Analysis of Social Networking Service Data for Smart Urban Planning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. New Tools for Enabling Informational Urbanism
2.2. Analysis of Social Network Sites
2.3. Analysis of Social Network Sites for Informational Urbanism
2.4. Findings
- Informational urbanism needs to be fed by valuable knowledge to be useful for designing smart urban planning actions. Big data technology and the IoT play a vital role in providing it, but they need to integrate different data sources and have deployment costs.
- The analysis of SNSs is a growing research discipline that has important implications in many areas of society. This analysis can be done from a human relation point of view, or from a content perspective. As a result, valuable information of the preferences, habits, and behaviors of citizens can be obtained.
- Using data from SNSs opens new possibilities to identify the real uses of urban spaces. This information contributes to the construction of the informational urbanism concept and opens new management possibilities to perform urban planning actions taking into account the dynamics of the city.
3. Analysis of Social Networking Services for Sport
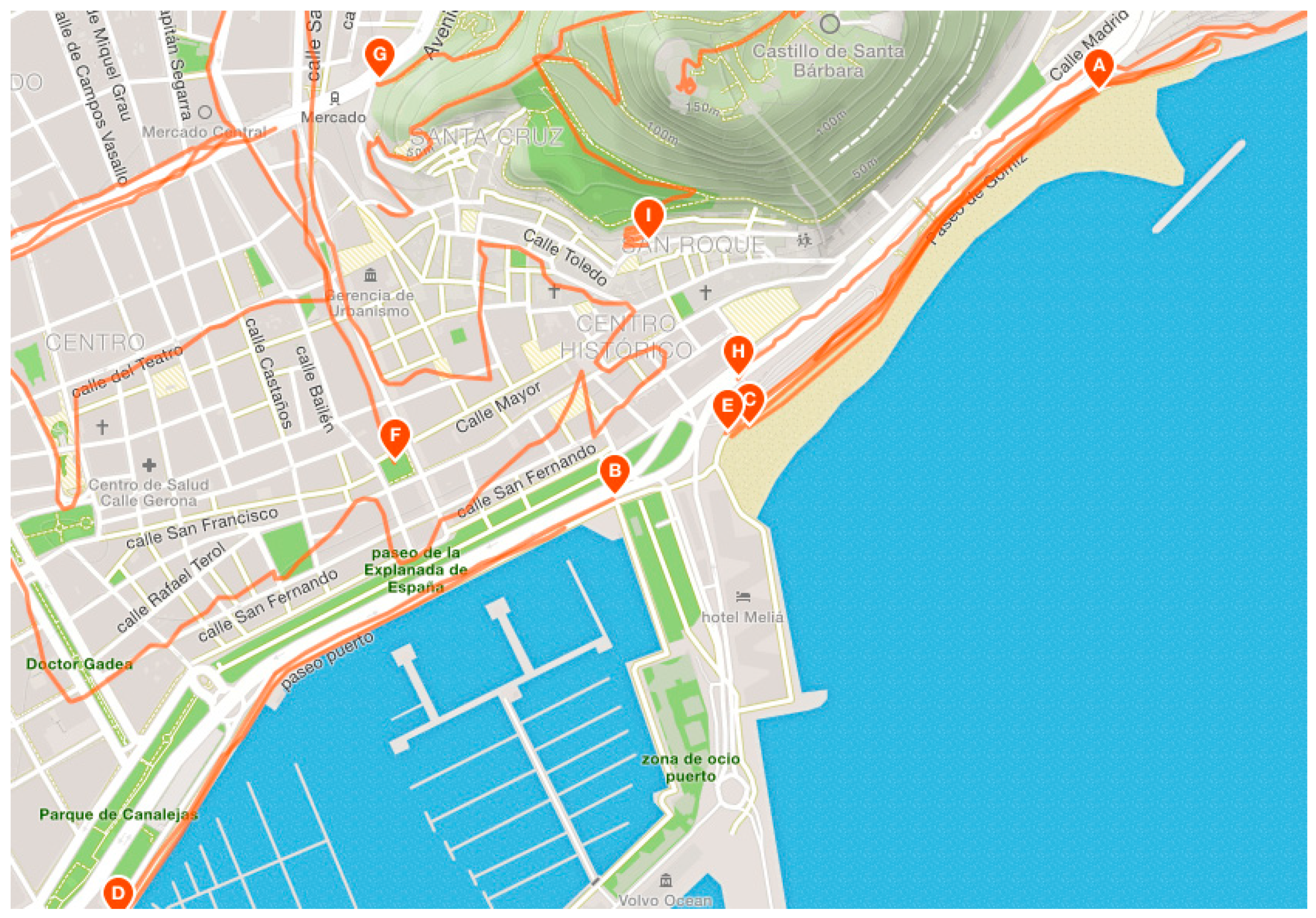
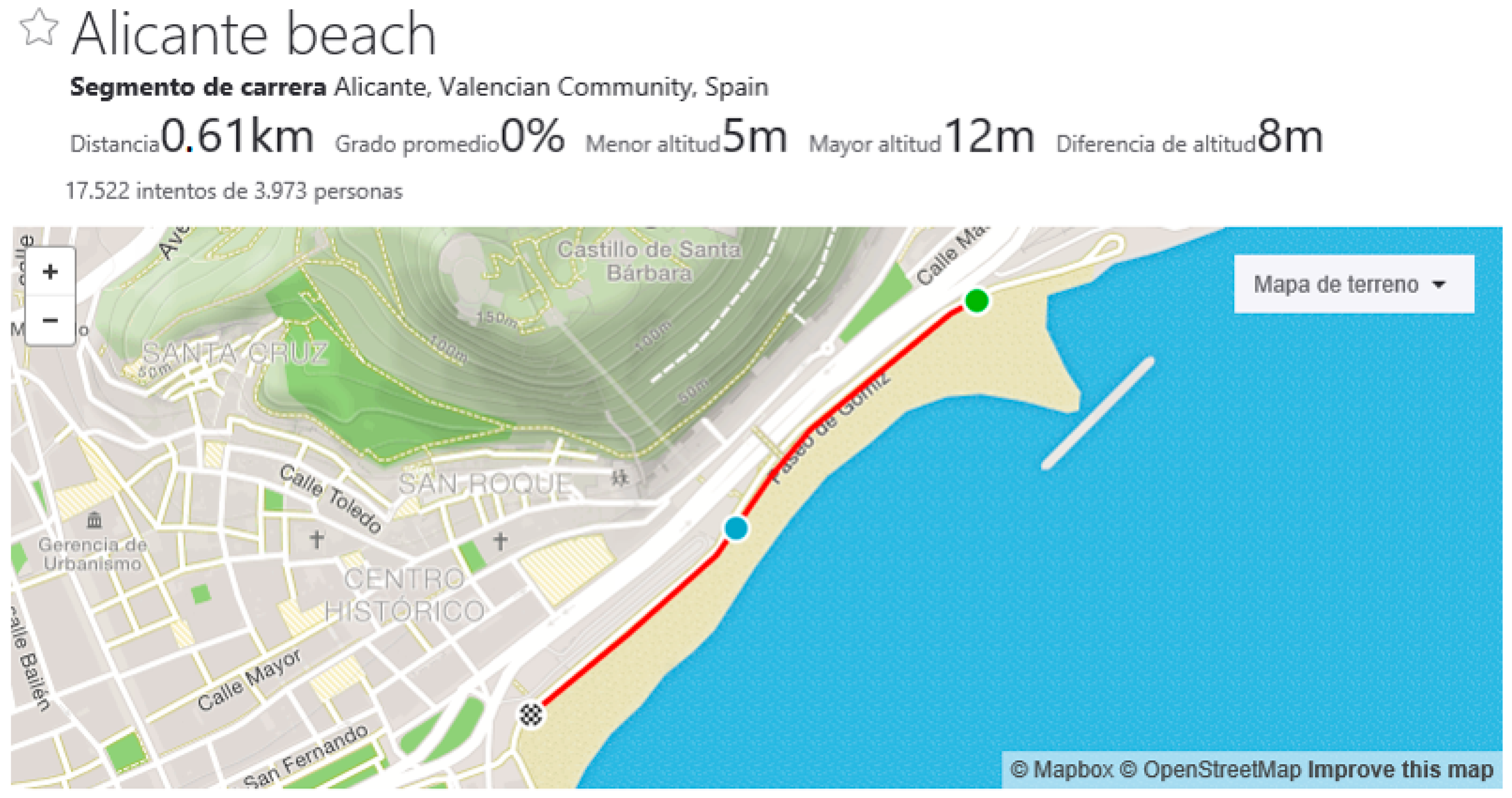
3.1. Data Visualization
3.2. Data Download
4. Smart Urban Planning
4.1. Methodology
4.2. Analysis and Proposals
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
 of the Generalitat Valenciana, Spain. The content of this publication is the exclusive responsibility of the University of Alicante and does not necessarily reflect the opinion of the Generalitat Valenciana.
