Abstract
Given the growing intent to prevent decay in environmental management, the present study seeks to unearth the impact of corporate environmental strategy on employees’ voluntary environmental behavior by regulating or facilitating their perceived psychological green climate. Research problems and research questions are built on the essence of multiple theories—goal-setting theory, social identity theory, and social learning theory for grounding the research model. A total of 294 replies were collected through a self-administered survey from diverse industrial panoramas. We used structural equation modeling (SEM) analytics via AMOS-version 20.0 for measuring the hypothesized results. The study revealed that the corporate environmental strategy is displaying an insignificant direct influence on voluntary environmental behavior. However, the corporate environmental strategy indirectly influences, via the mediation effect, voluntary environmental behavior of employees through their psychological green climate perception. Directions for future research are recommended based on insights from the implications and limitations of the study.
1. Introduction
Natural environment conservation has become one of the most globally talked about issues for the last few decades, as environmental degradation is posing numerous risks and challenges to human society and eco-systems [1]. The recent report of the World Bank has revealed that Bangladesh, with the lowest air quality in the world, is positioned among the nations most highly affected by pollution and other environmental health risks, and urban pollution costs in Bangladesh is about US$ 6.50 billion a year, which is about 3.40% of the 2015 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) [2]. In the face of a deteriorating natural environment and depleting natural resources, business organizations all over the world are presciently striving toward enhanced environmental conscientiousness and stewardship [3,4]. In response to this initiative, innumerable organizations have kicked off formulating formal and informal corporate environmental strategies [5].
The concept of corporate environmental strategy stems from the broader concept of corporate-level strategy, which represents an organization’s strategy concerning the sustainable business-natural environment [6,7]. Generally, it integrates environmental issues into the strategic planning of a business organization and, specifically, into the improvement of products and services and business processes that reduce the negative impact on the environment [8,9]. Additionally, sound corporate environmental strategy optimizes different competitive indicators of an organization, such as growing sales revenue and strong brand development [10,11], increased profit margin, lower operating cost, enhanced competitive advantage, and desirable employee outcomes [12].
Emanating from an understanding of positive psychology, both individual and organizational intents must work hand in hand to effectively address environmental degradation. In line with the finding of Huang [13], which responded to environmental concerns from a broader perspective, corporate initiative and individual, it is more than essential for firms to encourage and eventually modify employee behavior toward pro-environmental behavior, so that such behavior can be integrated with overall organizational environmental goals [14]. Researchers stressed that the role of individual behavior is one of the most important determinants in the preservation of the environment [15]. Corporate environmental strategy leads to employees’ psychological green climate, which is defined as employees’ perception with cues concerning which sorts of behaviors are anticipated, cherished, and rewarded by their organization [6,16]. A favorable psychological green climate contributes inputs that facilitate employees to convert their green behavioral intentions into voluntary environmental behavior. Thus, organizations should incline to introduce and convey a sound corporate environmental strategy that employees recognize in terms of a strong psychological pro-environmental climate to promote voluntary environmental behavior [6]. We posit that the corporate strategy for the environment creates the perception of a psychological green climate in the organization that enhances employees’ voluntary environmental behavior to protect their living organism based on the comprehensive understanding of the goal setting theory, social identity theory, and social learning theory in an integrated way [1,5]. Henceforth, the following research questions (RQ) are proposed to address in this present pursuit:
- RQ1.
- Does corporate environmental strategy influence employees’ voluntary environmental behavior?
- RQ2.
- Does psychological green climate mediate the influence of corporate environmental strategy on employees’ voluntary environmental behavior?
Additionally, the present study is going to contribute in numerous ways. Firstly, we observed that previous studies have Western-bias [17]. Very little focus, if not negligible, is observed in developing nations and eastern cases. The present study happens in Bangladesh, which is an emerging economy in the South Asian Nations. Secondly, we do not notice a good representation from different industries in prior studies. Most of the studies were conducted in the hotel industry [18], IT firms [3], and universities [19]. In some cases, those replies were only from a single firm [20] while using convenience sampling [21]. We collected data from a good representation of all industries that negates the concern against the generalizability of the findings [22]. Finally, we used multivariate data analysis in a multi-level perspective that extends the previous studies’ findings [23] to the fact that employees’ voluntary environmental behavior is affected by multiple level factors [3,14,18].
2. Theoretical Background of the Study
While the main objective of the study is to explore the influence of corporate environmental strategy on employees’ environmental behavior; however, it also sets forth investigating the mediating effect of employees’ psychological green climate on the relationship between corporate environmental strategy and voluntary environmental behavior. Given the gravity of the relationship among corporate environmental strategy, psychological green climate, and employees’ voluntary environmental behavior from the essence of positive psychology, the current study envisions the conceptual framework based on three theoretical perspectives.
Firstly, the goal setting theory asserts that a specific and even challenging goal along with requisite feedback contributes to an accelerating outcome. The underlined study of the impact of corporate environmental strategy on voluntary environmental behavior is based on the ground of the goal-setting theory, which pays focus on setting the right goal for the organization, and that, when accepted, the predetermined goal results in the miraculous outcome, even in the case of a very difficult one [24]. The theory’s conceptualization can be candidly articulated to fit the model in a way that setting corporate environmental strategy will facilitate the psychological green climate of employees toward voluntary environmental behavior [25]. Henceforth, employees will feel safe and secured psychologically because of the prevailing corporate environmental strategy. Moreover, employees feel an obligation when they were assigned to specific goals that were set by themselves or organization or both.
