Silicon Accumulation in Leaves Reduces the Herbivory by Invasive Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda and Enhances the Yield of Maize
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Details
2.2. Influence of Si and PGRs on the Incidence of FAW
2.3. Si and PGR Concentration in Leaves and the Influence of Si and PGRs on the Incidence of FAW
2.4. Yield and Cost Economics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
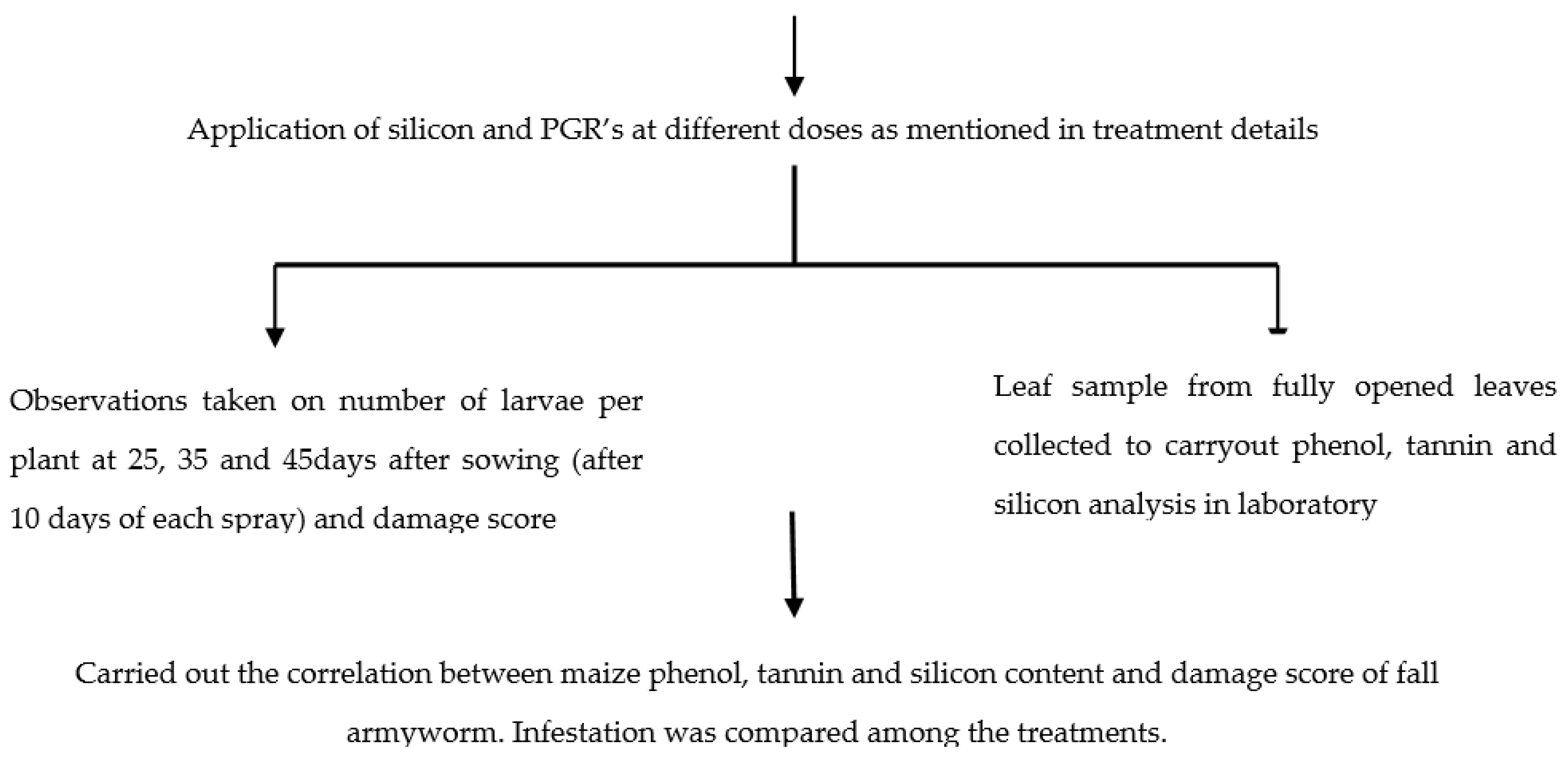
2.6. Flowchart of the Experiment
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Si and PGRs on the Incidence of FAW
3.2. Si and PGR Concentration in Leaves and the Influence of Si and PGRs on the Incidence of FAW
3.3. Yield and Cost Economics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durgesh, K.T.; Singh, V.P.; Lux, A.; Vaculik, M. Silicon in plant biology: From past to present, and future challenges. J. Experimental Bot. 2020, 71, 6699–6702. [Google Scholar]
- Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Kannan, M.; Prakash, N. Silicon as a natural plant guard against insect pests. In Silicon and Nano-Silicon in Environmental Stress Management and Crop Quality Improvement: Progress and Prospectes; Etesami, H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, A.; Hartley, S.; Singh, I.K. Silicon: Its ameliorative effect on plant defense against herbivory. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 6730–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaratna, W.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Dhananjaya, B.C.; Prakash, N.B. Effect of silicon and plant growth regulators on the biology and fitness of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, a recently invaded pest of maize in India. Silicon 2021, 14, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, R.; Moraes, J.C.; Auad, A.M.; Coelho, M.; Nascimento, A.M. Induction of resistance of corn plants to Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith, 1797) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) by application of silicon and gibberellic acid. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2017, 107, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, M.; Van Oosten, V.R.; Van Poecke, R.M.P.; Van Pelt, J.A.; Pozo, M.J.; Mueller, M.J.; Buchala, A.J.; Métraux, J.P.; Van Loon, L.C.; Dicke, M.; et al. Signal Signature and Transcriptome changes of arabidopsis during pathogen and insect attack. MPMI 2005, 18, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.F. Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2004, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, A.; Baldwin, I.T. Plant responses to insect herbivory: The emerging molecular analysis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 299–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, N.B.; Chandrashekar, N.; Mahendra, C.; Patil, S.U.; Thippeshappa, G.N.; Laane, H.M. Effect of foliar spray of soluble silicic acid on growth and yield parameters of wetland rice in hilly and coastal zone soils of Karnataka, South India. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavani, J.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Onkarappa, S.; Dhananjaya, B.C.; Prakash, N.B. Influence of rice husk biochar as a source of silicon on the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda incidence and growth and yield of Maize. Silicon 2023, 15, 4277–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Cheema, M.A.; Sher, A.; Ijaz, M.; Wasaya, A.; Yasir, T.A.; Abbas, T.; Hussain, M. Foliar applied silicon improves water relations, stay green and enzymatic antioxidants activity in late sown wheat. Silicon 2020, 12, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwethakumari, U.; Prakash, N.B. Effect of foliar application of silicic acid on soybean yield and seed quality under field conditions. