Journal Description
Sustainability
Sustainability
is an international, peer-reviewed, open-access journal on environmental, cultural, economic, and social sustainability of human beings, published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC), International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) and Urban Land Institute (ULI) are affiliated with Sustainability and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), GEOBASE, GeoRef, Inspec, RePEc, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Environmental Studies) / CiteScore - Q1 (Geography, Planning and Development)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Sustainability.
- Companion journals for Sustainability include: World, Sustainable Chemistry, Conservation, Future Transportation, Architecture, Standards, Merits, Bioresources and Bioproducts and Accounting and Auditing.
Impact Factor:
3.3 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.6 (2024)
Latest Articles
Drivers of AI–Sustainability: The Roles of Financial Wealth, Human Capital, and Renewable Energy
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9920; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219920 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly central to sustainable development, yet its advancement varies across G7 economies. This study employs Method of Moments Quantile Regression (MMQR) to examine how Financial Technology (FinTech), Economic Growth (EG), Human Capital (HC), and Renewable Energy Consumption (RENC) influence
[...] Read more.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly central to sustainable development, yet its advancement varies across G7 economies. This study employs Method of Moments Quantile Regression (MMQR) to examine how Financial Technology (FinTech), Economic Growth (EG), Human Capital (HC), and Renewable Energy Consumption (RENC) influence AI development in G7 countries from 2000 to 2022. By analyzing heterogeneous effects across quantiles, the study captures stage-specific drivers often overlooked in average-based models. Results indicate that FinTech and human capital significantly promote AI adoption in lower and middle quantiles, enhancing digital inclusion and innovation capacity, while RENC becomes relevant primarily at advanced stages of AI adoption. Economic growth exhibits negative or inconsistent effects, suggesting that GDP expansion alone is insufficient for technological transformation without alignment to supportive policies and institutional contexts. The lack of long-run cointegration further highlights the dominance of short- and medium-term dynamics in shaping the AI–sustainability nexus. These findings provide actionable insights for policymakers, emphasizing targeted FinTech development, skill-building initiatives, and renewable-powered AI solutions to foster sustainable and inclusive AI adoption. Overall, the study demonstrates how financial, human, and environmental factors jointly drive AI development, offering a mechanism-based perspective on technology-driven sustainable development in advanced economies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI for Sustainable Development: Applications and Impacts across Industries)
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Soil Stabilisation Using Water Treatment Sludge: Experimental Evaluation and Metaheuristic-Based Genetic Programming
by
Bidur Kafle and Abolfazl Baghbani
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9919; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219919 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Recycling water treatment sludge (WTS) offers a sustainable solution to reduce environmental waste and enhance soil stabilisation in geotechnical applications. This study investigates the mechanical performance of soil-sludge-cement-lime mixtures through an extensive experimental program and focuses on compaction characteristics and California Bearing Ratio
[...] Read more.
Recycling water treatment sludge (WTS) offers a sustainable solution to reduce environmental waste and enhance soil stabilisation in geotechnical applications. This study investigates the mechanical performance of soil-sludge-cement-lime mixtures through an extensive experimental program and focuses on compaction characteristics and California Bearing Ratio (CBR) values. Mixtures containing 40% soil, 50% sludge, and 10% lime achieved a CBR value of 58.7% and represented a 550% increase compared to untreated soil. Additionally, advanced predictive modelling using symbolic metaheuristic-based genetic programming (GP) techniques, including the Dingo Optimisation Algorithm (DOA), Osprey Optimisation Algorithm (OOA), and Rime-Ice Optimisation Algorithm (RIME), demonstrated exceptional accuracy in predicting CBR values. The GP-RIME model achieved an R2 of 0.991 and a mean absolute error (MAE) of 1.02 in predicting CBR values, significantly outperforming traditional regression methods. Four formulas are proposed to predict CBR values. This research highlights the dual benefits of sustainable WTS recycling and advanced modelling techniques, providing scalable solutions for environmentally friendly infrastructure development. This research aligns with global sustainability goals by valorising waste streams from water treatment plants. The reuse of sludge not only reduces landfill disposal but also lowers demand for energy-intensive binders, contributing to circular economy practice and sustainable infrastructure development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environmental Protection and Sustainable Ecological Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
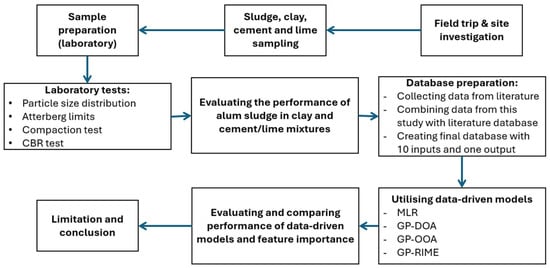
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Indigenous Lands Turned into Soy Farms Pose Threats to Sustainability in Brazil
by
Felipe Kamaroski and Juliano Morimoto
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9918; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219918 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Urban areas are growing, often at the expense of native ecosystems. As a result, indigenous lands (ILs) have become critical refuges for biodiversity, essential for sustainability and sit at the intersection of cultural, economic, and environmental interests. ILs play a double role in
[...] Read more.
Urban areas are growing, often at the expense of native ecosystems. As a result, indigenous lands (ILs) have become critical refuges for biodiversity, essential for sustainability and sit at the intersection of cultural, economic, and environmental interests. ILs play a double role in this context: they protect native biodiversity but are often framed as barriers to economic growth. In Brazil, nearly 14% of the territory is demarcated as ILs. This has led to conflicts with Brazil’s agricultural sector, particularly in the southernmost states, where agribusiness drives the economy. We hypothesize that this conflict leads to agricultural encroachment of ILs, which might become extension of farms, compromising their sustainability. We analyzed two decades of public data on soy coverage within ILs in Brazil’s southernmost states (Paraná, Santa Catarina, and Rio Grande do Sul) and found that soy cultivation in ILs increased by over 116% in the last two decades, peaking in 2019 at 177% above the 2001 baseline. We argue that ILs urgently need a framework that enables the communities therein to benefit from income originating from land lease, while ensuring that encroachment is limited and does not pose threats to native biodiversity. This can be challenging due to growing political pressure to weaken socioenvironmental protection and ILs’ demarcation but is nevertheless essential for the sustainable coexistence of urban areas, farms, and ILs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Urban Planning and Sustainable Land Use—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Prioritizing Sustainable Marketing Innovation for Pharmaceutical Firms in Indonesia
by
Zuldekra, Rokhani Hasbullah, Zenal Asikin and Tanti Novianti
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9917; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219917 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Indonesian pharmaceutical industry faces increasing pressure to achieve sustainable performance amid regulatory constraints and evolving healthcare demands. This study aims to identify and prioritize strategic dimensions of sustainable marketing innovation using the Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (Fuzzy AHP). Expert judgments were collected
[...] Read more.
