Abstract
Global challenges such as climate change, increasing urbanization and a lack of transparency of food chains, have led to the development of innovative urban food production approaches, such as rooftop greenhouses, vertical farms, indoor farms, aquaponics as well as production sites for edible insects or micro-algae. Those approaches are still at an early stage of development and partly unknown among the public. The aim of our study was to identify the perception of sustainability, social acceptability and ethical aspects of these new approaches and products in urban food production. We conducted 19 qualitative expert interviews and applied qualitative content analysis. Our results revealed that major perceived benefits are educational effects, revaluation of city districts, efficient resource use, exploitation of new protein sources or strengthening of local economies. Major perceived conflicts concern negative side-effects, legal constraints or high investment costs. The extracted acceptance factors deal significantly with the “unknown”. A lack of understanding of the new approaches, uncertainty about their benefits, concerns about health risks, a lack of familiarity with the food products, and ethical doubts about animal welfare represent possible barriers. We conclude that adaptation of the unsuitable regulatory framework, which discourages investors, is an important first step to foster dissemination of the urban food production approaches.
1. Introduction
1.1. Problem/Background
The question of how and where we will produce food in the future is central in times of climate change, growing world population, urbanization processes, decreasing availability of arable land and changing diets. The globalization of food chains makes it difficult to comprehend where food comes from and how it is produced [1,2]. This lack of transparency and reoccurring food scandals lead to an increased demand for local food [3]. Among consumers, there is a widespread perception that ‘local’ is more sustainable than ‘global’ [4]. This often goes hand-in-hand with strong opposition to conventionally produced food [5] which indicates that the prevailing food system is increasingly associated with unsustainable practices and the respective negative environmental impacts such as land and water degradation, the acceleration of climate change or a loss in biodiversity [6,7]. Both Brunori et al. [4] and Schmitt et al. [8] found that local food chains are more sustainable than global ones for attributes such as biodiversity, animal welfare, local added value and nutrition. In contrast, Born and Purcell [9] contest the generalization that local food systems are inherently more sustainable and socially just. A special form of local food production is urban agriculture, which is also related to a variety of sustainability benefits such as access to fresh, healthy and transparently produced food, strengthening local communities, recreation, fewer food miles, and an improvement of the micro-climate [10,11,12]. Changing views on food production have resulted in the development of a local food movement and conscious consumers who highly value sustainably produced food. Responding to this popularity, the supply side has reacted with structural changes and has moved production closer to the consumer [13]. Short urban agriculture food supply chains enable the provision of high-quality niche products such as perishable vegetables [14] for which producers can charge premium prices [15]. However, traditional forms of urban agriculture conducted open-air or on-soil also bear risks and limitations. Soil contamination, atmospheric, and polluted water can interfere with the food safety of the produce [16]. Furthermore, studies have shown that labor and natural inputs are used inefficiently compared to large-scale agriculture, questioning the sustainability of small-scale urban agriculture [17,18]. The uncertainty of how to sustainably meet the food demand of future generations and the emerging economic opportunities of changing consumer demands drive the development and promotion of innovative urban food production approaches. To achieve an efficiently produced yield of safe food, urban agriculture has advanced towards the use of high-tech equipment in a controlled environment [12,19,20]. Due to the special characteristics and limitations of such areas, these innovations are mostly designed to use space efficiently but also to tap synergies with the built environment of cities or social benefits unrelated to production [21]. The creative and adaptive force of cities can add innovative characteristics to existing growing methods or can result in completely new ways of producing food such as indoor farming, vertical farming, rooftop greenhouses, aquaponics, the farming of edible insects or the production of algae. All of these approaches can address the problems of current food production to a certain degree and have the potential to contribute to more sustainable food production in the future. However, they also bear risks and uncertainties, which might hamper their acceptance and diffusion. Consequently, both sides have to be explored and evaluated to fully understand the approaches.
1.2. Sustainability of Innovative Urban Food Production Approaches
This paper focuses on six different urban food production approaches (aquaponics, rooftop greenhouses, vertical farming, indoor farming, algae production and edible insects). Compared to the more traditional forms of urban agriculture (such as allotment gardens), those approaches are both more innovative and at the same time, due to their newness, less investigated.
Aquaponics is an approach that combines aquaculture and hydroculture. It enables the production of fish and leafy vegetables in cities [22]. This method uses resources more efficiently than aquaculture, as both nutrients and water are recycled [23]. The circulation of wastewater from the fish tank ensures fertilization of the plants and prevents nutrient discharge [24]. In contrast, Forchino et al. [25] concluded from their lifecycle analysis that high water and energy demand are obstacles for achieving economic and environmental sustainability.
In cities with a lack of open space, the implementation of vertical farms or the facilitation of rooftops for the implementation of greenhouses can be an efficient solution to produce food. Rooftop greenhouses can transform unutilized space on top of buildings into productive space [19]. High-tech rooftop greenhouses can create synergies with the buildings to which they are connected. Waste heat from the building can be used to heat the greenhouse, enabling food production in winter. CO2 emissions can also be used to foster plant growth [26]. Furthermore, a high share of the water demand can be covered using rainwater collected from the building [27]. Sanjuan-Delmas et al. [27] also assessed that CO2 emissions from food production in rooftop greenhouses are lower than in conventional greenhouses. However, they found a high demand for fertilizer and a substantial generation of leachate contributing to marine eutrophication. Other aspects that negatively affect sustainability are high operational costs and the need for further technological development for building-integrated circular rooftop greenhouses [27].
The dependency of agricultural productivity on the environment may be reduced by moving plant production indoors. Indoor farming can provide optimal growing conditions to maximize the yield per growing space and enable year-round production. Indoor farming can potentially ensure stable, location-independent harvests, especially in times of climate change and increasingly frequent extreme weather events [20]. In indoor farming, just as in vertical farming soil-less vertical plant-production systems are preferred, as they allow an efficient use of space and resources [28]. Maximum control over production methods can also reduce the use of fertilizer and pesticides and, as a consequence, reduce the environmental impact of food production [29].
Approaches such as insect or algae farming aim at producing novel foods that are not traditionally part of Western diets in order to meet the growing demand for protein. Compared to conventional animal husbandry insect farming is regarded as less resource-intensive and more environmentally friendly: insects convert feed mass into body mass more efficiently than cattle, pork or chicken. Also, the water demand of insects is minimal and rearing requires little space [30]. Furthermore, edible insects such as mealworms or grasshoppers emit less greenhouse gases and NH3 than cattle or pigs [31]. However, efficient mass-rearing systems are yet to be developed and the issue of competing uses of insect-feed raises questions about whether or not sustainability potential can be tapped [32]. Another new approach is algae farming. The farming of seaweed does not require manmade fertilizer or compete with other agricultural land uses. In the right environment, it grows both quickly and abundantly and contains essential nutrients. Some seaweeds such as the red algae Porphyra spec. produce a higher amount of protein per m2 (84 g) compared to soy beans (40 g/m2) or beef (5 g/m2) [33]. Microalgae also show considerable advantages with respect to land consumption when compared to land crops. However, the implementation of large-scale production is still very costly and technologically challenging [34]. Both the production of insects and algae bear potential for integration into the urban environment: rearing insects does not require much space and practical examples show that algae farming can be fitted to both house facades and interior walls (https://www.mint-engineering.de/en/home/).
Technical feasibility is a common barrier for different innovative food production approaches, and might be a reason why some developments do not advance beyond prototypes [35]. That is why the sustainability of new approaches to urban agriculture is often just calculated in models [28,36,37] and existing studies on aquaponics, rooftop greenhouses, vertical and indoor farming focus on the technological feasibility, production-process optimization or lifecycle analysis [19,23,36,38].
The viability of innovations is, however, not just dependent on technological feasibility. Social acceptability and perceptions of the innovation’s benefits are also crucial for its diffusion. As food production mainly takes place in rural areas, many urban dwellers are no longer familiar with it. Consumers might reject approaches that do not comply with their traditional views of agriculture. A lack of understanding of the innovation could also result in hurdles for the implementation from local authorities [35,39,40].
1.3. Research Gap
So far, the six approaches (aquaponics, rooftop greenhouses, vertical farming, indoor farming, algae production and edible insects) have mainly been considered individually: Questions of acceptability have been studied for edible insects and seaweed consumption to explore consumers’ willingness to include those foods into their diets [41,42,43,44,45]. Food neophobia and low familiarity with eating insects were identified as barriers for the adoption of insects as a meat substitute in Western societies [45]. Milicic et al. [46] explored consumers’ attitudes towards aquaponics products and found that few people were willing to pay higher prices for food produced in aquaponics. Comparative studies of the different approaches covering perception and acceptability rarely exist. Scholars compared the societal preferences of different approaches to urban agriculture and found that approaches such as vertical farming or aquaponics only find little acceptance [12,47]. As they are high-tech production systems, they are perceived as unnatural. In a different study, Specht et al. [35] compared the social acceptance and general perception of different types of building-related agriculture and concluded that perceived benefits promote the acceptance of production systems such as rooftop greenhouses and vertical farming.
Different innovative approaches to producing food in the city can provide identical or complementary benefits. Identifying commonalities and differences in the perceptions of these benefits and understanding the corresponding acceptability can provide hints for the chances that the innovation will be successful on the market. Furthermore, one single approach may not be a solution for sustainable urban food production. Using one frame to analyze all the different approaches can thus highlight the foci of these approaches and give ideas about how combining them in order to cover several sustainability aspects. The identification of common obstacles could also suggest alliances of different approaches among stakeholders to create a lobby and overcome existing barriers together. Hence, this paper aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the approaches of rooftop greenhouses, vertical farming, indoor farming, edible insects, aquaponics, and algae production, so as to enable an overarching comparison. The specific objectives are:
- to assess the perception of sustainability for the different approaches;
- to investigate the acceptance factors and acceptance barriers that might hinder successful establishment of the new approaches; and
- to identify common and complementary elements among the new approaches.
