Abstract
Circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) power generation technology is known to efficiently reduce the emission of air pollutants, such as SO2 and NO2, from coal combustion. however, CFBC coal ash contains high contents of free CaO, making it difficult to recycle. This research has been conducted to find ways to use the self-hardening property of CFBC coal ash, one of its inherent characteristics. As part of these efforts, the present study intended to investigate the properties and desulfurization efficiency of Ca-based desulfurization sorbents using CFBC fly-ash as a binder. Limestone powder was mixed with CFBC fly-ash and Ca(OH)2 to fabricate desulfurization sorbents, and it generated hydrate of cement, including portlandite, ettringite, and calcium silicate, etc. The compressive strength of the desulfurization absorbent prepared by CFBC fly ash and Ca(OH)2 was 72–92% that of the desulfurized absorbent prepared by using general cement as a binder. These absorbents were then compared in terms of desulfurization efficiency using a high-temperature fluidized bed reactor. It was confirmed that the desulfurization absorbents fabricated using CFBC fly-ash as a binder achieved the best performance in terms of absorption time, which reflects the time taken for them to remove over 90% of high-concentration SO2 gas, and the conversion ratio, which refers to the ratio of CaO turning into CaSO4.
1. Introduction
As one of the clean coal technologies (CCTs), circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) technology is being widely used as a solution for eco-friendly power generation thanks to its ability to effectively control the emission of sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxide generated by coal-fired power plants [1,2]. The technology also makes it possible to use low-rank coal, such as low-calorific coal and high-moisture coal, as well as biomass fuel. These economic benefits have recently convinced China and many other countries to adopt and utilize the technology. In Korea, 200 MWe CFBC power plants were introduced in the early 20th century in an attempt to more actively utilize coal resources, and the construction of a 2 GW power plant, composed of four units of 500 MWe CFBC boilers, has recently been completed. As a result, the country now has three CFBC power plants in operation.
A CFBC power plant is equipped with a boiler whose inside temperate reaches 850–900 °C, which allows it to generate less sulfur oxide and nitrogen oxide emissions than pulverized coal combustion (PC) power plants. Having said that, coal ash generated from CFBC power plants contains high contents of free CaO and CaSO4 (or gypsum anhydrite), which is generated from the limestone inserted to promote in-furnace desulfurization. This makes its use as a construction material difficult [3] because when various Ca-based compounds involved in the CFBC process are mixed with cement, they generate Ca(OH)2 and crystallize ettringite, which can result in excessive expansion and cracking [4]. Overall, the inability to use CFBC ash for construction will put greater financial burden on power-plant companies who have to treat the coal ash and maintain landfills. This will negatively affect the utility of the technology in terms of sustainability.
In attempts to promote the sustainable development of CFBC power generation technology, significant attention has been paid to recycling, based on the self-hardening property of CFBC coal ash, one of its intrinsic physicochemical characteristics. In many countries, and especially those operating large-scale CFBC power plants, such as China and Korea, research is being conducted to find ways to use CFBC fly-ash (hereinafter referred to as “CFA”) as a binder for controlled low-strength materials (CLSMs) [5]. Notably, in China, home to the largest number of CFBC power plants in operation, research has been underway on the application of CFA to CLSMs since early 2010. Zhang investigated the use of a combination of CFA and slag as a binder used to produce compressed bricks. Chen succeeded in developing technology to improve the binding power of cement mixtures by adding CFA and additives to aluminate cement for lightweight air bricks. Wu studied a method of using CFA as a binder for soil stabilization purposes [6,7,8]. On the domestic front, Cho investigated using CFA as a raw material for mine backfill, and Jang and Park conducted research to promote ettringite crystallization and pozzolanic reaction, which play important roles in improving the binding power of CFA. Kang assessed the feasibility of using two types of CFA as zero-OPC binders [3,9,10,11].
The present study aimed to promote the utility of CFA, one type of CFBC coal ash, by devising methods to use it as a raw material in binders added to fabricate CFBC desulfurization sorbents, which can then be reused in the power generation industry. This intended approach is a step forward, beyond its typical use of replacing cement as a binder. To this end, research was conducted to investigate the physical and chemical properties of desulfurization sorbents fabricated using limestone powder, which is typically disposed during the process of manufacturing desulfurization limestone, and CFA, OPC, and Ca(OH)2 as binders. These Ca-based desulfurization sorbents were tested under high-temperature fluidized bed reaction conditions, and compared with respect to their SO2 absorption time and the corresponding conversion ratio.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Images of a limestone specimen and two types of CFA, used to fabricate the high-temperature desulfurization sorbents in this study, are shown in Figure 1. High Ca limestone products, provided from a limestone mine located in Donghae-si, Gangwon-do, Korea, shown in Figure 1a, were used as the limestone powder. These limestone products were processed into thin-sliced specimens, and micrographic analysis was carried out using a polarizing microscope. As a result, the average size of the crystalline structures was determined to be 30–50 μm, confirming that these materials fall into the category of fine-micro crystalline limestone, as shown in Figure 1b. An image of fly ash (SCFA), collected from the 500 MW CFBC power plant of Samcheok Green Power, is shown in Figure 1c. Figure 1d shows an image of fly ash (YCFA), collected from the 230 MW CFBC Yeosu Thermoelectric Power Plant. The color of SCFA specimens was dark, dull brown while the YCFA was light brown. All of the limestone and CFA specimens used in the present study were dried at 105 °C for 24 h until they were sufficiently dehydrated before tests proceeded.