The Indonesian pharmaceutical industry faces increasing pressure to achieve sustainable performance amid regulatory constraints and evolving healthcare demands. This study aims to identify and prioritize strategic dimensions of sustainable marketing innovation using the Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (Fuzzy AHP). Expert judgments were collected from eight senior professionals across academia, industry, and government through structured online questionnaires and digital interviews. Six innovation dimensions (product, process, organization, price, promotion, and distribution) were evaluated. The analysis produced normalized priority weights, revealing that promotion (0.2384) and process (0.2253) innovations ranked highest, followed by product (0.1790) and price (0.1699), while distribution (0.1202) and organization (0.0672) held lower importance. These results highlight the critical role of ethical promotion, digital engagement, and operational excellence in strengthening competitive and sustainable market performance. A sensitivity analysis confirmed the stability of these rankings across varying fuzzification scales. By integrating the Resource-Based View (RBV) with Fuzzy AHP, this study contributes a reproducible framework for transforming expert knowledge into strategic priorities under uncertainty. The findings offer practical guidance for pharmaceutical firms to allocate innovation resources more effectively and enhance long-term sustainability.
Full article
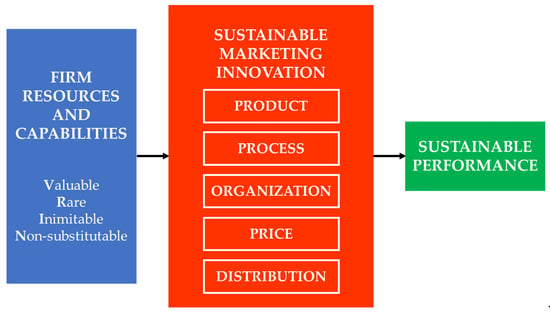
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Practice Primacy: Revisiting the Knowledge–Action Gap in Pro-Environmental Behavior with eXplainable AI
by
Xun Yang, Shensheng Chen, Tingting Liu, Junjie Luo and Yuzhen Tang
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9916; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219916 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Against the backdrop of an escalating global environmental crisis, bridging the “knowledge–action gap” in the pro-environmental behavior (PEB) of university students has become a key challenge for sustainable development education, aligning with SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
[...] Read more.
Against the backdrop of an escalating global environmental crisis, bridging the “knowledge–action gap” in the pro-environmental behavior (PEB) of university students has become a key challenge for sustainable development education, aligning with SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) and SDG 13 (Climate Action). Traditional linear models often struggle to capture the complex non-linearities and interaction effects when explaining this gap. To overcome this limitation, this study introduces an integrated “prediction-plus-explanation” framework using eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). Based on survey data from 463 university students in China, we constructed a high-precision PEB prediction model (Accuracy = 93.55%) using the CatBoost algorithm and conducted an in-depth analysis of its internal decision-making mechanisms with the SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) framework. The results reveal that a “Practice Primacy” model plays a dominant role in driving PEB: the formation of environmental habits, participation in environmental practices, and the investment of related resources are the overwhelmingly dominant factors in predicting individual behavior, with their cumulative contribution far exceeding that of traditional cognitive and attitudinal variables. Furthermore, heterogeneity analysis revealed significant group differences in these driving mechanisms: the behavioral decisions of male students tend to be more “value-driven,” while lower-division students are more susceptible to external educational interventions. By quantifying the non-linear effects and relative importance of each driver, this study offers a new “Action-to-Cognition” perspective for bridging the knowledge–action gap and provides robust, data-driven support for universities to design precise and differentiated intervention strategies, thus contributing to the achievement of SDGs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue A Quantitative Analysis and Interdisciplinary Approach to the Sustainable Development Goals)
►▼
Show Figures
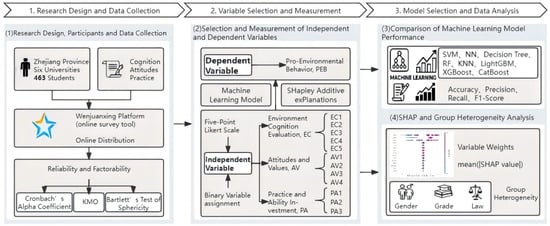
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Inverted U-Shaped Effect of Environmental Taxation on Green Innovation: The Roles of Corporate Environmental Responsibility and Green Finance
by
Qi Zhang, Liangqun Qi and Lawrence Loh
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9915; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219915 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Implementing environmental protection taxes implies a shift in environmental policy from government enforcement to market incentives, fostering long-term sustainability. Based on institutional theory, this study explores the nonlinear impact of environmental taxes on corporate green innovation and its influencing mechanism, by considering the
[...] Read more.
