Indicators of the Microbial Corrosion of Steel Induced by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Under the Influence of Certain Drugs
Abstract
1. Introduction
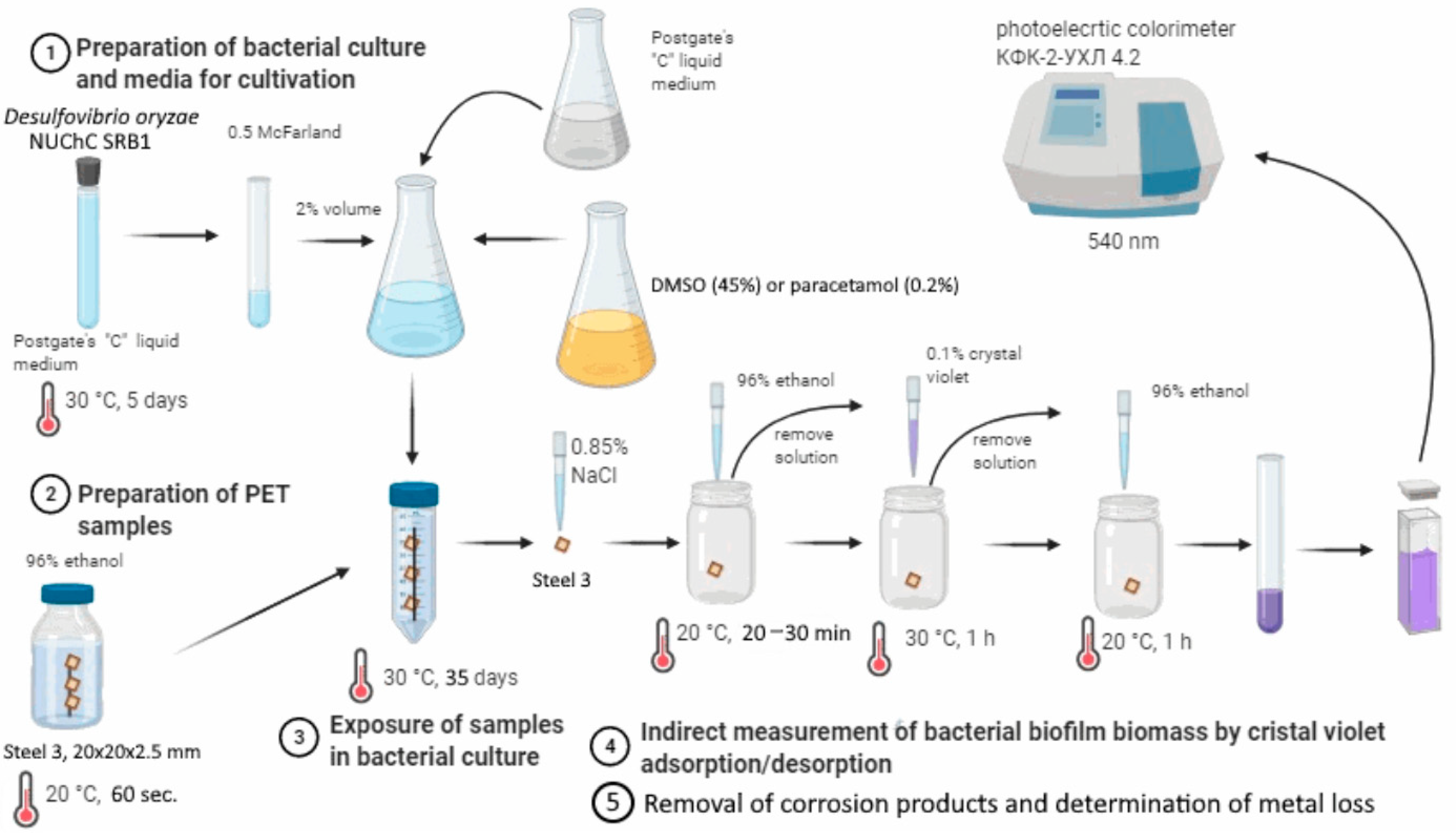
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain, Medium, and Cultivation Conditions
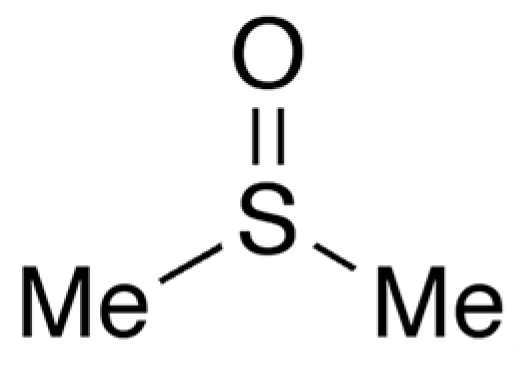
2.2. Medicinal Products Used in the Study
2.3. Study of the Sensitivity of SRB to DMSO
2.4. Study of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Indicators Under the Influence of DMSO and Paracetamol
2.5. Statistical Analysis of the Results of the Study
3. Results
3.1. Sensitivity of SRB to DMSO by the Dilution Method
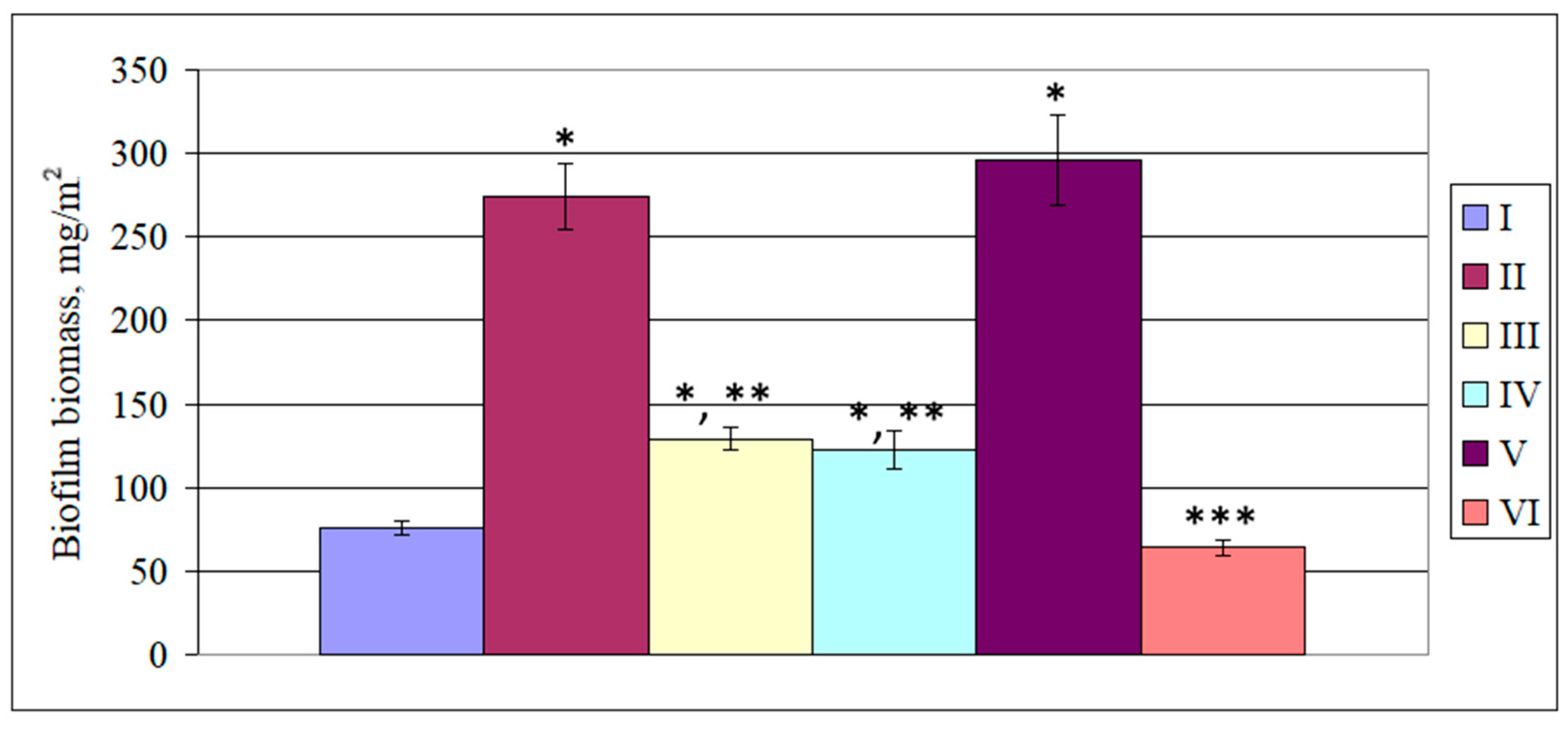
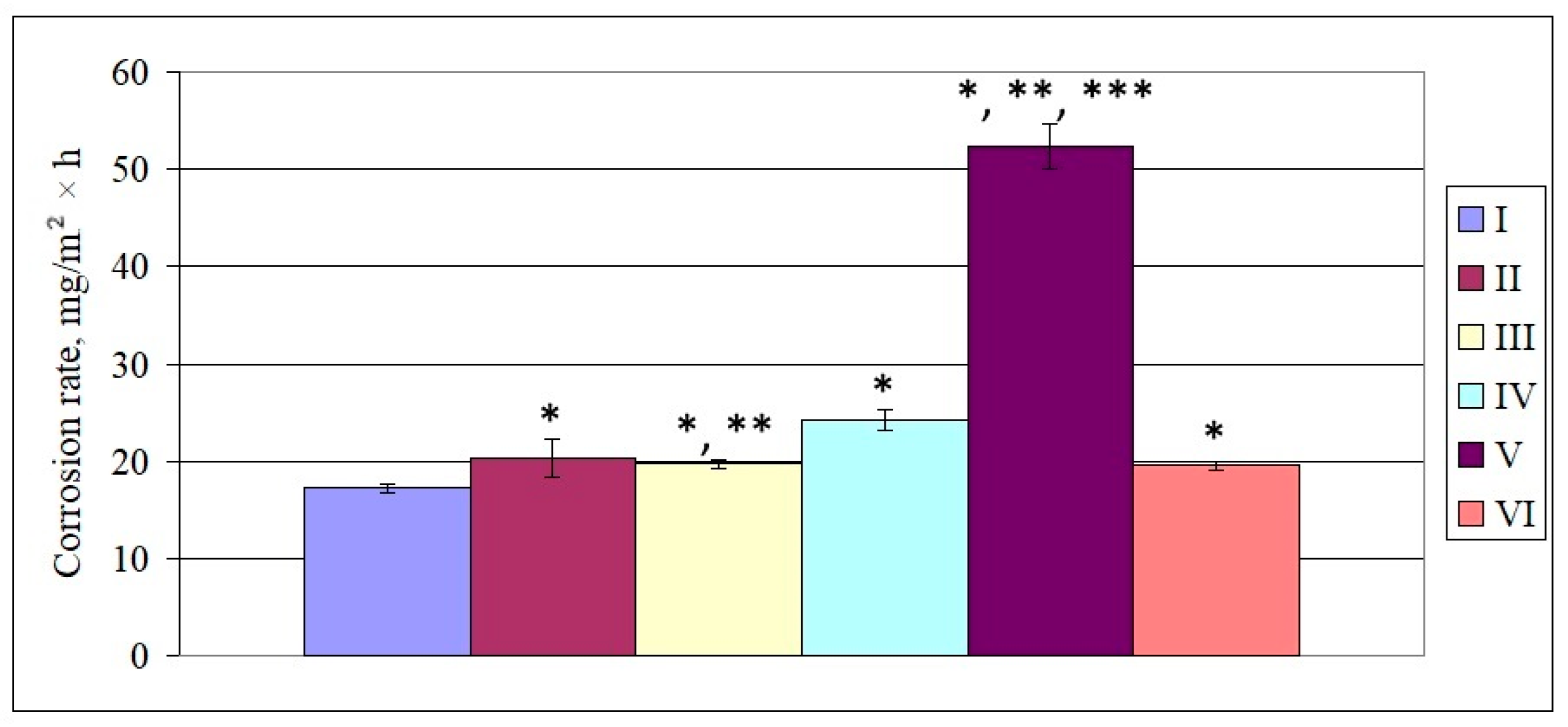
3.2. Indicators of the Microbial Corrosion of Steel Induced by SRB Under DMSO and Paracetamol Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beech, I.B.; Gaylarde, C. Recent advances in the study of biocorrosion: An overview. Rev. Microbiol. 1999, 30, 117–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaherdashti, R. Editorial: Microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC): Its mechanisms, technological, economic, and environmental impacts. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1249565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreyuk, K.; Kozlova, I.; Kopteva, Z.; Pilyashenko-Novokhatny, A.; Zanina, V.; Purish, L. Microbial Corrosion of Underground Structures; Naukova Dumka Publishing House: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2005; 258p. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar]
