A Study on the Relationship between Urban Residents’ Perception of Recreational Sports and Their Participation in Recreational Sports: Based on Gender Differences
Abstract
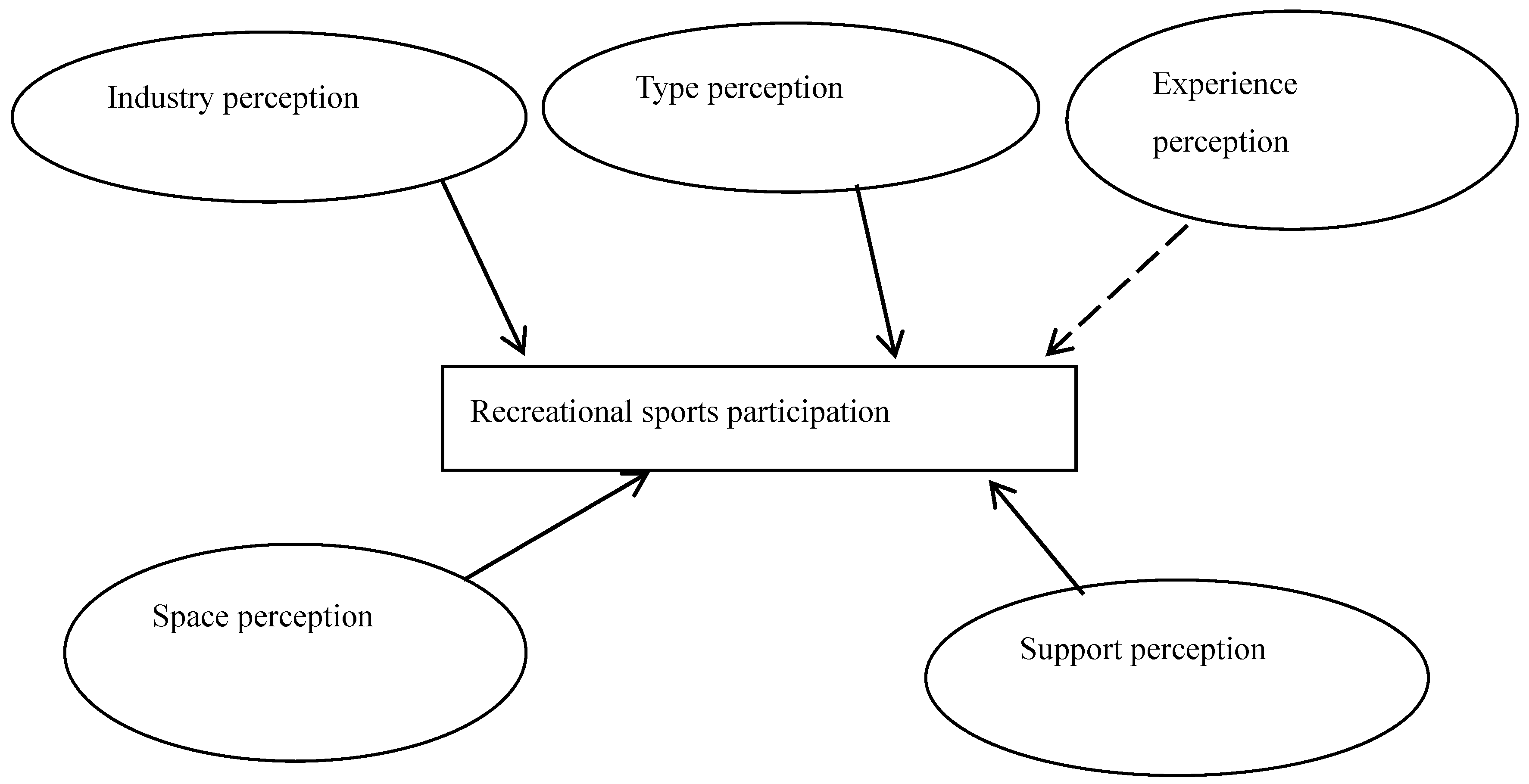
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants of Study
2.2. Measure for Data Collection
2.3. Data Collection Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive
3.2. EFA and CFA Results
3.3. Gender Differences in RS Participation
3.4. Gender Differences in RS Perception
3.5. Gender Differences in Association Between RS Participation and RS Perception
4. Discussion
5. Theoretical and Practical Implications
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicolai, E. Sport in Public Space: A Reclaimed Position for Sport-and Activity Structures in the Immediate Living Environment: A Design Study for Alkmaar West. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, Holland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Walker, G.J. The effects of urbanization, motivation, and constraint on Chinese people’s leisure-time physical activity. Leis. Sci. 2015, 37, 458–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Fu, H.; Li, J.; Jia, Y. Association between social and built environments and leisure-time physical activity among Chinese older adults-a multilevel analysis. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujala, U.M.; Mäkinen, V.P.; Heinonen, I.; Soininen, P.; Kangas, A.J.; Leskinen, T.H.; Rahkila, P.; Würtz, P.; Kovanen, V.; Sipilä, S.; et al. Long-term leisure-time physical activity and serum metabolome. Circulation 2013, 127, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiwanga, F.S.; Njelekela, M.A.; Diamond, M.B.; Bajunirwe, F.; Guwatudde, D.; Nankya-Mutyoba, J.; Kalyesubula, R.; Adebamowo, C.; Ajayi, I.; Reid, T.G.; et al. Urban and rural prevalence of diabetes and pre-diabetes and risk factors associated with diabetes in Tanzania and Uganda. Glob. Health Action 2016, 9, 31440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwa, K.; Acquah, L.; Gersh, B.J.; Mocumbi, A.O. Impact of socioeconomic status, ethnicity, and urbanization on risk factor profiles of cardiovascular disease in Africa. Circulation 2016, 133, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niclis, C.; Pou, S.A.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Steck, S.E.; Diaz MD, P. Proinflammatory dietary intake is associated with increased risk of colorectal cancer: Results of a case-control study in argentina using a multilevel modeling approach. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 70, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H.D.; Xiao, W.Y.; Wen, M.; Wei, R. Walkability, land use and physical activity. Sustainability 2016, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.M.; McAuley, E. Social cognitive influences on physical activity participation in long-term breast cancer survivors. Psycho-Oncol. 2013, 22, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.M.; Wójcicki, T.R.; McAuley, E. Social cognitive influences on physical activity behavior in middle-aged and older adults. J. Gerontol. Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2012, 1, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Borrego, F.; Corral-Pernía, J.; Martínez-Martínez, A.; Castañeda-Vázquez, C. Usage Behaviour of Public Spaces Associated with Sport and Recreational Activities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, I.; Williams, A. Understanding brand equity in campus recreational sports: A consumer-based perspective. Rec. Sports J. 2016, 40, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radicchi, E. Tourism and sport: Strategic synergies to enhance the sustainable development of a local context. Phys. Cul. Sport Stud. Res. 2013, 57, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.; Church, A. Lifestyle sports delivery and sustainability: Clubs, communities and user-managers. Int. J. Sport Policy Politics 2017, 9, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proios, M.; Doganis, G.; Athanailidis, I. Moral development and form of participation, type of sport, and sport experience. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2004, 99, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haudenhuyse, R.P.; Theeboom, M.; Coalter, F. The potential of sports-based social interventions for vulnerable youth: Implications for sport coaches and youth workers. J. Youth Stud. 2012, 15, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, M.L.; De Groot, R.H.; Savelberg, H.H.; Van Acker, F.; Kirschner, P.A. The association between objectively measured physical activity and academic achievement in Dutch adolescents: Findings from the GOALS study. