A Simplified Model for Assembly Precision Information of Complex Products Based on Tolerance Semantic Relations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Approach of Simplification of APIM
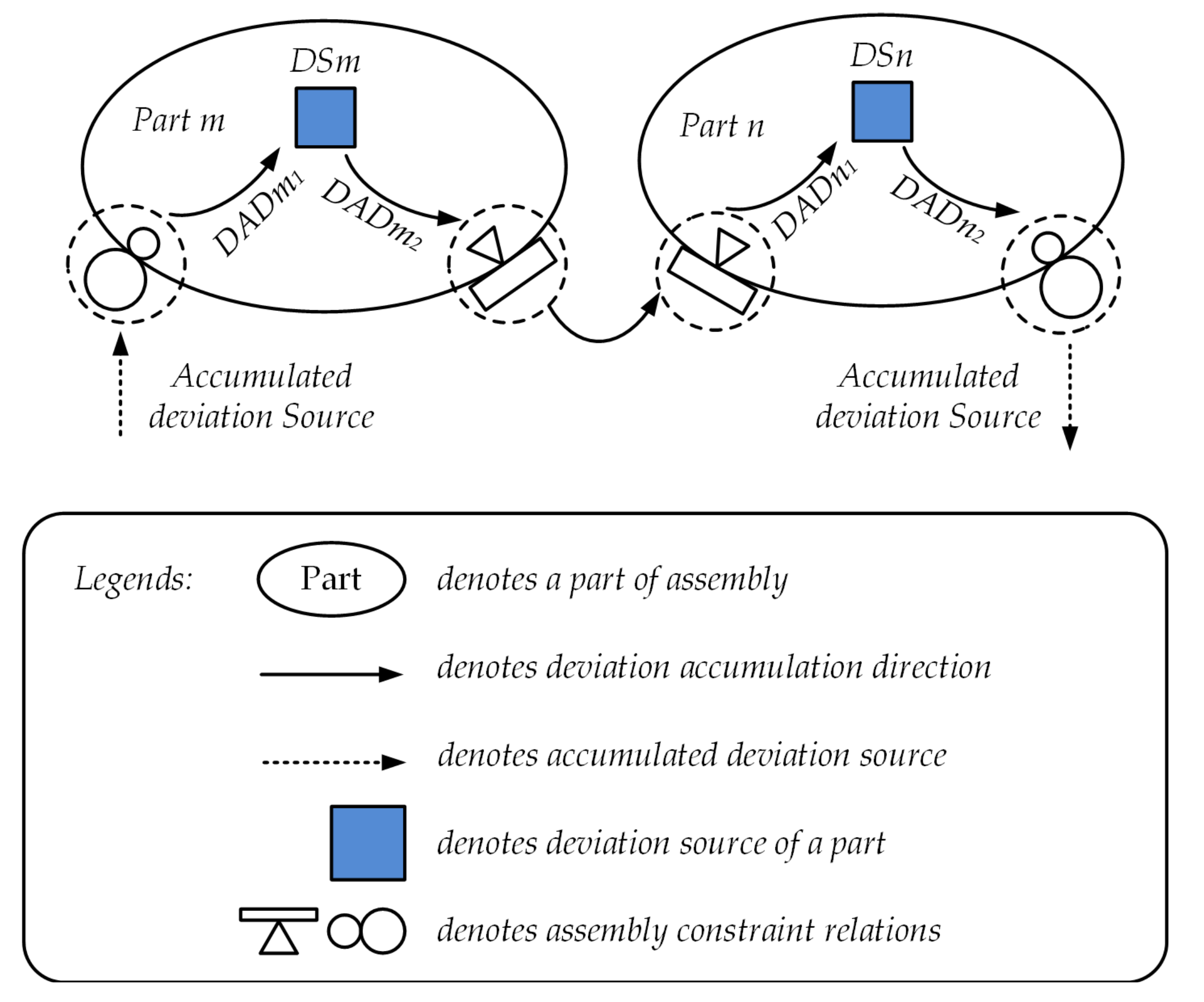
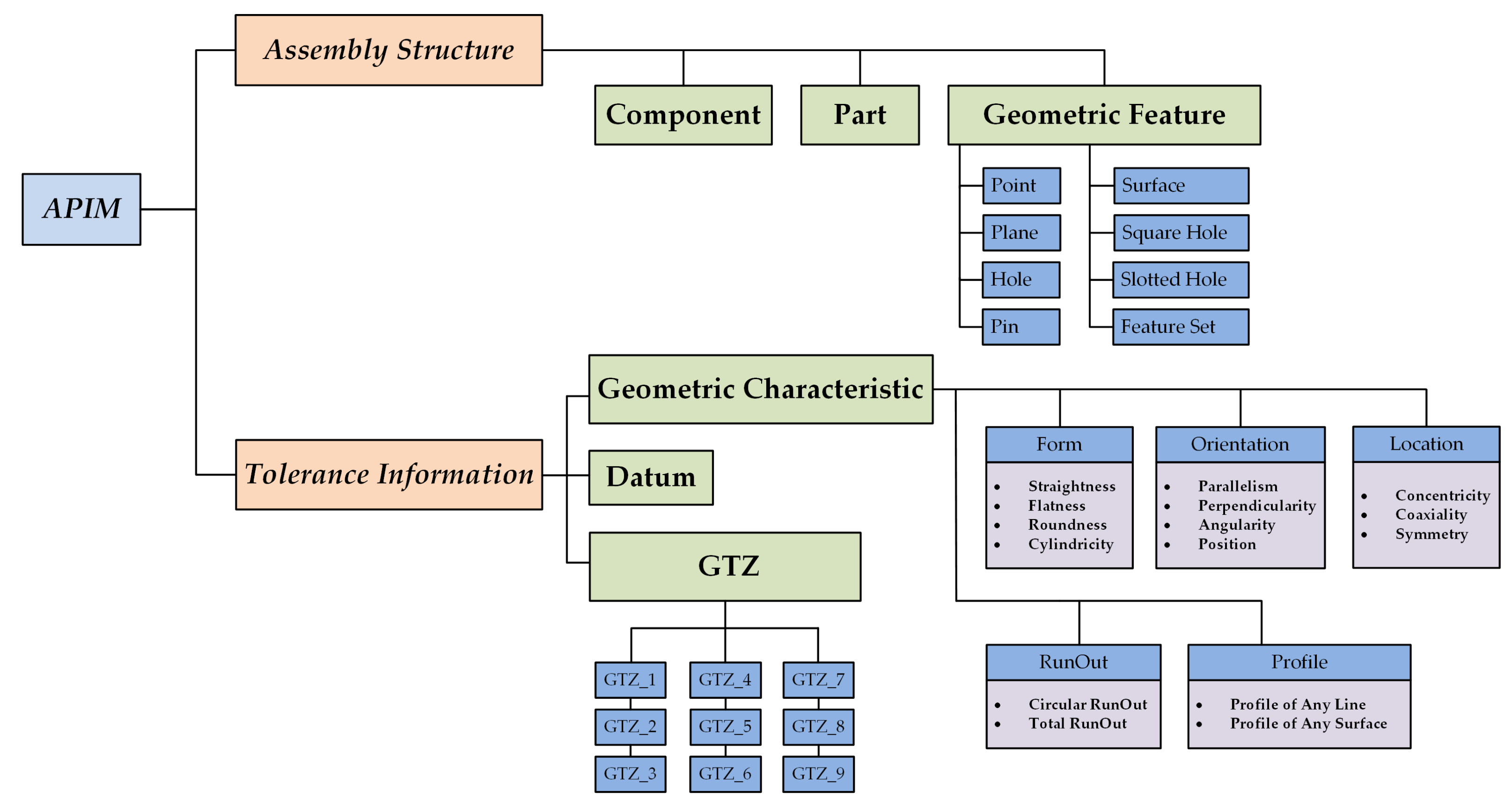
3.1. Representation of Structure Knowledge of APIM
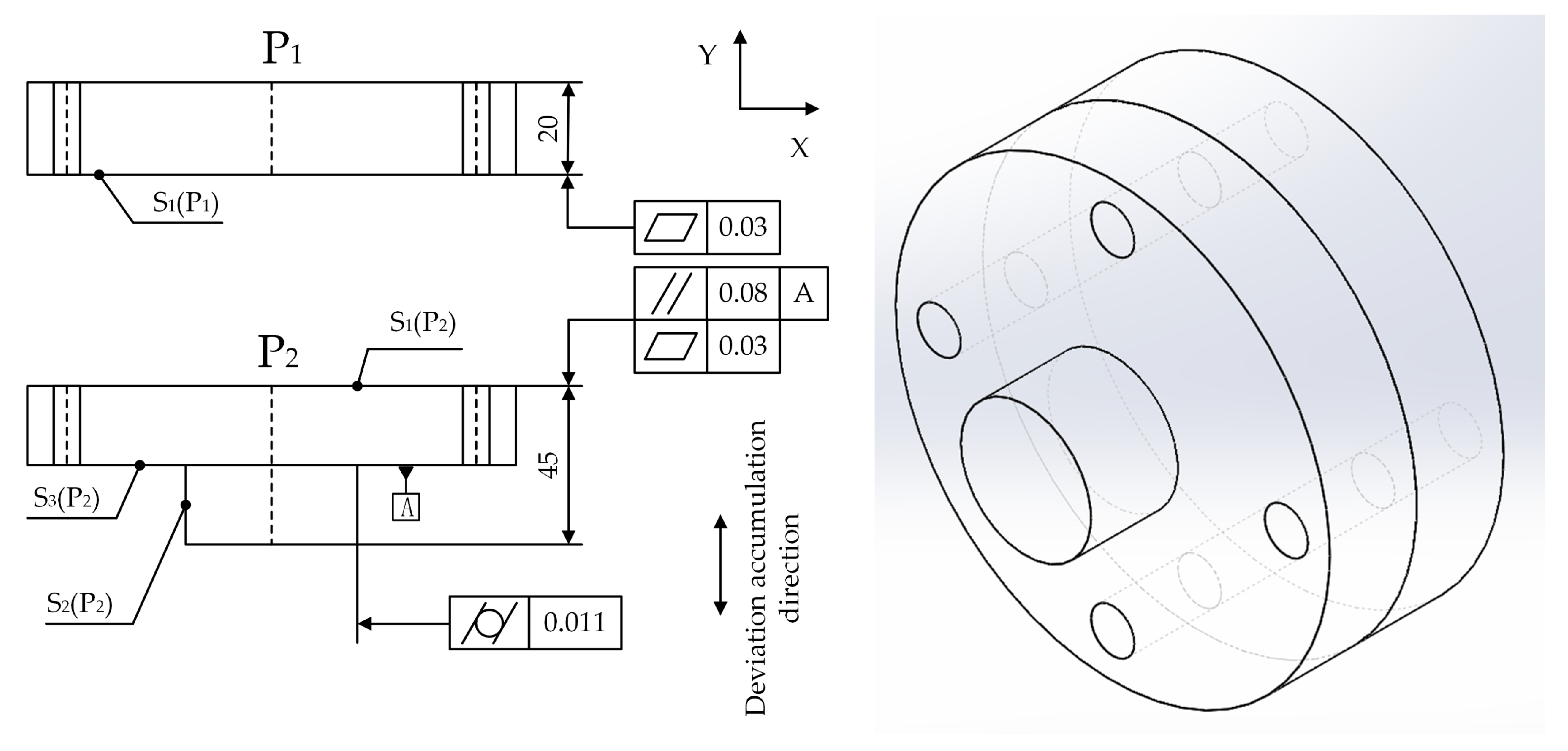
- has_Assembly_Relation(),
- has_Deviation_Accumulation_Direction(, Y-axis),
- has_Geometric_Feature(),
- has_Flatness(, flatness),
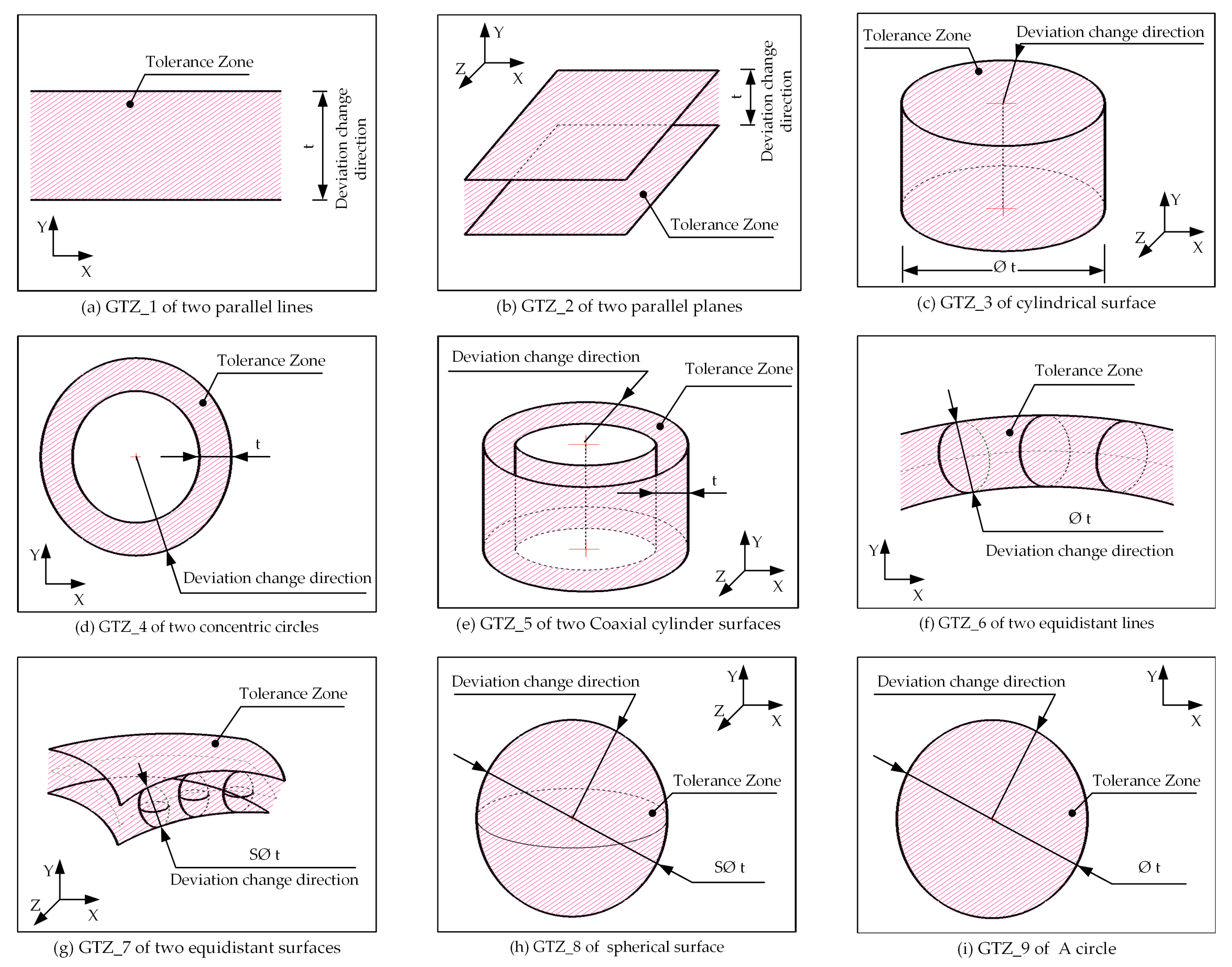
- has_GTZ(, GTZ_2),
- has_Deviation_Change_Direction(, Y-axis),
- has_Value_Of_Flatness(, 0.03f),
- has_Deviation_Accumulation_Direction(, Y-axis),
- has_Geometric_Feature(),
- has_Geometric_Feature(),
- has_Parallelism(, parallelism),
- has_GTZ(, GTZ_1),
- has_Datum(),
- has_Deviation_Change_Direction(, Y-axis),
- has_Value_Of_Parallelism(, 0.08f),
- has_Flatness(, flatness),
- has_GTZ(, GTZ_1),
- has_Deviation_Change_Direction(, Y-axis),
- has_Value_Of_Flatness(, 0.03f),
- has_Geometric_Feature(),
- has_Cylindricity(, cylindricity),
- has_GTZ(, GTZ_5),
- has_Deviation_Change_Direction(, X-axis),
- has_Value_Of_Cylindricity(, 0.011f)
3.2. Representation of Rule Knowledge of Simplification of APIM
3.2.1. Correlations between Deviation Change Direction and Deviation Accumulation Direction
- has_Cylindricity(, cylindricity),
- has_GTZ(, GTZ_5),
- has_Deviation_Change_Direction(, X-axis),
- has_Deviation_Accumulation_Direction(, Y-axis),
- has_Deviation_Change_Direction(, perpendicular_to_the_deviation_accumulation_
- direction),
- ->has_no_Influence_on(, assembly_precision)
3.2.2. Simplification of Multiple Geometric Characteristics Existing on a Geometric Feature
- has_GTZ(, GTZ_2),
- has_Parallelism(, parallelism),
- has_Flatness(, flatness),
- ->has_no_Flatness(, flatness)
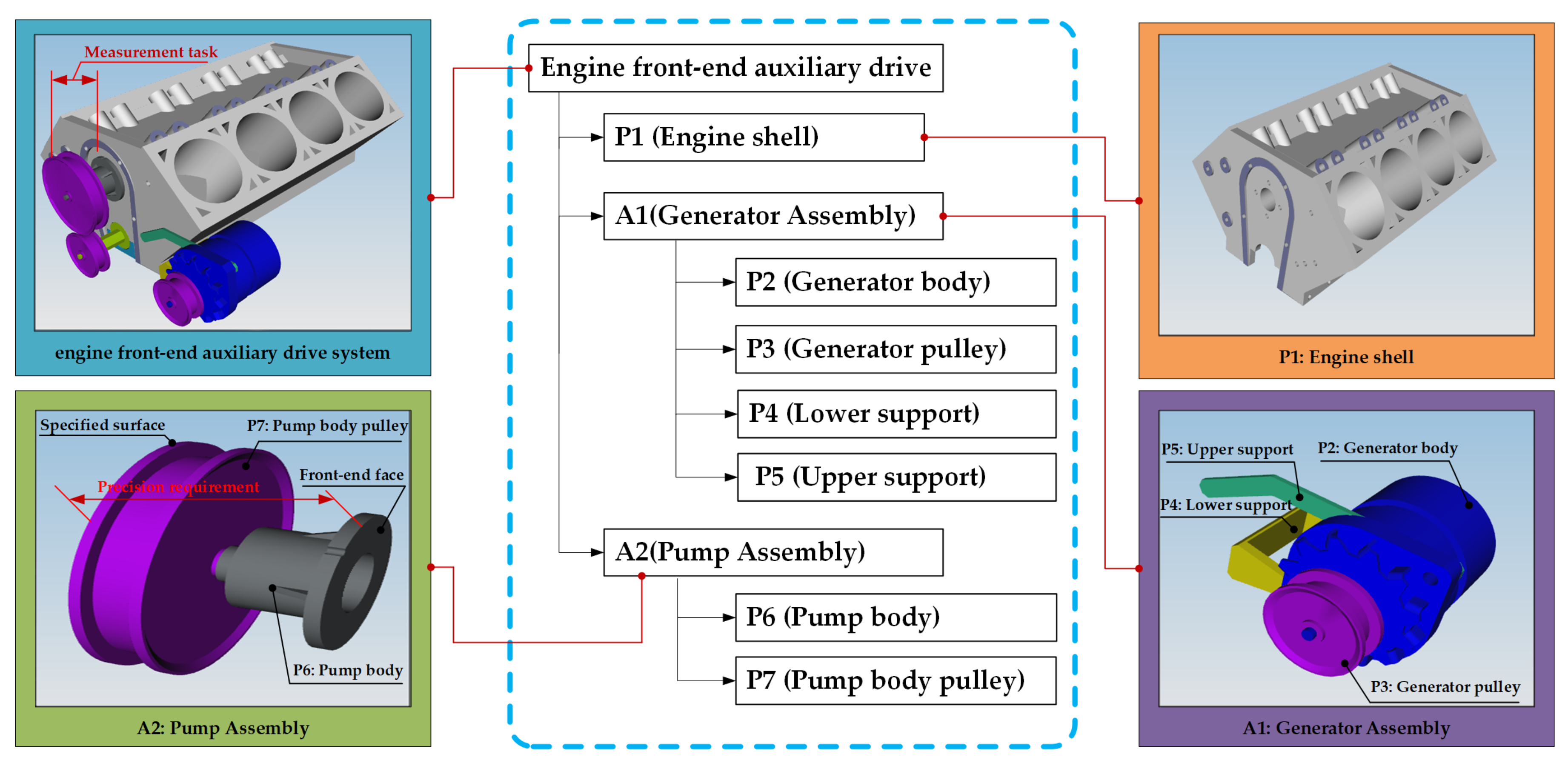
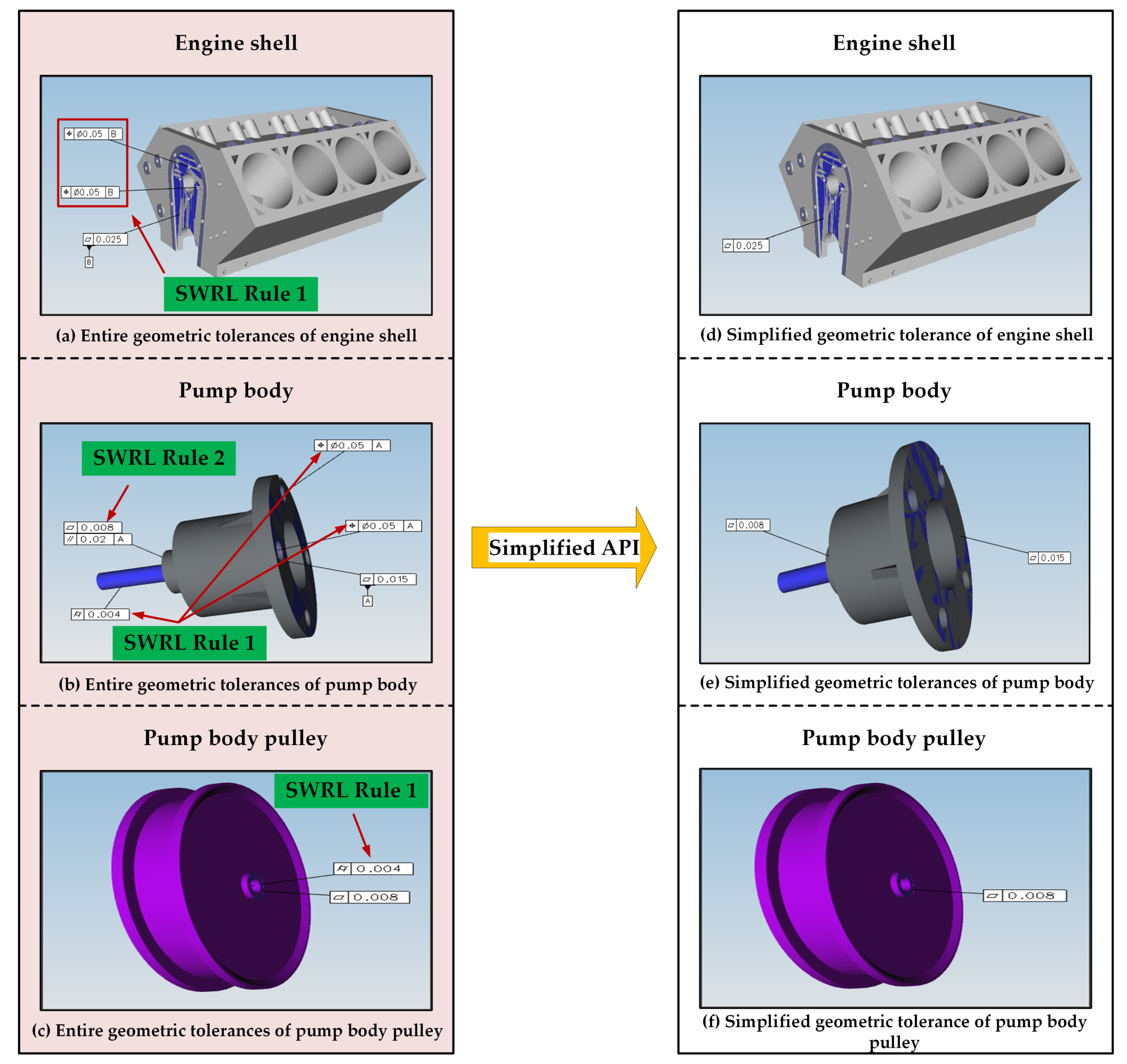
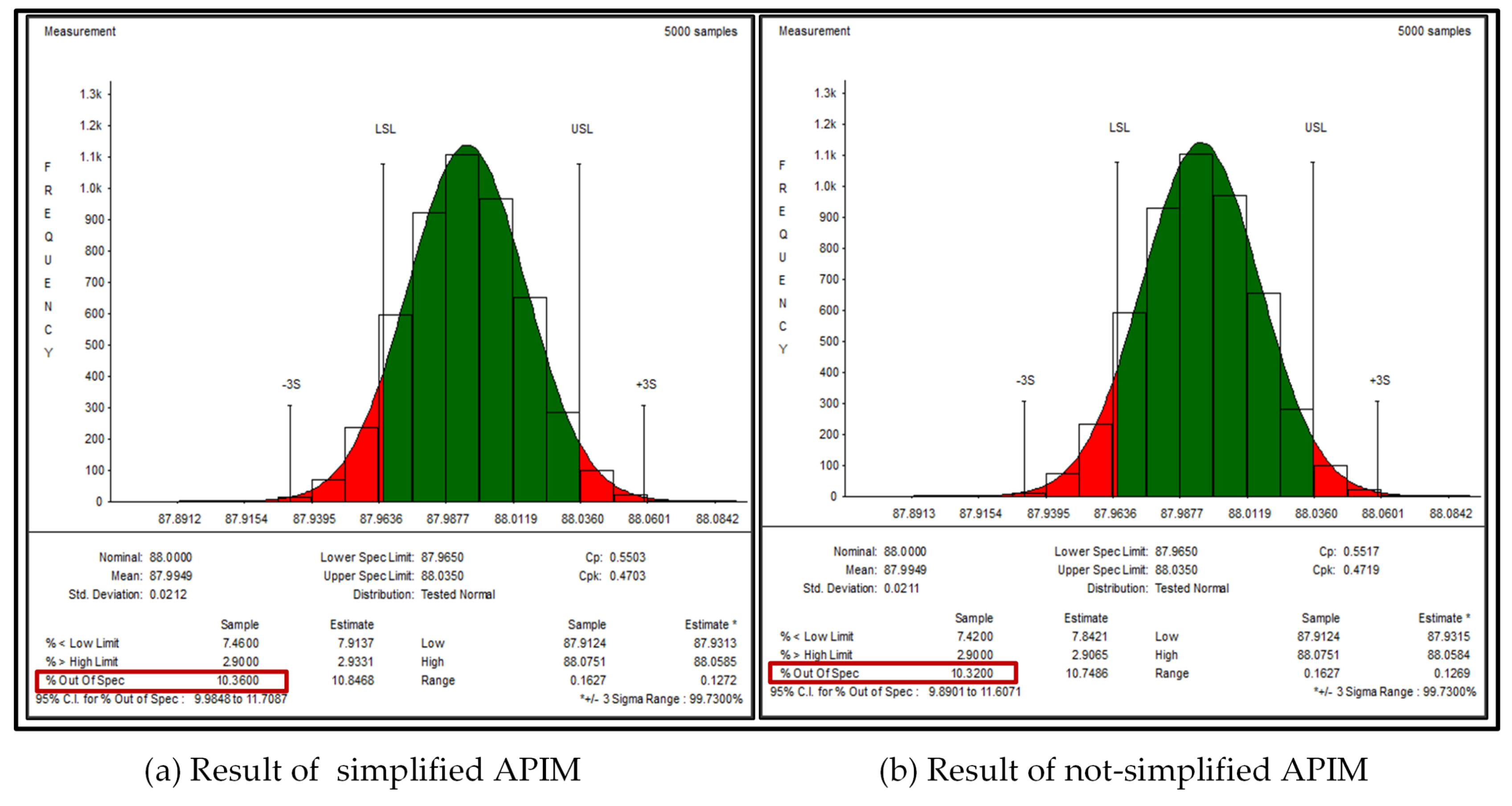
4. Case Study
5. Conclusions
- By considering complexity of APIM, this method of simplified semantic APIM is proposed mainly from the perspective of simplification of design tolerance of parts. In the process of simplification, tolerance semantic is the basis of simplification.
