Association of Health Information Literacy and Health Outcomes Among Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting and Sampling
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Instrument with Validity and Reliability
2.4.1. Socio-Demographic and Clinical Information
2.4.2. Health Information Literacy
2.4.3. Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice
2.4.4. Health Problem-Solving
2.4.5. Chronic Illness Resources
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Sample
3.2. Hypothesis 1: Greater HIL Would Be Positively Related to Better Health Outcomes (Self-Management Practice and Glycemic Control) After Controlling Covariates
3.3. Hypothesis 2: Behavioral Factors (Self-Management Knowledge, Self-Management Attitude, Health Problem-Solving) and Environmental Factors (Chronic Illness Resources) Mediate the Relationship Between Personal Factors (Sociodemographic Factors and HIL) and Health Outcomes (Self-Management Practice and Glycemic Control) After Controlling Covariates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Public Involvement Statement
Guidelines and Standards Statement
Use of Artificial Intelligence
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shipman, J.P.; Kurtz-Rossi, S.; Funk, C.J. The Health Information Literacy Research Project. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2009, 97, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griebel, L.; Enwald, H.; Gilstad, H.; Pohl, A.-L.; Moreland, J.; Sedlmayr, M. eHealth Literacy Research-Quo Vadis? Inf. Inform. Health Soc. Care 2018, 43, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutbeam, D.; Lloyd, J.E. Understanding and Responding to Health Literacy as a Social Determinant of Health. Annu. Rev. Public. Health 2021, 42, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkman, N.D.; Sheridan, S.L.; Donahue, K.E.; Halpern, D.J.; Viera, A.; Crotty, K.; Holland, A.; Brasure, M.; Lohr, K.N.; Harden, E.; et al. Health Literacy Interventions and Outcomes: An Updated Systematic Review. Evid. Rep./Technol. Assess. 2011, 199, 1–941. [Google Scholar]
- Visscher, B.B.; Steunenberg, B.; Heijmans, M.; Hofstede, J.M.; Devillé, W.; van der Heide, I.; Rademakers, J. Evidence on the Effectiveness of Health Literacy Interventions in the EU: A Systematic Review. BMC Public. Health 2018, 18, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lv, X.; Liang, J.; Dong, H.; Chen, C. The Development and Progress of Health Literacy in China. Front. Public. Health 2022, 10, 1034907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L. The level of health information literacy and its influencing factors in China from 2012 to 2017. Chin. J. Health Educ. 2020, 36, 875–879+895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliano, D.J.; Boyko, E.J. IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition scientific committee IDF DIABETES ATLAS. In IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; ISBN 978-2-930229-98-0. [Google Scholar]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of the Metabolic Syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Cui, J.; Song, L.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. Association Between Weight Gain From Young to Middle Adulthood and Metabolic Syndrome Across Different BMI Categories at Young Adulthood. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 812104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Ren, D.; Gary-Webb, T.L.; Dunbar-Jacob, J.; Erlen, J.A. Characterizing a Sample of Chinese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Selected Health Outcomes. Diabetes Educ. 2019, 45, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Hong, T.; Bi, Y.; Hu, D.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ji, L.; Zhu, D. Prevalence, Treatment Patterns and Control Rates of Metabolic Syndrome in a Chinese Diabetic Population: China Cardiometabolic Registries 3B Study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Diabetes Society Guideline for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in China (2020 Edition). Chin. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 37, 311–398.