Secondly, the social identity theory asserts a psychological association between organization and employees in an environmental management context [1]. The underlined theory sheds light on the tenet that, when an organization internalizes socially valued belongings and attributes; then, employees feel the compulsion to be identified with it [26]. According to this theory, an engaged employee toward the organization who has regard for environmental conservation is more likely to psychologically integrate it with the overall corporate environmental strategy of the organization. As per this theory, if an organization constitutes an environmental milestone to be realized, a socially identified employee with the organization will emulate and discharge a similar role that is in line with the corporate sanction.
Finally, the social learning theory postulates how the employees’ value or behavior changes over time through the imitation and modeling of other organisms [27]. The changed value or behavior happens through the observation from others or models that occurs from their priorities and preferences toward different objects, behaviors, or patterns [28]. In this response, Bandura [29] posited that social learning is the modeling or cognition through vicariously observing the phenomena in society. Thus, social learning is the consequences or changes in the responses or behaviors that are learned from the complex pattern of social behavior in the surrounding [30]. Guided by the corporate environmental strategy, an individual will deliberately internalize the environmental behavior of saving energy and environmental consumable, and therefore be proud of being a member of clean behavior.
Goal setting theory emphasizes the essence of having a corporate environmental strategy to affect employees’ deliberate environmental behavior. However, it fails to leap employees’ psychological transformation forward, such as how employees perceive the psychological environment to go or not go green. Social identity theory asserts how employees align them psychologically to identify with the corporate strategy. In response to the prevailing corporate environmental strategy, they feel an urgency to act in line with the former identifying them as a pro-environmentalist. Furthermore, social learning theory delineates that the presence of perceived psychological green climate due to the institutionalization of corporate environmental strategy establishes that pro-environmental behavior is a value to the firm and employees. Henceforth, the employees learn from both corporate environmental strategy and perceived green climate to behave in an environmental friendly way. Thereby, we design all of the hypotheses based on the empirical relevance of prior studies and the theoretical grounding from the interventions of goal setting theory, social identity theory, and social learning theory.
3. Literature Review
3.1. Corporate Environmental Strategy
The dynamic capability of crafting and executing a corporate environmental strategy is that it sustainably creates and captures the value to the future, i.e., competitive advantage, which, in turn, transforms a firm into the sustainable one in long-term in terms of profitable and successful performance [31,32]. In a resource-based view, Wernerfelt [33] advocated that, in formulating a corporate strategy, a firm must look, not only at core resources disposition, but also provide insight into the various aspect of their applicability. Surprisingly, the resource-based view fails to spot the comprehensive understanding of a firm’s competitive positioning, as the former does not integrate corporate strategy with the firm’s ecological paradigm, which is a vital component nowadays [34]. To the contrary, natural-resource-based aims at integrating resource-based view with environmental issues and concerns while incorporating a corporate environmental strategy to accomplish organizational sustainability. Epstein and Roy [35] epitomized the various aspects of a corporate environmental strategy, such as developing environmental program-oriented standards, applying environmental assessment criteria, deciding on getting an environmental certification, setting environmental objectives for facilities, and allocating required resources for implementing the selected programs. Again, following the tenet of dynamic capability, a firm must formulate a vital environmental strategy to keep it valid and sustainable at any harsh reality or any change [32].
3.2. Psychological Green Climate
The psychological climate is considered as a dominant contextual antecedent of impacting individual attitude and behavior in the field of organizational and environmental psychology [6,22]. The concept “psychological green climate” applies to organizations that attain sustainable goals and objectives through incorporating a wide array of environmentally friendly policies [4,36]. Norton et al. advanced the idea of the psychological green climate that represents employees’ shared realization and understanding about their organization’s guidelines, processes, and actions regarding ecological sustainability that reflects organizational green values, in tribute to earlier studies on organizational climate, green climate, and psychological climate [6,14]. Norton, Zacher, and Ashkanasy [16] delineated the psychological green climate of employees, which consists of green work climate cognizance of the organization and green work climate interpretations of colleagues. A study that was conducted at the individual level, focusing on psychological green climate, has revealed that a positive psychological green climate has significant influence on employees’ in-role green behavior and extra-role green behavior [14]. It holds that, if employees share everything similarly that an organization does, the former will deliberately follow the envisioned goal and strategy by the later. Additionally, the psychological green climate regards the employees’ perception and interpretation of the organizational rules, policies, and strategies regarding the corporate greenization [22]. Employees with the perception of corporate environmental strategy are motivated to engage in autonomous environmental behavior [6].
3.3. Voluntary Environmental Behavior
Although voluntary environmental behaviors in non-business settings are well studied, management scholars have started exploring the antecedents of voluntary environmental behavior in the business arena recently [3]. It involves individual initiative and goes beyond expectations about the sustainability of the natural environment [16]. The broad construct of voluntary environmental behavior refers to the work behavior that is consciously displayed by employees at any organizational level, directed toward conserving and/or improving the natural environment and making an inhabitable planet for the future generation by reducing resource consumption, saving energy, avoiding wastage production, recycling, and conserving water [37,38,39]. It involves prudential eco-friendly behavior that is not mentioned in the job description, and such corporate environmental citizenship behavior ensures the environmental sustainability of an organization, but they are out of control of any official environmental management system [3]. Recent studies show several antecedents predicting voluntary environmental behavior [3]. Organizational supports, such as corporate initiative for greenization, and corporate advocacy, and contextual factors, such as the organizational climate and green psychological climate, are worth mentioning [3,14,22].