- By considering the angle between deviation change direction and deviation accumulation direction, the influence of deviation source on deviation accumulation is preliminarily confirmed. A further discussion regarding to the situation that multiple geometric characteristics exist simultaneously on a geometric feature of a part, another basic principle of simplification of APIM is established.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| CAPP | Computer-Aided Process Planning |
| GD&T | Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing |
| OWL | Web Ontology Language |
| SWRL | Semantic Web Rule Language |
| GTZ | Geometric Tolerance Zone |
| APA | Assembly Precision Analysis |
| API | Assembly Precision Information |
| APIM | Assembly Precision Information Model |
| WC | Worst Case |
| RMS | Root Mean Square |
| MC | Monte Carlo |
| DOF | Degree Of Freedom |
| SDT | Small Displacement Torsor |
| TTRS | Technologically and Topologically Related Surface |
| CSG | Constructive Solid Geometry |
| B_rep | Boundary Representation |
| T-Map | Tolerance-Map |
References
- Samy, S.N.; ElMaraghy, H. A model for measuring complexity of automated and hybrid assembly systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 62, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.C.; Kuo, C.H. A novel statistical tolerance analysis method for assembled parts. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 3498–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, K.; Ravindran, D.; Kumar, M.S.; Islam, M.N. Concurrent tolerance allocation and scheduling for complex assemblies. Robot. Comput-Integr. Manuf. 2015, 35, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.J.; Ghenniwa, H.H.; Shen, W.M. Frame-based ontological view for semantic integration. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2012, 35, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armillotta, A. A method for computer-aided specification of geometric tolerances. Comput-Aided Des. 2013, 45, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantan, J.Y.; Qureshi, A.J. Worst-case and statistical tolerance analysis based on quantified constraint satisfaction problems and Monte Carlo simulation. Comput-Aided Des. 2009, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciosa, P.; Gerbino, S.; Patalano, S. Variational modeling and assembly constraints in tolerance analysis of rigid part assemblies: Planar and cylindrical features. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 49, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requicha, A.A.G. Toward a theory of geometric tolerancing. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1983, 2, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requicha, A.A.G.; Chan, S.C. Representation of geometric features, tolerances, and attributes in solid modelers based on constructive geometry. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. 1986, 2, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, F. A mathematical-model for geometric tolerances. J. Mech. Des. 1993, 115, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillyard, R.C.; Braid, I.C. Analysis of dimensions and tolerances in computer-aided mechanical design. Comput-Aided Des. 1978, 10, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossard, D.C.; Zuffante, R.P.; Sakurai, H. Representing dimensions, tolerances, and features in mcae systems. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 1988, 8, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, P. Analysis of tolerances and process inaccuracies in discrete part manufacturing. Comput-Aided Des. 1982, 14, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, K.W.; Gao, J.S.; Magleby, S.P.; Sorensen, C.D. Including geometric feature variations in tolerance analysis of mechanical assemblies. IIE Trans. 1996, 28, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrochers, A.; Riviere, A. A matrix approach to the representation of tolerance zones and clearances. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 1997, 13, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, E.; Joskowicz, L. Parametric kinematic tolerance analysis of general planar systems. Comput-Aided Des. 1998, 30, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, B.C. Dimension and tolerance modeling and transformations in feature based design and manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 1998, 9, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, U.; Li, B. Representation and interpretation of geometric tolerances for polyhedral objects—I. Form tolerances. Comput-Aided Des. 1998, 30, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, U.; Li, B. Representation and interpretation of geometric tolerances for