Living Labs for Rural Areas: Contextualization of Living Lab Frameworks, Concepts and Practices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. What Is a Living Lab?
1.2. Living Labs within the EU Framework
2. Tackling Innovation Challenges
2.1. Rural Challenges
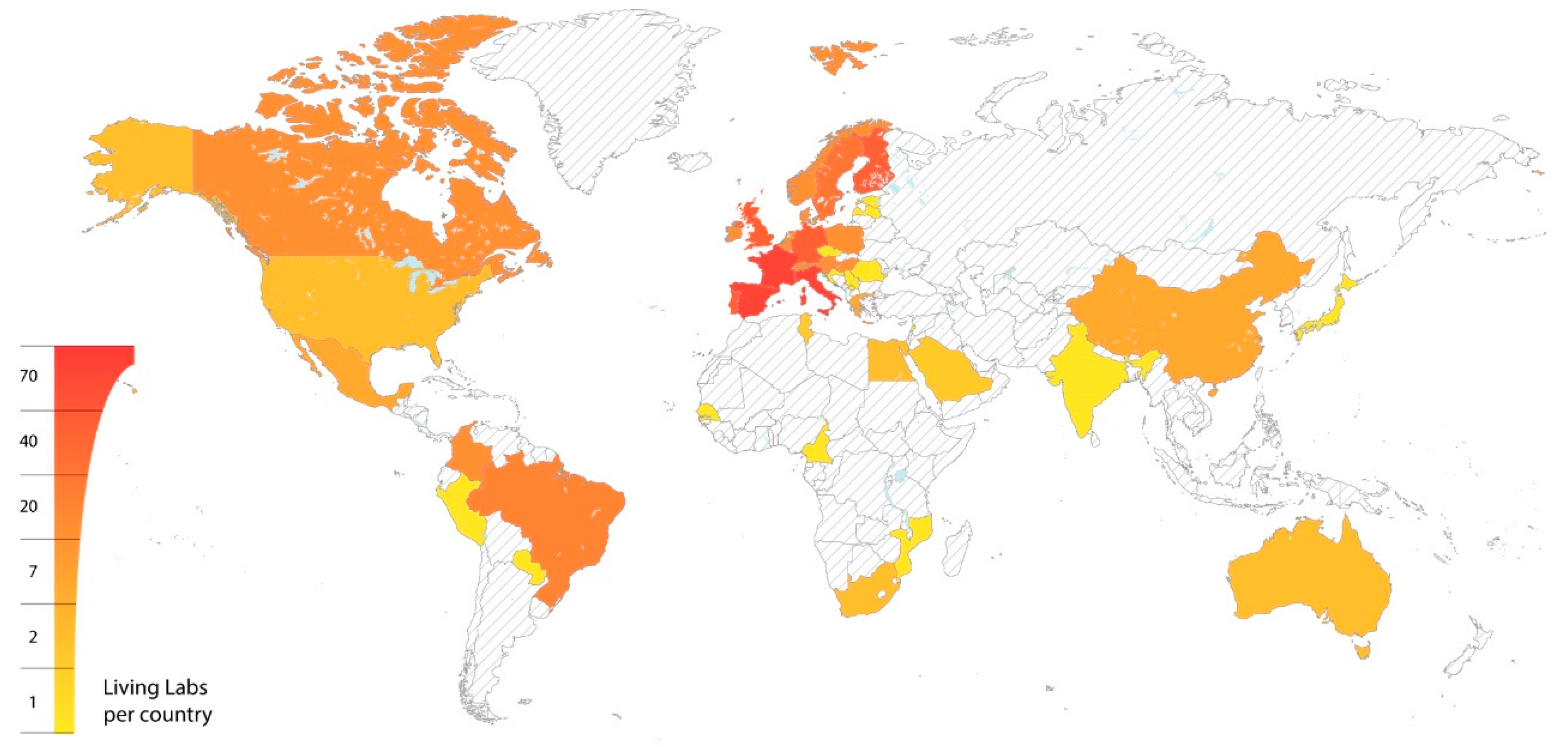
2.2. Living Laboratories, Projects and Research
2.3. Existing Rural Living Laboratories and Research
3. Discussion: Living Labs for Rural Areas
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed on 31 January 2019).
