Abstract
The intestinal microbiota of fish is predominantly composed of prokaryotic microorganisms, with research historically focused on bacteria. In contrast, the role of microeukaryotic organisms in the fish gut remains largely unexplored. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the diversity, ecology, and potential functions of intestinal microeukaryotes, particularly fungi and protozoans, in teleost fish. Fungi, especially Ascomycota and Basidiomycota phyla members, are consistently identified across species and may contribute to digestion, immune modulation, and microbial homeostasis. Protists, though often viewed as pathogens, also exhibit potential commensal or immunoregulatory roles, including the modulation of bacterial communities through grazing. Other eukaryotic taxa, including metazoan parasites, microalgae, and zooplankton, are commonly found as transient or diet-derived members of the gut ecosystem. While many of these organisms remain poorly characterized, emerging evidence suggests they may play essential roles in host physiology and microbial balance. The review highlights the need for improved detection methodologies, functional studies using gnotobiotic and in vitro models, and multi-kingdom approaches to uncover fish gut microeukaryotes’ ecological and biotechnological potential.
1. Introduction
The gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in the health and physiology of fish, engaging in complex interactions with the host that can be mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic. These interactions significantly influence key functions as detoxification, energy harvesting, barrier integrity, host development, immune modulation, production of antimicrobial compounds, and nutrient metabolism [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9].
Although relatively resilient, the composition of the gut microbiota can be shaped by a variety of factors, including microorganism-host interactions, host genetics, environmental variations, and diet composition, which is considered the most influential. When detrimental changes occur in intestinal microbiota, hosts may become more susceptible to pathogen proliferation and lose key microbiota-mediated functions, especially under stressful conditions or immune suppression [10,11,12,13]. Because of its broad physiological relevance, gut microbiota is regarded as an auxiliary organ [14].
Most research on fish gut microbiota has focused on prokaryotic microorganisms, which comprise over 95% of the microbial biomass. The core bacterial phyla include Fusobacteria, Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Cyanobacteria [15,16,17,18,19,20]. These prokaryotes contribute to host development, nutrient absorption, intestinal cell proliferation, disease prevention, and immune system function [21,22]. This core microbiota, or resident microbiota (autochthonous), is characterized by long-term colonization in the fish’s gut, forming a stable community specialized to grow and adhere to the gut mucus lining. It is based on shared microorganisms among comparable and consistently found species, regardless of environmental changes. Meanwhile, transient (allochthonous) microorganisms are short-term colonizers from food items and the surrounding water [23,24].
Archaea, another group of prokaryotes, represent a smaller fraction (1–5%) of the gut microbiota but fulfill specialized functions [25]. Methanogenic archaea are often found in the intestines of herbivorous fish or those consuming carbohydrate-rich diets. Though less abundant, they participate in fermentation and methane production, underscoring their role in digestive processes [26].
In contrast, microeukaryotic microorganisms comprise only 2% to 5% of the gut microbiota [27], and their role in fish remains largely underexplored [28,29]. Several challenges hinder their study, including low abundance relative to prokaryotes [30], their limited representation in genomic databases [28], and the transient nature of many microeukaryotes introduced through diet [31].
Microeukaryotic communities can be examined through sequencing and can be studied using metagenomics or amplicon sequencing. In the last case, sequencing the 18S rRNA and ITS (Internal Transcribed Spacer) gene marker is widely used for microeukaryotic profiling. The chosen gene marker will determine the community profile [32]. For instance, 18S rRNA is well suited for identifying higher-level taxonomic groups and assessing overall eukaryotic diversity [33]. On the other hand, ITS has a better probability of successful fungi identification, particularly the ITS1 and ITS2 regions, which are more variable and provide better resolution for distinguishing between closely related species and for studying intraspecific diversity. Additionally, microscopy provides more accurate quantitative results regarding abundance and biomass, while high-throughput sequencing provides a better estimate of the taxonomic richness of an ecosystem. The chosen biological marker and combining two methodological approaches yield more reliable and accurate results for eukaryotic diversity [34,35].
The presence of host DNA interferes with downstream analysis, and common molecular biomarkers often cross-react with host DNA, creating technical interferences that require refined detection strategies [36]. Among the strategies to overcome this challenge, it is proposed that during DNA extraction and chemical lysis, the detergents sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) increase yield while maintaining the integrity of the DNA in polysaccharide-rich organisms, such as plants or fungi [37]. In addition, the application of host blocking primers in fish samples improved the detection of protozoans and detected only the eukaryotic species of interest by binding to the host DNA [38].
Although some intestinal microeukaryotes are linked to disease, others may serve as commensal or beneficial members of the gut ecosystem [39]. They are hypothesized to contribute to microbiota balance and may engage in symbiotic relationships with their fish host. Therefore, this review aims to synthesize current knowledge on the teleost intestinal microeukaryotes in fish, focusing on their diversity, ecological and physiological functions, and future research directions, to understand their role in fish health and microbial ecology. The applied research in this review was conducted employing the following keywords: “microeukaryotes”, “microeukaryome”, “eukaryotic microorganisms”, and “fish gut microbiota”.
2. Diversity of Microeukaryotes in the Intestinal Microbiota
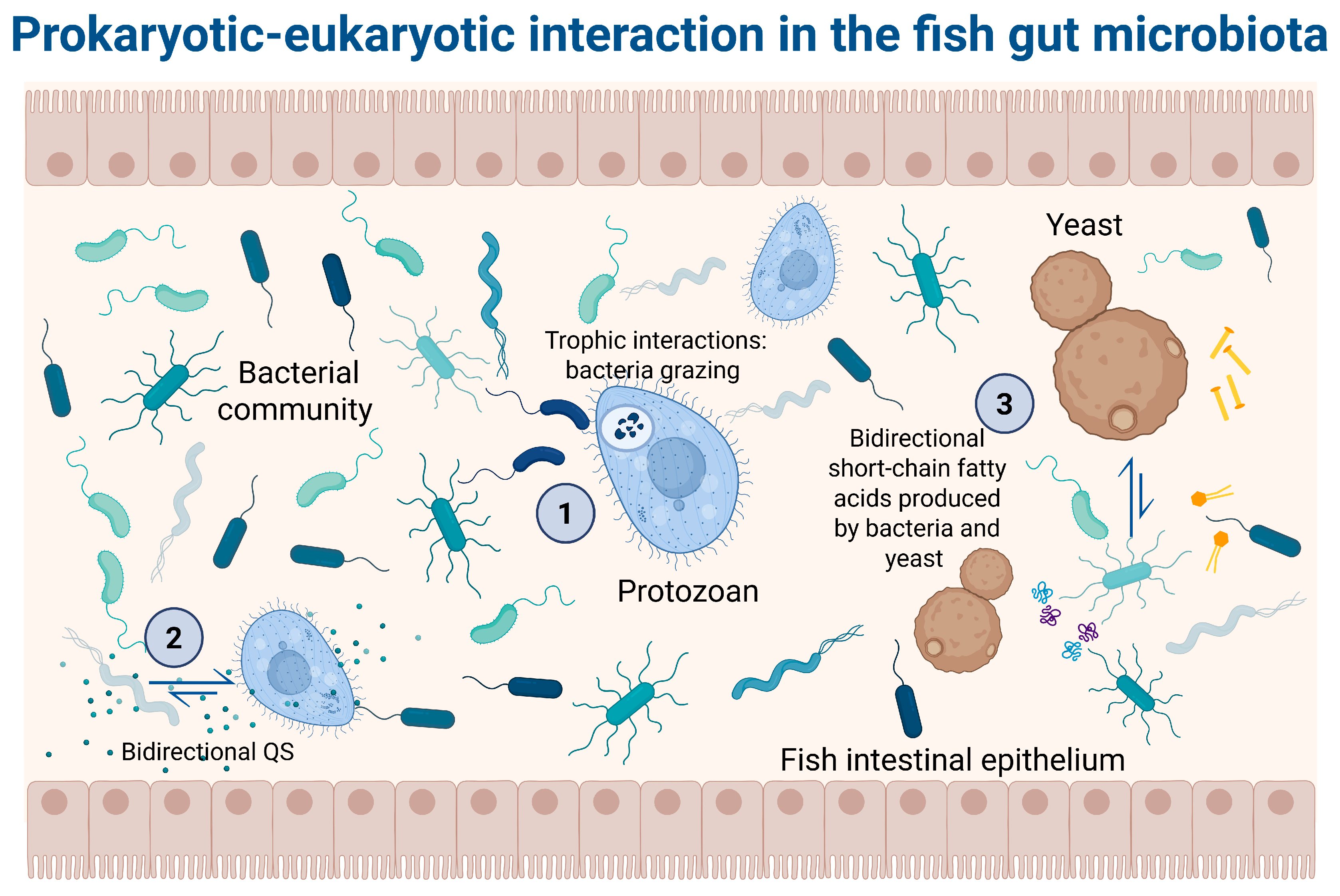
Microeukaryotic microorganisms inhabiting the intestinal tracts of fish represent a wide array of life forms, including fungi (both yeasts and filamentous types), metazoan parasites (e.g., nematodes, cestodes, helminths), and protozoans [39] (Figure 1). Although they are typically less abundant and diverse than prokaryotes [40], recent advances in sequencing technologies have enabled better characterization of these complex microbial components.