2. Materials and Methods
The overall research team consisted of 11 researchers, who conducted the interviews. We split into six subgroups (consisting of one, two or three members) for a deeper investigation of each innovative urban food production approach. Each of the subgroups worked on one of the following topics: aquaponics, rooftop greenhouses, vertical farming, indoor farming, algae production and edible insects.
Each subgroup selected an average of three experts to interview. We considered people experts if they had prolonged or intense experience in either practice or research in the respective field. The experts were identified via desk-research and inquired via email. Four experts were interviewed for indoor farming and rooftop greenhouses, while only two experts on aquaponics were included in the analysis. The interviewees’ selection aimed at reaching experts with in-depth knowledge on the respective approach and international reputation. The majority were experts from Germany. Experts from the U.S. were included for insect and algae production, which are less common in Germany. After contacting them, the subgroups met the experts in their professional environment or at other locations of their convenience. U.S. experts were interviewed through a video conference tool.
The 19 qualitative interviews were conducted (Table 1) between May and July 2018 and lasted, on average, 35 min.

Table 1.
Overview of the interviewed stakeholders: Interview No., expert category, expertise, and abbreviation as used for in-text direct citations. [* Abbreviations: RTG = Rooftop greenhouse; VF = Vertical farming; IF = Indoor farming; Insects = Insect farming; AP = Aquaponics; Algae = Algae production].
All interviewers were trained in advance for the interview situation and followed the standards for qualitative interviews as defined by Kuckartz [48]. For the face-to-face interviews, the interviews were conducted at the place the interviewees chose, while the researchers aimed to provide neutrality (e.g., no indication of desired responses) during the interview process. All interviewers used the same interview guideline with nine major parts, consisting of (1) an introduction to our research project, followed by questions about (2) the interviewees’ background, (3) the prominence of the innovative urban food production approaches, (4), assessments of social, environmental and economic benefits/potentials, (5) questions on public attitudes and social acceptance, (6) assessment of social, environmental and economic problems/conflicts, (7) valuation of practical examples, (8) the assessment of framework conditions, and (9) space for additional statements and acknowledgements.
The interviewers recorded and transcribed the interviews. For the manual analysis, the principles of qualitative content analysis by Kuckartz [48] were applied. We manually assigned codes to text fragments to classify the amount of data into fewer homogenous units.
For the case-oriented analysis, each interview was analyzed and assessed individually [49]. A case profile was created for each interviewee, summarizing the key messages plus citations for each section.
To develop an aggregated evaluation, a grid with social, ecological and economic benefits and conflicts was developed from the interview content. The individual profiles were browsed for catchwords and content denoting social, ecological and economic potential as well as conflicts, in the three dimensions of sustainability. In a second step, all factors affecting the acceptance of the approaches were extracted from the content. This enabled us to detect similarities and differences among the individual interview cases and to extract the most important statements based on a qualitative assessment and the number of times each aspect was mentioned.
In order to assess the contribution of the studied approaches to sustainable development, the “three-pillars-of-a-sustainable-development-model” was used, which builds on the sustainability concept introduced by the Brundtland Report in 1987 [50]. Sustainable development can only be assured if all three dimensions are implemented equally in environmental policies. Furthermore, innovative approaches and technologies are determined as major drivers of sustainable development [51,52].
3. Results and Discussion
Innovations often face reservations or even resistance. As long as those obstacles are not revealed, it is difficult to assess the chances of whether or not new food production approaches can be established [35]. Thus, it is important to explore and discuss the perceived potentials, conflicts and factors that influence acceptance and rejection of our approaches.
3.1. Perception of Sustainability
3.1.1. Social Sustainability
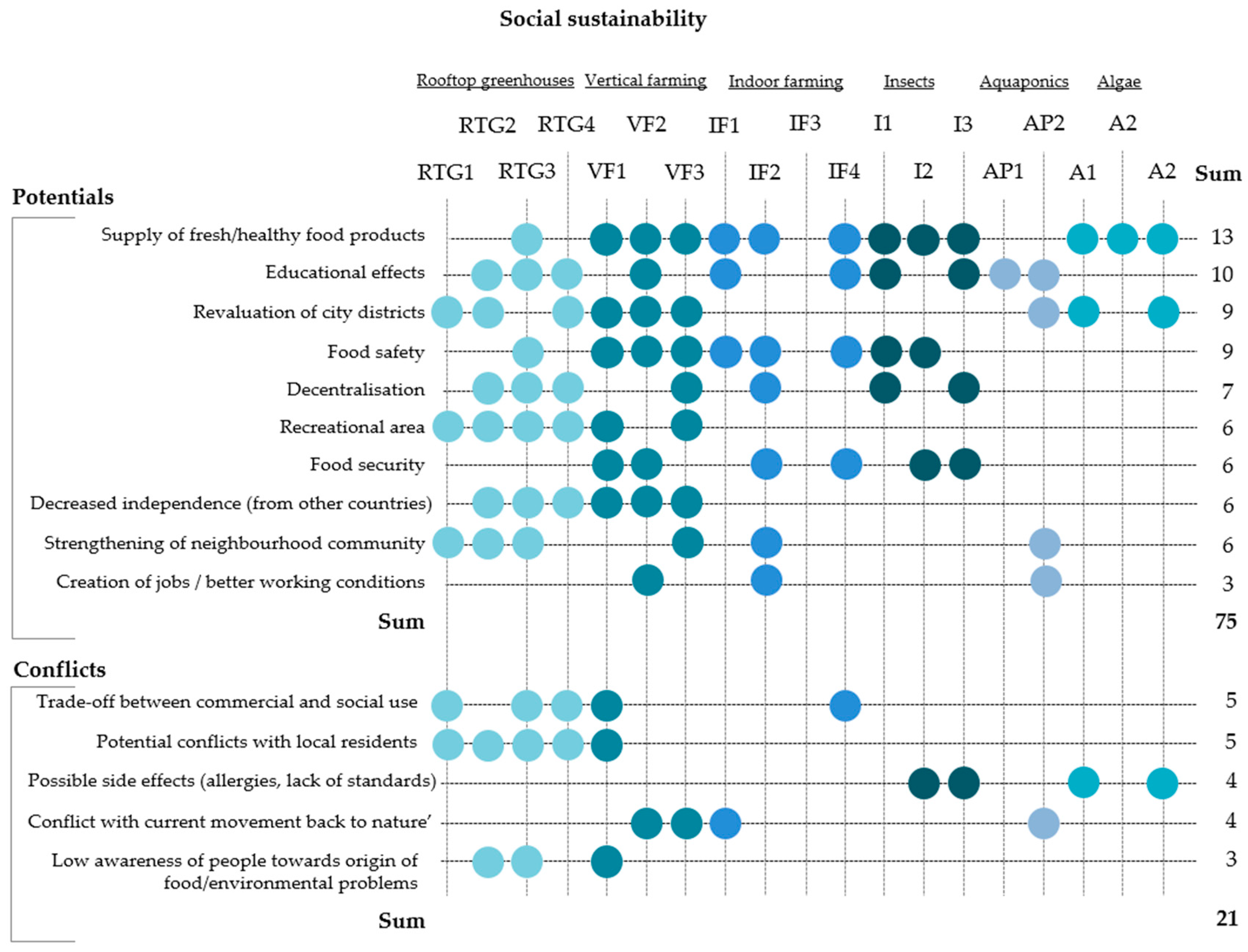
Social sustainability contains the requirement that every member of a society shall have equal and fair chances of development [51]. In this regard, the applied interview guideline included questions for collecting several expert opinions on the potential benefits and conflicts of innovative urban food production approaches in light of the social dimension of sustainability. The different opinions were summarized, categorized and coded. Figure 1 visualizes the results.
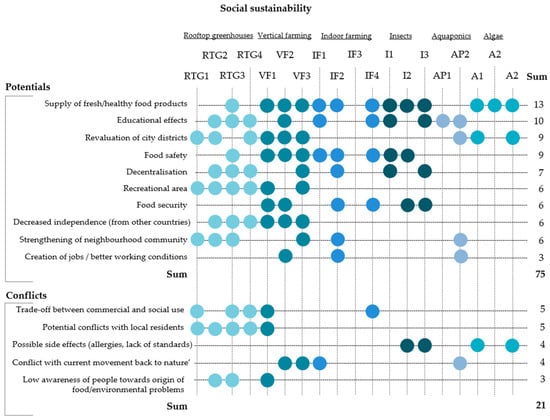
Figure 1.
Social sustainability of innovative urban farming production approaches. The point symbol (•) displays the mentioning of an aspect in the respective interview assigned to a certain code.
With regard to the social dimension of sustainability, the analysis revealed that the majority of stakeholders see major benefits in an improved supply of fresh and healthy food. They share the view that introducing new approaches for urban food production can shorten food-chains and improve access to locally and transparently produced food. This is particularly relevant for neighborhoods or cities with limited supplies of fresh food.
“… it is a real problem. You have certain areas of the city where food production has completely died off and now you just have a huge hypermarket somewhere on the outskirts and this means that large swathes are not supplied with fresh food.”(Vertical Farming Expert; VF3)
Due to high yields per unit area, urban agriculture is generally considered to contribute to urban food security especially in so called ‘food deserts’ [53]. Because of this high productivity, urban agriculture can potentially contribute to food security and access to healthy food, although product prices determine the affordability and thereby the target consumers (i.e., low-income; middle/upper income) [54]. For our particular approaches, such as building-related agriculture, some scholars raise the question of who is actually able to access the products [35]. Usually the products are sold at premium prices which does not make them affordable to everyone [55]. Busa et al. [56] point out that high prices for local food can lead to a separation and individualization of society, meaning that only well-off people are able to make “morally right” consumption decisions, while people who buy cheap food are villainized for their supposedly unsustainable consumption patterns.
