Abstract
Bats are natural reservoirs for many emerging viruses, including coronaviruses that were probably progenitors to human coronaviruses with epidemic and pandemic potential, which highlights the importance of screening studies of bat-derived viruses. This study investigates the prevalence and phylogenetic characteristics of coronaviruses in bat populations from the Rostov and Novosibirsk regions of Russia between 2021 and 2023. Utilizing PCR screening and sequencing, viruses belonging to the Alphacoronavirus genus were detected in several bat species, with prevalence rates ranging from 4.94% to 62.5%. Phylogenetic analysis of detected sequences revealed the presence of three subgenera: Pedacovirus, Myotacovirus, and Nyctacovirus. These sequences shared over 90% identity with alphacoronaviruses previously identified in bats across Northern Europe and Russia, underscoring the viruses’ wide geographic distribution and evolutionary connections. The results highlight the adaptability of alphacoronaviruses and the role of bat migratory behavior in their dispersal. The study underscores the importance of continuous monitoring and phylogenetic studies of bat-derived coronaviruses to better understand their ecological dynamics and potential zoonotic threats.
1. Introduction
Coronaviruses (CoVs) have a significant capacity for adaptation and evolution, driven by their rapid replication, RNA recombination, and the accumulation of mutations [1]. The ability for adaptation of CoVs allows them to overcome the interspecies barrier and infect new hosts, thereby expanding their ecological niche [2,3]. This, in turn, could pose a huge threat to public health and animal welfare, as cross-species transmissions give CoVs the possibility to obtain new genomic and phenotypic features through the adaptation to the new hosts, potentially leading to the emergence of pathogenic CoVs and their spillovers [4]. This hypothesis is supported by multiple studies where the evolutional paths of the emergence of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 and their potential progenitors’ genetic traces across various animal hosts were investigated [5,6]. The emergence of SARS-CoV in 2002 initiated investigative studies, whose purpose was to search for the origins of the outbreak. As a result, Guan et al. [5] in 2003 discovered SARS-like CoV with 99.8% genetic similarity to SARS-CoV in workers at an animal market in Shenzhen, as well as in animals, specifically Himalayan palm civets and raccoon dogs, pointing to the fact that this virus could be the SARS-CoV progenitor. A study with a similar aim to establish a SARS-CoV-2 ancestor was conducted by Crits-Christoph et al. [6], where they detected wildlife DNA belonging to civets, bamboo rats, and raccoon dogs in SARS-CoV-2-positive samples from Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market. Moreover, they discovered more animal-derived viruses in these samples, including hedgehog and canine CoVs [6]. These studies support the evidence that CoVs have an increased ability to cross-species transmission, and most importantly—dense contacts of animals of different species could be an ideal environment for the rapid evolution of CoVs. This justifies the need to study CoVs in wildlife to expand the data about their presence and phylogenetics, which could be a handful for further studies of genetic traces of emerging CoVs.
Bats are widely recognized as natural reservoirs of various CoVs [7]. Unique physiological features of the immune system of bats, such as limited inflammatory response, allow them to co-exist with a vast diversity of viruses for a long time [8,9]. Some studies show that bats could harbor progenitors of SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and other human coronaviruses [10,11]. However, it should be mentioned that there is no evidence of direct transmissions of CoVs from bats to humans—all known bat-derived CoVs had intermediate hosts in the chain of transmissions from bats to humans [12]. Nevertheless, given that there are bat species that are prone to synanthropy and live in close contact with domestic animals in urban areas, under-investigation of bats’ CoVs and other viruses poses a huge threat to public health and animal welfare [13]. Understanding the range and evolution of bat-derived CoVs not only provides information on the ecology of these viruses but also improves our ability to predict and mitigate zoonotic threats.
This study aimed at screening and phylogenetic characterization of CoVs in synanthropic bat populations from the Rostov and Novosibirsk regions of Russia.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.1.1. Rostov Region
Sampling from the bat population of the Rostov region (Russia) took place from November 2022 to March 2023 at the Rostov Bat Rehabilitation Center (Don State Technical University, Rostov-on-Don, Russia). The bats included in the study belonged to four species: the common noctule (Nyctalus noctula), the parti-coloured bat (Vespertilio murinus), Kuhl’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus kuhlii), and the serotine bat (Eptesicus serotinus). All bats were initially seized by volunteers from the Rostov Bat Rehabilitation Center, responding to Rostov household requests from November 2022 to March 2023. Collected colonies and individual bats were transferred to the rehabilitation center for veterinary examination and care. Each species was housed collectively, with 5 to 20 individuals per box, allowing socialization during rehabilitation and facilitating hibernation. While in the center, bats were fed superworms and mealworms. In late November 2022, they were placed into controlled hibernation at a constant temperature of 10 °C and remained in hibernation until early April 2023. In May 2023, healthy bats were released into the wild, while bats needing further rehabilitation were released later. Fecal samples, each at least 0.5 g, were collected from boxes housing the hibernating bats (once per box). Also, blood samples were collected from male N. noctula following the Smith et al. protocol [14]. Blood sampling from female N. noctula and other bat species was not conducted due to ethical considerations. Specifically, venipuncture in female bats was avoided to prevent potential risks to pregnant individuals (as only female E. serotinus were present at the rehabilitation center during sampling). Additionally, the smaller body size of species such as V. murinus and P. kuhlii made it challenging to safely obtain an adequate volume of blood. In addition to this, organ autopsies (brain, heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, and intestines) were obtained from bats that died due to natural reasons. All collected samples were labeled and stored at −80 °C. Overall, for this study, there were collected 648 samples from N. noctula, 41 from V. murinus, 84 from P. kuhlii, and 25 from E. serotinus at the Rostov Bat Rehabilitation Center. Table 1 summarizes the number and origins of samples from bats of the Rostov region analyzed in this study.

Table 1.
Summary of the samples obtained from bats at the Rostov Bat Rehabilitation Center for this study.
2.1.2. Novosibirsk Region
Sampling from the Novosibirsk (Russia) bat population took place in 2021 and 2023. During the summer, bats were captured manually in daytime roosting sites and natural shelters using mist nets. Mist nets, measuring 10 × 3 and 12 × 3 m, were set up near water bodies, on forest roads, and in other places where flying bats were detected. The capture began one hour before sunset and continued until 1 to 4 a.m. the following day. To locate roosting sites and refine capture locations, an ultrasonic microphone Pettersson M500-384 and the BatSound Touch Lite app (version 1.3.5, Pettersson Elektronik AB, Uppsala, Sweden) were used. During the winter, bats were captured manually in hibernacula sites located in caves in the Novosibirsk region, Russia.
To collect feces, the captured bats were held in individual cloth bags for 30 to 120 min. Feces were then transferred with tweezers from the bag and the bat’s body into sterile cryotubes. The tubes were labeled with a unique number and placed in a Dewar vessel with liquid nitrogen. Before collecting feces from each bat, the tweezers were sterilized by flame from a gas, petrol, or alcohol burner. Sterile urogenital swabs were used to take oral swabs for further analysis. Freshly deceased bats were dissected, and smears and samples of internal organs and blood were labeled and transported in the same way in cryotubes under liquid nitrogen vapor. When accessible, fresh fecal samples accumulating under the summer maternity colonies of bats were collected, labeled, and transported similarly. In this study, materials were collected from bats between 2021 and 2023, covering seven species: V. murinus (102 samples), pond bat (Myotis dasycneme [73 samples]), Sakhalin bat (Myotis petax [55 samples]), Hilgendorf’s tube-nosed bat (Murina hilgendorfi [14 samples]), Siberian bat (Myotis sibiricus [21 samples]), northern bat (Eptesicus nilssonii [9 samples]), N. noctula (2 samples). Additionally, 15 fecal samples were obtained from surfaces in the Barsukovskaya cave in the Novosibirsk region without determining the host species. Table 2 summarizes the number and origins of samples from bats of the Novosibirsk region analyzed in this study. The locations of the sampling sites (Rostov and Novosibirsk regions, Russia) were used for the generation of a geographical map, which is described in Section 2.5.