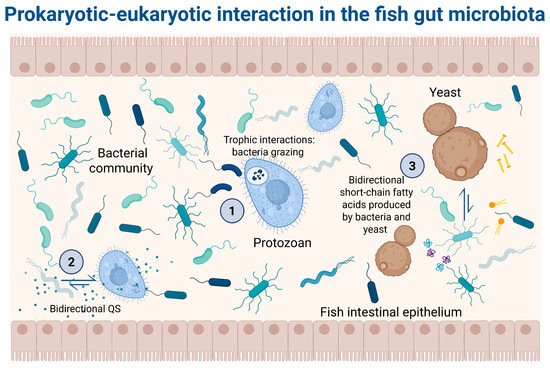
Figure 1.
Prokaryotic–eukaryotic interaction in the fish gut microbiota. (1) Trophic interaction: bacteria predation by protozoan, leading to nutrient regeneration, such as phosphorus and nitrogen. Moreover, protozoans may regulate bacterial community structure by grazing behavior, consuming more than 1000 bacterial cells per hour [41]. (2) Bidirectional quorum sensing (QS): Chemical signals produced by bacteria are used by protozoans to communicate among themselves. For example, bacteria can synthesize N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) that bind with the AHL receptors in some protozoans. Similarly, QS communication through the MHF [4-hydroxy-5-methylfuran-3 (2H)-one] production by fungi cells has been reported [42]. (3) Interaction through metabolite production: Bacteria release a diversity of metabolites that can be used by certain protozoans, such as short-chain fatty acids, like butyrate, produced by bacteria (Faecalibacterium and Roseburia). Yeasts like Saccharomyces boulardii can produce an antitoxic effect against toxins secreted by bacteria. Additionally, yeasts can produce an antimicrobial effect by the production of short-chain fatty acids and polyamines. Finally, protozoans like Tritrichomonas musculis influence the host’s metabolism to release free choline, which can be utilized by choline-utilizing bacteria, thereby promoting a healthier bacterial community [43,44].
In zebrafish, for example, the fungal phylum Ascomycota has been identified as dominant, accounting for approximately 87.5% of all fungal sequences, followed by Basidiomycota (6.8%), and a smaller proportion of Zygomycota and unclassified fungi (5.7%) [45]. Protozoans have been detected in marine fish; for instance, Blastocystis sp. was detected in herring, whiting, saithe, and mackerel [46]. Other eukaryotic taxa commonly found in the fish gut include crustaceans, mollusks, rotifers, copepods, and diatoms [47,48]. These findings collectively illustrate a surprisingly broad microeukaryotic diversity within the fish gut, many of which are structurally, behaviorally, and evolutionarily more complex than their prokaryote counterparts. Despite this diversity, defining a consistent profile for the fish intestinal microeukaryome remains challenging. The scarcity of reference sequences, variability in sampling and sequencing methods, and limited geographic and taxonomic coverage have prevented large-scale comparative analyses across fish species (Table 1).
A notable microeukaryotic feature is their genomic complexity. Fungal genomes, for example, range from 9 to nearly 180 megabases and encode between 10,000 and 25,000 genes, whereas bacterial genomes typically span less than 1 to 8 megabases and have 600 to ~6000 genes [42,49,50]. This greater complexity may confer broader functional capabilities; however, mutualistic or symbiotic roles in fish are still poorly defined compared to bacteria.
Emerging evidence suggests these microbes are involved in critical physiological processes, including beneficial activities. Their primary beneficial attribute, the probiotic function, has been associated with microeukaryotes from the digestive tract [39,51,52]. Some yeasts isolated from the gut of healthy salmonids, yellowtail, and croakers exhibit antagonistic activities against pathogens, promote intestinal maturation, and modulate antioxidant enzymes [53,54]. High intestinal microeukaryotic diversity has also been associated with reduced disease prevalence in healthy individuals [55,56], suggesting a potential protective role.
Recent studies suggest that certain ecological and immunological roles of gut microeukaryotes may be conserved across vertebrate lineages, including fish and mammals. For example, fungal genera such as Candida and Saccharomyces, commonly found in both mammalian and fish intestines, produce immunomodulatory compounds, including β-glucans and mannans, that can stimulate mucosal immunity and enhance barrier integrity [57,58]. Similarly, protozoans such as Blastocystis (once considered purely pathogenic) have been associated with increased bacterial diversity and reduced inflammation in both human and fish models, indicating a possible symbiotic or regulatory role [59,60]. Furthermore, protozoans have been shown to influence bacterial community structure through selective grazing in both mice and fish, suggesting a conserved top-down ecological impact [61]. Although functional studies in fish remain limited compared to those in mammals, these parallels suggest that microeukaryotes play evolutionarily conserved roles in host immune modulation, microbial homeostasis, and potentially even host metabolism. Integrating findings from both vertebrate groups could provide deeper insights into the ecological significance of microeukaryotes across animal microbiomes.
In summary, the intestinal microeukaryome in fish is taxonomically rich and functionally promising, though significantly underexplored. Future studies will be essential to determine whether observed taxa are transient dietary passengers or consistent, active members of the gut ecosystem, and what roles they may play in host physiology, health, and microbial balance. To distinguish whether microeukaryotes in the fish intestine are long-term residents or transients, researchers examine their location (mucosa-associated vs. gut contents), metabolic activity (via RNA-based sequencing), and persistence over time or diet changes. Microscopy and Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) can reveal whether they adhere to or interact with the intestinal lining, indicating colonization. Experimental approaches, such as controlled feeding trials or gnotobiotic models, further help confirm whether specific taxa can survive and establish in the gut. Together, these methods differentiate active, resident microeukaryotes from transient ones simply passing through the digestive tract.