Educational effects are seen as a further key social benefit. One frequently mentioned aspect is the re-connection of consumers to their food sources and how urban food production can help to bridge the producer–consumer gap. According to the experts, the new approaches can serve as demonstration and learning facilities and provide urban children easy access to education on food production. Rooftop greenhouses and aquaponics are especially considered to be suitable systems to provide education.
“I could also imagine that there are very positive ties in the social arena. Not only regarding rooftop greenhouses, but with urban gardening in general. Showing that to the children.”(Rooftop Greenhouse Expert; RTG3)
Nadal et al. [57] support our experts’ assertion for rooftop greenhouses. They claim that fitting greenhouses on existing school rooftops is a viable measure to foster environmental and nutrition education using pre-existing space. School buildings are often large, the statics are known, there is an existing social infrastructure and they are well located, which are generally good prerequisites for construction and accessibility [57]. For aquaponics, it was surprising that none of the experts named food supply as a potential benefit but they mentioned educational effects, even though most existing studies focus on the productivity and life-cycle analyses [22,23,25]. Hart [58] states that aquaponics can be a tool to convey interdisciplinary education and technological skills but can also be difficult to understand because of its technological complexity.
Another important point is the revaluation of city districts, which was stated by all of the experts, except for edible insects and indoor farming. This can comprise the place of production as a neighborhood meeting point to socialize or the beautification of the cityscape for example when vertical farming is used as a measure of architectural design.
However, Specht and Sanyé-Mengual [59] found that using rooftops to grow food might not be perceived as an aesthetic improvement to a building. Furthermore, the revaluation of city districts through urban agriculture can attract wealthy residents to working-class neighborhoods. Consequently, this may result in ‘green gentrification’ which is characterized by increased housing pressure and displacement of long-time residents and urban farmers [60].
Although social conflicts were generally mentioned less frequently, the experts agreed that rooftop greenhouses in particular could cause conflicts with local residents in mixed-use-buildings where clashes between commercial and social use can occur. More precisely, highly productive growing systems that provide fresh and healthy food might not allow public access, which would prevent their use for social activities. In this case, residents consider, for example, rooftop greenhouses as “other people using the roof above them” (Rooftop Greenhouse Expert, RTG3), which is, again, a form of social exclusion.
In countries such as Germany, there are strict regulations on food hygiene often restricting the access to commercial food production sites to trained staff only [61]. The proximity of agriculture to housing areas can also result in neighborhood disputes: The food production activities can result in smells or dust formation. If the production sites are openly accessible, there can also be negative impacts on the farming activities, for example if residents leave their dogs unattended [62].
Ethical concerns play a major role for the relatively novel approaches that involve animal keeping, namely edible insects and aquaponics (see Section 3.2.2 for detailed results and discussion).
3.1.2. Environmental Sustainability
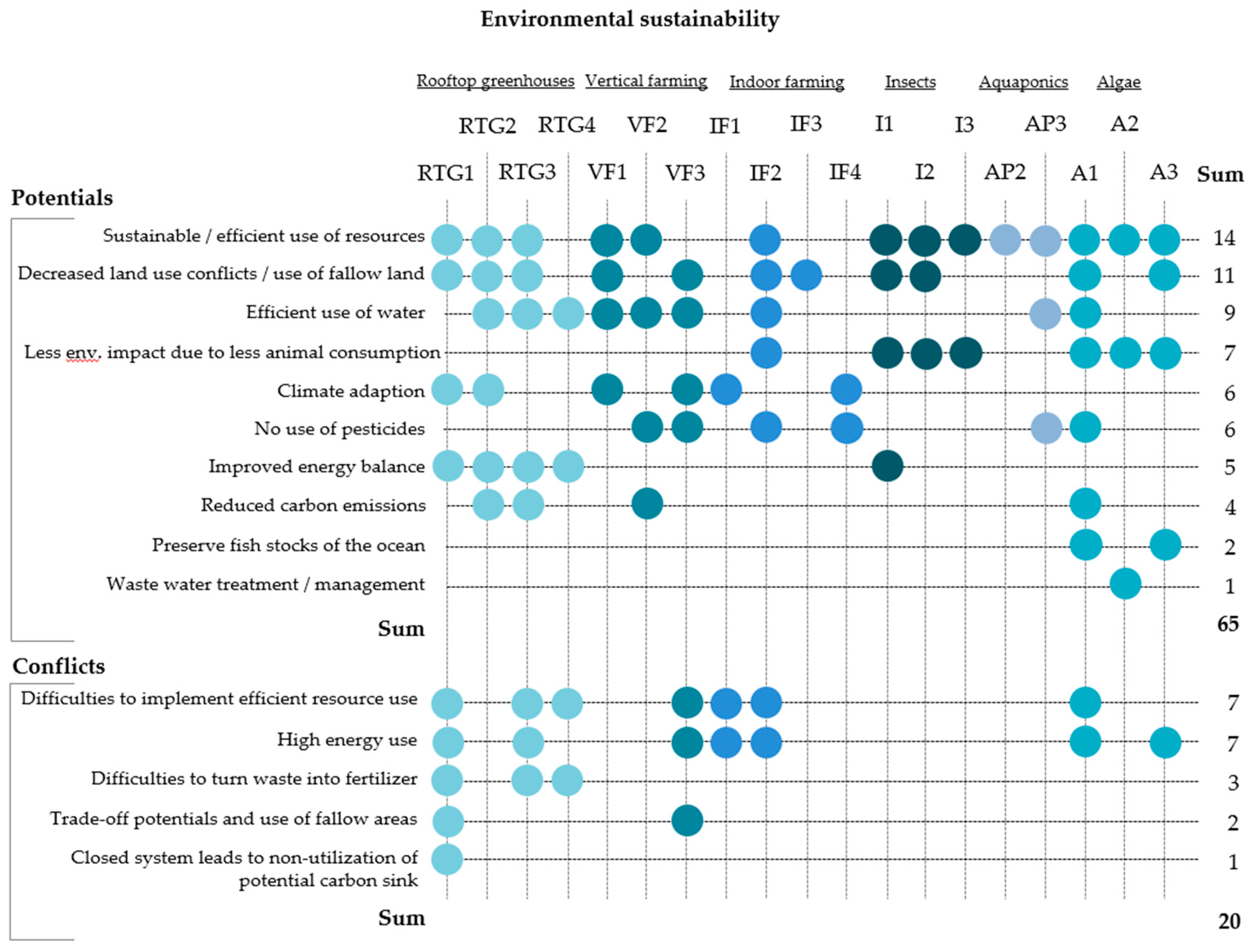
Environmental sustainability describes an efficient and cautious use of resources as well as the preservation and restoration of significant ecosystems and their services [51]. Considering this definition, questions regarding the environmental benefits and conflicts of innovative urban food production approaches were included in the interview guideline. Figure 2 visualizes the results.
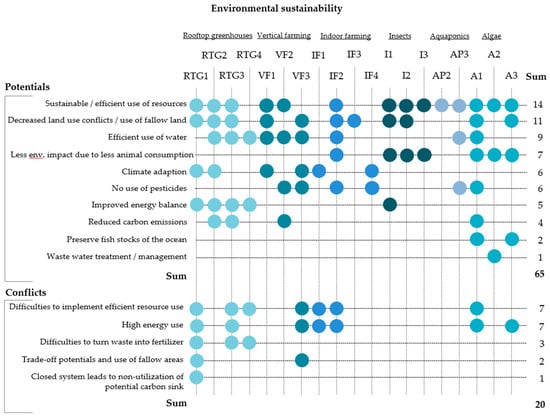
Figure 2.
Environmental sustainability of innovative urban farming production approaches. The point symbol (•) indicates the mentioning of an aspect which could be assigned to a certain code.
In the environmental dimension, most of the interviewees stated efficient resource-use as the major potential. This particularly includes the use and recycling of water, but also potentials for energy-efficiency through building-integrated approaches and optimized use of waste-heat as well as recycling organic waste.
A second prominent aspect is the potential for decreased land-use conflicts, given the options to make use of fallow areas and take pressure off agricultural land. It is noteworthy that environmental potentials are more frequently mentioned for edible insects and algae production than for other approaches. Experts stressed their potential as alternative protein sources, which makes them a potential substitute for meat or dairy, as less meat consumption leads to reduced environmental impacts. Regarding algae production, one expert claims:
“Algae production requires less space than animal production. We also have a better water budget, especially since we have the option of recycling water and keeping it running in a closed circuit.”(Algae Production Expert; Algae1)
While the experts outline the energy-efficiency of some of the approaches (such as aquaponics), the technological state of others such as indoor farming is not yet mature enough to reach the necessary level of efficiency, which also leads to a lower social acceptance of the system. Several experts question the positive input-output-relation, which gets emphasized by the difficulties that are addressed when it comes to the practical implementation of efficient resource use strategies.
“There are still negatives we have to talk about—like energy consumption—and we cannot ignore them. But they are all addressable. So I think improving the systems will also certainly improve the acceptance of the people.”(Indoor Farming Expert; IF1)
Our results suggest that the different approaches promise a broad variety of environmental improvements compared to large-scale food systems, but that these potentials are still difficult to exploit. Other scholars mostly confirm this finding [63]. When compared to traditional urban agriculture, which is considered to be resource inefficient in terms of labor and natural inputs [17,18], our results indicate that some of the high-tech urban agriculture approaches are still inefficient in terms of capital and energy demand. Local food production is not necessarily more environmentally friendly than national or global food systems, it always depends on the actual applied practices [9]. In accordance with our experts, scholars criticize the high energy demand and the lack of technical solutions for implementing resource efficiency in rooftop greenhouses or indoor farming [27,29,36]. Although not mentioned in our interviews, this also appears to be a problem for vertical farming. Al-Chalabi [36] found that, depending on the season, vertically grown lettuce requires two to five times more energy than conventionally produced lettuce. In contrast, the low resource demand of producing algae and insects stated in our interviews is confirmed by other scholars. Mealworms, for example, convert feed into biomass much more efficiently than pork, beef or chicken. Producing one kilogram of mealworm protein uses considerably less land, emits less greenhouse gases but requires the same amount of energy when compared to chicken, pork or beef [64]. However, more data on the environmental impacts of mass producing insects is required [65]. With regard to environmental sustainability, our experts raise an important question as to whether insect consumption is favorable to plant-based meat substitutes.
