Strategic Cross-Border Water Pollution in Songliao Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
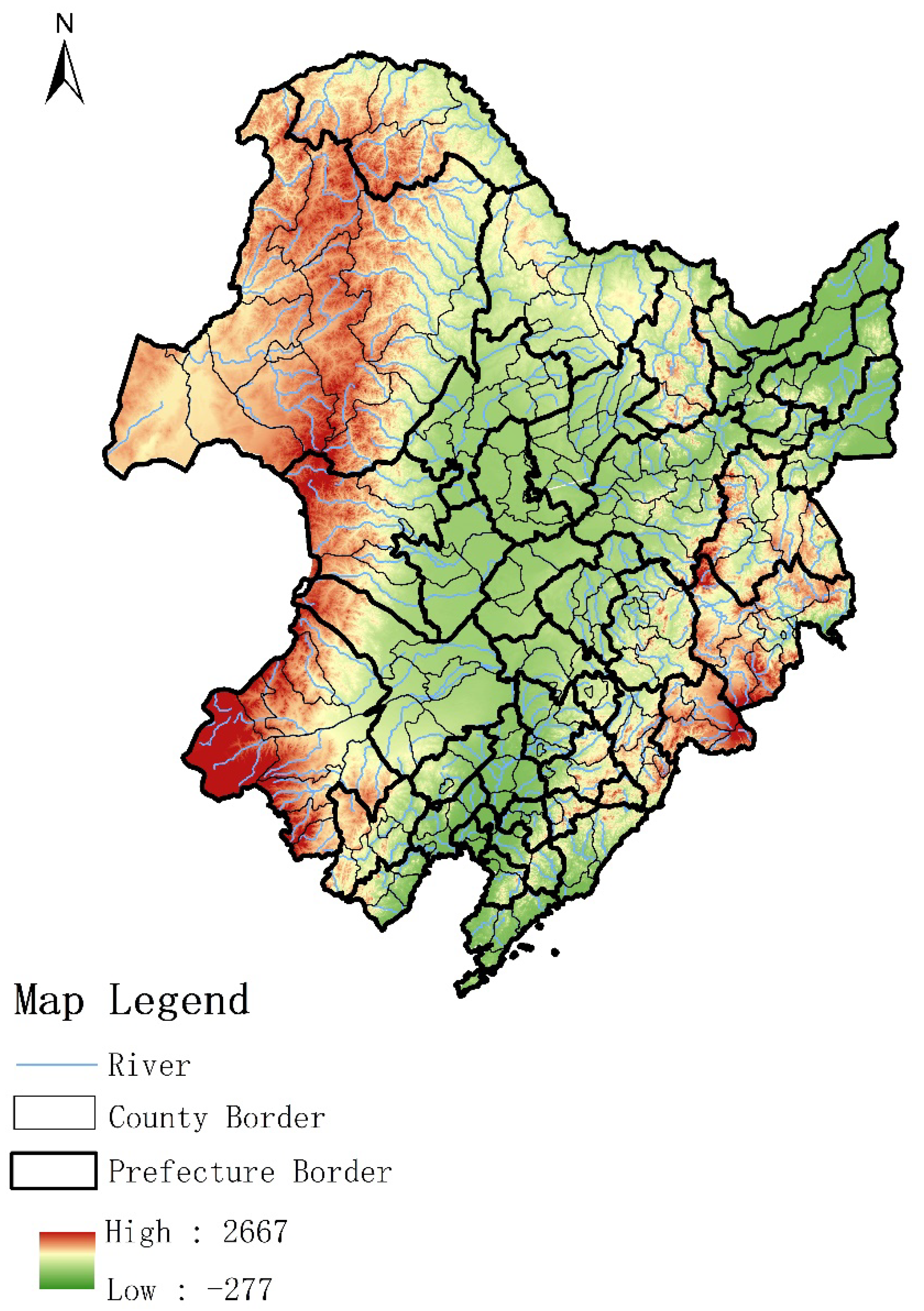
3.1. Sample Introduction
3.2. Empirical Design
3.2.1. Differences-in-Differences Method (DID) Model Setting
3.2.2. DDD (Differences-in-Differences-in-Differences) Model Setting
3.3. Variable Selection and Data Sources
3.3.1. Water Pollution Regulation Index
3.3.2. Enterprise Production Activity Indexes
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. DID
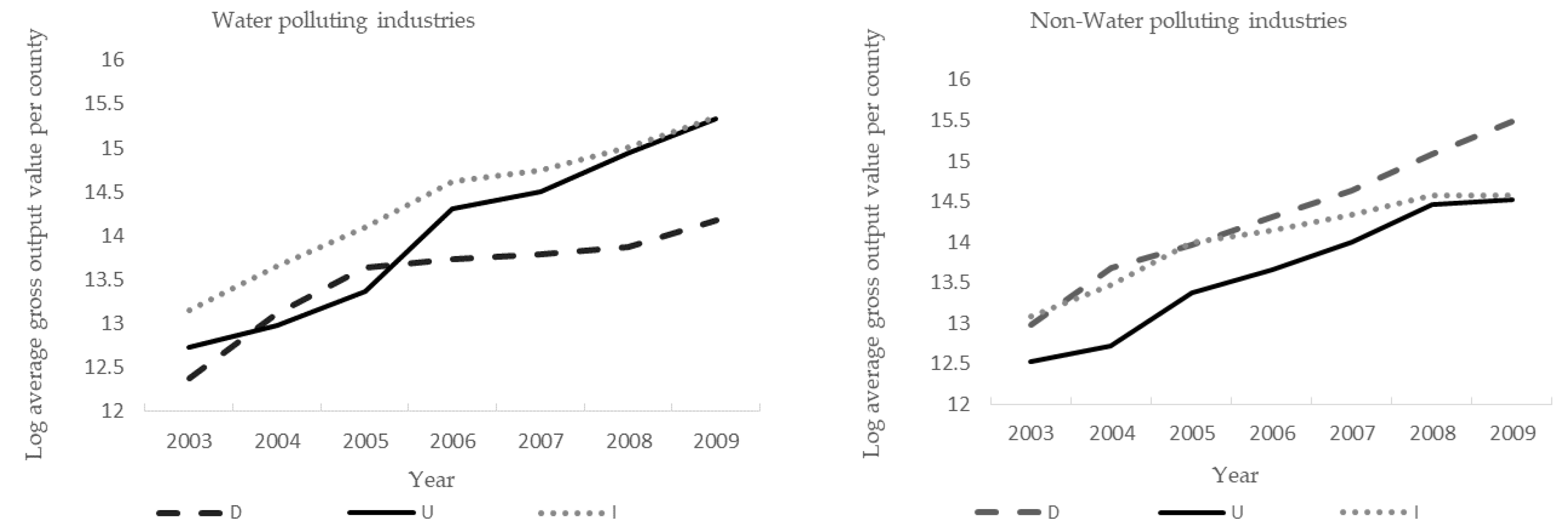
4.1.1. Identifying the Relationship between Regulation and Polluting Activities (Assumption 1)
4.1.2. Identification of Strategic Allocating Polluting Activities by Prefecture-Level Municipal Government (Assumption 2)
4.2. DDD
4.2.1. Identifying the Relationship between Regulation and Polluting Activities
4.2.2. Spatial Transfer of Water Polluting Activities
5. Other Robustness Checks
5.1. Time-lag of Policy Effectiveness
5.2. Enterprise Ownership
5.3. Enterprise Nationality
5.4. Enterprise Scale
5.5. Enterprise Location
6. Conclusions and Suggestions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sigman, H. International Spillovers and Water Quality in Rivers: Do Countries Free Ride? Am. Econ. Rev. 2002, 92, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luan, W.X.; Kang, M.J. COD pollution load of social and economic activities in Liaohe River Basin, China. Geogr. Res. 2013, 32, 1802–1813. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; He, M.; Zhou, Y. Distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediment of the Second Songhua River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 137, 329–342. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Q.; Shi, Y.; Xia, Q. Effectiveness of the policy of circular economy in China: A DEA-based analysis for the period of 11th five-year-plan. Resour. Conserv. Recysl. 2014, 83, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H.; Fan, Y.; Yu, S.M. Energy conservation and CO2, emission reduction in China’s 11th Five-Year Plan: A performance evaluation. Energy Econ. 2014, 46, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.E.; Li, P.; Zhao, D. Water Pollution Progress at Borders: The Role of Changes in China’s Political Promotion Incentives. Am. Econ. J. Econ. Policy 2015, 7, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Sun, L.; Qi, D. Using 137 Cs technique to quantify soil erosion and deposition rates in an agricultural catchment in the black soil region, Northeast China. Geomorphology 2012, 169, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Lee, H.F.; Zhang, W. Human-environment interactions within the West Liao River Basin in Northeastern China during the Holocene