Table 2.
Summary of the samples obtained from the bat population at the Novosibirsk region for this study.
2.2. RNA Extraction
To extract viral RNA, 50 mg of each fecal sample was homogenized in 500 μL of PBS, using vortexing to achieve a homogenous suspension. Following centrifugation at 11,000× g for 4 min, the supernatant was collected, with 100 μL reserved for subsequent RNA extraction. Viral RNA extraction from both blood serum and homogenized fecal supernatant samples was conducted using the RIBO-prep kit (AmpliSens, Moscow, Russia). Reverse transcription was then carried out with the REVERTA-L kit (AmpliSens).
2.3. Primers Design and In Silico Analysis of Their Sensitivity and Specificity
For CoVs screening in obtained samples from bats using nested PCR, primers were designed based on full-length sequences of bat CoVs from the GenBank database: KJ473802.1, KJ473795.1, OQ175075.1, OQ175069.1, KJ473796.1, OQ175082.1, OQ175077.1, KJ473808.1, MW450840.1, KJ473804.1, KF294280.1, KF294278.1, DQ666338.1, OR735434.1, OQ715753.1. Nucleotide sequence alignment was performed in the Mega11 software using the ClustalW algorithm [15]. The most conserved region of the gene responsible for synthesizing RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) was selected for primer design [16,17,18]. As a result, the following pairs of primers were designed: Covbat-F1 (5′-AAG TTY TAT GGY GGM TGG G-3′) and Covbat-R1 (5′-TGT TGA GAA CAA AAY TCA TGW GG-3′); Covbat-F2 (5′-GGY TGG GGA YTA TCC TAA RTG TGA-3′) and Covbat-R2 (5′-ATT ARC AVA CAA CRC CAT CRT C-3′). The online tool, Oligo Calculator, was used to verify the optimal primer structure and annealing temperature [19].
In silico PCR analysis was conducted to test the sensitivity (% of detectable target organisms) and specificity (% of detectable non-target organisms) of designed primers. For the comparison, primers for CoVs PCR detection from studies by Vijgen et al. [20], Watanabe et al. [21], and Holbrook et al. [22] were added to the analysis as controls. The command-line-based tool “primesearch” from the EMBOSS tool kit (version 6.6.0) was used for the in silico PCR. The maximum number of mismatches was set to two. For this analysis, two databases containing CoVs and viral reference genomes were compiled from the NCBI RefSeq database (12 November 2024) [23]. The CoVs reference genomes database contained 74 genome sequences belonging to the Coronaviridae family and was used to test sensitivity, while the viral reference genomes database contained 18,748 available viral genomes (CoVs included) and was implemented for specificity testing. Results were visualized as the heatmap using “ggplot2” package (version 3.5.1) [24].
2.4. PCR Screening and Sequencing
To detect CoVs within the PCR screening, we used two designed and in silico-tested primer pairs described above. Oligonucleotide synthesis, including degenerate primers, was performed by Evrogen (Moscow, Russia). PCR was conducted with PCR 5× ScreenMix (Evrogen) on a T100 Thermal Cycler (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA), with the following thermal profile: for the first primer pair—1 cycle at 93 °C for 5 min, 34 cycles at 93 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 20 s, 70 °C for 30 s, followed by 1 cycle at 70 °C for 5 min, and a final hold at 4 °C; for the second primer pair—1 cycle at 93 °C for 5 min, 34 cycles at 93 °C for 30 s, 59 °C for 20 s, 70 °C for 25 s, followed by 1 cycle at 70 °C for 5 min, and a final hold at 4 °C. Amplification products were visualized in 1.5% agarose gel through horizontal electrophoresis using the Gel Doc XR+ Gel Documentation System (BioRad). The prevalence of positive signals was expressed as percentages with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) with the normal approximation to the binomial calculation. Extraction and purification from the agarose gel were performed with the N-Gel kit (Biolabmix, Novosibirsk, Russia). Sequencing of the resulting amplicons was completed using a SeqStudio Genetic Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Briefly, for the Sanger reaction, the primers were used at a working concentration of 3.3 μM and the BigDye Terminator v3.1 direct cycle sequencing kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). For each sample, one reaction with the forward primer and one reaction with the reverse primer were conducted. The temperature profile for the reaction was as follows. Preliminary denaturation—95 °C for 1 min; 35 cycles: denaturation at 95 °C for 10 s, annealing at 50 °C for 20 s, elongation at 60 °C for 4 min; final elongation—60 °C, 5 min. The reactions were carried out using a T100 Thermal Cycler (BioRad). Following the sequencing reactions, purification was performed to remove unincorporated BigDye-ddNTP using isopropanol and ethanol. The precipitated DNA was dissolved in Hi-Di Formamide (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The quality of the sequencing was assessed using Sequencher 4.1.4 (Gene Codes Corporation, Ann Arbor, MI, USA). Evaluation criteria included the presence of clear chromatograms, the absence of overlapping peaks, and minimal noise corresponding to unincorporated BigDye-ddNTPs. Taxonomical identification of obtained sequences was conducted with BLAST+ (version 2.16.0) [25] and MetaBuli App (version 1.0.8) [26].
2.5. Bioinformatic Data Analysis
Detected and sequenced RdRp gene fragments were used for phylogenetic and nucleotide identity analyses. Sequences used in the phylogenetic analysis were obtained from the recently published study of CoVs’ surveillance in bat populations in Russia [27]. All data were downloaded from the NCBI GenBank database [28] using the entrez-direct package (version 21.6) [29]. A total of 64 sequences were included in the analysis. MAFFT software (version 7.525) was used for the multiple sequence alignment [30]. Unaligned fragments were trimmed with trimAl [31]. ModelFinder, implemented in IQ-TREE2, was used to identify the optimal substitution model [32]. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using IQ-TREE2 (version 2.3.0) [33] with the GTR + F + I + G4 substitution model. Branch support was evaluated using 1000 ultrafast bootstrap replicates [34]. The final phylogenetic tree was visualized with the “ggtree” package (version 1.14.6) [35].
Aligned sequences of the RdRp gene of CoVs included in the phylogenetic analysis were also used for the identity analysis within the Mega11 software [15]. Resulted identity matrix was visualized using the “ggplot2” package (version 3.5.1) [24]. GenBank records of CoVs’ sequences with identity above 90% were used for the generation of the geographic map with the representation of the spatial distribution of these CoVs. Construction of the map was implemented with the “rnaturalearth” (version 1.0.1) [36] and “ggplot2” (version 3.5.1) [24] packages.
