Understanding the Transition to a Bio-Based Economy: Exploring Dynamics Linked to the Agricultural Sector in Sweden
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodological Framework and Research Process
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Dynamics Governing the Expansion and Maintenance of Farming Activities
3.2. Employment of More Environmentally Friendly Practices in Conventional Agriculture
3.3. Identification of Dynamics Governing Biomass Availability
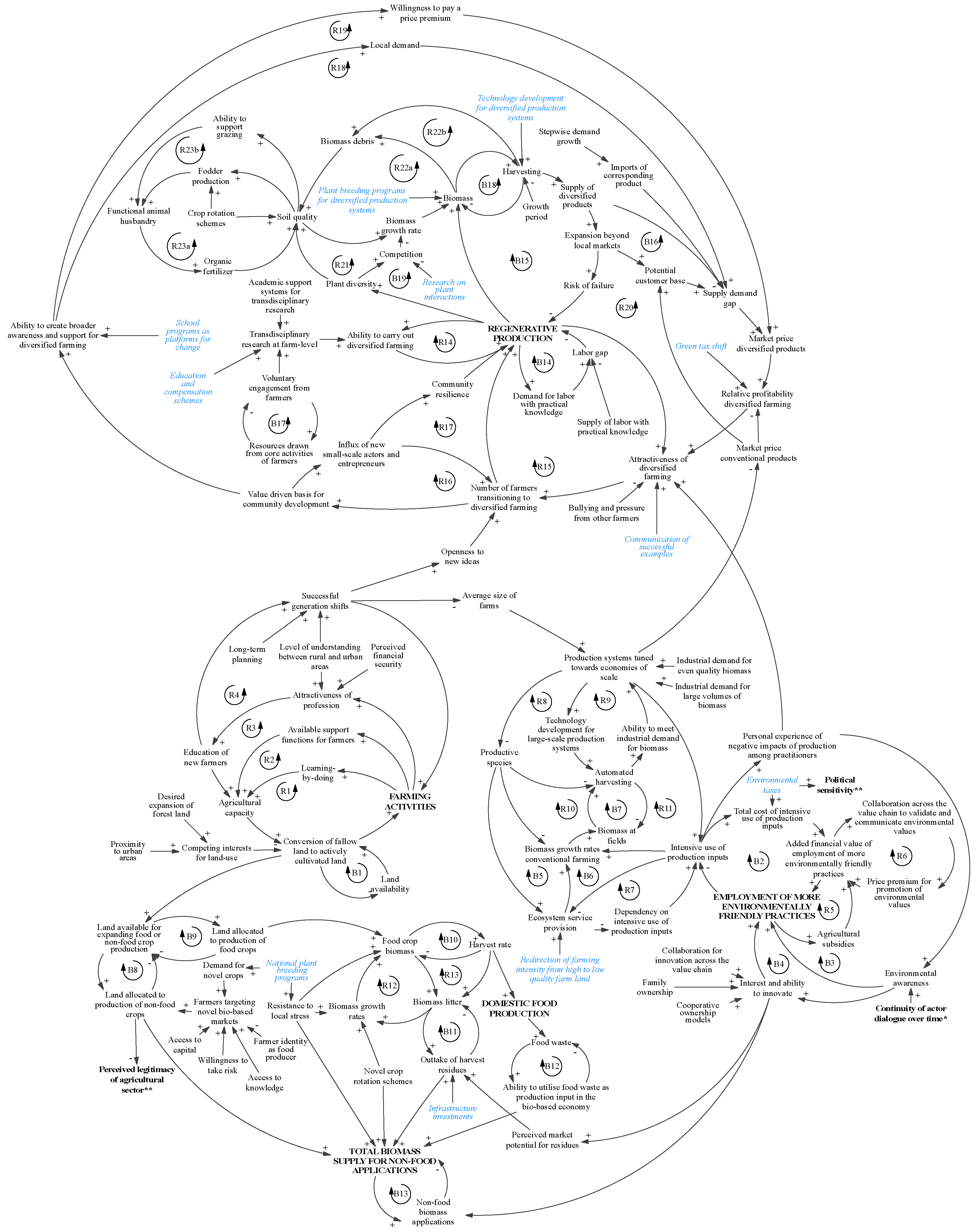
3.4. Introduction to Diversified Farming and Regenerative Production
3.4.1. The Transition to Diversified Farming and Regenerative Production
3.4.2. The Biophysical Basis for Diversified Farming and Regenerative Production
3.4.3. Dynamics Identified as Counteracting a Transition to Diversified Farming and Regenerative Production
3.5. Proposed Leverage Points and Interventions
3.5.1. Interventions Linked to Environmentally Friendly Practices and Biomass Availability
3.5.2. Interventions Linked to Diversified Farming and Regenerative Production
3.6. Interconnectedness between the Agricultural and Forestry Sectors
4. Transition Pathways towards a Bio-Based Economy
4.1. Summary of Proposed Interventions
4.2. Synergies and Trade-Offs
5. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- German Bioeconomy Council. Bioeconomy Policy (Part II) Synopsis of National Strategies around the World; German Bioeconomy Council: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, O.; Juan, M.G.S. How Sustainability Is Addressed in Official Bioeconomy Strategies at International, National and Regional Levels—An Overview; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Priefer, C.; Jörissen, J.; Frör, O. Pathways to Shape the Bioeconomy. Resources 2017, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugge, M.; Hansen, T.; Klitkou, A. What Is the Bioeconomy? A Review of the Literature. Sustainability 2016, 8, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, L.; Björnsdóttir, B.; Brandt, A.; Hildén, K.; Hreggviðsson, G.Ó.; Jacobsen, B.; Jessen, A.; Karlsson, E.N.; Lindedam, J.; Mäkelä, M.; et al. Development of the Nordic Bioeconomy; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- EU. Innovating for Sustainable Growth: A Bioeconomy for Europe. 2012. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/research/bioeconomy/pdf/official-strategy_en.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2017).
