Designing Business Solutions for Plastic Waste Management to Enhance Circular Transitions in Kenya
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Linear to Circular Approach
2.2. Priorities in a Circular Economy
2.3. Environmental Kuznets Curve Functioning in Developing Economies
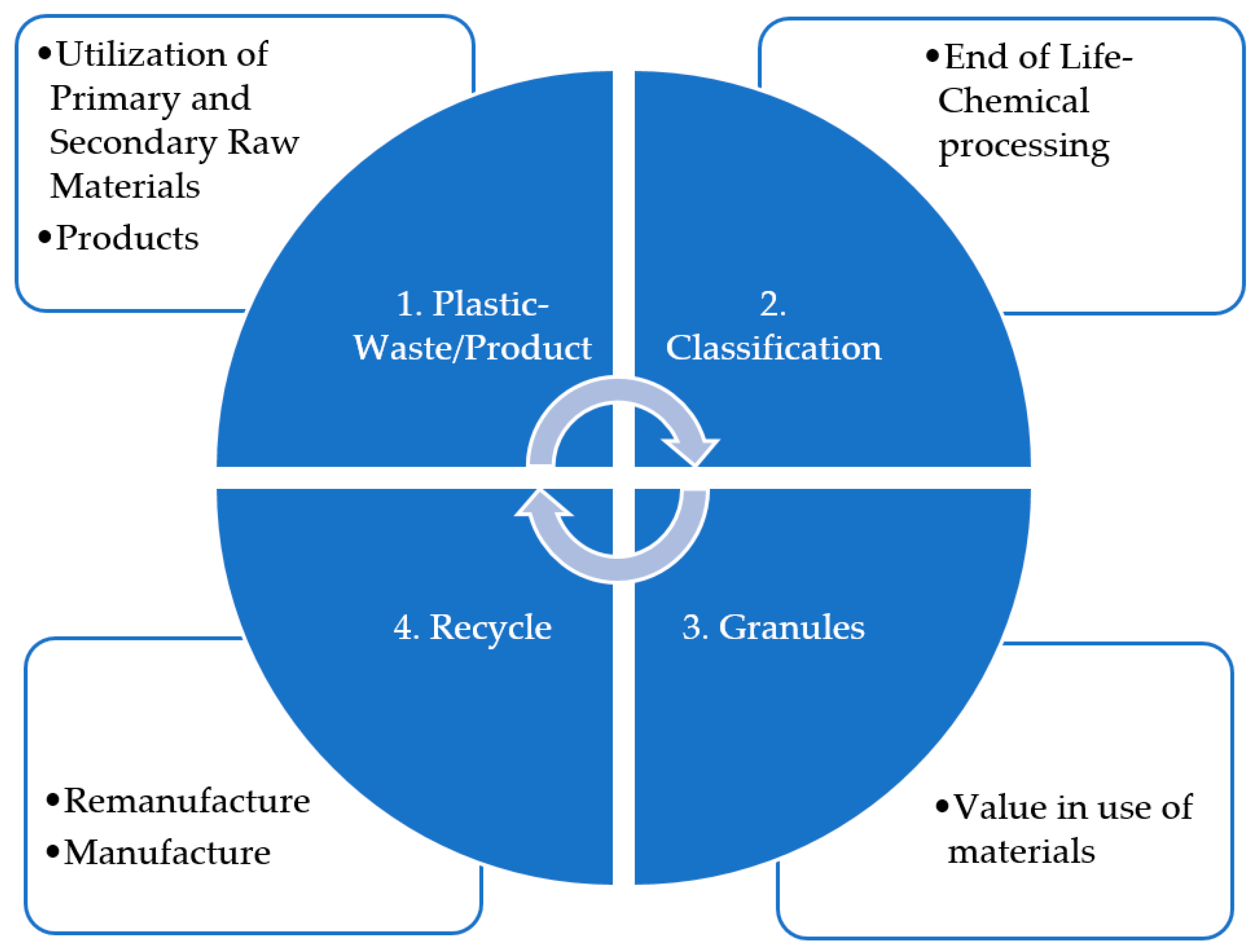
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Circular Economic Value

3.2. Data Collection and Research Boundaries

4. Results and Discussion
4.1. The Circular Economic Value of the Current State of Plastic Material Flow
4.2. Recommendations for Business Stakeholders
4.2.1. Key Partnerships
4.2.2. Key Activities and Resources
4.2.3. Value Proposition
4.2.4. Customer Relation
4.2.5. Distribution Channels and the Consumer Segment
4.2.6. Cost Structure and Revenue Streams
- Research and Development (R and D)
- Feasibility studies such as profitability, pilot test, SWOT analysis, production costs, capital and operating costs estimation
- Technology selection—mechanical and electrical
- Man-power selection and training
- Environmental compliance and safety audits
- Channel costs—raw material and vendor selection
- Processing plant design and outlay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nwabue, F.I.; Unah, U.; Itumoh, E.J. Production and characterization of smokeless bio-coal briquettes incorporating plastic waste materials. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2017, 8, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njeru, J. The urban political ecology of plastic bag waste problem in Nairobi, Kenya. Geoforum 2006, 37, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, S.N.; Noor, Z.Z.; Abba, A.H.; Yusuf, R.O.; Hassan, M.A.A. Review on life cycle assessment of integrated solid waste management in some Asian countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orset, C.; Barret, N.; Lemaire, A. How consumers of plastic water bottles are responding to environmental policies? Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, T.P. Reducing single-use plastic shopping bags in the USA. Waste Manag. 2017, 70, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinho, G.; Balaia, N.; Pires, A. The Portuguese plastic carrier bag tax: The effects on consumers’ behavior. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivers, N.; Shenstone-Harris, S.; Young, N. Using nudges to reduce waste? The case of Toronto’s plastic bag levy. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 188, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steensgaard, I.; Syberg, K.; Rist, S.; Hartmann, N.B.; Boldring, A.; Hansen, S.F. From macro- to microplastics - Analysis of EU regulation along the life cycle of plastic bags. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huysman, S.; De Schapmeester, J.; Ragaert, K.; Dewulf, J.; De Meester, S. Performance indicators for a circular economy: A case study on post-industrial plastic waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 120, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, M.; Nikolić, M. Drivers for development of circular economy—A case study of Serbia. Habitat Int. 2016, 56, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, N.; Kiesel, R.; Aumnate, C. Plastic Waste of the World: Increasing Potential of Recycling. In Understanding Plastics Recycling; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: Munich, Germany, 2017; pp. 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, K.; Maureaud, C.; Wilcox, C.; Hardesty, B.D. How successful are waste abatement campaigns and government policies at reducing plastic waste into the marine environment? Mar. Policy 2017. In Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelini, G.; Moraes, R.N.; Cunha, R.N.; Costa, J.M.H.; Ometto, A.R. From Linear to Circular Economy: PSS Conducting the Transition. Procedia CIRP 2017, 64, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobza, N.; Schuster, A. Building a responsible Europe—The value of the circular economy. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondello, G.; Salomone, R.; Ioppolo, G.; Saija, G.; Sparacia, S.; Lucchetti, C. Comparative LCA of Alternative Scenarios for Waste Treatment: The Case of Food Waste Production by the Mass-Retail Sector. Sustainability 2017, 9, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mativenga, P.T.; Sultan, A.A.M.; Agwa-Ejon, J.; Mbohwa, C. Composites in a Circular Economy: A Study of United Kingdom and South Africa. Procedia CIRP 2017, 61, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whicher, A.; Harris, C.; Beverley, K.; Swiatek, P. Design for circular economy: Developing an action plan for Scotland. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 172, 3237–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbinati, A.; Chiaroni, D.; Chiesa, V. Towards a new taxonomy of circular economy business models. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JICA. Preparatory Survey for Integrated Solid Waste Management in Nairobi City in the Republic of Kenya; CTI Engineering International Co., Ltd.: Nairobi, Kenya; NJS Consultants Co., Ltd.: Nairobi, Kenya, 2010.