Implementing environmental protection taxes implies a shift in environmental policy from government enforcement to market incentives, fostering long-term sustainability. Based on institutional theory, this study explores the nonlinear impact of environmental taxes on corporate green innovation and its influencing mechanism, by considering the complex interaction between innovation offsets and environmental costs. Utilizing data from Chinese A-share listed companies on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges during 2012 and 2023, the study reveals an inverse U-shaped relationship between environmental taxes and green innovation performance, within which corporate environmental responsibility functions as a mediator. Furthermore, the results also reveal that the relationship between environmental taxes and green innovation is positively moderated by the development level of regional green finance. In addition, the heterogeneity analyses show that the inverse U-shaped relationship is more pronounced among heavily polluting and large-scale firms, and firms in more marketized areas and areas with higher levels of intellectual property protection. The research enriches the literature on the dual-edged effects of environmental taxes anchored in green innovation and unpacks the internal mechanism of the effectiveness of environmental protection tax policy. It also provides practical implications for the design of tiered taxes and green finance policies aimed at achieving sustainable development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovation Management, Competition Strategies and Corporate Sustainability—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Generative AI Integration: Key Drivers and Factors Enhancing Productivity of Engineering Faculty and Students for Sustainable Education
by
Humaid Al Naqbi, Zied Bahroun and Vian Ahmed
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9914; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219914 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) technologies are revolutionizing productivity and creativity across educational and engineering contexts. This study addresses a critical gap by examining the key factors influencing the successful integration of GAI tools to enhance faculty and student productivity, with a focus on
[...] Read more.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) technologies are revolutionizing productivity and creativity across educational and engineering contexts. This study addresses a critical gap by examining the key factors influencing the successful integration of GAI tools to enhance faculty and student productivity, with a focus on higher education and its role in advancing sustainable development. Specifically, it investigates challenges, opportunities, and essential conditions for effective GAI adoption that support not only academic excellence but also the preparation of engineers capable of addressing global sustainability challenges in line with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 4 (Quality Education), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production). A preliminary literature review identified significant factors requiring attention, further refined through interviews with 14 students and 13 faculty members, and expanded upon via a survey involving 54 students and 42 faculty members. Participants rated the significance of various factors on a five-point Likert scale, allowing for the calculation of the Relative Importance Index (RII). The findings reveal that while compliance with ethical standards and bias mitigation emerged as the most significant concerns, mid-level considerations such as institutional support, training, and explainability are critical for fostering GAI adoption in sustainable learning environments. Foundational elements, including robust technical infrastructure, data security, and scalability, are vital for long-term success and alignment with responsible and sustainable innovation. Notably, this study highlights a divergence in perspectives between faculty and students regarding GAI’s impact on productivity, with faculty emphasizing ethical considerations and students focusing on efficiency gains. This study offers a comprehensive set of considerations and insights for guiding GAI integration in educational and engineering settings. It emphasizes the need for multidisciplinary collaboration, continuous training, and strong governance to balance innovation, responsibility, and sustainability. The findings advance theoretical understanding and provide practical insights for academia, policymakers, and technology developers aiming to harness GAI’s full potential in fostering sustainable engineering education and development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Engineering Education and Sustainable Development)
►▼
Show Figures
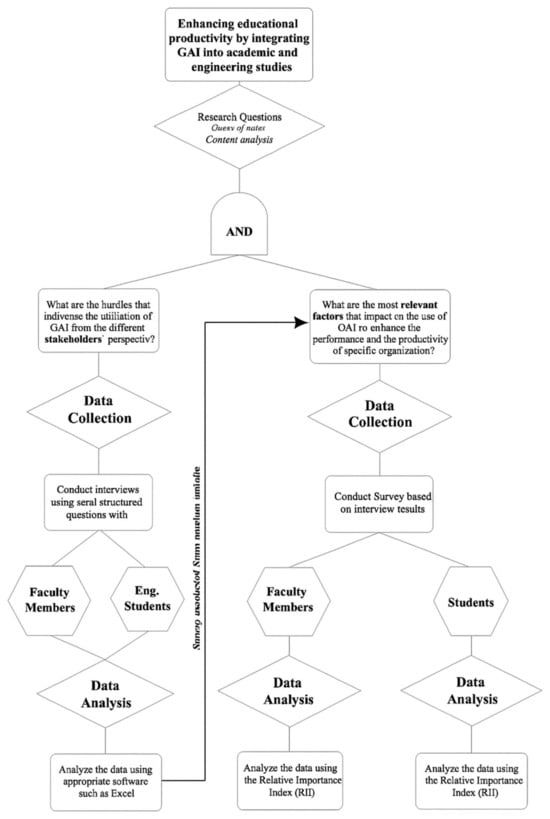
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Lignin Valorization from Lignocellulosic Biomass: Extraction, Depolymerization, and Applications in the Circular Bioeconomy
by
Tomas Makaveckas, Aušra Šimonėlienė and Vilma Šipailaitė-Ramoškienė
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9913; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219913 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Lignocellulosic biomass—the non-edible fraction of plants composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—is the most abundant renewable carbon resource and a key lever for shifting from fossil to bio-based production. Agro-industrial residues (straws, cobs, shells, bagasse, brewery spent grains, etc.) offer low-cost, widely available
[...] Read more.
Lignocellulosic biomass—the non-edible fraction of plants composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—is the most abundant renewable carbon resource and a key lever for shifting from fossil to bio-based production. Agro-industrial residues (straws, cobs, shells, bagasse, brewery spent grains, etc.) offer low-cost, widely available feedstocks but are difficult to process because their polymers form a tightly integrated, three-dimensional matrix. Within this matrix, lignin provides rigidity, hydrophobicity, and defense, yet its heterogeneity and recalcitrance impede saccharification and upgrading. Today, most technical lignin from pulping and emerging biorefineries is burned for energy, despite growing opportunities to valorize it directly as a macromolecule (e.g., adhesives, foams, carbon precursors, UV/antioxidant additives) or via depolymerization to low-molecular-weight aromatics for fuels and chemicals. Extraction route and severity strongly condition lignin structure linkages (coumaryl-, coniferyl-, and sinapyl-alcohol ratios), determining reactivity, solubility, and product selectivity. Advances in selective fractionation, reductive/oxidative catalysis, and hybrid chemo-biological routes are improving yields while limiting condensation. Remaining barriers include feedstock variability, solvent and catalyst recovery, hydrogen and energy intensity, and market adoption (e.g., low-emission adhesives). Elevating lignin from fuel to product within integrated biorefineries can unlock significant environmental and economic benefits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
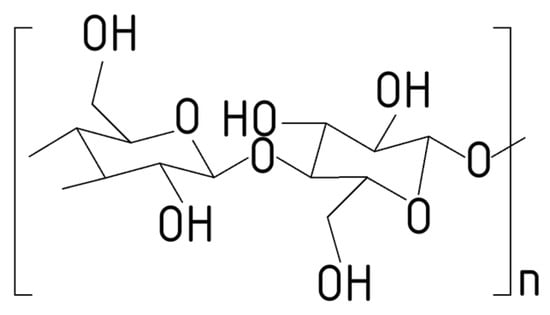
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Ventilation Control Methods for Energy Efficiency and Indoor Climate Stability: A Case Study of a Zoo Exhibition Room
by
Sylwia Szczęśniak, Michał Karpuk and Juliusz Walaszczyk
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9912; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219912 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
This study evaluates indoor thermal comfort and the energy performance of HVAC control strategies in the Congo Zone of a zoological facility located in Poland. The main objective in this zone is to maintain adequate relative humidity, which is more critical for plants
[...] Read more.