4. Development of the Hypothesis
4.1. Corporate Environmental Strategy and Voluntary Environmental Behavior
An organization’s success in introducing and implementing corporate environmental strategy largely relies on personal beliefs and the behavior of employees [4]. Corporate environmental strategy improves employees’ commitment toward the organization, voluntary environmental behavior, as well as the organization’s performance on environmental protection [1]. According to Norton et al. (2014), if an employee observes the presence of sustainable environmentally-responsive strategy, then it conveys a perceived signal that the company recognizes behavior that protects or benefits the natural environment [16]. It can be theorized via social identity theory that an employee will be fascinated to get attached to the organization by replicating voluntary environmental behavior [26,40]. The underlying merit of well-informed corporate environmental strategy is the generation of a favorable organizational climate, which, in turn, instigates employees to demonstrate voluntary environmental behavior [21]. Social learning theory also epitomizes that the creation of corporate environmental strategy is greatly imperative for an organization, since it allows its employees to feel proud about their organizations’ role-playing in the conservation of the environment, which encourages both employees’ commitment toward organizations and voluntary environmental behavior, resulting in the prosperous environmental performance of organizations [1]. Furthermore, the corporate environmental strategy also influences voluntary environmental behavior [14]. To conclude, we expected that corporate environmental strategy is positively related to voluntary environmental behavior and point the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Corporate environmental strategy influences voluntary environmental behavior.
4.2. Corporate Environmental Strategy and Psychological Green Climate
Well-formulated and well-circulated corporate environmental strategies are perceived to be a strong signal of organizational top-level support that positively affects the development of employees’ psychological climate to promote their involvement in improving the environmental performance of the company [36]. Concurrent literature on the psychological climate suggests that environmental strategies developed at any level–especially corporate environmental strategy, green transformational leadership, and individual green values are the important drivers that shape the psychological green climate of employees [22]. Therefore, employees’ regard for the organization’s corporate environmental sustainability is largely defined by the alignment of environmental issues with its strategies. Furthermore, Dumont, Shen, and Deng [14] and Norton, Zacher, and Ashkanasy [16] explored that the well-informed and perceived presence of the organization’s corporate environmental strategy directly or indirectly influences the psychological green climate. In connection with the statement above, we state the second hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Corporate environmental strategy impacts psychological green climate.
4.3. Psychological Green Climate and Voluntary Environmental Behavior
The psychological climate is a prodigal estimator of human behavior [41]. At the individual level of study, the psychological green climate has a significant influence on task-related environmental behavior and voluntary environmental behavior [14]. As Raineri and Paillé [21] asserted, if employees observe that conservation of the natural environment is valued, rewarded, and encouraged in their organization, then a deep sense of individual psychological green climate will be emerged and strengthened, and will thus be reflected through the displaying a high level of voluntary environmental behavior. Therefore, when an organization creates and nurtures a harmonious psychological green climate, it provides a strong sense of conviction that voluntary environmental behavior is safe, sound, and encouraged [22]. Similarly, Norton et al. (2017) found that, if employees perceive a strong psychological green climate, then the positive relationship between employees’ green behavioral intentions and employees’ next-day green behavior gets stronger [6]. Therefore, we introduce the third hypothesis according to the above discussion:
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
The psychological green climate influences voluntary environmental behavior.
Goal setting theory leaps forward conceptualization that the prevalence of corporate environmental strategy directly facilitates employees’ voluntary environmental behavior [14,21,42]. Similarly, the corporate environmental strategy contributes to the upliftment of perception and interpretation of employees toward corporate greenization. Henceforth, perceived organizational support through the development of corporate environmental strategy feeds to the enhancement of employees’ psychological climate toward corporate greenization [22,43]. Besides, prior research in management psychology and environmental psychology also documents that psychological green climate is a dominant contextual factor and the perceived presence or absence accelerates/inhibits the employees’ voluntary environmental behavior [6,14,22]. Thus, it is empirically evident that corporate environmental strategy influences psychological green climate [22], which, in consequence, results in voluntary environmental behavior [6]. It was also theorized by the extant study that corporate environmental strategy, directly and indirectly, influences employees’ voluntary environmental behavior [14]. Thus, it can be synthesized that psychological green climate mediates the influence of corporate environmental strategy on employees’ voluntary environmental behavior. To conclude, we posit our final hypothesis:
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
The influence of corporate environmental strategy on employees’ voluntary environmental behavior is mediated by psychological green climate.
The following research model (Figure 1) is proposed drawing on the empirical observations and essence from the theoretical underpinning of goal-setting theory, social learning theory, and social identity theory:
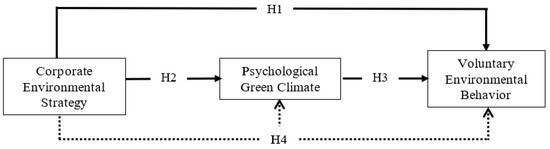
Figure 1.
Research Framework.
5. Research Methods
5.1. Participants
In order to obtain the primary data, both operational and functional level full-time employees working in a wide range of industries—steel, cement, ship-builder, ship-breaker, fertilizer, garments, tobacco, and consumer goods in Chattogram, Bangladesh—were taken into consideration as the population. The participation of the respondents was voluntary. Researchers personally visited the respondents’ workplace during office hours and delivered structured questionnaires along with 72 statements, in which no name or credentials were required to be disclosed, were distributed to a total of 440 employees between January and February 2019. 311 replies, out of those questionnaires, were received, which amounts to a 70.68% response rate. Of the remaining, 17 responses were excluded in the final data cleansing/screening process because of insufficiency or the incompleteness of answer, thus yielding the final sample size to be fixed to 294 executives.
