-
 Virtual Reality Education Increases Neurologic Immersion and Empathy in Nursing Students
Virtual Reality Education Increases Neurologic Immersion and Empathy in Nursing Students -
 Identifying Risk Factors for Delirium Through Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment in Older Adults Receiving Palliative Cancer Care
Identifying Risk Factors for Delirium Through Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment in Older Adults Receiving Palliative Cancer Care -
 Beyond Care: A Scoping Review on the Work Environment of Oncology Nurses
Beyond Care: A Scoping Review on the Work Environment of Oncology Nurses -
 Factors Contributing to Non-Adherence to Treatment Among Adult Patients with Long-Term Haemodialysis: An Integrative Review
Factors Contributing to Non-Adherence to Treatment Among Adult Patients with Long-Term Haemodialysis: An Integrative Review -
 Transition to Caregiver in Advanced Alzheimer’s Disease: Emotional Connection to Care Responsibility
Transition to Caregiver in Advanced Alzheimer’s Disease: Emotional Connection to Care Responsibility
Journal Description
Nursing Reports
Nursing Reports
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on nursing sciences published monthly online by MDPI (from Volume 10 Issue 1 - 2020).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PMC, PubMed, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 27.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Nursing) / CiteScore - Q2 (General Nursing)
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Healthcare Sciences and Services: Geriatrics, Journal of Ageing and Longevity, Healthcare, Hospitals, Hygiene, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health and Nursing Reports.
Impact Factor:
2.0 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.5 (2024)
Latest Articles
Translation, Cross-Cultural Adaptation, and Psychometric Validation of the Authentic Nurse Leadership Questionnaire for the Portuguese Context: A Methodological Study
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 362; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100362 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background: Authentic leadership is characterized by the authenticity and self-awareness of the leader, who acts with transparency and promotes positive outcomes in clinical practice and team management. In Portugal, there isn’t a tool available to assess nurses’ perceptions of authentic leadership in
[...] Read more.
Background: Authentic leadership is characterized by the authenticity and self-awareness of the leader, who acts with transparency and promotes positive outcomes in clinical practice and team management. In Portugal, there isn’t a tool available to assess nurses’ perceptions of authentic leadership in nursing. This study aimed to translate and cross-culturally adapt the Authentic Nurse Leadership Questionnaire (ANLQ) for the Portuguese context and to evaluate its psychometric properties. This instrument assesses nurses’ perceptions of the authentic leadership exercised by their leader. Methods: A methodological, descriptive, cross-sectional study with a quantitative approach was conducted. The translation and cross-cultural adaptation process followed the recommendations of internationally recognized guidelines. The Authentic Nurse Leadership Scale—Portuguese version (ANLS-PT) was administered to a sample of 406 nurses from various functional units in three primary healthcare centers. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis techniques were used. Reliability was established through a test–retest administration to 22 nurses at two different times, with a two-week interval. The internal consistency of the scale was assessed using Cronbach’s Alpha. Results: An instrument with 29 items and 3 dimensions was obtained, explaining 68.3% of the total variance. The identified dimensions were Caring and Decision-Making, Self-Awareness, and Relational Integrity and Ethics. The overall instrument showed an internal consistency of 0.97. Conclusions: The ANLS-PT proved to be a valid, reliable, and robust tool for assessing authentic leadership in the Portuguese cultural context and can be used in various nursing practice contexts.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Equality, Equity, Diversity and Inclusion in Rare Disease Research in the United Kingdom
by
Andrew E. P. Mitchell and Sondra Butterworth
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 361; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100361 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Inclusion of under-represented rare-disease communities in research remains limited, threatening representativeness and equity. Methods: To assess equality, equity, diversity, and inclusion in research and identify barriers to participation faced by the rare disease community, utilising a mixed-methods online survey of
[...] Read more.
Background: Inclusion of under-represented rare-disease communities in research remains limited, threatening representativeness and equity. Methods: To assess equality, equity, diversity, and inclusion in research and identify barriers to participation faced by the rare disease community, utilising a mixed-methods online survey of a convenience sample of community advocates using Likert scales and free response options. Results: The findings from seventeen stakeholders in the rare disease community showed unanimous agreement that anxiety, fear, safety concerns, and lack of trust hinder participation in research. A total of 82% agreed or strongly agreed that additional financial resources are needed, and 76% agreed or strongly agreed that research grant applications often lack sufficient funds. The free-text responses demonstrate that the rare disease communities are keen to be involved in research but faces barriers to inclusion. Rare disease communities are willing to participate in research, but those responsible for research need to address the challenges related to language, misconceptions and fear. Conclusions: Key legislation in the United Kingdom, specifically the Proposed Patient and Public Involvement Strategy 2020–2025, emphasises the importance of involving patients and the public in health and social care. This survey marks the first step toward gaining valuable insights into the challenges faced by this community in participating in healthcare research, which is crucial for developing a solid evidence base for their treatment and care. Involving stakeholders is essential in health and social care policy and practice, rooted in advocacy and social justice.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Caregiver Contribution to Patient Self-Care and Associated Variables in Older Adults with Multiple Chronic Conditions Living in a Middle-Income Country: Key Findings from the ‘SODALITY-AL’ Observational Study
by
Sajmira Adëraj, Manuela Saurini, Rocco Mazzotta, Edona Gara, Dasilva Taҫi, Alta Arapi, Vicente Bernalte-Martí, Alessandro Stievano, Ercole Vellone, Gennaro Rocco and Maddalena De Maria
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 360; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100360 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Multiple chronic conditions (MCCs) pose global health and social challenges, with caregiving often relying on family members, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). However, limited evidence exists regarding the factors influencing caregiver contribution (CC) to patient self-care among older adults