polyhedral objects. II. Size, orientation and position tolerances. Comput-Aided Des. 1999, 31, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmetti, B. Generation of functional tolerancing based on positioning features. Comput-Aided Des. 2006, 38, 902–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.U. Relative positioning of parts in assemblies using mathematical-programming. Comput-Aided Des. 1990, 22, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, R.; Turner, J.U. Relative positioning of variational part models for design analysis. Comput-Aided Des. 1994, 26, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serre, P.; Riviere, A. Analysis of Functional Geometrical Specification; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Nigam, S.D.; Turner, J.U. Review of Statistical Approaches to Tolerance Analysis. Comput-Aided Des. 1995, 27, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrochers, A.; Clement, A. A dimensioning and tolerancing assistance model for cad-cam systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 1994, 9, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantan, J.Y.; Ballu, A.; Mathieu, L. Geometrical product specifications—Model for product life cycle. Comput-Aided Des. 2008, 40, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requicha, A.A.G.; Voelcker, H.B. Solid modeling—A historical summary and contemporary assessment. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 1982, 2, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juster, N.P. Modeling and representation of dimensions and tolerances—A survey. Comput-Aided Des. 1992, 24, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.C.; Cutkosky, M.R. Representation and reasoning of geometric tolerances in design. AI EDAM-Artif. Intell. Eng. Des. Anal. Manuf. 1997, 11, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameta, G.; Davidson, J.K.; Shah, J.J. Tolerance-maps applied to a point-line cluster of features. J. Mech. Des. 2007, 129, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, U.; Liu, C.R. Feature-based representational scheme of a solid modeler for providing dimensioning and tolerancing information. Robot. Comput-Integr. Manuf. 1988, 4, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.F.