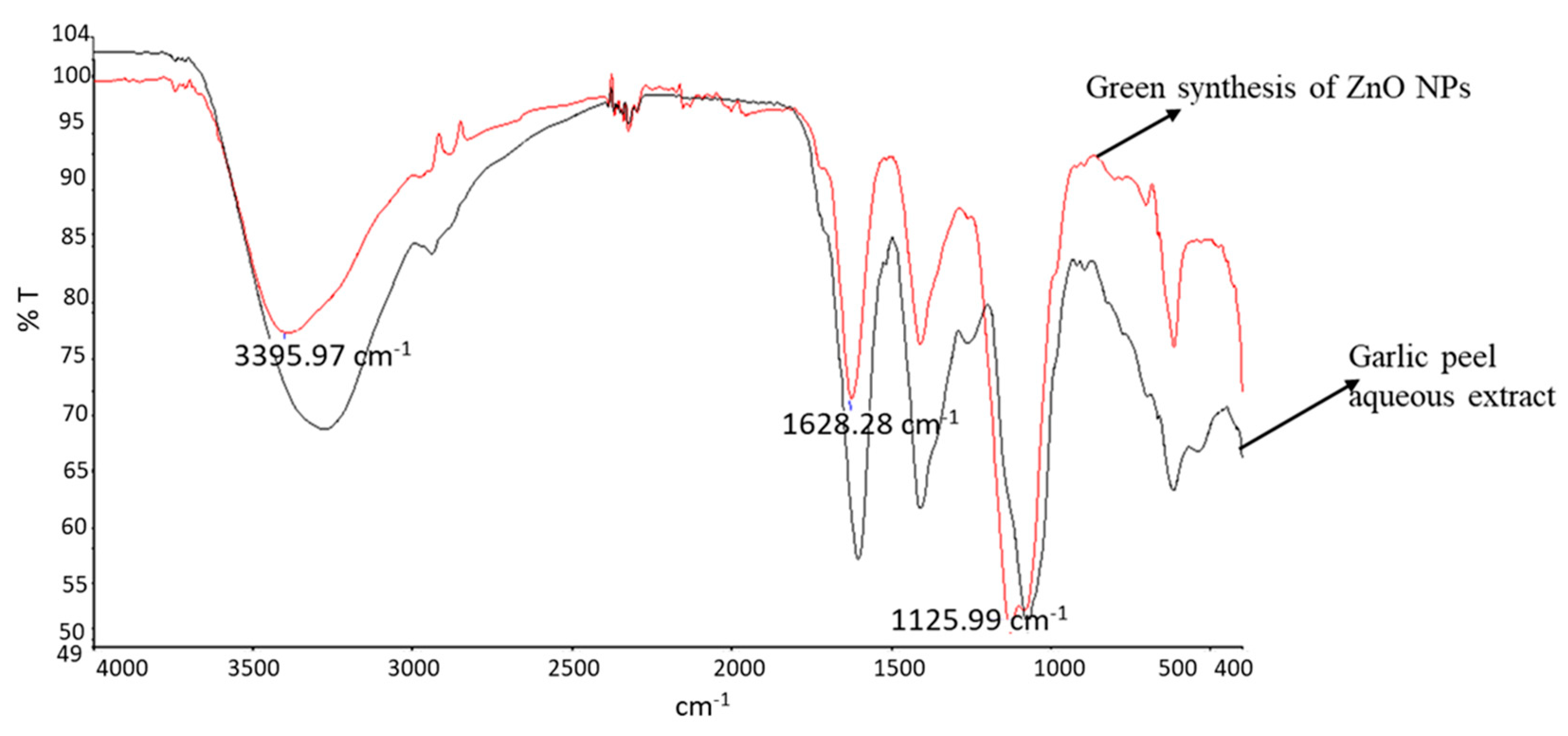
3.3. DLS and FTIR Analysis
3.4. Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
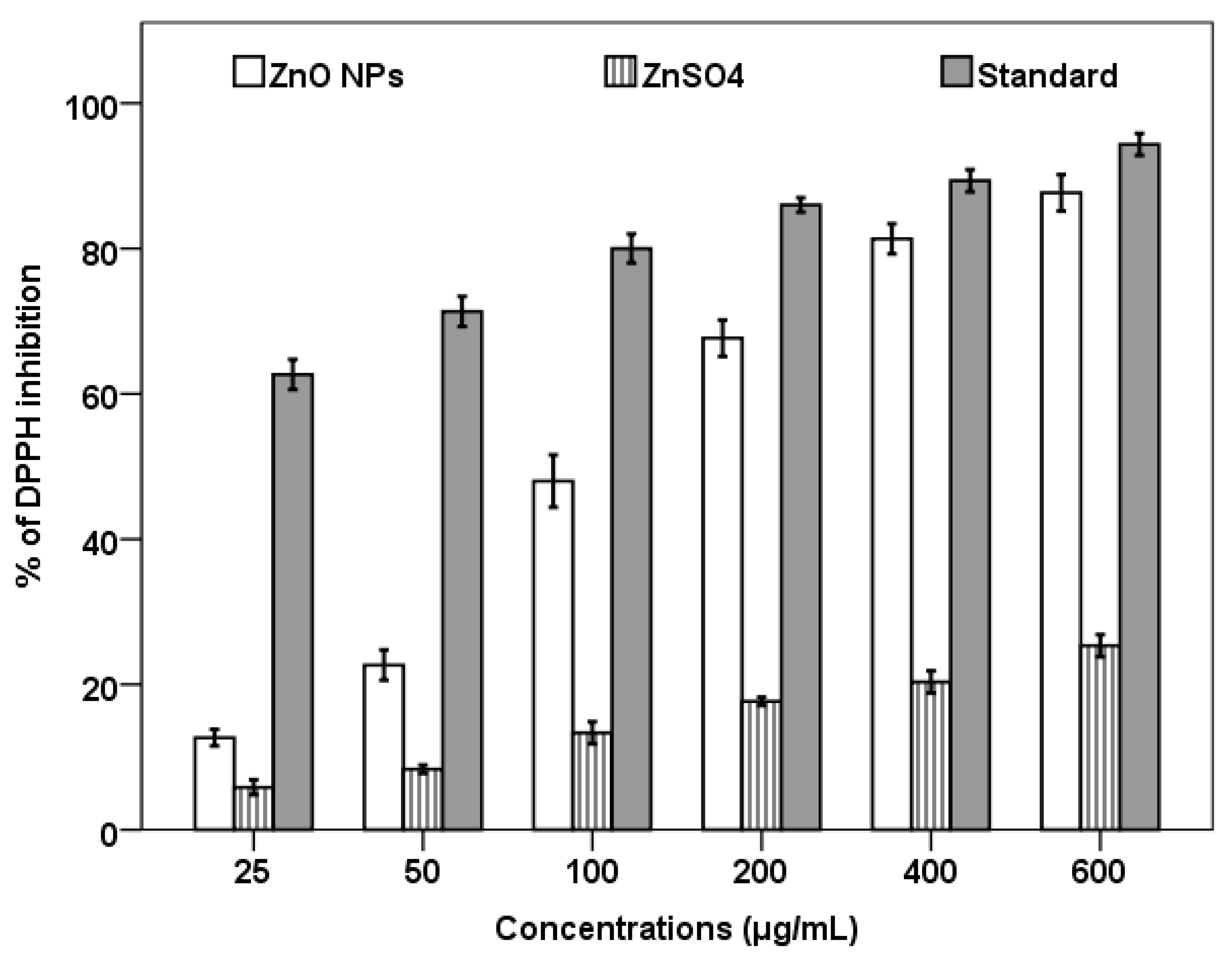
3.5. Antioxidant Activity of Biosynthesized ZnO NPs
3.6. In Silico Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahid, M.; Ijaz, N.; Shahid, B.; Tufail, T.; Ain, H.B.U.; Hussain, M.; Basharat, S.; Ikram, A.; Al Jbawi, E. Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles, their optimization and characterization. Cogent Food Agric. 2024, 10, 2293332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzinjy, A.A.; Azeez, H.H. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Eucalyptus globulus Labill. leaf extract and zinc nitrate hexahydrate salt. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifeanyichukwu, U.L.; Fayemi, O.E.; Ateba, C.N. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from pomegranate (Punica granatum) extracts and characterization of their antibacterial activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, M.; Gowtham, H.G.; Shilpa, N.; Singh, S.B.; Aiyaz, M.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Shivamallu, C.; Achar, R.R.; Silina, E.; Stupin, V.; et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles prepared through microbial mediated synthesis for therapeutic applications: A possible alternative for plants. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1227951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, R.; Tettey, F.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, K.R.; Parajuli, N.; Bhattarai, N. Bioinspired synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles and assessment of their cytotoxicity and antimicrobial efficacy. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MuthuKathija, M.; Sheik, M.B.M.; Rama, V. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Pisonia alba leaf extract and its antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2023, 15, 100400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Y.H.I.; Alghamdi, S.; Jabbar, B.; Marghani, D.; Beigh, S.; Abouzied, A.S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cymbopogon citratus extract and its antibacterial activity. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 32027–32042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoteleb, A.; Valdez-Salas, B.; Beltran-Partida, E.; Gonzalez-Mendoza, D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Abronia villosa as an alternative to control of pathogenic microorganisms. J. Renew. Mater. 2020, 8, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Sasani, G.M.; Lee, C.; Han, W.; Park, H.H.; Tafreshi, M.J. Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, L.P.; Sethuraman, B.D.; Subramani, M.; Mohandos, S. Green synthesised ZnO nanoparticles from Plectranthus amboinicus plant extract: Removal of safranin- o and malachite green dyes and anti-bacterial activity. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.F.; Islam, S.; Miah, M.A.S.; Huq, A.K.O.; Saha, A.K.; Mou, Z.J. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nano particles using Allium cepa L. waste peel extracts and its antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safawo, T.; Sandeep, B.; Pola, S.; Tadesse, A. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using tuber extract of anchote (Coccinia abyssinica (Lam.) Cong.) for antimicrobial and antioxidant activity assessment. OpenNano 2018, 3, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Jaiswal, A.; Tiwari, S.; Jamal, S.B.; Barh, D.; Azevedo, V.; Soares, S.C. An in silico identification of common putative vaccine candidates against treponema pallidum: A reverse vaccinology and subtractive genomics based approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.H.; Lee, J.A.; Park, S.Y.; Song, C.S.