3. Results
3.1. In Silico PCR Analysis of Designed Primers Sensitivity and Specificity
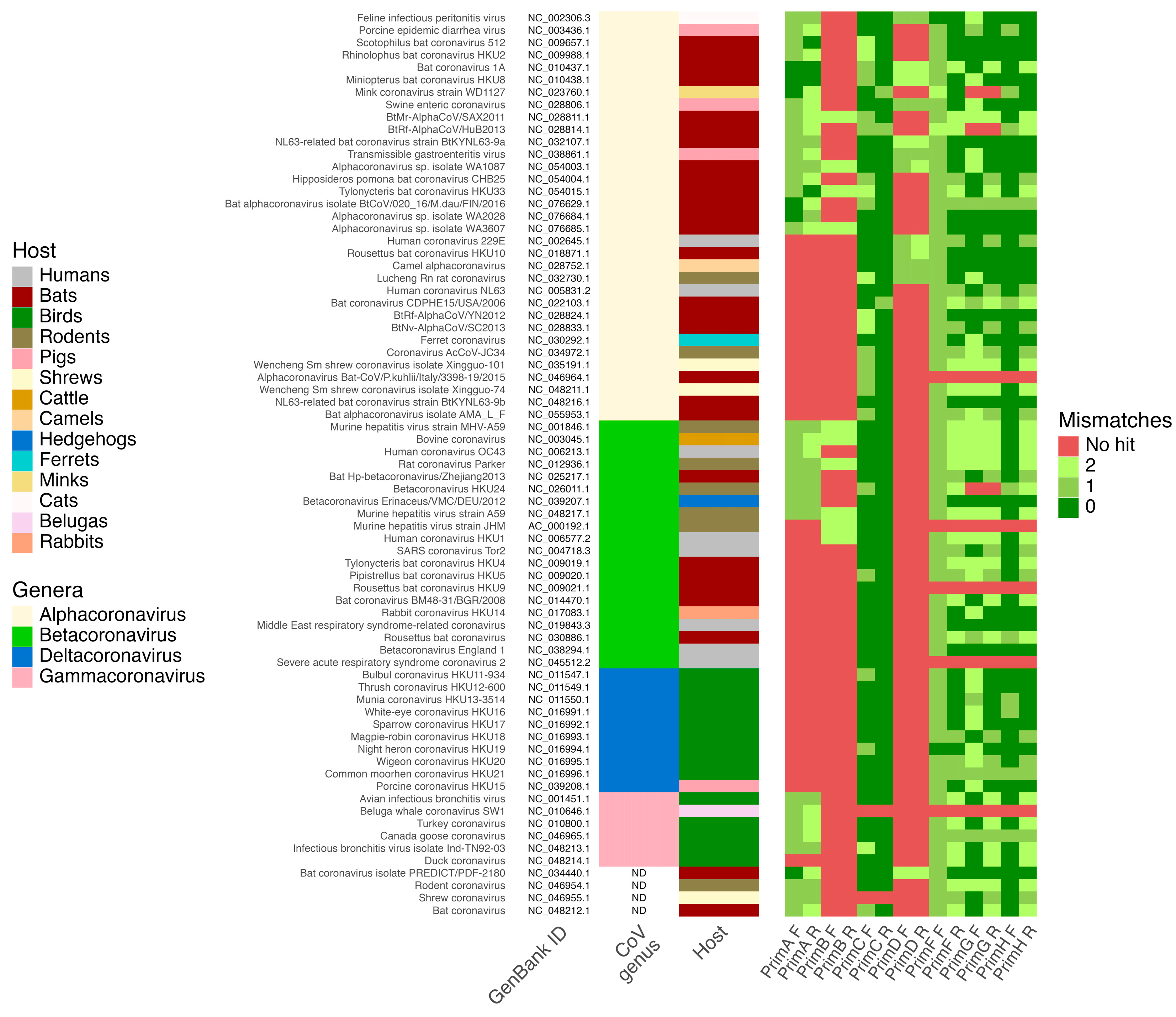
As a result of the in silico PCR assay, the first pair of designed primers for this study was able to detect at least 35 CoVs species, while the second pair should be able to detect 10 CoVs species, including bat-derived ones. These primer pairs showed no hits against other viruses, which assumes that their specificity for CoVs detection is 100%. Pan-CoV primers designed by Watanabe et al. [21] and included in this analysis as a control showed a decreased ability to detect a wide range of CoVs with the ability to detect in silico 11 CoVs species. Pairs of primers designed by Holbrook et al. [22] as modifications of Watanabe et al. [21] primers demonstrated better efficiency in pan-CoVs detection—69 out of 74 CoVs genomes included in the analysis were detected by these primers. The best performance in pan-CoVs detection in silico showed primers by Vijgen et al. [20], where they were not able to detect only two reference CoV genomes (Figure 1).
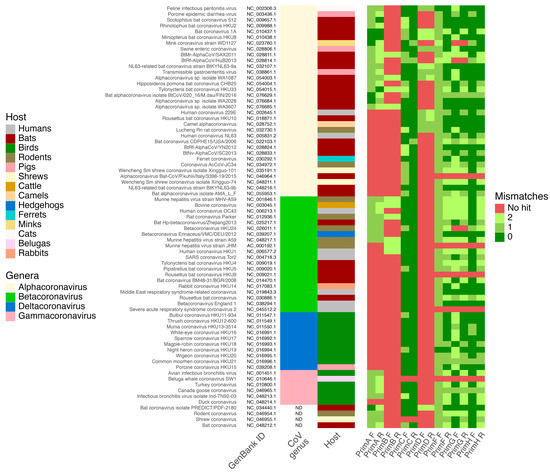
Figure 1.
Results of in silico PCR analysis of primers specificity and selectivity on 74 reference Coronaviridae genomes. Heatmap shows the number of mismatches for forward (F) and reverse (R) primers from this study (PrimA and PrimB), Vijgen et al. (PrimC) [20], Watanabe et al. (PrimD) [21], and Holbrook et al. studies (PrimF, PrimG, and PrimH) [22].
3.2. PCR Screening and Sequencing
As a result of PCR screening of bat populations in the Rostov and Novosibirsk regions, CoVs were detected in multiple samples across various bat species. In the Rostov region, CoVs-positive signals were identified in N. noctula, with 9 positive samples out of 557 collected in 2021, primarily from fecal samples (8/106 [4.94%, 95% CI 0.22–9.66%]). In 2022, 8 out of 91 samples from the same species tested positive, again mostly in fecal samples (8/76 [10.53%, 95% CI 3.63–17.43%]). Additionally, P. kuhlii exhibited 4 positive samples out of 28 in 2022, with CoVs RNA detected in fecal samples (4/15, 26.67%, 95% CI 7.79–49.05%).
In the Novosibirsk region, CoVs RNA was identified in M. dasycneme, M. petax, and M. sibiricus, V. murinus, and in bats’ fecal samples from surfaces in the Barsukovskaya cave. Notably, 6 out of 45 all samples collected from M. dasycneme tested positive in 2023, primarily in fecal samples (6/22, 27.27%, 95% CI 8.66–45.88%), and M. sibiricus exhibited a significant prevalence, with 6 positive signals out of 15 samples, including from oropharyngeal swabs (1/7, 14.29%, 95% CI 0–40.21%) and fecal samples (5/8, 62.5%, 95% CI 28.95–96.05%). Other notable findings are the detection of CoVs RNA in samples collected in 2021 and 2022, including positive signals in blood samples from M. petax (1/11 samples in 2021 [9.09%, 95% CI, 0–26.08%] and 1/18 in 2022 [5.56%, 95% CI, 0–16.14%]) and one blood sample from M. dasycneme in 2022. Also, 3 out of 15 samples from the Barsukovskaya cave tested positive for CoVs RNA (20%, 95% CI 0–40.24%). The positive results of PCR screening for CoVs RNA in collected samples from bats are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Summary of the positive samples on coronavirus prevalence according to the PCR screening based on samples obtained from the bat populations of the Rostov and Novosibirsk regions for this study.
After the detection of PCR products using electrophoresis, 21 of them were successfully sequenced. The amplification products from the remaining samples could not be sequenced due to their low concentrations, which were insufficient to support the sequencing reaction. There were six sequences obtained from the bats of the Rostov region. Sequences deposited in GenBank under accession numbers PQ439331.1 and PQ439332.1 were CoV RdRp sequences from P. kuhlii feces and PQ439335.1—from N. noctula feces. There were three identical RdRp CoV sequences from two fecal samples of P. kuhlii and one fecal sample of N. noctula. As the host species, location, date of the sample collection, and source of RNA extraction (and other remaining metadata) were identical in sequences obtained from P. kuhlii, they were deposited as one record in GenBank under the accession number PQ439333.1. The remaining identical sequences from N. noctula were deposited in GenBank under the accession number PQ439334.1.