- OECD. The Bioeconomy to 2030 Designing a Policy Agenda; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2009; Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/economics/the-bioeconomy-to-2030_9789264056886-en (accessed on 8 May 2018).
- El-Chichakli, B.; von Braun, J.; Lang, C.; Barben, D.; Philp, J. Five cornerstones of a global bioeconomy. Nat. News. 2016, 535, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formas. Swedish Research and Innovation Strategy for a Bio-Based Economy; Swedish Research Council for Environment, Agricultural Sciences and Spatial Planning, Formas: Stockholm, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, K.; Kautto, N. The Bioeconomy in Europe: An Overview. Sustainability 2013, 5, 2589–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The White House. National Bioeconomy Blueprint. Ind. Biotechnol. 2012, 8, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Refsgaard, K.; Teräs, J.; Kull, M.; Oddsson, G.; Jóhannesson, T.; Kristensen, I. The Rapidly Developing Nordic Bioeconomy: Exerpt from State of the Nordic Region 2018; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Skånberg, K.; Olsson, O.; Hallding, K. Den Svenska Bioekonomin: Definitioner, Nulägesanalys och Möjliga Framtider; Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Teräs, J.; Lindberg, G.; Johnsen, I.; Perjo, L.; Giacometti, A. Bioeconomy in the Nordic Region: Regional Case Studies; Nordregio Working Paper; Nordic Centre for Spatial Development: Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- SEPA. Sweden’s Environmental Objectives—An Introduction; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2016.
- IVL and Fossil Free Sweden. Hoppfulla Trender för ett Fossilfritt Sverige En Rapport från Initiativet Fossilfritt Sverige; IVL and Fossil Free Sweden: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017.
- Government of Sweden. The Swedish Government’s Overall EU Priorities for 2017; Government of Sweden: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017.
- Regeringskansliet. Fact Sheet: Proposal Referred to the Council on Legislation on a Climate Policy Framework for Sweden; Regeringskansliet: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017.
- Regeringskansliet. Innovation Partnership Programmes—Mobilising New Ways to Meet Societal Challenges. 2016. Available online: http://www.government.se/articles/2016/07/innovation-partnership-programmes--mobilising-new-ways-to-meet-societal-challenges/ (accessed on 5 April 2017).