- Knisz, J.; Eckert, R.; Gieg, L.M.; Koerdt, A.; Lee, J.S.; Silva, E.R.; Skovhus, T.L.; An Stepec, B.A.; Wade, S.A. Microbiologically influenced corrosion—More than just microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.J.; Lee, J.S. Microbiologically influenced corrosion: An update. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Xiang, Y.; Yan, W. Symbiosis of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Total General Bacteria Affects Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Carbon Steel. Coatings 2024, 14, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Cui, W. Corrosion of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on L245 Steel under Different Carbon Source Conditions. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welikala, S.; Al-Saadi, S.; Gates, W.P.; Panter, C.; Singh Raman, R.K. Sulphate reducing bacteria (SRB) biofilm development and its role in microbial corrosion of carbon steel. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1360869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwood, D.J. An Electrochemist Perspective of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2020, 1, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, T.F.; O’Toole, G.A. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, S.K.; Chowdhury, I.; Singh, R. Understanding the Mechanism of Bacterial Biofilms Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. Open Microbiol. J. 2017, 11, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grooters, K.E.; Ku, J.C.; Richter, D.M.; Krinock, M.J.; Minor, A.; Li, P.; Kim, A.; Sawyer, R.; Li, Y. Strategies for combating antibiotic resistance in bacterial biofilms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1352273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, B.; Fang, J. Study on the applicability of bactericides to prevent concrete microbial corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbanov, H.R.; Adigezalova, M.B. New multifunctional corrosion inhibitor of steel in formation water with oil containing hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide. Vopr. Khimii Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii 2023, 6, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, R.; Sand, W.; Mathivanan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Duan, J.; Hou, B. Comprehensive Review on the Use of Biocides in Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, W.; Xu, D.; Gu, T. Biocorrosion caused by microbial biofilms is ubiquitous around us. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 803–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, B.; Leinecker, N.; Watkin, E.; Somers, A.; Forsyth, M.; Machuca, L.L. Efficiency of a Novel Multifunctional Corrosion Inhibitor Against Biofilms Developed on Carbon Steel. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 803559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M. Antibacterial drugs as corrosion inhibitors for corrosion of aluminum in hydrochloric solution. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 1981–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W. An S2− responsive nanocontainer for inhibiting microbial corrosion caused by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 663, 131110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaszilcsin, N.; Kellenberger, A.; Dan, M.L.; Duca, D.A.; Ordodi, V.L. Efficiency of Expired Drugs Used as Corrosion Inhibitors: A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotmann, U.; Durand, M.J.; Thouand, G.; Eberlein, C.; Heipieper, H.J.; Gartiser, S.; Pagga, U. Microbiological toxicity tests using standardized ISO/OECD methods-current state and outlook. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotmann, U.; Pastor Flores, D.; Konrad, O.; Gendig, C. Bacterial Toxicity Testing: Modification and Evaluation of the Luminescent Bacteria Test and the Respiration Inhibition Test. Processes 2020, 8, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.E.; Anderson, K.; Citron, D.M.; Dzink-Fox, J.A.L.; Hackel, M.; Jenkins, S.G.; Knapp, C.; Koeth, L.; Schuetz, A.N.; Wexler, H. Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Anaerobic Bacteria, 9th ed.; M11; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; 64p, Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m11/ (accessed on 9 January 2025).