- George, D.A.R.; Lin, B.C.; Chen, Y. A circular economy model of economic growth. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 73, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eygen, E.; Laner, D.; Fellner, J. Circular economy of plastic packaging: Current practice and perspectives in Austria. Waste Manag. 2017, 72, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Cooper, T. Towards a Sustainable Business Model for Plastic Shopping Bag Management in Sweden. Procedia CIRP 2017, 61, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlbo, H.; Poliakova, V.; Mylläri, V.; Sahimaa, O.; Anderson, R. Recycling potential of post-consumer plastic packaging waste in Finland. Waste Manag. 2017, 71, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, M.T.; van Velzen, T.; Augustinus, A.; Soethoudt, H.; De Meester, S.; Ragaert, K. Predictive model for the Dutch post-consumer plastic packaging recycling system and implications for the circular economy. Waste Manag. 2017, 71, 62–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oghazi, P.; Mostaghel, R. Circular Business Model Challenges and Lessons Learned—An Industrial Perspective. Sustainability 2018, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchherr, J.; Reike, D.; Hekkert, M. Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, M.; Williander, M. Circular Business Model Innovation: Inherent Uncertainties. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2017, 26, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the environment, and human health: Current consensus and future trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwanza, B.G.; Mbohwa, C. Major Obstacles to Sustainability in the Plastic Industry. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 8, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayo, F.; García, R.; Diez, M.A. Modelling the Gieseler fluidity of coking coals modified by multicomponent plastic wastes. Fuel 2016, 165, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Chiang, K.Y. Gasification of non-recycled plastic packaging material containing aluminum: Hydrogen energy production and aluminum recovery. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 27532–27542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faussone, G.C. Transportation fuel from plastic: Two cases of study. Waste Manag. 2017, 73, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miandad, R.; Barakat, M.A.; Rehan, M.; Aburiazaiza, A.S.; Ismail, I.M.I.; Nizami, A.S. Plastic waste to liquid oil through catalytic pyrolysis using natural and synthetic zeolite catalysts. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owusu, P.A.; Banadda, N.; Zziwa, A.; Seay, J.; Kiggundu, N. Reverse engineering of plastic waste into useful fuel products. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 130, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldini, C.A.; Mattarelli, E.; Savioli, T.; Cantore, G.; Garbero, M.; Bologna, A. Performance, emission and combustion characteristics of a IDI engine running on waste plastic oil. Fuel 2016, 183, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tulaian, B.S.; Al-Shannag, M.J.; Al-Hozaimy, A.R. Recycled plastic waste fibers for reinforcing Portland cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, B. Investigation on the use of foamed plastic waste as natural aggregates replacement in lightweight mortar. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 99, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, A.; Yaghoubi, E.; Wong, Y.; Horpibulsuk, S. Recycled plastic granules and demolition wastes as construction materials: Resilient moduli and strength characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gil, A.; Fernández, A.; Arranz, A.; Lorenzana, A.; Nieto, D.V.; de Saja, J.A.; Ruiz-Herrero, J.L.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.; Merino, S. Mechanical and thermal performance of concrete and mortar cellular materials containing plastic waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 104, 298–310. [Google Scholar]
- Bhogayata, A.C.; Arora, N.K. Fresh and strength properties of concrete reinforced with metalized plastic waste fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorneycroft, J.; Orr, J.; Savoikar, P.; Ball, R. Performance of structural concrete with recycled plastic waste as a partial replacement for sand. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassim, A.K. Recycling of Polyethylene Waste to Produce Plastic Cement. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 8, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, T.O. Identification and segregation of materials in mixed waste. Technol. Adv. Work Waste 1992, 57, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezni, A.; Saber, N.B.; Alhadhrami, A.A.; Gobouri, A.; Aldalbahi, A.; Hay, S.; Santos, A.; Losic, D.; Altalhi, T. Highly biocompatible carbon nanocapsules derived from plastic waste for advanced cancer therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharuddin, A.; Dayana, S.; Faisal, A.; Daud, W.; Ashri, W.M.; Kheireddine, A.M. A review on pyrolysis of plastic wastes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Guo, J.; Zhang, W.; Summers, P.A.; Hall, P. From waste plastics to industrial raw materials: A life cycle assessment of mechanical plastic recycling practice based on a real-world case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1192–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, J. The Raw Materials Transition in the Amsterdam Metropolitan Area: Added Value for the Economy, Well-Being, and the Environment. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 59, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, J.; Konno, K.; Moriguchi, Y. Variability-based optimal design for robust plastic recycling systems. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 116, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarassy, C.; Horvath, B.; Borocz, M. The Interpretation of Circular Priorities to Central European Business Environment with Focus on Hungary. Visegr. J. Bioecon. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 6, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.G.; Lu, S.Y.; Mo, T.; Zeng, H. Brominated flame retardant emissions from the open burning of five plastic wastes and implications for environmental exposure in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basel Convention. Where are WEee in Africa? Findings from the Basel Convention E-Waste Africa Programme; Secretariat of the Basel Convention: Basel, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Panayotou, T. Empirical Tests and Policy Analysis of Environmental Degradation at Different Stages of Economic Development; Working Paper WP 238; Technology and Employment Programme, International Labour Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, B.; Bakosne, B.M.; Fogarassy, C. How does the European Unions’ climate policy function on global level?—The effects of “Carbon Leakage”. In Proceedings of the Science Connecting Nations: 2nd VUA YOUTH Conference, Godollo, Hungary, 23 November 2015; pp. 665–687. [Google Scholar]
- Suri, V.; Chapman, D. Economic growth, trade, and energy: Implications for the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol. Econ. 1998, 25, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, J.; Levinson, A. The simple analytics of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. J. Public Econ. 2001, 80, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.I. The Rise and Fall of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. World Dev. 2004, 32, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Laplante, B.; Wang, H.; Wheeler, D. Confronting the Environmental Kuznets Curve. J. Econ. Perspect. 2002, 16, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulali, U.; Solarin, S.A.; Ozturk, I. Investigating the presence of the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis in Kenya: An autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) approach. Nat. Hazards. 2015, 80, 1729–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjiku Mukui, N. Mass Balance of Plastics: Case Study for Nairobi City; University of Nairobi: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cobbing, M. Toxic Tech.: Not in Our Backyard—Uncovering the Hidden Flows of e-Waste; Full Report; Greenpeace: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ongondo, F.O.; Williams, I.D.; Cherrett, T.J. How are WEEE doing? A global review of the management of electrical and electronic wastes. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, D.N.; Drisse, M.N.B.; Nxele, T.; Sly, P.D. E-Waste: A Global Hazard. Ann. Glob. Health 2014, 80, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, D.; Wittmann, A. E-Waste Prevention, Take-back System Design and Policy Approaches; Solving the E-Waste Problem (STEP) Green Paper, 13 February 2015; United Nations University: Bonn, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fogarassy, C.; Horvath, B.; Kovacs, A.; Szoke, L.; Takacs-Gyorgy, K. A Circular Evaluation Tool for Sustainable Event Management—An Olympic Case Study. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2017, 14, 161–177. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski, M. Designing the Business Model for Circular Economy—Towards the Conceptual Framework. Sustainability 2016, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethető, A.; Vecsenyi, J. Vállalkozz okosan! -Az Ötlettől a Piacra Lépésig [In Eng: Venture Smart!—From the Idea to Entering the Market]; HVG könyvek [HVG books]: Budapest, Hungary, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vecsenyi, J.; Pethető, A. How can you define your new venture? From the Business Model Canvas, through Lean canvas to The Business Concept Map. In Proceedings of the II International Conference on University-Based Entrepreneurship and Regional Development: Theory, Empirics and Practical Implementation, Book of Abstract, Pécs, Hungary, 1–2 December 2017; pp. 