5.2. Sample Characteristics
Table 1 depicts the demographic information of the sample respondents (n = 294) i.e., (age, gender, work experience, educational qualification, and organization size) and their respective frequency. The respondents were requested to categorize the responses about their company’s corporate environmental strategy, psychological green climate, and voluntary environmental behavior. Of the final 294 respondents, 249 respondents (85%) were male, while 45 (15%) were female. The age of respondents ranged between 22 to 58 years, with an average age of 35.62 years and it was largely varied with 28%, 52%, 16%, and 4% being above 20, 30, 40, and 50 years old, in respect. In addition, the mean value of job experience of respondents was 9.98 years and a total of 71, 66, 99, and 58 respondents described their tenure experiences more than 1, 6, 11, and 15 years, respectively. Moreover, the respondents were highly educated: 165 (56%) designated a master degree as their highest education, 81 (28%) hold a bachelor degree, and 48 (16%) expressed other degrees, i.e., diploma degree. Finally, 102 respondents (35%) served companies with below 500 employees, 96 respondents (33%) worked for companies with 500–1000 employees, 70 respondents (24%) served companies with 1000–5000 employees, and 26 (9%) for companies that employed more than 5000 employees.

Table 1.
The Demographic profile of respondents.
5.3. Response Bias
Response bias is a common phenomenon that limits the generalizability of findings [44,45]. To prevent this concern, the authors took several precautionary measures. First, the respondents were assured of the privacy and confidentiality of their replies. They were also confirmed that the received data is only for academic use and will report on the overall industrial scenario. Respondents’ anonymity warrants accurate response that is free from social desirability bias [46]. Second, we made few changes to items representing a construct for making them understandable to informants. If the respondents do not understand the content of the statements, then they reply without understanding the questions. Content validity is demanded, yielding accurate response [47]. Third, we run the Harman’s one-factor test to scrutinize the variance that is explained by the factors. Estimates displayed that not a single factor explains more than 50% of the total variance. Finally, the correlation matrix is examined if there is any correlation that is above 0.90 between any two constructs. The highest correlation between any two is 0.690 (corporate environmental strategy and psychological green climate), which demonstrates a score of less than the minimum threshold [48].
5.4. Measurement Tools
We used survey measures from prior studies. Corporate environmental strategy is measured while using a construct that was developed by Ramus and Steger [36]. Two items were deleted due to the poor loading and the standardized regression weight. We adopted the psychological green climate construct that was used by Norton, Zacher, and Ashkanasy [16]. Finally, for measuring voluntary environmental behavior, we used the survey measure that was developed by Frese, et al. [49]. One item from this measure is also deleted from this construct, owing to the poor loading and standardized regression weight. Appendix A (Table A1) represents the items of all the measurement tools.
6. Findings
6.1. Model Evaluation
The present study applied structural equation modeling (SEM) to ensure the robustness and authenticity of the underlying model. The SEM is considered to result in an accurate estimation of the estimates of an integrated model [46,50,51]. The SEM is commonly used in the management science discipline [52,53]. It tested the observed model while using both the measurement model and structural model evaluation with a sample case of the bootstrapping method. We used AMOS version 20.0 to test both the measurement model and the structural model.
6.2. Measurement Model Evaluation
The measurement model tested confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) [54]. It tested whether the representing items truly represent the subject variables. The model shows a better fit model [χ²(113) = 269.86, CMIN/DF = 2.388, p = 0.000; GFI = 0.906, CFI = 0.948, TLI = 0.93, RMSEA = 0.069], which are above the minimum cut off value [55,56]. We also checked reliability and validity issues, cross-loading, and model fitness tests. Composite reliability, convergent validity, and discriminant validity are common estimators featuring reliability and validity concerns. Table 2 exhibits that the minimum composite reliability of any construct is 0.811 (>0.71) and the minimum average variance extracted (AVE) is 0.580 for the psychological green climate, which is also above the minimum threshold limit [57,58]. Discriminant validity is tested in Table 2 through the diagonal line among the latent variables, and it is found that the square root of the AVE of any variable is higher than their correlation with other variables. Figure 2 demonstrates the CFA analysis and estimates on their loading.

Table 2.
The criterion for validity in a correlation matrix.
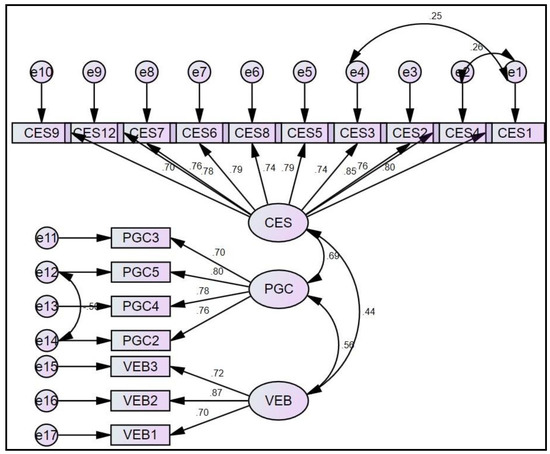
Figure 2.
Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) along with their item loading.
6.3. Structural model evaluation
We have used multiple criteria to evaluate the strength of the structural model. Henceforth, we scrutinized the model fit index, path estimates (β) along with their significance levels (p-value), and the coefficient of determination (R2). The estimated model fit indices show a very good fit [χ²(180) = 396.661, CMIN/DF = 2.204, p = 0.000; GFI = 0.887, CFI = 0.939, TLI = 0.929, RMSEA = 0.064] [55,56]. β- and R2-value were showed to be candidly good in line with the thresholds mentioned in Cohen [59]. According to Cohen [59] and Cohen [60], a score of larger than 0.12 for both β and R2 is satisfactory. Figure 3 demonstrates that only one path (βCES → VEB = 0.11) is less than 0.12, and the coefficient of determination for both cases is above 0.40 (i.e., R2PGC = 0.48, and R2VEB = 0.41), which is excellent [59,60]. Since the control variables other than gender are found to be significant in the correlation table (2), we also measured their effects on VEB. Interestingly, they are found to also be significant. The excerpts showed that age and education negatively impacts employees’ voluntary environmental behavior. However, tenure and size of the firm positively influence voluntary environmental behavior.
