Dynamic Simulation of Land Use Change of the Upper and Middle Streams of the Luan River, Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
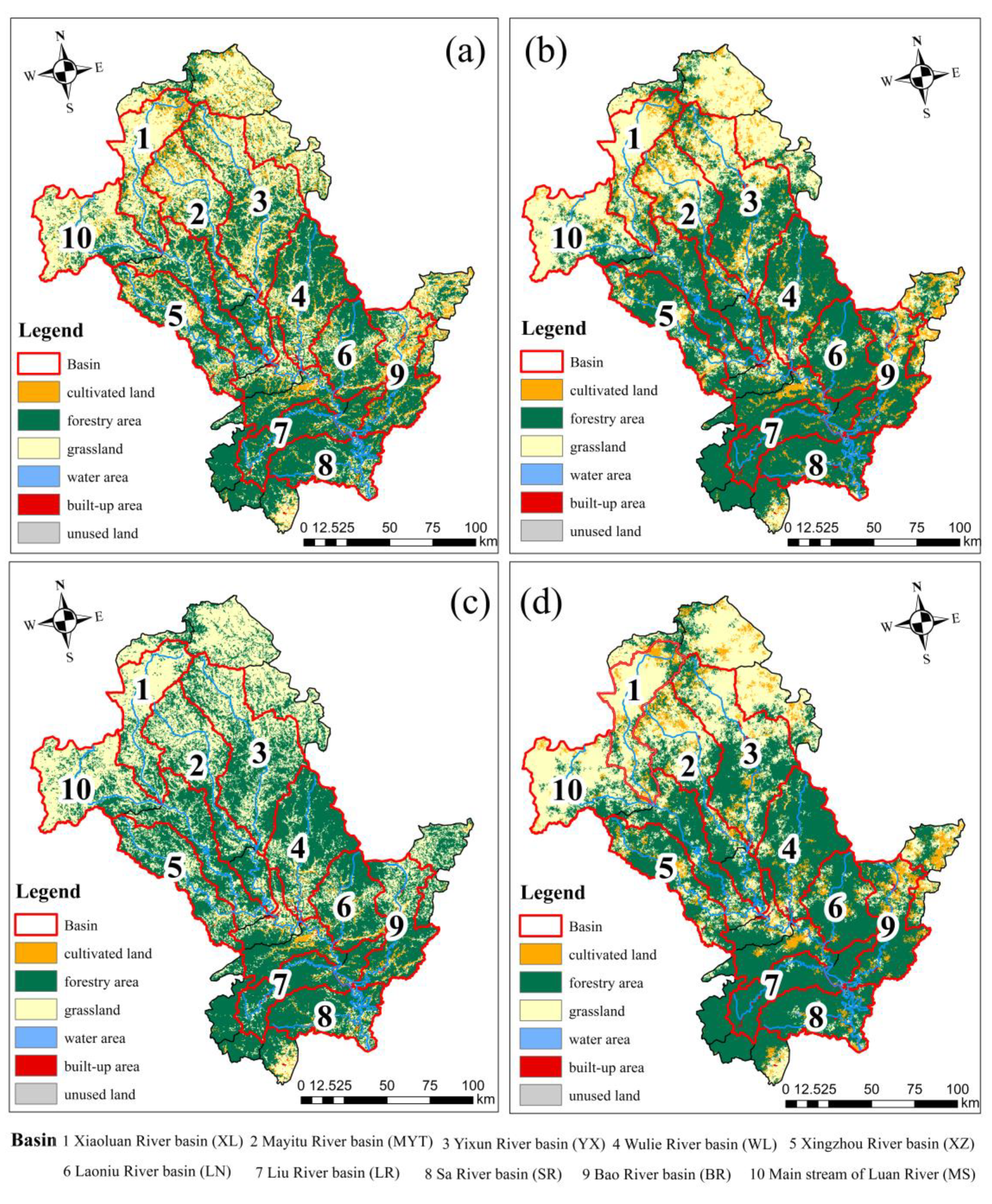
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Scenario Design
2.3.2. FLUS Model
3. Results
3.1. Quantifying Changes in Land Use
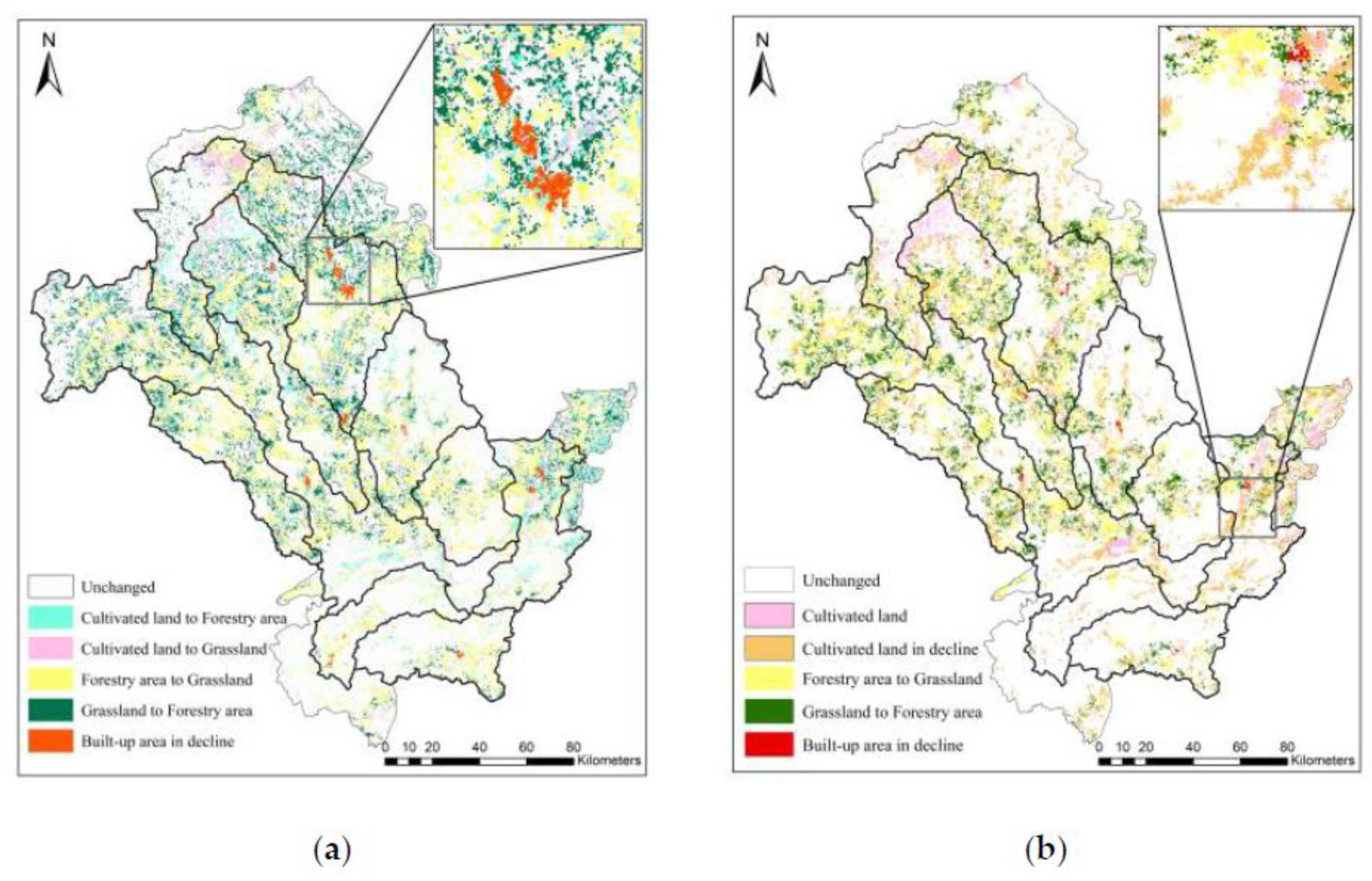
3.2. Spatial Allocation of Land Use Changes
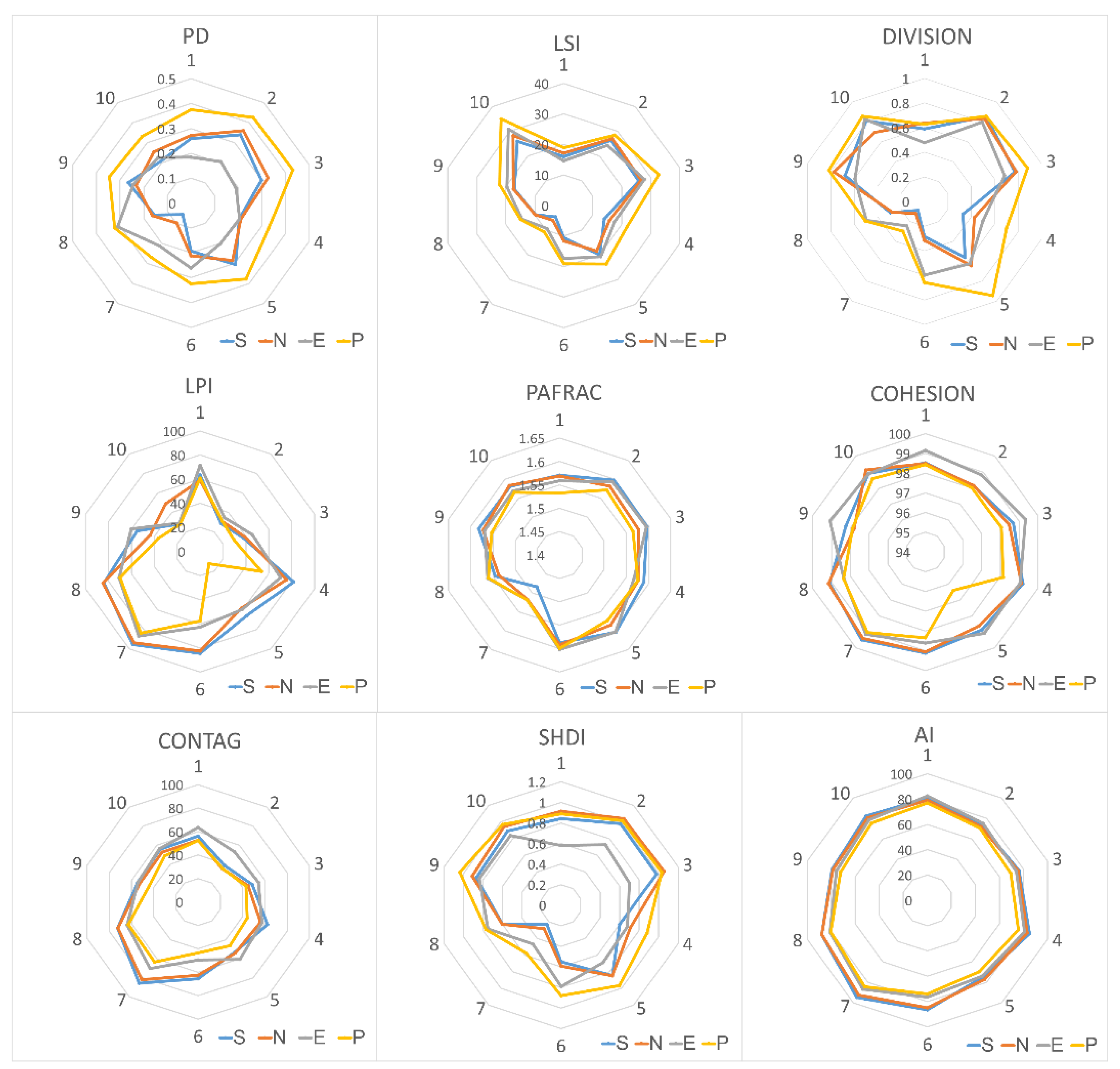
3.3. Landscape Patterns under Different Scenarios
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Scenarios Setting and Each Scenario Simulation
4.2. The Changes of Landscape Pattern
4.3. Availability of an Integrated Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, L.; Cui, X.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Rounsevell, M.; Murray-Rust, D.; Liu, Y. A simple global food system model. Agric. Econ. 2014, 60, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verburg, P.H.; Overmars, K.P. Combining top-down and bottom-up dynamics in land use modeling: Exploring the future of abandoned farmlands in Europe with the Dyna-CLUE model. Landsc. Ecol. 2009, 24, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, H.A.; Duraiappah, A.; Larigauderie, A. Evolution of natural and social science interactions in global change research programs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3665–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Gao, Q.; Peng, C.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L. Integrating global socio-economic influences into a regional land use change model for China. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 8, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, X.; Guan, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y. Simulation of Spatiotemporal Land Use Changes for Integrated Model of Socioeconomic and Ecological Processes in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, M.J.; Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Acosta-Michlik, L.; Leemans, R.; Schröter, D. The vulnerability of ecosystem services to land use change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 114, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samie, A.; Deng, X.; Jia, S.; Chen, D. Scenario-Based Simulation on Dynamics of Land-Use-Land-Cover Change in Punjab Province, Pakistan. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfu, D.A.I.; Liang, M.A. Review on land change modeling approaches. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 152–162. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, B.L.; Lambin, E.F.; Reenberg, A. The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20666–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J. Land-Use and Land-Cover Change: Local Processes and Global Impacts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Yueqing, X.; Xiaomei, S.; Jing, W. Advnces and prospects of spatial optimal allocation of land use. Prog. Geogr. 2009, 28, 791–797. [Google Scholar]
- Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Pedroli, B.; Erb, K.H.; Gramberger, M.; Busck, A.G.; Haberl, H.; Kristensen, S.; Kuemmerle, T.; Lavorel, S.; Lindner, M.; et al. Challenges for land system science. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C.; Derdouri, A.; Murayama, Y. Spatiotemporal Simulation of Future Land Use/Cover Change Scenarios in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debonne, N.; van Vliet, J.; Heinimann, A.; Verburg, P. Representing large-scale land acquisitions in land use change scenarios for the Lao PDR. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.; Ge, Y.; Ma, J. Application the Linear Programme to Calculate Water Environmental Capacity. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2009, 20, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Eisinger, E.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Stewart, T.J. Using Linear Integer Programming for Multi-Site Land-Use Allocation. Geogr. Anal. 2003, 35, 148–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.; Herwijnen, M.V.; Janssen, R.; Stewart, T. Evaluating Spatial Design Techniques for Solving Land-use Allocation Problems. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2005, 48, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.C.; Huang, G.H.; Zou, R.; Xu, Y.L.; Liu, L. An inexact multiobjective programming method and its application in the watershed environmental system planning—Environmental system planning of the Lake Erhai Basin. China Environ. Sci. 1999, 19, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, K.; Huang, B.; Wang, S.; Lin, H. Sustainable land use optimization using Boundary-based Fast Genetic Algorithm. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, T.J.; Janssen, R. A multiobjective GIS-based land use planning algorithm. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2014, 46, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, T.J.; Janssen, R.; Herwijnen, M.V. A genetic algorithm approach to multiobjective land use planning. Comput. Oper. Res. 2004, 31, 2293–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.J.; Guo, H.C.; Liu, Y.; Huang, K.; Wang, Z. On the progress in urban ecosystem dynamic modeling. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 2603–2614. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ou, J.; Li, X.; Ai, B. Combining system dynamics and hybrid particle swarm optimization for land use allocation. Ecol. Model. 