- Tkachuk, N.V.; Yanchenko, V.O.; Demchenko, N.R. Minimum inhibitory concentration of some 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]azepine derivatives against ammonifying bacteria isolated from the soil ferrosphere. BHT 2023, 1, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligman, A.M. Dimethyl Sulfoxide—Part 2. AMA 1965, 193, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwani, T.; Desai, K.; Patel, D.; Lawani, D.; Bahaley, P.; Joshi, P.; Kothari, V. Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials. Int. J. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sirenko, O.S.; Desyatnikova, O.V.; Gur’eva, V.B. Effectiveness of the disinfectant “Guanidez” on pathogens of infectious diseases of bees in laboratory conditions. Vet. Med. Inter-Dep. Subj. Sci. Collect. 2019, 105, 59–62. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar]
- Gracia, E.; Fernández, A.; Conchello, P.; Alabart, J.L.; Pérez, M.; Amorena, B. In vitro development of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms using slime-producing variants and ATP-bioluminescence for automated bacterial quantification. Luminescence 1999, 14, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herasimenka, Y.; Cescutti, P.; Sampaio Noguera, C.E.; Ruggiero, J.R.; Urbani, R.; Impallomeni, G.; Zanetti, F.; Campidelli, S.; Prato, M.; Rizzo, R. Macromolecular properties of cepacian in water and in dimethylsulfoxide. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.F.Z.R.; Alias, Z.; Karsani, S.A. Antibiofilm activity and mode of action of DMSO alone and its combination with afatinib against Gram-negative pathogens. Folia Microbiol. 2018, 63, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltabey, S.M.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Zaky, M.M.; Ibrahim, A.E.; Alrashdi, Y.B.A.; El Deeb, S.; Saleh, M.M. The Promising Effect of Ascorbic Acid and Paracetamol as Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Virulence Agents against Resistant Escherichia coli. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 6805–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, V.A., Jr.; Smedslund, T.H. Corrosion Inhibition of Dimethyl Sulfoxide. U.S. Patent 2948683A, 9 August 1960. United States Patent Office; 1–4. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/fe/1c/94/0cf01cc472821b/US2948683.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- Othman, N.K.; Salleh, E.M.; Dasuki, Z.; Lazim, A.M. Dimethyl Sulfoxide-Treated Starch of Dioescorea hispida as a Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Low Carbon Steel in Sodium Chloride Medium. In Corrosion Inhibitors, Principles and Recent Applications; Aliofkhazraei, M., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2018; pp. 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gorair, A.S.; Abdallah, M. Expired Paracetamol as Corrosion Inhibitor for Low Carbon Steel in Sulfuric Acid. Electrochemical, Kinetics and Thermodynamics Investigation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 210771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasić, Ž.Z.; Mihajlovic, M.B.; Radovanović, M.B.; Simonović, A.T.; Antonijevic, M.M. Experimental and theoretical studies of paracetamol as a copper corrosion inhibitor. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 327, 114817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Yu, X.Z.; Yue, D.M. Phytotoxicity of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to rice seedlings. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, S.A.S.; Galvis, D.G.V. Paracetamol ecotoxicological bioassay using the bioindicators Lens culinaris Med. and Pisum sativum L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 61965–61976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachuk, N.; Zelena, L.; Novikov, Y.; Taranenko, V. Phytotoxicity of dimethyl sulfoxide in the growth test. BHT 2024, 3, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, A.D.; Malin, G.; McEwan, A.G.; Liss, P.S. Determination of dimethyl sulfoxide in aqueous solution by an enzyme-linked method. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 4093–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makashova, O.E.; Zubova, O.L.; Zubov, P.M.; Migunova, R.K.; Babiychuk, L.O. Cryopreservation of cord blood hematopoietic progenitor cells in cryoprotective media containing different concentrations of DMSO and antioxidants. Ukr. J. Med. Biol. Sports 2017, 2, 234–238. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar]