Table 1.
Gut microeukaryote composition in fish species.
Table 1.
Gut microeukaryote composition in fish species.
| Fish Species | Microeukaryote Composition | Habitat and Feeding Habits | Ribosomal Gene Region | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zebrafish, Danio rerio | 87.5% Ascomycota and 6.8% Basidiomycota | Model study fish; omnivorous freshwater species | ITS2 | [45] |
| Amazonian catfish, Panaque nigrolineatus | 40% Dothideomycetes and 36% Sordariomycetes | Freshwater, wood-eating fish | ITS1 | [62] |
| Cobia Fish, Rachycentron canadum | 88% Ascomycota and 11% Basidiomycota | Carnivorous marine benthopelagic fish, Tropical fish | ITS2 | [63] |
| Grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella | 68.2% Ascomycota, 13.4% Basidiomycota, 12.1% Mortierellomycota, and 0.5% Chytridiomycota | Aquatic macrophytes, algae, invertebrates, and vertebrates | ITS1 and ITS2 | [64] |
| Black carp, Mylopharyngodon piceus | 68.6% Ascomycota, 12.3% Basidiomycota, 9.4% Mortierellomycota, and 1.07% Chytridiomycota | Mollusk-eating cyprinid fish native to eastern Asia | ITS1 and ITS2 | [64] |
| Bighead carp, Aristichthys nobilis | 39.3% Ascomycota, 42% Rozellomycota, and 1.4% Basidiomycota | Filter-feeding freshwater fish from Hongchaojiang Reservoir in Guangxi, China | ITS | [65] |
| Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niluticus | 48.9% Ascomycota, 2.4% Basidiomycota, and 0.6% Rozellomycota 90–98% Opisthokonta, 0.3–7.5% Bacillariophyta, and > 0.5% Archaeplastida | Wild tilapia from Lake Nasser, Egypt Feeding on plankton, some aquatic macrophytes, fish larvae, and decaying organic tissue | ITS 18S region V9 | [65] |
| Mullet, Mugil cephalus | Gut content mainly by Rotifera and Copepoda, followed by Bacillariophyceae and Chlorophyceae. | Inhabit coastal temperate and tropical waters | 18S |
3. Fungi in the Intestinal Microbiota of Fish
Fungi are key ecological players across ecosystems, functioning as mutualists, decomposers, and pathogens. They represent one of the most diverse biological kingdoms [66,67]. Within the gut ecosystem, fungi are increasingly recognized as integral microbiota members, contributing to host health through various physiological and immunological mechanisms [68,69]. Although fungal cells constitute a much smaller fraction of the intestinal microbiota than bacteria, they are significantly larger and possess greater genomic complexity [30,32,70].
In fish, intestinal fungi form structured communities interacting with bacteria and other microorganisms through synergistic, antagonistic, or symbiotic relationships (Table 2). These interactions are inferred to help preserve microbiota stability, regulate the mucosal barrier function, and support immune system development [58].
Among fungal phyla, Ascomycota is consistently reported as the dominant group in teleost intestines. For instance, studies on Barramundi (L. calcarifer), Golden Permit (T. blochii), Royal Pleco (Panaque nigrolineatus), the silver pompano (Trachinotus blochii), and Mangrove Red Snapper (Lutjanus argentimaculatus) have reported twelve genera from the Ascomycota phylum (Aspergillus, Penicillium, Talaromyces, Aureobasidium, Cladosporium, Fusarium, Clonostachys, Myrothecium, Parengyodontium, Trichoderma, Hypocrea, Microsphaeropsis) [62]. Three Basidiomycota genera (Schizophyllum, Rigidoporus, and Cutaneotrichosporon) were also identified [71]. In zebrafish, more than 15 fungal classes were detected across Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Zygomycota phyla, with Ascomycota comprising 87.5% of the identified sequences [45]. Similar patterns were observed in cobia fish (Rachycentron canadum), where the fungal microbiota consisted mainly of Ascomycota (~88%) and Basidiomycota (~11%), with Ascobulus identified as a novel core genus in fish [63].

Table 2.
Fungal activity and function in fish intestinal microbiota.
Table 2.
Fungal activity and function in fish intestinal microbiota.
| Fungal Species | Function/Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Debaryomyces hansenii | Gut maturation, increasing amylase secretion, and probiotic potential | [45,72,73] |
| Candida spp. | Associated with lipid metabolism and fermentation activities | [74] |
| Aureobasidium pullulans | Active against pathogenic yeast strains | [71,73] |
| Schizophyllum commune | Isolated from coral reef fish intestines; antimicrobial activity | [71] |
| Pichia kudriavzevii | Extracellular enzyme-producing (amylase, protease, lipase, cellulase, xylanase, and phytase) | [74] |
| Yarrowia lipolytica | Directing anti-Vibrio action and modulating the host’s innate immune system | [75] |
These taxonomic similarities across species suggest the existence of a conserved fungal core microbiota in fish. When the fungal diversity of three coral reef fish (Lates calcarifer, Trachinotus blochii, and Lutjanus argentimaculatus) was compared, similar taxonomic profiles among the three fish species were observed [71]. Further, species from the Ascomycota phylum, Debaryomyces hansenii and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa, are consistently found in salmonids regardless of the rearing condition. Moreover, Sordariomycetes and Tremellomycetes are fungal taxa found in wild and laboratory-reared zebrafish guts [45,76]. In addition, the anatomical location within the gut seems to influence fungal distribution. For example, yeast richness is generally higher in the foregut and midgut than in the hindgut, possibly reflecting the distinct physiological roles of these regions [71].
While the specific functions of many fungal taxa remain uncharacterized, some genera show promising contributions. For instance, Rhodotorula (Basidiomycota) and Debaryomyces (Ascomycota), frequently found in freshwater and marine fish, dominate the rainbow trout gut [77]. These yeasts produce immunostimulatory compounds such as β-glucans, nucleic acids, and mannan oligosaccharides that enhance host immunity and may protect against pathogens [63,78,79].
The enhancement of metabolic capacity is another contribution of fungi. In carnivores such as the red cusk-eel (Genypterus chilensis) and the Chilean hake (Seriolella violacea), fungal isolates have shown enzymatic activities including proteases, lipases, glycosidases, and phosphatases. These isolates included Rhodotorula mucilaginosa, Candida palmioleophila, Candida pseudorugosa, Cystobasidium slooffiae, and a member of the genus Yamadazyma, and their enzymatic profiles are aligned with dietary components such as phospholipids, algae, hydrolyzed marine proteins, and unsaturated fatty acids, suggesting that fungi contribute to digestive efficiency and metabolic capacity [80,81,82]. On the other hand, in the black carp and herbivorous carp, Ascomycota and Basidiomycota were the dominant phyla in the fish gut. Both phyla contain members capable of decomposing complex organic matter [64], providing additional metabolic capabilities to the fish.
Species from the Ascomycota phylum, including Candida, Debaryomyces, and Saccharomyces, are commonly found in freshwater and marine fish and are implicated in carbohydrate fermentation and potential probiotic activities [6,83]. Ascomycota includes species that produce digestive enzymes, which promote optimal growth and development by maximizing nutrient utilization and significantly influencing overall health and metabolism [74,78,84]. The conservative functions of the Ascomycota phylum within the gut in fish could be a result of its stability in the gut despite environmental factors [85]. Also, this group has the capability to modify the composition of lectin in the mucinous content of goblet cells, which plays an important role in gut health and condition [86]. Additionally, they can produce extracellular phytases, which are involved in the degradation of phytate [45]. Finally, it is reported that they are capable of alkaloid biosynthesis. The properties of these organic molecules include antimicrobial and antioxidant activity [87].