2013, 257, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, A.N. Rangelands destruction under population growth: The case of Iran. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1990, 6, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, R.; Herwijnen, M.V.; Stewart, T.J.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Multiobjective decision support for land-use planning. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2008, 35, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Tam, C.; Chen, X. Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9477–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, D.; Manson, S.; Janssen, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Deadman, P. Multi-Agent Systems for the Simulation of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change: A Review. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2003, 93, 314–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lantman, J.V.S.; Verburg, P.H.; Bregt, A.; Geertman, S. Core Principles and Concepts in Land-Use Modelling: A Literature Review; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, M.; Krugman, P.; Mori, T. On the evolution of hierarchical urban systems 1. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1999, 43, 209–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naboureh, A.; Rezaei Moghaddam, M.H.; Feizizadeh, B.; Blaschke, T. An integrated object-based image analysis and CA-Markov model approach for modeling land use/land cover trends in the Sarab plain. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Soepboer, W.; Veldkamp, A.; Limpiada, R.; Espaldon, V.; Mastura, S.S. Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: The CLUE-S model. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Overmars, K.P.; Huigen, M.G.A.; Groot, W.T.D.; Veldkamp, A. Analysis of the effects of land use change on protected areas in the Philippines. Appl. Geogr. 2006, 26, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.F.; Zhou, X.W. Projections of future land use changes: Multiple scenarios -based impacts analysis on ecosystem services for Wuhan city, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, J.A.; Zhang, Y. Coupling a land use model and an ecosystem model for a crop-pasture zone. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Pei, F. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowski, B.C.; Alexandridis, K.T.; Müller, D. Modelling urbanization patterns in two diverse regions of the world. J. Land Use Sci. 2006, 1, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, C.; Clarke, K.C. Toward Optimal Calibration of the SLEUTH Land Use Change Model. Trans. GIS 2007, 11, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.C.; Gaydos, L.J. Loose-coupling a cellular automaton model and GIS: Long-term urban growth prediction for San Francisco and Washington/Baltimore. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1998, 12, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohl, T.L.; Sayler, K.L.; Drummond, M.A.; Loveland, T.R. The FORE-SCE model: A practical approach for projecting land cover change using scenario-based modeling. J. Land Use Sci. 2007, 2, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Cornell, J.D.; Hall, C.A. Modeling the spatial pattern of land-use change with GEOMOD2: Application and validation for Costa Rica. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, J.; Gharagozlou, A.; Arjmandi, R.; Faryadi, S.; Adl, M. Predicting Urban Land Use Changes Using a CA–Markov Model. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 5565–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferchichi, A.; Boulila, W.; Farah, I.R. Reducing uncertainties in land cover change models using sensitivity analysis. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2017, 55, 719–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, J.P.; Scheffer, M.; Harms, B. Estimating habitat isolation in landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1992, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.B.; Xie, C.H.; Ke Ming, M.A.; Niu, J.Z.; Zhao, Y.T.; Wang, X.L. A vital method for constructing regional ecological security pattern:landscape ecological restoration and rehabilitation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2003, 23, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.Z.; Xia, B.C.; Chen, J.F. Dynamic analysis of the Guangzhou landscape eco-security pattern based on 3S technology. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 4323–4333. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.J.; Qiao, Q.; Li, D.H.; Yuan, H.; Wang, S.S. Ecological land use in three towns of eastern Beijing: A case study based on landscape security pattern analysis. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 20, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Dong, S. Ecological Security Assessment of Yuan River Watershed Based on Landscape Pattern and Soil Erosion. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, N.; Yang, M.H.; Lin, Z.L.; Yang, D.W.; Huang, Y. Landscape pattern changes of Xiamen coastal zone and their impacts on local ecological security. Chin. J. Ecol. 2012, 31, 3193–3202. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J. Land-Use and Land-Cover Change. Ambio 2006, 21, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Liu, W.; Cao, M. Impact of land use and land cover changes on ecosystem services in Menglun, Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 146, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, M.W.D.; Munoz, P.; dos Santos, J.R.; Alves, D.S. Land use and cover change modelling and scenarios in the Upper Uruguay Basin (Brazil). Ecol. Model. 