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.L. An integrated modeling method of unified tolerance representation for mechanical product. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 46, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.L.; Qin, Y.C.; Liu, X.J.; Huang, M.F.; Zhou, L.P.; Jiang, X.Q. Enriching the semantics of variational geometric constraint data with ontology. Comput-Aided Des. 2015, 63, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.C.; Lu, W.L.; Liu, X.J.; Huang, M.F.; Zhou, L.P.; Jiang, X.Q. Description logic-based automatic generation of geometric tolerance zones. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 79, 1221–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.C.; Lu, W.L.; Qi, Q.F.; Li, T.K.; Huang, M.F.; Scott, P.J.; Jiang, X.Q. Explicitly representing the semantics of composite positional tolerance for patterns of holes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 2121–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.R.; Qin, Y.C.; Huang, M.F.; Lu, W.L.; Chang, L. Constructing a meta-model for assembly tolerance types with a description logic based approach. Comput-Aided Des. 2014, 48, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.R.; Qin, Y.C.; Huang, M.F.; Lu, W.L.; Gao, W.X.; Du, Y.L. Automatically generating assembly tolerance types with an ontology-based approach. Comput-Aided Des. 2013, 45, 1253–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Han, S. Interoperability of product and manufacturing information using ontology. Concurr. Eng-Res. Appl. 2015, 23, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.C.; Lu, W.L.; Qi, Q.F.; Liu, X.J.; Huang, M.F.; Scott, P.J.; Jiang, X.Q. Towards an ontology-supported case-based reasoning approach for computer-aided tolerance specification. Knowl-Based Syst. 2018, 141, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Object Property | Data Property | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) has_Geometric_Characteristic | (2) has_no_Geometric_Characteristic | (10) has_Value_of_Tolerance_Zone | |||
| has_ Form_ Tolerance | has_Straightness | has_no_ Form_ Tolerance | has_no_Straightness | has_Value_of_ Form_ Tolerance_Zone | has_Value_of_Straightness |
| has_Roundness | has_no_Roundness | has_Value_of_Roundness | |||
| has_Cylindricity | has_no_Cylindricity | has_Value_of_Cylindricity | |||
