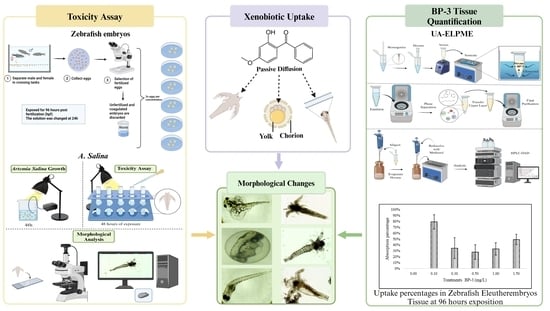
Toxicity of UV Filter Benzophenone-3 in Brine Shrimp Nauplii (Artemia salina) and Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Organism | Title/Authors | BP-3 Concentrations | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zebrafish Embryos (Danio rerio) | Hormonal activity, cytotoxicity, and developmental toxicity of UV filters [8] | Concentrations used: 1.00 mg/L–25.00 mg/L |
|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Effects of the UV filter benzophenone-3 (oxybenzone) at low concentrations in zebrafish (Danio rerio) [7] | Concentrations used: 0.010, 0.200, and 0.600 mg/L. |
|
| Tilapia fillets (Oreochromis urolepis hornorum) | Methodology for Analysis of UV filters in Tilapia using off-line MSPD followed by On-line SPE-LC-UV [17] | Concentrations used: 500 µg/mL with five UV filters. |
|
| Artemia salina (nauplii instar II/III) | Effect of 10 UV filters on the brine shrimp Artemia Salina and the marine microalga Tetraselmis sp. [18] | Concentrations used: 20 ng/L and 2 mg/L. |
|
| Artemia franciscana and Daphnia magna | Acute toxicity assessment of nine organic UV filters using a set of biotests [19] | Concentrations used: 10, 12.5 mg/L |
|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Lifetime exposure to benzophenone-3 at an environmentally relevant concentration leads to female–biased social behavior and cognition deficits in zebrafish [20] | Concentration used: 10 µg/L |
|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos | Embryonic benzophenone-3 exposure inhibited fertility in later-life female zebrafish and altered developmental morphology in offspring embryos [21] | Concentrations used: 0, 1, 10, 100 µg/L |
|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos | Comparison of developmental toxicity of benzophenone-3 and its metabolite benzophenone-8 in zebrafish [22] | Concentrations used: 1, 30, 300, 3000 µg/L |
|
| Adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Effects of oxybenzone on zebrafish behavior and cognition [23] | Concentrations used: 10, 100 and 1000 μg/L |
|
| Zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio) | Effects of Low Concentration Benzophenone-3 Exposure on the Sex Ratio and Offspring Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) [24] | Concentrations used: 0, 0.056, 2.3, and 38 μg/L |
|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae | Toxic effects and transcriptome analyses of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae exposed to benzophenones [25] | Concentrations used: 0.91 to 4.56 mg/L |
|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Environmental relevant concentrations of benzophenone-3 induced developmental neurotoxicity in zebrafish [26] | Concentrations used: 0.04 µM |
|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo | Thyroid Hormone-Disrupting Potentials of Major Benzophenones in Two Cell Lines (GH3 and FRTL-5) and Embryo-Larval Zebrafish [27] | Concentrations used: 0, 32, 100, and 320 µg/L |
|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Endocrine disrupting effect of the ultraviolet filter benzophenone-3 in zebrafish, Danio rerio [28] | The concentrations used: 100, 32, 500 mg/L |
|
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Xenobiotic for Artemia salina Nauplii Assay
2.2. Artemia salina Nauplii Toxicity Assay
2.3. Fish Maintenance and Breeding: Zebrafish
2.4. Reproduction Process
2.5. Preparation of Xenobiotic for a Zebrafish Embryo Assay
2.6. Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity Test
2.7. Ultrasound-Assisted Emulsified Liquid Phase Microextraction
2.8. Quantification of Oxybenzone
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Artemia salina Nauplii Toxicity
3.2. Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity
3.3. Teratogenic Effects
3.4. Quantification of Oxybenzone in Zebrafish Eleutheroembryos Tissue
