Significance of Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Nutrient Budgets in Tropical Sanya Bay, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Measurements
2.3. Radium Mass-Balance Model and Apparent Water Age Estimation
3. Results
3.1. Radium Isotopes in Sanya Bay
3.2. Parameters of the Estuary Water and of the Groundwater
4. Discussion
4.1. Apparent Water Age in Sanya Bay
4.2. SGD Estimation Using Radium Isotopes
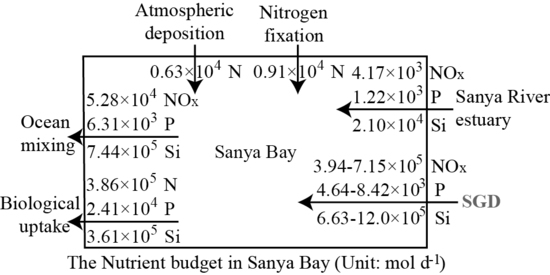
4.3. Nutrient Fluxes Via SGD into Sanya Bay and Their Contributions to the Nutrient Budgets
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| FSGD_226Ra (m3 d−1) | 2.16 × 102 | 2.46 × 105 | 4.08 × 105 | 1.25 × 106 | 3.86 × 105 | 1.39 × 106 |
| FSGD_228Ra (m3 d−1) | 3.32 × 102 | 4.69 × 105 | 1.11 × 105 | 2.35 × 106 | 1.18 × 106 | 2.67 × 106 |
References
- Booth, J.A.T.; McPhee-Shaw, E.E.; Chua, P.; Kingsley, E.; Denny, M.; Phillips, R.; Bograd, S.J.; Zeidberg, L.D.; Gilly, W.F. Natural intrusions of hypoxic, low pH water into nearshore marine environments on the California coast. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 45, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feely, R.A.; Sabine, C.L.; Hernandez-Ayon, J.M.; Ianson, D.; Hales, B. Evidence for upwelling of corrosive “acidified” water onto the continental shelf. Science 2008, 320, 1490–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, S.; Arnone, R.; Bergmann, T.; Bissett, W.P.; Crowley, M.; Cullen, J.; Gryzmski, J.; Haidvogel, D.; Kohut, J.; Moline, M.; et al. Biogeochemical impact of summertime coastal upwelling on the New Jersey Shelf. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2004, 109, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, B.A.; Chan, F.; Nielsen, K.J.; Fox, D.S.; Barth, J.A.; Huyer, A.; Lubchenco, J.; Menge, B.A. Upwelling-driven nearshore hypoxia signals ecosystem and oceanographic changes in the Northeast Pacific. Nature 2004, 429, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.O.; Morgan, C.A.; Peterson, W.T.; Di Lorenzo, E. Seasonal and interannual variation in the extent of hypoxia in the Northern California Current from 1998–2012. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 2279–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gilbert, D.; Gooday, A.J.; Levin, L.; Naqvi, S.W.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; Scranton, M.; Ekau, W.; Pena, A.; Dewitte, B.; et al. Natural and human-induced hypoxia and consequences for coastal areas: Synthesis and future development. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1443–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, W.-J.; Wang, Y.; Krest, J.; Moore, W. The geochemistry of dissolved inorganic carbon in a surficial groundwater aquifer in North Inlet, South Carolina, and the carbon fluxes to the coastal ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charette, M.A.; Buesseler, K.O.; Andrews, J.E. Utility of radium isotopes for evaluating the input and transport of groundwater-derived nitrogen to a Cape Cod estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dai, M.; Chen, W.; Huh, C.-A.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Charette, M.A. Charette, How significant is submarine groundwater discharge and its associated dissolved inorganic carbon in a river-dominated shelf system? Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1777–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. The Effect of Submarine Groundwater Discharge on the Ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosdorf, N.; Stieglitz, T.; Waska, H.; Duerr, H.H.; Hartmann, J. Submarine groundwater discharge from tropical islands: A review. Grundwasser 2015, 20, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porubsky, W.P.; Weston, N.B.; Moore, W.S.; Ruppel, C.; Joye, S.B. Dynamics of submarine groundwater discharge and associated fluxes of dissolved nutrients, carbon, and trace gases to the coastal zone (Okatee River estuary, South Carolina). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 131, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Dulaiova, H. Estimating the dynamics of groundwater input into the coastal zone via continuous radon-222 measurements. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 69, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaiova, H.; Gonneea, M.E.; Henderson, P.B.; Charette, M.A. Geochemical and physical sources of radon variation in a subterranean estuary—Implications for groundwater radon activities in submarine groundwater discharge studies. Mar. Chem. 2008, 110, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.C. Significant groundwater input to a coastal plain estuary: Assessment from excess radon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Moore, W.S.; Zhang, L.; Du, J.; Zhang, J. Using radium isotopes to estimate the residence time and the contribution of submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) in the Changjiang effluent plume, East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 35, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. Ages of continental shelf waters determined from 223Ra and 224Ra. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2000, 105, 22117–22122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S.; Krest, J. Distribution of 223Ra and 224Ra in the plumes of the Mississippi and Atchafalaya Rivers and the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Chem. 2004, 86, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Tan, Y.; Song, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Chen, R. The status of the ecological environment and a proposed protection strategy in Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 47, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-L.; Ling, J.; Long, L.-J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-S.; Dong, J.-D. Influence of human activity and monsoon dynamics on spatial and temporal hydrochemistry in tropical coastal waters (Sanya Bay, South China Sea). Chem. Ecol. 2012, 28, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jing, W.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Dai, M. Coastal acidification induced by tidal-driven submarine groundwater discharge in a coastal coral reef system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13069–13075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jing, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, E.; Dai, M. Tidal variability of nutrients in a coastal coral reef system influenced by groundwater. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. On biogeomorphology of Luhuitou fringing reef of Sanya city, Hainan Island, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2001, 46, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y. Variations of nutrient contents and their transportation estimate at Sanya Bay. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2005, 25, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Zheng, H. Current situation and utilization of water resources in Sanya City. Chin. Water Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 6, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Dong, J.-D.; Cai, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-S.; Long, L.-J.; Zhang, S. Monsoon-driven dynamics of environmental factors and phytoplankton in tropical Sanya Bay, South China sea. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2012, 41, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Peng, G.; Zhang, J. A preliminary study of Holocene stratigraphy and sea level changes along the coast of Hainan Island. Chin. J. Geol. 1979, 4, 350–358. [Google Scholar]