of the Generalitat Valenciana, Spain. The content of this publication is the exclusive responsibility of the University of Alicante and does not necessarily reflect the opinion of the Generalitat Valenciana.Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marsal-Llacuna, M.-L.; Fabregat-Gesa, R. Modeling citizens’ urban time-use using adaptive hypermedia surveys to obtain an urban planning, citizen-centric, methodological reinvention. Time Soc. 2016, 25, 272–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.; Lu, H.; Chirkin, A.; Klein, B.; Schmitt, G. Citizen Design Science: A strategy for crowd-creative urban design. Cities 2018, 72, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, H.; Gilart-Iglesias, V.; Hoyo, R.P.-D.; Andújar-Montoya, M.D. A Comprehensive System for Monitoring Urban Accessibility in Smart Cities. Sensors 2017, 17, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossling, S. ICT and transport behaviour: A conceptual review. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2018, 12, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.M.; Ellison, N.B. Social Network Sites: Definition, History, and Scholarship. J. Comput. Med. Commun. 2007, 13, 210–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suciu, B.F.; Albu, S.I.; Stefan, V.; Suciu, S.; Halunga, O.A.; Mohamad, R.T.; Hameed, C.; Butca, G. Monitoring of social networking sites. In Proceedings of the 2015 14th RoEduNet International—Networking in Education and Research (RoEduNet NER), Craiova, Romania, 24–26 September 2015; pp. 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persia, F.; D’Auria, D. A Survey of Online Social Networks: Challenges and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration (IRI), San Diego, CA, USA, 4–6 August 2017; pp. 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cuerva, A.; Ledezma, A.; Sanchis, A.; Iglesias, J.A. Social network analysis: Evolving Twitter mining. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Budapest, Hungary, 9–12 October 2016; pp. 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N. Social Network Analysis Tools. In Proceedings of the 2014 Fourth International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, Bhopal, India, 7–9 April 2014; pp. 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, H.M.; Pont, M.T.S.; Casado, G.D.M.; Iglesias, V.G. Management of social networks in the educational process. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 51, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, T.M.; Wang, W.; Xia, F.; Liu, H. Big Scholarly Data: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2017, 3, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, H.; Ferrández, A.; Gil, D.; Peral, J. A Computational Method for Enabling Teaching-Learning Process in Huge Online Courses and Communities. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2017, 18, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.H.-C.; Liu, J.S.; Lu, L.Y.Y. Recent Themes in Social Networking Service Research. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.; Kim, W.; Khan, G.F. Work engagement in organizations: a social network analysis of the domain. Scientometrics 2016, 109, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytras, M.D. The Semantic Electronic Government: knowledge management for citizen relationship and new assessment scenarios. Electron. Gov. Int. J. 2005, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, J.; Fietkiewicz, K.; Gremm, J.; Hartmann, S.; Ilhan, A.; Mainka, A.; Meschede, C.; Stock, W. Informational Urbanism. A Conceptual Framework of Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 50th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (2017), Hilton Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Delhoyo, R.; Mora, H.; Paredes, J.F. Using social network data to improve planning and design of smart cities. Urban Growth Circ. Econ. 2018, 179, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Kim, K.-J.; Maglio, P.P. Smart cities with big data: Reference models, challenges, and considerations. Cities 2018, 82, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M. Big data, smart cities and city planning. Dialog. Hum. Geogr. 2013, 3, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osman, A.M.S. A novel big data analytics framework for smart cities. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 91, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuotto, V.; Ferraris, A.; Bresciani, S. Internet of Things. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2016, 22, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, S.; Ferraris, A.; Del Giudice, M. The management of organizational ambidexterity through alliances in a new context of analysis: Internet of Things (IoT) smart city projects. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.M.; Ahmad, A.; Paul, A.; Rho, S.; Rho, S. Urban planning and building smart cities based on the Internet of Things using Big Data analytics. Comput. Netw. 2016, 101, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, M.; Arif, F. Smart urban planning using Big Data analytics to contend with the interoperability in Internet of Things. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 77, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatala, J.-P. Social Network Analysis in Human Resource Development: A New Methodology. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2006, 5, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souri, A.; Nourozi, M.; Rahmani, A.M.; Navimipour, N.J. A model checking approach for user relationship management in the social network. Kybernetes 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, S.; Faust, K. Social Network Analysis; Wasserman, S., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; ISBN 9780511815478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossche, P.V.D.; Segers, M. Transfer of training: Adding insight through social network analysis. Educ. Res. Rev. 2013, 8, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, R.-D.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, R.; Gómez-Gasquet, P.; Mula, J. Social network analysis: A tool for evaluating and predicting future knowledge flows from an insurance organization. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 114, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, S.; Lavelle, J.; Gunnigle, P. Mapping networks: Exploring the utility of social network analysis in management research and practice. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 76, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.C.-C.; Chiou, J.-S.; Hsiao, C.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; Li, H.-N. Effective marketing communication via social networking site: The moderating role of the social tie. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hastak, M. Social network analysis: Characteristics of online social networks after a disaster. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 38, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.V.; Monica, K.; Trishanka, M. A survey on big data analytics using social media data. In Proceedings of the 2017 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), Vellore, India, 21–22 April 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanillos, G.; Austwick, M.Z.; Ettema, D.; De Kruijf, J. Big Data and Cycling. Transp. Rev. 2016, 36, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuhadar, L.; Yang, R.; Lytras, M.D. The impact of Social Multimedia Systems on cyberlearners. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013, 29, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieglitz, S.; Mirbabaie, M.; Ross, B.; Neuberger, C. Social media analytics—Challenges in topic discovery, data collection, and data preparation. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 39, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immonen, A.; Pääkkönen, P.; Ovaska, E. Evaluating the Quality of Social Media Data in Big Data Architecture. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 2028–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Yuan, Q. The Evolution of Information and Communication Technology in Public Administration. Public Admin. Dev. 2015, 35, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthopoulos, L.; Fitsilis, P. Social networks in smart cities: Comparing evaluation models. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE First International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Guadalajara, Mexico, 25–28 October 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatsoglou, M.; Chatzakou, D.; Gkatziaki, V.; Vakali, A.; Anthopoulos, L. CityPulse: A Platform Prototype for Smart City Social Data Mining. J. Knowl. Econ. 2016, 7, 344–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorimer, P.A.; Diec, V.M.-F.; Kantarci, B. COVERS-UP: Collaborative Verification of Smart User Profiles for social sustainability of smart cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, T.; Poorthuis, A.; Zook, M. Social media and the city: Rethinking urban socio-spatial inequality using user-generated geographic information. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 142, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, R.T.; McPhearson, T. Social-media data for urban sustainability. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamstead, Z.A.; Fisher, D.; Ilieva, R.T.; Wood, S.A.; McPhearson, T.; Kremer, P. Geolocated social media as a rapid indicator of park visitation and equitable park access. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 72, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, L.; Borsi, K.; Rodrigues, L. The role of social network analysis on participation and placemaking. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martí, P.; Serrano-Estrada, L.; Nolasco-Cirugeda, A. Using locative social media and urban cartographies to identify and locate successful urban plazas. Cities 2017, 64, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Huang, Z. A Novel Popular Tourist Attraction Discovering Approach Based on Geo-Tagged Social Media Big Data. Int. J. Geoinf. 2017, 6, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encalada, L.; Boavida-Portugal, I.; Ferreira, C.C.; Rocha, J. Identifying Tourist Places of Interest Based on Digital Imprints: Towards a Sustainable Smart City. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mislove, A.; Koppula, H.S.; Gummadi, K.P.; Druschel, P.; Bhattacharjee, B. Growth of the flickr social network. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Emerging Technologies for Software-Defined and Reconfigurable Hardware-Accelerated Cloud Datacenters—ETCD’17 2008, Seattle, WA, USA, 18 August 2018; p. 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yuan, Q.; Cong, G.; Xu, D. Where your photo is taken: Geolocation prediction for social images. J Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 65, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Soliman, A.; Yin, D.; Wang, S. Depicting urban boundaries from a mobility network of spatial interactions: a case study of Great Britain with geo-located Twitter data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 71, 1293–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, R.; Zhang, L.F.; Lei, P.; Pau, G. Social Network Based Crowd Sensing for Intelligent Transportation and Climate Applications. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2018, 23, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacco, M.; Delmastro, F.; Ferro, E.; Gotta, A. Environmental Monitoring for Smart Cities. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 7767–7774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, M. Rhythms of the Collective Brain: Metastable Synchronization and Cross-Scale Interactions in Connected Multitudes. Complexity 2018, 2018, 4212509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wu, Y.; Wei, E.; Peng, T.-Q.; Liu, S.; Zhu, J.J.H.; Qu, H. Visual Analysis of Topic Competition on Social Media. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2013, 19, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Resch, B.; Summa, A.; Zeile, P.; Strube, M. Citizen-Centric Urban Planning through Extracting Emotion Information from Twitter in an Interdisciplinary Space-Time-Linguistics Algorithm. Urban Plann. 2016, 1, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Resch, B.; Summa, A.; Sagl, G.; Zeile, P.; Exner, J.P. Urban Emotions: Geo-Semantic Emotion Ex-Traction from Technical Sensors, Human Sensors and Crowdsourced Data, Progress in Location-Based Services; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Hong, H.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; El Saddik, A. City digital pulse: a cloud based heterogeneous data analysis platform. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 10893–10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Fu, C.-W.; Arisona, S.M.; Schubiger, S.; Burkhard, R.; Ma, K.-L. Visualizing the Relationship Between Human Mobility and Points of Interest. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2017, 18, 2271–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Chen, W.; Maciejewski, R. Spatial–temporal visualization of city-wide crowd movement. J. Vis. 2017, 20, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, H. Data-Driven Bicycle and Pedestrian Planning. 10 March 2017. Available online: https://medium.com/strava-metro/data-driven-bicycle-and-pedestrian-planning-40d209284481 (accessed on 29 October 2018).
- Selala, M.K.; Musakwa, W. The potential of strava data to contribute in non-motorised transport (nmt) planning in johannesburg. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMichael, S. Strava Moves into ‘Big Data’—London & Glasgow Already Signed up to Find out Where Cyclists Ride. Road.cc, 2014. Available online: https://road.cc/content/news/118098-strava-moves-big-data-london-glasgow-already-signed-find-out-where-cyclists-ride (accessed on 27 October 2018).
