Effects of Cropland Conversion and Climate Change on Agrosystem Carbon Balance of China’s Dryland: A Typical Watershed Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Method
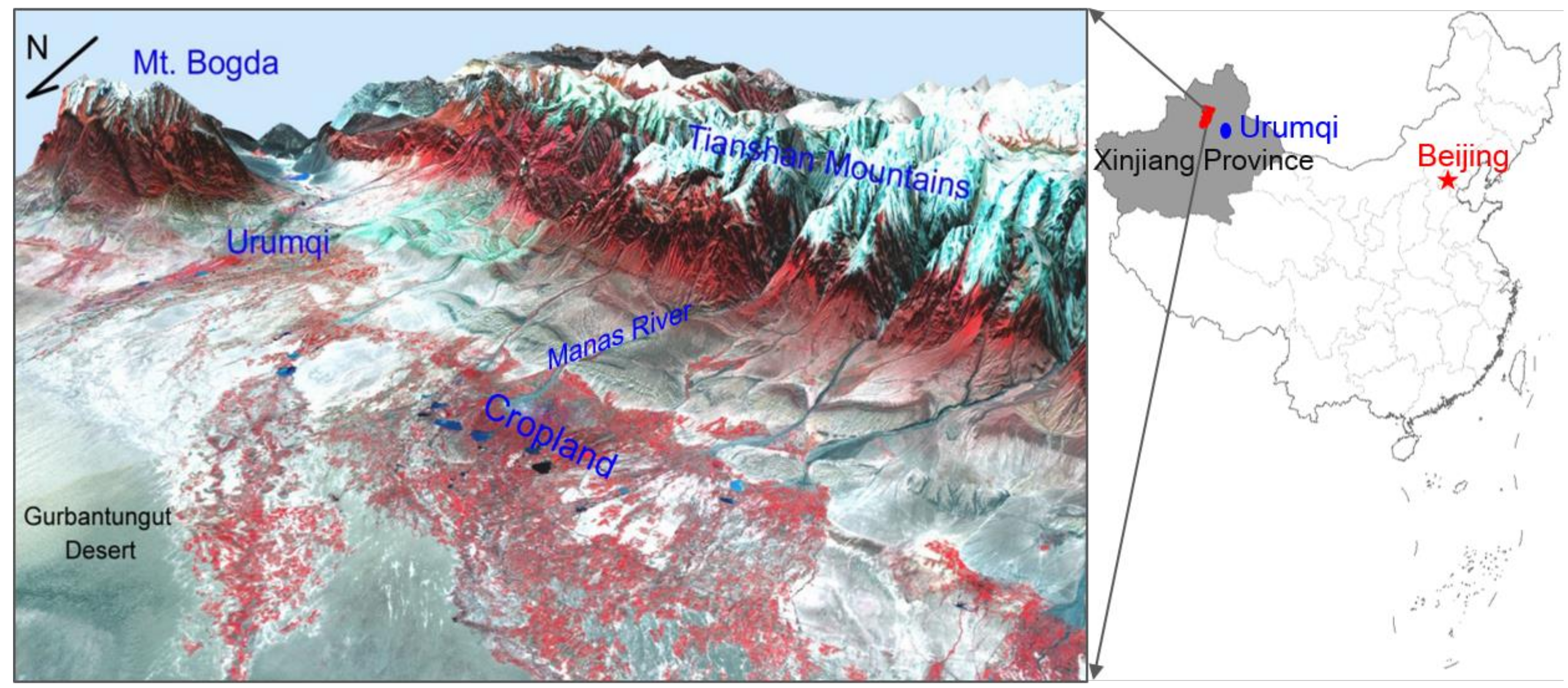
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Model Description and Datasets
2.2.1. AEM
2.2.2. C Bookkeeping Model
2.2.3. Model Simulation
2.2.4. Data Source
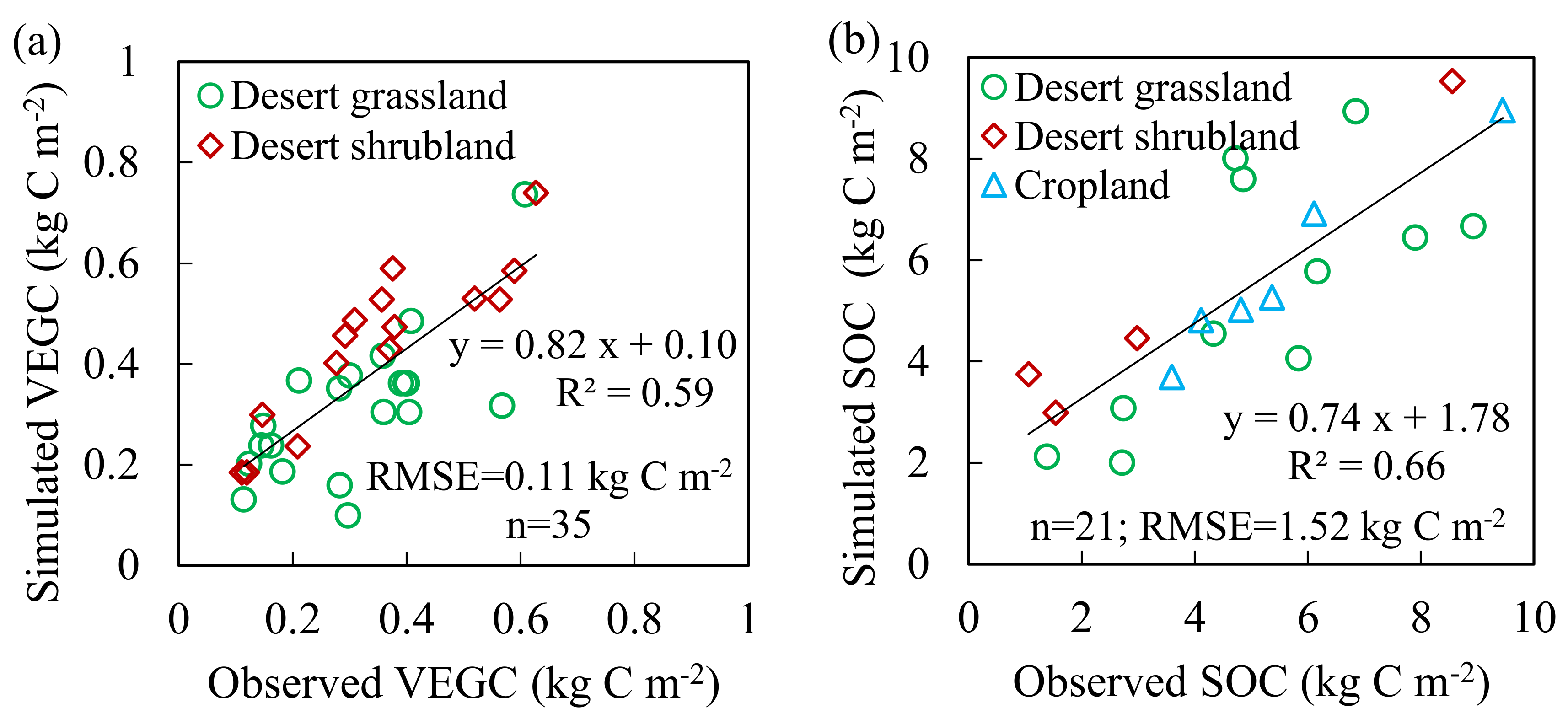
2.2.5. Additional Validation
3. Results
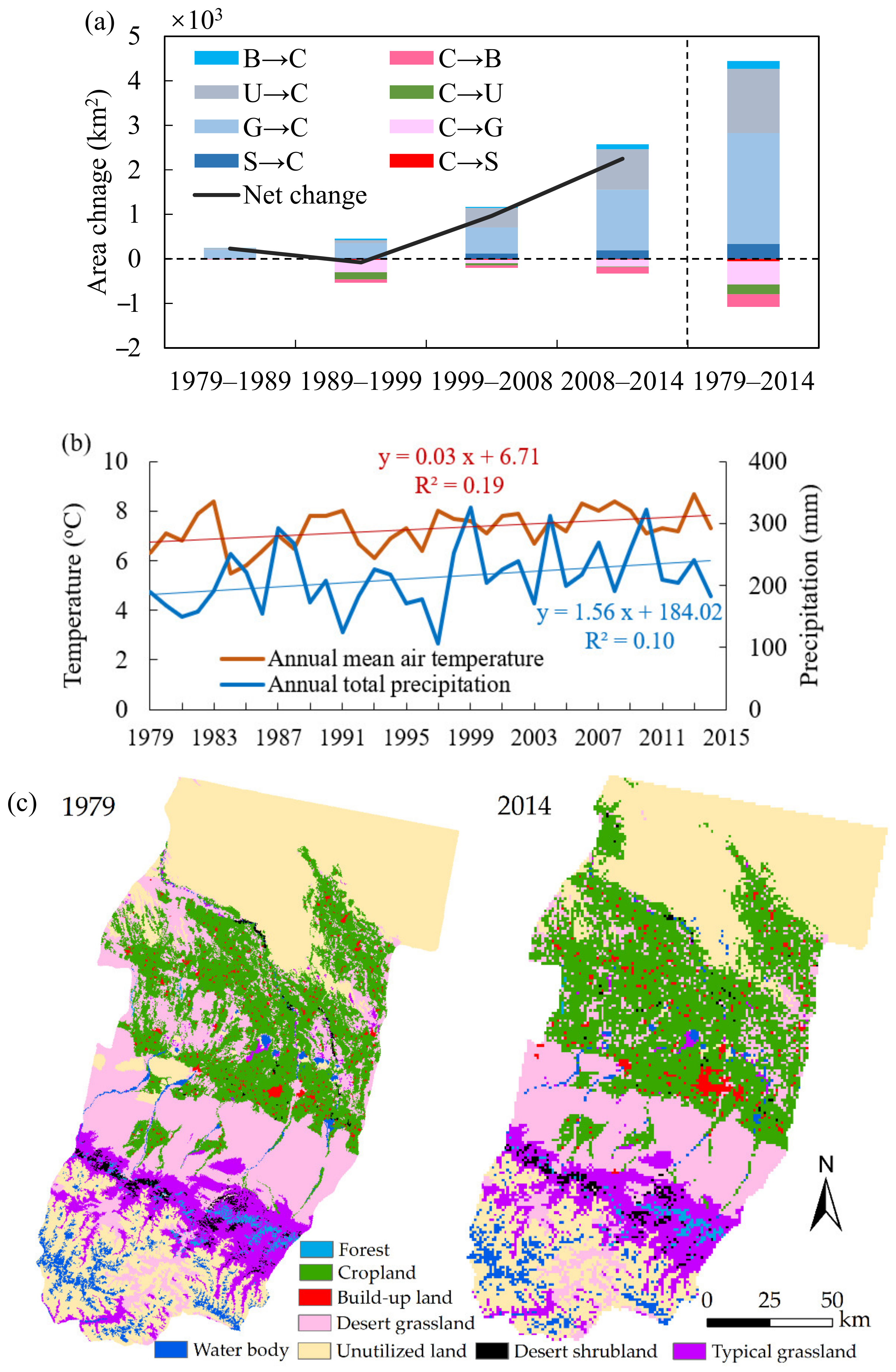
3.1. LULCC and CLM
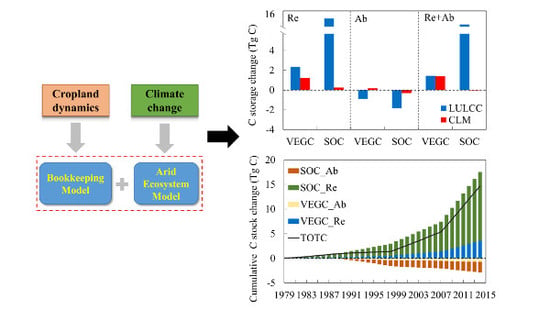
3.2. Combined Effects of LULCC and CLM on C Dynamics
3.3. Relative Effects of LULCC and CLM
4. Discussion
4.1. C Dynamics Affected by LULCC and CLM
4.2. Implications of Cropland Expansion
4.3. Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, G.P.; Zhou, C.H.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. A methodology of characterizing status and trend of land changes in oases: A case study of Sangong River watershed, Xinjiang, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Bai, J. The dominant role of heavy precipitation in precipitation change despite opposite trends in west and east of northern China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 4329–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Kang, E.; Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, R. Recent and future climate change in northwest china. Clim. Chang. 2007, 80, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Land Use/Cover Change in Arid Areas in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dang, Y.; Ren, W.; Tao, B.; Chen, G.; Lu, C.; Yang, J.; Pan, S.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Tian, H. Climate and Land Use Controls on Soil Organic Carbon in the Loess Plateau Region of China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Piao, S.; He, J.; Ma, W. Increasing terrestrial vegetation activity in China, 1982–1999. Sci. China Ser. C 2004, 47, 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Lomas, M.; Beer, C.; Liu, H.; Fang, J.; Friedlingstein, P.; Huang, Y.; Muraoka, H.; Son, Y.; et al. Contribution of climate change and rising CO2 to terrestrial carbon balance in East Asia: A multi-model analysis. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 75, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, B. NDVI-indicated decline in desertification in China in the past two decades. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L06402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; Ciais, P.; Peylin, P.; Huang, Y.; Sitch, S.; Wang, T. The carbon balance of terrestrial ecosystems in China. Nature 2009, 458, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Melillo, J.; Lu, C.; Kicklighter, D.; Liu, M.; Ren, W.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Pan, S.; et al. China’s terrestrial carbon balance: Contributions from multiple global change factors. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2011, 25, GB1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Luo, G.; Chen, X. Modeling the carbon dynamics of the dryland ecosystems in Xinjiang, China from 1981 to 2007—The spatiotemporal patterns and climate controls. Ecol. Model. 2013, 267, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, G.; Zhao, S.; Han, Q.; Li, C.; Fan, B.; Chen, Y. Effects of arable land change on regional carbon balance in Xinjiang. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; House, J.I.; Pongratz, J.; van der Werf, G.R.; DeFries, R.S.; Hansen, M.C.; Le Quéré, C.; Ramankutty, N. Carbon emissions from land use and land-cover change. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 5125–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Sequestering carbon in soils of arid ecosystems. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Smith, D.M.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Mortimore, M.; Batterbury, S.P.J.; Downing, T.E.; Dowlatabadi, H.; Fernández, R.J.; Herrick, J.E.; et al. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, R.A.; Hackler, J.L. Sources and sinks of carbon from land-use change in China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Luo, G.; Chen, X. Modeling plant structure and its impacts on carbon and water cycles of the Central Asian arid ecosystem in the context of climate change. Ecol. Model. 2013, 267, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitch, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gruber, N.; Jones, S.D.; Murray-Tortarolo, G.; Ahlström, A.; Doney, S.C.; Graven, H.; Heinze, C.; Huntingford, C.; et al. Recent trends and drivers of regional sources and sinks of carbon dioxide. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 653–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadell, J.G.; Schulze, E.D. Global potential of biospheric carbon management for climate mitigation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Kemp, P.R.; Ogle, K.; Fernández, R.J. Modifying the ‘pulse–reserve’ paradigm for deserts of North America: Precipitation pulses, soil water, and plant responses. Oecologia 2004, 141, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Zou, T. Ecophysiological response and morphological adjustment of two Central Asian desert shrubs towards variation in summer precipitation. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Luo, G.; Chen, X.; Maisupova, B.; Madaminov, A.A.; Han, Q.; Djenbaev, B.M. Carbon stock and its responses to climate change in Central Asia. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1951–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, R.A.; Hackler, J.L.; Lawrence, K.T. The U.S. Carbon Budget: Contributions from Land-Use Change. Science 1999, 285, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ren, W. Complex climatic and CO2 controls on net primary productivity of temperate dryland ecosystems over central Asia during 1980–2014. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2356–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Xu, H.; Fu, J.; Fan, Z.; Xu, X. Suitable oasis scale in a typical continental river basin in an arid region of China: A case study of the Manas River Basin. Quat. Int. 2013, 286, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y. The oasis expansion and eco-environment change over the last 50 years in Manas River Valley, Xinjiang. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yu, P.; Ling, H. Oasis evolution and water resource utilization of a typical area in the inland river basin of an arid area: A case study of the Manas River valley. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Xu, H.; Fu, J.; Liu, X. Surface runoff processes and sustainable utilization of water resources in Manas River Basin, Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Land 2012, 4, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Luo, G.; Lu, L.; Zhou, D.; Han, Q.; Xu, W.; Yin, C.; Zhu, L.; Dai, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Effects of land use change on landscape pattern of the Manas River watershed in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 