- Van Timmeren, A.; Keyson, D.V. Towards Sustainable Living. In Living Labs: Design and Assessment of Sustainable Living; Keyson, D.V., Guerra-Santin, O., Lockton, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Delft, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2017; pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mastelic, J.; Sahakian, M.; Bonazzi, R. How to keep a living lab alive? Digit. Policy Regul. Gov. 2015, 17, 12–25. Available online: https://www.emeraldinsight.com/doi/pdfplus/10.1108/info-01-2015-0012 (accessed on 24 February 2019). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zavratnik, V.; Kos, A.; Stojemnova Duh, E. Smart Villages: Comprehensive Review of Initiatives and Practices. Sustainability 2018, 10, 7. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/10/7/2559/htm (accessed on 21 July 2018). [CrossRef]
- U4IoT Consortium. Living Lab Methodology: Handbook; U4IoT Consortium. 2017. Available online: https://u4iot.eu/pdf/U4IoT_LivingLabMethodology_Handbook.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- Keyson, D.V.; Morrison, G.M.; Baedeker, C.; Liedtke, C. Living Labs to Accelerate Innovation. In Living Labs: Design and Assessment of Sustainable Living; Keyson, D.V., Guerra-Santin, O., Lockton, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Delft, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2017; pp. 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Westerlund, M.; Leminen, S.; Habib, C. Key Constructs and a Definition of Living Labs as Innovation Platforms. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2018, 8, 51–62. Available online: https://timreview.ca/article/1205 (accessed on 24 February 2019). [CrossRef]
- Burbridge, M.; Morrison, G.M.; van Rijn, M.; Silvester, S.; Keyson, D.V.; L Virdee, C.B.; Liedtke, C. Business Model for Sustainability in Living Labs. In Living Labs: Design and Assessment of Sustainable Living; Keyson, D.V., Guerra-Santin, O., Lockton, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Delft, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2017; pp. 391–403. [Google Scholar]
- Ballon, P.; Schuurman, D. Living Labs: Concepts, Tools and Cases. 2015, Volume 17. No. 4. Available online: https://www.emeraldinsight.com/doi/full/10.1108/info-04-2015-0024 (accessed on 24 February 2019).
- McPhee, C.; Leminen, S.; Westerlund, M.; Schuurman, D.; Ballon, P. Editorial: Innovation in Living Labs. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 3–6. Available online: https://timreview.ca/sites/default/files/article_PDF/Editorial_TIMReview_January2017.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Bergvall-Kåreborn, B.; Eriksson, C.I.; Ståhlbröst, A.; Svensson, J. A Milieu for Innovation—Defining Living Labs. In Proceedings of the 2nd ISPIM Innovation Symposium: Stimulating Recovery—The Role of Innovation Management, New York, NY, USA, 6–9 December 2009; Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/a210/711d9b9bc0a28daa8bb03cfa0f9813a01210.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2019).
- Dutilleul, B.; Birrer, F.A.J.; Mensink, W. Unpacking European Living Labs: Analysing Innovation’s Social Dimensions. Central Eur. J. Public Policy 2010, 4, 60–85. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2533251 (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Følstad, A. Living Labs for Innovation and Development of Information and Communication Technology: A Literature Review. Electron. J. Virtual Organ. Netw. 2008, 8, 99–131. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272566802_LIVING_LABS_FOR_INNOVATION_AND_DEVELOPMENT_OF_INFORMATION_AND_COMMUNICATION_TECHNOLOGY_A_LITERATURE_REVIEW (accessed on 21 January 2019).
- European Commission. Living Labs for User-driven Open Innovation: An Overview of the Living Labs Methodology, Activities and Achievements; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2009; Available online: https://www.eurosportello.eu/sites/default/files/Living%20Lab%20brochure_jan09_en_0.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Schuurman, D.; de Marez, L.; Ballon, P. Living Labs: A Systematic Literature Review. In Open Living Lab Days, Proceedings, Istanbul, Turkey. 2015. Available online: https://biblio.ugent.be/publication/7026155/file/7026171.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2019).