3.1.3. Economic Sustainability
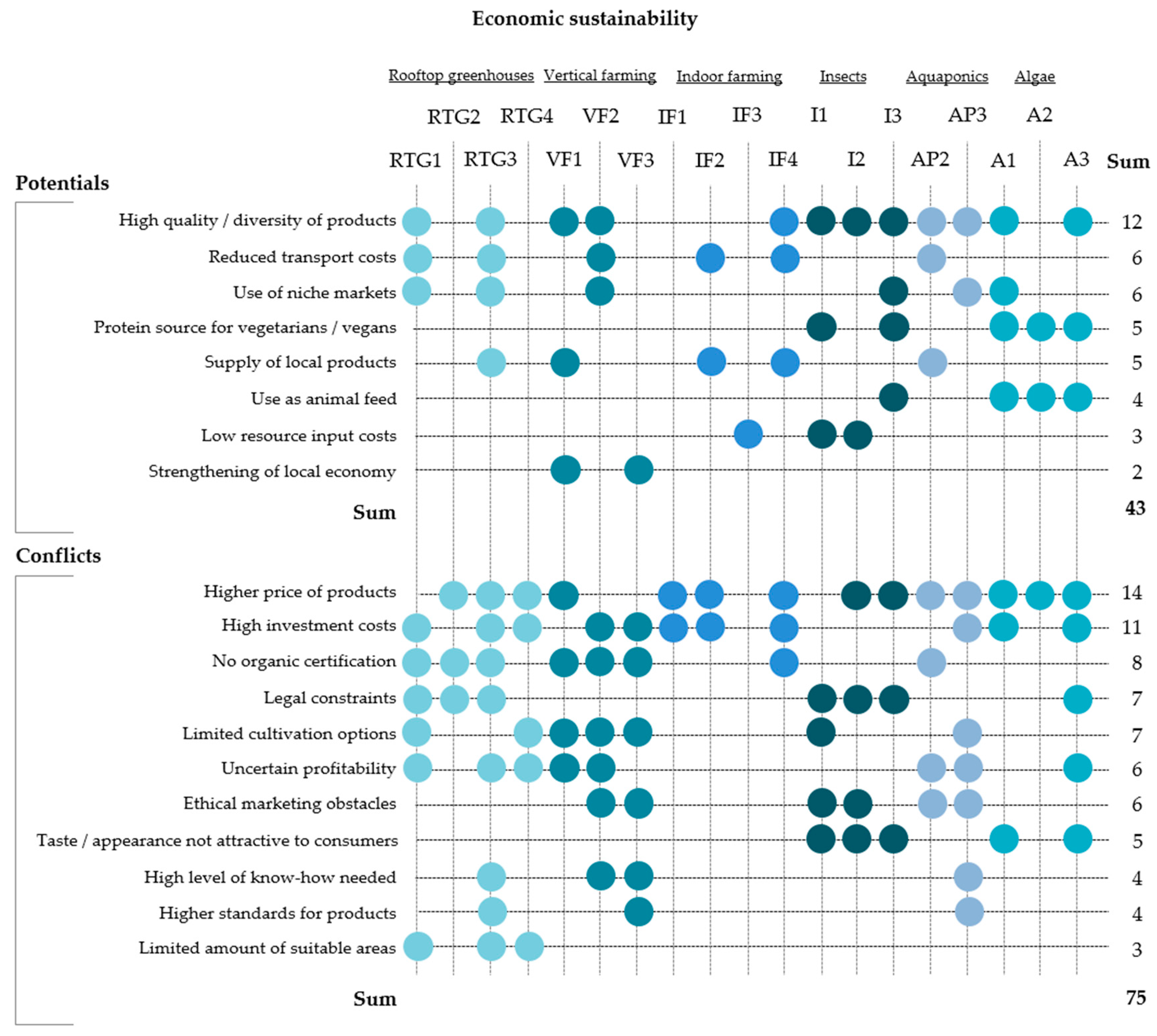
Economic sustainability describes the efficient and equal allocation of resources in a society. Since market interventions lead to distortions and, in the worst-case scenario, to a malfunction of the market mechanism, it is especially important that innovations have the potential to be economically viable in the future. If this is not guaranteed, it could be a serious market barrier for innovations, which emerge in the context of sustainable development. The experts’ assessment of economic benefits and conflicts of the new approaches is displayed in Figure 3.
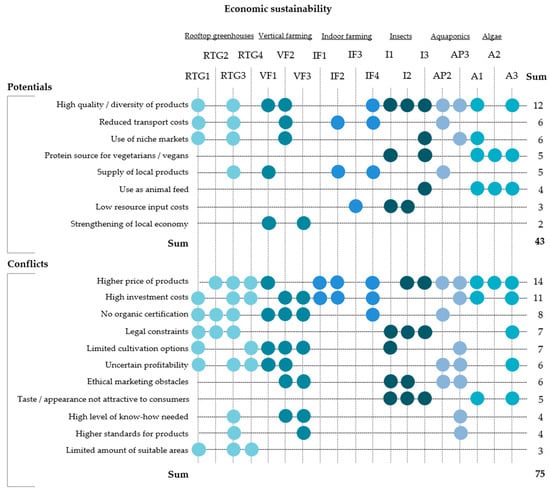
Figure 3.
Economic sustainability of innovative urban farming production approaches. The point symbol (•) displays the mentioning of an aspect which could be assigned to a certain code.
When it comes to the economic benefits of the new urban food production approaches, the most important aspects are the high quality, locality and diversity of products, as well as the reduced transport costs due to the close spatial linkage of production and consumption sites. According to an expert, the unique selling point is to offer sustainable products in the city, low on food miles.
Across all approaches, the interviewees agreed that niche markets are particularly important for product marketing. This especially applies to edible insects and algae production, which can be also used as alternative protein sources for vegetarians or vegans.
“A very small proportion of our customer base prefers this vegan and vegetarian diet. And this demographic is more willing to experiment, since their thinking is that: I am eating vegan or vegetarian because I want to do something good for the environment.”(Algae Production Expert; Algae1)
The provision of high quality products for niche markets as an economic potential for most approaches mentioned by our experts corresponds with the strategies of specialization and differentiation which are frequently adopted by urban farmers to perform successfully on the market [66]. Anticipating a growing demand for local food, all of our innovative approaches specialize in providing fresh food. Short transport distances can be a competitive advantage, especially for perishable food such as herbs or leafy greens [14] and the freshness of the products can be an added value that justifies a higher price [67]. Using differentiation strategies, urban food producers can further tap niche markets [68] and avoid competition with comparably cheaper products from conventional agriculture [28]. One of our experts mentioned sports nutrition as an example of a suitable niche market for insects due to their high protein content.
Most interviewees pointed out that major economic conflicts lie in the high investment costs of the new approaches, thereby leading to higher product prices. The generally uncertain profitability and difficulties in developing stable business models are further assessed as major concerns in the economic dimension and make it difficult for urban farmers to run a viable operation.
“Over time, a great deal of these farmers simply had to close down because it is not worth it. It is far too expensive.”(Vertical-Farming Expert; VF2)
Existing literature also points to market barriers such as high investment needs and high operational costs that can discourage interested producers to even start such an innovative approach but can also result in high retail prices, making it complicated to find a market for the products [29,55,65,67]. The high investment costs have also triggered a debate around the social and environmental justice drawbacks specific to innovative urban food production approaches. Specht et al. [69] reveal that the costs of building and maintaining intensive urban farms can be prohibitive and entails the risk of being dominated by large enterprises. This can lead to a concentration of ownership and operation among already well-resourced and well-connected groups, while small, not-for-profit groups often have difficulties financing such capital-intensive farms. Cohen and Reynolds [70] conclude, that urban food production is not in and of itself a sustainable or socially just practice, and that without attention to social equity, it can exacerbate economic and environmental disparities.
While the efficiency of producing a high output on a small area and year-round was mentioned by our indoor farm and edible insect experts, some authors still raise the question of whether small-scale production combined with high costs can be efficient overall [46].
Another impeding aspect is that, due to the certification requirements, organic standards cannot be achieved for soil-less production methods. These are commonly applied in rooftop greenhouses, vertical farming, indoor farming and aquaponics. Our experts argue that this could be an important marketing obstacle beside further legal constraints. In other studies, the need for certification standards to enable soil-less food production in the EU is expressed as well. Certification is, for example, mentioned as a measure to foster consumer trust and justify premium product prices [19,46,59].
3.1.4. Comparative Analysis on the Perception of Sustainability
The results displayed in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 show that, based on their specific characteristics, the different approaches are indeed evaluated differently.
Comparing the different dimensions of sustainability, benefits were most frequently mentioned in the social dimension, followed by the environmental and the economic dimension. Most conflicts where mentioned for the economic dimension and considerably less for environmental and social dimensions, where the numbers are about equal. The economic sustainability dimension is also the only dimension where conflicts were brought up more frequently than potentials. This implies that the approaches offer a broad range of social and ecological opportunities but are not yet sustainable from an economic point of view and that economic sustainability might be more difficult to achieve.
The result that the experts mentioned social and environmental potentials more often than economic ones could be interpreted as a trade-off between the sustainability dimensions. Other authors such as Sulewski et al. [71] also describe such a trade-off. They state that reaching a high degree of sustainability in one dimension, leads to a lower degree of sustainability in the other dimensions. Especially economic goals can hamper achieving other sustainability goals [72]. Furthermore, as sustainability is a normative description of how the world should be, it is never possible to fully reach this state [72].