- Powers, M.A.; Bardsley, J.K.; Cypress, M.; Funnell, M.M.; Harms, D.; Hess-Fischl, A.; Hooks, B.; Isaacs, D.; Mandel, E.D.; Maryniuk, M.D.; et al. Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Consensus Report of the American Diabetes Association, the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Academy of PAs, the American Association of Nurse Practitioners, and the American Pharmacists Association. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1636–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheerder, A.; van Deursen, A.; van Dijk, J. Determinants of Internet Skills, Uses and Outcomes. A Systematic Review of the Second- and Third-Level Digital Divide. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 34, 1607–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramallo-Fariña, Y.; García-Bello, M.A.; García-Pérez, L.; Boronat, M.; Wägner, A.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, L.; de Pablos-Velasco, P.; Llorente Gómez de Segura, I.; González-Pacheco, H.; Carmona Rodríguez, M.; et al. Effectiveness of Internet-Based Multicomponent Interventions for Patients and Health Care Professionals to Improve Clinical Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Evaluated Through the INDICA Study: Multiarm Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2020, 8, e18922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmarini, E.; Marciano, L.; Schulz, P.J. The Effectiveness of Visual-Based Interventions on Health Literacy in Health Care: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2024, 24, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweel, L.; Newman, A.; Michaelchuk, W.; Packham, T.; Goldstein, R.; Brooks, D. The Effect of Digital Interventions on Related Health Literacy and Skills for Individuals Living with Chronic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Med. Inf. Inform. 2023, 177, 105114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ran, X.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, K. Effects of Health Literacy Intervention on Health Literacy Level and Glucolipid Metabolism of Diabetic Patients in Mainland China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 1503446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butayeva, J.; Ratan, Z.A.; Downie, S.; Hosseinzadeh, H. The Impact of Health Literacy Interventions on Glycemic Control and Self-Management Outcomes among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. J. Diabetes 2023, 15, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sayah, F.; Majumdar, S.R.; Williams, B.; Robertson, S.; Johnson, J.A. Health Literacy and Health Outcomes in Diabetes: A Systematic Review. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2013, 28, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, K.; Shi, Y. The Effect of Health Literacy Intervention on Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutbeam, D. Health Literacy as a Public Health Goal: A Challenge for Contemporary Health Education and Communication Strategies into the 21st Century. Health Promot. Int. 2000, 15, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinn, D. Critical Health Literacy: A Review and Critical Analysis. Soc. Sci. Med. 2011, 73, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Hay, J.L.; Waters, E.A.; Kiviniemi, M.T.; Biddle, C.; Schofield, E.; Li, Y.; Kaphingst, K.; Orom, H. Health Literacy and Use and Trust in Health Information. J. Health Commun. 2018, 23, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Qian, X.; Chen, Z.; He, T. Health Literacy and Its Effect on Chronic Disease Prevention: Evidence from China’s Data. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.-W.; Kao, C.-W.; Lin, W.-S.; Chang, Y.-C. Factors Affecting Self-Care Maintenance and Management in Patients With Heart Failure: Testing a Path Model. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2019, 34, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Gao, M.; Chen, X.Y.; Sun, X.Y. Relationship between the five-factor model of personality traits and self-management attitude of patients with type 2 diabetes. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2020, 52, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; He, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Relationship between Health Information Literacy and Health Promoting Lifestyle among First-Degree Relatives of Patients with Colorectal Cancer in China: The Mediating Effect of Health Belief. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1178848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M. Association of eHealth Use, Literacy, Informational Social Support, and Health-Promoting Behaviors: Mediation of Health Self-Efficacy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Guo, X. The Community Health Supporting Environments and Residents’ Health and Well-Being: The Role of Health Literacy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wang, J. Exploring the Relationship between Health Information Literacy and Health Behaviors of the Elderly. Iran. J. Public Health 2023, 52, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paasche-Orlow, M.K.; Wolf, M.S. The Causal Pathways Linking Health Literacy to Health Outcomes. Am. J. Health Behav. 2007, 31 (Suppl. S1), S19–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill-Briggs, F. Problem Solving in Diabetes Self-Management: A Model of Chronic Illness Self-Management Behavior. Ann. Behav. Med. 2003, 25, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.; Ren, D.; Dunbar-Jacob, J.; Gary-Webb, T.L.; Erlen, J.A. Self-Management Behaviors, Glycemic Control, and Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetes. Nurs. Res. 2020, 69, E9–E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudjoe, J.; Delva, S.; Cajita, M.; Han, H.-R. Empirically Tested Health Literacy Frameworks. Health Lit. Res. Pract. 2020, 4, e22–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tajdar, D.; Lühmann, D.; Fertmann, R.; Steinberg, T.; van den Bussche, H.; Scherer, M.; Schäfer, I. Low Health Literacy Is Associated with Higher Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in Germany. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Foundations of Thought & Action: A Social Cognitive Theory; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, K.F.; Awal, A.; Mazumder, H.; Munni, U.R.; Majumder, K.; Afroz, K.; Tabassum, M.N.; Hossain, M.M. Social Cognitive Theory-Based Health Promotion in Primary Care Practice: A Scoping Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S73–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Luo, A.; Xie, W.; Hu, D. Development of Health Information Literacy Self-Rating Scale and Its Reliability and Validity Test. China J. Mod. Med. 2013, 23, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, A.; Wang, F.; Xie, W.; Xu, Z.; Luo, D. Health Information Literacy Status and Influencing Factors of Elderly Patients with Chronic Diseases in Changsha City. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2016, 36, 3554–3556. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X. The Research on the Relationship between Health Information Literacy, Diabetes Self-Management Behavior and Health Outcome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ye, Z.; Shen, X.; Tang, L.; Shao, J. The Development of Self-Management Knowledge, Atitude and Practice Scale for Metabolic Syndrome Patients. J. Nurses Train. 2018, 33, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill-Briggs, F.; Gemmell, L.; Kulkarni, B.; Klick, B.; Brancati, F.L. Associations of Patient Health-Related Problem Solving with Disease Control, Emergency Department Visits, and Hospitalizations in HIV and Diabetes Clinic Samples. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2007, 22, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Jin, P.; Ji, M. Reliability and Validity Testing of Chinese Version Health Problem Solving Scale. J. Nurs. Sci. 2023, 38, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasgow, R.E.; Toobert, D.J.; Barrera, M.; Strycker, L.A. The Chronic Illness Resources Survey: Cross-Validation and Sensitivity to Intervention. Health Educ. Res. 2005, 20, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Fan, L.; Ya, S. Reliability and Validity of Chronic Illness Resources Survey (Chinese Version) in Patients with Diabetes. Chin. Gen. Pract. 2014, 17, 2779–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis. J. Educ. Meas. 2013, 51, 335–337. [Google Scholar]
- Neeland, I.J.; Lim, S.; Tchernof, A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Rangaswami, J.; Ndumele, C.E.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Després, J.-P. Metabolic Syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meifang, Y.; Xue, S.; Jue, H.; Yina, T.U.; Jie, H.E.; Yiming, Z.; Hanyu, L.; Xiaohong, P.; Wenheng, Z.; Songzhao, Z.; et al. Metabolic syndrome increases Framingham risk score of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2016, 45, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.; Hovorka, R. Technology in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: Present Status and Future Prospects. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, S.L.; Schumann, K.P.; Hill-Briggs, F. Problem Solving Interventions for Diabetes Self-Management and Control: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 100, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, K.; Campbell, J.; Bugnon, M.; Henry, C.; Schaub, C.; Serex, M.; Elmers, J.; Desrichard, O.; Peytremann-Bridevaux, I. Factors Influencing Diabetes Self-Management in Adults: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2021, 19, 1003–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Guo, X.; Shi, Y. Moderating Effect of Health Information Literacy on Diabetic Knowledge Reserve and Self-Management Behavior of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. Pract. 2021, 25, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stormacq, C.; Wosinski, J.; Boillat, E.; Van den Broucke, S. Effects of Health Literacy Interventions on Health-Related Outcomes in Socioeconomically Disadvantaged Adults Living in the Community: A Systematic Review. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 1389–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanti, A.; Chan, D.N.S.; Parut, A.A.; So, W.K.W. Determinants and Outcomes of eHealth Literacy in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Lee, Y.W.; Kang, E.H.; Kang, H.J. Relationship Between Electronic Health Literacy and Self-Management in People With Type 2 Diabetes Using a Structural Equation Modeling Approach. J. Nurs. Res. 2024, 32, e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, T.; Benkert, R. Critical Health Literacy: Reflection and Action for Health. Health Promot. Int. 2022, 