A Bibliometric Analysis of Green Supply Chain Management Based on the Web of Science (WOS) Platform
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- This paper used a bibliometric method to analyze the trends and hot issues of green supply chain research. Compared with previous studies, this method can more directly reflect the main content of green supply chain research.
- (2)
- In the literature classification, we list nine categories, which helps readers understand and view the literature from different dimensions.
- (3)
- The strategic coordinate diagram is used to analyze the internal relationship between the themes and keywords of the current research on GSCM. This method has not been used in previous researches on green supply chain.
2. Data Sources and Analysis Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Analysis Method
3. Analysis of Document Characteristics of GSCM Research
3.1. Development Trend Analysis
3.2. Research Author Analysis
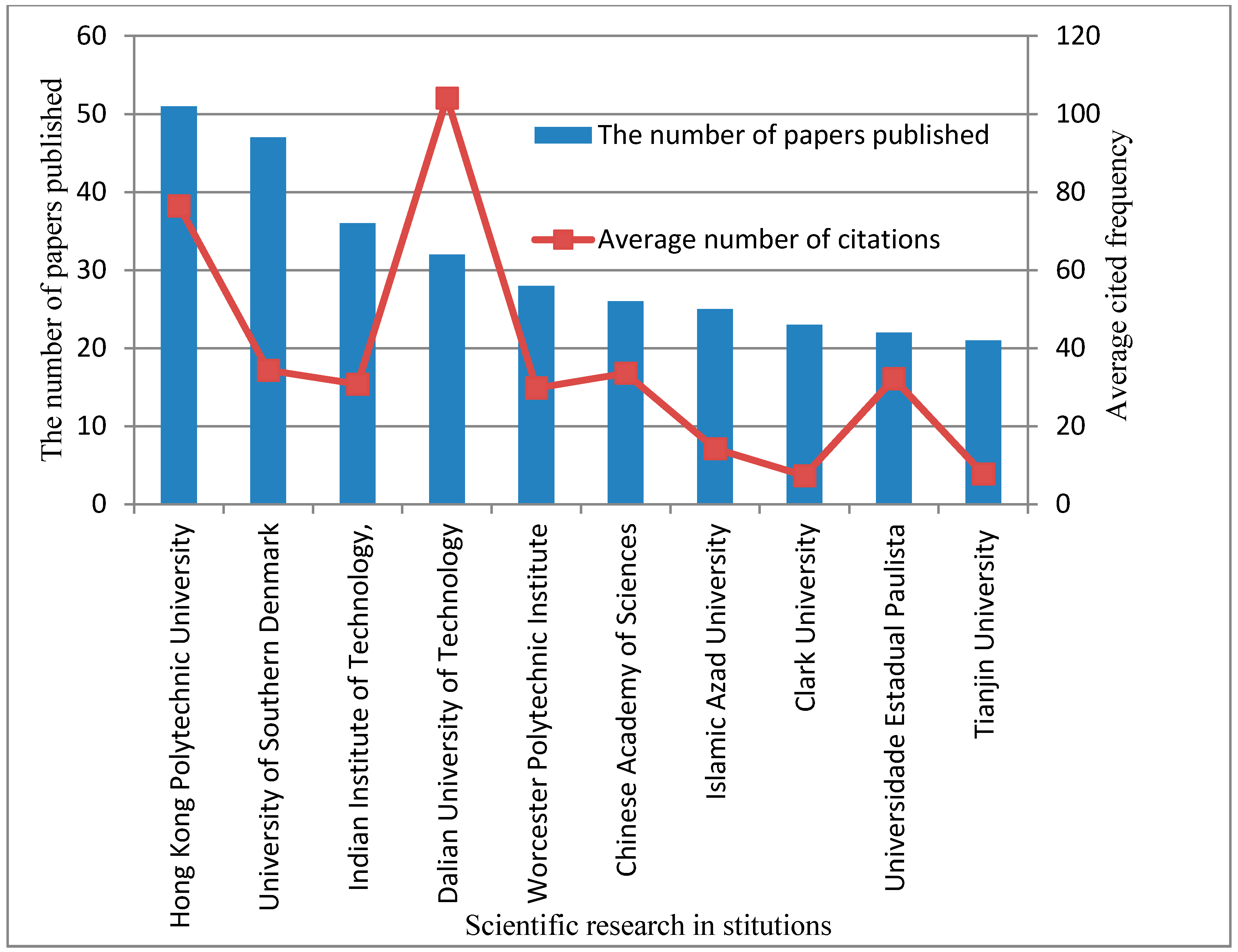
3.3. Analysis of the Research Institutions Affiliated with the Literature
3.4. Source of Literature and Analysis of Research Areas
3.5. GSCM Highly Cited Literature Analysis
4. Hotspots in GSCM Research
4.1. Co-Occurrence Keyword Visualization Analysis of Research Topics
4.2. Key Words Cluster Analysis in the Field of GSCM Research
4.3. GSCM Research Keywords Strategic Coordinate Graph Analysis
5. Conclusions and Suggestions for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sroufe, R.; Joseph, S. (Eds.) Strategic sustainability: The State of the Art in Corporate Environmental Management Systems; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Gong, R.F.; Zhao, L.J.; Ji, X.Q.; Xu, Y. A Green Supply-Chain Decision Model for Energy-Saving Products That Accounts for Government Subsidies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, L.; Akpınar, M.E.; Araz, C.; Ilgın, M.A. A green supplier evaluation system based on a new multi-criteria sorting method: VIKORSORT. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 114, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimnia, B.; Sarkis, J.; Davarzani, H. Green supply chain management: A review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 162, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badi, S.; Murtagh, N. Green supply chain management in construction: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-L.; Islam, M.S.; Karia, N.; Fauzi, F.A.; Afrin, S. A literature review on green supply chain management: Trends and future challenges. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, U.; Sroufe, R.; Kraslawski, A. Creativity enables sustainable development: Supplier engagement as a boundary condition for the positive effect on green innovation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimon, D. A Role of Quality in Creating a Green Supply Chain. Qual. Access Success 2016, 17, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J.; Lai, K.H. Institutional-based antecedents and performance outcomes of internal and external green supply chain management practices. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2013, 19, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Rahman, M.H.; Tumpa, T.J.; Moghul Rifat, A.A.; Paul, S.K. Examining price and service competition among retailers in a supply chain under potential demand disruption. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2018, 40, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyai, T.; Tamas, P. Optimization of Municipal Waste Collection Routing: Impact of Industry 4.0 Technologies on Environmental Awareness and Sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 16, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, T.; Giri, B.C. Two-way product recovery in a closed-loop supply chain with variable markup under price and quality dependent demand. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusi-Sarpong, S.; Gupta, H.; Sarkis, J. A supply chain sustainability innovation framework and evaluation methodology. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaway, A.P.; Wood, A.M.; Hedges, L.V. How to Do a Systematic Review: A Best Practice Guide for Conducting and Reporting Narrative Reviews, Meta-Analyses, and Meta-Syntheses. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2018, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira Gregorio, V.; Pié, L.; Terceño, A. A Systematic Literature Review of Bio, Green and Circular Economy Trends in Publications in the Field of Economics and Business Management. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, P.; Santoro, L.; Thomas, A. Environmental Sustainability in Third-Party Logistics Service Providers: A Systematic Literature Review from 2000–2016. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review. Br. J. Manag. 2003, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuring, S.; Müller, M.; Westhaus, M.; Morana, R. Conducting a Literature Review the Example of Sustainable Supply Chains; Springe: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Leydesdorff, L. Patterns of connections and movements in dual-map overlays: A new method of publication portfolio analysis. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 65, 334–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.; Hou, H.Y. Methods and Applications of Knowledge Mapping; People Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 11–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, J.; Balogh, P.; Oláh, J.; Kot, S.; Harangi Rákos, M.; Lengyel, P. Social Network Analysis of Scientific Articles Published by Food Policy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, P.D.; de Solla Price, D.; Griffith, B.C.; Moravcsik, M.J.; Stewart, J.A. Lotka’s Law: A Problem in Its Interpretation and Application. Soc. Stud. Sci. 1976, 6, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q.; Lai, K.H. An organizational theoretic review of green supply chain management literature. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 130, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q.; Lai, K.H. Examining the effects of green supply chain management practices and their mediations on performance improvements. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 1377–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, S.C. Sources of information on specific subjects. Engineering 1934, 137, 85–86. [Google Scholar]
- Vachon, S.; Klassen, R.D. Environmental management and manufacturing performance: The role of collaboration in the supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 111, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J.; Lai, K. Confirmation of a measurement model for green supply chain management practices implementation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 111, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.G.M.; Hong, P.; Modi, S.B. Impact of lean manufacturing and environmental management on business performance: An empirical study of manufacturing firms. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 129, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, M.; Govindan, K.; Sarkis, J.; Seuring, S. Quantitative models for sustainable supply chain management: Developments and directions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 233, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, R.; Bloemhof, J.; Mallidis, I. Operations Research for green logistics – An overview of aspects, issues, contributions and challenges. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 219, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassini, E.; Surti, C.; Searcy, C. A literature review and a case study of sustainable supply chains with a focus on metrics. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 140, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, C.; Sierra, V.; Rodon, J. Sustainable operations: Their impact on the triple bottom line. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 140, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageron, B.; Gunasekaran, A.; Spalanzani, A. Sustainable supply management: An empirical study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 140, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabat, A.; Govindan, K. An analysis of the drivers affecting the implementation of green supply chain management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahi, P.; Searcy, C. A comparative literature analysis of definitions for green and sustainable supply chain management. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 52, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, R.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Tien, F.C. Integration of artificial neural network and MADA methods for green supplier selection. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-W.; Hu, A.H. Applying hazardous substance management to supplier selection using analytic network process. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, N.P. Information Systems Innovation for Environmental Sustainability. Mis Q. 2010, 34, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pagell, M. Balancing priorities: Decision-making in sustainable supply chain management. J. Oper. Manag. 2011, 29, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J.; Lai, K. Green supply chain management implications for “closing the loop”. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2008, 44, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.-Y.; Chan, H.K.; Lettice, F.; Chung, S.H. The influence of greening the suppliers and green innovation on environmental performance and competitive advantage in Taiwan. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2011, 47, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lai, X.; Shi, N. A multi-objective optimization for green supply chain network design. Decis. Support Syst. 2011, 51, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyüközkan, G.; Çifçi, G. A novel hybrid MCDM approach based on fuzzy DEMATEL, fuzzy ANP and fuzzy TOPSIS to evaluate green suppliers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 3000–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.; Shankar, R.; Yadav, S.S.; Thakur, L.S. Supplier selection using fuzzy AHP and fuzzy multi-objective linear programming for developing low carbon supply chain. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 8182–8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Choy, K.L.; Ho, G.T.S.; Chung, S.H.; Lam, H.Y. Survey of Green Vehicle Routing Problem: Past and future trends. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 1118–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Klassen, R.D. Drivers and Enablers That Foster Environmental Management Capabilities in Small- and Medium-Sized Suppliers in Supply Chains. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2008, 17, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handfield, R.B. Green supply chain: Best practices from the furniture industry. Proc. Annu. Meet. Decis. Sci. Inst. USA 1996, 3, 1295–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Govindan, K.; Rajendran, S.; Sarkis, J.; Murugesan, P. Multi criteria decision making approaches for green supplier evaluation and selection: A literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 98, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sheyadi, A.; Muyldermans, L.; Kauppi, K. The complementarity of green supply chain management practices and the impact on environmental performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.K. Green supply-chain management: A state-of-the-art literature review. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2007, 9, 53–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Datta, P.P. Adoption of green supply chain management practices and their impact on performance: An exploratory study of Indian manufacturing firms. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 2085–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.H.; Feng, Y.T.; Choi, S.B. The role of customer relational governance in environmental and economic performance improvement through green supply chain management. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 155, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, F.E.; Cousins, P.D.; Lamming, R.C.; Faruk, A.C. The role of supply management capabilities in green supply. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2001, 10, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, W.B. The Mapping Knowledge Domains Based on Chinese Emotion Regulation Hotspots of Recent Decade. Psychol. Res. 2011, 4, 56–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.; Bauin, S.; Courtial, J.; Whittaker, J. Policy and the mapping of scientific change: A co-word analysis of research into environmental acidification. Scientometrics 1988, 14, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Jeong, Y.-I. Mapping Korea’s national RD domain of robot technology by using the co-word analysis. Scientometrics 2008, 77, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deif, A.M. A system model for green manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jansen, J.P.; Van Den Bosch, F.A.; Volberda, H.W. Exploratory innovation, exploitative innovation, and performance: Effects of organizational antecedents and environmental moderators. Manag. Sci. 2006, 52, 1661–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.B. The Cost of Regulation: OSHA, EPA and the Productivity Slowdown. Am. Econ. Rev. 1987, 77, 998–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Stavins, R.N. Dynamic Incentives of Environmental Regulations: The Effects of Alternative Policy Instruments on Technology Diffusion. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1995, 29, S43–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoie, P.; Patry, M.; Lajeunesse, R. Environmental regulation and productivity: Testing the porter hypothesis. J. Prod. Anal. 2008, 30, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsidisin, G.A.; Siferd, S.P. Environmental purchasing: A framework for theory development. Eur. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2001, 7, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, V.; Lenny Koh, S.C.; Baldwin, J.; Cucchiella, F. Natural resource based green supply chain management. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2012, 17, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hazen, B.T.; Cegielski, C.; Hanna, J.B. Diffusion of green supply chain management. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2011, 22, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarzadeh, A.; Fahimnia, B.; Rastegar, S. Green and Resilient Design of Electricity Supply Chain Networks: A Multiobjective Robust Optimization Approach. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2019, 66, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ye, H.; Qi, X.; Shui, W. Analysis on trilateral game of green supply chain. In Logistics: The Emerging Frontiers of Transportation and Development in China; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 575–581. [Google Scholar]
- Uygun, Ö.; Dede, A. Performance evaluation of green supply chain management using integrated fuzzy multi-criteria decision making techniques. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 102, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuring, S.; Müller, M. From a Literature Review to a Conceptual Framework for Sustainable Supply Chain Management. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J. How Green is the Supply Chain? Practice and Research. Ssrn Electron. J. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theyel, G. Management practices for environmental innovation and performance. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2000, 20, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J. Green supply chain management in China. Proc. Spie-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2004, 5262, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer, J.T.; Dewitt, W.; Keebler, J.S.; Min, S.; Nix, N.W.; Smith, C.D.; Zacharia, Z.G. Defining supply chain management. J. Bus. Logist. 2001, 22, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.C. A framework of supply chain management literature. Eur. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2001, 7, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Item | Source Publication | Number of Records | Research Areas | JCR Partition | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Journal of Cleaner Production | 333 | Environmental Sciences & Ecology | Q1 | 0.239 |
| 2 | International Journal of Production Economics | 134 | Operations Research & Management Science | Q1 | 0.096 |
| 3 | Sustainability | 131 | Environmental Sciences & Ecology | Q2 | 0.094 |
| 4 | International Journal of Production Research | 73 | Operations Research &Management Science | Q1 | 0.052 |
| 5 | Resources Conservation and Recycling | 48 | Engineering | Q1 | 0.035 |
| 6 | Computers Industrial Engineering | 39 | Computer Science | Q1 | 0.028 |
| 7 | Transportation Research part E Logistics and Transportation Review | 37 | Operations Research & Management Science | Q1 | 0.027 |
| 8 | Production Planning Control | 33 | Operations Research & Management Science | Q2 | 0.024 |
| 9 | European Journal of Operational Research | 25 | Business & Economics | Q1 | 0.018 |
| 10 | Industrial Management Data Systems | 25 | Engineering | Q1 | 0.018 |
| 11 | Expert Systems with Applications | 20 | Operations Research & Management Science | Q1 | 0.014 |
| 12 | Transportation Research Part D Transport and Environment | 16 | Transportation | Q1 | 0.012 |
| 13 | Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management | 15 | Business & Economics | Q2 | 0.011 |