- Swedish Forest Industries Federation. Skogsnäringen Driver Tillväxt i Världens Bioekonomi—Mål på Vägen mot Visionen; Swedish Forest Industries Federation: Stockholm, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Business Sweden. Bioeconomy in Sweden, Sector Overview. Business Opportunities in a Bioeconomy Growth Market; Business Sweden: Stockholm, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nordic Council of Ministers. Nordic Bioeconomy, 25 Cases for Sustainable Change; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pfau, S.F.; Hagens, J.E.; Dankbaar, B.; Smits, A.J.M. Visions of Sustainability in Bioeconomy Research. Sustainability 2014, 6, 1222–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, I. Securing a sustainable biomass supply in a growing bioeconomy. Glob. Food Secur. 2015, 6, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlat, N.; Dallemand, J.-F.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Nita, V. The role of biomass and bioenergy in a future bioeconomy: Policies and facts. Environ. Dev. 2015, 15, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, O.; Padel, S.; Levidow, L. The bio-economy concept and knowledge base in a public goods and farmer perspective. Bio-Based Appl. Econ. 2012, 1, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Staffas, L.; Gustavsson, M.; McCormick, K. Strategies and Policies for the Bioeconomy and Bio-Based Economy: An Analysis of Official National Approaches. Sustainability 2013, 5, 2751–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pülzl, H.; Kleinschmit, D.; Arts, B. Bioeconomy—An emerging meta-discourse affecting forest discourses? Scand. J. For. Res. 2014, 29, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavone, V.; Goven, J. (Eds.) Bioeconomies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, R.; van de Pol, M.; Philp, J. Define biomass sustainability: The future of the bioeconomy requires global agreement on metrics and the creation of a dispute resolution centre. Nature 2015, 523, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viaggi, D. Towards an economics of the bioeconomy: Four years later. Bio-Based Appl. Econ. 2016, 5, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Addeo, F. Bio-Based Economy for Europe: State of Play and Future Potential—Part 1. Report on the European Commission’s Public On-Line Consultation; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nebe, S. Bio-Based Economy in Europe: State of Play and Future Potential—Part 2 Summary of Position Papers Received in Response to the European Commission’s Public On-Line Consultation; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Golembiewski, B.; Sick, N.; Bröring, S. The emerging research landscape on bioeconomy: What has been done so far and what is essential from a technology and innovation management perspective? Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 29, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennich, T.; Belyazid, S.; Kopainsky, B.; Diemer, A. The Bio-Based Economy: Dynamics Governing Transition Pathways in the Swedish Forestry Sector. Sustainability 2018, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacko, M.; Martinuzzi, A.; Røpke, I.; Videira, N.; Antunes, P. Participatory systems mapping for sustainable consumption: Discussion of a method promoting systemic insights. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 106, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, J.D. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; Irwin/McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stave, K.A.; Kopainsky, B. A system dynamics approach for examining mechanisms and pathways of food supply vulnerability. J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 2015, 5, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.C. The emergence and use of diagramming in system dynamics: A critical account. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2008, 25, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner, A.; Littig, B.; Menz, W. Introduction: Expert Interviews—An Introduction to a New Methodological Debate. In Interviewing Experts; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Meadows, D.H. Whole earth models and systems. Co-Evol. Q. 1982, Summer, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Meadows, D.H. Thinking in Systems: A Primer; Chelsea Green Publishing: Hartford, VT, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Senge, P. The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organization (Revised and Updated); Random House, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lelea, M.A.; Roba, G.M.; Christinck, A.; Kaufmann, B. Methodologies for Stakeholder Analysis—For Application in Transdisciplinary Research Projects Focusing on Actors in Food Supply Chains; German Institute for Tropical and Subtropical Agriculture (DITSL): Witzenhausen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Barriball, K.L.; While, A. Collecting data using a semi-structured interview: A discussion paper. J. Adv. Nurs. 1994, 19, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, M.C.; Bradley, M.A. Data Collection Methods: Semi-Structured Interviews and Focus Groups; RAND Corporation: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Andersen, D.F. Building confidence in causal maps generated from purposive text data: Mapping transcripts of the Federal Reserve. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2012, 28, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Targeted Objective | Proposed Intervention | Desired Change | Potential Unintended Consequences, Sources of Policy Resistance, or Systemic Risk | Uncertainty and Examples of Questions Remaining to Explore |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employment of more environmentally friendly practices in conventional agriculture | “What if the intensity of agricultural production is leveled out?” (reducing farming intensity on high quality farm land while intensifying cultivation on low quality farm land at risk of becoming overgrown) | Environmental values and long-term productivity are promoted. | How to determine and achieve optimal land-use and farming practices? What would be the net-effect on biomass availability? | |