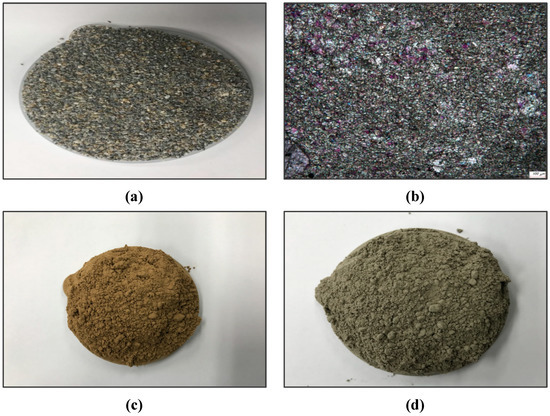

Figure 1.
Images of limestone and CFBC fly-ash samples. (a) and (b) is limestone particle and crystalline structure; (c) fly ash of Samcheok green power Co.; and (d) fly ash of Yeosu Coal Power Co.
The results of X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF, Primus2, Rigaku, Japan) of the limestone and CFA specimens are shown in Table 1. The limestone contains 52.9% of CaO, which corresponds to 94.6% when converted into CaCO3 content. The CaO contents of the SCFA and YCFA were similar at the 27% level, while the SO3 contents were about 8%. However, it should be noted that the SCFA was richer in MgO and Fe2O3, while the YCFA was relatively richer in SiO2 and Al2O3. This difference in chemical composition is considered to be due to the difference in the chemical content of the limestone products added to each desulfurization sorbent, as well as different operating conditions. Calcium hydrate (calcium hydroxide–ACS reagent ≥95.0%, Sigma-Aldrich, USA) were used as activators, which served to promote the self-hardening property of CFA.

Table 1.
The XRF chemical analysis of Limestone, CFBC fly-ash sample (mass %).
The results of X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD, D/MAX 2500V/PC, Rigaku, Japan) of the SCFA and YCFA are shown in Figure 2. The results show various peaks of Ca-based compounds contained in the SCFA and YCFA, as follows: lime (CaO) subjected to calcination only; calcium sulfate anhydrite (CaSO4), a product of the desulfurization process; and periclase (MgO), made of calcined dolomite. There were also peaks of quartz, calcium silicate (Ca2SiO4), and ye’elimite (Ca4Al6O12SO4) observed.
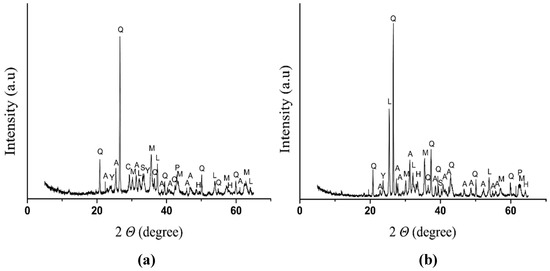
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of CFBC fly-ash: (a) SCFA (Samcheok Green Power Co.); (b) YCFA (Yeosu coal power Co.) [Q: quartz (SiO2), L: lime (CaO), A: anhydrate (CaSO4), M: magnetite (Fe3O4), H: hematite (Fe2O3), P: periclase (MgO), Y: ye’elimite (Ca4Al6O12SO4), C: calcite (CaCO3), and S: calcium silicate (Ca2SiO4)].
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Particle Size and Structure of CFBC Fly Ash
The particle shape and free CaO content of the CFA specimens us‘ed to fabricate the Ca-based desulfurization sorbents for in-furnace desulfurization purposes were analyzed. A particle size analyzer (PSA, LS13320, Beckman coulter, USA) and scanning electron microscope (SEM, S-4300, Hitachi, Japan) were employed to analyze the shape and size of the particles.
2.2.2. Free CaO Analysis of CFBC Fly Ash
Analysis of free CaO content was conducted via neutralization titration. First, 1 g of CFA was added to 50 mL of ethylene glycol at 60 °C and kept dissolved for 30 min. The dissolved solution was subjected to filtration through a Buchner funnel to separate solids from liquids. Two to three drops of bromo-cresol indicator (Bromo-cresol Green Solution, Duksan, Korea) were added to the filtered solution to make the solution blue. Finally, 0.1 mol of HCl solution was added to the solution in 0.01 mL increments using an automatic titration device. The content of free CaO was estimated by reading the volume of HCl solution added to turn the filtered solution yellow [12].