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 2018, 66, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, S.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Alam, P.; Siddique, K.H.; Ahmad, P. Interactive effect of 24-epibrassinolide and silicon alleviates cadmium stress via the modulation of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems and macronutrient content in Pisum sativum L. seedlings. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahanger, M.A.; Bhat, J.A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Rinklebe, J.; Ahmad, P. Integration of silicon and secondary metabolites in plants: A significant association in stress tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 6758–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.L.; Molina-ochoa, J.; Martinelli, S.; Skoda, S.R.; Isenhour, D.J.; Lee, D.J.; Krumm, J.T.; Foster, J.E. Population variation of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda in the Western Hemisphere. J. Insect Sci. 2007, 7, 1536–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Silvie, P.; Meagher, R.L.; Lopez, J.; Machado, V. Identification and comparison of fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) host strains in Brazil, Texas, and Florida. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2007, 100, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De FreitasBueno, R.C.O.; De Freitas Bueno, A.; Moscardi, F.; Postali Parra, J.R.; Hoffmann-campo, C.B. Lepidopteran larva consumption of soybean foliage: Basis for developing multiple-species economic thresholds for pest management decisions. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prowell, D.C.; Mcmichael, M.; Silvain, J.F. Multilocus genetic analysis of host use, introgression, and speciation in host strains of fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2004, 97, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goergen, G.; Kumar, P.L.; Sankung, S.B.; Togola, A.; Tamo, M. First report of outbreaks of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae), a new alien invasive pest in West and Central Africa. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshmukh, S.S.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Asokan, R.; Mahadeva Swamy, H.M.; Maruthi, M.S.; Pavithra, H.B.; Hegde, K.; Navi, S.; Prabhu, S.T.; Goergen, G. First report of the Fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), an alien invasive pest on maize in India. Pest Manag. Hort. Ecosyst. 2018, 24, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Shylesha, A.N.; Jalali, S.K.; Gupta, A.; Varshney, R.; Venkatesan, T.; Shetty, P.; Ojha, R.; Ganiger, P.C.; Navik, O.; Subaharan, K.; et al. Studies on new invasive pest Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and its natural enemies. J. Biol. Control 2018, 32, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swamy, H.M.; Asokan, R.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Prasad, Y.G.; Maruthi, M.S.; Shashank, P.R.; Devi, N.I.; Surakasula, A.; Adarsha, S.; Srinivas, A. Prevalence of “R” strain and molecular diversity of fall armyworm, Spodopterafrugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in India. Indian J. Entomol. 2018, 80, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallapur, C.P.; Naik, A.K.; Hagari, S.; Prabhu, S.T.; Patil, R.K. Status of alien pest fall armyworm, Spodopterafrugiperda (JE Smith) in Northern Karnataka. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 432–436. [Google Scholar]