| “What if financial instruments, such as environmental taxes, are used to a larger extent?” | Extracting and using fossil-based, finite resources would become relatively more expensive, promoting the employment of more environmentally friendly production practices. | The implementation, or prospect of implementing, such financial instruments could be perceived as a threat by some actors in the economy. If these interventions are linked to efforts to promote the bio-based economy, it could make the concept politically sensitive, reducing the ability to create a shared understanding of its objectives, and thereby hindering a broader transition to a bio-based economy. | How to “get the prices right” while simultaneously ensuring that the bio-based economy is perceived as an opportunity for a broad group of actors, also those currently not directly linked to bio-based sectors of the economy? | |
| Biomass availability (total biomass supply for non-food applications, domestic food production) | “What if infrastructure is developed, allowing better transport and handling of harvest residues from the agricultural sector?” | Harvest residues would be utilized as an input to the bio-based economy to a larger extent. Resource use efficiency would increase, while pressure on other sources of biomass would be reduced. | Nutrient loss due to the removal of harvest residues and litter from agricultural land. | How can circularity be achieved, specifically in terms of nutrient recycling? How to solve the perceived match-making problem, where primary producers have biomass they cannot sell while industrial biomass demand is not fulfilled? |
| “What if national plant breeding programs are further expanded?” | The resistance of plants to local stress, as well as the variability in chemical composition and plant characteristics, would increase. The demand for novel crops would grow, with a consequent increase in the number of farmers targeting new markets. | More land allocated to the production of non-food crops could make the perceived legitimacy of the agricultural sector decrease, lowering the overall ability to facilitate a transition to a bio-based economy. | What pathways make biomass demand and supply increase or decrease, and what are the consequences in terms of ability to meet biomass demand? Demand for novel crops is suggested to make the number of farmers allocating land to crop production for non-food purposes increase. What actors could take lead in this development, those currently active in the agricultural sector or completely new actors? | |
| Shift to regenerative production | “What if plant breeding programs for diversified production systems were implemented?” | The ability of diversified production systems to provide edible yields grows. | What are the design principles that would allow these systems to function optimally? How much food are these systems able to provide in a Nordic context? How do consumption patterns need to change to allow production to meet demand? | |
| “What if the knowledge base on plant interactions was expanded?” | Competition between species in diversified systems would be reduced, and productivity would thereby increase. | |||
| “What if education and compensation schemes to ensure that farmers can participate in transdisciplinary research programs were employed?” | The interest and ability of farmers to engage in transdisciplinary research would increase, contributing to both theoretical and practical knowledge supporting diversified farming. | How to ensure that the potential of the ideas generated in these research programs is leveraged? How to ensure that transdisciplinary research programs are supported in an academic setting? | ||
| “What if technology for diversified production systems was developed?” | Diversified production systems would become more efficient, leveraging the potential of technology to complement manual labor, and harvests would increase. | Whom should take the lead in this development? What will be the net effect on the labor market? | ||
| “What if taxation of labor was reduced, as part of a green tax shift?” | The relative profitability of the labor-intensive practices in diversified farming would increase, thereby strengthening the attractiveness of diversified farming. | With an increase in regenerative production, the demand for labor with practical skills would grow, increasing the labor gap. Unless measures are taken, this would limit a further expansion of regenerative production. | What are potential effects on the labor market and larger economy of reducing the tax burden on labor? | |
| “What if school programs were used as platforms for social change?” | Public procurement would support the expansion of diversified farming, through creating broader awareness. | What are suitable diets for a bio-based economy? What attitudinal changes are needed to support this change? How to implement these programs in a way so that they can be sustained over longer time periods? | ||
| “What if successful examples of diversified farming practices were communicated?” | The attractiveness of diversified farming would grow, making more farmers transition and the regenerative production increase. | As regenerative production increases, also an expansion beyond local markets might take place. This could entail larger competition and risk, and unless complementary measures are taken, a larger failure rate. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bennich, T.; Belyazid, S.; Kopainsky, B.; Diemer, A. Understanding the Transition to a Bio-Based Economy: Exploring Dynamics Linked to the Agricultural Sector in Sweden. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051504
Bennich T, Belyazid S, Kopainsky B, Diemer A. Understanding the Transition to a Bio-Based Economy: Exploring Dynamics Linked to the Agricultural Sector in Sweden. Sustainability. 2018; 10(5):1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051504
Chicago/Turabian StyleBennich, Therese, Salim Belyazid, Birgit Kopainsky, and Arnaud Diemer. 2018. "Understanding the Transition to a Bio-Based Economy: Exploring Dynamics Linked to the Agricultural Sector in Sweden" Sustainability 10, no. 5: 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051504
APA StyleBennich, T., Belyazid, S., Kopainsky, B., & Diemer, A. (2018). Understanding the Transition to a Bio-Based Economy: Exploring Dynamics Linked to the Agricultural Sector in Sweden. Sustainability, 10(5), 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051504