2.2.3. Prepared of (Ca-Based) Desulfurization Sorbents
Mixture proportions of the raw materials used to fabricate the Ca-based desulfurization sorbents in the present study are shown in Table 2. The mixture proportions of the limestone and the binder were set to 60:35, 70:25, and 80:15, and calcium hydrate was added at a concentration of 5% as an activator. As a control group, desulfurization sorbents using OPC as a binder were prepared, along with desulfurization sorbents fabricated by replacing the added activator with the same proportion of OPC.

Table 2.
Mixture proportion of desulfurization sorbent materials.
Figure 3 shows the method used to fabricate a mold to prepare samples for compressive strength tests using Ca-based desulfurization sorbent paste. Limestone was pulverized into powder of approximately D50 = 10 µm using an experimental ball mill, as defined under KS E 3600, and then used. The weight ratio of added mixture water was set to 30% of the combined weight of the limestone, binder, and activator, as shown in Table 2. Mixing was conducted using an automatic mixer. The produced paste was fabricated into a mold with dimensions of 40 × 40 × 160 mm and cured at 20 ± 2 °C for seven days and 28 days. Subsequently, SEM analysis and XRD analysis were performed on these cured sorbent specimens, for microscopic analysis of their binding shapes and chemical-content analysis, respectively.
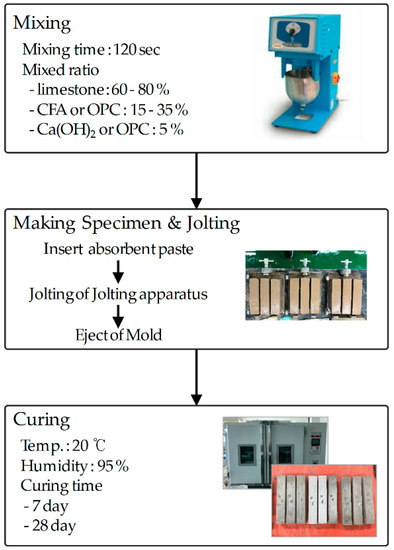
Figure 3.
Experimental method of compressive strength test.
2.2.4. Compressive Strength Test of Ca-Based Desulfurization Sorbents
The desulfurization efficiency of in-furnace desulfurization sorbents decreases as their particles become increasingly pulverized by particle collisions and the corresponding friction. These pulverized particles end up being discharged via a dust collector, which results in a higher loss of sorbents. As a result, the binding power of the binders used to fabricate desulfurization sorbents is a critical factor in determining their absorbing performance. To examine this factor, in the present study, the binding performance of CFA was analyzed via compressive strength testing of cement products.
The desulfurization sorbents manufactured in the present study were processed into specimens with specific dimensions under KS L ISO 679 (Method of Testing Cement—Determination of Strength). Subsequently, compressive strength tests were conducted on these specimens using a single-axis compressive strength tester. Here, the measurement data are expressed as the maximum failure load (N) exerted on a unit area (mm2), which is converted into the compressive strength Rc using a calculation program [13].
2.2.5. Desulfurization Test Using the FBC Reactor
Figure 4 shows a schematic diagram of the laboratory-scale fluidized bed reactor used in the present study, which was intended to simulate the internal environment of a fluidized bed reactor. The fluidized bed reactor is composed of gas feeds, a bubble fluidized bed-type reactor, and gas analyzer. The two gas feeders are designed to feed desulfurization-reaction gases and oxidation compressed air, respectively, which simulates the gas emission conditions of CFBC boilers. The bubble fluidized bed type reactor, composed of a preheating tube, bed, and riser zone, was designed to control the temperatures of the gases injected via a vertical tube furnace, and its main body. The gas analyzer was capable of real-time measurements of the concentrations of SO2, CO2, CO, and O2 contained in exhaust gases, which were discharged through a dust-collecting filter.
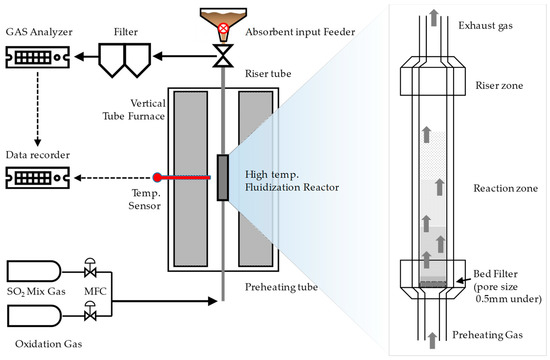
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the bubble fluidized bed type reactor.
A schematic of the desulfurization test method using the fluidized bed reactor is shown in Figure 5. Desulfurization limestone was pulverized into powder with a particle size of 0.2–0.4 mm using a pulverizer. This limestone powder was mixed with binding materials and processed into Ca-based desulfurization sorbents. These desulfurization sorbents were subjected to compressive strength tests, and the tested specimens were pulverized again and filtered through a separation sieve. In this way, specimens with a particle size of 0.4–1 mm were prepared and used.