This study evaluates indoor thermal comfort and the energy performance of HVAC control strategies in the Congo Zone of a zoological facility located in Poland. The main objective in this zone is to maintain adequate relative humidity, which is more critical for plants and animals than the indoor air temperature range. Long-term measurements were carried out to determine the variation of air system heat transfer as a function of outdoor air temperature. To determine the energy demand for heating, cooling, and air transport, eight control algorithms were analysed, each differing in a single detail but potentially affecting overall energy use and thermal comfort. The algorithms combined the following features: maintaining a constant supply or indoor air temperature; operating with a constant or modulated recirculation damper position; maintaining a constant or variable airflow (CAV or VAV); operating within the normal setpoint range or with an extended range of 1 °C; controlling temperature only or both temperature and humidity; and utilising or not utilising free cooling. The control algorithm operating in the facility maintained indoor humidity within acceptable limits for 98% of the year but failed to meet temperature requirements for 28% of the time. Refined strategies achieved energy savings of up to 74% in fan power and 80% in cooling demand, though often at the cost of reduced humidity control.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in the Sustainability of the Built Environment, Green Energy, and Building Energy Performance)
►▼
Show Figures
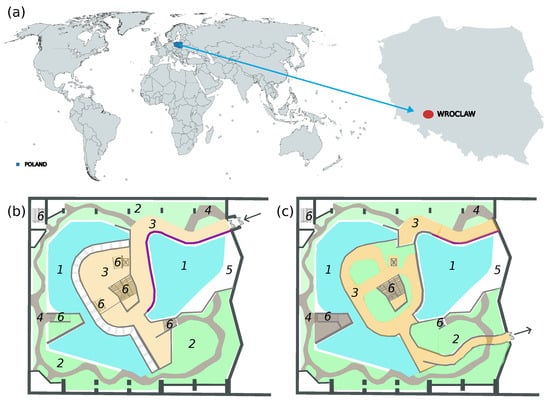
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Will Automated Vehicles Drive You to Move? Exploring and Predicting the Impact of AV Technology on Residential Relocation
by
Song Wang, Xin Tian, Zhixia Li, Shang Jiang, Wenjing Zhao, Shiyao Zhang, Hao (Frank) Yang and Guohui Zhang
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9911; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219911 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Automated vehicle (AV) technology is expected to alter travel behavior and residential location choices, yet the psychological motivations behind relocation decisions under current partial automation (Level 2) remain underexplored, as most studies focus on fully autonomous scenarios. This study explores why individuals might
[...] Read more.
Automated vehicle (AV) technology is expected to alter travel behavior and residential location choices, yet the psychological motivations behind relocation decisions under current partial automation (Level 2) remain underexplored, as most studies focus on fully autonomous scenarios. This study explores why individuals might relocate in response to AV availability in both short-term and long-term contexts and predicts how willingness to relocate changes as automation levels advance. In a survey of Kentucky residents, data were collected on demographic and economic characteristics, travel needs, built environment attributes, AV familiarity, comfort with different automation levels, and willingness to relocate if AVs were available. Multiple machine learning models with Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) were used to predict and interpret changes in relocation willingness. Results indicate that greater comfort with high-level automation and higher AV familiarity increase relocation intentions, particularly among men, older adults with higher incomes, and urban residents. SHAP analysis reveals that built environment, age, and comfort with fully autonomous driving are the most influential predictors of changes in relocation willingness. Findings inform land use and housing policy by identifying where perception-driven relocation pressures are likely to emerge and by outlining adaptive tools to guide spatial growth as AV technology advances.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable and Smart Transportation Systems)
Open AccessArticle
Simulation-Integrated Climate-Adaptive Pedestrian Design Explorations for Summer Thermal Comfort: The Case of Culturally Diversified Green Way Project in Seoul, South Korea
by
Gawon Bae, Eujin Julia Kim and Kwangmin Ham
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9910; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219910 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study investigates the effectiveness of climate-adaptive pedestrian design through greening strategies by integrating microclimate simulations in central Seoul. Utilizing ENVI-met 5.0, five pedestrian street typologies along the “Cultural Complex Axis” in central Seoul were analyzed for their thermal environments before and after
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the effectiveness of climate-adaptive pedestrian design through greening strategies by integrating microclimate simulations in central Seoul. Utilizing ENVI-met 5.0, five pedestrian street typologies along the “Cultural Complex Axis” in central Seoul were analyzed for their thermal environments before and after greening interventions. Results indicate that pedestrian greening improves thermal comfort across all sites, though cooling effects vary significantly with site-specific urban morphology and microclimatic factors such as wind flow. Notably, Hyehwa-ro exhibited the greatest reduction in Physiological Equivalent Temperature (PET) despite a modest increase in greenery, underscoring that cooling efficiency depends on more than vegetation quantity alone. Conversely, Jangchungdan-ro, with greater green coverage, observed diminished thermal improvements, which were mainly attributed to reduced wind velocity. The findings emphasize the need for context-sensitive, tailored greening approaches that particularly emphasize securing wind corridors and avoiding dense planting in narrow urban canyons to maximize cooling impacts. This study contributes by providing insights into both the research process and its outcomes through the exploration of thermal comfort simulations applied to a practical pedestrian renovation case.