- Divya, J.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Mallikarjuna, H.B.; Deshmukh, S. Does recently invaded fall armyworm, Spodopterafrugiperda displace native lepidopteran pests of maize in India? Curr. Sci. 2021, 120, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Divya, J.; Mallikarjuna, H.B.; Deshmukh, S.S.; Sunil, C. Cannibalistic nature and time of habitat occupancy of invasive maize fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda are the key factors for competitive displacement of native stem borer, Sesamia inferens in India. Curr. Sci. 2023, 124, 348–354. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh, S.S.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Prasanna, B.M.; Sannathimmappa, H.G.; Kavyashree, B.A.; Sharath, K.N.; Pradeep, P.; Patil, K.K.R. Economic analysis of pesticide expenditure for managing the invasive fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) by maize farmers in Karnataka, India. Curr. Sci. 2021, 121, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Ambarish, S.; Onkarappa, S.; Deshmukh, S.S.; Sunil, C. Whorl application of soil mixed chlorantraniliprole 18.5 SC is effective against invasive fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda JE Smith (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in maize. J. Entomol. Res. 2022, 46, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.M.; Ng, S.S.; Williams, W.P. Visual rating scales for screening whorl-stage corn for resistance to fall armyworm. Tech. Bull. (Miss. Agric. For. Exp. Stn.) 1992, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwins, R.E. Methods for estimation of tannin in grain sorghum and other food stuff. J. Agron. 1971, 63, 511–512. [Google Scholar]
- Datnoff, L.E.; Snyder, G.H.; Korndorfer, G.H. Silicon in Agriculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; p. 424. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, A.M.; Assis, F.A.; Moraes, J.C.; Souza, B.H.S. Silicon application promotes rice growth and negatively affects development of Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith). J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 142, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, P.; Farmer, E.E. Jasmonate and salicylate as global signals for defense gene expression. Curr. Opin. Plant Boil. 1998, 1, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Su, J.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Tan, J.F.; Han, Y.L. Effect of nitrogen application combined with silicon on density of Sitobionavenae and contents of biochemical materials of winter wheat at the late growth stage. J. PlantNutr. Fertil. 2013, 19, 832–839. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.S.; Lei, N.F.; Liu, Q. Defense signaling among interconnected ramets of a rhizomatous clonal plant, induced by jasmonic-acid application. Acta Oecol. 2011, 37, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekpoor, F.; Salimi, A.; Pirbalouti, A.G. Effect of jasmonic acid on total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of extract from the green and purple landraces of sweet basil. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chandramani, P.; Rajendran, R.; Sivasubramanian, P.; Muthiah, C. Management of hoppers in rice through host nutrition. J. Biopestic. 