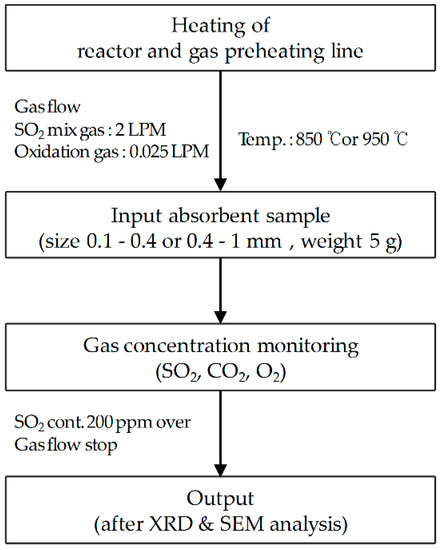
Figure 5.
Experimental method of desulfurization in the fluidized bed reactor.
The desulfurization reaction testing was carried out as follows. The temperature of the preheating tube and the environment temperature of the reactor were preheated to 850 and 950 °C, similar to the internal temperature of CFBC boilers, and subsequently mixed gases for the desulfurization reaction (2000 ppm of SO2, 10% of CO2, and N2 balance) and oxidation compressed air were injected at 2 LPM (liter per minute) and 0.025 LPM, respectively. After a while, the concentration of SO2, having passed through the fluidized bed reactor, became constant. Then 5 g of the prepared desulfurization sorbent specimen was added, and the change in concentration of the discharged SO2 was measured using the gas analyzer (GSR-1000, Sensoronic, Korea). When the concentration of SO2 contained in the exhaust gas exceeded 200 ppm, the gas feed was stopped, and the desulfurization sorbents remaining inside the fluidized bed reactor were collected. This was followed by chemical content analysis using XRD and XRF, and microstructure analysis using SEM.
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size and Structure of CFBC Fly Ash
Analysis of the particle size and microstructure of the SCFA and YCFA were conducted using the PSA and SEM, and the results are shown in Figure 6. The particle size distributions of the SCFA and YCFA are shown in Figure 6a,b, respectively. Here, the SCFA showed an “M”-shaped particle distribution, and its average particle size broadly varied between 10 and 30 µm. In the meantime, the YCFA showed an “A”-shaped particle distribution with an average particle size of 60 µm. Figure 6c,d show SEM images of the SCFA and YCFA particles. It was confirmed that, in the SCFA, larger particles tended to have more circular shapes, while the irregular-shaped particles of the YCFA tended to agglomerate, constituting large particles. Park reported that CFBC fly ash mixed spherical and irregular particles and that the amorphous particle component was a lime component. Free CaO, it is necessary to add additives that can control the reactivity of Ettringite and Pozzolan [14].

Figure 6.
Measurements of CFBC Fly ash particle size and SEM images.
To use CFA as a binder, appropriate fluidity and curing rate must be ensured so that the mixing and forming process can properly proceed. Irregular-shaped CFA, however, is known to have a high curing rate [15]. According to Li and Lim, when CLSMs, such as CFA, are used as binders, the water/binder ratio must be set higher to achieve the same level of fluidity as when OPC is used as a binder, because CLSMs have a larger specific surface area, due to their uneven particle size. They also contain a high content of free CaO, which is highly hygroscopic. However, a higher water/binder ratio leads to an increase in particle spacing [16,17]. Overall, an increase in the water/binder ratio has a negative effect when the binders are used to provide high mechanical strength, but it can be advantageous when porosity is a more important factor, as in desulfurization sorbents.
3.2. Free CaO Analysis of CFBC Fly Ash
Chemical composition analysis was carried out on the free CaO contained in the CFA, and the results are shown in Table 3. The amount of 0.1 N HCl standard solution injected in the neutralization titration tests can be converted, using Equation (1), into the concentration of free CaO remaining after the in-furnace desulfurization process, as shown below [18,19,20]:

Table 3.
Ratio of unreacted Ca sources (free CaO) in CFA.
Free CaO contents in the SCFA and YCFA samples measured using the ethylene glycol method are shown in Table 3. While SCFA showed the free CaO content of 9.46% and YCFA samples exhibited free CaO contents of 10.81%. Although the CaO contents in SCFA and YCFA were similar, their free CaO contents were different. Therefore, the free CaO contents vary by region. The difference in the free CaO content is considered to be due to the use of dolomite as a sorbent for the SCFA. The free CaO contained in the SCFA and YCFA is converted into Ca(OH)2 when mixture water is injected during the manufacturing process of the desulfurization sorbents. This Ca(OH)2 is likely to participate in the formation of cement compounds or the desulfurization process.