Full article
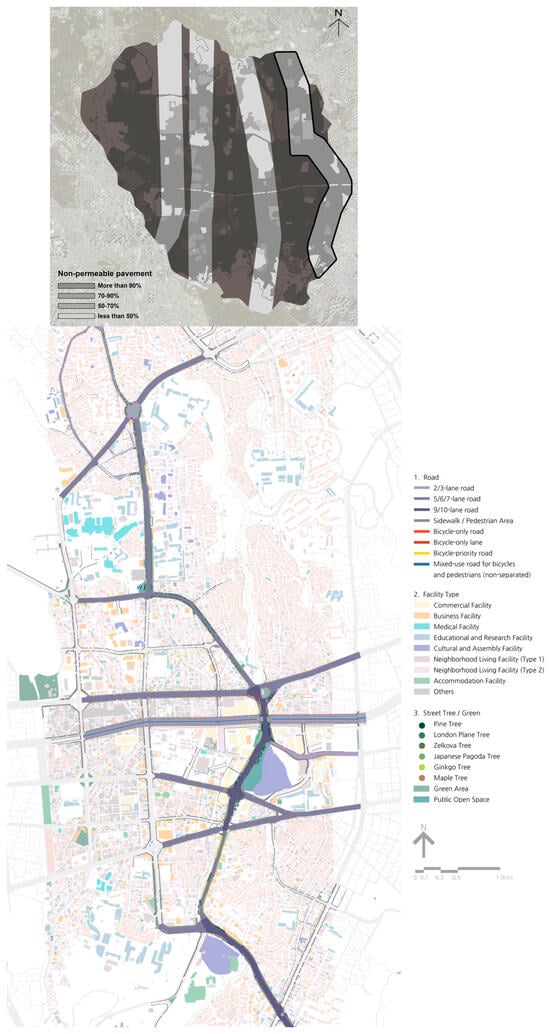
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating the Effect of Talent Management Practices on Sustainable Competitive Advantage in Private-Sector Organizations
by
Razaz Waheeb Attar, Amal Alanazi and Amal Hassan Alhazmi
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9909; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219909 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Talent management is an important strategic tool to improve sustainable organization performance and competitiveness in the contemporary business environment. Even though there are increasingly more studies around this topic in the world, studies in the context of Saudi Arabia, and more specifically in
[...] Read more.
Talent management is an important strategic tool to improve sustainable organization performance and competitiveness in the contemporary business environment. Even though there are increasingly more studies around this topic in the world, studies in the context of Saudi Arabia, and more specifically in the private sector, are still scarce, forming the research gap that this study aims to fill. The study is designed to explore the effect of human resource practices on employee innovation, organization resilience, and sustainable competitive advantage in the Saudi private-sector organizations based on the Resource-Based Variability (RBV) theory as a theoretical perspective. Data were gathered from 366 structured questionnaires, and the hypotheses were tested by employing the relevant statistical tools. The results supported the first hypothesis (H1), showing that there is a positive influence of the practices of talent management on the innovation of the employees, and the second hypothesis (H2) showing the correlation between these practices and organizational resilience. The third hypothesis (H3) showed that talent management practices are significant in the attainment of a sustainable competitive advantage. The findings affirm that the adoption of sound approaches for the attraction, development, and retention of talent has a part in the consolidation of innovation, resilience, and the accomplishment of competitive advantage. The most important theoretical and applied implications of the study are discussed at the end, along with the limitations of the study and suggestions for future research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancing Management Practices Through Digital Marketing and Sustainable Innovation)
►▼
Show Figures
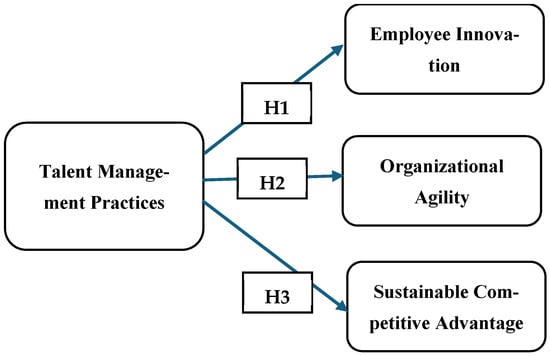
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Balancing Forecast Accuracy and Emissions for Hourly Wind Power at Dumat Al-Jandal: Sustainable AI for Zero-Carbon Transitions
by
Haytham Elmousalami, Felix Kin Peng Hui and Aljawharah A. Alnaser
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9908; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219908 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
This paper develops a Sustainable Artificial Intelligence-Driven Wind Power Forecasting System (SAI-WPFS) to enhance the integration of renewable energy while minimizing the environmental footprint of deep learning computations. Although deep learning models such as CNN, LSTM, and GRU have achieved high accuracy in
[...] Read more.
This paper develops a Sustainable Artificial Intelligence-Driven Wind Power Forecasting System (SAI-WPFS) to enhance the integration of renewable energy while minimizing the environmental footprint of deep learning computations. Although deep learning models such as CNN, LSTM, and GRU have achieved high accuracy in wind power forecasting, existing research rarely considers the computational energy cost and associated carbon emissions, creating a gap between predictive performance and sustainability objectives. Moreover, limited studies have addressed the need for a balanced framework that jointly evaluates forecast precision and eco-efficiency in the context of large-scale renewable deployment. Using real-time data from the Dumat Al-Jandal Wind Farm, Saudi Arabia’s first utility-scale wind project, this study evaluates multiple deep learning architectures, including CNN-LSTM-AM and GRU, under a dual assessment framework combining accuracy metrics (MAE, RMSE, R2) and carbon efficiency indicators (CO2 emissions per computational hour). Results show that the CNN-LSTM-AM model achieves the highest forecasting accuracy (MAE = 29.37, RMSE = 144.99, R2 = 0.74), while the GRU model offers the best trade-off between performance and emissions (320 g CO2/h). These findings demonstrate the feasibility of integrating sustainable AI into wind energy forecasting, aligning technical innovation with Saudi Vision 2030 goals for zero-carbon cities and carbon-efficient energy systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Energy Systems and Applications)
Open AccessArticle
Sustainability and Circularity in Electrical Installations: Insights from Belgian Construction Professionals
by
Asma Salimi Sofla and Chiara Piccardo
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9907; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219907 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Electrical and electronic installations (EEIs) are essential to modern building functionality, yet they remain insufficiently addressed in circular economy (CE) strategies and sustainability frameworks. This study examines how CE principles are understood and applied to EEI in the Flemish construction sector, utilising a
[...] Read more.