2009, 2, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Jeer, M.; Yele, Y.; Sharma, K.C.; Prakash, N.B. Exogenous application of different silicon sources and potassium reduces pink stem borer damage and improves photosynthesis, yield and related parameters in wheat. Silicon 2021, 13, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhao, K.R.; Bansal, A.; Rout, G.R. Silicon amendment induces synergistic plant defense mechanism against pink stem borer (Sesamia inferens Walker.) in finger millet (Eleusine coracana Gaertn.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, I.O.; Panda, S.K.; Dash, A.B. Effect of organic and inorganic silicon amendments against yellow stem borer (Scirpophaga incertulas Walker) and leaf folder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Guenee) of rice in costal Odisha. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Artyszak, A. Effect of silicon fertilization on crop yield quantity and quality a literature review in Europe. Plants 2018, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Shaheen, M.R.; Soh, A.; Al-Samarai, G.F. Growth response of corn (Zea maize L.) to proline and gibberellic acid spray under different irrigation levels. Int. J. Bot. Res. 2014, 4, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Kumawat, N.; Tomar, I.S.; Dudwe, T.S.; Yadav, R.; Sahu, Y.K. Effect of gibberllic acid on growth, yield and economics of maize (Zea mays L.) under Jhabua Hills of Madhya Pradesh. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 5, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Laing, M.D.; Gatarayiha, M.C.; Adandonon, A. Silicon use for pest control in agriculture: A review. In Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association, Durban, South Africa, 18–20 July 2006; Volume 80, pp. 278–286. [Google Scholar]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagaratna, W.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Dhananjaya, B.C.; Prakash, N.B.; Deshmukh, S.S.; Sunil, C.; Hossain, M.A.; Mallikarjuna, H.B. Silicon Accumulation in Leaves Reduces the Herbivory by Invasive Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda and Enhances the Yield of Maize. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2023, 14, 701-713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14030052
Nagaratna W, Kalleshwaraswamy CM, Dhananjaya BC, Prakash NB, Deshmukh SS, Sunil C, Hossain MA, Mallikarjuna HB. Silicon Accumulation in Leaves Reduces the Herbivory by Invasive Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda and Enhances the Yield of Maize. International Journal of Plant Biology. 2023; 14(3):701-713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagaratna, Wangi, Chicknayakanahalli Marulasiddappa Kalleshwaraswamy, Bhakthanakatte Chandrappa Dhananjaya, Nagabovanalli B. Prakash, Sharanabasappa S. Deshmukh, Chandrashekar Sunil, Mohammad Anwar Hossain, and Hosamane Basvarajappa Mallikarjuna. 2023. "Silicon Accumulation in Leaves Reduces the Herbivory by Invasive Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda and Enhances the Yield of Maize" International Journal of Plant Biology 14, no. 3: 701-713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14030052
APA StyleNagaratna, W., Kalleshwaraswamy, C. M., Dhananjaya, B. C., Prakash, N. B., Deshmukh, S. S., Sunil, C., Hossain, M. A., & Mallikarjuna, H. B. (2023). Silicon Accumulation in Leaves Reduces the Herbivory by Invasive Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda and Enhances the Yield of Maize. International Journal of Plant Biology, 14(3), 701-713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14030052