Most domestic research on CFBC coal ash applications uses a hydrated reaction method which measures the weight change that occurs during the conversion of CaO into Ca(OH)2, triggered by the addition of mixture water. However, that method has problems when the free CaO content is low. In China, a phenyl formic acid titration method under GB/T 176-2008 (Methods for Chemical Analysis of Cement) was enacted and has been used [21]. To measure the free CaO content of CFA in the present study, an ethylene glycol method, which is widely used to analyze the concentration of CaO contained in slag, a byproduct of the iron and steel industry, was employed.
3.3. Mineral Composition Analysis of Ca-Based Sorbents
XRD analysis was performed to analyze of the Ca-based in-furnace desulfurization sorbents. which were fabricated in the present study with various type of binders. The results are shown in Figure 7. In the six types of sorbents made of limestone powder, CFA, and Ca(OH)2, the formation of portlandite and calcium silicate hydrate, closely related to self-curing, were observed, and the peak for ettringite was also observed.

Figure 7.
XRD pattern of desulfurization sorbent using CFA or OPC as binder [calcite (CaCO3), portlandite (Ca(OH)2), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2), quartz (SiO2), calcium silicate (Ca2SiO4), ettringite (Ca6Al2(SO4)3(OH)12·26H2O), and muscovite (KAl2(AlSi3O10) (FOH)2)].
In contrast, in SFO70, containing 5% OPC replacement of Ca(OH)2, only the ettringite peak was observed. Figure 7a–f shows the XRD results of the sorbents containing SCFA and YCFA as binders, and the observed peaks here correspond to calcite, dolomite, quartz, and calcium hydroxide, along with a slight amount of calcium silicate. Figure 7g–i shows the results for sorbents containing OPC as a binder. They are portlandite peak is observed. Figure 7j shows the result for the sorbent containing OPC instead of Ca(OH)2 as an activator. This sample showed a peak containing Moscovite and different mineral components compared to other samples.
Overall, it was confirmed that the CaO contained in CFA is converted into Ca(OH)2 via hydration and used for the formation of ettringite, while the Ca(OH)2 added as an activator contributes to the formation of calcium silicate hydrate. According to the 2012 report by Heng et al., the self-curing property of CFA is achieved with a combination of the following three processes: the crystal growth of portlandite (Ca(OH)2), the formation of ettringite (3CaO·Al2O3·3CaSO4·32H2O) by activated alumina reacting to gypsum (CaSO4) and Ca(OH)2, and the formation of calcium silicate hydrate (CSH) by silica reacting to Ca(OH)2 [22].
SEM analysis was observe the bonding and pore shapes form of the sorbent, and the results are shown in Figure 8. SEM images at 5000× magnification showed that, in all specimens, the spacing between particles tended to increase with decreasing content of binders. In contrast to the sorbent specimens containing high CFA content, SFC80, and YFC80 with low CFA content, as well as the samples containing OPC, were found to be composed of particles with rough surfaces on which small, needle-shaped crystals were formed. These observations confirmed that the content of binders was a critical factor in determining the volume of pores between particles. Accordingly, it is expected that increasing the content of binders beyond the level in SFC60 and YFC60 would contribute to increasing the mechanical strength of sorbents, but sharply reduce the size of pores between particles, thereby significantly degrading desulfurization efficiency.

Figure 8.
SEM images of desulfurization sorbent samples.
In contrast, decreasing the binder content below that of SFC80 and YFC80 would lead to a decrease in the amount of hydrates which would otherwise be formed between limestone powder particles, significantly reducing their binding power. In the OPS specimens, fabricated using OPC as a binder, a large number of needle-shaped crystals were formed on the surfaces of the particles and, therefore, these specimens are considered to provide relatively high mechanical strength.
3.4. Compressive Strength Test of Ca-Based Desulfurization Sorbents
When binders containing cement-based compounds, such as CFA, are used to fabricate desulfurization sorbents, their compressive strength is affected by various factors, as follows: the mixture proportion of binders, strength of paste, paste-aggregate adhesion (here, limestone powder) strength, water/binder ratio, and porosity. In the present study, the effects of the mixture proportion of binders and curing time on the compressive strength of desulfurization sorbents were investigated. The porosity and the strength of the paste, which are closely related to overall strength, were fixed.
The compressive strengths of the desulfurization sorbents fabricated using CFA and OPC as binders were measured, and the results are shown in Table 4. The samples were tested for six times. Measurement uncertainty is calculated so that the mean of the four data excluded the most extreme (high and low) values. The seven-day strength of SFC60, containing 35% SCFA, was determined to be 11 MPa, about 35% lower than that of the sorbents containing 35% OPC instead of SCFA. The 28-day strength was measured to be 16.3 MPa. The seven-day strength of SFC70, containing 25% SCFA, was 7.7 MPa, about 10% lower than that of the sorbents containing 25% OPC, and the 28-day strength was 11.5 MPa, about 25% lower.

Table 4.
Results of compressive strength test.