Optimum. Quat. Int. 2016, 426, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Yang, L.; Liu, L. Environmental incidents in China: Lessons from 2006 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.H.; Miao, X.; Zang, H. Information Disclosure on Hazards from Industrial Water Pollution Incidents: Latent Resistance and Countermeasures in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, Z.; Chen, B. Prevention and control policy analysis for energy-related regional pollution management in China. Appl. Energy 2016, 166, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q. Fiscal decentralization and environmental pollution: Evidence from Chinese panel data. China Econ. Rev. 2015, 36, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Industrial water pollution, water environment treatment, and health risks in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigman, H. Cross-border spillovers and decentralization of environmental policies. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2005, 50, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, W.H. Regulation on Trans-boundary Water Pollution: A Study on Inter-judiciary River-basin Pollution in China. Chin. Econ. Q. 2008, 7, 447–464. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.M. Study on the Differential Game and Strategy of Water Pollution Control. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2014, 24, 93–101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, J. Spatial heterogeneity and cross-border pollution: A contingent valuation (CV) study on the Xijiang River drainage basin in south China. China Econ. Rev. 2015, 36, 101–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscomb, M.; Mobarak, A.M. Decentralization and Pollution Spillovers: Evidence from the Re-drawing of County Borders in Brazil. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2017, 84, 464–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.C. Coupling Relationship between Polluting Industrial Agglomeration and Water Environment Pollution in Southern Jiangsu of Taihu Lake Basin. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 954–962. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.H.; Ma, M. Study on Pollution Emission Behavior of Regional Enterprises under the Local Government Environmental Regulation Competition. J. Beijing Inst. Techchol. 2018, 20, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, B. Westward movement of new polluting firms in China: Pollution reduction mandates and location choice. J. Comp. Econ. 2017, 45, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.J.; Zheng, D.; Lei, P. Evolution of spatial pattern of industrial wastewater pollution emission in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Kahn, M.E.; Liu, Y. The consequences of spatially differentiated water pollution regulation in China. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 88, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Q. Polluting thy neighbor: Unintended consequences of China’s pollution reduction mandates. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2016, 76, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashenfelter, O.; Card, D.E. Using the Longitudinal Structure of Earnings to Estimate the Effect of Training Programs. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1985, 67, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantly, C.; Tong, L.; Tatsushi, O. Quantile treatment effects in difference in differences models under dependence restrictions and with only two time periods. J. Econ. 2018, 206, 395–413. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, M.S.; Florax, R.J.G.M. Difference-in-differences techniques for spatial data: Local autocorrelation and spatial interaction. Econ. Lett. 2015, 137, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Q. How China achieved its 11th Five-Year Plan emissions reduction target: A structural decomposition analysis of industrial SO2 and chemical oxygen demand. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X. Long-term trends in NO2 columns related to economic developments and air quality policies from 1997 to 2016 in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.Y.; Wang, X.Z.; Li, Y.J. Carbon Footprint Analyses and Potential Carbon Emission Reduction in China’s Major Peach Orchards. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, H.X.; Liu, B.B. Environmental regulation and the Pollution Haven Hypothesis: Do environmental regulation measures matter? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ramanathan, R. Exploring the relationships between different types of environmental regulations and environmental performance: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, M.K. Internal Government Assessments of the Quality of Governance in China. Stud. Comp. Int. Dev. 2015, 50, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, L.; Zeng, H. Does water disclosure cause a rise in corporate risk-taking?—Evidence from Chinese high water-risk industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Report on the First National Census of Polluting Sources; Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese)
- Nie, H.H.; Jiang, T.; Yang, R.D. Current Situation and Potential Problems in the Use of China’s Industrial Enterprise Database. Available online: http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SJJJ201205011.htm (accessed on 10 December 2018). (In Chinese).