Similarly, the Basidiomycota phylum has genera (Cryptococcus and Rhodotorula) also implicated in gut health through their metabolic byproducts and immunological interactions [88]. Although less prevalent, Chytridiomycota contribute to the breakdown of complex polymers, particularly in fish that consume algae or detritus, while Mortierellomycota may influence lipid metabolism and immune responses [89], although further research is needed to fully understand their functions. These fungal communities work synergistically with bacterial populations to enhance digestive efficiency, bolster pathogen resistance, and maintain gut homeostasis.
Hypothesized functions, based on studies in mammals, further suggest that gut fungi may influence bile acid metabolism, barrier integrity, and even neural signaling via the gut–brain axis. For instance, Candida and Saccharomyces can transform bile acids, potentially impacting lipid metabolism and microbial dynamics [90]. Fungal components like mannan and chitin may also interact with host epithelial and immune cells to strengthen mucosal defenses [57], mechanisms critical in fish, particularly under environmental stress or pathogen exposure. Furthermore, fungal dysbiosis has been linked to behavioral and cognitive alterations in rodent models, opening questions about whether similar mechanisms might operate in fish [91].
Although functional evidence in fish is still emerging, these findings collectively support the idea that fungi are not passive gut inhabitants but may actively contribute to host physiology and gut homeostasis. Since most available research focuses on the influence of the fish environment and its modification of the gut microbiota, continued investigation, including gnotobiotic and multi-omics approaches, is essential to elucidate their ecological and metabolic roles. Notably, the use of gnotobiotic models allows the exclusion of environmental factors and their influence on the structure and interactions of fungi, protists, and prokaryotes.
Furthermore, the recurrence of specific fungal taxa such as Debaryomyces and Rhodotorula across diverse fish species suggests a possible conservation of functional traits like immune modulation and digestive enzyme production. Although interspecific variability exists, the consistent detection of these taxa across freshwater and marine environments implies that certain physiological roles, including the stimulation of host immunity and maintenance of gut homeostasis, may be conserved among teleosts.
4. Protists in the Fish Intestinal Microbiota
Protists are a diverse group of unicellular microeukaryotes that inhabit moist and aquatic environments, where they play a crucial role in ecological and trophic networks [92,93]. This group includes both autotrophic microorganisms (e.g., microalgae) [94] and heterotrophic protozoans, which can be classified by their locomotion strategies, such as flagella, cilia, and pseudopodia. Furthermore, among protozoans are the apicomplexans, which are exclusively parasitic and characterized by an apical complex (organelles underlying the oral structure) [93,95]. Additionally, protozoans exhibit a variety of reproductive methods, including the alternation between life stages (trophozoites and cysts), asexual reproduction through binary fission, and sexual reproduction; some protozoans can reproduce sexually and asexually [93]. This complex reproductive strategy allows some ciliate protozoans to modify their reproduction and feeding behavior based on the bacterial community available in the environment, thereby altering the media parameters [96].
Protozoans, in particular, are often overlooked in gut microbiota studies due to their relatively low abundance compared to bacteria. However, they are increasingly recognized as functionally relevant symbionts because of their interactions with bacterial communities [59]. Although many protozoans in fish have been traditionally viewed as pathogens, they have gained positive recognition; Blastocystis sp., a controversial protozoan in mammals, has been proposed as a marker of gut health [97], raising questions about similar roles in fish. Still, there is a lack of information about how protozoans integrate into an ecosystem primarily enriched with commensal bacteria [61].
Microscopy and molecular studies have revealed a variety of protozoan taxa inhabiting the fish gut. Notable examples include Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, Trichodina spp., Hexamita spp., and Spironucleus spp., found across various freshwater and marine species [98,99]. While some of these protozoans are known pathogens, others thrive in a commensal or opportunistic relationship with the host. Their presence suggests potential roles in shaping the gut ecology by directly interacting with host tissues or feeding on bacterial populations, thus shaping microbiota composition and dynamics. For instance, protists can consume up to 1000 bacterial cells per hour, positioning them as top-down regulators of microbial populations in the gut [93]. This grazing behavior, in turn, affects both bacterial abundance and community structure. Conversely, the stability and presence of protozoans are also shaped by bacterial diversity and nutrient availability, highlighting a reciprocal relationship between these microbial groups [61,100].
In Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from Lake Nasser, Egypt, gut microbiota analysis revealed that more than 90% of 18S rRNA sequences belonged to the flagellate group Opisthokonta, with diatoms (Bacillariophyta) representing less than 7.5% [47]. In another case, the ciliate Balantidium polyvacuolum was shown to increase bacterial diversity and promote the abundance of phyla such as Fusobacteria and Chloroflexi, associated with immune function, in Xenocyprinae fishes. Interestingly, infected fish were reported to be healthier than their uninfected counterparts [60]. Similar findings were observed with Balantidium ctenopharyngodoni in grass carp, where its presence correlated with increased levels of Clostridium and higher creatine concentration in the hindgut, indicative of enhanced physiological performance [101]. In other vertebrate models, protozoans can trigger mucosal immune responses, such as interleukin-18 release via inflammasome activation, which promotes protective Th1 and Th17 immune responses [102,103].
Nevertheless, many protozoans in fish are still primarily associated with disease [104]. Their presence is often accompanied by increased bacterial diversity and signs of inflammation or tissue disruption, as seen in other host systems [105,106]. Additionally, protozoans may act as vectors for bacterial pathogens [107] or exacerbate dysbiosis by modifying bacterial diversity in the gut microbiota [100]. For example, the ciliate Nyctotherus sp. was reported to reduce Proteobacteria abundance in Mesonauta festivus (Amazonian cichlid), a pattern associated with dysbiosis [108].
Notably, many protozoans in the fish gut may reflect dietary intake rather than established symbiotic relationships. In many cases, they are transient members that do not colonize the gut but instead pass through with ingested material.
Overall, intestinal protists in fish are multifaceted. While some act as pathogens, others may provide immunological benefits, regulate bacterial populations, or enhance gut health (Table 3). The dynamic nature of their interactions with the host and bacterial communities underscores the need for further investigation. Deciphering the ecological and functional significance of these protists will be crucial for a comprehensive understanding of gut microbiota in fish.

Table 3.
Protists’ activity and function in fish intestinal microbiota.
5. Other Microeukaryotes in the Fish Intestinal Microbiota
Beyond fungi and protozoans, various microeukaryotic organisms have been detected in the gastrointestinal tracts of fish. These include parasitic and free-living members of phyla such as Nematoda, Streptophyta, Platyhelminthes, and Acanthocephala, as well as taxa from mollusks, crustaceans, and zooplanktonic organisms. For instance, in the flag cichlid (Mesonauta festivus), 18S rRNA sequencing revealed a high prevalence of metazoan microeukaryotes in the gut, including Nyctotherus sp., Chromadorea (nematodes), Cestoda, Trematoda, and Neoechinorhynchida (acanthocephalans) [108]. These organisms are often linked to parasitism and are particularly common in detritivorous or omnivorous tropical fish, where trophic networks increase the likelihood of exposure to a wide range of environmental microeukaryotes.