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Multiple chronic conditions (MCCs) pose global health and social challenges, with caregiving often relying on family members, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). However, limited evidence exists regarding the factors influencing caregiver contribution (CC) to patient self-care among older adults with MCCs in these settings. Aim: The aim of this study was to examine the associations between caregivers’ and patients’ socio-demographic characteristics and patients’ clinical variables and the CC to patient self-care behaviors in adults with MCCs in an LMIC context. Methods: This multicenter, cross-sectional study included patient–caregiver dyads recruited from outpatient and community settings across Albania, between August 2020 and April 2021. CC was assessed using the Caregiver Contribution to Self-Care of Chronic Illness Inventory scale (CC-SCCII). Three multivariable linear regression models were used to explore associations with the three dimensions of CC to self-care maintenance, monitoring, and management. Results: Caregivers were mostly female, children, or spouses with a high level of education and employed. Patients were primarily female and had low education. Hypertension and diabetes were the most prevalent. Older and employed caregivers contributed less to CC to self-care maintenance, while higher education and caregiving experience increased it. Living with the patient and being a spouse reduced CC to self-care monitoring, whereas more caregiving hours and experience improved it. CC to self-care management was negatively influenced by cohabitation, presence of a second caregiver, and being a spouse, but improved with more caregiving hours. Conclusions: Socio-demographic and caregiving factors differently influence CC to self-care dimensions in older adults with MCCs in an LMIC. Tailored caregiver support programs are essential to enhance caregiver involvement and improve MCC patient outcomes in LMICs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Self-Management of Chronic Disease)
Open AccessReview
Recent Advances in Ultrasound-Guided Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Insertion
by
Amélie Bruant and Laure Normand
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 359; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100359 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
This narrative review addresses ongoing controversies and advancements concerning ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous (IV) catheter insertion, and the impact of ultrasound guidance on success rate, procedural time, patient and staff experience, complications and costs, as well as requirements for its use. Growing evidence suggests
[...] Read more.
This narrative review addresses ongoing controversies and advancements concerning ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous (IV) catheter insertion, and the impact of ultrasound guidance on success rate, procedural time, patient and staff experience, complications and costs, as well as requirements for its use. Growing evidence suggests that ultrasound-guided insertion of peripheral IV catheter represents a superior technique across various patient populations, particularly those presenting with difficult IV access (DIVA). Key findings highlight significant improvements in first-attempt success rates, reduction of procedural complications, and enhanced patient comfort. Ultrasound-guided insertion is also associated with an increase in catheter dwell time, a reduction in repeat procedures and in central line placements, leading to improved resource utilization and the potential for substantial long-term cost-effectiveness, despite the cost of initial investment and training. However, obtaining these improvements involves a critical importance for standardized training, adherence to rigorous aseptic techniques, and generalization of the transformative impact of ongoing technological advancements in ultrasound devices. The collective body of evidence supports the widespread adoption of ultrasound-guided peripheral IV cannulation as an evidence-based best practice in modern healthcare.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Nursing Education and Leadership)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seeking Something Beyond Themselves: A Concept Analysis of Spiritual Awakening Experiences at the End of Life
by
Manuela Monteiro, Joel Vitorino, Marina G. Salvetti and Carlos Laranjeira
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 358; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100358 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: End-of-life (EoL) experiences are critically important for everyone involved, giving rise to a set of needs that extend far beyond bio-physiological aspects, to encompass the spiritual dimension as the core of human beings. Understanding the processes of spiritual awakening (SA) assists palliative
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: End-of-life (EoL) experiences are critically important for everyone involved, giving rise to a set of needs that extend far beyond bio-physiological aspects, to encompass the spiritual dimension as the core of human beings. Understanding the processes of spiritual awakening (SA) assists palliative care professionals in enhancing the quality of care provided to individuals with life-threatening illnesses, as well as to their families. SA is a fundamental occurrence linked to the fulfilment of our spiritual needs when facing an existential crisis, such as the proximity of death. However, its conceptual boundaries need to be clarified to provide qualified and humanized palliative care. Therefore, this study aims to identify the key attributes, antecedents, consequents, and empirical referents of SA at EoL, as well as to clarify the concept’s existing ambiguities. Methods: Walker and Avant’s eight-step concept analysis was used. A literature search was conducted in May 2025 across three databases (PubMed, CINAHL and Scopus). Results: Following the review, 21 articles were included for analysis. The concept analysis revealed four main attribute domains: (1) sensory–perceptual domain; (2) affective/cognitive domain; (3) relational domain; and (4) transcendental domain. Moreover, spiritual consciousness and the existential matrix were antecedents to this concept; revaluation of beliefs, finding spiritual serenity and inner freedom, fostering spiritual growth, and the desire to leave a legacy were its consequences. Conclusions: The concept of SA at the EoL reveals itself to be a complex and multifactorial phenomenon, with a profound impact on a person’s confrontation with finitude. Recognizing and integrating SA into palliative care allows for a more comprehensive understanding of human consciousness. To deal with SA experiences in healthcare settings, a multifaceted approach is needed. This encompasses acknowledging spirituality as a determinant of health, including spiritual care in standard practice, and offering education and training on spiritual care competence for healthcare practitioners. Further transdisciplinary research should be undertaken to explore SA phenomenological variations, guide clinical interventions, and evaluate SA impacts on spiritual well-being and spiritual growth.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Development of a Care Model for Sarcopenic Obesity in Older Adults: Participatory Action Research
by
Nuchthida Samaisong, Chomchuen Somprasert and Lisa Pawloski
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 357; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100357 - 5 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Problem: Sarcopenic obesity (SO) is characterized by significant muscle loss combined with obesity, and it is mostly prevalent among older adults. Consequences include a heightened incidence of falls and a greater susceptibility to non-communicable diseases. Thailand currently lacks a care model for SO
[...] Read more.