2018, 384, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbold, T. Future effects of climate and land-use change on terrestrial vertebrate community diversity under different scenarios. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.A.; Dang, Y.F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.C. Simulation of future land-use scenarios in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region under the effects of multiple factors. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1907–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Q.; Zhao, W.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhai, R.J. Influence of land use change on the ecosystem service trade-offs in the ecological restoration area: Dynamics and scenarios in the Yanhe watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadolahi, Z.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Sakieh, Y.; Mirkarimi, S.H.; Baral, H.; Azimi, M. Dynamic trade-off analysis of multiple ecosystem services under land use change scenarios: Towards putting ecosystem services into planning in Iran. Ecol. Complex. 2018, 36, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Zhang, W. The evolution of the modern Luanhe River delta, north China. Geomorphology 1998, 25, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowett, A.J. China’s Water Crisis: The Case of Tianjin (Tientsin). Geogr. J. 1986, 152, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, D.; Huang, G.; Huang, Q. Integrative Modeling and Strategic Planning for Regional Sustainability under Climate Change. Adv. Earth Sci. 2014, 29, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Xinxiao, Y.; Jiangkun, Z.; Yousheng, W. Ecological and Hydrological Responses of Watershed to Human Activities and Climate Change; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoliang, S.; Zhiyong, Y.; Denghua, Y.; Ying, L.; Zhe, Y. On hydrological response to land-use /cover change in Luanhe River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dong, M.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Using a water quality index to assess the water quality of the upper and middle streams of the Luanhe River, northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Yu, X. Distinguishing human and climate influences on streamflow changes in Luan River basin in China. Catena 2016, 136, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Meteorogical Information Center. Available online: http://data.cma.cn (accessed on 20 March 2015).