Based on samples collected from the bats of the Novosibirsk region, 15 sequences of CoVs RdRp were obtained. GenBank records PQ450471.1 and PQ450476.1 contain sequences from RNA samples extracted from M. dasycneme, while PQ450483.1 represents sequences from the same bat species but from the blood sample. Sequences PQ450481.1 and PQ450482.1 were obtained from RNA extracted from the blood of M. petax. Two unique sequences obtained from M. sibiricus were deposited under accession numbers PQ450473.1 (feces) and PQ450480.1 (oropharyngeal swab). Two unique sequences were obtained from samples collected from the Barsukovskaya cave—PQ450478.1 and PQ450479.1. There were three identical sequences from two fecal samples from M. dasycneme, one fecal sample from M. sibiricus, and one sample from Barsukovskaya cave. Identical samples from M. dasycneme were deposited in one record (PQ450472.1) due to identical metadata, while samples from M. sibiricus and Barsukovskaya cave were deposited as separate records—PQ450475.1 and PQ450477.1, respectively. There were also two identical sequences from M. dasycneme feces, which were deposited as one record due to identical metadata—PQ450474.1.
All sequences belonged to the Alphacoronavirus genus (alphaCoV) according to their taxonomical identification.
3.3. Phylogenetic and Nucleotide Sequence Identity Analysis of Detected Coronaviruses
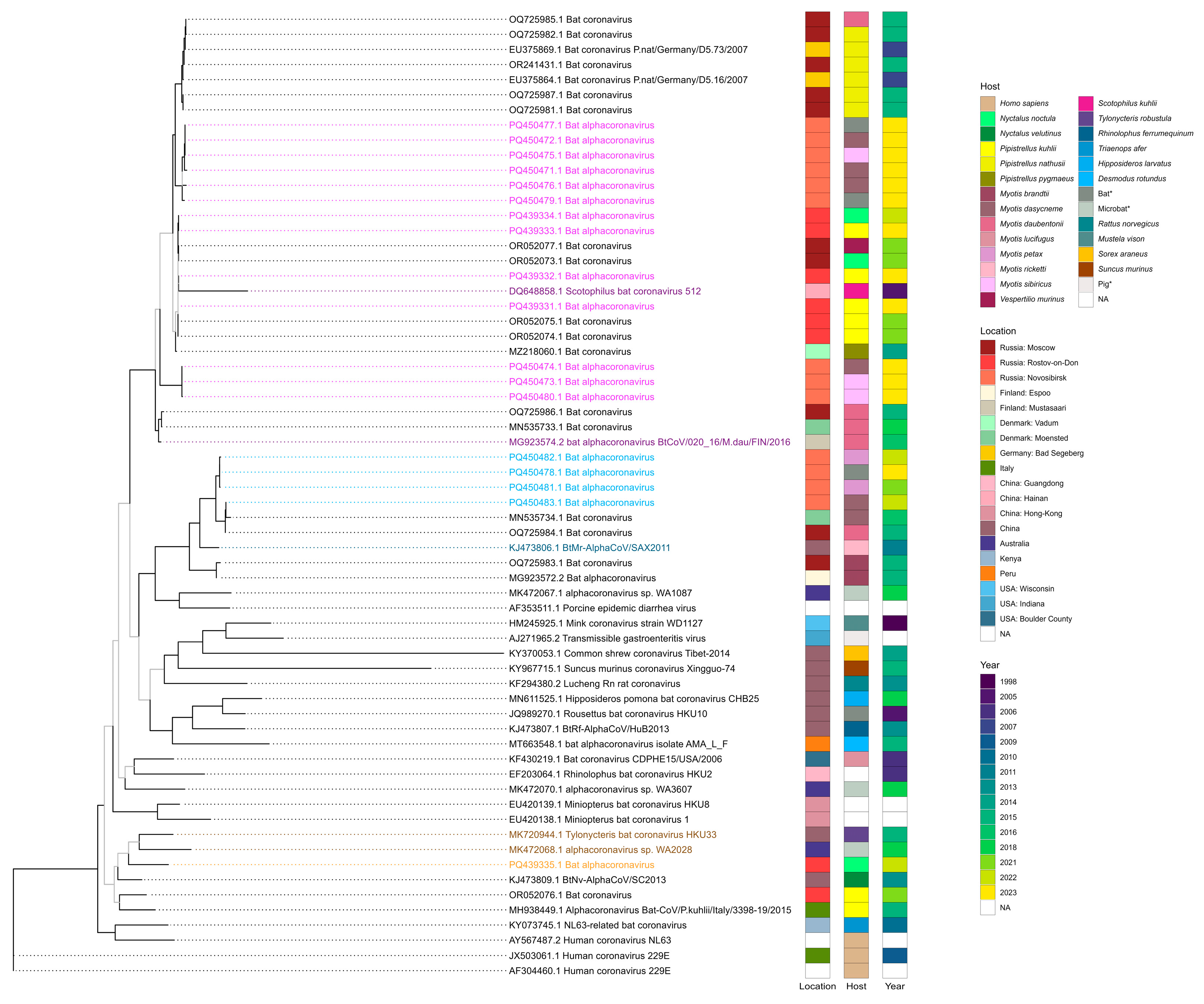
According to the results of the phylogenetic analysis of RdRp sequences, viruses detected in this study appeared in clades with three alphaCoVs subgenuses—Pedacovirus, Myotacoviruses, and Nyctacovirus. Four records from the Rostov region (PQ439331.1, PQ439332.1, PQ439333.1, and PQ439334.1) and nine records from the Novosibirsk region (PQ450477.1, PQ450472.1, PQ450475.1, PQ450471.1, PQ450476.1, PQ450479.1, PQ450474.1, PQ450473.1, and PQ450480.1) within this study appeared in one clade with pedacoviruses—Scotophilus bat coronavirus 512 (DQ648858.1) detected in the lesser Asiatic yellow bat (Scotophilus kuhlii) in China in 2005 [37] and bat alphacoronavirus BtCoV/020_16/M.dau/FIN/2016 (MG923574.2) detected in Daubenton’s bat (Myotis daubentonii) in Finland in 2016 (unpublished study). Four records from Novosibirsk obtained in this study (PQ450482.1, PQ450478.1, PQ450481.1, and PQ450483.1) were in one clade with Myotacovirus—BtMr-AlphaCoV/SAX2011 (KJ473806.1) discovered in a sample obtained from Rickett’s big-footed bat (Myotis pilosus) in China in 2011 [38]. The remaining sequence from the Rostov region (PQ439335.1) was in one clade with nyctacoviruses—alphacoronavirus sp. WA2028 (MK472068.1), which was identified in microbat of unknown species from Australia in 2018 (unpublished study), and Tylonycteris bat coronavirus HKU33 (MK720944.1), which was isolated from a sample from the greater bamboo bat (Tylonycteris robustula) collected in 2015 in China [39]. The annotated phylogenetic tree is shown in Figure 2.