With regard to the different approaches and their respective contribution to the different sustainability dimensions, our results reveal tendencies as well. Our findings underline the great importance of the social opportunities of approaches such as rooftop greenhouses and vertical farming. The considerable number of social potentials for insect production was rather surprising to us with respect to the ‘yuck factor’ of the approach. Algae production exhibited only a few social potentials, perhaps due to a lack of possibilities for designing underwater food production in an interactive and accessible way.
In contrast, algae production was assessed as very promising in the environmental dimension, especially in terms of resource demand. The same accounts for rooftop greenhouses, however, doubts in realizing these potentials were more present for this approach.
Economic sustainability benefits were slightly more often mentioned for algae and insects when compared to the other approaches. On the one hand, this is surprising, because algae and insect production are novel technologies that face many restrictions. On the other hand, they also result in novel food products with special properties such as nutritional values. Due to their ‘newness’, algae and insects might appear more exceptional, and could therefore bear a higher marketing potential than vegetables from building-related agriculture which have to compete with the same vegetables produced in a more traditional way.
3.2. Impeding Acceptance Factors
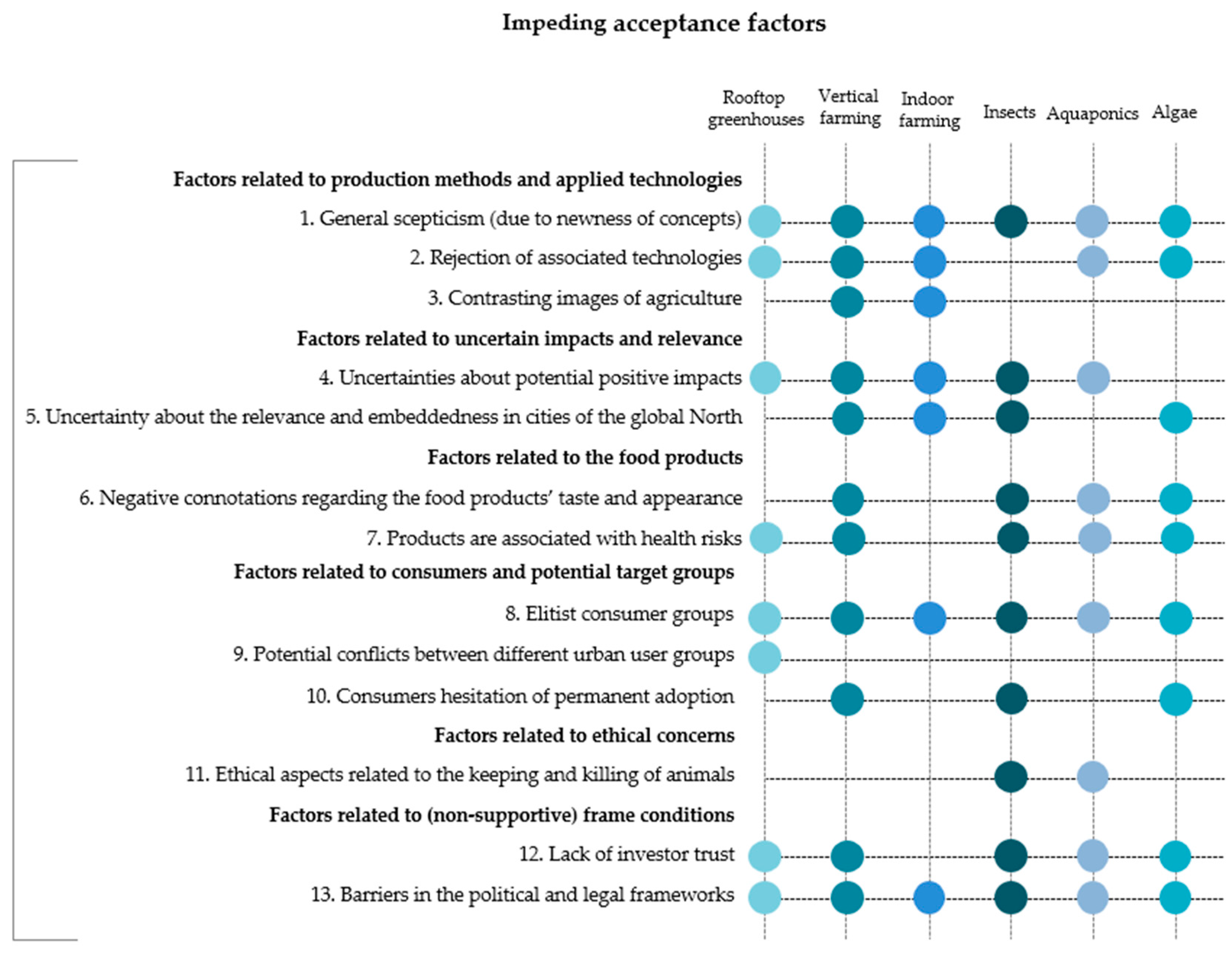
In the past, scholars have addressed the importance of acceptance for the successful introduction of new approaches [59,73,74,75,76]. Frequently, new approaches fail in the first stage of their introduction—often during the market implementation phase—because they are not accepted by society or potential users [77,78]. Therefore, social acceptance is a key factor in whether the introduction of an innovation succeeds or fails. According to Endruweit and Trommsdorff [79] factors attached to the new approach refer to the object’s specific attributes. Key factors include perceived social, economic and environmental risks and benefits but also product- or technology-related aspects [12]. As the perceived benefits are already sufficiently covered in the previous section, the following paragraph delves deeper into those acceptance factors, which might hinder the successful implementation of the new approaches (Figure 4).
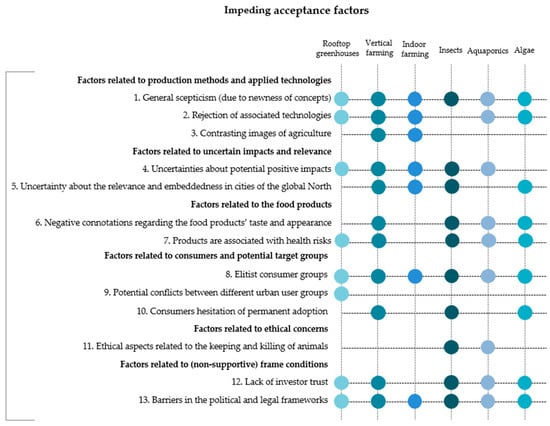
Figure 4.
Overview of impeding acceptance factors derived from the expert interviews. The point symbol (•) displays the mentioning of an aspect which could be assigned to a certain code. The single interview cases were displayed as aggregates for each approach.
3.2.1. Factors Related to Production Methods and Applied Technologies
Throughout the interviews, our experts report that potential consumers meet the new food production approaches with a certain critical presumption. They explain this is because those approaches are largely unknown among the general public. Even if people have already heard of them, a lack of concrete knowledge creates uncertainties and also leads to general skepticism. Some approaches are better known than others, e.g., rooftop greenhouses are more familiar than algae production. However, the experts witnessed that both knowledge and acceptance of new food production approaches are increasing overall, particularly among the younger population. This is also due to the growing media coverage.
Interviewees frequently describe a rejection of the associated technologies, particularly for those approaches that use soil-less growing techniques, such as indoor farming, vertical farming and rooftop greenhouses. Those approaches are often perceived as “unnatural” and “too futuristic” by the general public, and clash with prevailing images of agriculture.
“There is this romantic image of the field and that we all get our organic salad from the farmer around the corner. In reality, that is rarely the case. (…) There is a real demand for working with actual soil and being outside and far away from anything industrial. And vertical farming simply doesn’t align with this notion. In fact, it is the complete opposite. (…) Somebody once said: That sounds like mass plant-growing!”(Vertical-Farming Expert; VF2)
The romanticized image of food production associated with nature and rurality has already been identified as an acceptance-hindering factor, both for agricultural technologies in general [80] and for innovative urban food production approaches [35]. Socio-cultural values and morals, but also religion, can cause rejection of high-tech food production when it is considered as an interference with nature [81]. The complexity of technological production systems such as rooftop greenhouses or indoor farming systems furthermore face mistrust because consumers simply have difficulties understanding them [35]. The willingness to pay more for familiar vegetables produced using innovative technology might only increase for a few people, as a study on aquaponics showed [46].
3.2.2. Factors Related to Uncertain Impacts and Relevance
Uncertainties about potentially positive impacts of the new approaches (see Section 3.1) lead to negative perceptions and hinder the acceptance of these approaches. Doubts are particularly prevalent regarding the environmental balance (see Section 3.1.2) and economic viability (see Section 3.1.3). Due to the small-scale production, our experts perceive it, for example, as difficult for rooftop greenhouse operators to compete with conventional large-scale farms producing the same vegetables.
Experts express further uncertainties about the relevance and embeddedness of the approaches in cities of the global North. Approaches such as indoor and vertical farming are expected to have higher relevance in countries with higher technology appreciation, more urgent problems with land scarcity, water availability or air pollution, such as Asian megacities. Additionally, consumer acceptance of insect and algae-production is potentially higher in countries that already have a cultural tradition of insect- or algae consumption.
Furthermore, the environmental balance of high-tech farming systems has to be credibly improved and verified. Especially in Europe, sovereignty on food purchasing decisions is important to consumers. As long as the benefits of a new food-related technology are not evident to them, consumers tend to stick to their dietary routines instead of exposing themselves to unknown technologies. External pressures could lead to a lower rejection of food produced with innovative food technologies. For example, in regions with high food insecurity, people do not have a choice to deny food that is produced in a certain way. As long as external pressure such as the mentioned lack of space does not occur, some benefits of new food technologies may be irrelevant in a certain region and it can be difficult to increase consumers’ acceptance [82].
3.2.3. Factors Related to the Food Products
The results reveal existing negative attitudes towards the food products’ taste and appearance. In the case of algae or insects, there is a clear expectation of disgust for the products’ appearance and form. Insects, in particular, evoke negative connotations of “death and unhygienic conditions” (Insect cook; Insects1). The green color of algae might be a deterrent for a potential alternative protein source.