2067–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Ding, J.; Karamage, F. Isolating and Quantifying the Effects of Climate and CO2 Changes (1980–2014) on the Net Primary Productivity in Arid and Semiarid China. Forests 2017, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, K.M.; Curran, L.M.; Asner, G.P.; Pittman, A.M.; Trigg, S.N.; Marion Adeney, J. Carbon emissions from forest conversion by Kalimantan oil palm plantations. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulp, C.J.E.; Nabuurs, G.-J.; Verburg, P.H. Future carbon sequestration in Europe—Effects of land use change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 127, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammat, A.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Peng, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Myneni, R.B.; Piao, S. Drought and spring cooling induced recent decrease in vegetation growth in Inner Asia. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 178–179, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tang, G.; Sheng, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, M. Effects of cultivation on organic carbon fractionation and aggregate stability in Xinjiang oasis soils. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Tian, C. Contents of soil organic carbon in newly reclaimed field in arid desert zone. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2008, 22, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H. A Study on Growth Characteristic and Biomass of Poplar Plantation. Chinese Academy of Forestry: Beijing, Chin, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; He, X.; Song, N. Changes of plant community biomass and soil nutrients during the vegetation succession on abandoned cultivated land in desert steppe region. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 3145–3149. [Google Scholar]
- Xinjiang and Central Asia Data Center. Available online: http://midasia.geodata.cn/Portal/index.jsp (accessed on 27 May 2015).
- ASTER GDEM v.2. Available online: http: //gdem.ersdac.jspacesystems.or.jp/ (accessed on 21 March 2014).
- Nachtergaele, F.; Velthuizen, H.v.; Verelst, L. Harmonized World Soil Database; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Roma, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- CDIAC. Available online: http://cdiac.esd.ornl.gov/ftp/trends/co2/maunaloa.co2 (accessed on 4 April 2015).