37, daac114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Samkange-Zeeb, F.; Kolschen, J.; Herrmann, R.; Hübner, W.; Barnils, N.P.; Brand, T.; Zeeb, H.; Schüz, B. Interventions to Promote Health Literacy among Working-Age Populations Experiencing Socioeconomic Disadvantage: Systematic Review. Front. Public. Health 2024, 12, 1332720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stormacq, C.; Van den Broucke, S.; Wosinski, J. Does Health Literacy Mediate the Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and Health Disparities? Integrative Review. Health Promot. Int. 2019, 34, e1–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Liu, T.; Liu, R.; Yang, H.; Liu, C. Effectiveness of Digital Health Literacy Interventions in Older Adults: Single-Arm Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e48166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vaart, R.; Drossaert, C. Development of the Digital Health Literacy Instrument: Measuring a Broad Spectrum of Health 1.0 and Health 2.0 Skills. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | N (%) | Mean ± SD or M(IQR) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 47.00 (18.00) | |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 137(60.9) | |
| Female | 88 (39.1) | |
| Residence | ||
| Urban | 166 (73.8) | |
| Rural | 59 (26.2) | |
| Years of Education | 12.00 (7.00) | |
| Educational attainment | ||
| Primary school | 8 (3.6) | |
| Junior high | 50 (22.2) | |
| High school | 47 (20.9) | |
| College level | 111 (49.3) | |
| Graduate level | 9 (4.0) | |
| Employment status | ||
| Full-time | 123 (54.7) | |
| Retired | 68 (30.2) | |
| Other | 34 (15.1) | |
| Occupation | ||
| Office clerks | 67 (29.8) | |
| Workers | 49 (21.8) | |
| Commercial personnel | 45 (20.0) | |
| Service employees | 49 (21.8) | |
| Farmers | 15 (6.7) | |
| Household income(monthly), CNY | ||
| <3000 | 13 (5.8) | |
| 3000–4999 | 40 (17.8) | |
| 5000–7999 | 44 (19.6) | |
| ≥8000 | 128 (56.9) | |
| Marital status | ||
| Married | 179 (79.6) | |
| Unmarried | 46 (20.4) | |
| Medical costs | ||
| Medical insurance | 215 (95.6) | |
| Other | 10 (4.4) | |
| HILSS | 16.83 ± 2.96 | |
| HIC | 3.00 (0.75) | |
| HIS | 6.19 ± 1.53 | |
| HIE | 3.20 (0.85) | |
| HIA | 2.32 (0.75) | |
| HIM | 2.50 (0.75) | |
| Knowledge | 19.00 (4.00) | |
| Attitude | 37.00 (6.00) | |
| HPSS | 17.22 (4.81) | |
| CIRS | 62.12 ± 11.74 | |
| Practice | 42.00 (15.00) | |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 27.37 (5.20) | |
| ≥24 | 189 (84.0) | |
| Waist, cm | 97.00 (12.50) | |
| Comorbidities, n | ||
| Hypertension | 110 (48.9) | |
| Dyslipidemia | 194 (86.2) | |
| Coronary heart disease | 27 (12.0) | |
| Ischemic stroke | 20 (8.9) | |
| Systolic Blood pressure | 133.00 (21.00) | |
| Diastolic Blood pressure | 84.00 (13.00) | |
| Triglyceride, mmol/L | 1.96 (1.63) | |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 4.99 (1.66) | |
| Lipoprotein, mmol/L | 1.12 (0.41) | |
| HDL | 3.22 ± 1.00 | |
| LDL | 16.83 ± 2.96 | |
| HbA1c, mmol/L | 8.80 (3.55) | |
| ≥7.0 (%) | 175 (77.8) | |
| Variables | Age | YED | HILSS | Knowledge | Attitude | HPSS | CIRS | Practice | HbA1c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1 | ||||||||
| YED | −0.454 ** | 1 | |||||||
| HILSS | −0.190 ** | 0.399 ** | 1 | ||||||
| Knowledge | 0.020 | 0.143 * | 0.354 ** | 1 | |||||
| Attitude | −0.041 | 0.117 | 0.308 ** | 0.431 ** | 1 | ||||
| HPSS | 0.094 | 0.023 | 0.379 ** | 0.302 ** | 0.434 ** | 1 | |||
| CIRS | 0.140 * | 0.072 | 0.353 ** | 0.362 ** | 0.499 ** | 0.454 ** | 1 | ||
| Practice | 0.457 ** | −0.211 ** | 0.207 ** | 0.321 ** | 0.392 ** | 0.519 ** | 0.516 ** | 1 | |
