Algal Remediation of Wastewater Produced from Hydrothermally Treated Septage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Septage Feedstock Preparation
2.2. Algae Sepcies Identification
2.3. Algae Growth and Sampling
2.4. Raw and Remediated Process Water and Algal Sample Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toufiq Reza, M.; Freitas, A.; Yang, X.; Hiibel, S.; Lin, H.; Coronella, C.J. Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of cow manure: Carbon and nitrogen distributions in HTC products. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2016, 35, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, D.; Peng, C.; Liu, X.; Xu, G. Process characteristics of hydrothermal treatment of antibiotic residue for solid biofuel. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambaldorj, G.; Takahashi, M.; Yoshikawa, K. Liquid Fertilizer Production from Sewage Sludge by Hydrothermal Treatment. Available online: http://www.esi.nagoya-u.ac.jp/h/isets07/Contents/Proceedings/FinalManuscript/Session05/1121Ganchimeg.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- McGaughy, K.; Reza, M.T. Recovery of Macro and Micro-Nutrients by Hydrothermal Carbonization of Septage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhan, H.; Yin, X.; Wu, C. The transformation pathways of nitrogen in sewage sludge during hydrothermal treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekpo, U.; Ross, A.B.; Camargo-Valero, M.A.; Fletcher, L.A. Influence of pH on hydrothermal treatment of swine manure: Impact on extraction of nitrogen and phosphorus in process water. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, B.; Mumme, J.; Erlach, B. Anaerobic treatment of waste water derived from hydrothermal carbonization. In Proceedings of the 20th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, Milan, Italy, 18–22 June 2012; pp. 683–692. [Google Scholar]
- Baroutian, S.; Smit, A.M.; Andrews, J.; Young, B.; Gapes, D. Hydrothermal degradation of organic matter in municipal sludge using non-catalytic wet oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, W.; Dong, R. Two-phase anaerobic digestion of municipal solid wastes enhanced by hydrothermal pretreatment: viability, performance and microbial community evaluation. Appl. Energy 2017, 189, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.A.; Davey, M.P.; Dennis, J.S.; Horst, I.; Howe, C.J.; Lea-Smith, D.J.; Smith, A.G. Biodiesel from algae: challenges and prospects. Energy Biotechnol.—Environ. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Curtis, W.R. Proton stoichiometric imbalance during algae photosynthetic growth on various nitrogen sources: toward metabolic pH control. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherholz, M.L.; Curtis, W.R. Achieving pH control in microalgal cultures through fed-batch addition of stoichiometrically-balanced growth media. Bmc Biotechnol. 2013, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellebust, J.A.; Ahmad, I. Regulation of Nitrogen Assimilation in Green Microalgae. Biol. Oceanogr. 1989, 6, 241–255. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Hu, B.; Shi, A.; Ma, X.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Ruan, R. Cultivation of a microalga Chlorella vulgaris using recycled aqueous phase nutrients from hydrothermal carbonization process. Adv. Biol. Waste Treat. Bioconversion Technol. 2012, 126, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Raouf, N.; Al-Homaidan, A.A.; Ibraheem, I.B.M. Microalgae and wastewater treatment. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acién Fernández, F.G.; Fernández Sevilla, J.M.; Molina Grima, E. Costs Analysis of Microalgae Production. In Biofuels from Algae, 2nd ed.; Pandey, A., Chang, J.-S., Soccol, C.R., Lee, D.-J., Chisti, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 551–566. [Google Scholar]
- Abinandan, S.; Shanthakumar, S. Challenges and opportunities in application of microalgae (Chlorophyta) for wastewater treatment: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UTEX. Available online: https://utex.org/pages/search-results?q=2168 (accessed on 18 June 2019).
- Blair, M.F.; Kokabian, B.; Gude, V.G. Light and Growth Medium Effect on Chlorella Vulgaris Biomass Production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M.J.; Garcin, C.; van Hille, R.P.; Harrison, S.T.L. Interference by pigment in the estimation of microalgal biomass concentration by optical density. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 85, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Pollution Control Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-87553-047-5.
