Adsorption Behavior of Inorganic and Organic Phosphate by Iron Manganese Plaques on Reed Roots in Wetlands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Fe–Mn Plaque Collection
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Kinetics
2.5. Adsorption Isotherms
2.6. Adsorption Thermodynamics
2.7. Competitive Adsorption
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
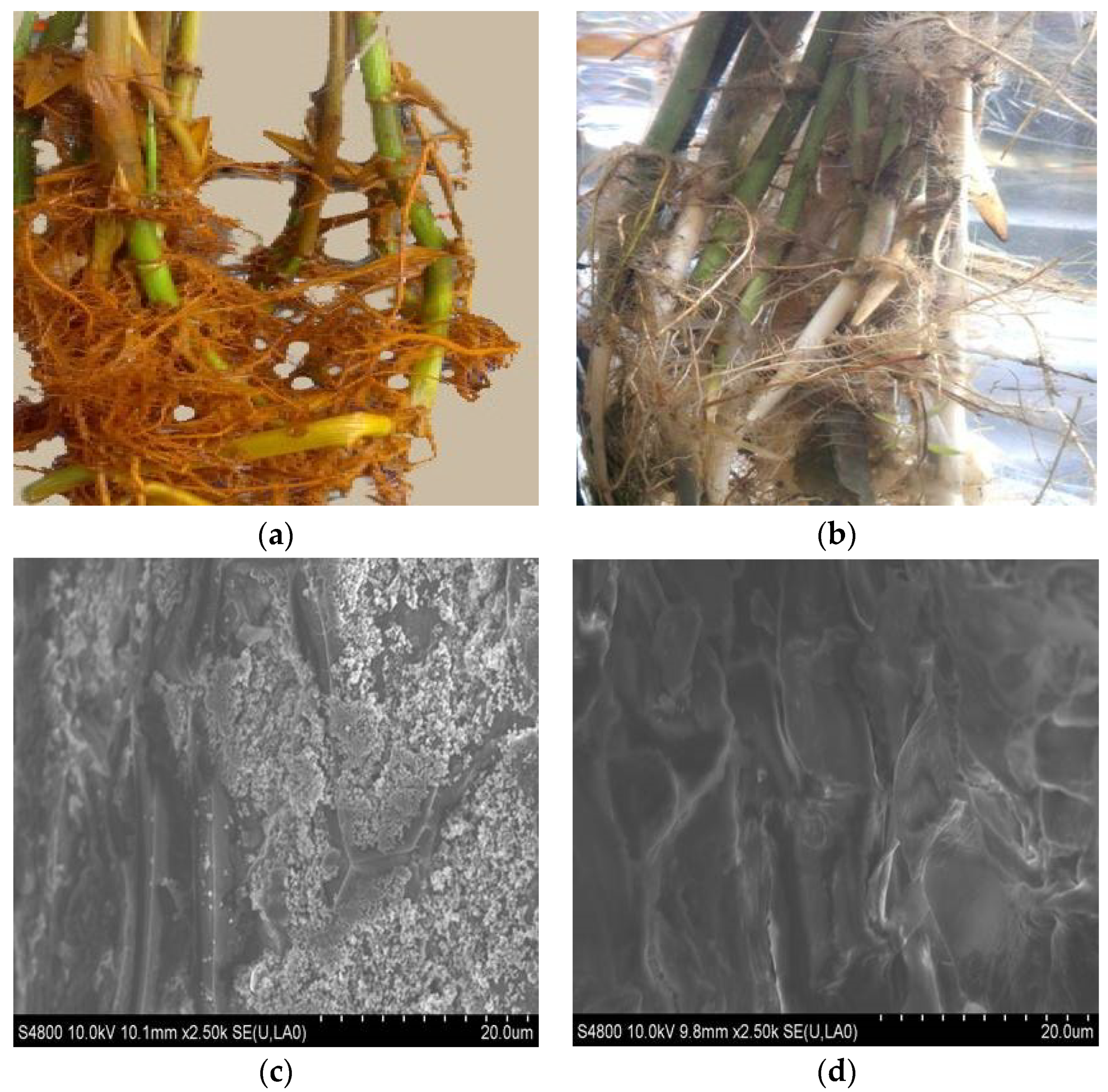
3.1.1. SEM Analysis
3.1.2. XPS Analysis
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
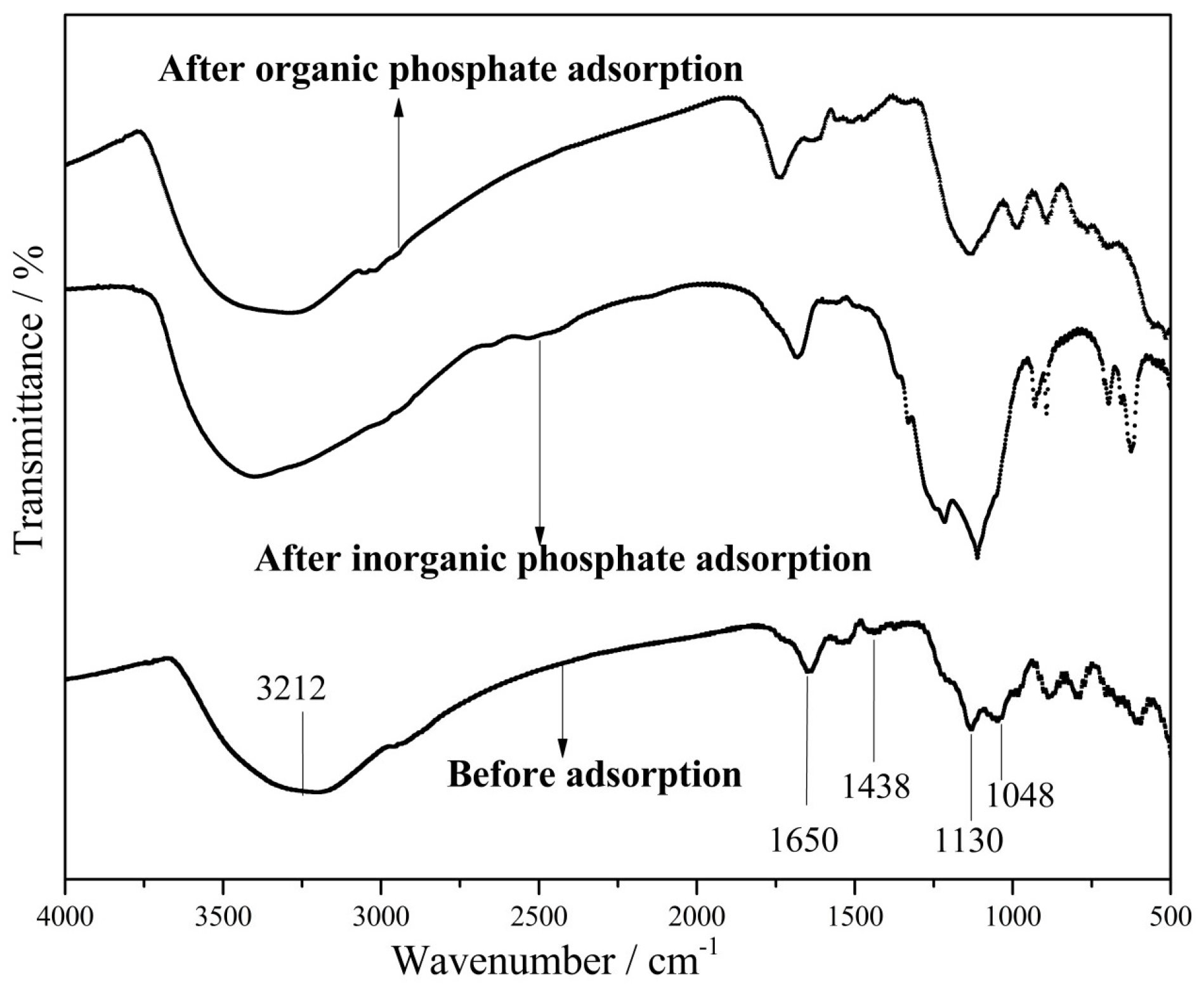
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism
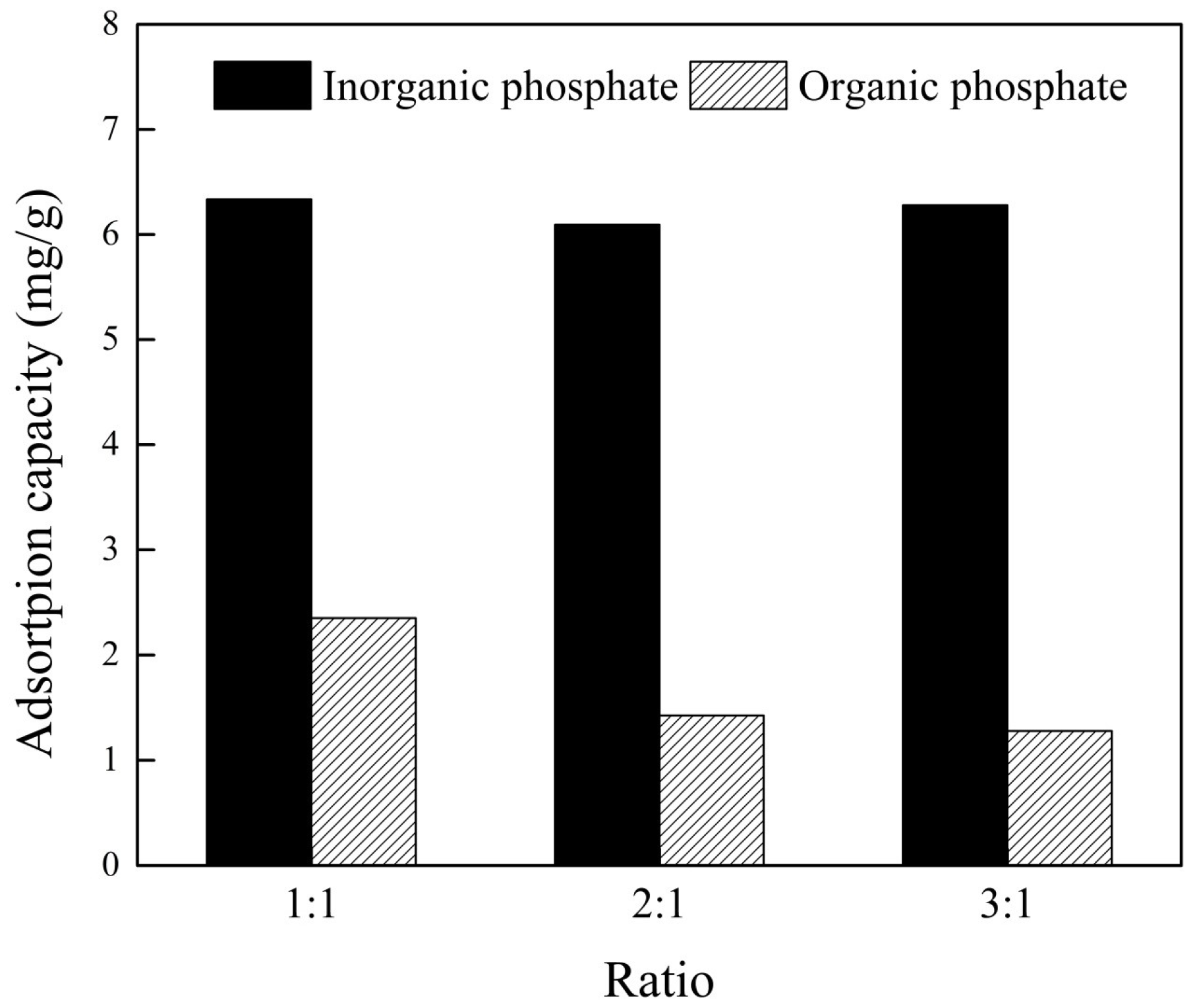
3.6. Competitive Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, B.; Gautier, M.; Rivard, C.; Sanglar, C.; Michel, P.; Gourdon, R. Effect of aging on phosphorus speciation in surface deposit of a vertical flow constructed wetland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4903–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.; Saint, C.P.; Kirkham, M.B.; Chowdhury, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; et al. Root Iron Plaque on Wetland Plants as a Dynamic Pool of Nutrients and Contaminants. Adv. Agron. 2016, 138, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Cui, Z.; He, G.; Huang, L.; Chen, M. Phosphorus adsorption onto clay minerals and iron oxide with consideration of heterogeneous particle morphology. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Xiao, H.; Peng, H.; Deng, S. Effects of iron plaque on phosphorus uptake by Pilea cadierei cultured in constructed wetland. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 11, 1508–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Yao, Q.; Yu, Z. Particulate phosphorus speciation and phosphate adsorption characteristics associated with sediment grain size. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Ji, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Yao, G. Phosphorus removal enhancement of magnesium modified constructed wetland microcosm and its mechanism study. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gao, B.; Jia, W.; Miao, A.; Xiao, L.; Yang, L. Highly efficient removal of nitrogen and phosphorus in an electrolysis-integrated horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetland amended with biochar. Water Res. 2018, 139, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.; Muntaha, S.; Rashid, M.; Sun, G.; Hasnat, A. Industrial wastewater treatment in constructed wetlands packed with construction materials and agricultural by-products. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melia, P.M.; Cundy, A.B.; Sohi, S.P.; Hooda, P.S.; Busquets, R. Trends in the recovery of phosphorus in bioavailable forms from wastewater. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilton, A.N.; Powell, N.; Guieysse, B. Plant based phosphorus recovery from wastewater via algae and macrophytes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, R. Pore characterization and its impact on methane adsorption capacity for organic-rich marine shales. Fuel 2016, 181, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansel, C.M.; Fendorf, S.; Sutton, S.; Newville, M. Characterization of Fe plaque and associated metals on the roots of mine-waste impacted aquatic plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3863–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Yan, Z. Iron plaque formation and heavy metal uptake in Spartina alterniflora at different tidal levels and waterlogging conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, L.H.; Wen, S.F.; Peng, C.S.; Xing, B.S.; Li, F.M. Effect of Iron Plaque on Root Surfaces on Phosphorus Uptake of Two Wetland Plants(in Chinese). Environ. Sci. 2010, 31, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.X.; Yu, G.W.; Cao, X.Y.; Zhong, H.T. Effect of migration of amorphous iron oxide on phosphorous spatial distribution in constructed wetland with horizontal sub-surface flow. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 53, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wu, K.; Zeng, L. Removal of phosphorus by a composite metal oxide adsorbent derived from manganese ore tailings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217–218, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Vosátka, M.; Vogel-Mikus, K.; Kavčič, A.; Kelemen, M.; Šepec, L.; Pelicon, P.; Skála, R.; Valero Powter, A.R.; Teodoro, M.; Michálková, Z.; Komárek, M. Nano Zero-Valent Iron Mediated Metal(loid) Uptake and Translocation by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbioses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7640–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boghi, A.; Roose, T.; Kirk, G.J.D. A Model of Uranium Uptake by Plant Roots Allowing for Root-Induced Changes in the soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3536–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z. Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the batch biosorption of nickel(II) ions onto Chlorella vulgaris. Process Biochem. 2002, 38, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.C.; Ibe, A.H.; Rivera, K.K.P.; Arazo, R.O.; de Luna, M.D.G. Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution by adsorbents synthesized from groundwater treatment residuals. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Ye, Z. Root porosity, radial oxygen loss and iron plaque on roots of wetland plants in relation to zinc tolerance and accumulation. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Leng, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Dai, Q. Iron plaque formation on roots of different rice cultivars and the relation with lead uptake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Qu, B.; Li, M. Phosphorus mobilization in the Yeyahu Wetland: Phosphatase enzyme activities and organic phosphorus fractions in the rhizosphere soils. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 124, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, J.H.; Zhu, Y.G.; Huang, Y.Z.; Hu, H.Q.; Christie, P. Sequestration of As by iron plaque on the roots of three rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars in a low-P soil with or without P fertilizer. Environ. Geochem. Health 2005, 27, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Canning, G.W.; Bancroft, G.M. XPS study of reductive dissolution of 7Å-birnessite by H3AsO3, with constraints on reaction mechanism. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lǚ, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Zhao, X.; Sun, L.; Qu, J. Adsorptive removal of phosphate by a nanostructured Fe-Al-Mn trimetal oxide adsorbent. Powder Technol. 2013, 233, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhao, D. Controlling phosphate releasing from poultry litter using stabilized Fe-Mn binary oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Han, Q.; Li, J.; Li, H. The behavior of phosphate adsorption and its reactions on the surfaces of Fe–Mn oxide adsorbent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 76, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Adsorptive removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions using iron oxide tailings. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ye, X.; Jia, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Phosphorus sorption-desorption and effects of temperature, pH and salinity on phosphorus sorption in marsh soils from coastal wetlands with different flooding conditions. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, M.G.; Dickson, K.L.; Saleh, F.; Waller, W.T.; Doyle, R.D.; Hudak, P. Recovery and fractionation of phosphorus retained by lightweight expanded shale and masonry sand used as media in subsurface flow treatment wetlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4621–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unuabonah, E.I.; Adebowale, K.O.; Olu-Owolabi, B.I. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of lead (II) ions onto phosphate-modified kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štandeker, S.; Novak, Z.; Knez, Ž. Adsorption of toxic organic compounds from water with hydrophobic silica aerogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.; Maity, A.; Ghosh, U.C. Manganese associated nanoparticles agglomerate of iron(III) oxide: Synthesis, characterization and arsenic(III) sorption behavior with mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Jiang, H.; Gong, H.; Su, T. Absorption of ammonia on tantalum hydroxide synthesized by a hydrofluoric acid method. Transit. Met. Chem. 2011, 36, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, C.; Brigante, M.; Antelo, J.; Avena, M. Kinetics of phosphate adsorption on goethite: Comparing batch adsorption and ATR-IR measurements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Baldy, V.; Périssol, C.; Korboulewsky, N. Influence of plants on microbial activity in a vertical-downflow wetland system treating waste activated sludge with high organic matter concentrations. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S158–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, G.; Liu, C. Screening of phosphate-removing substrates for use in constructed wetlands treating swine wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Different Phosphate | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Qe (mg/g) | K1 (1/min) | R2 | Qe(mg/g) | K2 (g/mg/min) | |