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heurung, A.R.; Raju, S.I.; Warshaw, E.M. Benzophenones. Dermatitis 2014, 25, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruszkiewicz, J.A.; Pinkas, A.; Ferrer, B.; Peres, T.V.; Tsatsakis, A.; Aschner, M. Neurotoxic effect of active ingredients in sunscreen products, a contemporary review. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheman, A.; Jacob, S.; Katta, R.; Nedorost, S.; Warshaw, E.; Zirwas, M.; Selvo, N. Miscellaneous products: Trends and alternatives in deodorants, antiperspirants, sunblocks, shaving products, powders, and wipes: Data from the American Contact Alternatives Group. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2011, 4, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, S.D.; Ternes, T.A. Water Analysis: Emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal Chem. 2018, 90, 398–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmer, M.E.; Buser, H.R.; Müller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Occurrence of some organic UV filters in wastewater, in surface waters, and in fish from Swiss lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, C.A.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Segal, R.; Fauth, J.; Knutson, S.; Bronstein, O.; Ciner, F.R.; Jeger, R.; Lichtenfeld, Y.; Woodley, C.M.; et al. Toxicopathological Effects of the Sunscreen UV Filter, Oxybenzone (Benzophenone-3), on Coral Planulae and Cultured Primary Cells and Its Environmental Contamination in Hawaii and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 70, 265–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüthgen, N.; Zucchi, S.; Fent, K. Effects of the UV filter benzophenone-3 (oxybenzone) at low concentrations in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 263, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balázs, A.; Krifaton, C.; Orosz, I.; Szoboszlay, S.; Kovács, R.; Csenki, Z.; Urbányi, B.; Kriszt, B. Hormonal activity, cytotoxicity and developmental toxicity of UV filters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 131, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, C.; Givens, J.; Stien, D.; Matallana-Surget, S.; Lebaron, P. Bioaccumulation and toxicological effects of uv-filters on marine species. In Sunscreens in Coastal Ecosystems; Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 94, pp. 85–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Hain, E.; Timm, A.; Blaney, L. Bioaccumulation of estrogenic hormones and UV-filters in red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, S.; Kawahara, A. Zebrafish: A model vertebrate suitable for the analysis of human genetic disorders. Congenit. Anom. 2014, 54, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/OCDE. OECD Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 1992; Volume 8, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 210: Fish, Early-Life Stage Toxicity Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2009; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 212: Fish, Short-term toxicity test on embryo and sac-fry stages. In Guidelines for the Testing Chemicals, Section 2: Effects on Biotic Systems; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 1998; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammer, E.; Carr, G.J.; Wendler, K.; Rawlings, J.M.; Belanger, S.E.; Braunbeck, T. Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 149, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmos-Espejel, J.J.; Mogica-García, Ó.E.; Duran-Gasca, G.J.; Carmona-López, M.L. Methodology for Analysis of UV Filters in Tilapia Using Off-line MSPD Followed by On-line SPE–LC/UV. Chromatographia 2020, 83, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorel, E.; Clergeaud, F.; Jaugeon, L.; Rodrigues, A.M.S.; Lucas, J.; Stien, D.; Lebaron, P. Effect of 10 UV filters on the brine shrimp Artemia salina and themarinemicroalga Tetraselmis sp. Toxics 2020, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcin, S.; Aleksander, A. Acute toxicity assessment of nine organic UV filters using a set of biotests. Toxicol. Res. 2023, 39, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Dong, H.; Tao, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Lin, J.; Huang, C.; Dong, Q. Lifetime exposure to benzophenone-3 at an environmentally relevant concentration leads to female–biased social behavior and cognition deficits in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Yang, Q.; Jing, M.; Sun, X.; Tian, L.H.; Huang, X.; Wan, W.; Ye, H.; Zhang, T.; Hong, F. Embryonic benzophenone-3 exposure inhibited fertility in later-life female zebrafish and altered developmental morphology in offspring embryos. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 49226–49236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chan, X.; Liu, X.; Li, N.; Nie, Y.; Lu, G. Comparison of developmental toxicity of benzophenone-3 and its metabolite benzophenone-8 in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 258, 106515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.L.P.; Luchiari, A.C. Effects of oxybenzone on zebrafish behavior and cognition. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zheng, D.; Gong, S. Effects of Low Concentration Benzophenone-3 Exposure on the Sex Ratio and Offspring Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Yeung, K.; Kwok, M.L.; Chung, C.T.; Hu, X.L.; Chan, K.M. Toxic effects and transcriptome analyses of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae exposed to benzophenones. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Yang, Q.; Jing, M.; Sun, X.; Tian, L.H.; Huang, X.; Wan, W.; Ye, H.; Zhang, T.; Hong, F. Environmental relevant concentrations of benzophenone-3 induced developmental neurotoxicity in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.J.; Moon, H.B.; Choi, K. Thyroid Hormone-Disrupting Potentials of Major Benzophenones in Two Cell Lines (GH3 and FRTL-5) and Embryo-Larval Zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8858–8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnberg, K.L.; Petersen, G.; Albrektsen, M.; Minghlani, M.; Awad, S.; Holbech, B.; Green, J.; Bjerregaard, P.; Holbech, H. Endocrine-disrupting effect of the ultraviolet filter benzophenone-3 in zebrafish, Danio rerio. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2833–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, M.; Daniels, J.; Arslan, Z.; Farah, I.O. Effects of aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on Artemia salina: Assessment of nanoparticle aggregation, accumulation, and toxicity. Environ. Monit. Assess 2013, 185, 3339–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, S.; Ramazani, A.; Hamidi, M.; Naji, T. Artemia salina as a model organism in toxicity assessment of nanoparticles. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, Y.; Altinok, I.; Ilhan, H.; Sokmen, M. Determination of TiO2 and AgTiO2 Nanoparticles in Artemia salina: Toxicity, Morphological Changes, Uptake and Depuration. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhu, S.; Li, J.; Hui, X.; Wang, G.X. The developmental toxicity, bioaccumulation and distribution of oxidized single walled carbon nanotubes in: Artemia salina. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, J.; Verlooy, L.; Buenafe, O.E.; de Witte, P.A.M.; Esguerra, C.V.; Crawford, A.D. Evaluation of 14 Organic Solvents and Carriers for Screening Applications in Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, E.E.; Csiszar, S.A.; Roush, K.S.; Davies, I.A. National scale down-the-drain environmental risk assessment of oxybenzone in the United States. Integr. Environ. Assess Manag. 2021, 17, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple Method of Estimating Fifty per Cent Endpoints. 1938. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/aje/article-abstract/27/3/493/99616 (accessed on 20 June 2019).
- Morgan, R.M.; Kundomal, Y.R.; Hupp, E.W. SAS probit analysis for cadmium mortality. Environ. Res. 1982, 29, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangapandi, V.; Pushpanathan, T. Comparison of the Artemia salina and Artemia fransiscana bioassays for toxicity of Indian medicinal plants. J. Coast. Life Med. 2014, 2, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shah, P.; Wu, F.; Liu, P.; You, J.; Goss, G. Potentiation of lethal and sub-lethal effects of benzophenone and oxybenzone by UV light in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 235, 105835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, M.; De Haro, H.; Deng, X.; Rempel, M.A.; Lavado, R.; Schlenk, D. Estrogenic activity and reproductive effects of the UV-filter oxybenzone (2-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl-methanone) in fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 90, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incardona, J.P.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L. Defects in cardiac function precede morphological abnormalities in fish embryos exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 196, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, P.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Hepatic oxidative stress biomarker responses in freshwater fish Carassius auratus exposed to four benzophenone UV filters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 119, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsson, B.; Vargesson, N.; Danielsson, C. Teratogenicity and Reactive Oxygen Species after transient embryonic hypoxia: Experimental and clinical evidence with focus on drugs causing failed abortion in humans. Reprod. Toxicol. 