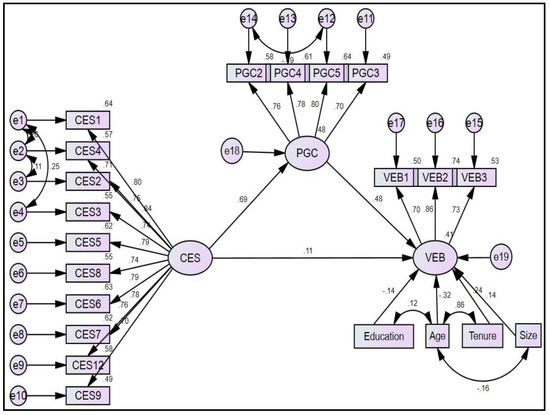
Figure 3.
Structural model.
7. Result and Discussion
7.1. Result
We have no concern to proceed for testing the hypothesized results since estimates on the structural model and measurement model are satisfactory. Table 3 revealed the results of our propositions. We proposed in H1 that the corporate environmental strategy significantly predicts employees’ voluntary environmental behavior. The given table displayed that the estimated results that are derived for H1 is not significant [β = 0.114, tstatistics = 1.377, p = 0.168(>0.05)]. Hence, our proposed hypothesis, H1, is not supported. In H2, we hypothesized that there is a significant impact of corporate environmental strategy on psychological green climate. The estimates realized are exhibiting that the effect is significant (β = 0.691, tstatistics = 9.595, p < 0.000). Thus, the result supports our H2, i.e. H2 is accepted. Finally, we also proposed in H3 that psychological green climate positively impacts voluntary environmental behavior. The results demonstrated that this effect is also significant (β = 0.481, tstatistics = 5.194, p < 0.000). Therefore, H3 is also supported.

Table 3.
Testing the hypotheses.
H4 hypothesized that psychological green climate mediates the influence of corporate environmental strategy on voluntary environmental behavior. We examined the testing of the mediation effect on the influence of corporate environmental strategy on voluntary environmental behavior before and after mediation in response to this hypothesis [52,61]. We observed that a direct effect (c) before adding the mediating effects demonstrates the highly significant influence. However, when we added mediator variables, we detected that the previously significant path (c) now becomes insignificant. According to the theory of mediation analysis, the previously significant direct effect (c) must either disappear (full mediation) or be significantly reduced (for partial mediation) to have mediation effects [46,52,61]. Table 4 depicted that the previous significant direct effect (c) (β = 0.443, tstatistics = 6.667, p < 0.163) turns into an insignificant direct effect (c/) (β = 0.114, tstatistics = 1.377, p < 0.163) meaning that the significant indirect effect (CES → PGC → VES) makes the direct effect insignificant. The coefficient of determination has also been increased from 0.296 (R2) to 0.477 (ΔR2 = 0.181). We also run the Sobel [62] test to rationalize the decision of the significance of the mediation effect. The estimates reported that the indirect effect is significant (z-statistics = 4.624, p < 0.000). Hence, there is a full mediation of effect psychological green climate. Hence, H4 is supported.

Table 4.
Result of mediation (PGC as a mediating variable).
7.2. Discussion
A mounting interest among management scientists and environmental scientists is observed on unearthing the role of corporate environmental strategy in shaping human behavior at work. In the present study, a model is developed and empirically tested whether the corporate environmental strategy has a significant influence on psychological green climate. Firstly, incoherent with our prediction, the result implied that there is no significant direct influence [β = 0.114, tstatistics = 1.377, p = 0.168 (>0.05)] of corporate environmental strategy on voluntary environmental behavior, which, in consequence, rejects H1. This result contradicts the early findings, and the notion of goal setting theory, the presence of corporate environmental strategy has a positive direct effect on the voluntary environmental behavior [16]. It means that the pertinence of voluntary environmental behavior does not exclusively rely on the developing corporate environmental strategy. Accordingly, it can be argued that introducing corporate environmental strategy alone may be a prolific and efficient means to persuade psychological green climate of employees in name only.
However, as consistent with previous research on environmental management [6,14], we discovered that the corporate environmental strategy is a vital predictor of psychological green climate [(β = 0.691, tstatistics = 9.595, p < 0.000)]. Therefore, H2 is supported. This result also gives similar results with the study of Dumont, Shen, and Deng [14]. It happens because natural environmental consideration in formulating organizational long-term strategic goals and objectives conveys a positive psychological signal toward employees where eco-friendly behavior and eco-initiatives will not be reprimanded, thus resulting in a congenial psychological green climate. Furthermore, the result is found to be consistent with the conceptualizations of goal setting and social learning theories. In line with the conceptualizations from these theories, employees are inclined to internalize the psychological green climate once they notice that the organization has a corporate environmental strategy to protect the planet [24,25,27,30].
The result of the study indicates that the psychological green climate is also positively impacting voluntary environmental behavior [(β = 0.481, tstatistics = 5.194, p < 0.000)], yielding the acceptance of H3 [14,21]. The reason behind this result is that employees’ psychological green climate plays a significant role in shaping voluntary environmental behavior. That is, employees with a positive psychological green climate toward the protection of environment tend to demonstrate significantly more voluntary environmental behavior that goes beyond their job requirements. Because, having observed their organization’s strategic decision toward reducing ecological problems or the preservation of the natural environment, a conducive psychological green climate is supposed to have emerged, which drives employees to exhibit environmental behavior and undergo a great sense of positive individual environmental stewardship. It goes in line with the observation of social learning theory to the fact that individuals incline to nurture what they have learned from their surroundings [27,30]. Social identity theory also supports this, which underscores that employees try to get attached or identical with corporate goals [26]. In response to it, individuals are psychologically transformed into deliberate contributors to discharge voluntary environmental behavior to align themselves with corporate aims.