Background/Problem: Sarcopenic obesity (SO) is characterized by significant muscle loss combined with obesity, and it is mostly prevalent among older adults. Consequences include a heightened incidence of falls and a greater susceptibility to non-communicable diseases. Thailand currently lacks a care model for SO in older adults. Objective/Purpose: This study utilizes participatory-action research (PAR) to develop a care model for sarcopenic obesity in Thailand. Design and Methodology: In-depth interviews with 25 older adults with SO and focus group discussions with 12 stakeholders were conducted to develop a preliminary care model. An action research spiral process was utilized with 15 older adults with SO over 16 weeks. Findings: We developed a culturally sensitive care model for SO in older adults. This study demonstrates that a participatory-action research (PAR) method for behavior transformation, highlighting health awareness and SO literacy, is crucial for behavior change. Conclusions and Implications: The behavior change process using transformative behaviors facilitated internal changes. This approach helps individuals to understand interconnected factors through personal experiences, leading to profound understanding and readiness for deep, continuous, and meaningful behavioral changes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Healthy, Safe and Active Aging, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Video-Based Education on Activities of Daily Living and Wound Healing of Patients with Total Hip Replacement: Randomised Controlled Trials
by
Ayse Sinem Tas and Ismet Eser
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 356; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100356 - 4 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background and Purpose: There remains a need for effective and accessible education methods to support recovery after total hip replacement. To evaluate the effects of video-based education on daily living activities and wound healing of patients undergoing total hip replacement surgery. Methods: A
[...] Read more.
Background and Purpose: There remains a need for effective and accessible education methods to support recovery after total hip replacement. To evaluate the effects of video-based education on daily living activities and wound healing of patients undergoing total hip replacement surgery. Methods: A randomised controlled trial was used. Eligible participants were those aged 18 years and over who had undergone total hip replacement surgery in a training and research hospital. The intervention group received video-based training, while the control group received only routine care. Results: Patients in the video-based training group showed significantly greater improvement in daily living activities, hip function, and wound healing on postoperative days 5 and 30 compared to the control group (p < 0.01). Conclusions: Video-based education significantly improved daily living activities, hip function, and wound healing in patients undergoing total hip replacement. Clinicaltrials ID: NCT06523829
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nursing Interventions to Improve Healthcare for Older Adults)
Open AccessArticle
Development and Content Validation of a Person-Centered Care Instrument for Healthcare Providers
by
Krishan Soriano, Sora Nakatani, Kaito Onishi, Hirokazu Ito, Youko Nakano, Yoshiyuki Takashima, Yueren Zhao, Allan Paulo Blaquera, Ryuichi Tanioka, Feni Betriana, Gil Platon Soriano, Yuko Yasahura, Kyoko Osaka, Matsuko Kataoka, Misao Miyagawa, Masashi Akaike, Minoru Irahara and Tetsuya Tanioka
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 355; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100355 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Despite the increasing recognition of person-centered care (PCC), existing evaluation tools often have profession-specific limitations, lacking broad applicability across interdisciplinary contexts. This study aimed to develop and validate the Person-Centered Care Instrument (PCCI), designed to assess the competence of healthcare providers
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Despite the increasing recognition of person-centered care (PCC), existing evaluation tools often have profession-specific limitations, lacking broad applicability across interdisciplinary contexts. This study aimed to develop and validate the Person-Centered Care Instrument (PCCI), designed to assess the competence of healthcare providers from diverse professions. Methods: Using a two-round modified Delphi technique, ten experts validated an initial pool of 63 items. The process assessed both face validity (overall appropriateness) and content validity using a 9-point Likert scale and the Item-level Content Validity Index (I-CVI). Items with a median rating of 6 or higher and an I-CVI of ≥0.70 were retained. Results: The final PCCI consists of 37 items, with a scale-level content validity index of 0.65. Three items achieved universal agreement among the experts (I-CVI = 1.0). For the final 37-item PCCI, the Scale-level Content Validity Index (S-CVI) was 0.65, and the index based on universal agreement was 0.22. Conclusions: The developed PCCI demonstrated good face and content validity, making it a valid and broadly applicable tool for assessing competence in delivering PCC. This instrument can support quality improvement initiatives and help promote a culture of empathy and respect in healthcare.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Management of Constipation in Hypothyroidism: Evaluating Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Interventions
by
Eman M. Gaber Hassan, Sharell Lewis, Sajedah Fawzi Alsadiq, Salha Ali Almarhoon, Hanan Mufareh Alsubeh, Sana Mohammad Alboori, Khulood Abdulghafour Al Marzooq, Fatimah Saleh Al Awami and Mohammad Daud Ali
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 354; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100354 - 29 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background/Objective: Chronic constipation is a common gastrointestinal disorder that can be caused by a variety of factors, such as demographic, lifestyle, and medical disorders like hypothyroidism. Its prevalence varies worldwide, affecting quality of life and leading to specialized management strategies. To explore hypothyroidism
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Chronic constipation is a common gastrointestinal disorder that can be caused by a variety of factors, such as demographic, lifestyle, and medical disorders like hypothyroidism. Its prevalence varies worldwide, affecting quality of life and leading to specialized management strategies. To explore hypothyroidism patients’ knowledge and practice regarding constipation and evaluate the perceived effectiveness of pharmacological and non-pharmacological management approaches. Methods: A descriptive, cross-sectional design was used to collect the data from a private hospital in the eastern region of Saudi Arabia from January to May 2025. A convenient sample of 300 individuals with hypothyroidism completed the Bowel Habits Questionnaire. Results: Most participants knew that hypothyroidism could cause constipation, but they reported that they did not have more knowledge about it. Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, especially increase water intake, fiber intake, and exercise, were commonly used by the participants, and they perceived these approaches to be effective. There were strong correlations between constipation frequency and age, disease duration, and the use of constipation management methods. A strong association was found between constipation management strategies and treatment effectiveness. Conclusion: Age, disease duration, and constipation management strategies significantly affect constipation in hypothyroidism patients. Drinking plenty of water and eating more fiber are two very effective non-pharmacological strategies. It is recommended that nurses who integrate routine bowel health education and lifestyle guidance into care plans consider the gap in patient knowledge regarding the relationship between hypothyroidism and constipation, to enhance patients’ self-management and contribute to better health outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Clinical and Rehabilitative Nursing in Chronicity)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProtocol
Healthcare Access Among Individuals Who Practice Chemsex in Brazil: A Scoping Review Protocol
by
Isadora Silva de Carvalho, Lariane Angel Cepas, Álvaro Francisco Lopes de Sousa, Talita Morais Fernandes, Talia Gomes Luz, Jean Carlos Soares da Silva, Augusto da Silva Marques, Caíque Jordan Nunes Ribeiro, Shirley Veronica Melo Almeida Lima, Anderson Reis de Sousa, Carlos Arterio Sorgi, Ricardo Nakamura and Ana Paula Morais Fernandes
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 353; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100353 - 27 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Chemsex, the intentional use of psychoactive substances to enhance sexual experiences, is an emerging public health issue in Brazil, associated with increased risks of sexually transmitted infections and complex psychosocial vulnerabilities. Despite the universal coverage provided by the Unified Health System (SUS),
[...] Read more.
Background: Chemsex, the intentional use of psychoactive substances to enhance sexual experiences, is an emerging public health issue in Brazil, associated with increased risks of sexually transmitted infections and complex psychosocial vulnerabilities. Despite the universal coverage provided by the Unified Health System (SUS), individuals who practice chemsex often encounter barriers to healthcare, including stigma, discrimination, and a lack of specialized services. To date, no comprehensive reviews appear to synthesize evidence on how this population accesses healthcare in the Brazilian context; existing knowledge remains fragmented across individual studies. Objectives: The aim is to map and synthesize the available evidence regarding access to health services among people who engage in chemsex in Brazil, identifying health needs, professional demands, barriers, and facilitators. Methods: The protocol follows the Joanna Briggs Institute methodology for scoping reviews and PRISMA-ScR guidelines. A systematic search will be conducted in MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase, Scopus, SciELO, and LILACS for studies published between 2014 and 2024 in Portuguese, English, or Spanish. Data will be summarized using descriptive and narrative synthesis, presented in tables and thematic categories. Studies will be included if they address chemsex or sexualized drug use in Brazil and report on healthcare access, regardless of gender identity, sexual orientation, or drug type. Studies that do not address chemsex, focus on drug use outside a sexual context, or are unrelated to Brazil will be excluded. Expected results: The review is expected to identify key barriers and facilitators to healthcare access, highlight knowledge gaps for underrepresented groups, and support recommendations for research, policy, and practice to improve care for people engaging in chemsex in Brazil. By focusing on an underexplored intersection of drug use, sexuality, and healthcare access in Latin America, this study aims to provide an innovative contribution to public health literature.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Development and Validation of a Tool to Assess Healthcare Professionals’ Views on Parental Presence During Neonatal Resuscitation
by
Paraskevi Volaki, Rozeta Sokou, Abraham Pouliakis, Nikoleta Aikaterini Xixi, Zoi Iliodromiti, Styliani Paliatsiou, Georgios Kafalidis, Theodora Boutsikou, Theodoros Xanthos and Nicoletta Iacovidou
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 352; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100352 - 26 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Childbirth is a natural and joyfully anticipated life event for parents and relatives. Yet, in some cases, it can be a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention, i.e., neonatal resuscitation. The majority of newborns breathe spontaneously; a small number, though, may receive
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Childbirth is a natural and joyfully anticipated life event for parents and relatives. Yet, in some cases, it can be a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention, i.e., neonatal resuscitation. The majority of newborns breathe spontaneously; a small number, though, may receive basic life support (assisted transition), and an even smaller but clinically significant number require advanced life support (resuscitation). Within the context of family-centered care, the presence of parents during resuscitation has emerged as a factor with potential implications for emotional adjustment, communication with healthcare providers, and early parent–infant bonding. However, the presence of family members during neonatal resuscitation remains a subject of ongoing debate among healthcare professionals (HCPs). Despite increasing recognition of its potential benefits, HCPs’ views on parental presence during such critical procedures have not been extensively investigated in Greece. This study aims at developing and validating a tool to assess healthcare professionals’ views on parental presence during neonatal resuscitation. Methods: A preliminary questionnaire was developed based on the principles of family-centered care and adapted to the Greek population. The first phase included expert assessment of validity, clarity, and relevance using a modified Delphi method. Item Content Validity Index (I-CVI) and Scale CVI (S-CVI) were calculated. Pilot testing was conducted to assess test–retest reliability. Reliability was assessed using the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) and Bland–Altman analyses. The study followed the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, ensuring anonymity, informed consent, and confidentiality. Results: The questionnaire includes 37–50 items allocated in four sections. It demonstrated excellent content validity (CVI = 1.00) and good test–retest reliability (ICC = 0.86). Qualitative feedback indicated that the tool is user-friendly and comprehensive. Interestingly, participants expressed genuine concerns regarding the implementation of parental presence in neonatal resuscitation. Conclusions: The questionnaire development process led to a comprehensive tool, ready for large-scale testing in order to further establish its validity and internal consistency.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Improving Good Practices for Patient Safety in an Emergency Department Based on Multidisciplinary Training Using Simulation Techniques
by
Francisco Javier Redondo Calvo, Victor Baladrón González, María Ángeles Tebar Betegón, Alejandro Martínez Arce, Gema Verdugo Moreno, Juan Fernando Padin, Laura Muñoz de Morales-Romero, Alberto Bermejo-Cantarero and Natalia Bejarano Ramírez
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 351; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100351 - 26 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: We present a multidisciplinary training experience based on simulation techniques and critical resource management implemented in the emergency department. Methods: Simulation courses/workshops were conducted with a multidisciplinary team from the Hospital Emergency Department. The timeline for their development includes a
[...] Read more.