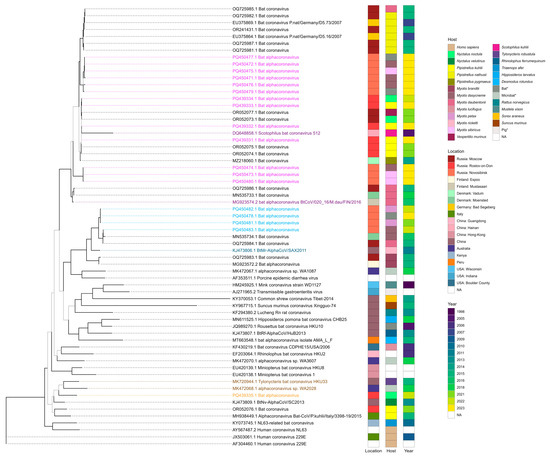
Figure 2.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree constructed using GTR + F + I + G4 substitution model based on alphacoronavirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase nucleotide sequences. Bootstrap values above 70 are displayed as black branches and lower than 70—as grey branches. Coronaviruses definitively classified as pedacoviruses (DQ648858.1 and MG923574.2), myotacovirus (KJ473806.1), and nyctacoviruses (MK472068.1 and MK720944.1) are highlighted as dark purple, dark blue, and dark orange, respectively. Coronaviruses detected in our study that appeared in clades with these alphacoronavirus subgenera are highlighted as light purple, light blue, and light orange, respectively. * The exact host species is unknown for samples collected from Barsukovskaya cave, other records regarding the host identity were retrieved from GenBank.
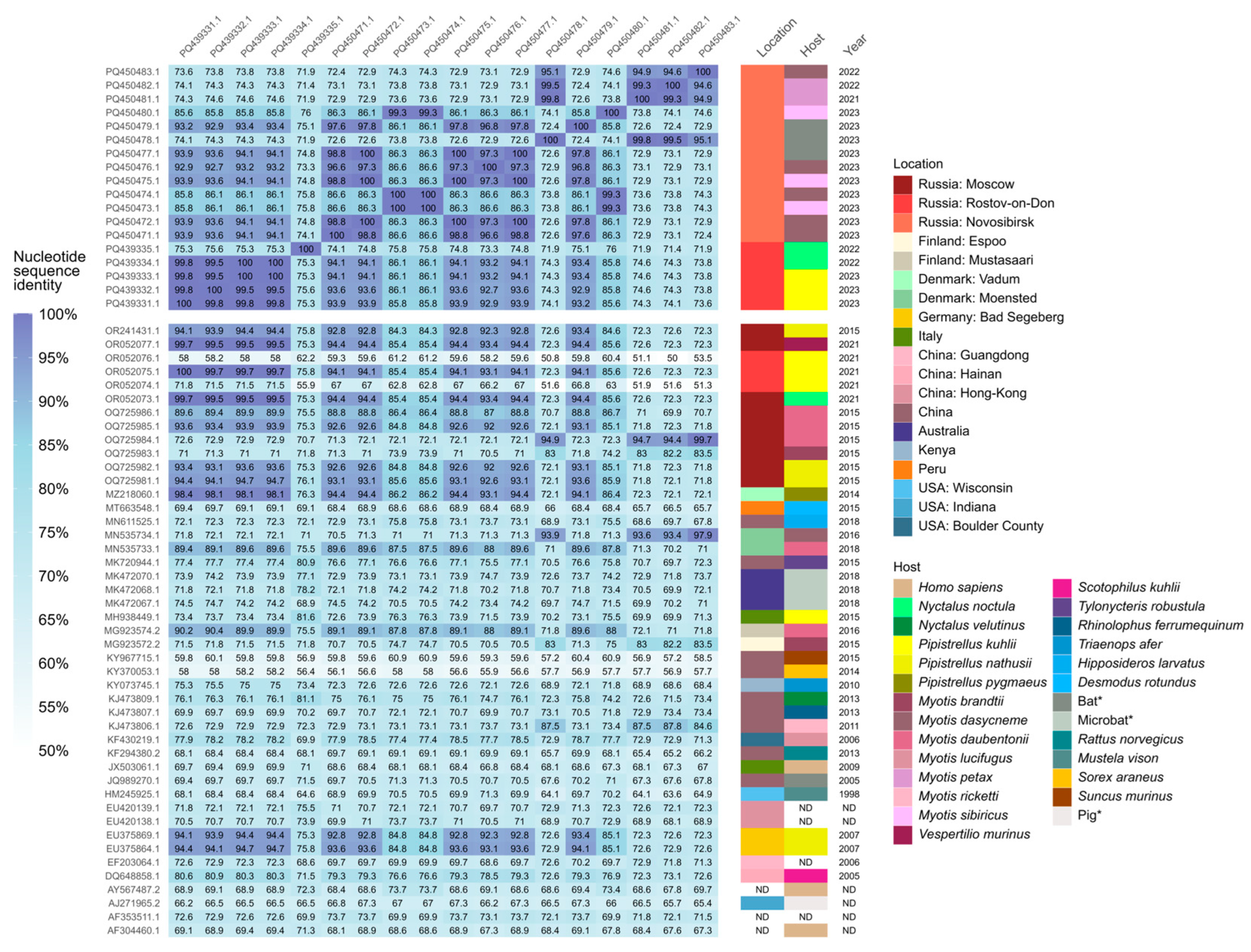
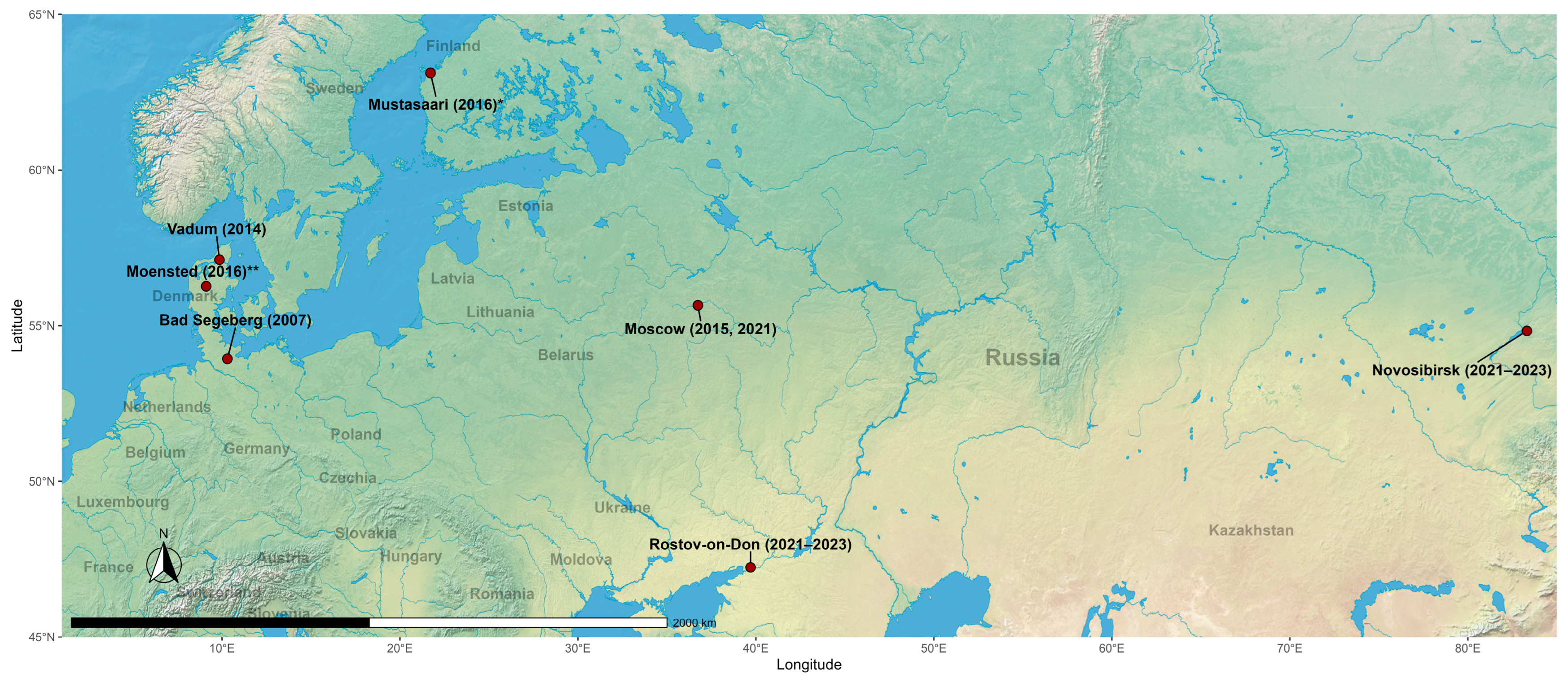
According to the results of the CoVs’ RdRp sequences identity analysis, sequences obtained from the Rostov region had identity above 90% with sequences from the Novosibirsk region from this study, and also with alphaCoVs records from Moscow in 2015 (OR241431.1, OQ725985.1, OQ725982.1, OQ725981.1) and 2021 (OR052077.1, OR052073.1) and Rostov region in 2021 (OR052075.1) from Korneenko et al. [27] study, from Denmark, Vadum in 2014 (MZ218060.1) from Lazov et al. [40] study, from Finland, Mustasaari in 2016 (MG923574.2, unpublished study), and from Germany, Bad Segeberg in 2007 (EU375869.1 and EU375864.1) [41]. AlphaCoVs’ sequences from the Novosibirsk region shared the same identity higher than 90% with the above-written records, except for records from Finland. Additionally, sequences from Novosibirsk had >90% identity with a previously unmentioned record from Moscow in 2015 (OQ725984.1) from Korneenko et al. [27] study and with the record from Denmark, Moensted in 2016 (MN535734.1) from Lazov et al. [40] study. All sequences from these records were obtained from bat-derived samples (Figure 3). Also, interestingly, alphaCoV’s RdRp gene sequence obtained from RNA extracted from P. kuhlii fecal sample collected in 2023 in Rostov region from our study (PQ439331.1) was 100% identical to the record of the same gene sequence detected in the fecal sample of the same bat species in 2021 (OR052075.1) from Korneenko et al. [25] study. The geographical representation of locations with the records of alphaCoVs that shared identity above 90% based on RdRp sequences is shown in Figure 4.