2023, 122, 108488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlecht, C.; Klammer, H.; Jarry, H.; Wuttke, W. Effects of estradiol, benzophenone-2 and benzophenone-3 on the expression pattern of the estrogen receptors (ER) alpha and beta, the estrogen receptor-related receptor 1 (ERR1) and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in adult ovariectomized rats. Toxicology 2004, 205, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogoda, H.M.; Hammerschmidt, M. Molecular genetics of pituitary development in zebrafish. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 18, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nica, G.; Herzog, W.; Sonntag, C.; Hammerschmidt, M. Zebrafish pit1 mutants lack three pituitary cell types and develop severe dwarfism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, R.; Legler, J.; Legradi, J. Alterations in locomotor activity of feeding zebrafish larvae as a consequence of exposure to different environmental factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4085–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, J.; Deutsch, A. Pigment pattern formation in zebrafish during late larval stages: A model based on local interactions. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 232, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guellec, D.; Morvan-Dubois, G.; Sire, J.-Y. Skin Development in Bony Fish with Particular Emphasis on Collagen Deposition in the Dermis of the Zebrafish (Danio rerio). 2004. Available online: https://www.ijdb.ehu.es (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Kim, S.; Choi, K. Occurrences, toxicities, and ecological risks of benzophenone-3, a common component of organic sunscreen products: A mini-review. Environ. Int. 2014, 70, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Chemical analysis and ecotoxicological effects of organic UV-absorbing compounds in aquatic ecosystems. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voices of the Bay. Fishery Science-Biology & Ecology. 2011. Available online: http://zebra.sc.edu/smell/nitin/nitin.html (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Suh, S.; Pham, C.; Smith, J.; Mesinkovska, N.A. The banned sunscreen ingredients and their impact on human health: A systematic review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Organism | LC10 (mg/L) | LC20 (mg/L) | LC30 (mg/L) | LC50 (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artemia salina | 24 h | Graph estimation | <0.100 | 0.417 ± 0.239 | 1.881 ± 0.802 | 3.254 ± 0.611 |
| Probit | 0.088 ± 0.034 | 0.277 ± 0.160 | 0.734 ± 0.394 | 3.191 ± 2.023 | ||
| Average | 0.088 ± 0.0340 | 0.347 ± 0.099 | 1.308 ± 0.811 | 3.223 ± 0.044 | ||
| 48 h | Graph estimation | ---- | 0.300 ± 0 | 0.427 ± 0.154 | 1.829 ± 0.641 | |
| Probit | 0.112 ± 0.049 | 0.188 ± 0.068 | 0.301 ± 0.065 | 0.677 ± 0.044 | ||
| Average | 0.112 ± 0.049 | 0.244 ± 0.079 | 0.364 ± 0.089 | 1.253 ± 0.815 | ||
| Danio rerio embryo | 24 h | Probit | 0.581 ± 3.595 | 1.016 ± 0.624 | 1.773 ± 1.238 | 4.193 ± 3.596 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz-Román, M.I.; Casiano-Muñiz, I.M.; Román-Velázquez, F.R. Toxicity of UV Filter Benzophenone-3 in Brine Shrimp Nauplii (Artemia salina) and Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 537-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14020032
Ortiz-Román MI, Casiano-Muñiz IM, Román-Velázquez FR. Toxicity of UV Filter Benzophenone-3 in Brine Shrimp Nauplii (Artemia salina) and Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2024; 14(2):537-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz-Román, Melissa I., Ileska M. Casiano-Muñiz, and Felix R. Román-Velázquez. 2024. "Toxicity of UV Filter Benzophenone-3 in Brine Shrimp Nauplii (Artemia salina) and Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos" Journal of Xenobiotics 14, no. 2: 537-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14020032
APA StyleOrtiz-Román, M. I., Casiano-Muñiz, I. M., & Román-Velázquez, F. R. (2024). Toxicity of UV Filter Benzophenone-3 in Brine Shrimp Nauplii (Artemia salina) and Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Journal of Xenobiotics, 14(2), 537-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14020032