“When I think of the meat substitute industry, the colour green doesn’t come to mind at all. Nobody would eat green meat. Again, there is a certain mindset. What is green meat? It is mold, it is rotten, I don’t want to eat that.”(Algae production expert, Algae1)
Vegetables from urban production are also associated with health risks. The experts report a lack of consumer trust in the products’ quality, given that the urban environment in which they are produced is considered “unsafe” and affected by urban pollution, particularly by heavy metals and air-borne dust.
Indeed, it is a common finding that consumers are concerned about the safety of food produced in cities [35]. As all of our researched approaches can be conducted in a fully controlled environment, most urban contamination risks can be excluded [53]. In contrast to vegetable production, the production of edible insects is a relatively new sector in Western countries. That means that food safety standards have just been established and it is expensive to comply with them. Moreover, there is still a lack of research with respect to the food safety and allergenic potentials of edible insects [83]. With novel foods, just as the aforementioned novel technologies, it is especially important for the consumer to know or be able to observe the specific advantages of the food product before they favor it over an already familiar product [84,85]. While algae and edible insects are already an established part of diets elsewhere in the world, they face food neophobia or aversion in Western countries [33,45,86]. Piha et al. [42] found that educational strategies, such as improving consumers’ knowledge, creates higher acceptance for edible insects in Northern Europe, where entomophagy is not common.
3.2.4. Factors Related to Consumers and Potential Target Groups
One common criticism of the new approaches is that they target elitist consumer groups and exclusive market niches, and that products are not available for everyone. High investment risks and competitive markets lead to a situation that experts describe as “profit-and company-driven” business development. This is evaluated as a negative counter-model to grassroots- or citizen-driven initiatives. Interviewees appraise that the products would not be affordable to those who would need them most, but rather for “yuppies and hipsters” (Vertical farming expert; VF2).
Overall, the experts see hesitation from consumers regarding the permanent adoption of the new approaches. Even if there is acceptance and openness for a certain product, and the respective consumers are willing to try insect flour, micro-algae powder or lettuce from an urban rooftop farm, there is still a barrier to overcome before they are bought and integrated as part of a daily food consumption routine.
Finally, the approaches might not be suitable for mixed use-buildings or neighborhoods (see Section 3.1.1 for detailed results and discussion). Production activity within the urban fabric could potentially create conflicts, as it evokes noise and smell.
There are different opinions on whether consumers are willing and able to change their habits at all. Food choices are often not based on in-depth reasoning on pros and cons of a certain food (see Section 3.2.2 and Section 3.2.3), but rather, on habits [87]. Brand and Wissen [88] argue that even a high awareness of environmental problems does not sufficiently change consumer patterns, as they are usually deeply embedded in existing routines. In contrast, van Huis et al. [89] are convinced that diets can change quickly, and name sushi as an example of how a certain type of food can reach global popularity. From a social viewpoint, we have to discuss who benefits from a newly emerging regional food supply. Commercial urban farms currently sell their products at a premium price [67]. Consequently, the products are more likely to be accessible to people who possibly already pay attention to a balanced diet and are not restricted in their food choices due to their economic situation [82].
3.2.5. Factors Related to Ethical Concerns
Ethical concerns are most relevant for those approaches that involve the keeping and killing of animals. For aquaponics production, experts share the view that one must be particularly sensitive about securing the well-being of the fish that are kept in the tanks in high quantities and densities. A more general debate on keeping and killing insects was opened regarding the integration of insect production into the urban factory/fabric.
“Ethical conflicts are certainly going to emerge if this approach makes a more significant impact on the market. Of course, it is an animal product and living beings have been killed in order to manufacture the insect products. These animals are invertebrates, which means there is a real debate around whether they feel pain or not.”(Insect cook; Insects1)
It becomes obvious that doubts and concerns and therefore the possibility of an approach being rejected is higher once animals are involved.
Both our results and other studies exhibited that keeping animals in the city triggers animal welfare concerns [43], which adds another challenge for the acceptance of aquaponics and edible insect rearing [12]. In general, concerns about animal welfare are increasing among consumers. As animal welfare is considered as a demand-driven concern [90], transparent product information and clear labeling are very important purchase criteria that foster trust in products and respectively sales [68]. For successful labeling, though, it is necessary to explore which information should be provided to which consumer segments [90]. The opportunity to make altruistic purchase decisions considering ethical production is again highly dependent on the economic situation of a consumer [82].
3.2.6. Factors Related to (Non-Supportive) Framework Conditions
Finally, impeding acceptance factors can also be found in the form of non-supportive legal and market-related framework conditions. First, experts state that beside the consumer-side, acceptance on the investor-side is crucial. As the new approaches have barely been proven as business concepts, investors are hesitant to take the risk, which creates difficulties for potential operators. Moreover, barriers in the political and legal framework hinder the implementation processes. In some cases, the legal situation is unclear or complex (e.g., regarding the regulation of rooftop greenhouses in building legislation), which prevents operators from reliably drafting their business activities.
“We have made much more progress in terms of research and development. We haven’t quite got our performance up to the desired level yet. The state actually has enough parameters it can adjust in order to drive this kind of approach, but hasn’t gotten around to doing so yet.”(Managing director, building-integrated urban farm; RTG3)
Other regulations are seriously hindering potential activities, such as the EU “Novel food regulation” which restricts certain new areas of food production, and which affects micro-algae and insect production.
Indeed, urban agriculture in general and our approaches in particular face several legal obstacles. First of all, urban farms are not generally eligible for EU funding. They are often too small to be included in CAP pillar I funding and since they are located in urban areas, they are also excluded from pillar II. Hence, EU member states make case-by-case decisions on whether urban farming projects receive financial resources [11]. Due to the novelty of our investigated approaches, existing laws are often not applicable, which can cause additional constraints. Due to its innovative characteristics, it can be difficult to implement building-related agriculture in compliance with existing local building laws [35]. The production of novel foods such as algae and edible insects is also highly regulated in the EU [83,91]. For insects, legislation still differs from country to country, often leaving companies in grey zones. Consequently, even with sufficient demand from consumers, incentives for developing this sector are very low [44]. However, a joint definition of rules based on trusting cooperation between governments, businesses and science is crucial for the establishment of a new market [42].
3.3. Limitations of the Study and Propositions for Future Research
Innovative urban food production approaches are a very new field of research and development. The results presented in this paper point to a range of open questions, research gaps and options for future research. The results reveal the existence of reservations and perceived risks related to the urban integration of innovative food production approaches. As previously elaborated by Specht [92] most of these conflicts are formed based on individual normative considerations and can be linked to personal preferences, attitudes and/or opinions. In some cases, they are shaped by something we could label as “food neophobia”. For future research, it would be very promising to delve deeper into the underlying reasons for rejecting new urban food production approaches based on these types of conflicts.
As our study revealed, the experts expect potential advantages of innovative food production approaches in the improved resource- and CO2 efficiency, but they also raise doubts regarding the overall input-output-ratio. In fact, very few studies exist that investigate this overall ecological balance and those that exist are generated on a single- case basis. [38,63]. To negate or validate the assumptions regarding the environmental impacts, the overall CO2 balance of products (including life cycle assessments at all stages of construction and consumption) must be further scientifically quantified [92].
The aspect of social justice and accessibility was also repeatedly stressed. High investment costs of projects and the targeting of elitist consumer groups are a common critique, while the question remains: How can innovative food production approaches be supported and encouraged, that operate less exclusively, pay attention to social equity and do not exacerbate economic and environmental disparities?
Methodologically, one weakness was the large number of different interviewers within our research team. Even though all interviewers were trained in advance, used the exact same interview guideline, and most interviews were conducted in teams of two, there is still a risk of inconsistencies, caused by an “interviewer effect” (each interviewer has his or her own interview style, insecurities, level of patience, etc.). Further, our study relied on a comparably small sample size. In future works, the sustainability aspects and acceptance factors could be applied to studies with larger samples for comparative purposes, in which our results could serve as hypotheses (qualitatively or quantitatively) to be tested. It would further be promising to gain further insights into their importance and weighting in different spatial contexts.
Our study revealed, that the topic of innovative food production approaches has grown considerably in the past few years and is gaining increasing importance. It would be worth re-visiting the topic again in a few years’ time, to see how the field has developed and if the perception and acceptance has changed over time.
In the innovation context, existing studies typically focus on one specific aspect: they either address technological development or questions of social acceptance. As laid out in our study, social acceptance and perception play a major role for the successful development and implementation of innovative food production approaches. We suggest, that for future research on innovative food production approaches, technology development and its social acceptance should be understood as two sides of the same coin. Therefore, instead of isolating the questions of technology and acceptance, future research should acknowledge that those two are closely related and that successful diffusion can only be achieved by an integrated consideration of the relationship between technology and acceptance.
4. Conclusions
The aim of this paper was to assess sustainability benefits of six innovative approaches that potentially contribute to future urban food supply and to identify acceptance barriers for their dissemination. According to our experts, each of the innovative food production approaches exhibits a broad variety of sustainability aspects and benefits. At the same time, the general public is perceived as increasingly interested in the approaches. These two overarching findings from our interviews can be interpreted as a favourable basis for dissemination and future viability. While we could not find clear patterns where sustainability benefits of different approaches complement each other, a combination of different approaches makes sense for an urban food supply that ensures a balanced diet. Algae and insects were considered to be a good protein source and vegetables from indoor farming, vertical farming and rooftop greenhouses can provide vitamins. However, there are also significant barriers to overcome on many levels.
Scepticism and a certain lack of knowledge on the consumer side depict an obstacle for dissemination throughout all approaches. Our experts brought up possible ethical concerns for the animal-related food production approaches of insect farming and aquaponics and possible rejection of food produced in high-tech systems such as indoor farms or vertical farms. Furthermore, algae and insects are not traditionally part of peoples’ diets in the global north and can trigger disgust or food neophobia, which is another acceptance obstacle to overcome. The variety of acceptance barriers suggests that different approaches appeal to different consumer segments, which should be addressed accordingly. On the level of practical implementation, the experts assessed a lack of efficient technological solutions to innovative food production and hence, to tapping the sustainability potentials completely. Due to their innovative character, all of our researched food production approaches face legal regulations that hinder their expansion. Again, these aspects minimize the interest of potential investors.