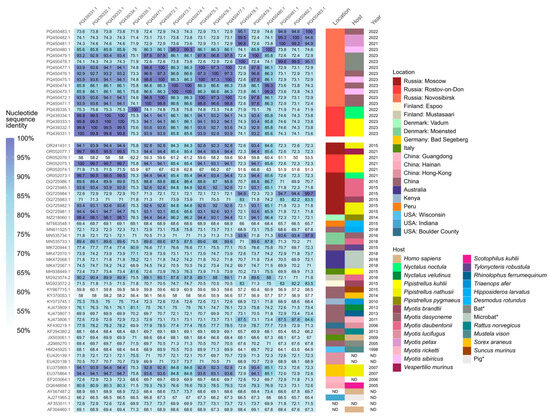
Figure 3.
Identity matrix of alphacoronaviral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase sequences. * The exact host species is unknown for samples collected from Barsukovskaya cave, other records regarding the host identity were retrieved from GenBank.
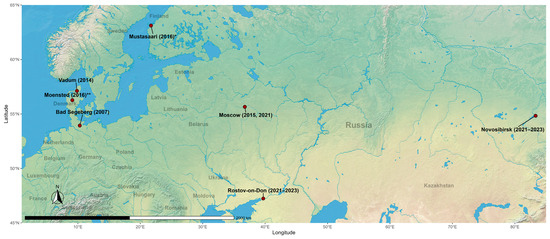
Figure 4.
Locations where there were detected bat-derived alphacoronaviruses that shared an identity above 90% with the viruses identified in this study. * Record from Finland, Mustasaari had >90% identity only with alphacoronaviruses identified in the Rostov region within this study. ** Record from Denmark, Moensted had >90% identity only with alphacoronaviruses identified in the Novosibirsk region within this study.
4. Discussion
This study reports the results of screening and phylogenetic analysis of CoVs in bat populations from the Rostov and Novosibirsk regions of Russia. The findings of this study provide insights into the distribution and genetic diversity of bat-derived CoVs in these regions.
The primers designed in this study for PCR screening of bat-derived CoVs demonstrated relatively high sensitivity and full specificity in detecting CoVs. In silico PCR analysis confirmed the primers’ capacity to detect a broad range of CoVs without cross-reacting with non-CoVs genomes using a reference genomic database. This is evidenced by their ability to detect in silico 35 and 10 CoVs species with no hits against other viruses, respectively, which is higher than primers from the Watanabe et al. [21] study. However, it should be mentioned that the designed primers had lower performance in terms of selectivity to detect CoVs in comparison to primers for pan-CoVs PCR assay designed by Vijgen et al. [18] and Holbrook et al. [22]. Interestingly, Holbrook et al. [22] positioned their primers as improved modifications of primers by Watanabe et al. [21], and our in silico PCR analysis corroborates their findings. Nevertheless, primers designed in our study are valid for screening bat-derived CoVs, as they showed the ability to detect most of the reference bat CoV genomes. This is also supported by the fact that these primer pairs allowed us to detect and sequence CoVs that are homologous to the reference genomes of CoVs that are detectable in silico by our primers, for example, bat alphacoronavirus BtCoV/020_16/M.dau/FIN/2016 (RefSeq: NC_076629.1, and GenBank: MG923574.2) and BtMr-AlphaCoV/SAX2011 (RefSeq: NC_028811.1, and GenBank: KJ473806.1) (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3).
The prevalence of CoVs in bats observed in our study generally aligns with findings from other studies conducted in Russia, emphasizing a consistent occurrence of CoVs in various bat species across different regions. In our study, CoVs were detected in fecal samples with notable prevalence rates, such as 4.94% (8/106, 95% CI 0.22–9.66%) in 2021 and 10.53% (8/76, 95% CI 3.63–17.43%) in 2022 in N. noctula and 26.67% (4/15, 95% CI 7.79–49.05%) in P. kuhlii from the Rostov region, and up to 62.5% (5/8, 95% CI 28.95–96.05%) in M. sibiricus from the Novosibirsk region. Although, we should mention that the number of samples collected from some bat species does not allow us to make definitive conclusions. Nonetheless, these results, particularly the results of screening in the Rostov region, generally correspond to one of our previous studies conducted in 2021, where CoV RNA was detected in 5 out of 150 bats from Southern Russia with an overall CoV prevalence of 3.33% [42]. In another study conducted in Russia by Yashina et al. [43], there was a notable prevalence of CoV RNA in 20.63% (13/63) of samples from bats of the Dagestan Republic, Russia. Also, in this study, CoVs RNA was detected in 10% (1 out of 10) samples from bats of the Kemerovo region and 4.76% (1 out of 21) samples from bats of the Altai Republic. In the Korneenko et al. [27] study of CoV surveillance in bats in Moscow, Moscow region, Joshkar-Ola, and Rostov-on-Don, the overall prevalence of CoV RNA was observed in 30% of the investigated samples (13 of 43). However, we cannot find the screening results of this study reliable, as there were only two samples from Joshkar-Ola and three samples from Rostov-on-Don. In another notable study by Speranskaya et al. [44], CoVs were detected in 50% of samples (13 out of 26) from bats of the Moscow region. Thus, the CoV prevalence in bat populations of different regions in Russia differs. Further studies with larger sample sizes need to be conducted to obtain more reliable insights into CoVs’ prevalence and their dynamics in bat populations in Russia.