Finally, we hypothesized in H4 that psychological green climate mediates the influence of corporate environmental strategy on voluntary environmental behavior. The studied result depicts that, after adding the mediating variable previously assumed be a significant direct effect (without a mediator), it turned insignificant. It signifies that the existence of psychological green climate expedites the influences of corporate environmental strategy on voluntary environmental behavior. The findings of Dumont, Shen, and Deng partially support this result [14]. This hypothesized relation is also advanced with the observations of social identity theory [26], goal setting theory [25], and social learning theory [27,30], as we have figured out that employees desire to be identical with the organization’s corporate goal and also serve and facilitate the firm in the way their surroundings desire them.
8. Conclusions
The ultimate success of corporate environmental strategy hinges upon the free and spontaneous pro-environmental behaviour of employees at their workplaces. We paid attention to investigate how corporate environmental strategy encourages employees’ voluntary environmental behavior by creating a strong sense of psychological green climate. The findings revealed that the corporate environmental strategy significantly explains the psychological green climate, which, in turn, enhances voluntary environmental behavior, like engaging in energy-saving behavior, waste reduction behavior, and resource recycling behavior. The result sheds light on the accurate crafting of corporate environmental strategy for building an enthusiastic pro-environmentalist in the workplace. It also lens on the articulating employees’ positive perception, impression, and interpretations of corporate initiative into implementable action programs in an environmentally friendly way. Finally, to elicit the most complete benefit in terms of autonomous environmental behavior, organizations are demanded not only to formulate a realistic corporate environmental strategy, but also instil and circulate a pessimistic glimpse of these green initiatives among the ultimate performers.
8.1. Theoretical Contributions
The current study contributes to advancing the knowledge-base and to adding empirical evidence in the literature of environmental psychology and management psychology through exploring corporate and individual environmental initiatives. Until today, there is an exponential growth of studies regarding environmental behavior. However, this research contributes to business practices, industries, and academia in a numerous ways. First, prior studies noted various environmental initiatives on corporate policy [8], strategy [36], sustainable policy [16], sustainable corporate strategy [31], and environmental management practices [31]. Surprisingly, none of them demonstrated how individual pro-environmental behavior is improved through the facilitation of workplace psychological climate. Hence, the present study showed how corporate environmental strategy facilitates voluntary environmental behavior through the mediation of psychological green climate. Second, inconclusive findings and conclusions from the mediation and moderation estimates of previous studies, such as Norton, Zacher and Ashkanasy [16], Dumont, Shen, and Deng [14], and Zhou, Zhang, Lyu, and Zhang [22] motivate us to test the mediation effect of the psychological green climate. Accordingly, our estimates showed that psychological green climate fully mediates the impact of corporate environmental strategy on voluntary environmental behavior. Third, extant literature showed that most of the previous studies has some concerns on their generalizability, because some studies include only one firm [14,63,64], while many others include a particular industry, such as education [21,22], hotel [1,18], packaging [14], service [6,65], state-owned enterprise [66], IT, and construction firms [3]. To draw an accurate insight of the result, we ensured a good representation from multiple industries. Finally, a quick preview of the previous research draws an impression that there is an Western-bias in research, because very few (particularly in China) are available in other than Western countries [1,40]. Most of the researchers recommend studying in the other context or countries for ensuring the external validity of the used construct. Thus, the present study will add empirical interpretation in the Bangladesh context.
8.2. Managerial Implications
The empirical research findings of the study provide critical insights for the organizations that are committed to encouraging and nurturing voluntary environmental behavior, which is unofficial and unrewarded, but morally appreciated. Firstly, the corporate environmental strategy has a greater impact on building the psychological green climate perception in the employees’ mind and thereby ensures voluntary environmental behavior at work. Accordingly, it is important for the organizations to publish environmental policies, reports, provide environmental training to employees, and transmit environmental targets in reducing the use of toxic-chemicals, non-reusable resources, etc. As a result, employees’ informed perception and logical interpretation of the organizational decisions and actions for environmental sustainability will foster building a green psychological climate. Secondly, employees’ psychological green climate also plays a vital role in forming voluntary environmental behavior. This conclusion suggests that organizations should take necessary steps in upholding a positive psychological green climate of employees. Positive impression and interpretation regarding the environmental initiatives of the organization will result in more voluntary environmental behavior. Ultimately, a comprehensive and dominant corporate environmental strategy is required to be sustainably developed and efficiently disseminated to employees, so that they will have a strong psychological green climate that exhibits more sustainable voluntary environmental behaviour. Finally, apart from the workplace, voluntary environmental behavior has caught attention among educators. In this regard, academia and administrators of educational institutes must exhibit their positive concerns toward the minimal use of paper, electricity saving, and recycling of used resources. Furthermore, more and more research is demanded from academia regarding minimizing the consumption of resources and accelerating the conservation of earthen resources.