Background: We present a multidisciplinary training experience based on simulation techniques and critical resource management implemented in the emergency department. Methods: Simulation courses/workshops were conducted with a multidisciplinary team from the Hospital Emergency Department. The timeline for their development includes a preliminary analysis of needs, objectives, and scenario design, development of the simulation course, and finally, areas of implementation. In this last phase, the teaching team prepares a document and/or report/summary of the activity in which, among other things, the aspects with the greatest capacity for improvement or the areas for implementation of safety measures are determined. A total of 112 healthcare professionals (doctors, nurses, and care assistants) participated in this training program. Its design consisted of the following stages: a preliminary analysis of training needs, the establishment of objectives and scenario design, the development of the simulation workshop, and finally, a report on areas for improvement in patient safety identified during the workshop learning process. Results: The workshops enabled us to identify areas for improvement and develop local protocols/recommendations aimed at improving patient safety in the emergency department, such as standardizing a protocol to guide us in managing resources in crisis situations, a protocol for airway management, a protocol for massive transfusion, and a review of the triage process. In addition, we added value by incorporating cognitive aids and visual tools into the standardization of processes. Conclusions: For resource management in this type of crisis in the hospital emergency setting, it is essential to use a debriefing process guided by experienced instructors after a specific experiential learning experience through simulation scenarios. This helps to contextualize and analyze the advantages and disadvantages of general recommendations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessConference Report
‘Looking Back and Looking Forward’—Insights into the 20th European Doctoral Conference in Nursing Science (EDCNS)
by
Lena Maria Lampersberger, Selvedina Osmancevic, Eva Pichler, Baptiste Lucien and Sebastian Rosendahl Huber
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 350; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100350 - 26 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: The European Doctoral Conference in Nursing Science provides a unique platform for doctoral students in nursing and health sciences to present their research in a supportive environment. Celebrating its 20th anniversary, the 2024 conference embraced the motto “looking back and looking
[...] Read more.
Background: The European Doctoral Conference in Nursing Science provides a unique platform for doctoral students in nursing and health sciences to present their research in a supportive environment. Celebrating its 20th anniversary, the 2024 conference embraced the motto “looking back and looking forward,” offering an opportunity to reflect on the development of nursing science and future challenges. Results: Held at the Medical University of Graz, Austria, the conference hosted 90 participants from 13 countries. It featured two keynote lectures, three workshops, 48 presentations, and a science slam. Abstract submissions underwent peer review to ensure the quality of presentations. The presentations highlighted key challenges and opportunities across nursing practice, healthcare work environments, education and digitalization in nursing, and health perspectives. Topics included, for example, workforce retention, artificial intelligence in nursing practice, leadership in error management, and culturally sensitive care. The keynotes emphasized the importance of patient and public involvement in research and the benefits of survey data in nursing science. Workshops imparted knowledge and skills regarding funding acquisition, guideline development, and effective research presentation. A science slam introduced innovative and creative ways to present research. Conclusions: The conference showcased the evolving landscape of nursing science, emphasizing the importance of evidence-based practice, supportive working conditions, and constructive collaboration. It demonstrated the enthusiasm and readiness of a new generation of researchers to advance nursing science in a rapidly changing healthcare environment.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Retractions in Nursing from Publications Between 2000 and 2024: A Bibliometric Analysis Using Retraction Watch
by
María Paz Contreras-Muñoz, Cristian Zahn-Muñoz, Elizabeth Solís-Albanese and Ezequiel Martínez-Rojas
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 349; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100349 - 26 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
There has been a significant increase in scientific publications in recent years, and the nursing field has been no exception. Consequently, the number of publications containing errors that lead to document retractions has also increased. It is essential to understand and delve into
[...] Read more.