In the meantime, both seven-day strengths and 28-day strengths were lower when YCFA was added than when SCFA was added. This phenomenon is considered to be due to the difference in particle size and chemical composition. When OPC was used as a binder, the resulting compressive strength was very high in cases where its mixture proportion was 35%. However, the compressive strength significantly decreased as its mixture proportion decreased.
Having said that, it should be noted that OPC costs $40–90 per ton and, thus, a large amount of added OPC will significantly increase the overall production costs of desulfurization sorbents. When compared with SFC70 containing 25% SCFA and 5% Ca(OH)2, and SFO70 containing 25% SCFA and 5% OPC, their initial strengths were at a similar level, but the later-stage strengths, i.e., the 28-day strengths, were much lower in SFO70 than in SFC70. These results confirm that Ca(OH)2, added to a sorbent as an activator, reduces the water/binder ratio, increasing its curing rate at an early stage while, in the meantime, affecting the formation of cement hydrates, which contribute to the increased compressive strength after seven days of curing.
3.5. Desulfurization Tests Using the FBC Reactor
The sorption time and utilization coefficient of the Ca-based desulfurization sorbents, fabricated using CFA as a binder in the present study, were investigated in comparison with limestone, an existing desulfurization sorbent. For the desulfurization efficiency measurement tests, typical desulfurization limestone specimens were prepared along with desulfurization sorbent specimens fabricated using 15, 25, and 35% SCFA as a binder, to compare the desulfurization properties of existing limestone sorbents and those manufactured in the present study. Additionally, to investigate the effect of CFA and other types of binders on desulfurization properties, desulfurization efficiency measurements were conducted on sorbent specimens fabricated using 25% YCFA and 25% OPC as binders. The effect of Ca(OH)2 on the sorption efficiency was investigated by measuring the desulfurization efficiency of the sorbent specimens containing 5% OPC as replacement of Ca(OH)2.
Figure 9 shows the measured concentrations of SO2 passing through the fluidized bed reactor loaded with limestone and Ca-based desulfurization sorbents, including SFC60, SFC70, and SFC80. The average sorption time of the limestone specimen with a particle size of 0.1–0.2 mm was measured to be 40 min, and about 60 min for a particle size of 0.2–0.4 mm. The sorption time was shorter when the particle size was smaller, and this phenomenon was attributed to the fact that part of the limestone specimen with smaller particle size was discharged by the dust collector, and failed to participate in the reaction. When SCFA was used as a binder, the absorption time was determined to be as follows: 80–90 min for SFC60, 120–130 min for SFC70, and 100–120 min for SFC80. As a control group, the desulfurization performance of sorbents fabricated using YCFA as a binder were tested and it was confirmed that the YCFA-based sorbents provided slightly better performance than the SCFA-based ones. In the meantime, the OPC-based sorbents were slightly inferior to the two types of CFA-based sorbents in desulfurization performance. The absorption time of the SCFA-based sorbents, however, was significantly reduced when its activator was replaced with OPC. These observations lead to the conclusion that the addition of Ca(OH)2 not only increases the compressive strength of a sorbent but also improves its desulfurization performance.

Figure 9.
Absorption time measurements of Ca-based desulfurization sorbents.
XRD analysis was carried out to analyze the chemical contents of the desulfurization-reaction products, and the efficiency of the sorbents, or coefficient of utilization, was estimated from the measured sulfur content, as shown in Table 5. SEM images of sorbent surfaces after the desulfurization reaction are shown in Figure 10. The efficiency of utilization was calculated by substituting into Equation (2) the theoretical content of sulfur when CaO is completely converted into CaSO4 [23].
(at a theoretical sulfur content ratio of 23.5%).

Table 5.
Result of X-ray analysis and coefficients of utilization.

Figure 10.
SEM images of sorbent surface after desulfurization reaction.
The average absorption times for both limestone specimens with a particle size of 0.1–0.2 mm and 0.2–0.4 mm were measured to be less than 60 min, while the corresponding utilization efficiency was 30.9% on average. Additionally, SEM analysis results of the reaction products confirmed that all air voids and pores on the surface of the sorbents were blocked.
When SCFA was used as a binder, the average absorption time was as follows: 120 min for SFC70, where over 90% of SO2 was removed; and 90–100 min for SFC60 and SFC80, respectively. With regard to the efficiency of utilization, however, SFC60 provided the best performance at 94% on average, followed by SFC70 at 91% and SFC80 at 87.6%. This means that the efficiency of utilization tends to decrease with decreasing content of binders and increasing content of sorbents, i.e., limestone. The reason that the binder content affects the absorption time and efficiency of utilization lies in the varying structural properties of sorbents. For example, the volume of pores very depending on the mixture proportion of limestone powder and binders, which are the materials for the sulfurization reaction. The average absorption time of the SCFA-based sorbents was larger than the YCFA-based ones when the binder concentration was the same, which was 130 min. The corresponding efficiency of utilization was 93% on average.