Electrical and electronic installations (EEIs) are essential to modern building functionality, yet they remain insufficiently addressed in circular economy (CE) strategies and sustainability frameworks. This study examines how CE principles are understood and applied to EEI in the Flemish construction sector, utilising a national survey of 32 professionals and, among them, five expert interviews. Results confirm that energy-efficient technologies, such as LED lighting and the integration of renewable energy, are widely adopted. In contrast, circular practices, including reuse, modularity, and design for disassembly, remain relatively rare. Respondents acknowledged the importance of lifecycle thinking but reported limited access to practical tools, clear guidelines, and market or regulatory incentives to support its implementation. Circular business models, such as leasing and take-back schemes, are recognised in theory but not widely adopted in practice. At the same time, stakeholder engagement often occurs too late to influence circular outcomes. Overall, the findings suggest that strengthening interdisciplinary cooperation, improving knowledge exchange, and defining clearer project requirements could help translate circular principles into everyday professional practice. This study provides an initial evidence base for improving professional awareness and integrating circular principles into EEI design and procurement, contributing to more circular and sustainable EEI within the construction sector.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Engineering and Science)
►▼
Show Figures
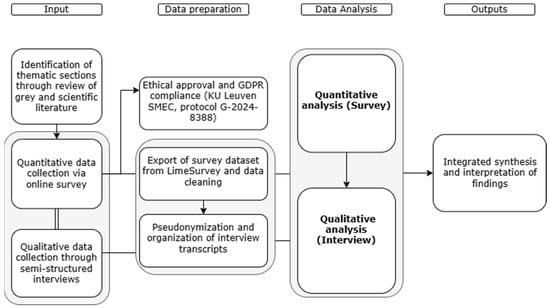
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ecological Outcomes and Societal Transformation: Multiple Visions for Adaptation in the Great Barrier Reef
by
Gillian Paxton, Stewart Lockie, Rana Dadpour, Henry A. Bartelet and Bruce Taylor
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9906; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219906 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Fears regarding the future of coral reefs are reflected in a growing scientific effort, worldwide, to help corals survive and adapt to the impacts of climate change through new management strategies. To be viable, these strategies must not only be ecologically beneficial and
[...] Read more.
Fears regarding the future of coral reefs are reflected in a growing scientific effort, worldwide, to help corals survive and adapt to the impacts of climate change through new management strategies. To be viable, these strategies must not only be ecologically beneficial and technically feasible; they must be developed in partnership with Indigenous peoples and sensitive to the needs and aspirations of local communities, stakeholders and broader publics. This paper synthesizes insights from a comprehensive program of qualitative and quantitative social research, conducted through Australia’s Reef Restoration and Adaptation Program, exploring local community and public perspectives on the Great Barrier Reef (GBR) and the prospect of assisted adaptation. While the results of this research indicate strong support for prospective interventions to help the GBR, they also demonstrate that local communities and the broader Australian public hold multiple visions for the GBR’s future and engage in careful processes to imagine and evaluate assisted adaptation. We discuss the implications of this complexity for the development of technically robust and socially responsible adaptation intervention in the GBR, emphasizing the opportunities it presents for robust and inclusive dialogue, knowledge building, and governance around these strategies. Community and public support, we conclude, is contingent on moving beyond the seemingly straightforward question of whether or not people support intervention and towards forms of engagement that allow space for social and cultural diversity and the co-creation of ethically grounded adaptation pathways.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Science and Management Approaches to Support Coral Reefs in a Time of Rapid Climate Change)
►▼
Show Figures
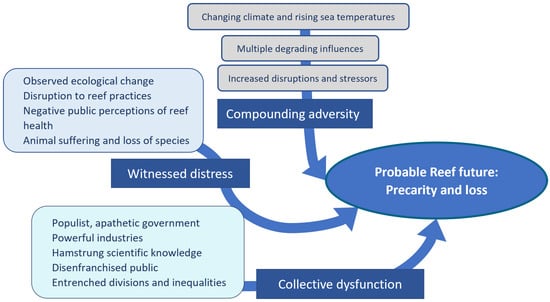
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multicriteria Optimization of Nanocellulose-Reinforced Polyvinyl Alcohol and Pyrrolidone Hydrogels
by
Nuno Costa, João Lourenço, Joana Cabalú, Ana Branco and Célio G. Figueiredo-Pina
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9905; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219905 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Developing new materials for human cartilage replacement is a hot research topic. These materials have multiple properties of interest, so selecting a new material (hydrogel) is a multi-attribute decision-making problem. A case study illustrates the application of a structured approach and tools to
[...] Read more.
Developing new materials for human cartilage replacement is a hot research topic. These materials have multiple properties of interest, so selecting a new material (hydrogel) is a multi-attribute decision-making problem. A case study illustrates the application of a structured approach and tools to solve this problem type. Ten hydrogels, most of which are new formulations, were evaluated based on three attributes. The weights assigned to the attributes were identified using three methods from the literature, in addition to those previously assigned by an expert. Since the hydrogel properties showed some variability, Monte Carlo simulations were carried out using triangular distribution. Ten thousand decision matrices were built and 10,000 rankings were generated by each of the ten multicriteria decision-making methods employed in this study. Ranking similarity was evaluated through the PS index, whose values ensure consistency and reliability of the results achieved. Rank acceptability and pairwise indexes were used to identify the most promising hydrogels. Two hydrogels were identified as the most promising for further study, for any of the four sets of weights used. Both are annealed nanocellulose-reinforced polyvinyl alcohol and pyrrolidone hydrogels. The robustness of this result is supported on the values of acceptability and pairwise indexes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Decision-Making in Sustainable Management)
Open AccessArticle
A Conceptual Framework for Sustainable Human Resource Management: Integrating Green Practices, Ethical Leadership, and Digital Resilience to Advance the SDGs
by
Buyung Kurniawan, Marnis, Samsir and Jahrizal
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9904; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219904 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article develops a conceptual framework of Sustainable Human Resource Management (Sustainable HRM) by integrating three critical dimensions: Green HRM practices, ethical and responsible leadership, and digital resilience in HR systems. Positioned within the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the study addresses
[...] Read more.