There has been a significant increase in scientific publications in recent years, and the nursing field has been no exception. Consequently, the number of publications containing errors that lead to document retractions has also increased. It is essential to understand and delve into this phenomenon within nursing research. Objective: This study aims to identify and analyze the retractions of scientific publications in nursing research worldwide between 2000 and 2024. Methodology: This is a descriptive and cross-sectional study with a bibliometric approach. Data were collected using the Retraction Watch database, from which 408 retracted documents related to nursing research were extracted. Results: Over the last 25 years (2000–2024), a total of 408 documents in the nursing field have been retracted, with the majority concentrated in the 2020–2024 period, accounting for 84.8%. Ethical misconduct was the cause of retraction in 87.3% of the cases. Of the 408 retracted documents, 42.6% involved human participants in research or control groups, totaling 21,369 patients who were part of flawed studies. Conclusions: It is crucial that nursing research remains rigorous and adheres to bioethical standards, as these guide evidence-based nursing practice. Flawed literature can have significant consequences for patient health and care.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Mediating Role of Inner Strength in the Relationship Between Biological Factors and Depressive Symptoms
by
Jia Jiao, Rewadee Jenraumjit, Shirley Worland, Saifon Bunyachatakul, Bijing He and Tinakon Wongpakaran
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 348; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100348 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Depression is a significant public health concern, with working mothers at greater risk due to combined biological and psychosocial stressors. Recent evidence suggests that inner strength may play a mediating role in the link between biological risks and depression. Objectives: The primary
[...] Read more.
Background: Depression is a significant public health concern, with working mothers at greater risk due to combined biological and psychosocial stressors. Recent evidence suggests that inner strength may play a mediating role in the link between biological risks and depression. Objectives: The primary objective was to determine whether inner strength mediates the relationship between biological risk factors (hormonal fluctuations, smoking, alcohol use, family psychiatric history, and physical diseases) and depressive symptoms among Chinese working mothers. A secondary objective was to assess the prevalence of depressive symptoms in this population, measured with the OI-Depression subscale (Outcome Inventory-21). Methods: A cross-sectional online survey was conducted with 330 Chinese working mothers aged 30–45 years, using validated instruments to measure depression, inner strength, and parental stress. Mediation analysis evaluated the indirect effect of inner strength, while covariate-adjusted regression analyses explored associated factors. Results: Biological risk factors showed a significant direct effect (β = 0.584, p < 0.001) and an indirect effect through inner strength (indirect effect = 0.623, 95% CI [0.294, 0.962]. The Sobel test indicated that the indirect effect of biological risk factors on depressive symptoms through inner strength was statistically significant (z = 3.67, p < 0.001). The prevalence of clinically significant depressive symptoms was 38.2%. Conclusions: Biological factors significantly contribute to depressive symptoms, but inner strength partially mediates this relationship, suggesting that interventions to enhance inner strength may help reduce depression risk in working mothers. Further research should investigate strategies to build inner resilience in this population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mental Health Nursing)
Open AccessArticle
The Experience of the Nursing Licensure Examination Among Newly Graduated Nurses: A Qualitative Study
by
Flavia Pantaleo, Chiara Mastroianni, Michela Piredda, Alessandro Stievano, Natascia Mazzitelli, Laura Iacorossi, Maria Grazia De Marinis and Anna Marchetti
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 347; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100347 - 24 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The nursing licensure examination is the final assessment of the university curriculum, certifying that students have acquired the competencies necessary for practicing the profession. Understanding the meaning and usefulness attributed to this test can contribute to the international debate on its
[...] Read more.
Background: The nursing licensure examination is the final assessment of the university curriculum, certifying that students have acquired the competencies necessary for practicing the profession. Understanding the meaning and usefulness attributed to this test can contribute to the international debate on its value and potential continuation. In Italy, most studies in this field involve Directors of Degree Courses, while research on the lived experience of newly graduated nurses in facing the examination is lacking. Objective: The objective of this study is to explore the lived experience of newly graduated nurses during the licensure examination. Methods: A qualitative phenomenological study was conducted. Video–audio-recorded interviews were conducted and analyzed using Giorgi’s descriptive method, inspired by Husserl’s philosophy. Results: Fifteen nurses participated. The thematic analysis of the interviews revealed four significant areas: preparation and support received, ambivalent experience of the exam, emotions experienced during the exam, and the symbolic value ascribed to the exam itself. Each thematic area was further articulated into subthemes, for a total of ten analytical subdimensions. The licensure examination holds multiple meanings for new graduates: an opportunity for verification, a rite of passage, but also an emotionally charged event. While it represents a fundamental moment for constructing a professional identity, it also requires critical reflection on assessment methods, the fairness of the system, and the true educational value of the examination. Conclusions: Understanding the elements that influence the examination experience can help educators improve student preparation and promote a smoother transition to the professional role.