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, J.B. A review of vaccine development and research for industry animals in Korea. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2012, 1, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.I.; Ferdous, S.; Jewel, N.A.; Akter, A.; Mahmud, Z.; Islam, M.M. Identification of potential drug targets by subtractive genome analysis of Escherichia coli O157:H7: An in silico approach. Adv. Appl. Bioinform. Chem. 2015, 8, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.D.A.; Khan, M.D.A.; Sharmin, T.; Hasan Mazumder, M.D.H.; Chowdhury, A.S. Identification of putative drug targets in Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) using computer aided protein data analysis. Gene 2016, 575, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Fulekar, M.H. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using garlic skin extract and its characterization. J. Nanostructures 2020, 10, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ikram, I.; Zain, M. Assessment of antibacterial and antifungal activity of cream incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized via ginger and garlic extract. J. Xian Med. Univ. 2023, 19, 1135–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, M.; Steinegger, M.; Söding, J. MMseqs software suite for fast and deep clustering and searching of large protein sequence sets. Bioinform. Oxf. Engl. 2016, 32, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugham, B.; Pan, A. Identification and characterization of potential therapeutic candidates in emerging human pathogen Mycobacterium abscessus: A novel hierarchical in silico approach. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2022: A general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D912–D917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lin, Y. DEG 5.0, a database of essential genes in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D455–D458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; Nielsen, H.; Winther, O.; Teufel, F. Predicting the subcellular location of prokaryotic proteins with DeepLocPro. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, X.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Zhu, F. Therapeutic target database update 2022: Facilitating drug discovery with enriched comparative data of targeted agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1398–D1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, D.; Gaulton, A.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; De Veij, M.; Félix, E. ChEMBL: Towards direct deposition of bioassay data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D930–D940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnan, C.N.; Zeller, M.; Kayala, M.A.; Vigil, A.; Randall, A.; Felgner, P.L. High-throughput prediction of protein antigenicity using protein microarray data. Bioinform. Oxf. Engl. 2010, 26, 2936–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, P.C.M.; Da Silva, L.M.R.; Magalhaes, F.E.A.; Cunha, F.E.T.; Ferreira, M.J.G.; de Figueiredo, E.A.T. Garlic (Allium sativum L.) peel extracts: From industrial by-product to food additive. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, Y.A.; Azb, M.A.; Ragab, I.H.M.; Abd El-Azim, M. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of deverra tortuosa and their cytotoxic activities. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Qasim, S.; Ansari, M.; Shah, A.A.; Rehman, H.U.; Shah, M.N. Green synthesis of zinc nanoparticles and their effects on growth and yield of Pisum sativum. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droepenu, E.K.; Asare, E.A.; Wee, B.S.; Wahi, R.B.; Ayertey, F.; Kyene, M.O. Biosynthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoaggregates using aqueous extract from Anacardium occidentale leaf: Comparative study of different precursors. Beni Suef Univ. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawadi, S.; Katuwal, S.; Gupta, A.; Lamichhane, U.; Thapa, R.; Jaisi, S. Current research on silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, e6687290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheo, A.R.; Vithiya, B.S.M.; Arul Prasad, T.A.; Mangesh, V.L.; Perumal, T.; Al-Qahtani, W.H. Cytotoxic, Antidiabetic, and Antioxidant Study of Biogenically Improvised Elsholtzia blanda and Chitosan-Assisted Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 10954–10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedurkar, S.; Maurya, C.; Mahanwar, P. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Ixora Coccinea Leaf Extract—A Green Approach. Open J. Synth. Theory Appl. 2016, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrefaey, A.A.K.; El-Gamal, A.D.; Hamed, S.M.; El-belely, E.F. Algae-mediated biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Cystoseira crinite (Fucales; Sargassaceae) and it’s antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño-Martínez, N.; Salas Orozco, M.F.; Martínez-Castañón, G.A.; Torres Méndez, F.; Ruiz, F. Molecular mechanisms of bacterial resistance to metal and metal oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, V.; Mishra, N.; Gadani, K.; Solanki, P.S.; Shah, N.A.; Tiwari, M. Mechanism of anti-bacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticle against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkanna, M.M.; Neelagund, S.E.; Rajashekarappa, K.K. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) and their biological activity. SN Appl. Sci. 2018, 1, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taran, M.; Rad, M.; Alavi, M. Biosynthesis of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles by Halomonas elongata IBRC-M 10214 in different conditions of medium. BioImpacts BI 2018, 8, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.; Jermy, B.R.; Akhtar, S.; Borgio, J.F.; Abdul Azeez, S.; Ravinayagam, V. Isolation and characterization of a novel thermophile; Bacillus haynesii, applied for the green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2072–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.S.; Jeong, W.; Woo, H.A.; Lee, S.M.; Park, S.; Rhee, S.G. Characterization of mammalian sulfiredoxin and its reactivation of hyperoxidized peroxiredoxin through reduction of cysteine sulfinic acid in the active site to cysteine. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 50994–51001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



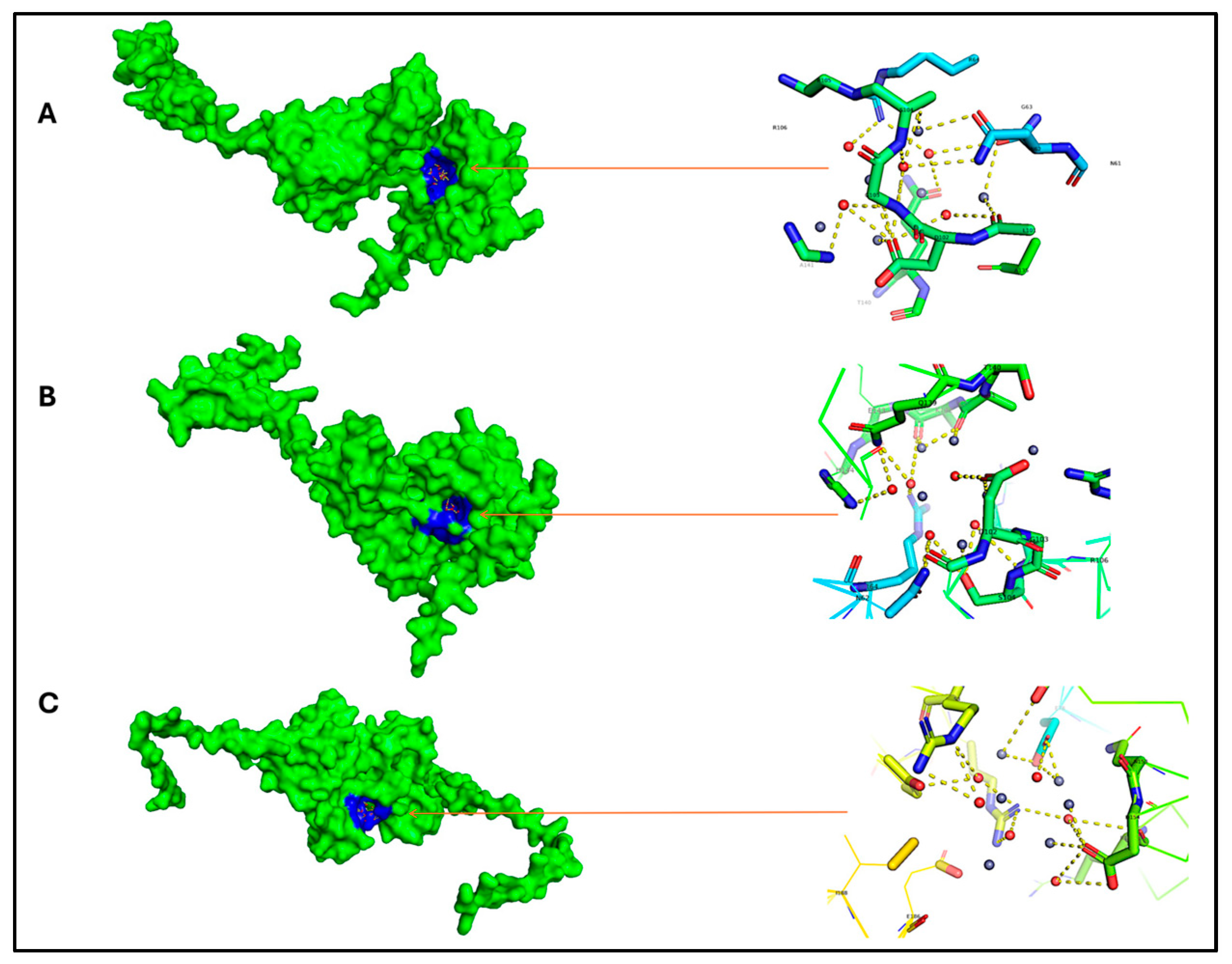
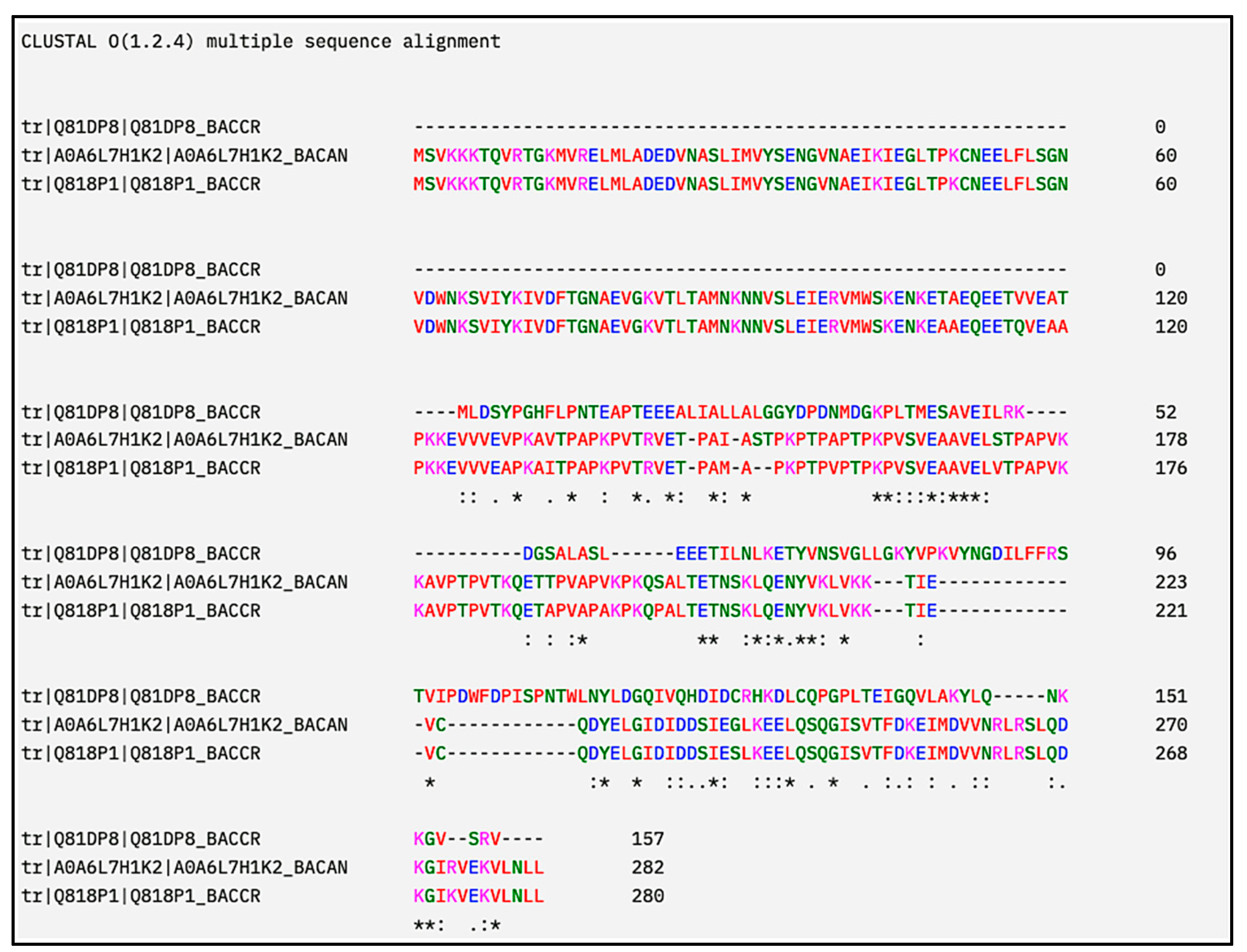
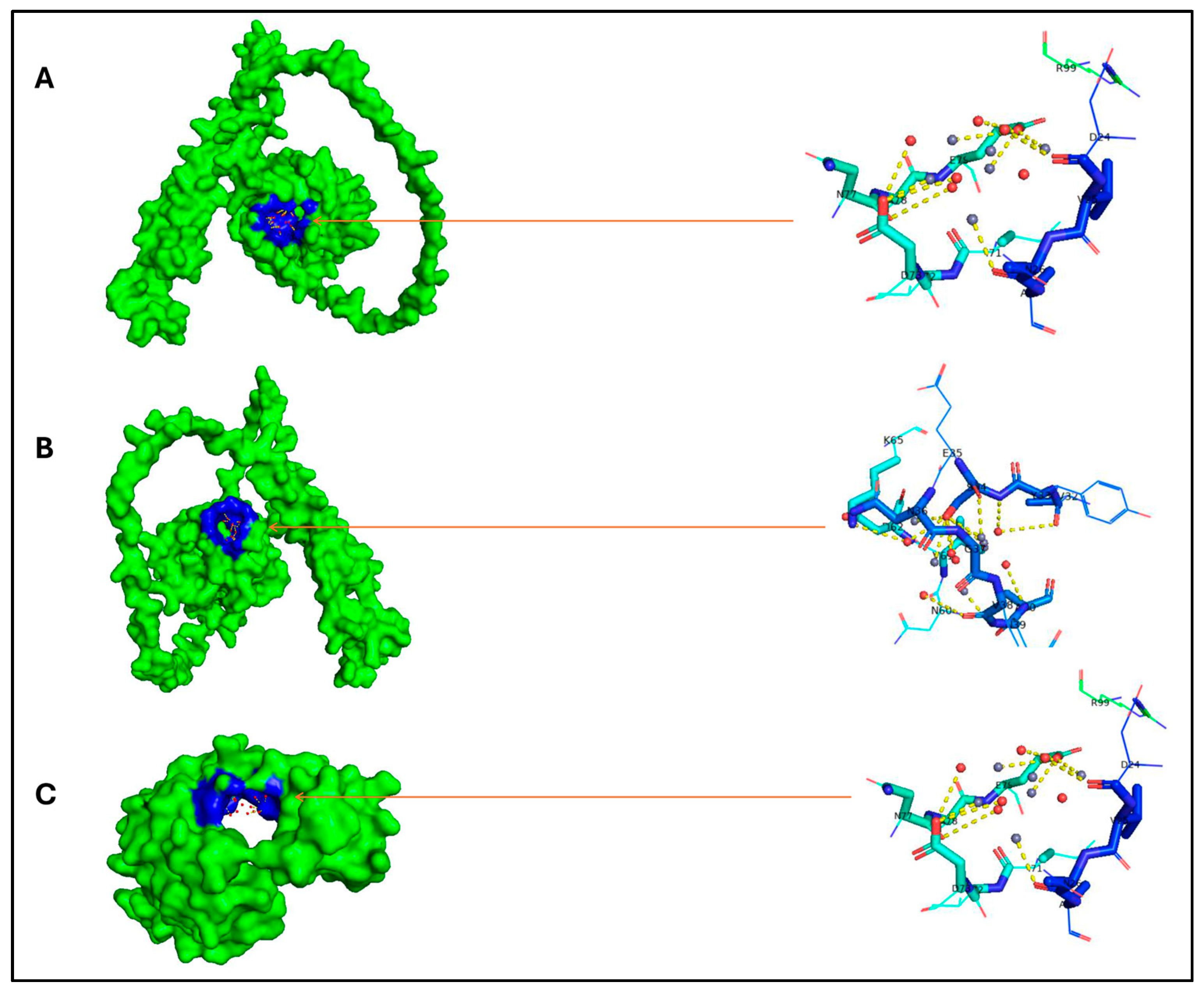
| Organism | Proteome ID | Tax ID | Protein Count | Target No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. cereus | UP000000594 | 1392 | 5493 | 1 |
| UP000027822 | 574376 | 4374 | 0 | |
| UP000220020 | 64104 | 5787 | 0 | |
| UP000001417 | 226900 | 5240 | 2 | |
| K. pneumonia | UP000007841 | 1125630 | 5728 | 1 |
| UP000255382 | 574 | 6726 | 2 | |
| UP000326328 | 2590872 | 48 | 0 |
| Organism | Tax ID | Accession | Pfam | Antigenecity Score | Binding Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. cereus | 1392 | A0A6L7H1K2 | No domains found | 0.88 | −3.3 |