Overall, action needs to be taken on several levels to foster adoption and dissemination. Actors from those different levels can use the information from our study to take respective measures in their field of action: interested practitioners can use our results as an orientation for their own setup and consumer communication. Urban planners can assess which approach or combination of approaches might be most suitable to the condition of a certain city and lawmakers can become aware of the legal barriers and act accordingly. As adaptive processes on different levels usually take time, we estimate the diffusion pace of the researched approaches to be slow. An accelerating external factor could be a crisis or ongoing severe environmental degradation and a growing awareness thereof. We consider an adaption of the legal framework as a necessary first step towards breaking the cycle of obstacles and laying the foundation for a successful diffusion of innovative food production.
Author Contributions
K.S. designed and supervised the research. K.S. and F.Z. conceptualized the data collection, collected the data, transcribed and analyzed the data, and wrote the paper. H.S., J.B. and J.K. conceptualized the data collection, collected the data, transcribed and analyzed the data and contributed to the manuscript. M.R. facilitated the research and revised the paper.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We conducted our research within the program initiative “bologna.lab” from the Humboldt University of Berlin. The program of the specific “Q-Team” ‘Innovative approaches of urban food production—acceptance, potentials, and risks’ lead by Kathrin Specht, aimed at cross-faculty teaching and learning to enable junior researchers to develop and implement a research process on an interdisciplinary topic. The total research team consisted of 11 researchers. We would like to acknowledge our entire research team as well as the experts who participated in our interviews. We appreciate the time and effort that the reviewers have taken to comment on our paper and we want to thank them for their useful suggestions concerning our manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Feldmann, C.; Hamm, U. Consumers’ perceptions and preferences for local food: A review. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 40, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, C.; Hamm, U. Local and/or organic: a study on consumer preferences for organic food and food from different origins: Consumer preferences for local and/or organic food. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2016, 40, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, R. European and United States farmers’ markets: Similarities, differences and potential developments. In Proceedings of the 113th EAAE seminar. A Resilient European Food Industry and Food Chain in a Challenging World, Chania, Crete, Greece, 3–6 September 2009; Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/58131/ (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Brunori, G.; Galli, F.; Barjolle, D.; van Broekhuizen, R.; Colombo, L.; Giampietro, M.; Kirwan, J.; Lang, T.; Mathijs, E.; Maye, D.; et al. Are Local Food Chains More Sustainable than Global Food Chains? Considerations for Assessment. Sustainability 2016, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoll, F.; Specht, K.; Opitz, I.; Siebert, R.; Piorr, A.; Zasada, I. Individual choice or collective action? Exploring consumer motives for participating in alternative food networks. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2018, 42, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Bustamante, M.; Ahammad, H.; Clark, H.; Dong, H.; Elsiddig, E.A.; Haberl, H.; Harper, R.; House, J.; Jafari, M.; et al. Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use (AFOLU). In Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Edenhofer, O., Pichs-Madruga, R., Sokona, Y., Farahani, E., Kadner, S., Seyboth, K., Adler, A., Baum, I., Brunner, S., Eickemeier, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 811–922. [Google Scholar]
- Meynard, J.-M.; Dedieu, B.; Bos, A.P. Re-design and co-design of farming systems. An overview of methods and practices. In Farming Systems Research into the 21st Century: The New Dynamic; Darnhofer, I., Gibbon, D., Dedieu, B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 405–429. ISBN 978-94-007-4502-5. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, E.; Galli, F.; Menozzi, D.; Maye, D.; Touzard, J.-M.; Marescotti, A.; Six, J.; Brunori, G. Comparing the sustainability of local and global food products in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, B.; Purcell, M. Avoiding the Local Trap: Scale and Food Systems in Planning Research. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2006, 26, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angotti, T. Urban agriculture: Long-term strategy or impossible dream? Public Health 2015, 129, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piorr, A.; Zasada, I.; Doernberg, A.; Zoll, F.; Ramme, W.; European Parliament; Directorate-General for Internal Policies; Policy Department B: Structural and Cohesion Policies; European Parliament. Research for AGRI Committee—Urban and Peri-Urban Agriculture in the EU; Committee on Agriculture and Rural Development: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; ISBN 978-92-846-2952-7. [Google Scholar]
- Specht, K.; Weith, T.; Swoboda, K.; Siebert, R. Socially acceptable urban agriculture businesses. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.C.; Salois, M.J. Local versus organic: A turn in consumer preferences and willingness-to-pay. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2010, 25, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schans, J.W.; Wiskerke, J.S.C. Urban agriculture in developed economies. In Sustainable Food Planning; Viljoen, A., Wiskerke, J.S.C., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 245–258. [Google Scholar]
- Hinrichs, C. Embeddedness and local food systems: notes on two types of direct agricultural market. J. Rural Stud. 2000, 16, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortman, S.E.; Lovell, S.T. Environmental Challenges Threatening the Growth of Urban Agriculture in the United States. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougall, R.; Kristiansen, P.; Rader, R. Small-scale urban agriculture results in high yields but requires judicious management of inputs to achieve sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodhouse, P. Beyond Industrial Agriculture? Some Questions about Farm Size, Productivity and Sustainability: Questions about Farm Size, Productivity and Sustainability. J. Agrar. Chang. 2010, 10, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benis, K.; Turan, I.; Reinhart, C.; Ferrão, P. Putting rooftops to use—A Cost-Benefit Analysis of food production vs. energy generation under Mediterranean climates. Cities 2018, 78, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despommier, D. Farming up the city: the rise of urban vertical farms. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 388–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, A.; Silva, E.; Colquhoun, J. Innovation in urban agricultural practices: Responding to diverse production environments. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2015, 30, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, D.C.; Fry, J.P.; Li, X.; Hill, E.S.; Genello, L.; Semmens, K.; Thompson, R.E. Commercial aquaponics production and profitability: Findings from an international survey. Aquaculture 2015, 435, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Malone, S.; Morris, Z.; Weissburg, M.; Bras, B. Combined Fish and Lettuce Cultivation: An Aquaponics Life Cycle Assessment. Procedia CIRP 2018, 69, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blidariu, F.; Grozea, A. Increasing the Economical Efficiency and Sustainability of Indoor Fish Farming by Means of Aquaponics—Review. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Forchino, A.A.; Gennotte, V.; Maiolo, S.; Brigolin, D.; Mélard, C.; Pastres, R. Eco-designing Aquaponics: A Case Study of an Experimental Production System in Belgium. Procedia CIRP 2018, 69, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.I.; Baeza, E.; Heuvelink, E.; Rieradevall, J.; Muñoz, P.; Ercilla, M.; Stanghellini, C. Productivity of a building-integrated roof top greenhouse in a Mediterranean climate. Agric. Syst. 2017, 158, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuan-Delmás, D.; Llorach-Massana, P.; Nadal, A.; Ercilla-Montserrat, M.; Muñoz, P.; Montero, J.I.; Josa, A.; Gabarrell, X.; Rieradevall, J. Environmental assessment of an integrated rooftop greenhouse for food production in cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, C.; Adenaeuer, L. Up, Up and Away! The Economics of Vertical Farming. J. Agric. Stud. 2014, 2, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, K.; Siebert, R.; Hartmann, I.; Freisinger, U.B.; Sawicka, M.; Werner, A.; Thomaier, S.; Henckel, D.; Walk, H.; Dierich, A. Urban agriculture of the future: an overview of sustainability aspects of food production in and on buildings. Agric. Hum. Values 2014, 31, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A. Potential of Insects as Food and Feed in Assuring Food Security. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; van Itterbeeck, J.; Heetkamp, M.J.W.; van den Brand, H.; van Loon, J.J.A.; van Huis, A. An Exploration on Greenhouse Gas and Ammonia Production by Insect Species Suitable for Animal or Human Consumption. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, D.; Swift, J.A.; Field, L.M. Opportunities and hurdles of edible insects for food and feed. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaweed Sustainability: Food and Non-Food Applications; Tiwari, B.K., Troy, D.J., Eds.; Elsevier/AP: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 978-0-12-418697-2. [Google Scholar]