| has_Flatness | has_no_Flatness | has_Value_of_Flatness | |||
| has_ Location_ Tolerance | has_Coaxiality | has_no_ Location_ Tolerance | has_no_Coaxiality | has_Value_of_ Location_ Tolerance_Zone | has_Value_of_Coaxiality |
| has_Concentricity | has_no_Concentricity | has_Value_of_Concentricity | |||
| has_Position | has_no_Position | has_Value_of_Position | |||
| has_Symmetry | has_no_Symmetry | has_Value_of_Symmetry | |||
| has_ Orientation_ Tolerance | has_Angularity | has_no_ Orientation_ Tolerance | has_no_Angularity | has_Value_of_ Orientation_ Tolerance_Zone | has_Value_of_Angularity |
| has_Parallelism | has_no_Parallelism | has_Value_of_Parallelism | |||
| has_Perpendiculaity | has_no_Perpendiculaity | has_Value_of_Perpendiculaity | |||
| has_ RunOut_ Tolerance | has_Circular_RunOut | has_no_ RunOut_ Tolerance | has_no_Circular_RunOut | has_Value_of_ RunOut_ Tolerance_Zone | has_Value_of_Circular_RunOut |
| has_Total_RunOut | has_no_Total_RunOut | has_Value_of_Total_RunOut | |||
| has_ Profile_ Tolerance | has_Profile_of_Any_Line | has_no_ Profile_ Tolerance | Has_no_ Profile_of_Any_Line | has_Value_of_ Profile_ Tolerance_Zone | has_Value_of_ Profile_of_Any_Line |
| has_Profile_of_Any_Surface | Has_no_ Profile_of_Any_Surface | has_Value_of_ Profile_of_Any_Surface | |||
| (3) has_GTZ | (4) has_Assembly_Relation | (5) has_Datum | (6) has_Geometric_Feature | ||
| (7) has_Direction | Has_deviation_change_direction | (8) has_Influence_on | |||
| Has_deviation_accumulation_direction | (9) has_no_Influence_on | ||||
| Number | Relations of Deviation Change Direction and Deviation Accumulation Direction |
|---|---|
| SR.1-1 | has_Deviation_Changing_Direction(?x, perpendicular_to_the_deviation_accumulation_direction) ->has_no_Influence_on(?x,assembly_precision) |
| SR.1-2 | has_Deviation_Changing_Direction(?x, not_perpendicular_to_the_deviation_accumulation_direction) ->has_Influence_on(?x,assembly_precision) |
| Geometric Characteristic | GTZ_1 | GTZ_2 | GTZ_3 | GTZ_4 | GTZ_5 | GTZ_6 | GTZ_7 | GTZ_8 | GTZ_9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Form Tolerance | Straightness | • | • | • | ||||||
| Flatness | • | |||||||||
| Roundness | • | |||||||||
| Cylindricity | • | |||||||||
| Orientation Tolerance | parallelism | • | • | • | ||||||
| perpendicularity | • | • | • | |||||||
| Angularity | • | • | ||||||||
