Exploring the Antibacterial Potential of Bile Salts: Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Cell Growth in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Bacterial Cultures
2.3. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.4. Colony Forming Unit (CFU) Analysis
2.5. Biofilm Inhibition
2.6. Change in the Biofilm Structure
2.7. Effect on Nucleic Acid and Protein Leakage
2.8. Inhibition of S. aureus Biofilm Virulence
2.9. Evaluation of P. aeruginosa Virulence Factors
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Effect of Bile Salts
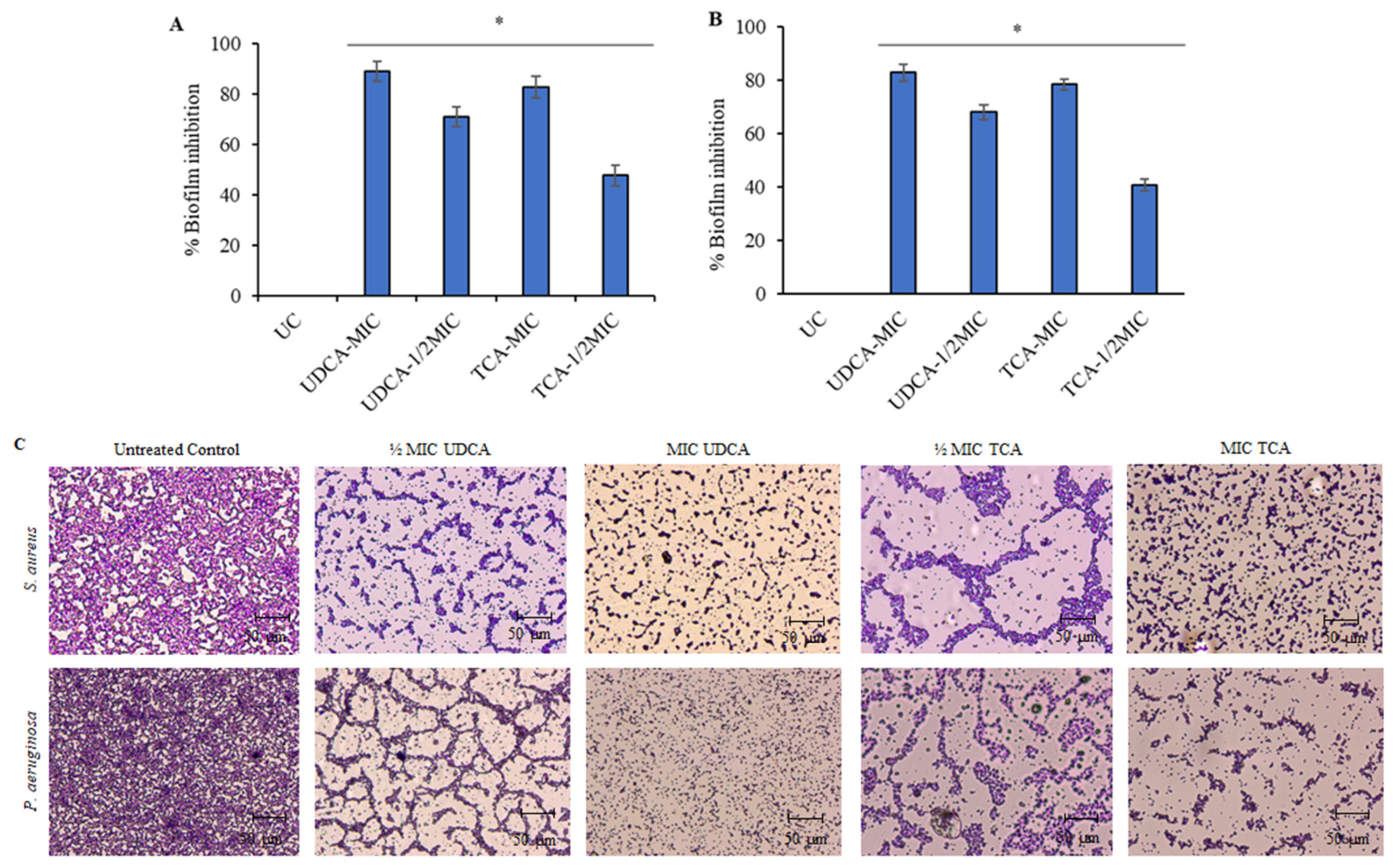
3.2. Effect on Biofilm
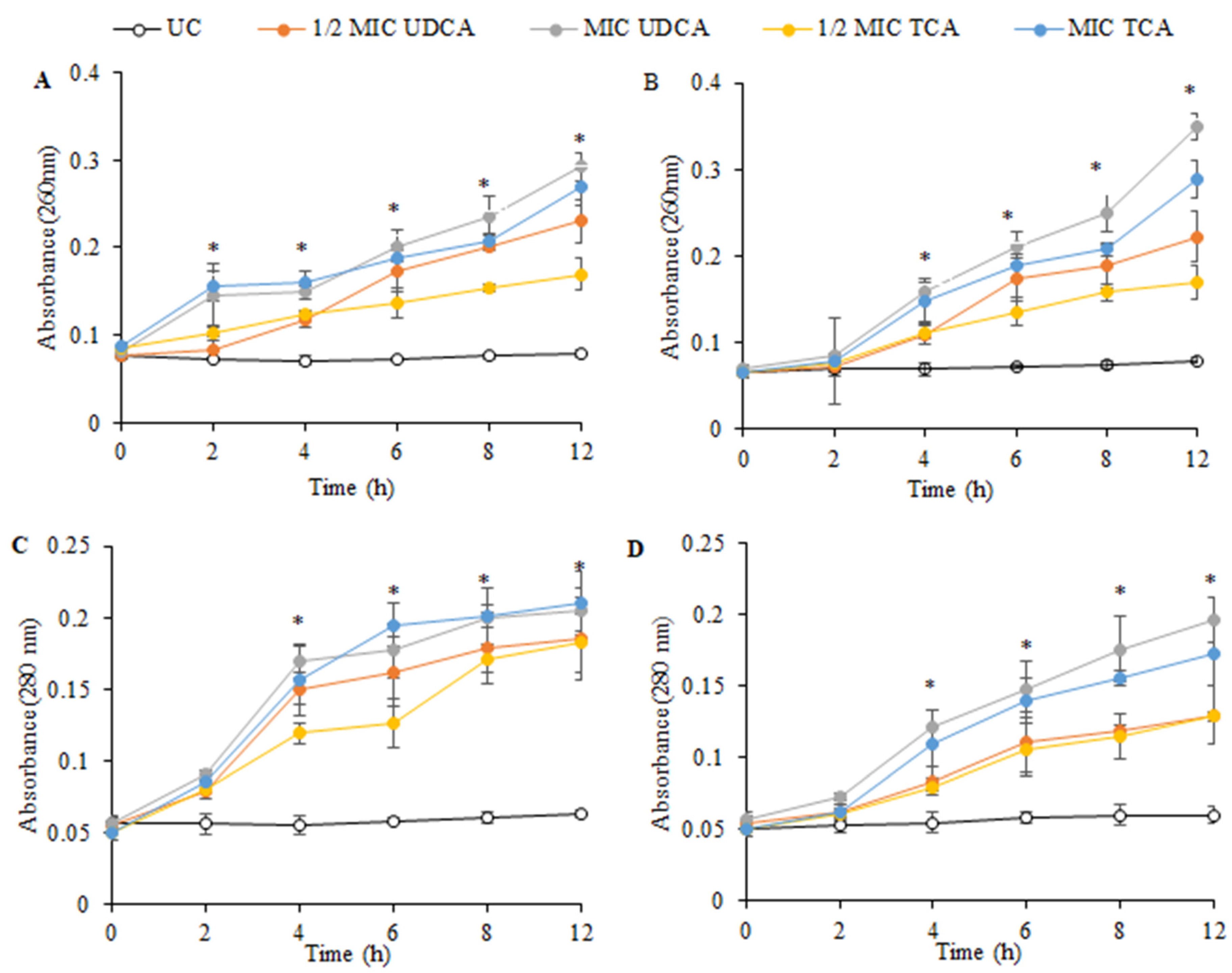
3.3. Effect on Cellular Constituents
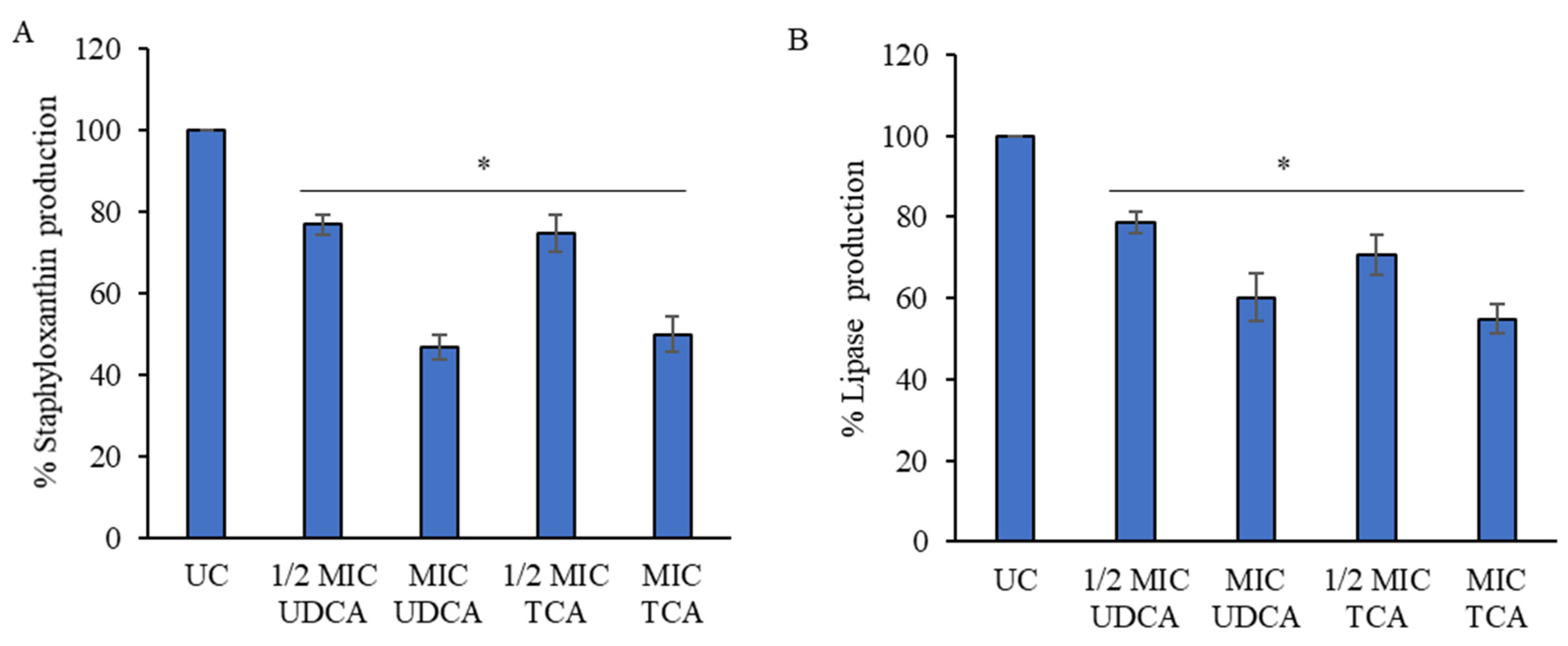
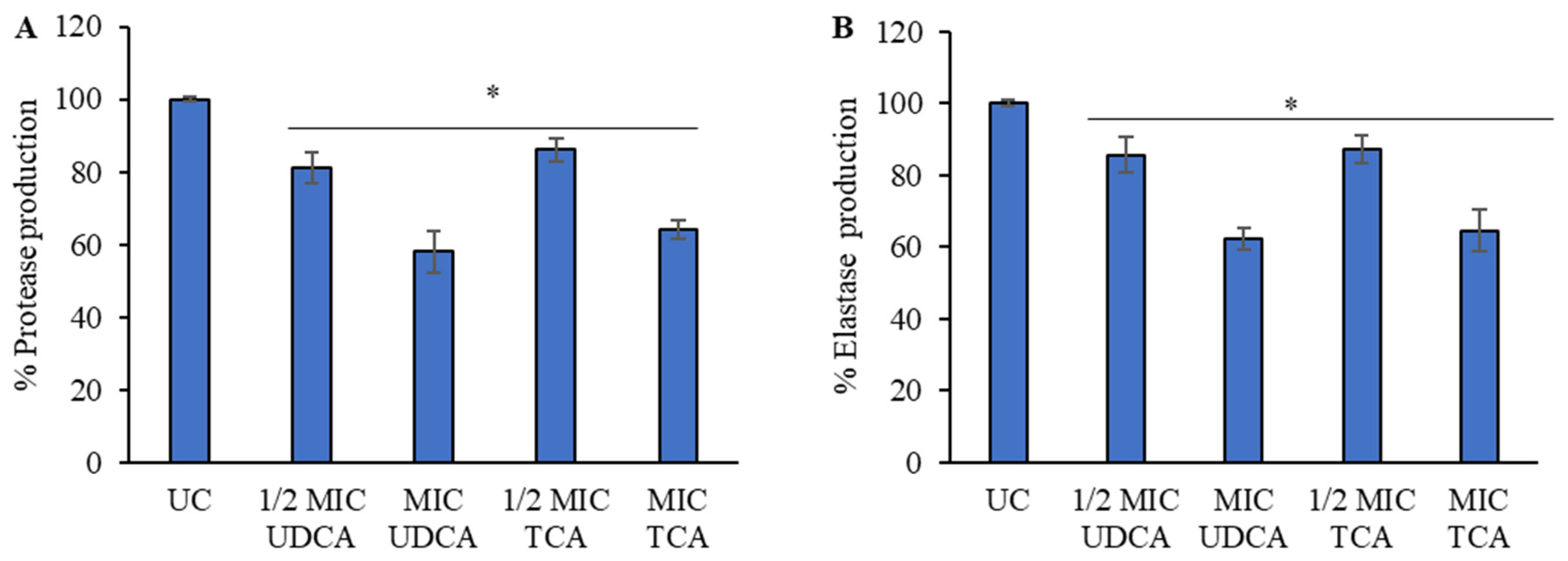
3.4. Effect on Virulence Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diarmaid, H.; Anders, K. Discovery and preclinical development of new antibiotics. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Renwick, M.J.; Brogan, D.M.; Mossialos, E. A systematic review and critical assessment of incentive strategies for discovery and development of novel antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renwick, M.J.; Simpkin, V.; Mossialos, E. Targeting Innovation in Antibiotic Drug Discovery and Development: The Need for a One-Health, One-Europe, One-World Framwork; Health Policy Series No. 45; European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–133. ISBN 9789289050401. [Google Scholar]
- 2021 Antibacterial Agents in Clinical and Preclinical Development: An Overview and Analysis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 9789240047655.
- Sutherland, I.W. The biofilm matrix—An immobilized but dynamic microbial environment. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Moser, C.; Wang, H.-Z.; Høiby, N.; Song, Z.-J. Strategies for combating bacterial biofilm infections. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2014, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryers, J.D. Medical Biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 100, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnsholt, T. The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections. APMIS 2013, 121 (Suppl. 136), 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, G.A.; Swogger, E.; Wolcott, R.; deLancey Pulcini, E.; Secor, P.; Sestrich, J.; Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S. Biofilms in chronic wounds. Wound Repair. Regen. 2008, 16, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, A.K.; Geringer, M.R.; Hong, S.J.; Leung, K.P.; Mustoe, T.A.; Galiano, R.D. In vivo modeling of biofilm-infected wounds: A review. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 178, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholmerich, J.; Becher, M.S.; Schmidt, K.; Schubert, R.; Kremer, B.; Feldhaus, S.; Gerok, W. Influence of hydroxylation and conjugation of bile salts on their membrane-damaging properties–studies on isolated hepatocytes and lipid membrane vesicles. Hepatology 1984, 4, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, M.; Brunel, J.M. Bile Acid Derivatives: From Old Molecules to a New Potent Therapeutic Use: An Overview. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3613–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Gregorio, M.C.; Cautela, J.; Galantini, L. Physiology and Physical Chemistry of Bile Acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, N.; Keely, S.J. Bile acids in regulation of intestinal physiology. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2009, 11, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroka, C.J.; Boyer, J.L. Biosynthesis and trafficking of the bile salt export pump, BSEP: Therapeutic implications of BSEP mutations. Mol. Asp. Med. 2014, 37, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xu, C.; Feng, B.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z. Critical roles of bile acids in regulating intestinal mucosal immune responses. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 17562848211018098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Q.; Carey, M.C. Therapeutic uses of animal biles in traditional Chinese medicine: An ethnopharmacological, biophysical chemical and medicinal review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9952–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, R.; Grande, R.; Butrico, L.; Rossi, A.; Settimio, U.F.; Caroleo, B.; Amato, B.; Gallelli, L.; de Franciscis, S. Chronic wound infections: The role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M07-A10; Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically—Tenth Edition. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015.