- Jenson, S.K. Applications of Hydrologic Information Automatically Extracted From Digital Elevation Models. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 5, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidigan, M.L.G.; Sanou, C.L.; Ragatoa, D.S.; Fafa, C.O.; Mishra, V.N. Assessing Land Use/Land Cover Dynamic and Its Impact in Benin Republic Using Land Change Model and CCI-LC Products. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, Q.; Peng, C.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L. A Simple Global Food System Model. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 8, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resource and Environment Data Cloud Platform. Available online: http://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 28 May 1990).
- Open Street Map. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- McGarigal, K. Landscape Pattern Metrics. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.D.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Chen, W.H.; Li, S.M. Improvement of the Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Service Value Based on Per Unit Area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Sahle, M.; Saito, O.; Fürst, C.; Demissew, S.; Yeshitela, K. Future land use management effects on ecosystem services under different scenarios in the Wabe River catchment of Gurage Mountain chain landscape, Ethiopia. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 14, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, T.; Cai, C.; Li, Z.; Teng, M. Scenarios Simulation of Spatio-Temporal Land Use Changes for Exploring Sustainable Management Strategies. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yirsaw, E.; Wu, W.; Shi, X.P.; Temesgen, H.; Bekele, B. Land Use/Land Cover Change Modeling and the Prediction of Subsequent Changes in Ecosystem Service Values in a Coastal Area of China, the Su-Xi-Chang Region. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Huang, S. Landscape Ecological Risk Responses to Land Use Change in the Luanhe River Basin, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 16631–16652. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y. Estimation and analysis of ecosystem service value in beijing-tianjin-hebei region. Environ. Prot. Circ. Econ. 2017, 37, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, J.; Qian, G.; Niu, J.; Liang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, A. What is sustainablilty science? Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Amini Parsa, V.; Salehi, E. Spatio-temporal analysis and simulation pattern of land use/cover changes, case study: Naghadeh, Iran. J. Urban Manag. 2016, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, Y. Study on land use change in chengde city, hebei province. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2017, 38, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vliet, J.; Bregt, A.K.; Hagen-Zanker, A. Revisiting Kappa to account for change in the accuracy assessment of land-use change models. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| LID | NP | PD | LSI | PAFRAC | SHDI | AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 10966 | 0.35 | 76.95 | 1.57 | 1.00 | 74.71 |
| N | 7910 | 0.25 | 60.35 | 1.59 | 0.98 | 80.32 |
| E | 6525 | 0.21 | 65.44 | 1.58 | 0.80 | 78.58 |
| S | 7243 | 0.23 | 57.34 | 1.60 | 0.94 | 81.33 |
| Unit:10_8$ | 2010 | Natural Scenario | Ecological Scenario | Sustainable Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values of Ecosystem Eervices | 32.03 | 33.32 | 34.92 | 33.89 |
| Economic Ealues | 102.71 | 108.95 | 87.91 | 104.07 |
| Total Values | 134.74 | 142.27 | 122.83 | 137.97 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Guan, M.; Jiang, H.; Wang, L. Dynamic Simulation of Land Use Change of the Upper and Middle Streams of the Luan River, Northern China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184909
Xu X, Guan M, Jiang H, Wang L. Dynamic Simulation of Land Use Change of the Upper and Middle Streams of the Luan River, Northern China. Sustainability. 2019; 11(18):4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184909
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xia, Mengxi Guan, Honglei Jiang, and Lingfei Wang. 2019. "Dynamic Simulation of Land Use Change of the Upper and Middle Streams of the Luan River, Northern China" Sustainability 11, no. 18: 4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184909
APA StyleXu, X., Guan, M., Jiang, H., & Wang, L. (2019). Dynamic Simulation of Land Use Change of the Upper and Middle Streams of the Luan River, Northern China. Sustainability, 11(18), 4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184909