| Citing Frequency | Author (Year) | The Titles of the Articles | Literature Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 579 | Sarkis et al. (2011) | An organizational theoretic review of green supply chain management literature [24]. | International journal of production economics |
| 563 | Vachon et al. (2008) | Environmental management and manufacturing performance: The role of collaboration in the supply chain [27]. | |
| 437 | Zhu, Q et al. (2008) | Confirmation of a measurement model for green supply chain management practices implementation [28]. | |
| 316 | Yang et al. (2011) | Impact of lean manufacturing and environmental management on business performance: An empirical study of manufacturing firms [29]. | |
| 349 | Brandenburg et al. (2014) | Quantitative models for sustainable supply chain management: Developments and directions [30]. | European Journal of Operational Research |
| 290 | Dekker et al. (2012) | Operations Research for green logistics—An overview of aspects, issues, contributions and challenges [31]. | |
| 332 | Hassini et al. (2012) | A literature review and a case study of sustainable supply chains with a focus on metrics [32]. | International journal of production economics |
| 211 | Gimenez et al. (2012) | Sustainable operations: Their impact on the triple bottom line [33]. | |
| 235 | Ageron et al. (2012) | Sustainable supply management: An empirical study [34]. | |
| 303 | Diabat et al. (2011) | An analysis of the drivers affecting the implementation of green supply chain management [35]. | Resource conservation and recycling |
| 293 | Ahi et al. (2013) | A comparative literature analysis of definitions for green and sustainable supply chain management [36]. | Journal of cleaner production |
| 234 | Kuo et al. (2010) | Integration of artificial neural network and MADA methods for green supplier selection [37]. | |
| 205 | Hsu et al. (2009) | Applying hazardous substance management to supplier selection using analytic network process [38]. | |
| 269 | Melvill et al. (2010) | Information systems innovation for environmental sustainability [39]. | MIS Quarterly |
| 247 | Wu et al. (2011) | Balancing priorities: Decision-making in sustainable supply chain management [40]. | Journal of Operations Management |
| 244 | Zhu et al. (2008) | Green supply chain management implications for “closing the loop” [41]. | Transportation research part E-logistics and transportation review |
| 212 | Chiou et al. (2011) | The influence of greening the suppliers and green innovation on environmental performance and competitive advantage in Taiwan [42]. | |
| 243 | Wang et al. (2011) | A multi-objective optimization for green supply chain network design [43]. | Decision support systems |
| 302 | Buyukozkan et al. (2012) | A novel hybrid MCDM approach based on fuzzy DEMATEL, fuzzy ANP and fuzzy TOPSIS to evaluate green suppliers [44]. | Expert systems with applications |
| 233 | Shaw et al. (2012) | Supplier selection using fuzzy AHP and fuzzy multi-objective linear programming for developing low carbon supply chain [45]. | |
| 216 | Lin et al. (2014) | Survey of Green Vehicle Routing Problem: Past and future trends [46]. | |
| 213 | Lee et al. (2008) | Drivers and Enablers That Foster Environmental Management Capabilities in Small- and Medium-Sized Suppliers in Supply Chains [47]. | Production and Operations Management |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, R.; Xue, J.; Zhao, L.; Zolotova, O.; Ji, X.; Xu, Y. A Bibliometric Analysis of Green Supply Chain Management Based on the Web of Science (WOS) Platform. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123459
Gong R, Xue J, Zhao L, Zolotova O, Ji X, Xu Y. A Bibliometric Analysis of Green Supply Chain Management Based on the Web of Science (WOS) Platform. Sustainability. 2019; 11(12):3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123459
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Ruifeng, Jian Xue, Laijun Zhao, Oleksandra Zolotova, Xiaoqing Ji, and Yan Xu. 2019. "A Bibliometric Analysis of Green Supply Chain Management Based on the Web of Science (WOS) Platform" Sustainability 11, no. 12: 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123459
APA StyleGong, R., Xue, J., Zhao, L., Zolotova, O., Ji, X., & Xu, Y. (2019). A Bibliometric Analysis of Green Supply Chain Management Based on the Web of Science (WOS) Platform. Sustainability, 11(12), 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123459