- Volkova, N.; Yukhta, M.; Chernyschenko, L.; Stepaniuk, L.; Sokil, L.; Goltsev, A. The effectiveness of biopolymers application for cryopreservation of the fragments of convoluted seminiferous tubules of prepubertal rat’s testis. JCOT 2019, 7, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, C.; Nguyen, A.K.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Fang, W.; Han, B.; Hoang, B.X.; Tran, H.D. Application of dimethyl sulfoxide as a therapeutic agent and drug vehicle for eye diseases. JOPT 2021, 37, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriotti, K.; Capriotti, J.A. Dimethyl sulfoxide: History, chemistry, and clinical utility in dermatology. JCAD 2012, 5, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Peterkin, E. A new reliable method for dimethyl sulfoxide analysis in wastewater: Dimethyl sulfoxide in philadelphia’s three water pollution control plants. WER 2007, 79, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) Health and Safety Information. Bulletin 106. Gaylord Chemical Company, L.L.C. 2007, pp. 1–16. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/file.PostFileLoader.html?id=547d95e4d2fd6436518b468c&assetKey=AS%3A273644578639890%401442253359624 (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Dimethyl sulfoxide. Molecule of the Week Archive. Chemistry for Life. ACS 2021. Available online: https://www.acs.org/molecule-of-the-week/archive/d/dimethyl-sulfoxide.html (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Freo, U.; Ruocco, C.; Valerio, A.; Scagnol, I.; Nisoli, E. Paracetamol: A review of guideline recommendations. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acetaminophen. Molecule of the Week Archive. Chemistry for Life. ACS 2014. Available online: https://www.acs.org/molecule-of-the-week/archive/a/acetaminophen.html (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Al-Kaf, A.G.; Naji, K.M.; Abdullah, Q.Y.M.; Edrees, W.H.A. Occurrence of Paracetamol in Aquatic Environments and Transformation by Microorganisms: A Review. COPS 2017, 1, 341–355. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322041109_Occurrence_of_Paracetamol_in_Aquatic_Environments_and_Transformation_by_Microorganisms_A_Review (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Tkachuk, N.; Zelena, L.; Mazur, P.; Lukash, O. Genotypic, physiological and biochemical features of Desulfovibrio strains in a sulfidogenic microbial community isolated from the soil of ferrosphere. EQ 2020, 31, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachuk, N.; Zelena, L.; Lukash, O.; Mazur, P. Microbiological and genetic characteristics of Bacillus velezensis bacillibactin-producing strains and their effect on the sulfate-reducing bacteria biofilms on the poly(-ethylene terephthalate) surface. EQ 2021, 32, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachuk, N.; Zelena, L. Bacterial sulfidogenic community from the surface of technogenic materials in vitro: Composition and biofilm formation. Biofouling 2023, 39, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachuk, N.; Zelena, L.; Mazur, P. Properties of anaerobic bacteria from ferrosphere crucial for biofilm development. EQ 2021, 32, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachuk, N.; Zelena, L. Microbiological indicators of the biofilms microparticles of quartz sand and polypropylene after short-term exposure in soil. Biofouling 2024, 40, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, R.; Sun, Y.; Yan, Z. Application of Biomass Corrosion Inhibitors in Metal Corrosion Control: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeont. Electr. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Wu, Q.; Bai, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Jin, S.; Wu, Y.; Duan, K. Potential Use of Dimethyl Sulfoxide in Treatment of Infections Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7159–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.Y.; May, J.M.; Cegelski, L. Dimethyl sulfoxide and ethanol elicit increased amyloid biogenesis and amyloid-integrated biofilm formation in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3369–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, K.; Browne, J.; Hollanders, M.; Benkendorff, K. Out of control: The need for standardised solvent approaches and data reporting in antibiofilm assays incorporating dimethyl-sulfoxide (DMSO). Biofilm 2022, 4, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basch, H.; Gadebusch, H.H. In vitro antimicrobial activity of dimethylsulfoxide. Appl. Microbiol. 