- Che, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Che, Z. Comparison of the distribute characteristics of the suspended sediments between the Sanya River mouth and offshore water body. Chin. J. Hainan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2010, 28, 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Rama; Moore, W.S. Using the radium quartet for evaluating groundwater input and water exchange in salt marshes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4645–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S.; Arnold, R. Measurement of 223Ra and 224Ra in coastal waters using a delayed coincidence counter. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1996, 101, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. Radium isotope measurements using germanium detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 1984, 223, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.Q.; Dai, M.H.; Kao, S.J.; Gan, J.P.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.F.; Zhai, W.D.; Wang, L. Nutrient dynamics and biological consumption in a large continental shelf system under the influence of both a river plume and coastal upwelling. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S.; Blanton, J.O.; Joye, S.B. Estimates of flushing times, submarine groundwater discharge, and nutrient fluxes to Okatee Estuary, South Carolina. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froelich, P.N.; Bender, M.L.; Luedtke, N.A. The marine phosphorus cycle. Am. J. Sci. 1982, 282, 474–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zee, C.; Roevros, N.; Chou, L. Phosphorus speciation, transformation and retention in the Scheldts estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands) from the freshwater tidal limits to the North Sea. Mar. Chem. 2007, 106, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krest, J.M.; Rama, W.S.M. 226Ra and 228Ra in the mixing zones of the Mississippi and Atchafalaya Rivers: Indicators of groundwater input. Mar. Chem. 1999, 64, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, W.; Moore, W.S.; Li, Q.; Yan, X.; Qi, D.; Jiang, Y. Net subterranean estuarine export fluxes of dissolved inorganic C, N, P, Si, and total alkalinity into the Jiulong River estuary, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 149, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Dulaiova, H.; Siringan, F.; Foronda, J.; Wattayakorn, G.; Rungsupa, S.; Kontar, E.A.; Ishitobi, T. Groundwater discharge as an important land-sea pathway into Manila Bay, Philippines. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 24, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.J.; Rapaglia, J.P.; Cochran, J.K.; Bokuniewicz, H.J. Radium mass-balance in Jamaica Bay NY: Evidence for a substantial flux of submarine groundwater. Mar. Chem. 2007, 106, 419–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-W.; Hwang, D.W.; Kim, G.; Lee, W.C.; Oh, H.T. Nutrient inputs from submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) in Masan Bay, an embayment surrounded by heavily industrialized cities, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3181–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Ryu, J.-W.; Hwang, D.W. Radium tracing of submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) and associated nutrient fluxes in a highly-permeable bed coastal zone, Korea. Mar. Chem. 2007, 109, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Du, J.; Moore, W.S.; Zhang, G.; Su, N.; Zhang, J. Nutrient inputs to a Lagoon through submarine groundwater discharge: The case of Laoye Lagoon, Hainan, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 111–112, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.K. Spatial and seasonal variations of Cyanobacteria and their nitrogen fixation rates in Sanya Bay, South China Sea. Sci. Mar. 2008, 72, 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Li, T.; Cai, C.; Huang, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Dong, J.; Zhang, S. Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton and bacterioplankton biomass in Sanya Bay, northern South China Sea. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, M.A. The Si-C-N ratio of marine diatoms—Interspecific variability and the effect of some environmental variables. J. Phycol. 1985, 21, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Sci. Prog. 1960, 11, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Officer, C.B. Discussion of the behavior of nonconservative dissolved constituents in estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 1979, 9, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, K.M.; Leung, K.Y.; Tanner, P.A. Observational and modeling study of dry deposition on surrogate surface in a South China Sea city: Implication of removal of atmospheric crustal particles. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 164, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titlyanov, E.A.; Titlyanova, T.V.; Belous, O.S.; Kalita, T.L. Inventory change (1990s–2010s) in the marine flora of Sanya Bay (Hainan Island, China). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2015, 95, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, M.J.; Smith, S.V. C-N-P Ratio of Benthic Marine Plants. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1983, 28, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Qi, Y. Coastal upwelling off Eastern Hainan Island observed in the summer of 2013. Chin. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2016, 35, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Chislock, M.F.; Doster, E.; Zitomer, R.A.; Wilson, A.E. Eutrophication: Causes, consequences, and controls in aquatic ecosystems. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2013, 4, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, R.F.; Chan, F.; Conley, D.J.; Garnier, J.; Doney, S.C.; Marino, R.; Billen, G. Coupled biogeochemical cycles: Eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Station | Latitude | Longitude | Water Depth (m) | Temp (°C) | Salinity | 223Ra | σ | 224Ra | σ | 226Ra | σ | 228Ra | σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dpm 100 L−1 | |||||||||||||
| J1 | 18.2718 | 109.4565 | 8 | 22.80 | 33.60 | 1.79 | 0.20 | 33.86 | 0.36 | 10.81 | 0.45 | 33.73 | 1.30 |
| J2 | 18.2623 | 109.4423 | 9 | 22.66 | 33.62 | 0.80 | 0.13 | 21.52 | 0.68 | 10.50 | 0.39 | 31.74 | 1.09 |
| J3 | 18.2531 | 109.4298 | 12 | 22.70 | 33.64 | 1.56 | 0.16 | 30.04 | 0.38 | 10.91 | 0.50 | 37.95 | 1.44 |
| J4 | 18.2409 | 109.4118 | 11 | 22.81 | 33.70 | 0.60 | 0.14 | 11.92 | 0.40 | 10.78 | 0.39 | 28.24 | 1.02 |
| J5 | 18.2261 | 109.3909 | 15 | 22.90 | 33.70 | 0.52 | 0.15 | 17.61 | 0.89 | 10.19 | 0.41 | 28.02 | 1.10 |
| W1 | 18.2555 | 109.4832 | 5 | 23.12 | 33.70 | 1.36 | 0.23 | 26.66 | 0.39 | 12.04 | 0.49 | 30.35 | 1.23 |
| W2 | 18.2466 | 109.4672 | 12 | 22.93 | 33.72 | 0.83 | 0.13 | 12.88 | 0.32 | 10.92 | 0.41 | 26.22 | 1.02 |
| W3 | 18.2306 | 109.4413 | 16 | 22.97 | 33.89 | 0.59 | 0.13 | 11.93 | 0.53 | 10.63 | 0.43 | 23.11 | 1.06 |
| W4 | 18.2154 | 109.4244 | 5 | 23.12 | 33.70 | 0.52 | 0.11 | 12.82 | 0.30 | 10.73 | 0.39 | 24.03 | 0.98 |
| P1 | 18.2355 | 109.4940 | 5 | 22.98 | 33.62 | 1.22 | 0.19 | 42.60 | 0.85 | 11.93 | 0.54 | 28.87 | 1.34 |
| P2 | 18.2296 | 109.4797 | 11 | 23.01 | 33.67 | 0.97 | 0.17 | 23.57 | 0.34 | 10.56 | 0.49 | 31.94 | 1.27 |
| P3 | 18.2213 | 109.4660 | 16 | 22.75 | 33.84 | 0.54 | 0.13 | 15.49 | 0.59 | 10.99 | 0.41 | 24.26 | 1.08 |
| P4 | 18.2105 | 109.4464 | 12 | 22.71 | 33.89 | 0.77 | 0.11 | 15.32 | 0.36 | 10.83 | 0.32 | 28.14 | 0.85 |
| P5 | 18.1931 | 109.4296 | 26 | 22.69 | 33.81 | 1.38 | 0.11 | 18.51 | 0.65 | 10.95 | 0.33 | 28.90 | 0.89 |
| L1 | 18.2219 | 109.4812 | 7 | 22.76 | 33.84 | 0.65 | 0.10 | 13.65 | 0.40 | 9.71 | 0.42 | 26.42 | 1.15 |
| L2 | 18.2193 | 109.4812 | 11 | 22.81 | 33.85 | 0.74 | 0.11 | 22.99 | 0.67 | 11.98 | 0.44 | 26.33 | 1.16 |
| L3 | 18.2201 | 109.4749 | 12 | 22.79 | 33.84 | 0.78 | 0.11 | 14.49 | 0.28 | 9.77 | 0.41 | 25.24 | 1.06 |