| Location Tolerance | Position | • | • | • | • | • | ||||
| Coaxiality | • | • | ||||||||
| Symmetry | • | |||||||||
| RunOut Tolerance | Circular RunOut | • | • | |||||||
| Total RunOut | • | • | ||||||||
| Profile Tolerance | Profile of Any Line | • | ||||||||
| Profile of Any Surface | • | |||||||||
| GTZ | Number | Multiple Geometric Characteristics Existing on a Geometric Feature |
|---|---|---|
| GTZ_1 | SR.2-1 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_1),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Parallelism(?x, parallelism) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) |
| SR.2-2 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_1),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Perpendiculaity(?x, perpendiculaity) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) | |
| SR.2-3 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_1),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Position(?x, position) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) | |
| GTZ_2 | SR.2-4 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Parallelism(?x, parallelism) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) |
| SR.2-5 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Perpendiculaity(?x, perpendiculaity) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) | |
| SR.2-6 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Angularity(?x, angularity) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) | |
| SR.2-7 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Position(?x, position) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) | |
| SR.2-8 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Symmetry(?x, symmetry) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) | |
| SR.2-9 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Flatness(?x, flatness), has_Parallelism(?x, parallelism) ->has_no_Flatness(?x, flatness) | |
| SR.2-10 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Flatness(?x, flatness), has_Perpendiculaity(?x, perpendiculaity) ->has_no_Flatness(?x, flatness) | |
| SR.2-11 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Flatness(?x, flatness), has_Angularity(?x, angularity) ->has_no_Flatness(?x, flatness) | |
| SR.2-12 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Flatness(?x, flatness), has_Position(?x, position) ->has_no_Flatness(?x, flatness) | |