- Niitamo, V.P.; Kulkki, S.; Eriksson, M.; Hribernik, K.A. State-of-the-Art and Good Practices in the Field of Living Labs. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Technology Management Conference (ICE), Milan, Italy, 26–28 June 2006; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7477081 (accessed on 26 February 2019).
- Pierson, J.; Lievins, B. Configurig Living Labs for a ‘Thick’ Understanding of Innovation. Available online: https://anthrosource.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/j.1559-8918.2005.tb00012.x (accessed on 24 March 2019).
- What are Living Labs. Available online: https://enoll.org/about-us/what-are-living-labs/ (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Almirall, E.; Lee, M.; Wareham, J. Mapping Living Labs in the Landscape of Innovation Methodologies. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2012, 2, 12–18. Available online: https://timreview.ca/article/603 (accessed on 21 March 2019). [CrossRef]
- Hagy, S.; Morrison, G.M.; Elfstrand, P. Co-Creation in Living Labs. In Living Labs: Design and Assessment of Sustainable Living; Keyson, D.V., Guerra-Santin, O., Lockton, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Delft, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2017; pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Korošak, T.S.; Zavratnik, V.; Kos, A.; Duh, E.S. Report of Participatory Tools, Methods and Techniques. In Deliverable DT3.1.1 of the project Smart Villages; University of Ljubljana: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Markopoulos, P.; Rauterberg, G.W.M. LivingLab: A White Paper. IPO Annu. Prog. Rep. 2000, 35, 53–65. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2406991_Livinglab_A_White_Paper (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- The Lisbon Strategy in Short. Available online: https://portal.cor.europa.eu/europe2020/Profiles/Pages/TheLisbonStrategyinshort.aspx (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- The Helsinki Manifesto. Available online: http://elivinglab.org/files/Helsinki_Manifesto_201106.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- The 10th Wave for ENoLL Membership is now Open! Available online: https://openlivinglabdays16.wordpress.com/2015/12/10/the-10th-wave-for-enoll-membership-is-now-open/ (accessed on 20 June 2019).
- MedLab Consortium. MedLab: Final Publication. Available online: https://www.programmemed.eu/uploads/tx_ausybibliomed/Medlab_1_FINAL_PUBLICATION_EN.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Living Labs for Regional Innovation Ecosystems. Available online: http://s3platform.jrc.ec.europa.eu/living-labs (accessed on April 2019).
- European Commission. LIVING LABs. Available online: http://s3platform.jrc.ec.europa.eu/documents/20182/117542/S2E_Fiche_Living_Labs.pdf/994eafb3-4393-415b-a36d-d8cf6f33d44c (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Collaboration at Rural. Available online: http://www.c-rural.eu/index.php (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Santonen, T.; Creazzo, L.; Griffon, A.; Bódi, Z.; Aversano, P. Cities as Living Labs—Increasing the Impact of Investment in the Circular Economy for Sustainable Cities. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/info/files/research_and_innovation/rise/cities_as_living_labs.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Cross-Border Co-Creation Living Laboratories for Local Development. Available online: https://europa.eu/regions-and-cities/programme/sessions/24_en (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Zavratnik, V.; Kos, A.; Duh, E.S. Smart Villages in Slovenia: Examples of Good Pilot Practices. In Smart Villages in the EU and Beyond; Visvizi, A., Lytras, M.D., Mudri, G., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK; pp. 125–138, GB, In Press.
- Herrera, N.R. The Emergence of Living Lab Method. In Living Labs: Design and Assessment of Sustainable Living; Keyson, D.V., Guerra-Santin, O., Lockton, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Delft, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2017; pp. 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Trejo, F.; Pereira, L.D.; Guzmán, J.G.; de la Cruz, M.N. Living Labs and Rural Development: Towards a Policy Agenda. In Living Labs for Rural Development: Results from the C@R Integrated Project; Schaffers, H., Guzmán, J.G., de la Cruz, M.N., Merz, C., Eds.; TRAGSA: Madrid, Spain; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2010; pp. 227–246. Available online: http://www.c-rural.eu/dmdocuments/[email protected] (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Ståhlbröst, A.; Holst, M. Botnia Living Lab—For Sustainable Smart Cities and Regions; Luleå University of Technology: Luleå, Sweden, 2016; Available online: https://www.ltu.se/cms_fs/1.157454!/file/LTU%20Broschyr%20Botnian%20Living%20Lab%20210x148_lowres.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Hasselkuβ, M.; Baedeker, C.; Liedtke, C. Social Practices as a Main Focus in Living Lab Research. In Living Labs: Design and Assessment of Sustainable Living; Keyson, D.V., Guerra-Santin, O., Lockton, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Delft, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2017; pp. 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- LiveRUR. Available online: https://liverur.eu/project/ (accessed on 21 February 2019).