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Osterwalder, A.; Pigneur, Y. Business Model. Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Neffa, G.C.; Lourenco, S.V.M.; Acordi, V.P.E.B.; de Oliveira, C.G.M.J.; Vasconcelos, F.M.A. Management of plastic wastes at Brazilian ports and diagnosis of their generation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öncel, M.S.; Bektas, N.; Bayar, S.; Engin, G.; Caliskan, Y.; Salar, L.; Yetis, Ü. Hazardous wastes and waste generation factors for plastic products manufacturing industries in Turkey. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areeprasert, C.; Asingsamanunt, J.; Srisawat, S.; Kaharn, J.; Inseemeesak, B.; Phasee, P.; Khaobang, C.; Siwakosit, W.; Chiemchaisri, C. Municipal Plastic Waste Composition Study at Transfer Station of Bangkok and Possibility of its Energy Recovery by Pyrolysis. Energy Procedia 2017, 107, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, R.; Abdul Raman, A.A. Carbon dioxide emission reduction through cleaner production strategies in a recycled plastic resin producing plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousta, K.; Ordonez, I.; Bolton, K.; Dahlén, L. Support for designing waste sorting systems: A mini review. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupo, E.; Moroni, M.; La Marca, F.; Fulco, S.; Pinzi, V. Investigation on an innovative technology for wet separation of plastic wastes. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroni, M.; Lupo, E.; La Marca, F. Hydraulic separation of plastic wastes: Analysis of liquid-solid interaction. Waste Manag. 2017, 66, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Ge, X.; Chen, M. Waste-to-energy: Dehalogenation of plastic-containing wastes. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalargaris, I.; Tian, G.; Gu, S. The utilization of oils produced from plastic waste at different pyrolysis temperatures in a DI diesel engine. Energy 2017, 131, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, A.; Braccini, A.M.; Poponi, S.; Mosconi, E.M. A Meta-Model of Inter-Organisational Cooperation for the Transition to a Circular Economy. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Mishra, D.K. Thermolysis of waste plastics to liquid fuel. A suitable method for plastic waste management and manufacture of value-added products-A world prospective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, B.M.; de Marco, I.; Adrados, A.; López-Urionabarrenechea, A.; Solar, J.; Gastelu, N. Possibilities and limits of pyrolysis for recycling plastic rich waste streams rejected from phones recycling plants. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.; Hardesty, B.D.; Brooks, A.L.; Friend, T.; Teleki, K.; Fabres, J.; Beaudoin, Y.; Bamba, A.; Francis, J.; Ribbink, A.J.; et al. Challenges and emerging solutions to the land-based plastic waste issue in Africa. Mar. Policy 2017. In Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Klepacka, A.M.; Florkowski, W.J.; Braman, K. Determinants of recycling common types of plastic product waste in environmental horticulture industry: The case of Georgia. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradus, R.H.J.M.; Nillesen, P.H.L.; Dijkgraaf, E.; van Koppen, R.J. A Cost-effectiveness Analysis for Incineration or Recycling of Dutch Household Plastic Waste. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 135, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Pascucci, S. Institutional incentives in circular economy transition: The case of material use in the Dutch textile industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 155, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, Y.M.B.; Iritani, D.; Pavan, A.L.; Ometto, A. Theoretical contribution of industrial ecology to circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Key partners:
| Key activities:
| Value proposition:
| Customer relation:
| Customer segment:
|
Key resource:
| Distribution channel:
| |||
Cost structure:
| Revenue stream:
| |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horvath, B.; Mallinguh, E.; Fogarassy, C. Designing Business Solutions for Plastic Waste Management to Enhance Circular Transitions in Kenya. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051664
Horvath B, Mallinguh E, Fogarassy C. Designing Business Solutions for Plastic Waste Management to Enhance Circular Transitions in Kenya. Sustainability. 2018; 10(5):1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051664
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorvath, Balint, Edmund Mallinguh, and Csaba Fogarassy. 2018. "Designing Business Solutions for Plastic Waste Management to Enhance Circular Transitions in Kenya" Sustainability 10, no. 5: 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051664
APA StyleHorvath, B., Mallinguh, E., & Fogarassy, C. (2018). Designing Business Solutions for Plastic Waste Management to Enhance Circular Transitions in Kenya. Sustainability, 10(5), 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051664