| Inorganic Phosphate | 0.927 | 5.11 | 0.0132 | 0.989 | 5.42 | 0.0004 |
| Organic phosphate | 0.906 | 3.33 | 0.0391 | 0.965 | 3.48 | 0.0017 |
| Different Phosphate | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Qm (mg/g) | KL | R2 | KF (mg/g) | n | |
| Inorganic phosphate | 0.991 | 7.69 | 9.29 | 0.962 | 6.75 | 2.17 |
| Organic phosphate | 0.992 | 3.66 | 12.41 | 0.782 | 2.91 | 2.94 |
| Adsorbent | Type | Phosphate Species | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe–Mn plaque | Natural | Inorganic | 7.69 | This study |
| Organic | 3.66 | |||
| Fe–Mn oxide | Synthetic | Inorganic | 18.4 | [28] |
| Iron oxide tailing | Synthetic | Inorganic | 8.2 | [29] |
| Marsh soil | Natural | Inorganic | 0.26 | [30] |
| Expanded shale | Natural | Total | 0.52 | [31] |
| Temperature (K) | Inorganic Phosphate Adsorption | Organic Phosphate Adsorption | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kd | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (J/mol) | Kd | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (J/mol) | |
| 293 | 25.36 | −7.88 | −19.15 | −38.58 | 47.76 | −9.40 | −67.05 | −198.37 |
| 298 | 21.53 | −7.60 | 21.84 | −7.64 | ||||
| 303 | 19.04 | −7.42 | 12.08 | −6.28 | ||||
| 308 | 16.62 | −7.20 | 10.92 | −6.12 | ||||
| 313 | 15.42 | −7.12 | 7.52 | −5.25 | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Du, X.; Gao, C.; Yu, Z. Adsorption Behavior of Inorganic and Organic Phosphate by Iron Manganese Plaques on Reed Roots in Wetlands. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4578. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124578
Zhu Y, Du X, Gao C, Yu Z. Adsorption Behavior of Inorganic and Organic Phosphate by Iron Manganese Plaques on Reed Roots in Wetlands. Sustainability. 2018; 10(12):4578. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124578
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yingjie, Xiaoli Du, Can Gao, and Zhenya Yu. 2018. "Adsorption Behavior of Inorganic and Organic Phosphate by Iron Manganese Plaques on Reed Roots in Wetlands" Sustainability 10, no. 12: 4578. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124578
APA StyleZhu, Y., Du, X., Gao, C., & Yu, Z. (2018). Adsorption Behavior of Inorganic and Organic Phosphate by Iron Manganese Plaques on Reed Roots in Wetlands. Sustainability, 10(12), 4578. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124578