- Project—Mediterranean Living Lab for Territorial Innovation. Available online: https://www.keep.eu/project/1642/mediterranean-living-lab-for-territorial-innovation (accessed on 21 February 2019).
- MedLab consortium. MedLab—Mediterranean Living Lab for Terrirorial Innovation. Available online: http://www.ins-med.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/11/BROCHURE-MedLab.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2019).
- European Commission. Advanced Pilots of Living Labs Operating in Networks. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/191724/factsheet/en (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Ballon, P. Open Innovation by Living Labs Across Borders: The APOLLON Project. Available online: http://livinglabs-ghent.fi-week.eu/files/2010/12/1110-Ballon-01.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- CentraLab Consortium. CentraLab: User Driven Innovation for Regional Development. Available online: http://centralivinglab.eu/index.php/en/documents/finish/130-promotion/734-centralab-user-driven-innovation-for-regional-development-final-publication (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- LEADERS. Approach for Establishment and Operating of Living Labs. Available online: https://www.user-participation.eu/planning-the-process/step-5-participatory-methods/development-of-services-or-products/leaders (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- CentraLab: Central European Living Lab for Territorial Innovation. Available online: http://centralivinglab.eu/index.php/en/ (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- SusLabNWE Consortuim. Sustainable Labs North West Europe. 2014. Available online: http://suslab.eu/fileadmin/suslab/Images/SusLab_brochure_2014_1.0.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- NordForsk. A Transnational Nordic Smart City Living Lab Pilot. Available online: https://www.nordforsk.org/en/programmes-and-projects/projects/a-transnational-nordic-smart-city-living-lab-pilot (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Ståhlbröst, A.; Holst, M. The Living Lab Methodology Handbook; Social Informatics at Luleå University of Technology and CDT: Luleå, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, P.; Schuurman, D.; Ståhlbröst, A.; Vervoort, K. Living Lab Methodology: Handbook, U4IoT Consortium. 2017. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/1146321#.XSaO2qQRXIU (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- User Engagement for Large Scale Pilots in the Internet of Things. Available online: https://u4iot.eu/ (accessed on 21 February 2019).
- ROBUST: Rural-Urban Europe. Available online: https://rural-urban.eu/ (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- European Commission. Using Living Labs to Roll out Sustainable Strategies for Energy Poor Individuals. 2018. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/214803/factsheet/en (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Step-In Project. Available online: https://www.step-in-project.eu/ (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Matheson, R. Small European Nation Becomes a “Living Lab” for Urban Innovation Researchers. MIT News, 2017. Available online: http://news.mit.edu/2017/european-nation-andorra-living-lab-media-lab-urban-innovation-1013 (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- Andorra Living Lab. Available online: https://www.media.mit.edu/projects/andorra-living-lab/overview/ (accessed on 21 February 2019).
- Rahal, M. What I Know About Building a Living Lab: Ersin Pamuksüzer. Wamda, 1 August 2017. Available online: https://www.wamda.com/memakersge/2017/08/building-living-lab-ersin-pamuks%C3%BCzer (accessed on 21 February 2019).
- 14 Başakşehir Living Lab, Istanbul. Available online: http://basaksehir-livinglab.com/BLL/home/ (accessed on 21 Fabruary 2019).