While generally considered pathogenic, some helminths have demonstrated immunomodulatory effects in other hosts. In humans, for example, helminth infections in patients with early-stage multiple sclerosis have been associated with a halt in disease progression and the emergence of myelin-recognizing regulatory T cells (Treg) in the peripheral blood [112]. These findings raise interesting possibilities about the complex and potentially beneficial immunological roles of intestinal helminths in other vertebrates, including fish.
Eukaryotes such as crustaceans, mollusks, and fish larvae have also been found within the fish gut microbiota, often reflecting dietary intake rather than resident microbiota. In Oreochromis niloticus (Nile tilapia), members of the Ostracoda class (small crustaceans) were among the most abundant gut microeukaryotes detected [47]. Similarly, fish larvae such as Gobiocypris rarus and zooplankton like Acanthocyclops vernalis have been recovered from the guts of silver carp, grass carp, bighead carp, and blunt snout bream larvae [113]. In these cases, the shared presence of dietary microeukaryotes across multiple species likely reflects overlapping food sources rather than stable colonization. As such, these organisms are better described as transient microbiota, introduced with the diet and unlikely to contribute significantly to gut homeostasis or host physiology. A key challenge is distinguishing between core microeukaryotic residents and transient taxa derived from diet or environment. While genera like Candida and Debaryomyces appear across diverse fish species and may represent core components, others, such as diatoms or copepods, are likely dietary artifacts. Longitudinal studies and gnotobiotic models are needed to clarify colonization dynamics.
While nematodes, flatworms, and other helminths are often associated with pathogenesis, their broader ecological roles in the gut remain poorly characterized. Some, like Capillaria acanthopagri, have been identified as parasites of Acanthopagrus schlegelii (Blackhead seabream), and cestodes like Khawia sinensis are known to infect carp (Cyprinus carpio) [114,115]. Although these organisms may influence nutrient availability, tissue damage, or immune activation, they generally do not exhibit the mutualistic or commensal properties observed in fungal and protozoan communities. Instead, their presence is often linked to parasitism, resource competition, or diet-derived transience, with unclear or limited contributions to gut microbiota functionality.
In conclusion, while these other microeukaryotic taxa reveal the ecological complexity of the gut environment, their significance appears less critical than that of fungi and protozoans. Nonetheless, they may serve as indicators of environmental exposure, dietary habits, or parasitic burden and merit further study in the context of fish health and aquaculture.
6. Perspectives
Based on the previous research findings, we established the following perspectives. Despite recent advances in fish microbiome research, the microeukaryotic component of the intestinal microbiota remains significantly understudied compared to its prokaryotic counterpart. Understanding the diversity, ecology, and function of intestinal microeukaryotes is a promising research frontier with the potential to uncover new mechanisms of host-microbe interactions, immune modulation, and metabolic integration.
Environmental factors influencing microeukaryotic microbiota require thorough investigation. Factors such as diet, antibiotic use, and fish farming practices may differentially affect the composition and function of gut microeukaryotes, but the mechanisms behind this are not yet understood. Comparative studies across species and populations are essential to determine how these microorganisms vary and which environmental drivers shape these differences. The interactions between microeukaryotes and bacteria play a critical role in gut microbiota. Understanding how these interactions influence gut health and disease could provide novel insights into microbiota dynamics. In this regard, evaluating the in vitro relationship between gut prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes is crucial for comprehending their ecological interactions and collective impact on host health. These microbes influence each other through competition, predation, and metabolite exchange, shaping community composition and function. In vitro models offer controlled settings to study these dynamics, helping to uncover mechanisms that remain obscured in complex in vivo systems. Such research is especially valuable for developing microbiota-based interventions in aquaculture and other applied settings. Additionally, investigating the evolutionary relationships between these taxonomic groups, their hosts, and their adaptation mechanisms within the gut environment is essential for a comprehensive understanding of microbiota function.
On the other hand, using gnotobiotic models to study the relationship between gut prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes is essential for uncovering their functional roles in a controlled host context. This approach allows for precise manipulation of microbial communities, providing conditions to isolate and assess specific interkingdom interactions and their effects on host physiology. By eliminating the complexity of natural microbiota, gnotobiotic systems can offer deeper insight into how prokaryotic and eukaryotic members influence immune responses, nutrient absorption, and microbial balance.
Identifying and characterizing gut microeukaryotes presents a significant challenge in research on eukaryotic microbiota due to their greater complexity than that of prokaryotic microbiota. Therefore, developing advanced methodologies and technologies for accurate identification, quantification, and functional analysis is essential. Integrative approaches that combine multi-omics technologies with advanced imaging and in vivo experimentation will be essential for unveiling the ecological roles and metabolic contributions of microeukaryotes within the gut ecosystem. Moreover, interdisciplinary collaborations among parasitologists, microbiologists, immunologists, and aquaculture researchers are needed to bridge existing knowledge gaps and accelerate discovery in this underexplored area. As aquaculture expands, understanding the functional relevance of microeukaryotic communities in fish may contribute to sustainable farming practices. Microeukaryotes could indicate gut health, environmental stress, or even components of next-generation probiotics tailored for aquaculture species. These findings carry practical implications for aquaculture. Understanding the functional roles of gut microeukaryotes opens avenues for their biotechnological application, such as the development of tailored microbial consortia to enhance disease resistance, stress tolerance, and feed efficiency. For instance, probiotic yeasts like Debaryomyces have demonstrated benefits in larval fish by stimulating digestive enzyme activity and promoting immune readiness [45,54]. Additionally, microeukaryotic diversity may serve as an indicator of gut resilience under environmental or dietary challenges, providing a diagnostic tool for health monitoring in aquaculture systems. Therefore, future research must focus on taxonomic identification, functional relevance, and application, positioning microeukaryotes as central players in host–microbiota interactions within aquatic environments.
Hypothetically, intestinal microeukaryotes could be developed as functional components in aquaculture biotechnology. Several studies have demonstrated the probiotic potential of gut-derived yeasts, such as Debaryomyces hansenii and Yarrowia lipolytica, in improving fish immunity and growth. Likewise, protozoans that influence bacterial community composition through grazing or competitive exclusion could, in theory, be used to stabilize gut microbiota under stressful farming conditions. In addition, shifts in the abundance or diversity of specific microeukaryotic taxa might one day serve as early-warning bioindicators of intestinal dysbiosis, disease onset, or environmental stressors. These potential applications, while still speculative, highlight the untapped value of microeukaryotes in promoting sustainable aquaculture and warrant targeted investigation using controlled in vivo and in vitro models. Additionally, they may also serve as bioindicators of gut health or environmental stress, especially in intensive aquaculture systems. Thus, integrating microeukaryotic biomarkers into routine aquaculture diagnostics and exploring targeted microbial supplementation could enhance sustainability and disease prevention strategies.