According to the taxonomical identification, detected viruses belong to the alphaCoV genus, and the results of the phylogenetic analysis suggest that there were probably detected two subgenera in bat populations of Rostov and Novosibirsk regions—pedacoviruses and myotacoviruses. Additionally, alphaCoV, probably belonging to the nyctacovirus subgenus, was detected in the Rostov region. These three genera were previously detected in bat populations in Russia—Korneenko et al. reported their occurrence in Moscow in 2015 and 2021 and Rostov-on-Don in 2021. According to the results of phylogenetic and sequence identity analysis, we also detected pedacovirus in P. kuhlii from Rostov Bat Rehabilitation Center in 2023, which is probably the same pedacovirus Korneenko et al. discovered in the P. kuhlii captured in the wild in 2021. This consistency highlights the stability and persistence of this alphaCoV subgenus in Southern Russian bat populations over time. Pedacoviruses were also detected by Yashina et al. in mouse-eared bats in the Altai Republic and Kemerovo region of Russia in 2020 and 2023, respectively [43], but, unfortunately, we were not able to include these records in our comparative analyses, as we were not able to find them in publicly available databases. Nevertheless, the available data already suggest that sequences obtained in this study belong to three alphaCoV subgenera—Pedacovirus, Myotacovirus, and Nyctacovirus. However, we find it important to state that we cannot make definitive conclusions regarding this, as short RdRp fragments could not have enough resolution for taxonomical outcomes on the subgenus level. Further studies involving cultivation and high-throughput sequencing approaches need to be conducted to make conclusions on other taxonomical levels, including characterization on the species level [45].
The sequence identity analysis and geographical distribution of homologous alphaCoVs analyzed in this study reveal important insights into the wide geographic dispersal and evolutionary dynamics of these viruses. High sequence identity (>90%) was observed between alphaCoVs detected in bat populations from Southern Russia (Rostov region) and Siberia (Novosibirsk region), as well as with alphaCoV sequences from Northern Europe (Finland, Denmark, and Germany) and Central Russia (Moscow). This widespread geographical distribution underscores the ecological adaptability and potential for alphaCoVs to spread across vast and diverse regions, likely facilitated by the migratory behavior of certain bat species. Notably, all highly homologous alphaCoVs from the above-mentioned regions were detected in bats belonging to the family Vespertilionidae, such as N. noctula, V. murinus, P. kuhlii, and M. daubentoniid, which are widely distributed in Eurasia, and are migratory bat species that can fly on long distances [46,47,48]. Multiple studies have shown that the bats’ ability to fly contributes to their virome spread, which in turn contributes to spillovers of emerging viruses in different regions [49,50,51].
This study has several limitations that need to be acknowledged. First, the sample size for some bat species was relatively small, which makes the conclusions about the distribution of CoVs within these populations less definitive. Additionally, the study relied on RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene sequences for phylogenetic analysis, which may lack sufficient resolution for taxonomic classification at finer levels. The reliance on the PCR-based method for the screening, while sensitive, also means that only known or closely related coronaviruses could be detected, potentially overlooking more divergent or novel viruses that could be discovered in further studies implementing the genomic investigation [52,53,54]. Nevertheless, the study provides valuable data on the diversity and prevalence of alphaCoVs in bat populations from the Rostov and Novosibirsk regions, contributing to a broader understanding of their geographic distribution.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we discovered alphacoronaviruses in bats belonging to the Vespertilionidae family with an overall prevalence of 4.94–26.67% in samples collected from various bat species in the Rostov region in 2022–2023 and 5.56–62.5% in samples collected from various bat species in the Novosibirsk region in 2022–2023. According to the phylogenetic analysis of acquired sequences, these alphacoronaviruses appeared in clades with viruses belonging to three subgenuses—Pedacovirus, Myotacoviruses, and Nyctacovirus, which were earlier observed in bats of Southern and Central Russian regions. Sequences of detected alphacoronaviruses were more than 90% identical to those previously discovered in bat populations of Finland, Denmark, and Germany, which expands our knowledge on the geographical distribution of bat-derived alphacoronaviruses with the occurrence in Northern Europe, Central and Southern Russia and Siberia. Further studies incorporating cultivation and genomic assay approaches could uncover patterns in the molecular evolution and zoonic potential of these alphacoronaviruses and offer crucial insights for managing potential spillovers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.V.O., A.Y.A. and A.M.S.; methodology, K.A.S., M.A.S. and A.D.M.; software, I.V.P. (Igor V. Popov) and I.V.P. (Ilia V. Popov); validation, E.V.T. and D.A.B.; formal analysis, K.A.S. and I.A.S.; investigation, A.A.M. and A.V.M.; resources, E.A.L., A.M.E. and A.M.S.; data curation, K.A.S. and I.V.P. (Ilia V. Popov); writing—original draft preparation, O.V.O., I.V.P. (Igor V. Popov) and I.V.P. (Ilia V. Popov); writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, I.V.P. (Igor V. Popov), I.V.P. (Ilia V. Popov) and S.D.T.; supervision, A.M.S.; project administration, O.V.O.; funding acquisition, O.V.O. and I.V.P. (Igor V. Popov). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The reported study was funded by the Russian Science Foundation project 23-64-00005 (PCR screening and sequencing) and the State funded budget project 122120600015-2 (sampling).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The reported study does not involve the results of any in vivo intervention experiments. Handling of animals at the bat rehabilitation center and sampling were approved by the local ethics committee of Don State Technical University (Protocol No. 5 2022).
Data Availability Statement
Detected alphaCoVs RdRp gene sequences were deposited in the GenBank under accession numbers PQ439331.1, PQ439332.1, PQ439333.1, PQ439334.1, PQ439335.1, PQ450471.1, PQ450472.1, PQ450473.1, PQ450474.1, PQ450475.1, PQ450476.1, PQ450477.1, PQ450478.1, PQ450479.1, PQ450480.1, PQ450481.1, PQ450482.1, and PQ450483.1. The pipeline used for the in silico and bioinformatic data analysis has been deposited in GitHub: https://github.com/PopovIILab/PhoACr (accessed on 22 December 2024).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support of the team of the bat rehabilitation center of the Don State Technical University. Igor V. Popov expresses his deep gratitude to Sergey A. Nedospasov for his guidance and Olga G. Ilchenko for her valuable advice on bat conservation strategies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ji, W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zai, J.; Li, X. Cross-species transmission of the newly identified coronavirus 2019-nCoV. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, A.M.; McDaneld, T.G.; Harhay, G.P.; Das, S.; Loy, J.D.; Hause, B.M. Recent emergence of bovine coronavirus variants with mutations in the hemagglutinin-esterase receptor binding domain in US cattle. Viruses 2022, 14, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhama, K.; Patel, S.K.; Sharun, K.; Pathak, M.; Tiwari, R.; Yatoo, M.I.; Malik, Y.S.; Sah, R.; Rabaan, A.A.; Panwar, P.K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 jumping the species barrier: Zoonotic lessons from SARS, MERS and recent advances to combat this pandemic virus. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 37, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnik, I.; Popov, I.V.; Sereda, S.; Popov, I.V.; Chikindas, M.; Ermakov, A. Coronavirus infections of animals: Future risks to humans. Biol. Bull. 2021, 48, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.J.; Zheng, B.J.; He, Y.Q.; Liu, X.L.; Zhuang, Z.X.; Cheung, C.L.; Luo, S.W.; Li, P.H.; Zhang, L.J.; Butt, K.M.; et al. Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science 2003, 302, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crits-Christoph, A.; Levy, J.I.; Pekar, J.E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Singh, R.; Hensel, Z.; Gangavarapu, K.; Rogers, M.B.; Moshiri, N.; Garry, R.F.; et al. Genetic tracing of market wildlife and viruses at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic. Cell 2024, 187, 5468–5482.e5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Kulcsar, K.; Misra, V.; Frieman, M.; Mossman, K. Bats and coronaviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Cobo, J.; Lopez-Roig, M. Bats and Emerging Infections: An Ecological and Virological Puzzle. In Emerging and Re-Emerging Viral Infections: Advances in Microbiology, Infectious Diseases and Public Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 6, pp. 