To be more specific, YFC70 provided higher desulfurization efficiency than SFC70. This is considered to be due to a combination of the following two factors: YFC70’s material characteristics, including higher content of free CaO than SFC70, and its structural properties. It contained a larger volume of pores, because it had looser particle bonds and, thus, lower compressive strength.
Since the pore structure of YFC70 was larger and clearer than in SFC70, as shown in SEM images, the structural factor is considered to be more dominant than the material factor. However, the seven-day compressive strength of YFC70 was as low as 70% that of SFC70. Therefore, it is expected that a larger portion of free sorbents will be discharged via he dust-collector, i.e., there will be a larger loss of sorbent.
In contrast, the OPC-based sorbents provided slightly lower desulfurization efficiency than the CFA-based sorbents when the binder concentration was the same. Notably, SEM image analysis confirmed that most of the pores on the surfaces of the reaction products were blocked in those OPC-based sorbents. Accordingly, decreasing the OPC mixture proportion will not effectively improve desulfurization efficiency, because pore blockage will be accelerated.
In the meantime, SFO70, fabricated using OPC instead of Ca(OH)2 as an activator, showed very low absorption time and efficiency of utilization, which implies that, as mentioned above, adding Ca(OH)2 as an activator, contributes to improving the desulfurization efficiency to some extent.
In the present study, the Ca-based desulfurization sorbents fabricated using CFA as a binder showed excellent absorption time and utilization efficiency, and this large discrepancy in desulfurization performance was considered to be due to their structural and calcination properties. These Ca-based desulfurization sorbents have a structure composed of small limestone powder particles bonded together, where relatively uniform-sized pores are formed between the powder particles. These pores facilitate gas diffusion and absorption reaction processes.
According to 1999 research by Laursen et al., sorbents can be divided into the following three types according to their structural shape: an unreacted core structure, where gas diffusion proceeds from the surface of their large particles inward; a network structure, where diffusion reactions proceed along pores located between their small particles; and a uniform structure, where their particle size is so small that the diffusion rate of gases can be neglected. [24] Accordingly, the rate and efficiency of reactions can be significantly affected by the structure type of the sorbents used. The Ca-based desulfurization sorbents used in the present study were fabricated by combining fine limestone powder with a particle size of 10–20 μm with CFA. These desulfurization sorbents with a particle size of 0.2–0.4 mm clearly fall into the network structure type category.
In the present study, it was also found that the calcination property of sorbents affected their desulfurization efficiency, and there are two reasons for that. One is that the difference in the particle size of the limestone used as a sorbent leads to a difference in calcination time. In 2003, Jung et al. reported that macro-pores and micro-pores were most actively formed when the calcination temperature was 900 °C. The reason is that smaller particles provide less heat transfer resistance, thereby promoting the formation of both macro-pores and micro-pores. It should, however, be noted that increasing the calcination temperature in an attempt to accelerate calcination will lead to a sintering reaction. In that case, the coalescence of micro-pores will occur in parallel with crystal growth, therefore degrading desulfurization efficiency. This implies that sorbents that can be quickly calcined at relatively low temperatures are more advantageous in the desulfurization reaction. The other reason is associated with the Ca(OH)2 contained in the CFA added as a binder and activators. In 1996, Tsuchiai et al. showed that Ca(OH)2, when calcined and hydrated, had a plate-like structure with a size of about 8 µm and thus provided a larger BET surface area with better pore distribution than limestone. Accordingly, this calcined and hydrated Ca(OH)2 was determined to be much more efficient in reacting with, and removing, SO2 [25].
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the use of fly coal ash generated from these CFBC power plants as a binding material for the fabrication of Ca-based in-furnace desulfurization sorbents. The major findings of the present study are as follows:
(1) CFBC fly ash is shows the potential for these sorbents to be used as binders for Controlled Low Strength Materials (CLSMs). Chemical analysis by XRD of these manufactured desulfurization sorbents confirmed the formation of cement compounds, i.e., calcium silicate and ettringite. It was also confirmed that sorbents fabricated using CFBC fly ash and Ca(OH)2, when combined in an appropriate proportion as a binder, achieved the strength of 7–15 MPa.
(2) The Ca-based desulfurization sorbents fabricated using CFBC ash as a binder showed excellent desulfurization performance, including absorption times two to three times longer than limestone, and high utilization efficiency of over 90%. The improved absorption time and utilization efficiency of these CFBC ash-based sorbents were considered to be due to their network structure.
(3) As desulfurization sorbents, these materials are also capable of efficiently utilization free CaO from CFBC coal ash. To ensure the sustainable development of CFBC power plants going forward, research on the application of binders for CLSMs fabricated using CFBC byproducts has to continue.
Author Contributions
Conceived and Wrote the manuscripts, C.B.; Analyzed the data J.S. and M.C.; Advice and revised the Manuscript, J.C. and J.A. and K.C.; All authors agreed with the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is partly supported by Korea Institute of Energy Technology and Planning (KETEP), Korea.