- Xin, L.; Hong-Ying, H.; Ke, G.; Ying-Xue, S. Effects of different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth, nutrient uptake, and lipid accumulation of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5494–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Min, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, R. Cultivation of Green Algae Chlorella sp. in Different Wastewaters from Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Chen, P.; Min, M.; Zhou, W.; Martinez, B.; Zhu, J.; Ruan, R. Characterization of a microalga Chlorella sp. well adapted to highly concentrated municipal wastewater for nutrient removal and biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5138–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanelas, I.T.D.; Ruiz, J.; Arbib, Z.; Chinalia, F.A.; Garrido-Pérez, C.; Rogalla, F.; Nascimento, I.A.; Perales, J.A. Comparing the use of different domestic wastewaters for coupling microalgal production and nutrient removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, S.J. Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus by Chlorella sorokiniana cultured heterotrophically in ammonia and nitrate. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, P.S.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Wong, Y.S. Effect of algal density on nutrient removal from primary settled wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 89, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducey, T.F.; Collins, J.C.; Ro, K.S.; Woodbury, B.L.; Griffin, D.D. Hydrothermal carbonization of livestock mortality for the reduction of pathogens and microbially-derived DNA. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gander, M.; Jefferson, B.; Judd, S. Aerobic MBRs for domestic wastewater treatment: a review with cost considerations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2000, 18, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhola, V.; Desikan, R.; Santosh, S.K.; Subburamu, K.; Sanniyasi, E.; Bux, F. Effects of parameters affecting biomass yield and thermal behaviour of Chlorella vulgaris. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
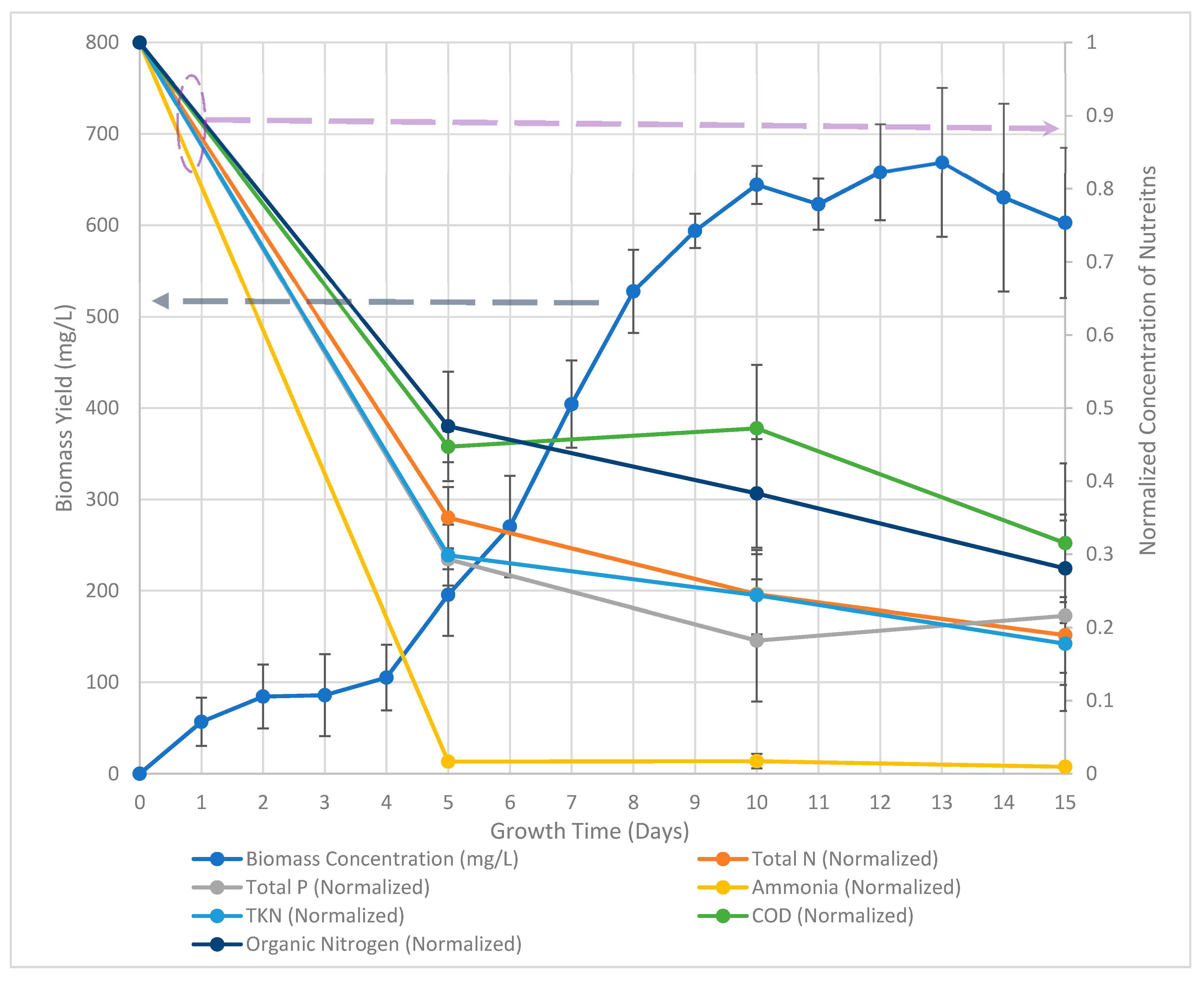
| Day | Biomass (mg/L) | Total N (mg/L) | TKN (mg/L) | NO3-N (mg/L) | NH3-N (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | Total P (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | 48.0 ± 0.3 | 38.7 ± 1.7 | 9.3 ± 1.3 | 14.5 ± 3.2 | 716 ± 4 | 1.05 ± 0.13 |
| 5 | 195.7 | 16.8 ± 2.1 | 11.6 ± 1.9 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 320 ± 20 | 0.31 ± 0.02 |
| 10 | 644.3 | 11.8 ± 2.7 | 9.5 ± 2.6 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 340 ± 60 | 0.18 ± 0.08 |
| 15 | 602.8 | 9.1 ± 2.5 | 6.9 ± 2.4 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 230 ± 80 | 0.24 ± 0.17 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McGaughy, K.; Abu Hajer, A.; Drabold, E.; Bayless, D.; Reza, M.T. Algal Remediation of Wastewater Produced from Hydrothermally Treated Septage. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123454
McGaughy K, Abu Hajer A, Drabold E, Bayless D, Reza MT. Algal Remediation of Wastewater Produced from Hydrothermally Treated Septage. Sustainability. 2019; 11(12):3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123454
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcGaughy, Kyle, Ahmad Abu Hajer, Edward Drabold, David Bayless, and M. Toufiq Reza. 2019. "Algal Remediation of Wastewater Produced from Hydrothermally Treated Septage" Sustainability 11, no. 12: 3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123454
APA StyleMcGaughy, K., Abu Hajer, A., Drabold, E., Bayless, D., & Reza, M. T. (2019). Algal Remediation of Wastewater Produced from Hydrothermally Treated Septage. Sustainability, 11(12), 3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123454