- LivigLabs ict: Apulia Innovation in Progress. Available online: http://livinglabs.regione.puglia.it/web/guest (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Turku. Available online: https://civitas.eu/eccentric/turku (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- E-Institute. Available online: https://www.ezavod.si/en (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- ROBUST, Ljubljana. Available online: https://rural-urban.eu/living-lab/ljubljana (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- AV Living Lab: BTC City Ljubljana. Available online: https://avlivinglab.com/ (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Turk Mehes, K.; Living Lab InnoRenew, Izola, Slovenia. Personal Communication, May 2019.
- Kállai, T. State-of-the-Art in Utilizing Living Labs Approach to User Centric ICT Innovation—Automotive, Rural, eEnginieering and Renewable Energy LLs in Hungary. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Management, Enterprise and Benchmarking, MEB 2006, Budapest, Hungary, 2006; Available online: https://s3.amazonaws.com/academia.edu.documents/4111799/kallai_0.pdf?response-content-disposition=inline%3B%20filename%3DState-of-the-art_in_utilizing_Living_Lab.pdf&X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Credential=AKIAIWOWYYGZ2Y53UL3A%2F20190711%2Fus-east-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20190711T055440Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&X-Amz-Signature=6fa88e044a3aaacca69ce75de61bc95b326ec8c10a911bc37519c34dbe839e95 (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Rio Nacimento Living Lab. Available online: http://staging.enoll.org/node/115 (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Smart Rural Living Lab. Available online: http://staging.enoll.org/livinglab/smart-rural-living-lab (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Matias, L. New Innovation Concept Smart Rural: Inspiring Innovation in the Rural World. 2018. Available online: http://www.reseau-pwdr.be/sites/default/files/SmartRural-apresent18_ENG_wallon.compressed.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Kallai, T. Deliverable 3.1: Report of Case Studies on Rural Living Lab’s Definitions, November 2018. Available online: https://liverur.eu/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/D-3.1-Report-of-Case-studies-on-rural-living-labs-definitions.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- IRP. Global Resources Report 2019: Natural Resources for the Future We Want; United Nations Environmant Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019; Available online: https://www.resourcepanel.org/sites/default/files/documents/document/media/unep_252_global_resource_outlook_2019_web.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2019).
- Tirziu, A.-M.; Vrabie, C. Living Labs Instruments of Social Innovation in Rural Areas. MPRA, 2017. Available online: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/79868/1/MPRA_paper_79868.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Zurita, L.; Kallai, T. Rural Living Labs—User Based Innovation for the Rural Areas. In Proceedings of the EFITA Conference, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 6–8 July 2009; Available online: https://www.academia.edu/36856923/Rural_living_labs-user_based_innovation_for_the_rural_areas (accessed on 21 February 2019).
| Emergence | Focus | Challenges | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Living Lab | 1990s | Involvement of end users in the development of new technologies and ICT solutions in real-life environments. | Conducting user testing outside of laboratory environments; issues of trust and data protection; developing products and services required by people. |
| Rural Living Lab | 2000s | Development of rural areas through involvement of local communities, relevant local stakeholders and stakeholders form different sectors. | Great sensibility to local environments and its complexities: working with communities, small and sparsely populated areas, specific local challenges; poor digital literacy. |
| Sustainable Living Lab | after 2010 | Sustainable approaches to rural development while focusing on behaviors and experiences of daily practices. | Encompassing different components of sustainability: ecological, social and economic, circular economy and following the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs); sustainable digital tools. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zavratnik, V.; Superina, A.; Stojmenova Duh, E. Living Labs for Rural Areas: Contextualization of Living Lab Frameworks, Concepts and Practices. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11143797
Zavratnik V, Superina A, Stojmenova Duh E. Living Labs for Rural Areas: Contextualization of Living Lab Frameworks, Concepts and Practices. Sustainability. 2019; 11(14):3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11143797
Chicago/Turabian StyleZavratnik, Veronika, Argene Superina, and Emilija Stojmenova Duh. 2019. "Living Labs for Rural Areas: Contextualization of Living Lab Frameworks, Concepts and Practices" Sustainability 11, no. 14: 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11143797
APA StyleZavratnik, V., Superina, A., & Stojmenova Duh, E. (2019). Living Labs for Rural Areas: Contextualization of Living Lab Frameworks, Concepts and Practices. Sustainability, 11(14), 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11143797