This article develops a conceptual framework of Sustainable Human Resource Management (Sustainable HRM) by integrating three critical dimensions: Green HRM practices, ethical and responsible leadership, and digital resilience in HR systems. Positioned within the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the study addresses the lack of theoretical integration across the fragmented literature. The framework highlights employee well-being as the central mediating construct linking HRM practices to sustainability outcomes, connecting micro-level engagement, meso-level HR systems and leadership ethics, and macro-level policy and ESG alignment. This explicitly demonstrates the multi-level (micro–meso–macro) nature of the framework. The proposed model advances theory by extending HRM beyond organizational boundaries, offering Sustainable HRM as a boundary-spanning and original perspective that links people management to global sustainability agendas. Using a five-stage conceptual development process including literature synthesis, construct definition, integrative framework building, formulation of conceptual propositions, and the design of a future research agenda—this study explicitly acknowledges its conceptual nature to set appropriate reader expectations and ensures methodological transparency in framework development. The study further contributes (1) to theory by clarifying how Green HRM, ethical leadership, and digital resilience interact through employee well-being to advance sustainability; (2) to practice by providing HR leaders with pathways to embed sustainability into core processes; and (3) to policy by informing regulators on HRM’s role in achieving SDGs. Ultimately, the framework positions HRM as a strategic enabler of sustainable development.
Full article
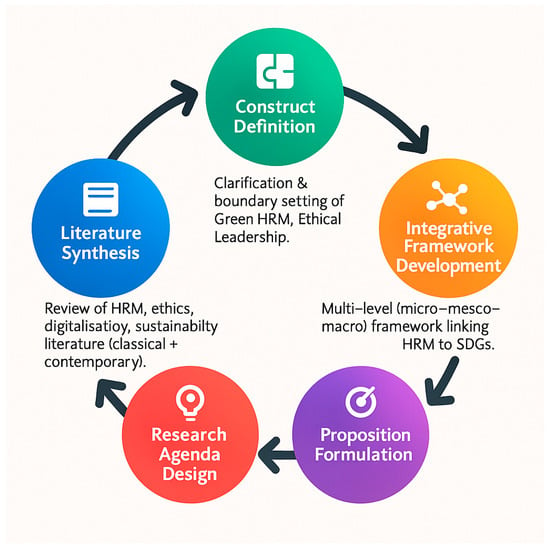
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Land Use and Carbon Stock Under Multiple Scenarios Based on the PLUS-InVEST Model: A Case Study of Chengdu
by
Lin Li, Yu Feng, Junjie He, Zheng Yang and Yiwen He
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9903; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219903 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Under the context of global climate change and China’s dual carbon strategy (DCS), the impact of land use/land cover change (LULCC) on regional carbon stocks has garnered increasing attention. As a key economic and ecological hub in Southwest China, Chengdu has undergone significant
[...] Read more.
Under the context of global climate change and China’s dual carbon strategy (DCS), the impact of land use/land cover change (LULCC) on regional carbon stocks has garnered increasing attention. As a key economic and ecological hub in Southwest China, Chengdu has undergone significant urbanization over the past two decades, and it is necessary to quantitatively assess how shifts in land use affect its carbon stock function. This study integrates multi-period remote sensing data from 2000 to 2020, combining socioeconomic and natural environmental drivers. The PLUS model was employed to simulate land use in 2030 under four scenarios: Natural Development Scenario (NDS), Urban Development Scenario (UDS), Conservation of Cropland Scenario (CPS), and Ecological Protection Scenario (EPS). The InVEST model was then used to calculate changes in carbon stocks and their spatial distribution characteristics. The results indicate the following: (1) From 2000 to 2020, Chengdu’s cropland decreased by 1188.6174 km2, while built-up land increased by 1006.5465 km2, resulting in a net carbon stock decrease of approximately 3.25 × 106 t, with carbon gains from forest restoration offsetting part of the cropland-to-built-up loss; (2) Under all scenarios, built-up land exhibited an expansion trend, with the UDS showing the most significant increase, reaching 1919.2455 km2. In the EPS, the forest increased to 4035.258 km2, achieving the largest carbon stock increase of 8.5853 × 106 t. (3) Chengdu’s carbon stock exhibits a spatial distribution pattern characterized by “high in the northwest, low in the center”. High-value areas are concentrated in the ecologically sound Longmen Mountains and Longquan Mountains, while low-value areas are primarily located in urban built-up zones and their peripheries. The study indicates that rationally controlling the expansion of Built-up land, strengthening ecological restoration, and protecting forests can effectively enhance Chengdu’s carbon sink capacity and achieve regional low-carbon and sustainable development. This study aims to address the gap in carbon stock assessments under different development scenarios at the urban scale in Southwest China, and to provide a scientific basis for Chengdu’s regional spatial planning, ecological conservation, low-carbon development, and sustainable land management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Urban and Rural Development)
►▼
Show Figures
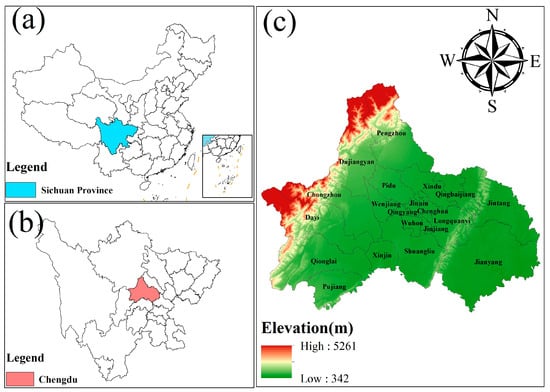
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Coastal Wetland Conservation and Urban Sustainable Development Synergy Pathway Research: Insights from Qingdao and Weihai for Qinhuangdao
by
Wei Xiong, Junjie Li and Bangfan Liu
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9902; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219902 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study addresses the critical challenge of balancing coastal wetland conservation with urban sustainable development, a pivotal issue for ecological civilization in rapidly developing regions. Through an in-depth analysis of Qingdao and Weihai—exemplary cases in Shandong Province—this research systematically investigates mechanisms for achieving
[...] Read more.