- Yang, K.; He, J.; Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Cheng, C.C.K. On downward shortwave and longwave radiations over high altitude regions: Observation and modeling in the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; He, J.; Qin, J.; Shi, J.; Du, J.; He, Q. Improving land surface temperature modeling for dry land of China. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D20104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Luo, G.; Li, C.; Xu, W. Modeling the grazing effect on dry grassland carbon cycling with Biome-BGC model. Ecol. Complex. 2014, 17, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Reynolds, J.F.; Hui, D. Responses of dryland soil respiration and soil carbon pool size to abrupt vs. gradual and individual vs. combined changes in soil temperature, precipitation, and atmospheric [CO2]: A simulation analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 2274–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, P.; David, F.; Philippe, C.; Ranga, B.M.; Niels, A.; Jian, B.; Gregoire, B.; Josep, G.C.; Frederic, C.; Yi, Y.L.; et al. Contribution of semi-arid ecosystems to interannual variability of the global carbon cycle. Nature 2014, 509, 600–603. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Tian, H.; Tao, B.; Huang, Y.; Pan, S. China’s crop productivity and soil carbon storage as influenced by multifactor global change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 2945–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Clair, S.B.; Lynch, J.P. The opening of Pandora’s Box: Climate change impacts on soil fertility and crop nutrition in developing countries. Plant Soil 2010, 335, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; Goodale, C.L. Effects of Land-Use Change on the Carbon Balance of Terrestrial Ecosystems. In Ecosystems and Land Use Change; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Nutini, F.; Boschetti, M.; Brivio, P.A.; Bocchi, S.; Antoninetti, M. Land-use and land-cover change detection in a semi-arid area of Niger using multi-temporal analysis of Landsat images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 4769–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuti, T.; Luo, G. Analysis of land cover change and its driving forces in a desert oasis landscape of Xinjiang, northwest China. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, K.; Alexander, V.P.; Daniel, M.; Tobias, K.; Volker, C.R.; Andrey, D.; Alexey, T.; Manfred, F. Long-term agricultural land-cover change and potential for cropland expansion in the former Virgin Lands area of Kazakhstan. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054012. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjeet, J.; Jiquan, C.; Nan, L.; Burkhard, W. Land cover/land use change in semi-arid Inner Mongolia: 1992–2004. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045010. [Google Scholar]