- Graversgaard, M.; Hedelin, B.; Smith, L. Opportunities and Barriers for Water Co-Governance—A Critical Analysis of Seven Cases of Diffuse Water Pollution from Agriculture in Europe, Australia and North America. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Takala, J.; Liu, Y. A combinatorial optimization model for enterprise patent transfer. Inf. Technol. Manag. 2015, 16, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwayama, Y.; Brozović, N. Optimal Management of Environmental Externalities with Time Lags and Uncertainty. Envirin. Resour. Econ. 2016, 68, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lu, Y.; Wu, M. Does Environmental Regulation Drive away Inbound Foreign Direct Investment? Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment in China. J. Dev. Econ. 2016, 123, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.E.; Du, D.L. The Evolution of Economic Development Level in Northeast China and Its Spatial Differentiation Mode Scince 2003. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar]

| Variable | Max | Min | Mean | S.D. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polluting enterprise industrial output value (in RMB 1000) | 109,255,517 | 48,101 | 8,378,143 | 33,812,897 |
| Nonpolluting enterprise industrial output value (in RMB 1000) | 117,367,556 | 12,011 | 10,824,156 | 50,305,103 |
| Number of new polluting enterprises | 52 | 0 | 5.603 | 9.35 |
| Number of old polluting enterprises | 32 | 0 | 4.115 | 6.893 |
| 1.622 | 0.0002 | 0.276 | 0.55 | |
| Environment protection related text proportion (%) | 5.452 | 1.115 | 3.309 | 1.208 |
| The Dependent Variable: Log (Total Output Value in Each Industry in Each Region in Each Year) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Polluting Industries | Non Water Polluting Industries | |||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| −0.827 *** | ||||
| (−20.77) | ||||
| −1.736 *** | ||||
| (−4.07) | ||||
| 1.910 *** | 0.385 | |||
| (14.739) | (0.632) | |||
| 0.050 | 0.022 | 0.319 * | 0.062 | |
| (0.012) | (0.25) | (1.787) | (1.40) | |
| 1.162 *** | 0.683 * | 0.547 ** | 1.319 ** | |
| (3.086) | (1.671) | (2.08) | (2.249) | |
| 3.821 *** | 0.991 ** | 1.847 *** | 0.764 | |
| (16.613) | (2.32) | (5.142) | (0.716) | |
| 4.103 *** | 2.839 *** | 3.978 *** | 2.440 *** | |
| (17.836) | (5.083) | (9.002) | (4.463) | |
| 4.400 *** | 3.349 *** | 4.442 *** | 3.771 *** | |
| (19.277) | (6.325) | (12.634) | (8.27) | |
| 4.276 *** | 4.660 *** | 2.933 *** | 2.108 ** | |
| (18.835) | (8.758) | (3.015) | (3.658) | |
| Region fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 1519 | 1519 | 1519 | 1519 |
| R2 | 0.605 | 0.630 | 0.794 | 0.745 |
| The Dependent Variable: Log (Total Output Value in Each Industry in Each Region in Each Year) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| −0.403 *** | ||||
| (−15.796) | ||||
| −0.310 *** | ||||
| (−8.515) | ||||
| −0.484 *** | ||||
| (−10.643) | ||||
| −0.466 *** | ||||
| (−9.943) | ||||
| −0.121 *** | ||||
| (−5.024) | ||||
| −0.211 *** | ||||
| (−6.416) | ||||
| −0.235 *** | ||||
| (−6.821) | ||||
| −0.333 *** | ||||
| (−9.09) | ||||
| −0.418 *** | ||||
| (−6.236) | ||||
| 0.258 *** | ||||
| (−7.172) | ||||
| 0.391 *** | ||||
| (−5.009) | ||||
| 0.496 *** | ||||
| (−7.103) | ||||
| −0.292 ** | ||||
| (−2.814) | ||||
| 0.247 *** | ||||
| (−2.107) | ||||
| 0.358 *** | ||||
| (−3.268) | ||||
| 0.375 *** | ||||
| (−4.018) | ||||
| County-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Industry-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region-industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 3038 | 3038 | 1848 | 1848 |