Full article
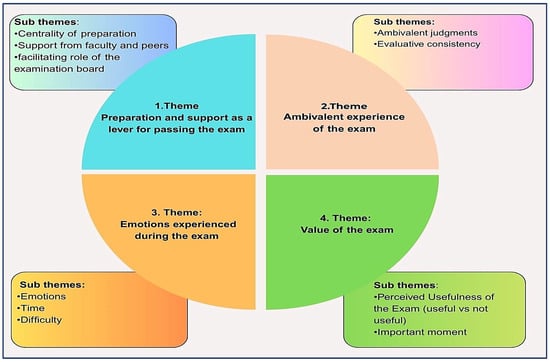
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Awareness of Care Managers Concerning Grief Care for Older Bereaved Individuals Living Alone Following the Loss of Their Spouse: A Qualitative Research
by
Kazumi Hirano
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 346; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100346 - 24 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Japan has the most rapidly aging population worldwide, with older adults expected to reach 38.7% by 2070. Furthermore, individuals ≥ 60 years old desire to spend their final days at home. Following the establishment of the Long-Term Care Insurance System in
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Japan has the most rapidly aging population worldwide, with older adults expected to reach 38.7% by 2070. Furthermore, individuals ≥ 60 years old desire to spend their final days at home. Following the establishment of the Long-Term Care Insurance System in 2000, care managers at home care support facilities continually assist most older adults receiving home care. Moreover, home-based end-of-life care is expected to increase. Therefore, the care manager’s role will be crucial in providing end-of-life care support and offering grief care to bereaved families following a patient’s passing. In this study, we aimed to clarify the perceptions of care managers regarding grief care for older bereaved individuals following the loss of their spouse and living alone. Methods: Seventeen care managers with prior experience in grief care for older bereaved individuals who became independent after the death of their spouse were interviewed. The 17 care managers comprised 2 men and 15 women, aged between their late 30s and early 60s. Qualitative data analysis was performed. Results: The following five categories were generated regarding the perceptions of care managers: necessity of supporting older bereaved individuals, ambivalent feelings towards grief care, death considerations, need for reflection, and challenges in implementing grief care. Conclusions: Care managers recognized the importance of maintaining a continued relationship before death, including the need for assessing older bereaved individuals, and collaborating with multiple professions in grief care.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Influence of the Catecholamine Syringe Changeover Method on Patients’ Blood Pressure Variability: A Single-Center Retrospective Study
by
Yuta Niitsu, Takumi Tsuchida, Ryuta Sato, Juna Shintaku and Koichi Iwasa
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(10), 345; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15100345 - 23 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: In Japan, evidence on catecholamine syringe exchange methods is limited, with practices varying across facilities and individuals. In this study, we aimed to determine the effect of the catecholamine syringe exchange method on blood pressure variability in intensive care unit patients.
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: In Japan, evidence on catecholamine syringe exchange methods is limited, with practices varying across facilities and individuals. In this study, we aimed to determine the effect of the catecholamine syringe exchange method on blood pressure variability in intensive care unit patients. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 119 patients (308 syringe exchanges) who underwent catecholamine syringe exchange between 1 April 2020 and 31 March 2022. Patient characteristics for the double-pumping changeover (DPC) and quick syringe changeover (QC) groups were matched and compared using propensity scores. A sub-analysis focused on patients with severe shock with systolic blood pressures ≤ 90 mmHg. Logistic regression analysis was used to examine factors influencing blood pressure variability during the catecholamine syringe changeover. Results: Neither propensity score matching nor the sub-analysis for patients with shock revealed significant differences in the coefficient of variation or absolute systolic/diastolic/mean blood pressure within 15 min of syringe exchange in the two groups. Logistic regression revealed that age was the sole risk factor affecting blood pressure variability during syringe changeover (odds ratio: 1.018, 95% confidence interval: 1.001–1.036), while syringe changeover methods did not contribute to circulating variability (odds ratio: 1.186, 95% confidence interval: 0.672–2.092). Conclusions: Differences between the DPC and QC methods did not significantly affect blood pressure variability during catecholamine syringe changeovers. However, in older adult patients, catecholamine syringe changeover may be more likely to cause blood pressure variability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Critical Care Nursing)
►▼
Show Figures
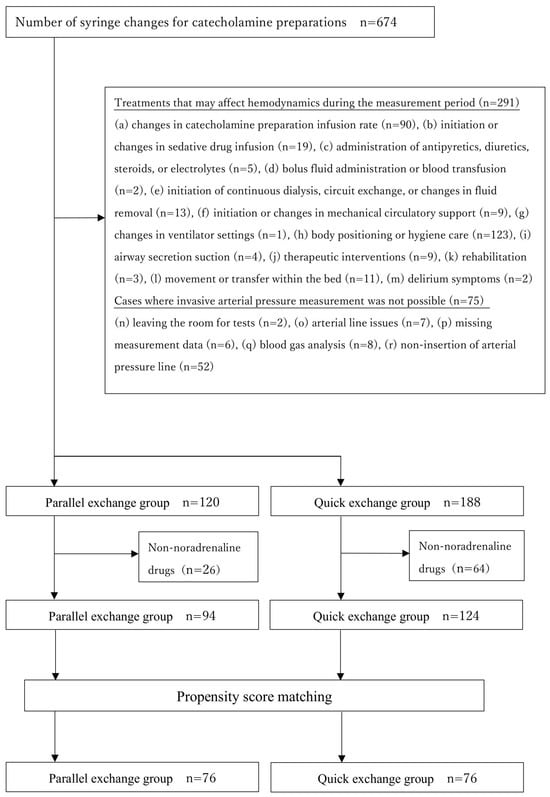
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nurses’ Attitudes, Environmental Perceptions and Involvement in Research: A Multisite Study
by
Amanda J. Hessels, Ulanda Marcus-Aiyeku, Mani Paliwal, Carrie Ann Catanzaro, Kimberly Dimino, Jessica Crowley, Jessica Miszlay, Maria Manzella, Kimkyla Kritch, Rachel Kilpatrick, Kim Kranz, Serpouhi S. Vartivarian and Barbara McGoey
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(9), 344; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15090344 - 22 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Although evidence-based practice is widely promoted in nursing, direct care nurses remain underrepresented in research activities. This study aimed to assess nurses’ attitudes toward research, their perceptions of the organizational research environment, and their levels of involvement, as well as identify key
[...] Read more.