- Praveen, N.; Morton, C.D.; Macedo, N.M.; Victoria, C.D.; Chengquan, H.; Gibbs, K.H.; Bolfe, L.E. Forest carbon emissions from cropland expansion in the Brazilian Cerrado biome. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 025004. [Google Scholar]
- Galford, G.L.; Melillo, J.M.; Kicklighter, D.W.; Mustard, J.F.; Cronin, T.W.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Cerri, C.C. Historical carbon emissions and uptake from the agricultural frontier of the Brazilian Amazon. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciais, P.; Bombelli, A.; Williams, M.; Piao, S.L.; Chave, J.; Ryan, C.M.; Henry, M.; Brender, P.; Valentini, R. The carbon balance of Africa: Synthesis of recent research studies. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 2038–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, R.A.; Hackler, J.L. Emissions of carbon from land use change in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Ren, W.; Lu, C.; Alley, K.D.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Pan, S.; Virji, H. Terrestrial carbon balance in tropical Asia: Contribution from cropland expansion and land management. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 100, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassmann, K.M.; Joos, F.; Fischer, G. Simulating effects of land use changes on carbon fluxes: Past contributions to atmospheric CO2 increases and future commitments due to losses of terrestrial sink capacity. Tellus B 2008, 60, 583–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhao, X.; Bai, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, H.; Xie, Z.; Shi, X.; Wu, B.; et al. Carbon pools in China’s terrestrial ecosystems: New estimates based on an intensive field survey. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Huang, B.; Zhao, S.; Wu, J.; Xie, D.; et al. Economics- and policy-driven organic carbon input enhancement dominates soil organic carbon accumulation in Chinese croplands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4045–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Luo, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Effect of Land Use History and Pattern on Soil Carbon Storage in Arid Region of Central Asia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Krause, C.; Cobb, N. Climate change and human activities: A case study in Xinjiang, China. Clim. Chang. 2010, 99, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hanjra, M.A.; Hua, F.; Shu, Y.; Li, Y. Analysis of climate variability in the Manas River Valley, North-Western China (1956–2006). Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2013, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Liu, H.; Zhan, K. Long-term changes of Tamarix-vegetation in the oasis-desert ecotone and its driving factors: Implication for dryland management. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, G. Carbon Cycle in Dryland Ecosystems of Central Asia, 1st ed.; China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, S. Estimation of regional irrigation water requirement and water supply risk in the arid region of Northwestern China 1989–2010. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 128, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, G.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Xu, H.; Bai, J. Modelling evapotranspiration in a Central Asian desert ecosystem. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3680–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Xinjiang Water Resources. Xinjiang Water Resources Bulletin 2010; Bureau of Xinjiang Water Resources: Xinjiang, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Luo, G.; Xia, J.; Zhou, K.; Lou, S.; Ye, M. Ecological response to the climate change on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2005, 48, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, T.; Bernauer, T.; Guiennet, R.; Sellars, S.; Robertson, A.; Mankin, J.; Bauer-Gottwein, P.; Yakovlev, A. Will climate change exacerbate water stress in Central Asia? Clim. Chang. 2012, 112, 881–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, A.; Bolch, T.; Stoffel, M.; Solomina, O.; Beniston, M. Climate change impacts on glaciers and runoff in Tien Shan (Central Asia). Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Yongjian, D.; Shiyin, L.; Lianghong, J.; Kunpeng, W.; Zongli, J.; Wanqin, G. Changes of glacial lakes and implications in Tian Shan, central Asia, based on remote sensing data from 1990 to 2010. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044052. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S. Land Use/Cover Change impacts on water table change over 25 years in a desert-oasis transition zone of the Heihe River Basin, China. Water 2016, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, A.; Sitch, S.; Pongratz, J.; Stocker, B.D.; Ciais, P.; Poulter, B.; Bayer, A.D.; Bondeau, A.; Calle, L.; Chini, L.P.; et al. Historical carbon dioxide emissions caused by land-use changes are possibly larger than assumed. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Relationships between carbon fluxes and environmental factors in a drip-irrigated, film-mulched cotton field in arid region. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Tian, C. Carbon Dioxide Fluxes and Concentrations in a Cotton Field in Northwestern China: Effects of Plastic Mulching and Drip Irrigation. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
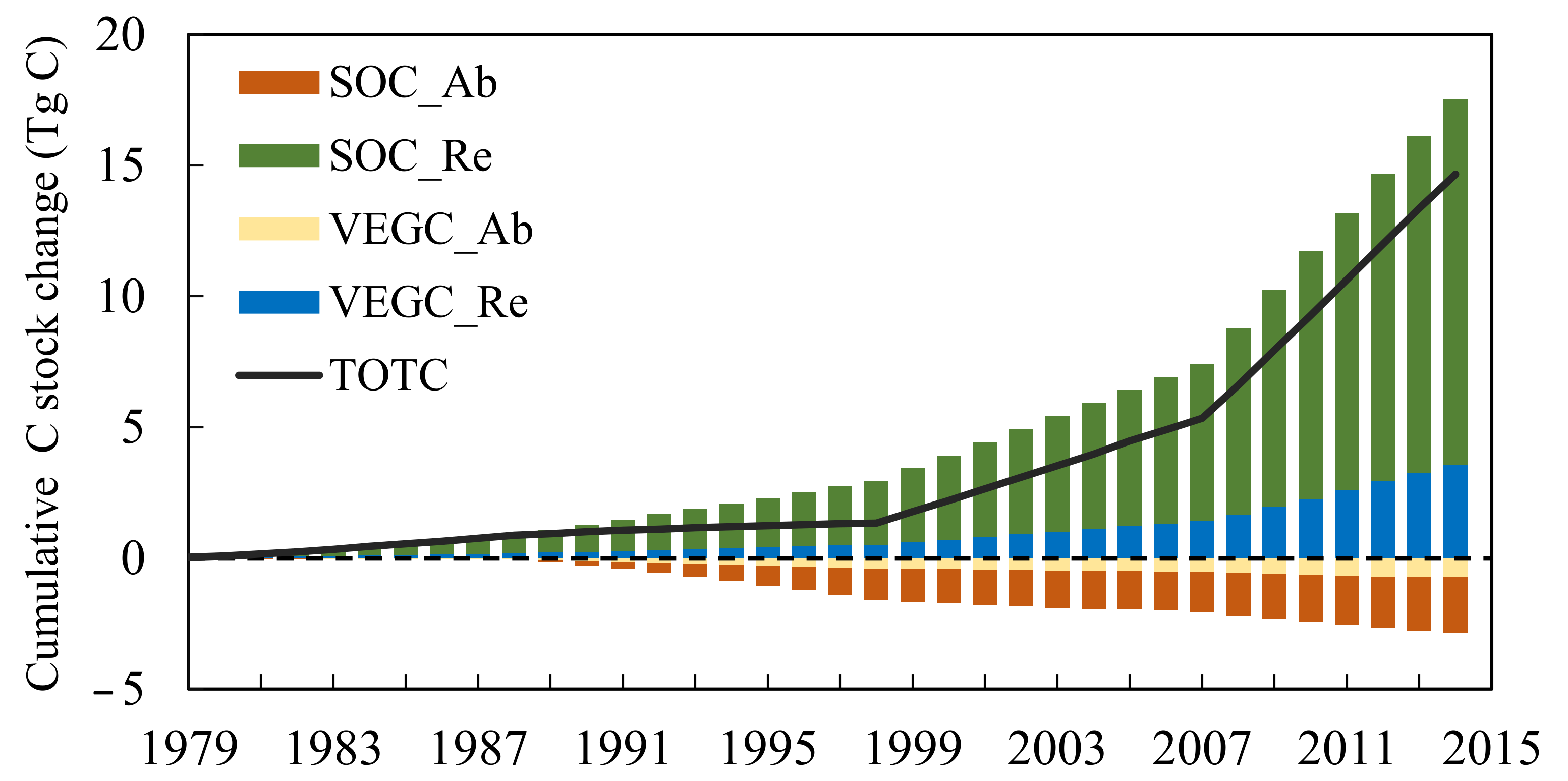
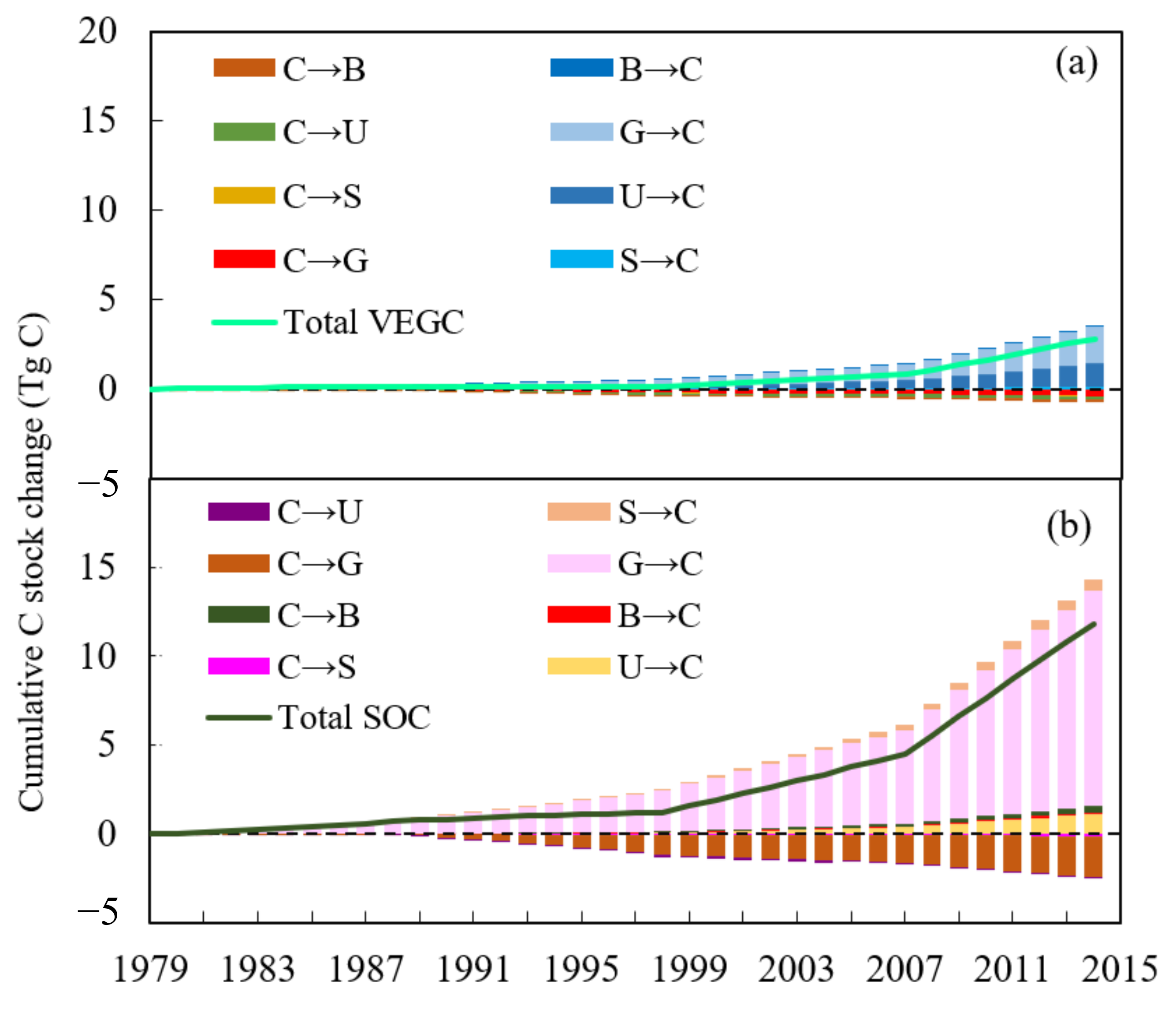
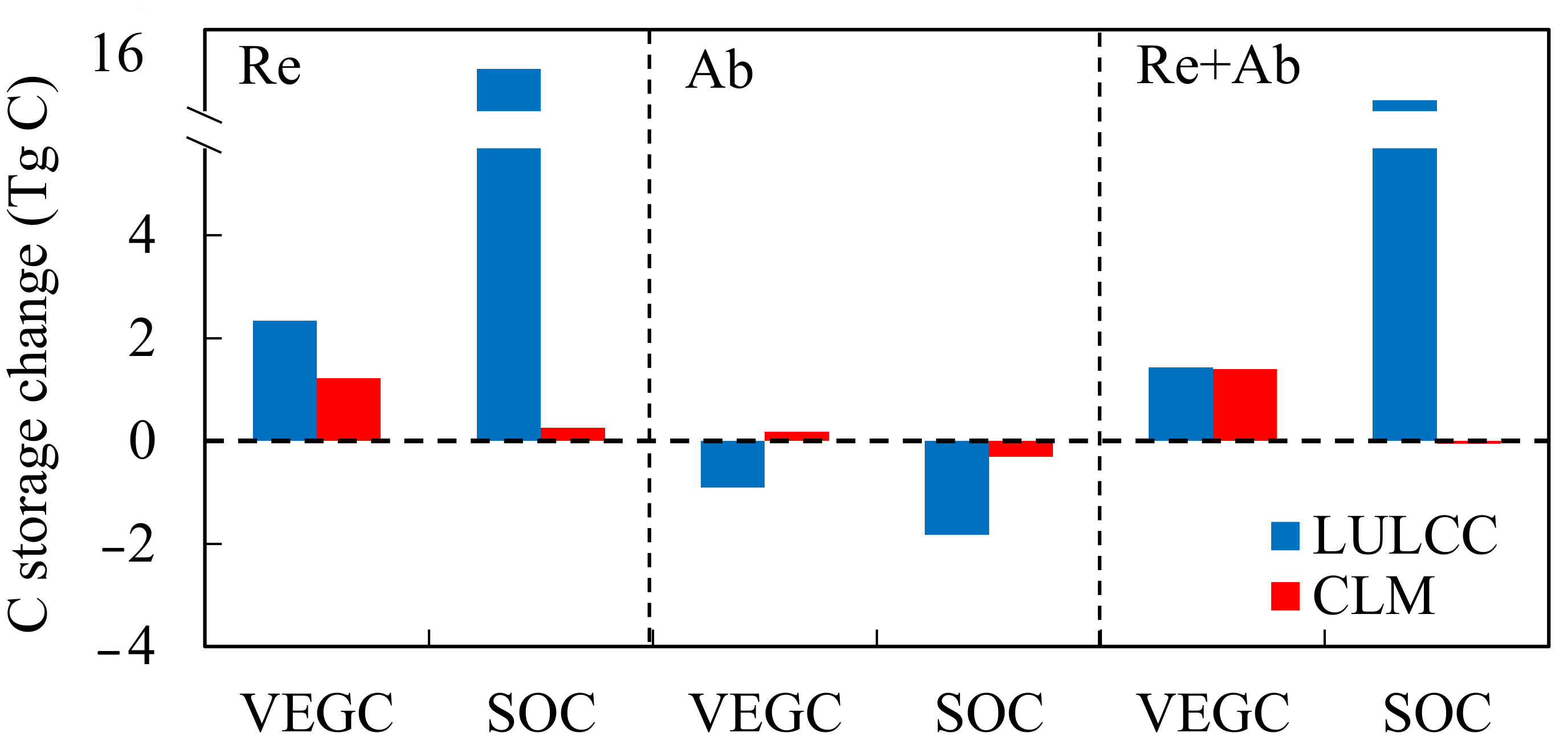
| Description | Desert Shrubland | Desert Grassland | Unutilized Land | Built-Up Land | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The allocation ratio of plant biomass into different C pools when reclaiming | |||||
| 1-year immediate C pool | 0.27 | 0.50 | 0.50 | This study | |
| 15-year short-lived C pool | 0.40 | This study | |||
| Debris C pool | 0.33 | 0.50 | 0.50 | [33] | |