- Zeile, P.; Resch, B.; Exner, J.-P.; Sagl, G. Urban Emotions: Benefits and Risks in Using Human Sensory Assessment for the Extraction of Contextual Emotion Information in Urban Planning. In Planning Support Systems and Smart Cities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, À.D. The Human Smart Cities Manifesto: A Global Perspective; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Marsal-Llacuna, M.-L.; Leung, Y.T.; Ren, G.-J. Smarter urban planning: match land use with citizen needs and financial constraints. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications, Santander, Spain, 20–23 June 2011; pp. 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, S.; Crawford, S. The Responsive City: Engaging Communities through Data-Smart Governance; John Wiley & Sons: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-118-91090-0. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, A.; Campolargo, M. From Smart Cities to Human Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2015 48th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Kauai, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2015; pp. 2336–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, B. Strava Fitness Tracking Map Reveals Military Bases, Movements in War Zones. USA Today. 29 January 2018. Available online: https://eu.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2018/01/29/strava-war-zones/1073975001/ (accessed on 27 October 2018).
- Strava. Available online: https://www.strava.com/heatmap (accessed on 27 October 2018).
- Berezan, O.; Krishen, A.S.; Agarwal, S.; Kachroo, P. The pursuit of virtual happiness: Exploring the social media experience across generations. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 89, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, J. Alicante Cierra el año 2017 con una Cifra Récord de Turistas. Available online: https://alicantepress.com/art/35852/alicante-cierra-el-ano-2017-con-una-cifra-record-de-turistas (accessed on 30 October 2018). (In Spanish).
- Ferraris, A.; Erhardt, N.; Bresciani, S. Ambidextrous work in smart city project alliances: unpacking the role of human resource management systems. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2017, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods, 5th ed.; Sage Publications: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781452242569. [Google Scholar]
- Flyvbjerg, B. Five Misunderstandings about Case-Study Research. Qual. Inq. 2006, 12, 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Delhoyo, R.; Andújar-Montoya, M.D.; Mora, H.; Gilart-Iglesias, V. Unexpected consequences in the operation of urban environments. Kybernetes 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadais, T.; Boulanger, M.; Trudeau, F.; Rivard, M.-C. Environments favorable to healthy lifestyles: A systematic review of initiatives in Canada. J. Sport Health Sci. 2018, 7, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marans, R.W. Quality of urban life & environmental sustainability studies: Future linkage opportunities. Habitat Int. 2015, 45 Pt 1, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecredy, G.; Pickett, W.; Janssen, I. Street Connectivity is Negatively Associated with Physical Activity in Canadian Youth. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 3333–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Netto, V.M.; Meirelles, J.; Ribeiro, F.L. Social Interaction and the City: The Effect of Space on the Reduction of Entropy. Complexity 2017, 2017, 6182503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