- Draaisma, R.B.; Wijffels, R.H.; (Ellen) Slegers, P.; Brentner, L.B.; Roy, A.; Barbosa, M.J. Food commodities from microalgae. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, K.; Siebert, R.; Thomaier, S. Perception and acceptance of agricultural production in and on urban buildings (ZFarming): A qualitative study from Berlin, Germany. Agric. Hum. Values 2016, 33, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Chalabi, M. Vertical farming: Skyscraper sustainability? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 18, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchino, A.A.; Lourguioui, H.; Brigolin, D.; Pastres, R. Aquaponics and sustainability: The comparison of two different aquaponic techniques using the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). Aquac. Eng. 2017, 77, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyé-Mengual, E.; Oliver-Solà, J.; Montero, J.I.; Rieradevall, J. An environmental and economic life cycle assessment of rooftop greenhouse (RTG) implementation in Barcelona, Spain. Assessing new forms of urban agriculture from the greenhouse structure to the final product level. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, K.; Siebert, R.; Thomaier, S.; Freisinger, U.; Sawicka, M.; Dierich, A.; Henckel, D.; Busse, M. Zero-Acreage Farming in the City of Berlin: An Aggregated Stakeholder Perspective on Potential Benefits and Challenges. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4511–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyé-Mengual, E.; Anguelovski, I.; Oliver-Solà, J.; Montero, J.I.; Rieradevall, J. Resolving differing stakeholder perceptions of urban rooftop farming in Mediterranean cities: promoting food production as a driver for innovative forms of urban agriculture. Agric. Hum. Values 2015, 33, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, C.; Siegrist, M. Consumer perception and behaviour regarding sustainable protein consumption: A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piha, S.; Pohjanheimo, T.; Lähteenmäki-Uutela, A.; Křečková, Z.; Otterbring, T. The effects of consumer knowledge on the willingness to buy insect food: An exploratory cross-regional study in Northern and Central Europe. Food Qual. Prefer. 2018, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J. Consumer acceptance of insect-based foods in the Netherlands: Academic and commercial implications. Appetite 2016, 107, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, S.; Moruzzo, R.; Riccioli, F.; Paci, G. European consumers’ readiness to adopt insects as food. A review. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, W. Profiling consumers who are ready to adopt insects as a meat substitute in a Western society. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 39, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miličić, V.; Thorarinsdottir, R.; Santos, M.; Hančič, M. Commercial Aquaponics Approaching the European Market: To Consumers’ Perceptions of Aquaponics Products in Europe. Water 2017, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyé-Mengual, E.; Specht, K.; Krikser, T.; Vanni, C.; Pennisi, G.; Orsini, F.; Gianquinto, G.P. Social acceptance and perceived ecosystem services of urban agriculture in Southern Europe: The case of Bologna, Italy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuckartz, U. Qualitative Text Analysis. In A Guide to Methods, Practice and Using Software, 1st ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4462-6774-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kuckartz, U. Qualitative Inahltsanalyse. Methoden, Praxis und Computerunterstützung, 3rd ed.; Beltz Juventa: Weinheim, Germany; Basel, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Brundtland Report: Report of the World. Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher Bundestag Abschlußbericht der Enquete-Kommission, Schutz des Menschen und der Umwelt—Ziele und Rahmenbedingungen Einer Nachhaltig Zukunftsverträglichen Entwicklung” * Konzept Nachhaltigkeit Vom Leitbild zur Umsetzung. 1998. Available online: http://dipbt.bundestag.de/doc/btd/13/112/1311200.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Dearing, A. Sustainable Innovation: Drivers and Barriers. In Innovation and the Environment; OECD: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Eigenbrod, C.; Gruda, N. Urban vegetable for food security in cities. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.; Reynolds, K.; Sanghvi, R. Five Borough Farm: Seeding the Future of Urban Agriculture in New York City; Chou, J., Ed.; Design Trust for Public Space: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 0-9777175-6-9. [Google Scholar]
- Thomaier, S.; Specht, K.; Henckel, D.; Dierich, A.; Siebert, R.; Freisinger, U.B.; Sawicka, M. Farming in and on urban buildings: Present practice and specific novelties of Zero-Acreage Farming (ZFarming). Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2015, 30, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busa, J.H.; Garder, R. Champions of the Movement or Fair-weather Heroes? Individualization and the (A)politics of Local Food, Antipode 2015, 47, 323–341. [Google Scholar]
- Nadal, A.; Pons, O.; Cuerva, E.; Rieradevall, J.; Josa, A. Rooftop greenhouses in educational centers: A sustainability assessment of urban agriculture in compact cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, E.R. Implementation of Aquaponics in Education: An Assessment of Challenges, Solutions and Success. Master’s Thesis, University of Massachusetts Amherst, Amherst, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Specht, K.; Sanyé-Mengual, E. Risks in urban rooftop agriculture: Assessing stakeholders’ perceptions to ensure efficient policymaking. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 69, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbicca, J. Urban Agriculture, Revalorization, and Green Gentrification in Denver, Colorado. In the Politics of Lands; Bartley, T., Ed.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2019; Volume 26, pp. 149–170. ISBN 978-1-78756-428-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bundesministerium für Ernährung und Landwirtschaft (BMEL) Rechtsgrundlagen für die Lebensmittelhygiene. Available online: https://www.bmel.de/DE/Ernaehrung/SichereLebensmittel/Hygiene/_Texte/Rechtsgrundlagen.html (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Pearson, L.J.; Pearson, L.; Pearson, C.J. Sustainable urban agriculture: stocktake and opportunities. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2010, 8, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.; Hauschild, M.; Fernández, J.; Birkved, M. Urban versus conventional agriculture, taxonomy of resource profiles: a review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; de Boer, I.J.M. Environmental Impact of the Production of Mealworms as a Protein Source for Humans—A Life Cycle Assessment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schlüter, O.K. Potential and challenges of insects as an innovative source for food and feed production. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schans, J.W. van der Urban Agriculture in the Netherlands. Urban Agric. Mag. RUAF 2010, 24, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Benis, K.; Ferrão, P. Commercial farming within the urban built environment—Taking stock of an evolving field in northern countries. Glob. Food Secur. 2018, 17, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pölling, B.; Sroka, W.; Mergenthaler, M. Success of urban farming’s city-adjustments and business models—Findings from a survey among farmers in Ruhr Metropolis, Germany. Land Use Policy 2017, 69, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, K.; Reynolds, K.; Sanyé-Mengual, E. Community and Social Justice Aspects of Rooftop Agriculture. In Rooftop Urban Agriculture; Orsini, F., Dubbeling, M., de Zeeuw, H., Gianquinto, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 277–290. ISBN 978-3-319-57719-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, N.; Reynolds, K. Resource needs for a socially just and sustainable urban agriculture system: Lessons from New York City. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2015, 30, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulewski, P.; Kłoczko-Gajewska, A.; Sroka, W. Relations between Agri-Environmental, Economic and Social Dimensions of Farms’ Sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, V.; Gremmen, B.; Wesselink, R. Philosophy Documentation Center Dealing with the Wicked Problem of Sustainability in advance: The Role of Individual Virtuous Competence. Bus. Prof. Ethics J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüsing, B.; Bierhals, R.; Bührlen, B.; Friedewald, M.; Kimpeler, S.; Menrad, K.; Wengel, J.; Zimmer, R.; Zoche, P. Technikakzeptanz und Nachfragemuster als Standortvorteil; Fraunhofer ISI: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lucke, D. Akzeptanz: Legitimität in der “Abstimmungsgesellschaft”; Leske + Budrich: Leverkusen, Germany, 1995; ISBN 3-8100-1496-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, A.; Luz, F.; Suda, M.; Weiland, U. Steigerung der Akzeptanz von FFH-Gebieten; BfN-Skripten; Bundesamt für Naturschutz -BfN-: Bonn, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, M.; Keppler, D. Modelle der Technikorientierten Akzeptanzforschung—Überblick und Reflexion am Beispiel Eines Forschungsprojekts zur Implementierung Innovativer Technischer Energieeffizienz-Maßnahmen; Zentrum Technik und Gesellschaft (ZTG): Berlin, Germany, 2013; Available online: https://depositonce.tu-berlin.de/bitstream/11303/4758/1/schaefer_keppler.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Schwerdtner, W.; Freisinger, U.B.; Siebert, R.; Werner, A. Partizipative Roadmaps für Innovationen zur Förderung der Regionalentwicklung. Praxisleitfaden; Leibniz Centre for Agricultural Landscape Research (ZALF): Müncheberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schwerdtner, W.; Siebert, R.; Busse, M.; Freisinger, U. Regional Open Innovation Roadmapping: A New Framework for Innovation-Based Regional Development. Sustainability 2015, 7, 2301–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endruweit, G.; Trommsdorff, G. Wörterbuch der Soziologie; UTB; 2; völlig neubearbeitete und erw. Aufl.; Lucius & Lucius: Stuttgart, Germany, 2002; ISBN 3-8282-0172-5. [Google Scholar]
- Food Systems Failure: the Global Food Crisis and the Future of Agriculture; Rosin, C.J.R., Ed.; Earthscan Food and Agriculture; Earthscan: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-1-84971-229-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ronteltap, A.; van Trijp, J.C.M.; Renes, R.J.; Frewer, L.J. Consumer acceptance of technology-based food innovations: Lessons for the future of nutrigenomics. Appetite 2007, 49, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, D.; Chaturvedi, S.; Li, Q.; Ladikas, M. New Food Technologies in Europe, India and China. In Science and Technology Governance and Ethics; Ladikas, M., Chaturvedi, S., Zhao, Y., Stemerding, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 111–124. ISBN 978-3-319-14692-8. [Google Scholar]
- House, J. Insects as food in the Netherlands: Production networks and the geographies of edibility. Geoforum 2018, 94, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frewer, L. Consumer Perceptions and Novel Food Acceptance. Outlook Agric. 1998, 27, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frewer, L.J.; Bergmann, K.; Brennan, M.; Lion, R.; Meertens, R.; Rowe, G.; Siegrist, M.; Vereijken, C. Consumer response to novel agri-food technologies: Implications for predicting consumer acceptance of emerging food technologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, D.; Skallerud, K.; Paul, N. Who Eats Seaweed? An Australian Perspective. J. Int. Food Agribus. Mark. 2018, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.R.H.; de Jong, A.E.I.; de Jonge, R.; Frewer, L.J.; Nauta, M.J. Improving Food Safety in the Domestic Environment: The Need for a Transdisciplinary Approach. Risk Anal. 2005, 25, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, U.; Wissen, M. Crisis and continuity of capitalist society-nature relationships: The imperial mode of living and the limits to environmental governance. Rev. Int. Polit. Econ. 2013, 20, 687–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; van Huis, A., Van Itterbeck, J., Klunder, H., Mertens, E., Halloran, A., Muir, G., Vantomme, P., Eds.; FAO forestry paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013; ISBN 978-92-5-107595-1. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhonacker, F.; Verbeke, W. Public and Consumer Policies for Higher Welfare Food Products: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2014, 27, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigani, M.; Parisi, C.; Rodríguez-Cerezo, E.; Barbosa, M.J.; Sijtsma, L.; Ploeg, M.; Enzing, C. Food and feed products from micro-algae: Market opportunities and challenges for the EU. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 42, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, K. The Introduction and Implementation of “Zero-Acreage Farming (ZFarming)”. Potentials, limitations, and Acceptance; Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).