| R2-adj | 0.429 | 0.852 | 0.844 | 0.93 |
| The Dependent Variable | Log (Number of New Water Polluting Enterprises +1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | I | B | A | I | B | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| 1.431 *** | −0.096 ** | −0.211 *** | ||||
| (19.436) | (−2.016) | (−6.810) | ||||
| 1.028 *** | −0.771 *** | −0.868 *** | ||||
| (4.957) | (−3.493) | (−4.079) | ||||
| The Dependent Variable | Log (Number of Old Water Polluting Enterprises +1) | |||||
| A | I | B | A | I | B | |
| (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | |
| −0.023 | −0.127 * | −1.073 *** | ||||
| (−0.475) | (−1.674) | (−6.939) | ||||
| −0.017 | −0.066 ** | −0.749 *** | ||||
| (−0.250) | (−2.000) | (−5.463) | ||||
| Region-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Industry-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| County-industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 1176 | 686 | 1176 | 868 | 336 | 644 |
| The Dependent Variable: Log (Total Output Value in Each Industry in Each Region in Each Year) | ||
|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | |
| 0.012 | ||
| 0.047 | ||
| −0.590 *** | ||
| −0.682 *** | ||
| 0.036 | ||
| 0.113 * | ||
| −0.485 *** | ||
| −0.732 *** | ||
| County-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes |
| Industry-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes |
| Region-industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 3038 | 1848 |
| R2-adj | 0.822 | 0.861 |
| The Dependent Variable: Log (Total Output Value in Each Industry in Each Region in Each Year +1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) All | (2) SOE | (3) Private | (4) Foreign | (5) Domestic | (6) Large | (7) Small | |
| −0.403 *** (15.796) | −0.036 (−0.214) | −0.412 *** (−12.973) | −0.006 (−0.38) | −0.388 *** (−2.813) | −0.091 (−0.596) | −0.129 *** (−3.117) | |
| Region-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Industry-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| County-industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 |
| R2-adj | 0.702 | 0.564 | 0.638 | 0.263 | 0.526 | 0.505 | 0.640 |
| The Dependent Variable: Log (Total Output Value in Each Industry in Each Region in Each Year +1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) All | (2) Heilongjiang | (3) Jilin | (4) Liaoning | (5) Inner Mongolia | (6) Industrial Zone | (7) Non-Industrial | |
| 0.403 *** (15.796) | −0.296 ** (−2.063) | −0.607 *** (−3.981) | −0.345 ** (−2.12) | −0.088 (−0.719) | −0.118 (−0.978) | −0.212 *** (−2.725) | |
| Region-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Industry-year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| County-industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 | 3038 |
| R2-adj | 0.702 | 0.613 | 0.721 | 0.552 | 0.656 | 0.578 | 0.710 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, G.; Xiu, C.; Zhao, C.; Ding, Z. Strategic Cross-Border Water Pollution in Songliao Basin. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124713
Yu G, Xiu C, Zhao C, Ding Z. Strategic Cross-Border Water Pollution in Songliao Basin. Sustainability. 2018; 10(12):4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124713
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Guanyi, Chunliang Xiu, Changsong Zhao, and Zhengliang Ding. 2018. "Strategic Cross-Border Water Pollution in Songliao Basin" Sustainability 10, no. 12: 4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124713
APA StyleYu, G., Xiu, C., Zhao, C., & Ding, Z. (2018). Strategic Cross-Border Water Pollution in Songliao Basin. Sustainability, 10(12), 4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124713