| 226900 | Q818P1 | No domains found | 0.83 | −4.9 | |
| 226900 | Q81DP8 | No domains found | 0.72 | −4.0 | |
| K. pneumonia | 1125630 | A0A0H3GZ74 | PF02195 PF08775 | 0.76 | −5.0 |
| 574 | A0A377YWZ3 | PF02195 PF08775 | 0.77 | −5.4 | |
| 574 | A0A377YX32 | PF02195 PF18090 | 0.52 | −5.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelmoteleb, A.; Valdez-Salas, B.; Beltran-Partida, E.; Mendez-Trujillo, V.; González-Mendoza, D.; Tzintzun-Camacho, O.; Roumia, A.F. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Garlic Peel Extract and Their Antibacterial Potential. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 1655-1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030110
Abdelmoteleb A, Valdez-Salas B, Beltran-Partida E, Mendez-Trujillo V, González-Mendoza D, Tzintzun-Camacho O, Roumia AF. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Garlic Peel Extract and Their Antibacterial Potential. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(3):1655-1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030110
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelmoteleb, Ali, Benjamín Valdez-Salas, Ernesto Beltran-Partida, Vianey Mendez-Trujillo, Daniel González-Mendoza, Olivia Tzintzun-Camacho, and Ahmed F. Roumia. 2024. "Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Garlic Peel Extract and Their Antibacterial Potential" Microbiology Research 15, no. 3: 1655-1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030110
APA StyleAbdelmoteleb, A., Valdez-Salas, B., Beltran-Partida, E., Mendez-Trujillo, V., González-Mendoza, D., Tzintzun-Camacho, O., & Roumia, A. F. (2024). Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Garlic Peel Extract and Their Antibacterial Potential. Microbiology Research, 15(3), 1655-1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030110