Background: Although evidence-based practice is widely promoted in nursing, direct care nurses remain underrepresented in research activities. This study aimed to assess nurses’ attitudes toward research, their perceptions of the organizational research environment, and their levels of involvement, as well as identify key barriers and facilitators to engagement within a comprehensive healthcare system. This study also explored how racial and ethnic diversity within the nursing workforce may shape research engagement and contribute new perspectives to the field. Methods: A cross-sectional electronic survey was administered to registered nurses across 10 hospitals in a Northeast U.S. health system. The survey instrument assessed research attitudes, environment, involvement (past, present, future), and demographics. Descriptive and inferential statistics, including matched-pairs t-tests, were used to analyze responses. Results: Of 7655 invited nurses, 1094 responses were analyzed. Respondents were predominantly female (88.5%), White (56.8%), and employed full-time (87.1%) as clinical staff nurses (77.3%). While 54.8% had completed a formal research course (mainly within the past 1–3 years), informal research and statistics training were uncommon (17.4% and 5.4%, respectively). Nurses reported highly positive attitudes toward research (composite M = 2.15, SD = 0.51), especially its role in guiding practice, professional growth, and education. However, actual involvement was low. The most common current activities included practice change based on research (20.7%) and participation in committees (18.8%). Anticipated future engagement increased substantially, particularly in collaboration (+21.3%), committee participation (+20.6%), and IRB submission (+18.2%). The research environment was perceived as under-resourced, particularly in terms of protected time, funding, and mentorship. Statistically significant gaps were observed between perceived present and desired future supports (p < 0.01 for all 15 items). The Research Awareness Index revealed high rates of uncertainty about available resources (e.g., 66.1% did not know if internal funding existed). Conclusions: Nurses demonstrate strong positive attitudes and a desire to engage in research, including more advanced roles. Yet structural and informational barriers, particularly a lack of protected time, mentorship, and awareness of existing supports, limit participation. Investments in infrastructure, communication, and accessible development pathways are needed to translate nurses’ readiness into active research engagement. Implications: Institutions should prioritize making research support more visible and navigable while investing in mentorship, protected time, and user-friendly infrastructure. Addressing both facets will empower a highly motivated nursing workforce to engage in and lead practice-relevant research.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Escape Room in Nursing Fundamentals Course: Students’ Opinions, Engagement, and Gameful Experience
by
Dragana Simin, Aleksandra Plećaš Đurić, Branimirka Aranđelović, Dragana Živković and Dragana Milutinović
Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15(9), 343; https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15090343 - 19 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: During the past decade, incorporating innovative teaching strategies for active learning, such as the use of escape rooms (ERs), has effectively contributed to the acquisition of the necessary skills. This study aimed to assess students’ opinions, engagement, and gameful experience, and to
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: During the past decade, incorporating innovative teaching strategies for active learning, such as the use of escape rooms (ERs), has effectively contributed to the acquisition of the necessary skills. This study aimed to assess students’ opinions, engagement, and gameful experience, and to analyse the impact of engagement and gameful experience on students’ opinions about ER activity. Methods: This descriptive-analytical, quantitative, and interventional cross-sectional study was conducted among first-year nursing students enrolled in the Nursing Fundamentals course. The ER activities took place in a faculty classroom. The measure included a questionnaire for assessing students’ opinions about ER activity, engagement while learning through play, and the Gameful Experience Scale. Results: The students reported very positive opinions on the outcomes of escape room activities. According to the students’ perception, solving puzzles required a high level of cognitive, emotional, physical, and other engagement. The experience of learning through play contributed to their increased enjoyment, absorption, and creative thinking, with a low level of negative effects and dominance. Enjoyment, immersion, and creative thinking during the gameful experience explained 49.0% of the variance in students’ opinions on ER activity. Conclusions: ER enabled students to consolidate knowledge from various fields within one lesson, encouraging them to be highly engaged and think creatively, giving them a sense of enjoyment in learning and motivation for further learning.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Healthcare, Pharmacy, Clinics and Practice, Nursing Reports, EJIHPE
Advancing the Knowledge and Application of Health Behavior Theories
Topic Editors: Yifei Liu, Dhananjay NayakankuppamDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Brain Sciences, IJERPH, JAL, Nursing Reports, Nutrients, Healthcare
Healthy, Safe and Active Aging, 2nd EditionTopic Editors: Antonella Lopez, Andrea Bosco, Alessandro Oronzo Caffò, Elisabetta Ricciardi, Giuseppina Spano, Luigi TinellaDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
Hospitals, IJERPH, Nursing Reports, Healthcare
Health Services Optimization, Improvement, and Management: Worldwide Experiences
Topic Editors: Alexandre Morais Nunes, Diogo Filipe da Cunha FerreiraDeadline: 30 April 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Nursing Reports
Mental Health and Well-Being of Nursing Students: Challenges, Interventions, and Future Directions
Guest Editors: Lorena Gutiérrez-Puertas, Montserrat Monserrat HernándezDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
Nursing Reports
Innovations and Challenges in Cardiovascular Nursing
Guest Editors: Michał Czapla, Izabella UchmanowicDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
Nursing Reports
Clinical and Rehabilitative Nursing in Chronicity
Guest Editors: Rafael Alves Bernardes, Vitor Parola, Hugo Leiria NevesDeadline: 30 November 2025
Special Issue in
Nursing Reports
Sustainable Practices in Nursing Education
Guest Editors: Cristina Álvarez-García, Maria Dolores López FrancoDeadline: 15 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Nursing Reports
Feature Review Papers in Mental Health Nursing Section
Collection Editors: Daniel Bressington, Martin Jones, Allison Wang, Daisy Dexing Zhang, Worku Animaw Temesgen
Topical Collection in
Nursing Reports
Feature Review Papers in Artificial Intelligence and Digital Innovations in Nursing Care Section
Collection Editors: Niall Higgins, Xujuan Zhou








