Does the Polycentric Urban Region Contribute to Economic Performance? The Case of Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Data and Methods
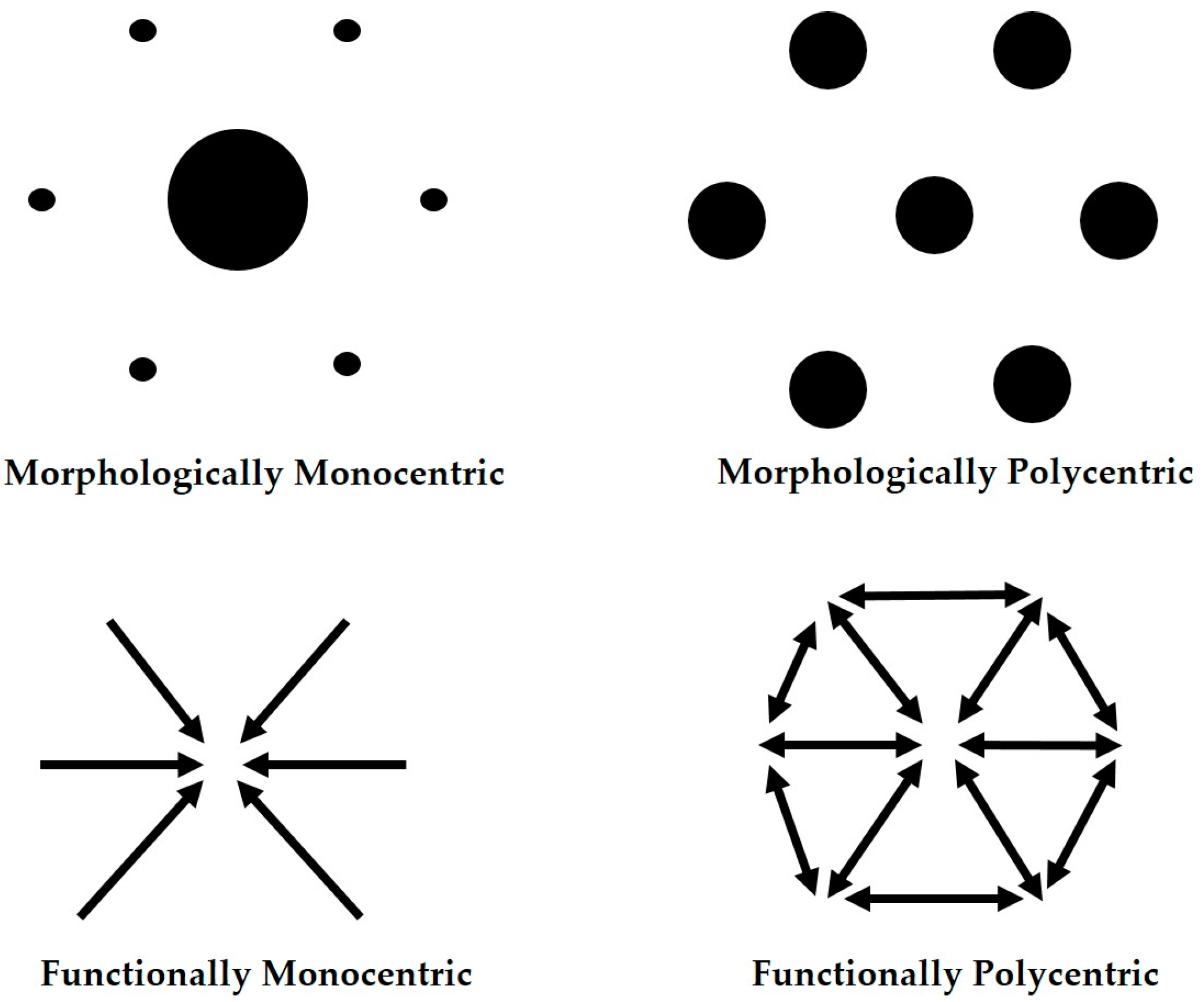
3.1. Defining the Functional Urban Regions
3.2. Measuring Polycentricity and Other Variables
3.3. Regression Model and Control Varibles
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Cities and Counties Listed for Each of the Functional Urban Regions
| Region No. | Cities and Counties |
|---|---|
| 1 | Seoul (25 districts), Incheon (10 districts), Suwon, Seongnam, Uijeonbu, Anyang, Bucheon, Gwangmyeong, Pyeongtaek, Dongducheon, Ansan, Goyang, Gwacheon, Guri, Namyangju, Osan, Siheung, Gunpo, Uiwang, Hanam, Yongin, Paju, Anseong, Gimpo, Hwaseong, Gwangju 1, Yangju, Pocheon, Yeoncheon, Yangpyeong, Cheolwon |
| 2 | Busan (16 districts), Gimhae, Milyang, Yangsan, Changwon, Uiryeong, Haman, Changnyeong |
| 3 | Daegu (8 districts), Gimcheon, Gumi, Yeongcheon, Gyeongsan, Gunwee, Cheongdo, Goryeong, Seongju, Chilgok, Hapcheon |
| 4 | Gwangju (5 districts), Naju, Damyang, Gokseong, Hwasun, Yeonggwang, Jangseong |
| 5 | Daejeon (5 districts), Okcheon, Yeongdong, Gongju, Nonsan, Gyeryong, Geumsan, Buyeo |
| 6 | Jeonju, Gunsan, Iksan, Jeongeup, Namwon, Gimje, Wanju, Jinan, Muju, Jangsu, Imsil, Sunchang, Buan, Seocheon |
| 7 | Cheonan, Asan, Sejong, Chungju, Jeongju, Boeun, Jincheon, Goesan, Eumsung, Jeungpyeong |
| 8 | Ulsan (5 districts) |
| 9 | Mokpo, Jangheung, Gangjin, Haenam, Yeongyang, Muan, Hampyeong, Wando, Jindo, Sinan |
| 10 | Jecheon, Danyang, Andong, Yeongju, Sangju, Mungyeong, Uisung, Cheongsong, Yecheon, Bonghwa |
| 11 | Gangneung, Donghae, Taebaek, Sokcho, Samcheok, Yeongwol, Pyeongchang, Jeongsun, Goseong, Yangyang |
| 12 | Jinju, Tongyeong, Sacheon, Geoje, Namhae, Hadong, Sancheong, Hamynag, Geochang |
| 13 | Chuncheon, Wonju, Hongcheon, Hoengseong, Hwacheon, Yanggu, Inje, Icheon, Yeoju, Gapyeong |
| 14 | Yeosu, Suncheon, Gwangyang, Gurye, Goheung, Boseong |
| 15 | Boryeong, Seosan, Dangjin, Cheongyang, Hongseon, Yesan, Taean |
| 16 | Pohang, Gyeongju, Yeongduk, Uljin, Ulreung |
| 17 | Jeju, Seguipo |
References
- Vandermotten, C.; Halbert, L.; Roelandts, M.; Cornut, P. European planning and the polycentric consensus: Wishful thinking? Reg. Stud. 2008, 42, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezzi, M.; Veneri, P. Assessing polycentric urban systems in the oecd: Country, regional and metropolitan perspectives. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2015, 23, 1128–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyler, M.; Kloosterman, R.C.; Sokol, M. Polycentric puzzles—Emerging mega-city regions seen through the lens of advanced producer services. Reg. Stud. 2008, 42, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, S. European briefing: Polycentricity in european spatial planning: From an analytical tool to a normative agenda. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2003, 11, 979–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X. How did urban polycentricity and dispersion affect economic productivity? A case study of 306 chinese cities. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2018, 173, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Shaw, D. Polycentric development practice in master planning: The case of china. Int. Plan. Stud. 2018, 23, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, B.; Li, W. The economic performance of urban structure: From the perspective of polycentricity and monocentricity. Cities 2017, 68, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, E.; Burger, M.J. Spatial structure and productivity in us metropolitan areas. Environ. Plan. A 2010, 42, 1383–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneri, P.; Burgalassi, D. Questioning polycentric development and its effects. Issues of definition and measurement for the italian nuts-2 regions. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2012, 20, 1017–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, J. The polycentric urban region: A closer inspection. Reg. Stud. 2004, 38, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Derudder, B.; Wang, M. Polycentric urban development in china: A multi-scale analysis. Environ. Plan. B: Urban. Anal. City Sci. 2017, 45, 953–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J.; Evans, D.M.; Pain, K. Application of the interlocking network model to mega-city-regions: Measuring polycentricity within and beyond city-regions. Reg. Stud. 2008, 42, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauhut, D. Polycentricity—One concept or many? Eur. Plan. Stud. 2017, 25, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.J.; Van Der Knaap, B.; Wall, R.S. Polycentricity and the multiplexity of urban networks. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2014, 22, 816–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N. Functional polycentricity: A formal definition in terms of social network analysis. Urban Stud. 2007, 44, 2077–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloosterman, R.C.; Musterd, S. The polycentric urban region: Towards a research agenda. Urban Stud. 2001, 38, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Goei, B.; Burger, M.J.; Van Oort, F.G.; Kitson, M. Functional polycentrism and urban network development in the greater south east, united kingdom: Evidence from commuting patterns, 1981–2001. Reg. Stud. 2010, 44, 1149–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, E.; Burger, M.J. Stretching the concept of ‘borrowed size’. Urban Stud. 2017, 54, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.J.; Meijers, E.J.; Hoogerbrugge, M.M.; Tresserra, J.M. Borrowed size, agglomeration shadows and cultural amenities in north-west europe. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2015, 23, 1090–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESPON. Potentials for Polycentric Development in Europe; Nordregio Estocolmo: Stockholm, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, C.; Arisona, S.M.; Huang, X.; Batty, M.; Schmitt, G. Detecting the dynamics of urban structure through spatial network analysis. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 2178–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.D.; Rae, A. An economic geography of the united states: From commutes to megaregions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosvall, M.; Bergstrom, C.T. An information-theoretic framework for resolving community structure in complex networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7327–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancichinetti, A.; Fortunato, S. Community detection algorithms: A comparative analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 056117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselin, L. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Environment at a Glance 2015: Oecd Indicators; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Shin, H. Negotiating the polycentric city-region: Developmental state politics of new town development in the seoul capital region. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 1333–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Korea. 2015 Population and Housing Census Sample Survey Report: Migration, Commuting and Disability; Statistics Korea: Daejeon, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Phelps, N.; Fallon, R.; Williams, C. Small firms, borrowed size and the urban-rural shift. Reg. Stud. 2001, 35, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camagni, R.; Capello, R. Second-rank city dynamics: Theoretical interpretations behind their growth potentials. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2015, 23, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, E.J.; Burger, M.; Hoogerbrugge, M. Borrowing size in networks of cities: City size, network connectivity and metropolitan functions in europe. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2016, 95, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, N.A. Clusters, dispersion and the spaces in between: For an economic geography of the banal. Urban Stud. 2004, 41, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labor productivity | 4.267 | 0.331 | 3.625 | 5.171 |
| Capital-labor ratio | 2.141 | 1.664 | −2.515 | 5.379 |
| Human capital | −1.128 | 0.312 | −1.859 | −0.423 |
| Population size | 11.762 | 1.064 | 9.035 | 13.934 |
| Morphological polycentricity | 0.023 | 0.307 | −0.888 | 0.872 |
| Functional polycentricity | 0.536 | 0.817 | 0.244 | 0.622 |
| Variables | Model 1 City | Model 2 City | Model 3 City | Model 4 City | Model 5 Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | OLS | OLS | SEM | OLS | |
| Constant | 4.318 (0.371) *** | 3.807 (0.122) *** | 3.912 (0.389) *** | 3.69 (0.418) *** | 2.681 (0.671) *** |
| Capital–labor ratio | 0.104 (0.011) *** | - | 0.106 (0.01) *** | 0.103 (0.011) *** | 0.233 (0.018) *** |
| Level of education | 0.243 (0.098) *** | - | 0.253 (0.095) *** | 0.284 (0.095) *** | −0.309 (0.192) |
| Population size | −0.143 (0.028) *** | - | -0.147 (0.027) *** | −0.146 (0.026) *** | −0.211 (0.037) *** |
| Morphological polycentricity | - | 0.193 (0.103) * | 0.308 (0.083) *** | 0.259 (0.104) ** | 0.37 (0.055) *** |
| Functional polycentricity | - | −0.717 (0.186) *** | −0.598 (0.148) *** | −0.668 (0.197) *** | −0.68 (0.116) *** |
| Lambda | - | - | - | 0.385 (0.083) *** | - |
| Observation | 227 | 227 | 227 | 227 | 17 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.369 | 0.062 | 0.412 | 0.487 | 0.959 |
| Moran’s I | 5.853 *** | 7.726 *** | 5.029 *** | - | - |
| Robust LM lag | 4.589 *** | 1.815 | 4.302 *** | - | - |
| Robust LM error | 23.971 *** | 44.436 *** | 15.715 *** | - | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, K.; Seo, M. Does the Polycentric Urban Region Contribute to Economic Performance? The Case of Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114157
Kwon K, Seo M. Does the Polycentric Urban Region Contribute to Economic Performance? The Case of Korea. Sustainability. 2018; 10(11):4157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114157
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Kyusang, and Minho Seo. 2018. "Does the Polycentric Urban Region Contribute to Economic Performance? The Case of Korea" Sustainability 10, no. 11: 4157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114157
APA StyleKwon, K., & Seo, M. (2018). Does the Polycentric Urban Region Contribute to Economic Performance? The Case of Korea. Sustainability, 10(11), 4157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114157