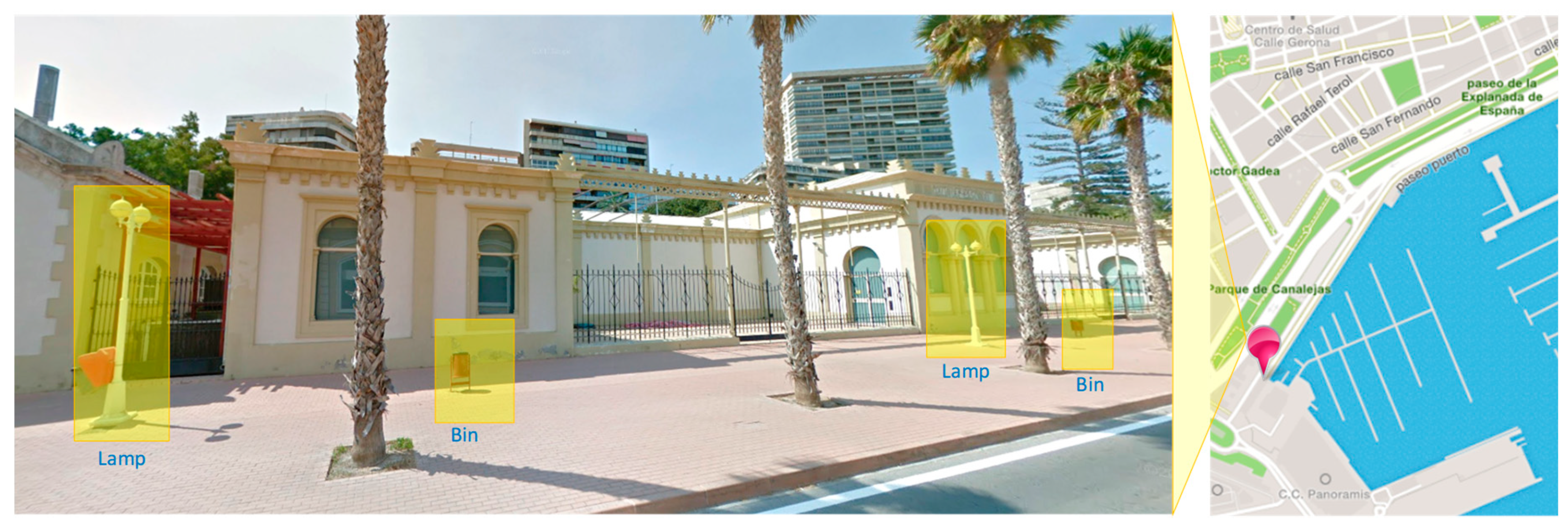









| Social Network | Web Site |
|---|---|
 | http://www.atletosports.com/ This is a is a sports social network to connects athletes with each other to facilitate games or other athletic activities |
 | https://www.strava.com/ Social network to share activities with a broad social community of registered users |
 | http://www.mapmyrun.com/ Social network to share the sports activity linked to the sports products company Under Armor |
 | https://www.runtastic.com/ Social network to track and manage health and fitness data |
 | https://runkeeper.com/ It is a top social network that helps people get out the door and stick with running. |
 | https://www.sports-tracker.com/ Social network where sports enthusiasts can access to public workouts, every day |
 | https://www.gotzam.com/ Social network to share sport events and activities among users |
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| KML (Keyhole Markup Language) | Designed by Google for representing geographic data in three dimensions. It is used by Google Earth (https://developers.google.com/kml/schema/kml21.xsd) |
| GPX (GPS eXchange Format) | It is an open standard for the interchange of GPS data between applications and Web services (https://www.topografix.com/GPX/1/1/gpx.xsd) |
| TCX (Training Center XML) | Designed by Garmin and used to track an sport activity with a mobile device (https://www8.garmin.com/xmlschemas/TrainingCenterDatabasev2.xsd) |
| GTM (GPS TrackMaker) | Designed by TrackMaker for creating routes and detailed maps from GPS information (https://www.trackmaker.com/) |
| GeoJSON | Open format based on JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) for encoding a variety of geographic data structures (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7946) |
| GML (Geography Markup Language) | Designed by Open Geospatial Consortium for representing geographic information (http://www.opengeospatial.org/standards/gml) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mora, H.; Pérez-delHoyo, R.; Paredes-Pérez, J.F.; Mollá-Sirvent, R.A. Analysis of Social Networking Service Data for Smart Urban Planning. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4732. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124732
Mora H, Pérez-delHoyo R, Paredes-Pérez JF, Mollá-Sirvent RA. Analysis of Social Networking Service Data for Smart Urban Planning. Sustainability. 2018; 10(12):4732. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124732
Chicago/Turabian StyleMora, Higinio, Raquel Pérez-delHoyo, José F. Paredes-Pérez, and Rafael A. Mollá-Sirvent. 2018. "Analysis of Social Networking Service Data for Smart Urban Planning" Sustainability 10, no. 12: 4732. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124732
APA StyleMora, H., Pérez-delHoyo, R., Paredes-Pérez, J. F., & Mollá-Sirvent, R. A. (2018). Analysis of Social Networking Service Data for Smart Urban Planning. Sustainability, 10(12), 4732. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124732