| L4 | 18.2105 | 109.4674 | 20 | 22.76 | 33.85 | 0.70 | 0.11 | 13.82 | 0.42 | 10.59 | 0.42 | 25.53 | 1.13 |
| L5 | 18.2111 | 109.4582 | 21 | 22.74 | 33.85 | 1.17 | 0.13 | 17.63 | 0.33 | 11.27 | 0.38 | 25.90 | 0.96 |
| L6 | 18.1965 | 109.4694 | 23 | 22.79 | 33.82 | 0.84 | 0.12 | 16.34 | 0.38 | 10.21 | 0.43 | 23.77 | 0.95 |
| L7 | 18.1966 | 109.4601 | 32 | 22.83 | 33.86 | 0.84 | 0.18 | 14.26 | 0.76 | 10.53 | 0.41 | 26.03 | 1.08 |
| L8 | 18.1964 | 109.4476 | 25 | 22.78 | 33.88 | 0.43 | 0.15 | 12.18 | 0.40 | 9.58 | 0.43 | 27.01 | 1.20 |
| H1 | 18.2348 | 109.4977 | nd * | 22.88 | 31.70 | 1.69 | 0.50 | 64.75 | 0.74 | 15.45 | 0.70 | 43.75 | 1.85 |
| LE01 | 18.0000 | 110.0000 | 96 | 29.62 | 33.33 | nd | nd | nd | nd | 5.92 | 0.42 | 11.70 | 1.42 |
| Parameter | Value | Unit | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estuary | FR | River discharge | 0.88 | m3 s−1 | [24,25] |
| 226RaR | Estuary water 226Ra | 15.5 ± 0.7 | dpm 100 L−1 | This study | |
| 228RaR | Estuary water 228Ra | 43.8 ± 1.9 | |||
| CTSM | Concentration of total suspended matter | 25.33 | mg L−1 | ||
| fd | Fraction of desorbed radium from particles | 0.43 | - | [37] | |
| 226Rap | 226Ra on particles | 2.5 | dpm g−1 | [36] | |
| 228Rap | 228Ra on particles | 2.09 | |||
| Sediment | 228Fsed | 228Ra diffusive flux | 2.1 | dpm m−2 d−1 | |
| 226Fsed | 226Ra diffusive flux | 0.27 | [8] | ||
| Groundwater | 226RaGW | Groundwater 226Ra | 246 ± 36 | dpm 100 L−1 | This study |
| 228RaGW | Groundwater 228Ra | 435 ± 18 | |||
| Sanya Bay | 226RaB | Bay water 226Ra | 10.75 ± 0.66 | ||
| 228RaB | Bay water 228Ra | 27.81 ± 3.59 | |||
| VB | Volume of the bay investigated | 1.04 × 109 | m3 | ||
| AB | Surface area of the bay investigated | 6.49 × 107 | m2 | ||
| τ | Residence time | 7.2 ± 3.2 | day | ||
| Ocean | 226RaO | Ocean water 226Ra | 5.92 ± 0.42 | dpm 100 L−1 | |
| 228RaO | Ocean water 228Ra | 11.70 ± 1.42 | |||
| Radium | Formula in Equation (1) | Value | Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226Ra | Sources | Sanya River | FR·226RaR | 1.17 × 107 | dpm d−1 |
| FR·fd·226Rap·CTSM | 2.07 × 106 | ||||
| Sediment diffusion | AB·226Fsed | 4.24 × 107 | |||
| Groundwater | FSGD·226RaGW | 6.87 × 109 | |||
| Sink | Mixing | VB·(226RaB − 226RaO)/τ | 6.93 × 109 | ||
| 228Ra | Sources | Sanya River | FR·228RaR | 3.32 × 107 | |
| FR·fd·228Rap·CTSM | 1.73 × 106 | ||||
| Sediment diffusion | AB·228Fsed | 1.01 × 109 | |||
| Groundwater | FSGD·228RaGW | 2.21 × 1010 | |||
| Sink | Mixing | VB·(228RaB − 228RaO)/τ | 2.31 × 1010 | ||
| Region | SGD Rate (cm d−1) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Manila Bay, Philippines | 0–26 | [38] |
| Jamaica Bay, USA | 1.5–17 | [39] |
| Masan Bay, Korea | 6.1–7.1 | [40] |
| Yeogil Bay, Korea | 20 | [41] |
| Eastern coast of Hainan Island, China | 10–29 | [42] |
| Sanya Bay, China | 4.3 ± 2.1–7.8 ± 4.1 | This study |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jing, W. Significance of Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Nutrient Budgets in Tropical Sanya Bay, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020380
Wang G, Wang S, Wang Z, Jing W. Significance of Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Nutrient Budgets in Tropical Sanya Bay, China. Sustainability. 2018; 10(2):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020380
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guizhi, Shuling Wang, Zhangyong Wang, and Wenping Jing. 2018. "Significance of Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Nutrient Budgets in Tropical Sanya Bay, China" Sustainability 10, no. 2: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020380
APA StyleWang, G., Wang, S., Wang, Z., & Jing, W. (2018). Significance of Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Nutrient Budgets in Tropical Sanya Bay, China. Sustainability, 10(2), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020380