Acknowledgments
The present study was performed as a research task (no. 20141010101880) under the auspices of Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) with the 2015 financial resources of Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Oka, S.N.; Anthony, E.J. Fluidized Bed Combustion; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 1–31. ISBN 0-8247-4699-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cuenca, M.A.; Anthony, E.J. Pressurized Fluidized Bed Combustion; BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL: London, UK, 1995; pp. 80–113. ISBN 978-94-011-0617-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.H.; Choi, Y.C. Development of non-sintered zero-OPC Binders using circulating fluidized bed combustion ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlica, J.; Brandstetr, J.; Odler, I. Possibilities of utilizing solid residues from pressured fluidized bed coal combustion (PSBC) for the production of blended cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, R.E.; Sellakumar, K.; Bland, A.E. Utilization of CFB Fly ash for Construction Applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fluidized Bed Combustion, Livingston, NJ, USA, 16–19 May 1999; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Qian, J.; You, C.; Hu, C. Use of circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash and slag in autoclaved brick. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z. Utilization of circulating fluidized bed fly ash for the preparation of foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 54, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chi, M.; Huang, R. Characteristics of CFBC fly ash and properties of cement-based composites with CFBC fly ash and coal-fired fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Lee, Y.M.; Nam, S.Y.; Kim, C.S.; Seo, S.K.; Jo, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Ahn, J.W. A Basic Study on the Development of Backfill Material with Fly Ash and Bottom Ash of Circulating Fluid Bed Combustion. J. Korea Inst. Build. Constr. 2018, 18, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.G.; Park, S.M.; Chung, S.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, H.K. Utilization of circulating fluidized bed combustion ash in producing controlled low-strength materials with cement or sodium carbonate as activator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, H.K. Binder chemistry of sodium carbonate-activated CFBC fly ash. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Baek, C.S.; Cho, J.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Yoon, D.Y.; Cho, K.H. Desulfurization Efficiency of Lime Absorbent in In-Furnace Desulfurization as Fly Ash Binder in Power Plant. J. Korean Inst. Resour. Recycl. 2018, 27, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS) Homepage. KS L ISO 679: Methods of Testing Cements—Determination of Strength. Available online: https://standard.go.kr/KSCI/standardIntro/getStandardSearchView.do (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- Park, J.T.; Oh, H.S. A Study on the Pozzolan Reactivity and Mechanical Characteristic of Blended Portland Cements using CFBC Fly Ash. J. Rec. Constr. Resour. 2018, 6, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- National Digital Science Library (of Korea) Homepage. Development of Commercialization and Manufacturing System for Zero Emission Binder Using Recycling Resource—Technological Innovation Promotion Study Project (2nd Report). Available online: http://www.ndsl.kr/ndsl/search/detail/report/reportSearchResultDetail.do?cn=TRKO201500019492 (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- Li, X.G.; Chen, Q.B.; Huang, K.Z.; Ma, B.G.; Wu, B. Cementitious properties and hydration mechanism of circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) desulfurization ashes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Choo, H.W.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, C.H. The Characterization of Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) Using High CaO Fly Ash without Chemical Alkaline Activator. J. Korean Geo-Environ. Soc. 2016, 17, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S.; Lim, H.S.; Ismail, M.A. Quantitative evaluation of free CaO in electric furnace slag using the ethylene glycol method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Lee, H.S. An Experimental Study on the Free-CaO Quantitative Analysis in the Aging Period of the Electric Arc Furnace Slag. Proc. Korea Concr. Inst. 2014, 26, 349–350. [Google Scholar]
- Chie, H.B.; Lim, H.S.; Lee, H.S. A Study on the Content Evaluation of Free-CaO in Electric Arc Furnace Oxidizing Slag and Reduction Slag in accordance with its Collection Location at Open-air Storage Yard. J. Archit. Inst. Korea 2014, 34, 419–420. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.H.; Baek, C.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, M.K.; Cho, K.H.; Ahn, J.W. Study on the Free CaO Analysis of Coal Ash in the Domestic Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion using ethylene glycol method. J. Energy Eng. 2017, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Li, Q.; Zhai, J. Investigation on the hydration of CFBC fly ash. Fuel 2012, 98, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.M.; Jo, H.D.; Choi, W.K.; Park, Y.S.; Keel, S.I.; Lee, H.G. Study on Calcination Characteristics of Limestones for In-Furnace Desulfurization in Oxy-Fuel Combustion. J. KSEE 2009, 31, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Laursen, K.; Duo, W.; Grace, J.R.; Lim, J. Sulfation and reactivation characteristics of nine limestones. Fuel 1999, 79, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiai, H.; Ishizuka, T.; Ueno, T.; Hattori, H.; Kita, H. Highly active absorbent for SO2 removal prepared from coal fly ash. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).