1968, 16, 1953–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notman, R.; Noro, M.; O’Malley, B.; Anwar, J. Molecular basis for dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) action on lipid membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13982–13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ménorval, M.A.; Mir, L.M.; Fernández, M.L.; Reigada, R. Effects of dimethyl sulfoxide in cholesterol-containing lipid membranes: A comparative study of experiments in silico and with cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Ismail, S.; Ahmad, H.A.; Awad, H.M.; Tawfik, A.; Ni, S.-Q. Dosage-Dependent Toxicity of Universal Solvent Dimethyl Sulfoxide to the Partial Nitrification Wastewater Treatment Process. ACS ES&T Water 2023, 3, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, J.; Miao, Q.; Cao, H.Y.; Xiong, F.; Lee, T.; El-Baz, A.; Xie, L.; Ni, S.Q. Achieving Stable Partial Denitrification by Selective Inhibition of Nitrite Reductase with the Biosafe Aprotic Solvent DMSO. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 21242–21250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdman, H.E.; Hsieh, J.J.S. Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) Effects on Four Economically Important Crops. Agron. J. 1969, 61, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, A.R.; Lattwein, K.R.; Lemmens-den Toom, N.A.; Snijders, S.V.; Kooiman, K.; Verbon, A.; van Wamel, W.J.B. Paracetamol modulates biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus clonal complex 8 strains. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seleem, N.M.; Atallah, H.; Abd El Latif, H.K.; Shaldam, M.A.; El-Ganiny, A.M. Could the analgesic drugs, paracetamol and indomethacin, function as quorum sensing inhibitors? Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihotang, T.S.U.; Widodo, A.D.W.; Arfijanto, M.V. Comparison of doses of paracetamol or ibuprofen to inhibit the formation of biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria. Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 6, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.R.; Zhu, B.; Swerhone, G.D.; Roy, J.; Tumber, V.; Waiser, M.J.; Topp, E.; Korber, D.R. Molecular and microscopic assessment of the effects of caffeine, acetaminophen, diclofenac, and their mixtures on river biofilm communities. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaylord Chemical Company, L.L.C. Dimethyl Sulfoxide Recovery, Engineering & Environmental. Available online: https://www.gaylordchemical.com/process-safety-and-technology/dmso-recovery-engineering-environmental/ (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- Rastogi, R.B.; Singh, M.M.; Singh, K.; Maurya, J.L. Electrochemical Behavior of Mild Steel in Dimethyl Sulfoxide Containing Hydrochloric Acid. Port. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 28, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, T.L.; Donaldben, M.N.; Costa, M.C.; Carlier, J.D. Putative role of Flavobacterium, Dokdonella and Methylophilus strains in paracetamol biodegradation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-E.; Chang, B.-V. Microbial Communities Associated with Acetaminophen Biodegradation from Mangrove Sediment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Sarkar, T.K.; Chouhan, A.; Dasgupta, D.; Khatri, O.P.; Ghosh, D. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of wastewater pipeline and its mitigation by phytochemicals: Mechanistic evaluation based on spectroscopic, microscopic and theoretical analyses. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 364, 119960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiu, Y.Y.; Sharma, K.R.; Shi, T.; Song, Y.; Sun, J.; Liang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Jiang, F. Hydrogen sulfide control in sewer systems: A critical review of recent progress. Water Res. 2023, 240, 120046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alef, K.; Kleiner, D. Rapid and sensitive determination of microbial activity in soils and in soil aggregates by dimethylsulfoxide reduction. Biol. Fert. Soils 1989, 8, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebler, C.; Slezak, D. Microbial activity in aquatic environments measured by dimethyl sulfoxide reduction and intercomparison with commonly used methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebler, C.; Slezak, D. Microbial DMSO reduction is widespread among microorganisms and is therefore proposed as a reliable activity parameter. SIL Proceedings 1922–2010 2000, 27, 2492–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkers, H.M.; Van Der Maarel, M.J.E.C.; Van Gemerden, H.; Hansen, T.A. Dimethylsulfoxide reduction by marine sulfate-reducing bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 136, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McCrindle, S.L.; Kappler, U.; McEwan, A.G. Microbial dimethylsulfoxide and trimethylamine-N-oxide respiration. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2005, 50, 147–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles-Robledillo, J.M.; Torregrosa-Crespo, J.; Martínez-Espinosa, R.M.; Pire, C. DMSO Reductase Family: Phylogenetics and Applications of Extremophiles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebbe, D.A.; Gruender, C.; Dlugosch, L.; Lõhmus, K.; Rolfes, S.; Könneke, M.; Chen, Y.; Engelen, B.; Schäfer, H. Microbial drivers of DMSO reduction and DMS-dependent methanogenesis in saltmarsh sediments. ISME J. 2023, 17, 2340–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, M.; Kim, M.; Akob, D.M.; Basu, P.; Stolz, J.F. Impact of the Dimethyl Sulfoxide Reductase Superfamily on the Evolution of Biogeochemical Cycles. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0414522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Zhu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, J. Degradation of paracetamol by pure bacterial cultures and their microbial consortium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 3687–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waghmode, M.S.; Lende, S.B.; Gaikwad, P.R.; Patil, N.N.; Khisti, U.V. Studies on Biodegradation of Acetaminophen by Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis NCIB 3610(T). Curr. World Environ. 2023, 18, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utami, T.S.; Arbianti, R.; Hidayatullah, I.M.; Yusupandi, F.; Hamdan, M.; Putri, N.F.; Riyadi, F.A.; Boopathy, R. Paracetamol degradation in a dual-chamber rectangular membrane bioreactor using a microbial fuel cell system with a microbial consortium from sewage sludge. CSCEE 2024, 9, 100551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żur, J.; Wojcieszyńska, D.; Hupert-Kocurek, K.; Marchlewicz, A.; Guzik, U. Paracetamol—Toxicity and microbial utilization. Pseudomonas moorei KB4 as a case study for exploring degradation pathway. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Haikal, N.K.K.; Razali, I.A.; Wan Hanafi, W.N.; Geraldi, A.; Ni’Matuzahroh, F.; Tay, C.C. Sustainable bioremediation of acetaminophen using bacteria: A review. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2023, 18, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Altamirano, M.J.; Maza-Márquez, P.; Montemurro, N.; Pérez, S.; Rodelas, B.; Osorio, F.; Pozo, C. Insights into the removal of pharmaceutically active compounds from sewage sludge by two-stage mesophilic anaerobic digestion. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Compound | Mass, g/L of Distilled Water |
|---|---|
| KH2PO4 | 0.5 |
| NH4Cl | 1.0 |
| Na2SO4 | 4.5 |
| CaCl2 × 6H2O | 0.06 |
| MgSO4 × 7H2O | 0.06 |
| sodium lactate | 3.5 |
| sodium citrate | 0.3 |
| Symbol | D. oryzae NUChC SRB1 | Steel 3 | DMSO | Paracetamol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | − 1 | + | − | − |
| II | + 2 | + | − | − |
| III | + | + | + | − |
| IV | − | + | + | − |
| V | + | + | − | + |
| VI | − | + | − | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tkachuk, N.; Zelena, L.; Novikov, Y. Indicators of the Microbial Corrosion of Steel Induced by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Under the Influence of Certain Drugs. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16010021
Tkachuk N, Zelena L, Novikov Y. Indicators of the Microbial Corrosion of Steel Induced by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Under the Influence of Certain Drugs. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleTkachuk, Nataliia, Liubov Zelena, and Yaroslav Novikov. 2025. "Indicators of the Microbial Corrosion of Steel Induced by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Under the Influence of Certain Drugs" Microbiology Research 16, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16010021
APA StyleTkachuk, N., Zelena, L., & Novikov, Y. (2025). Indicators of the Microbial Corrosion of Steel Induced by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Under the Influence of Certain Drugs. Microbiology Research, 16(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16010021