| SR.2-13 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_2),has_Flatness(?x, flatness), has_Symmetry(?x, symmetry) ->has_no_Flatness(?x, flatness) | |
| GTZ_3 | SR.2-14 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_3),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Parallelism(?x, parallelism) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) |
| SR.2-15 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_3),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Perpendiculaity(?x, perpendiculaity) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) | |
| SR.2-16 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_3),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Angularity(?x, angularity) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) | |
| SR.2-17 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_3),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Position(?x, position) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) | |
| SR.2-18 | has_GTZ(?x, GTZ_3),has_Straightness(?x, straightness), has_Coaxiality(?x, coaxiality) ->has_no_Straightness(?x, straightness) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, D. A Simplified Model for Assembly Precision Information of Complex Products Based on Tolerance Semantic Relations. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4482. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124482
Shi X, Tian X, Wang G, Zhang M, Zhao D. A Simplified Model for Assembly Precision Information of Complex Products Based on Tolerance Semantic Relations. Sustainability. 2018; 10(12):4482. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124482
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xiaolin, Xitian Tian, Gangfeng Wang, Min Zhang, and Dongping Zhao. 2018. "A Simplified Model for Assembly Precision Information of Complex Products Based on Tolerance Semantic Relations" Sustainability 10, no. 12: 4482. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124482
APA StyleShi, X., Tian, X., Wang, G., Zhang, M., & Zhao, D. (2018). A Simplified Model for Assembly Precision Information of Complex Products Based on Tolerance Semantic Relations. Sustainability, 10(12), 4482. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124482