This study addresses the critical challenge of balancing coastal wetland conservation with urban sustainable development, a pivotal issue for ecological civilization in rapidly developing regions. Through an in-depth analysis of Qingdao and Weihai—exemplary cases in Shandong Province—this research systematically investigates mechanisms for achieving synergistic win–win outcomes. Employing a mixed-methods approach, including systems analysis to deconstruct governance frameworks, comparative case study to identify transferable strategies, and policy deduction to formulate actionable pathways, the study reveals how integrated approaches yield tangible results. Qingdao’s “Five Ocean Usages” concept and Weihai’s segmented coastal zoning have significantly improved key ecological metrics. By contrast, Qinhuangdao faces pronounced challenges, including degraded wetlands, spatial conflict between ports and core habitats, and underdeveloped synergistic governance. To address these, the study proposes a targeted strategy for Qinhuangdao, emphasizing a data-informed “wetland+” multi-format integration plan, the establishment of wetland mitigation banking and green finance instruments, digitally enabled public participation, and deeper policy alignment with national strategies such as Maritime Power. This research provides both a replicable analytical framework and practical guidance for coastal cities seeking to realize “development within protection and protection within development”.
Full article
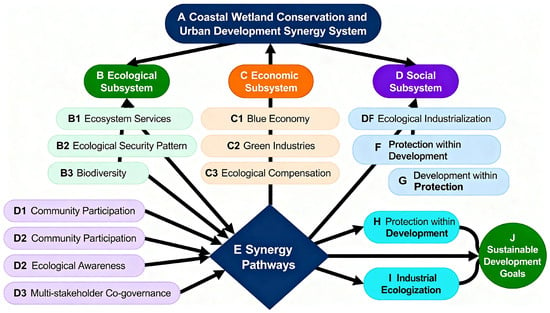
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Does Low-Carbon Pilot City Policy Reduce Transportation CO2 Emissions? Evidence from China
by
Beisi Tian, Changwei Yuan, Hujun Wang, Xinhua Mao, Ningyuan Ma, Jiannan Zhao and Yuchen Guo
Sustainability 2025, 17(21), 9901; https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219901 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Transportation is one of the major carbon dioxide (CO2)-emitting industries, facing substantial reduction pressure under low-carbon sustainable development. Cities are key to reducing transportation CO2 emissions, and the Low-Carbon City Pilot Policy (LCCPP) is essential to advance the development of
[...] Read more.
Transportation is one of the major carbon dioxide (CO2)-emitting industries, facing substantial reduction pressure under low-carbon sustainable development. Cities are key to reducing transportation CO2 emissions, and the Low-Carbon City Pilot Policy (LCCPP) is essential to advance the development of low-carbon cities and achieve peak-carbon and carbon-neutral targets. In this paper, we analyse the effect of the LCCP on transportation CO2 emissions using a multiperiod difference-in-differences (DID) method with data from 284 Chinese cities between 2006 and 2020. The results indicate a substantial reduction in urban transportation CO2 emissions through the LCCP, and that the enhancement of urban public transportation levels and residents’ green mobility are effective ways to accomplish this. This conclusion is upheld after conducting various robustness tests. Examination of the heterogeneity of the results and spatial analysis revealed that the LCCPP significantly reduced transportation CO2 emissions in eastern, western, and low-economy cities in China, but not in central and high-economy cities, that the reduction effect was better for southern, non-resource-based cities than for northern, resource-producing cities, and that it exerted notable spillover effects in surrounding cities. The results of this paper offer valid policy insights and practical guidance to maximise the CO2 reduction effects of the LCCP in the transportation sector.
Full article
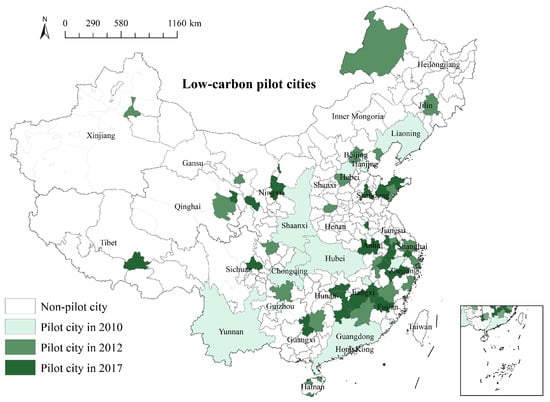
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Sustainability Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Atmosphere, Buildings, Climate, Environments, Sustainability, Earth
Climate, Health and Cities: Building Aspects for a Resilient Future
Topic Editors: Ferdinando Salata, Virgilio Ciancio, Simona MannucciDeadline: 20 November 2025
Topic in
Economies, Resources, Agriculture, Agronomy, Sustainability
Zero Hunger: Health, Production, Economics and Sustainability
Topic Editors: Richard John Roberts, José-María Montero, María del Carmen Valls Martínez, Viviane Naimy, José Manuel Santos-JaénDeadline: 30 November 2025
Topic in
Buildings, CivilEng, Energies, Sustainability
Energy Systems in Buildings and Occupant Comfort
Topic Editors: Eusébio Z. E. Conceição, Hazim B. AwbiDeadline: 20 December 2025
Topic in
Education Sciences, Future Internet, Information, Sustainability
Advances in Online and Distance Learning
Topic Editors: Neil Gordon, Han ReichgeltDeadline: 31 December 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Sustainable Building: Renewable and Green Energy Efficiency
Guest Editors: Reihaneh Aghamolaei, Mohammad Reza GhaaniDeadline: 7 November 2025
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Measurement Systems, Models, Tools, and Innovative Techniques for Sustainable Urban Planning and Regeneration
Guest Editors: Simona Tondelli, Mauro Francini, Gabriele Bitelli, Francesco Lamonaca, Elisa ConticelliDeadline: 7 November 2025
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Maple Syrup and Sugar Crops: Market and Climate Challenges and Potential Pathways for Sustainable Development
Guest Editor: Qingbin WangDeadline: 9 November 2025
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Artificial Intelligence in Sustainable Transportation
Guest Editors: Ye Li, Dominique Gruyer, Meiting TuDeadline: 10 November 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Advanced Methodologies for Sustainability Assessment: Theory and Practice
Collection Editor: Fausto Cavallaro
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Indicators, Assessment Tools, and Rating Systems for Mainstreaming Sustainability in Urban Planning and Development
Collection Editor: Ayyoob Sharifi
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Sustainability in Product Development
Collection Editor: Juan Manuel Muñoz Guijosa
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Urban Green Infrastructure for Climate-Proof and Healthy Cities
Collection Editors: Rosemarie Stangl, Ulrike Pitha, Daniela Haluza, Ingrid Kaltenegger