7. Conclusions
Studying intestinal eukaryotic microorganisms in fish is crucial for understanding their roles in host health and well-being. These microorganisms, including fungi, protists, and other microeukaryotes, play essential roles in nutrient digestion, immune system modulation, and interactions with various gut microbiota components. Fungi significantly contribute to nutrient decomposition and maintain intestinal health while facilitating the production of immunostimulant compounds and digestive processes through specific enzymes. Meanwhile, although often regarded as parasites, protists can also fulfill commensal and mutualistic roles. The diversity and complexity of these microorganisms highlight their importance in the intestinal ecology of fish. Understanding their functions and interactions can enhance aquaculture practices and promote sustainability in the sector. Future research should focus on exploring this diversity and the impacts of these microorganisms on fish health, aiming to optimize aquaculture practices and ensure the health and well-being of fish populations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.-P. and F.V.-A.; investigation, J.S.O.G.-F., M.M.-P., F.V.-A., E.G.-V.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S.O.G.-F., M.M.-P., F.V.-A., D.M.-F.; writing—review and editing, M.M.-P., L.R.M.-C., Y.M.-M.; visualization, M.M.-P., E.G.-V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- McFall-Ngai, M.; Hadfield, M.G.; Bosch, T.C.; Carey, H.V.; Domazet-Lošo, T.; Douglas, A.E.; Dubilier, N.; Eberl, G.; Fukami, T.; Gilbert, S.F.; et al. Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, R.M.; Dourado, M.N.; Araújo, W.L. Microbial interactions: Ecology in a molecular perspective. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47 (Suppl. 1), 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, U.; Steinert, M.; Hacker, J. Common molecular mechanisms of symbiosis and pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Kang, D.W.; DiBaise, J.K. Effects of gut microbes on nutrient absorption and energy regulation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2012, 27, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Boutin, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Derome, N. Teleost microbiomes: The state of the art in their characterization, manipulation and importance in aquaculture and fisheries. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, W.B.; Lindsay, E.; Payne, C.J.; Brodie, C.; Kazlauskaite, R. The role of the gut microbiome in sustainable teleost aquaculture. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20200184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Dai, W.; Li, C. Advances, challenges, and directions in shrimp disease control: The guidelines from an ecological perspective. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6947–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-G.; Malo, M.E.; Tschirhart, T.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dadachova, E.; Sun, J. Effects of Melanized Bacteria and Soluble Melanin on the Intestinal Homeostasis and Microbiome In Vivo. Toxics 2023, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kers, J.G.; Velkers, F.C.; Fischer, E.A.J.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Lamot, D.M.; Stegeman, J.A.; Smidt, H. Take care of the environment: Housing conditions affect the interplay of nutritional interventions and intestinal microbiota in broiler chickens. Anim. Microbiome 2019, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, R.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Stress-induced immune dysfunction: Implications for health. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, T.J.; Jemielita, M.; Baker, R.P.; Schlomann, B.H.; Logan, S.L.; Ganz, J.; Melancon, E.; Eisen, J.S.; Guillemin, K.; Parthasarathy, R. Host Gut Motility Promotes Competitive Exclusion within a Model Intestinal Microbiota. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S. Do an Altered Gut Microbiota and an Associated Leaky Gut Affect COVID-19 Severity? mBio 2021, 12, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Albores, F.; Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; Cicala, F.; Lago-Leston, A.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Therapeutic modulation of fish gut microbiota, a feasible strategy for aquaculture? Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, C.J.; Beiko, R.G. A phylogenomic view of ecological specialization in the Lachnospiraceae, a family of digestive tract-associated bacteria. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, Q. Comparative study on the gut microbiotas of four economically important Asian carp species. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, S.; Gras-Leguen, C.; Le Vacon, F.; Potel, G.; de La Cochetiere, M.F. Development of intestinal microbiota in infants and its impact on health. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Saito, H.; Tani, S.; Ikeo, R.; Kawai, K. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiome from tilapia species across several regions in Japan. Aquaculture 2023, 576, 739809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, F.; Wu, J.; Du, Z.Y.; Zhang, M. Influence of Endogenous and Exogenous Estrogenic Endocrine on Intestinal Microbiota in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Limbu, S.M.; Shen, M.; Zhai, W.; Qiao, F.; He, A.; Du, Z.Y.; Zhang, M. Environmental concentrations of antibiotics impair zebrafish gut health. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Xu, X.; Shao, N.; He, J.; Li, P.; Xu, P.; Hu, J.; Qin, W.; Wang, B.; Xu, G. Integrative analysis of microbiome and metabolome reveals the linkage between gut microbiota and carp growth. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Félix, D.; Garibay-Valdez, E.; Vargas-Albores, F.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Fish disease and intestinal microbiota: A close and indivisible relationship. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 820–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lv, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, F.; Sheng, R.; Qin, Y.; Rao, L.; Lu, T.; Sun, L. Comparative study of gut content microbiota in freshwater fish with different feeding habits: A case study of an urban lake. J. Fish Biol. 2025, 106, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyholm, L.; Odriozola, I.; Martin Bideguren, G.; Aizpurua, O.; Alberdi, A. Gut microbiota differences between paired intestinal wall and digesta samples in three small species of fish. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaci, N.; Borrel, G.; Tottey, W.; O’Toole, P.W.; Brugère, J.-F. Archaea and the human gut: New beginning of an old story. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 16062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuphal, N.; Singha, K.P.; Sardar, P.; Sahu, N.P.; Shamna, N.; Kumar, V. Scope of archaea in fish feed: A new chapter in aquafeed probiotics? Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1668–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, P.D.; Marchesi, J.R. Micro-eukaryotic diversity of the human distal gut microbiota: Qualitative assessment using culture-dependent and -independent analysis of faeces. ISME J. 2008, 2, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Campo, J.; Bass, D.; Keeling, P.J. The eukaryome: Diversity and role of microeukaryotic organisms associated with animal hosts. Funct. Ecol. 2020, 34, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener Parfrey, L.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R. Microbial Eukaryotes in the Human Microbiome: Ecology, Evolution, and Future Directions. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, N.; Wang, J.; Zeng, J.; Lo, E.; Moon, D.H.; Luk, K.; Braun, R.O.; Burroughs, L.M.; Keel, S.B.; Reilly, C.; et al. Small-Molecule PAPD5 Inhibitors Restore Telomerase Activity in Patient Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 896–909.e898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan-Nash, A.D.; Korry, B.J.; Mylonakis, E.; Belenky, P. Cross-Domain and Viral Interactions in the Microbiome. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2019, 83, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, R.M.; Gao, Z.M.; Bougouffa, S.; Qian, P.-Y. Optimal Eukaryotic 18S and Universal 16S/18S Ribosomal RNA Primers and Their Application in a Study of Symbiosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Chi, L.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, X.; Tu, P.; Li, B.; Yin, J.; Gao, N.; Shen, W.; Schnabl, B. An Introduction to Next Generation Sequencing Bioinformatic Analysis in Gut Microbiome Studies. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, I.; Kasapidis, P.; Karakassis, I.; Pitta, P. A Comparison of DNA Metabarcoding and Microscopy Methodologies for the Study of Aquatic Microbial Eukaryotes. Diversity 2021, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heravi, F.S.; Zakrzewski, M.; Vickery, K.; Hu, H. Host DNA depletion efficiency of microbiome DNA enrichment methods in infected tissue samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 170, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langsiri, N.; Meyer, W.; Irinyi, L.; Worasilchai, N.; Pombubpa, N.; Wongsurawat, T.; Jenjaroenpun, P.; Luangsa-ard, J.J.; Chindamporn, A. Optimizing fungal DNA extraction and purification for Oxford Nanopore untargeted shotgun metagenomic sequencing from simulated hemoculture specimens. mSystems 2025, 10, e01166-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patchett, A.L.; Rigby, M.L.; Wynne, J.W. Improved 18S rDNA profiling of parasite communities in salmonid tissues using a host blocking primer. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukeš, J.; Stensvold, C.R.; Jirků-Pomajbíková, K.; Wegener Parfrey, L. Are Human Intestinal Eukaryotes Beneficial or Commensals? PLOS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, P.J.; Campo, J.D. Marine Protists Are Not Just Big Bacteria. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R541–R549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, L.; Shinn, A.P.; Pratoomyot, J.; Bastos Gomes, G. Unveiling associations between ciliate parasites and bacterial microbiomes under warm-water fish farm conditions—A review. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1097–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Albores, F.; Garibay-Valdez, E.; Medina-Félix, D.; Martínez-Porchas, M. The micro-eukaryotic community: An underrated component of the mammalian gut microbiota? Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1123513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audebert, C.; Even, G.; Cian, A.; Loywick, A.; Merlin, S.; Viscogliosi, E.; Chabé, M. Colonization with the enteric protozoa Blastocystis is associated with increased diversity of human gut bacterial microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, X.; Liu, M.; Xu, S.; Jing, Q.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. A Murine Commensal Protozoan Influences Host Glucose Homeostasis by Facilitating Free Choline Generation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e02413-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriyappagouder, P.; Kiron, V.; Lokesh, J.; Rajeish, M.; Kopp, M.; Fernandes, J. The Intestinal Mycobiota in Wild Zebrafish Comprises Mainly Dothideomycetes While Saccharomycetes Predominate in Their Laboratory-Reared Counterparts. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantois, N.; Lamot, A.; Seesao, Y.; Creusy, C.; Li, L.L.; Monchy, S.; Benamrouz-Vanneste, S.; Karpouzopoulos, J.; Bourgain, J.L.; Rault, C.; et al. First Report on the Prevalence and Subtype Distribution of Blastocystis sp. in Edible Marine Fish and Marine Mammals: A Large Scale-Study Conducted in Atlantic Northeast and on the Coasts of Northern France. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaied, H.E.; Soliman, T.; Abu-Taleb, H.T.; Goto, H.; Jenke-Kodam, H. Phylogenetic characterization of eukaryotic and prokaryotic gut flora of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, along niches of Lake Nasser, Egypt, based on rRNA gene high-throughput sequences. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2019, 11, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaied, H.; Taleb, H.; Wassel, M.; Rashed, M. Composition of eukaryotic and prokaryotic rRNA gene phylotypes in guts of adults and fingerlings of Mugil Cephalus inhabiting an Egyptian Mediterranean Estuary. J. Phylogenetics Evol. Biol. 2021, 4, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Bae, H. The diversity of fungal genome. Biol. Proced. Online 2015, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koduru, S.K. Chapter 24—The Impact of Bioinformatics Tools in the Development of Antimicrobial Drugs and Other Agents. In Recent Developments in Applied Microbiology and Biochemistry; Buddolla, V., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseyin, C.E.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cotter, P.D.; Scanlan, P.D. Forgotten fungi-the gut mycobiome in human health and disease. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 479–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensvold, C.R. Pinning down the role of common luminal intestinal parasitic protists in human health and disease—Status and challenges. Parasitology 2019, 146, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruffo, M.; Navarrete, N.; Salgado, O.; Díaz, A.; López, P.; García, K.; Feijóo, C.G.; Navarrete, P. Potential probiotic yeasts isolated from the fish gut protect zebrafish (Danio rerio) from a Vibrio anguillarum challenge. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Mazurais, D.; Gatesoupe, J.; Quazuguel, P.; Cahu, C.; Zambonino-Infante, J. Dietary probiotic live yeast modulates antioxidant enzyme activities and gene expression of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. Aquaculture 2010, 300, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rook, G.A.; Raison, C.L.; Lowry, C.A. Microbial ‘old friends’, immunoregulation and socioeconomic status. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 177, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliev, I.D.; Leonardi, I. Fungal dysbiosis: Immunity and interactions at mucosal barriers. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.V.; Leonardi, I.; Iliev, I.D. Gut Mycobiota in Immunity and Inflammatory Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 1365–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabé, M.; Lokmer, A.; Ségurel, L. Gut protozoa: Friends or foes of the human gut microbiota? Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Zou, H.; Li, M.; Wang, G. Alterations of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids induced by Balantidium polyvacuolum in the hindgut of Xenocyprinae fishes providing new insights into the relationship among protozoa, gut microbiota and host. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1295456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Gao, J.; Kou, Y.; Meng, L.; Zheng, X.; Liang, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Commensal bacteria impact a protozoan’s integration into the murine gut microbiota in a dietary nutrient-dependent manner. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00303-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marden, C.L.; McDonald, R.; Schreier, H.J.; Watts, J.E.M. Investigation into the fungal diversity within different regions of the gastrointestinal tract of Panaque nigrolineatus, a wood-eating fish. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinoso, S.; Gutiérrez, M.S.; Reyes-Jara, A.; Toro, M.; García, K.; Reyes, G.; Argüello-Guevara, W.; Bohórquez-Cruz, M.; Sonnenholzner, S.; Navarrete, P. Feed Regime Slightly Modifies the Bacterial but Not the Fungal Communities in the Intestinal Mucosal Microbiota of Cobia Fish (Rachycentron canadum). Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.-X.; Wu, J.-Q.; Liu, J.-L.; Tan, Z.-J. Association of Fungi in the Intestine of Black Carp and Grass Carp Compared with their Cultured Water. Aquac. Res. 2023, 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; He, A. Comparison of fungal community composition within different intestinal segments of tilapia and bighead carp. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, A.; Hector, A. Getting the measure of biodiversity. Nature 2000, 405, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, J.P.; Mueller, G.M. An estimate of the lower limit of global fungal diversity. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, E.; Penders, J.; Venema, K. Fungal-Bacterial Interactions in the Human Gut of Healthy Individuals. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satala, D.; Bras, G.; Kozik, A.; Rapala-Kozik, M.; Karkowska-Kuleta, J. More than Just Protein Degradation: The Regulatory Roles and Moonlighting Functions of Extracellular Proteases Produced by Fungi Pathogenic for Humans. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffnagle, G.B.; Noverr, M.C. The emerging world of the fungal microbiome. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J.; Xu, D.; Yang, Q.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, X. Diversity and Antimicrobial Activity of Intestinal Fungi from Three Species of Coral Reef Fish. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, D.; Zambonino, J.; Cahu, C.; Gatesoupe, F.J.; Vázquez-Juárez, R.; Lésel, R. Effect of live yeast incorporation in compound diet on digestive enzyme activity in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. Aquaculture 2002, 204, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yue, L.; Chi, Z.; Wang, X. Marine killer yeasts active against a yeast strain pathogenic to crab Portunus trituberculatus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 80, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Ghosh, K. Enumeration of gut associated extracellular enzyme-producing yeasts in some freshwater fishes. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruffo, M.; Navarrete, N.C.; Salgado, O.A.; Faúndez, N.B.; Gajardo, M.C.; Feijóo, C.G.; Reyes-Jara, A.; García, K.; Navarrete, P. Protective yeasts control V. anguillarum pathogenicity and modulate the innate immune response of challenged zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raggi, P.; Lopez, P.; Diaz, A.; Carrasco, D.; Silva, A.; Velez, A.; Opazo, R.; Magne, F.; Navarrete, P.A. Debaryomyces hansenii and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa comprised the yeast core gut microbiota of wild and reared carnivorous salmonids, croaker and yellowtail. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatesoupe, F. Live yeasts in the gut: Natural occurrence, dietary introduction, and their effects on fish health and development. Aquaculture 2007, 267, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Gatlin, D.M., III. Nucleotide nutrition in fish: Current knowledge and future applications. Aquaculture 2006, 251, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesh, J.; Fernandes, J.M.; Korsnes, K.; Bergh, O.; Brinchmann, M.F.; Kiron, V. Transcriptional regulation of cytokines in the intestine of Atlantic cod fed yeast derived mannan oligosaccharide or β-glucan and challenged with Vibrio anguillarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Reiriz, M.J.; Labarta, U.; Ferreiro, M.J. Effects of commercial enrichment diets on the nutritional value of the rotifer (Brachionus plicatilis). Aquaculture 1993, 112, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamre, K. Nutrient profiles of rotifers (Brachionus sp.) and rotifer diets from four different marine fish hatcheries. Aquaculture 2016, 450, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, B.; Ruiz, J.J.; Gutiérrez, M.S.; Alveal, K.; Caruffo, M.; Oliva, M.; Flores, H.; Silva, A.; Toro, M.; Reyes-Jara, A.; et al. Cultivable Yeast Microbiota from the Marine Fish Species Genypterus chilensis and Seriolella violacea. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajardo, K.; Rodiles, A.; Kortner, T.M.; Krogdahl, Å.; Bakke, A.M.; Merrifield, D.L.; Sørum, H. A high-resolution map of the gut microbiota in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): A basis for comparative gut microbial research. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Chi, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, G.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Production, characterization and gene cloning of the extracellular enzymes from the marine-derived yeasts and their potential applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 236–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Harikrishnan, R.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Ringø, E. Fungi and Actinobacteria: Alternative Probiotics for Sustainable Aquaculture. Fishes 2023, 8, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanahuja, I.; Ruiz, A.; Firmino, J.P.; Reyes-López, F.E.; Ortiz-Delgado, J.B.; Vallejos-Vidal, E.; Tort, L.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Cerezo, I.M.; Moriñigo, M.A.; et al. Debaryomyces hansenii supplementation in low fish meal diets promotes growth, modulates microbiota and enhances intestinal condition in juvenile marine fish. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naya-Català, F.; Piazzon, M.C.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Diet and Host Genetics Drive the Bacterial and Fungal Intestinal Metatranscriptome of Gilthead Sea Bream. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 883738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, L.; Hao, J.; Cai, W.; Qin, M.; Gao, Q.; Nie, M.; Qi, D.; Ma, R. Effects of plant-derived protein and rapeseed oil on growth performance and gut microbiomes in rainbow trout. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Li, G.; Huang, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B. The Gut Microbiota and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2017, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer, S.S.; Hwang, S.; Clayton, J.B. Antibiotic-induced gut dysbiosis and cognitive, emotional, and behavioral changes in rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1237177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burki, F.; Sandin, M.M.; Jamy, M. Diversity and ecology of protists revealed by metabarcoding. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R1267–R1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, R. Non-pathogenic protozoa. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.K. Protozoans: Animals or Protists? Int. J. Life Sci. 2021, 9, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.A. Evolution of the Apicomplexa: Where are we now? Trends Parasitol. 2009, 25, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.B.; Hutson, K.S.; Domingos, J.A.; Villamil, S.I.; Huerlimann, R.; Miller, T.L.; Jerry, D.R. Parasitic protozoan interactions with bacterial microbiome in a tropical fish farm. Aquaculture 2019, 502, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzo, G.L.; Mittinty, M.N.; Llamas, B.; Andrews, J.M.; Weyrich, L.S. Individuals with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Have an Altered Gut Microbiome Composition of Fungi and Protozoa. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, L.; Quilichini, Y.; Marchand, B. Sparicotyle chrysophrii (Van Beneden and Hesse 1863) (Monogenea: Polyopisthocotylea) parasite of cultured Gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata (Linnaeus 1758) (Pisces: Teleostei) from Corsica: Ecological and morphological study. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timur, G.; Karataş Steinum, S.; Akayli, T.; Demircan, M.D.; Yardimci, R. A histopathological study of Hexamitiasis in farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fry in Turkey. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2009, 29, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, E.R.; Lynch, J.; Froment, A.; Lafosse, S.; Heyer, E.; Przeworski, M.; Blekhman, R.; Segurel, L. Variation in rural African gut microbiota is strongly correlated with colonization by Entamoeba and subsistence. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Bu, X.; Zhou, W.; Zeng, Q.; Qin, T.; Wu, S.; Li, W.; Zou, H.; Li, M.; Wang, G. Interactions between Balantidium ctenopharyngodoni and microbiota reveal its low pathogenicity in the hindgut of grass carp. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudnovskiy, A.; Mortha, A.; Kana, V.; Kennard, A.; Ramirez, J.D.; Rahman, A.; Remark, R.; Mogno, I.; Ng, R.; Gnjatic, S. Host-protozoan interactions protect from mucosal infections through activation of the inflammasome. Cell 2016, 167, 444–456.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardinha-Silva, A.; Alves-Ferreira, E.V.C.; Grigg, M.E. Intestinal immune responses to commensal and pathogenic protozoa. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 963723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, P.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.; Ryan, C.; Stanton, C.; Cotter, P. The intestinal protist Blastocystis is not a common member of the healthy infant gut microbiota in a Westernized country (Ireland). Parasitology 2018, 145, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieves-Ramírez, M.; Partida-Rodríguez, O.; Laforest-Lapointe, I.; Reynolds, L.; Brown, E.; Valdez-Salazar, A.; Morán-Silva, P.; Rojas-Velázquez, L.; Morien, E.; Parfrey, L. Asymptomatic intestinal colonization with protist Blastocystis is strongly associated with distinct microbiome ecological patterns. Msystems 2018, 3, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Ringø, E.; Merrifield, D.L. The gut microbiota of fish. In Aquaculture Nutrition: Gut Health, Probiotics and Prebiotics; Merrifield, D., Ringø, E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 75–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet. Res. 2017, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, N.; Sylvain, F.-E.; Holland, A.; Luis Val, A.; Derome, N. Gut microbiota of an Amazonian fish in a heterogeneous riverscape: Integrating genotype, environment, and parasitic infections. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02755-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Xiong, J.; Li, M.; Bu, X.; Jiang, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Zou, H.; Miao, W. Genome assembly of a symbiotic balantidia (Balantidium ctenopharyngodoni) in fish hindgut. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulke, C.A.; Martins, M.L.; Watral, V.G.; Humphreys, I.R.; Spagnoli, S.T.; Kent, M.L.; Sharpton, T.J. A longitudinal assessment of host-microbe-parasite interactions resolves the zebrafish gut microbiome’s link to Pseudocapillaria tomentosa infection and pathology. Microbiome 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jiang, D.; Wang, Q.; Chang, O.; Yin, J.; Yu, M.; Pan, H. Host–Microbiota–Parasite Interactions in Grass Carp: Insights from Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Infection. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, J.; Farez, M.F. Does helminth activation of toll-like receptors modulate immune response in multiple sclerosis patients? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Feng, W.; Yan, Q.; Gong, Y. Host species as a strong determinant of the intestinal microbiota of fish larvae. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, T.; Kuchta, R.; Oros, M. Tapeworms as pathogens of fish: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1883–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravec, F.; Nagasawa, K.; Madinabeitia, I. A new species of Capillaria (Nematoda: Capillariidae) from the intestine of the marine fish Acanthopagrus schlegelii schlegelii (Sparidae) from Japan. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).