| The stable SOC density in cropland (g C m−2) | 6507 | 8529 | 3609 | 9940 | [33] |
| The time to reach a new equilibrium SOC level after Re (Ts) (year) | 10 | 20 | 10 | 20 | [12,34] |
| The fast SOC change time after Re (Tf) (year) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | [34,35] |
| The time to reach the equilibrium VEGC level after arable land Ab (Trv) (year) | 10 | 20 | 10 | 20 | [34,36,37] |
| The time to reach the new equilibrium SOC level after arable land Ab (Trs) (year) | 10 | 20 | 10 | 20 | [12,34] |
| Scenario | Re | Ab | Climate | Region | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOverall | 1979–2014 | 1979–2014 | 1979–2014 | Re and Ab areas | Combined effects of climate and cropland area change |
| SCLM_Re | 1979–2014 | NA | 1979–2014 | Re area | Coupled effects of climate and Re |
| SRe_only | 1979–2014 | NA | 1979 | Re area | Isolated effects of Re |
| SCLM_only_Re | NA | NA | 1979–2014 | Re area | Climate effects over Re area |
| SCLM_Ab | NA | 1979–2014 | 1979–2014 | Ab area | Coupled effects of climate and Ab |
| SAb_only | NA | 1979–2014 | 1979 | Ab area | Isolated effects of Ab |
| SCLM_only_Ab | NA | NA | 1979–2014 | Ab area | Climate effects over Ab area |
| Area (km2)Re/Ab | Re | Ab | TOTC Change | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGC | SOC | VEGC | SOC | |||
| 1979–1988 | 244.71/13.28 | 71.58 | 287.20 | −71.23 | −2.10 | 336.54 |
| 1989–1998 | 455.66/534.94 | 74.78 | 379.41 | −72.69 | −225.29 | 48.00 |
| 1999–2007 | 1169.32/203.18 | 85.27 | 339.74 | −79.16 | −179.74 | 323.77 |
| 2008–2014 | 2575.93/326.90 | 119.16 | 441.86 | −82.66 | −264.98 | 458.69 |
| Total area and Weighted average | 4445.61/1078.30 | 103.08 | 400.08 | −76.91 | −225.99 | 345.81 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Han, Q.; Luo, G.; Zhao, C.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, D. Effects of Cropland Conversion and Climate Change on Agrosystem Carbon Balance of China’s Dryland: A Typical Watershed Study. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124508
Li C, Han Q, Luo G, Zhao C, Li S, Wang Y, Yu D. Effects of Cropland Conversion and Climate Change on Agrosystem Carbon Balance of China’s Dryland: A Typical Watershed Study. Sustainability. 2018; 10(12):4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124508
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chaofan, Qifei Han, Geping Luo, Chengyi Zhao, Shoubo Li, Yuangang Wang, and Dongsheng Yu. 2018. "Effects of Cropland Conversion and Climate Change on Agrosystem Carbon Balance of China’s Dryland: A Typical Watershed Study" Sustainability 10, no. 12: 4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124508
APA StyleLi, C., Han, Q., Luo, G., Zhao, C., Li, S., Wang, Y., & Yu, D. (2018). Effects of Cropland Conversion and Climate Change on Agrosystem Carbon Balance of China’s Dryland: A Typical Watershed Study. Sustainability, 10(12), 4508. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124508