| HbA1c | −0.306 ** | 0.148 * | −0.146 * | −0.178 ** | −0.084 | −0.289 ** | −0.227 ** | −0.351 ** | 1 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | B | SE | t | p Value | 95% CI | B | SE | t | p Value | 95% CI |
| Age | 0.324 | 0.051 | 6.379 | <0.001 | 0.224; 0.424 | 0.254 | 0.040 | 6.395 | <0.001 | 0.176; 0.332 |
| Gender | 4.669 | 1.243 | 3.755 | <0.001 | 2.218; 7.119 | 3.031 | 1.006 | 3.012 | 0.003 | 1.048; 5.014 |
| YED | 0.013 | 0.217 | 0.061 | 0.951 | −0.414; 0.441 | −0.186 | 0.167 | −1.111 | 0.268 | −0.516; 0.144 |
| Employment status | −0.975 | 0.876 | −1.113 | 0.267 | −2.701; 0.751 | −0.761 | 0.669 | −1.137 | 0.257 | −2.079; 0.558 |
| Household income | −0.153 | 0.723 | −0.212 | 0.833 | −1.578; 1.272 | −0.651 | 0.560 | −1.161 | 0.247 | −1.755; 0.454 |
| Attitude | 0.330 | 0.126 | 2.621 | 0.009 | 0.082; 0.578 | |||||
| HPSS | 0.853 | 0.146 | 5.852 | <0.001 | 0.566; 1.140 | |||||
| CIRS | 0.238 | 0.050 | 4.805 | <0.001 | 0.141; 0.336 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | B | SE | t | p Value | 95% CI | B | SE | t | p Value | 95% CI |
| Age | −0.054 | 0.013 | −4.07 | <0.001 | −0.080; −0.028 | −0.050 | 0.013 | −3.896 | <0.001 | −0.076; −0.025 |
| YED | 0.018 | 0.051 | 0.350 | 0.727 | −0.083; 0.119 | 0.072 | 0.053 | 1.377 | 0.170 | −0.031; 0.176 |
| Employment status | 0.133 | 0.226 | 0.589 | 0.557 | −0.312; 0.578 | 0.126 | 0.218 | 0.58 | 0.563 | −0.303; 0.555 |
| HPSS | −0.119 | 0.044 | −2.683 | 0.008 | −0.207; −0.032 | |||||
| HIE | −0.643 | 0.263 | −2.446 | 0.015 | −1.161; −0.125 |
| 95% CI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paths | Effect | SE | p Value | Lower | Upper |
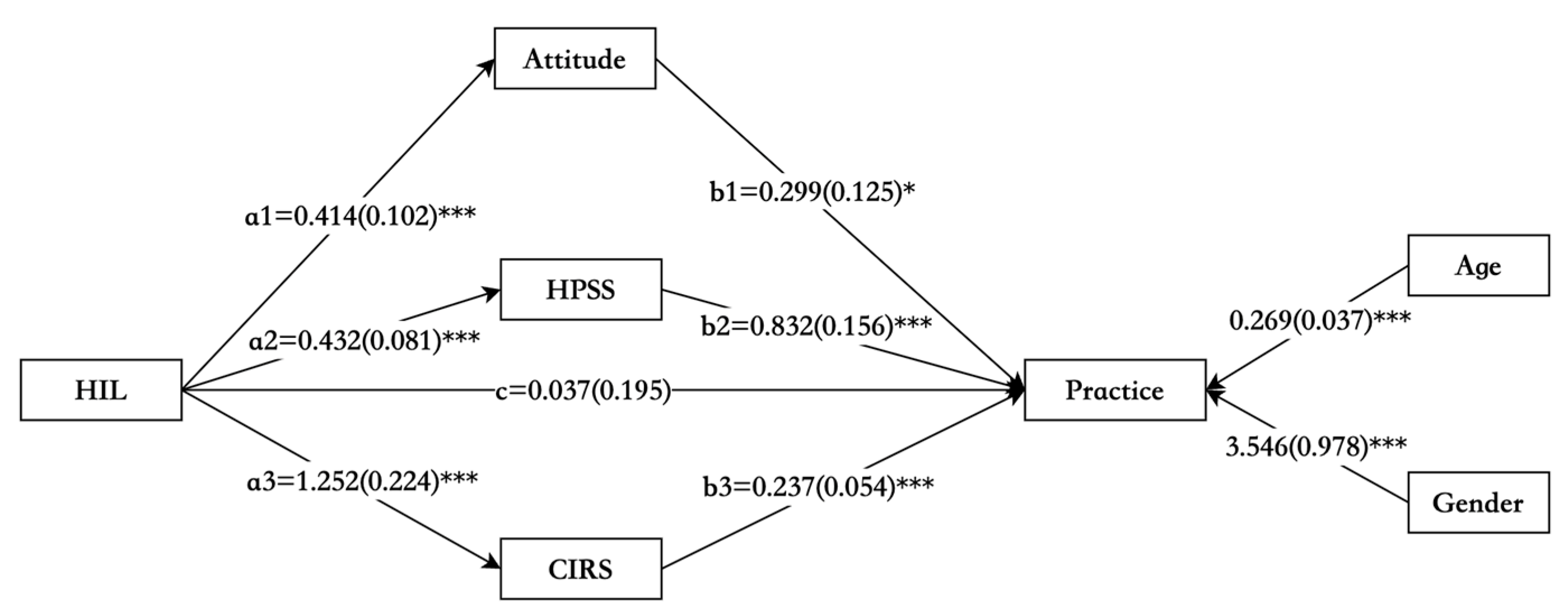
| Path1: HIL to Attitude to Practice | 0.124 | 0.062 | 0.044 | 0.026 | 0.269 |
| Path2: HIL to HPSS to Practice | 0.360 | 0.104 | 0.001 | 0.177 | 0.583 |
| Path3: HIL to CIRS to Practice | 0.297 | 0.083 | <0.001 | 0.161 | 0.494 |
| Total indirect effect | 0.780 | 0.152 | <0.001 | 0.509 | 1.096 |
| Direct effect: HIL to Practice | 0.037 | 0.195 | 0.850 | −0.338 | 0.427 |
| Total effect: HIL to Practice | 0.817 | 0.189 | <0.001 | 0.438 | 1.182 |
| 95% CI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paths | Effect | SE | p Value | Lower | Upper |
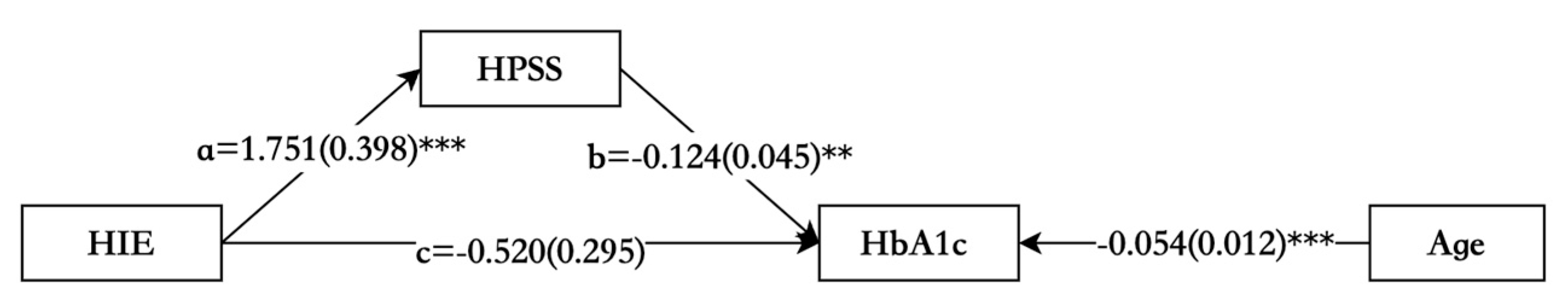
| Total indirect effect: | −0.217 | 0.101 | 0.032 | −0.448 | −0.057 |
| Direct effect: | −0.520 | 0.295 | 0.078 | −1.094 | 0.074 |
| Total effect: | −0.737 | 0.265 | 0.005 | −1.235 | −0.183 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.; Qi, X.; Li, A.; Dong, H.; Wang, X.; Ji, M. Association of Health Information Literacy and Health Outcomes Among Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15030090
Wu K, Qi X, Li A, Dong H, Wang X, Ji M. Association of Health Information Literacy and Health Outcomes Among Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Nursing Reports. 2025; 15(3):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15030090
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kailu, Xiaoyan Qi, Aihua Li, Huan Dong, Xiaojing Wang, and Meihua Ji. 2025. "Association of Health Information Literacy and Health Outcomes Among Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome" Nursing Reports 15, no. 3: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15030090
APA StyleWu, K., Qi, X., Li, A., Dong, H., Wang, X., & Ji, M. (2025). Association of Health Information Literacy and Health Outcomes Among Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Nursing Reports, 15(3), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15030090