- Wilson, C.; Lukowicz, R.; Merchant, S.; Valquier-Flynn, H.; Caballero, J.; Sandoval, J.; Okuom, M.; Huber, C.; Brooks, T.D.; Wilson, E.; et al. Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment Methods for Biofilm Growth: A Mini-review. Res. Rev. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 6, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Banskota, S.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. Indole and 7-benzyloxyindole attenuate the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 4543–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Moreno, L.V.; Pabón-Baquero, L.C.; Prieto-Rodriguez, J.A.; Patiño-Ladino, O.J. Bioactive Compounds from P. pertomentellum That Regulate QS, Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factor Production of P. aeruginosa. Molecules 2023, 28, 6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Luqman, A.; Bitschar, K.; Hertlein, T.; Dick, J.; Ohlsen, K.; Broker, B.; Schittek, B.; Gotz, F. Stapphylococcal (phosphor)lipases promote biofilm formation and host cell invasion. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, C.; Maia, C.J.; Domingues, F.; Bücker, R.; Oleastro, M.; Ferreira, S. Evaluation of Bile Salts on the Survival and Modulation of Virulence of Aliarcobacter butzleri. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, K.P.; Chanin, R.B.; Sistrunk, J.R.; Rasko, D.A.; Fink, P.J.; Barry, E.M.; Nataro, J.P.; Faherty, C.S. Analysis of Shigella flexneri resistance, biofilm formation, and transcriptional profile in response to bile salts. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e01067-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekarforoush, S.; Jaladat, A.M.; Hadadi, M.; Salehi, Z.; Shakib, N.H.; Parvizi, M.M.; Motamedifar, M. In Vitro Anti-bacterial Effect of Ox-bile Against Some Important Gram-positive and Gram-negative Bacteria. Trends Med. Sci. 2022, 2, e136719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, J.P.; Cayuela, C.; Antoine, J.M.; Schneider, F. Isolation and characterization of a Lactobacillus amylovorus mutant depleted in conjugated bile salt hydrolase activity: Relation between activity and bile salt resistance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Gui, W.; Koo, I.; Smith, P.B.; Allman, E.L.; Nichols, R.G.; Rimal, B.; Cai, J.; Liu, Q.; Patterson, A.D. The microbiome modulating activity of bile acids. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 979–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, B.C.; Kirkpatrick, R.; Marcellino, D.; Travelstead, A.; Pilipenko, V.; Krasa, H.; Bremer, J.; Dong, L.J.; Cooper, M.D. Bile salts: Natural detergent for the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuman, D.M.; Bajaj, R.S.; Lin, Q. Adsorption of mixtures of bile salt taurine conjugates to lecithin-cholesterol membranes: Implications for bile salt toxicity and cytoprotection. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.; Lowe, P.J.; Billington, D. Membrane lipid composition and susceptibility to bile salt damage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 588, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Elsherbini, A.M.; Shaldam, M.A. Glyceryl trinitrate blocks staphyloxanthin and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Afr. Health Sci. 2019, 19, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.N.; Liu, G.Y.; Yeaman, M.R.; Nast, C.C.; Proctor, R.A.; Mckinnell, J.; Bayer, A.S. Carotenoid-related alteration of cell membrane fluidity impacts Staphylococcus aureus susceptibility to host defence peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Larrota, J.S.; Eckhard, U. An Introduction to bacterial biofilms and their proteases, and their roles in host infection and immune evasion. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Test Compound | S. aureus ATCC 25923 | P. aeruginosa MTCC 1688 |
|---|---|---|
| MIC (µg/mL) | MIC (µg/mL) | |
| UDCA | 1300 | 1500 |
| TCA | 2000 | 3000 |
| Ox bile salt | ND | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tyagi, A.; Kumar, V.; Joshi, N.; Dhingra, H.K. Exploring the Antibacterial Potential of Bile Salts: Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Cell Growth in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 1269-1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030085
Tyagi A, Kumar V, Joshi N, Dhingra HK. Exploring the Antibacterial Potential of Bile Salts: Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Cell Growth in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(3):1269-1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030085
Chicago/Turabian StyleTyagi, Anuradha, Vinay Kumar, Navneet Joshi, and Harish Kumar Dhingra. 2024. "Exploring the Antibacterial Potential of Bile Salts: Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Cell Growth in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus" Microbiology Research 15, no. 3: 1269-1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030085
APA StyleTyagi, A., Kumar, V., Joshi, N., & Dhingra, H. K. (2024). Exploring the Antibacterial Potential of Bile Salts: Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Cell Growth in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology Research, 15(3), 1269-1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030085