8.3. Limitations and Future Research Direction
The present study inherently contains numerous theoretical and empirical significances. However, it can not deny its self-containing limitations from research design and sample design, and conditioning that is based on a mediation model alone. Future researchers must employ a mixed method of research by employing an appropriate sampling design. Another distinct limitation is the use of cross-sectional data, which might prevent the generalization of the findings that were derived from the present study. Thus, it is likely that the use of both interview or longitudinal data can prevent future researchers from the concerns of generalizability of the result. Despite the present study using multiple theories to ground the model, it still lacks the multi-level perspective of understanding voluntary environmental behavior. Thus, we recommend future researchers to depict the model in a multi-level analysis. Finally, we have tested the regression model through the use of a mediated model. Interestingly, the effects of confounding factors or intervening factors on the models above were not adequately studied. The study suggests that future researchers will focus on the identification and application of moderator variables, i.e., ethical leadership, environment role, and environmental norms, and eco-helping.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.D., S.R.B., M.M.A.K.J. and M.A.U.; methodology, M.A.U.; validation, A.K.D., S.R.B. and M.M.A.K.J.; formal analysis, M.A.U.; investigation, A.K.D., S.R.B. and M.M.A.K.J.; data curation, A.K.D., S.R.B. and M.M.A.K.J.; writing—original draft preparation, S.R.B. and M.A.U.; writing—review and editing, A.K.D., S.R.B., M.M.A.K.J. and M.A.U.; supervision, M.A.U.; funding acquisition, A.K.D. and M.M.A.K.J.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Measurement tools.
Table A1.
Measurement tools.
| Corporate Environmental Strategy, Ramus and Steger [36] |
| My company publishes an environmental policy |
| My company has specific targets for environmental performance |
| My company publishes an annual environmental report |
| My company uses an environmental management system |
| My company applies environmental considerations in purchasing decisions |
| My company provides environmental training to employee |
| My company makes employees responsible for company environmental performance |
| My company uses life cycle analysis of products/services |
| My company’s management understands/addresses issue of sustainable development |
| My company systematically reduces use of toxic chemicals/fuel |
| My company applies the same environmental standards anywhere |
| Psychological Green Climate, Norton, Zacher and Ashkanasy [16] |
| My company is interested in supporting environmental degradation causes |
| My company believes that it is important to protect the environment |
| My company is concerned with becoming more environmentally friendly |
| My company would like to be seen as environmentally friendly |
| Voluntary Environmental Behavior, Frese, Fay, Hilburger, Leng and Tag [49] |
| I take chance to get actively involved in environmental protection at work |
| I take initiative to act in environmentally-friendly ways at work |
| I do more for the environment at work than I was expected to |
References
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, W.G.; Choi, H.-M.; Phetvaroon, K. The effect of green human resource management on hotel employees’ eco-friendly behavior and environmental performance. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 76, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WB. Enhancing Opportunities for Clean and Resilient Growth in Urban Bangladesh: Country Environmental Analysis 2018; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.; Kim, Y.; Han, K.; Jackson, S.E.; Ployhart, R.E. Multilevel Influences on Voluntary Workplace Green Behavior: Individual Differences, Leader Behavior, and Coworker Advocacy. J. Manag. 2017, 43, 1335–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-J. Hotels’ environmental policies and employee personal environmental beliefs: Interactions and outcomes. Tour. Manag. 2014, 40, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L.; Barling, J. Greening organizations through leaders’ influence on employees’ pro-environmental behaviors. J. Organ. Behav. 2013, 34, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T.A.; Zacher, H.; Parker, S.L.; Ashkanasy, N.M. Bridging the gap between green behavioral intentions and employee green behavior: The role of green psychological climate. J. Organ. Behav. 2017, 38, 996–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón-Correa, J.A.; Sharma, S. A Contingent Resource-Based View of Proactive Corporate Environmental Strategy. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2003, 28, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.B. Corporate environmental strategies and actions. Manag. Decis. 2001, 39, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraj-Andrés, E.; Martínez-Salinas, E.; Matute-Vallejo, J. Factors affecting corporate environmental strategy in Spanish industrial firms. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2009, 18, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo Wee, Y.; Quazi, H.A. Development and validation of critical factors of environmental management. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2005, 105, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.G.; Hong, P.; Modi, S.B. Impact of lean manufacturing and environmental management on business performance: An empirical study of manufacturing firms. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 129, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.A.; Hasnan, N.; Osman, N.H. Environmental issues and corporate performance: A critical review. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 2, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H. Media use, environmental beliefs, self-efficacy, and pro-environmental behavior. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, J.; Shen, J.; Deng, X. Effects of Green HRM Practices on Employee Workplace Green Behavior: The Role of Psychological Green Climate and Employee Green Values. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2017, 56, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy-Leboyer, C.; Bonnes, M.; Chase, J.; Ferreira-Marques, J.; Pawlik, K. Determinants of Pro-Environmental Behaviors. Eur. Psychol. 1996, 1, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T.A.; Zacher, H.; Ashkanasy, N.M. Organisational sustainability policies and employee green behaviour: The mediating role of work climate perceptions. J. Environ. Psychol. 2014, 38, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, G. Antecedents of employee electricity saving behavior in organizations: An empirical study based on norm activation model. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zientara, P.; Zamojska, A. Green organizational climates and employee pro-environmental behaviour in the hotel industry. J. Sustain. Tour. 2018, 26, 1142–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillé, P.; Mejía Morelos, J.H.; Raineri, N.; Stinglhamber, F. The Influence of the Immediate Manager on the Avoidance of Non-green Behaviors in the Workplace: A Three-Wave Moderated-Mediation Model. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderploeg, J.; Lee, S.-E. Factors Influencing Pro-Environmental Behaviors in Craft Businesses. Cloth. Text. Res. J. 2019, 37, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raineri, N.; Paillé, P. Linking Corporate Policy and Supervisory Support with Environmental Citizenship Behaviors: The Role of Employee Environmental Beliefs and Commitment. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 137, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, D.; Lyu, C.; Zhang, H. Does Seeing “Mind Acts Upon Mind” Affect Green Psychological Climate and Green Product Development Performance? The Role of Matching Between Green Transformational Leadership and Individual Green Values. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansla, A.; Gamble, A.; Juliusson, A.; Gärling, T. The relationships between awareness of consequences, environmental concern, and value orientations. J. Environ. Psychol. 2008, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, E.A.; Latham, G.P. New directions in goal-setting theory. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2006, 15, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, Y.; Slowik, L.H. Enriching Goal-Setting Theory with Time: An Integrated Approach. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2004, 29, 404–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajfel, H.; Turner, J. (Eds.) The Social Identity Theory of Intergroup Behavior; Nelson-Hall: Chicago, IL, USA, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 7–24. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, H.M. Social learning of work values in organizations. J. Appl. Psychol. 1978, 63, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S.K. Social Learning (Cognitive) Theory and Implications for Human Resource Development. Adv. Dev. Hum. Resour. 2004, 6, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social learning of moral judgments. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1969, 11, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.R.V.; Luthans, F. A Social Learning Approach to Organizational Behavior. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1980, 5, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, A. Modeling corporate sustainability strategy. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strateg. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernerfelt, B. A resource-based view of the firm. Strateg. Manag. J. 1984, 5, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.L. A Natural-Resource-Based View of the Firm. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1995, 20, 986–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.J.; Roy, M.-J. Implementing a corporate environmental strategy: Establishing coordination and control within multinational companies. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2007, 16, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramus, C.A.; Steger, U. The Roles of Supervisory Support Behaviors and Environmental Policy in Employee “Ecoinitiatives” at Leading-Edge European Companies. Acad. Manag. J. 2000, 43, 605–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocirlan, C.E. Environmental workplace behaviors: Definition matters. Organ. Environ. 2017, 30, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmuss, A.; Agyeman, J. Mind the Gap: Why do people act environmentally and what are the barriers to pro-environmental behavior? Environ. Educ. Res. 2002, 8, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T.A.; Parker, S.L.; Zacher, H.; Ashkanasy, N.M. Employee green behavior: A theoretical framework, multilevel review, and future research agenda. Organ. Environ. 2015, 28, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Dumont, J.; Deng, X. Employees’ perceptions of green HRM and non-green employee work outcomes: The social identity and stakeholder perspectives. Group Organ. Manag. 2018, 43, 594–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, D.M. Issues of level in organizational research: Multi-level and cross-level perspectives. Res. Organ. Behav. 1985, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkis, J.; Gonzalez-Torre, P.; Adenso-Diaz, B. Stakeholder pressure and the adoption of environmental practices: The mediating effect of training. J. Oper. Manag. 2010, 28, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillé, P.; Boiral, O.; Chen, Y. Linking environmental management practices and organizational citizenship behaviour for the environment: A social exchange perspective. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2013, 24, 3552–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, P.M. Common Method Bias in Marketing: Causes, Mechanisms, and Procedural Remedies. J. Retail. 2012, 88, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, N.P. Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2012, 63, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.A.; Mahmood, M.; Fan, L. Why Individual Employee Engagement Matters for Team Performance? Mediating Effects of Employee Commitment and Organizational Citizenship Behaviour. Team Perform. Manag. Int. J. 2019, 25, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.T.; Fan, L.; Uddin, M.A.; Abdul Kader Jilani, M.M.; Begum, S. Linking transformational leadership with employees’ engagement in the creative process. Manag. Res. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, P.A.; Liang, H.; Xue, Y. Understanding and mitigating uncertainty in online exchange relationships: A principal-agent perspective. MIS Q. 2007, 31, 105–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frese, M.; Fay, D.; Hilburger, T.; Leng, K.; Tag, A. The concept of personal initiative: Operationalization, reliability and validity in two German samples. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 1997, 70, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howladar, M.H.R.; Rahman, M.S.; Uddin, M.A. Deviant Workplace Behavior and Job Performance: The Moderating Effect of Transformational Leadership. Iran. J. Manag. Stud. 2018, 11, 147–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Uddin, M.A.; Das, A.K.; Mahmood, M.; Sohel, S.M. Do Transformational Leaders Engage Employees in Sustainable Innovative Work Behaviour? Perspective from a Developing Country. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Mahmood, M.; Uddin, M.A. Supportive Chinese supervisor, innovative international students: A social exchange theory perspective. Asia Pac. Educ. Rev. 2019, 20, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.; Uddin, M.A.; Luo, F. Influence of Transformational Leadership on Employees’ Creative Process Engagement: A Multi-Level Analysis. Manag. Decis. 2019, 57, 741–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W. Commentary: Issues and Opinion on Structural Equation Modeling. MIS Q. 1998, 22, vii–xvi. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T. Examining continuance usage of mobile Internet services from the perspective of resistance to change. Inf. Dev. 2014, 30, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.; Coughlan, J.; Mullen, M. Structural equation modelling: Guidelines for determining model fit. Electron. J. Bus. Res. Methods 2008, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, M.E. Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. Sociol. Methodol. 1982, 13, 290–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, L.M.; Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q. How transformational leadership and employee motivation combine to predict employee proenvironmental behaviors in China. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 35, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, V.; Wesselink, R.; Studynka, O.; Kemp, R. Encouraging sustainability in the workplace: A survey on the pro-environmental behaviour of university employees. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 106, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruepert, A.; Keizer, K.; Steg, L.; Maricchiolo, F.; Carrus, G.; Dumitru, A.; García Mira, R.; Stancu, A.; Moza, D. Environmental considerations in the organizational context: A pathway to pro-environmental behaviour at work. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2016, 17, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kura, K.M. Linking Environmentally Specific Transformational Leadership and Environmental Concern to Green Behaviour at Work. Glob. Bus. Rev. 2016, 17, 1S–14S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).