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Baker, M.L.; Kulcsar, K.; Misra, V.; Plowright, R.; Mossman, K. Novel insights into immune systems of bats. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ge, X.; Wang, L.F.; Shi, Z. Bat origin of human coronaviruses. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ji, J.; Chen, X.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, T.; Song, H.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y. Identification of novel bat coronaviruses sheds light on the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses. Cell 2021, 184, 4380–4391.e4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Dicks, L.M.; Popov, I.V.; Karaseva, A.; Ermakov, A.M.; Suvorov, A.; Tagg, J.R.; Weeks, R.; Chikindas, M.L. Probiotics at war against viruses: What is missing from the picture? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brussel, K.V.; Holmes, E.C. Zoonotic disease and virome diversity in bats. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 52, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.S.; Jong, C.E.D.; Field, H.E. Sampling small quantities of blood from microbats. Acta Chiropterologica 2010, 12, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis, version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.; Huang, Y.; Lau, S.; Yuen, K. Coronavirus Genomics and Bioinformatics Analysis. Viruses 2010, 2, 1804–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E. The phylogeny of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases of positive-strand RNA viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72 Pt 9, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillen, H.; Kokic, G.; Farnung, L.; Dienemann, C.; Tegunov, D.; Cramer, P. Structure of replicating SARS-CoV-2 polymerase. Nature 2020, 584, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibbe, W.A. OligoCalc: An online oligonucleotide properties calculator. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W43–W46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijgen, L.; Moës, E.; Keyaerts, E.; Li, S.; Ranst, M.V. A pancoronavirus RT-PCR assay for detection of all known coronaviruses. In SARS-and Other Coronaviruses: Laboratory Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Masangkay, J.S.; Nagata, N.; Morikawa, S.; Mizutani, T.; Fukushi, S.; Alviola, P.; Omatsu, T.; Ueda, N.; Iha, K.; et al. Bat coronaviruses and experimental infection of bats, the Philippines. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, M.G.; Anthony, S.J.; Navarrete-Macias, I.; Bestebroer, T.; Munster, V.J.; van Doremalen, N. Updated and validated pan-coronavirus PCR assay to detect all coronavirus genera. Viruses 2021, 13, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI reference sequences (RefSeq): A curated non-redundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D61–D65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H.; Wickham, H. Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Steinegger, M. Metabuli: Sensitive and specific metagenomic classification via joint analysis of amino acid and DNA. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korneenko, E.V.; Samoilov, A.E.; Chudinov, I.K.; Butenko, I.O.; Sonets, I.V.; Artyushin, I.V.; Yusefovich, A.P.; Kruskop, S.V.; Sinitsyn, S.O.; Klyuchnikova, E.O.; et al. Alphacoronaviruses from bats captured in European Russia in 2015 and 2021 are closely related to those of Northern Europe. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 12, 1324605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D67–D72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kans, J. Entrez direct: E-Utilities on the UNIX Command Line. In Entrez Programming Utilities Help; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.Y. ggtree: An R package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, A.; South, M.A. R Package: Rnaturalearth. World Map Data from Natural Earth, Version 0.1.0. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rnaturalearth/rnaturalearth.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Fan, X.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Dong, B.; Liu, W.; Cheung, C.; et al. Prevalence and genetic diversity of coronaviruses in bats from China. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7481–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; Ren, X.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Qian, Z.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Deciphering the bat virome catalog to better understand the ecological diversity of bat viruses and the bat origin of emerging infectious diseases. ISME J. 2016, 10, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.; Wong, A.C.; Zhang, L.; Luk, H.K.; Kwok, J.S.; Ahmed, S.S.; Cai, J.-P.; Zhao, P.S.; Teng, J.L.; Tsui, S.K.; et al. Novel bat alphacoronaviruses in southern China support Chinese horseshoe bats as an important reservoir for potential novel coronaviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazov, C.M.; Belsham, G.J.; Bøtner, A.; Rasmussen, T.B. Full-genome sequences of alphacoronaviruses and astroviruses from myotis and pipistrelle bats in Denmark. Viruses 2021, 13, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloza-Rausch, F.; Ipsen, A.; Seebens, A.; Göttsche, M.; Panning, M.; Drexler, J.F.; Petersen, N.; Annan, A.; Grywna, K.; Müller, M.; et al. Detection and prevalence patterns of group I coronaviruses in bats, northern Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, I.V.; Ohlopkova, O.V.; Donnik, I.M.; Zolotukhin, P.V.; Umanets, A.; Golovin, S.N.; Malinovkin, A.V.; Belanova, A.A.; Lipilkin, P.V.; Lipilkina, T.A.; et al. Detection of coronaviruses in insectivorous bats of Fore-Caucasus, 2021. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashina, L.N.; Zhigalin, A.V.; Abramov, S.A.; Luchnikova, E.M.; Smetannikova, N.A.; Dupal, T.A.; Krivopalov, A.V.; Vdovina, E.D.; Svirin, K.A.; Gadzhiev, A.A.; et al. Coronaviruses (Coronaviridae) of bats in the northern Caucasus and south of western Siberia. Probl. Virol. 2024, 69, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashina, L.N.; Zhigalin, A.V.; Abramov, S.A.; Luchnikova, E.M.; Smetannikova, N.A.; Dupal, T.A.; Krivopalov, A.V.; Vdovina, E.D.; Svirin, K.A.; Gadzhiev, A.A.; et al. Identification and genetic characterization of MERS-related coronavirus isolated from Nathusius’ pipistrelle (Pipistrellus nathusii) near Zvenigorod (Moscow region, Russia). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, A.D.; Chapman, D.; Dixon, L.; Chantrey, J.; Darby, A.C.; Hall, N. Application of next-generation sequencing technologies in virology. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1853–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnert, L.S.; Kramer-Schadt, S.; Teige, T.; Hoffmeister, U.; Popa-Lisseanu, A.; Bontadina, F.; Ciechanowski, M.; Dechmann, D.K.N.; Kravchenko, K.; Presetnik, P.; et al. Variability and repeatability of noctule bat migration in Central Europe: Evidence for partial and differential migration. Proc. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20182174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, T.C.; Mohammed, O.B.; Alagaili, A.N. Phylogenetic and demographic insights into Kuhl’s Pipistrelle, Pipistrellus kuhlii, in the Middle East. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnell, G.F.; Smith, R.; Smith, T. 33 million year old Myotis (Chiroptera, Vespertilionidae) and the rapid global radiation of modern bats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; Anderson, D.E. Viruses in bats and potential spillover to animals and humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.; Wang, L.-F. Bats and their virome: An important source of emerging viruses capable of infecting humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, C.E.; Rozins, C.; Guth, S.; Boots, M. Reservoir host immunology and life history shape virulence evolution in zoonotic viruses. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolatti, E.M.; Viarengo, G.; Zorec, T.M.; Cerri, A.; Montani, M.E.; Hosnjak, L.; Casal, P.E.; Bortolotto, E.; Di Domenica, V.; Chouhy, D.; et al. Viral metagenomic data analyses of five new world bat species from Argentina: Identification of 35 novel DNA viruses. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z. Metagenomic analysis of viruses from bat fecal samples reveals many novel viruses in insectivorous bats in China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4620–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Fagbo, S.F.; Alagaili, A.N.; Nitido, A.; Williams, S.H.; Ng, J.; Lee, B.; Durosinlorun, A.; Garcia, J.A.; Jain, K.; et al. A viral metagenomic survey identifies known and novel mammalian viruses in bats from Saudi Arabia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).