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2014, 36, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, C.M.; Siperstein, G.N. The sport experience of athletes with intellectual disabilities: A national survey of Special Olympics athletes and their families. Adapt. Phys. Act. Q. 2009, 26, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baños, R.; Ruiz-Juan, F.; Baena-Extremera, A.; García-Montes, M.; Ortiz-Camacho, M. Leisure-time physical activity in relation to the stages of changes and achievement goals in adolescents: Comparative study of students in Spain, Costa Rica, and Mexico. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlén, J. Urgent expectations and silenced knowledge on spontaneous sport space as public health promoter and sport stimulator. Eur. J. Sport Soc. 2011, 8, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, A.A.; Besenyi, G.M.; Kaczynski, A.T.; Wilhelm Stanis, S.A.; Blake, C.E.; Barr-Anderson, D.J. Investigating issues of environmental injustice in neighborhoods surrounding parks. J. Leis. Res. 2015, 47, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbinson, S.J.; Hayman, J.A.; Livingston, P.M. Prevalence of health promotion policies in sports clubs in Victoria, Australia. Health Promot. Int. 2006, 21, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayle, E. Switzerland: The organisation of sport and policy towards sport federations, in Sport Policy Systems and Sport Federations. In Sport Policy Systems and Sport Federations; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2017; pp. 263–282. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.M. Personality, leisure statisfaction and subjective well-being of serious leisure participates. Soc. Behav. Pers. 2014, 7, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, G.; Bélanger-Gravel, A.; Amireault, S.; Vohl, M.C.; Pérusse, L. The effect of mere-measurement of cognitions on physical activity behavior: A randomized controlled trial among overweight and obese individuals. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, R.E.; Courneya, K.S.; Blanchard, C.M.; Plotnikoff, R.C. Prediction of leisure-time walking: An integration of social cognitive, perceived environmental, and personality factors. Int. J. Behav. Nut. Phys. Act. 2007, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigné, J.E.; Mattila, A.S.; Andreu, L. The impact of experiential consumption cognitions and emotions on behavioral intentions. J. Serv. Mark. 2008, 22, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social cognitive theory: An agentic perspective. Ann. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 52, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M. Six views of embodied cognition. Psy. Bull. Rev. 2002, 9, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, D.; Cerin, E.; Conway, T.L.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Owen, N.; Kerr, J.; Cardon, G.; Sallis, J.F. Interacting psychosocial and environmental correlates of leisure-time physical activity: A three-country study. Health Psychol. 2014, 33, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polistina, K. Internal colonization of holistic outdoor leisure (HOL) through sport: An unsustainable option. Leis. Loisir 2012, 36, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.Q.; Che, S.Q.; Xie, C.K.; Tian, S. Understanding Shanghai residents’ perception of leisure impact and experience satisfaction of urban community parks: An integrated and IPA method. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruch, N.; Melzer, K.; Mäder, U. Duration, frequency, and types of children’s activities: Potential of a classification procedure. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2013, 11, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb-Clark, D.A.; Kassenboehmer, S.C.; Schurer, S. Healthy habits: The connection between diet, exercise, and locus of control. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2014, 98, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnally, J.C.; Bernstein, I. Psychometric Theory, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lindwall, M.; Rennemark, M.; Halling, A.; Berglund, J.; Hassmén, P. Depression and exercise in elderly men and women: Findings from the Swedish national study on aging and care. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2007, 15, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, D.L.; Kerstetter, D.L.; Anderson, D.M. Stigma consciousness as a predictor of children’s participation in recreational vs. competitive sports. J. Sport Behav. 2008, 31, 276–297. [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä, S.; Aaltonen, S.; Korhonen, T.; Rose, R.J.; Kaprio, J. Diversity of leisure-time sport activities in adolescence as a predictor of leisure-time physical activity in adulthood. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X. A dynamic econometric analysis of sport development and economic growth in China. J. Phys. Educ. 2012, 19, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y. Service quality of sports centers and customer loyalty. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Log. 2017, 29, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Liu, Z.X. Study on the leisure sports attitude and behavior characteristics of Chinese professional women-mainly professional women aged 26–55 in urban areas of Beijing. Sport Sci. 2011, 45, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.L.; Gu, X.F.; Li, N. Study on site selection planning of community public sports facilities. China Sport Sci. Tech. 2016, 52, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Flowers, E.P.; Freeman, P.; Gladwell, V.F. A cross-sectional study examining predictors of visit frequency to local green space and the impact this has on physical activity levels. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warde, A. Cultural capital and the place of sport. Cult. Trends 2006, 15, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K.; Smith, D.R. Mistrust surrounding vaccination recommendations by the Japanese government: Results from a national survey of working-age individuals. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lera-López, F.; Wicker, P.; Downward, P. Does government spending help to promote healthy behavior in the population? Evidence from 27 European countries. J. Public Health 2015, 38, e5–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downward, P.; Rasciute, S. The relative demands for sports and leisure in England. Eur. Sport Manag. Q. 2010, 10, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicker, P.; Hallmann, K.; Breuer, C. Analyzing the impact of sport infrastructure on sport participation using geo-coded data: Evidence from multi-level models. Sport Manag. Rev. 2013, 16, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplanidou, K.; Gibson, H.J. Predicting behavioral intentions of active event sport tourists: The case of a small-scale recurring sports event. J. Sport Tour. 2010, 15, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L. Evolutionary neuroandrogenic theory and universal gender differences in cognition and behavior. Sex Roles 2011, 64, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, K.B.; Prince, S.A.; Tricco, A.C.; Connor-Gorber, S.; Tremblay, M. A comparison of indirect versus direct measures for assessing physical activity in the pediatric population: A systematic review. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2009, 4, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollman, J.; Okely, A.D.; Hardy, L. A hitchhiker’s guide to assessing young people’s physical activity: Deciding what method to use. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2009, 12, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Male% (N) | Female% (N) | x2 (p) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic conditions | Study sites | Hangzhou | 20.00 (153) | 17.9 (137) | 2.00 (0.36) |
| Chengdu | 20.00 (153) | 17.0 (130) | |||
| Shanghai | 11.9 (91) | 13.1 (100) | |||
| Age | <18 years | 9.7 (74) | 5.2 (40) | 14.36 (0.01) | |
| 18–25 years | 10.3 (79) | 8.8 (67) | |||
| 26–35 years | 10.2 (78) | 8.9 (68) | |||
| 36–45 years | 9.3 (71) | 9.0 (69) | |||
| 46–55 years | 6.0 (46) | 8.1 (62) | |||
| ≥56 years | 6.4 (49) | 8.0 (61) | |||
| Marital status | Single | 22.6 (173) | 15.4 (118) | 11.11 (0.01) | |
| Married without child | 4.8 (37) | 4.6 (35) | |||
| Married with child | 22.4 (171) | 25.7 (196) | |||
| Divorced or widow | 2.1 (16) | 2.4 (18) | |||
| Occupation | Managerial/professional | 11.7 (91) | 10.3 (79) | 9.87 (0.02) | |
| White-collar | 14.7 (109) | 14.1 (105) | |||
| Blue-collar | 9.4 (69) | 12.2 (93) | |||
| Unemployed or student | 16.1 (128) | 11.5 (90) | |||
| Educational background | Junior high school | 5.1 (39) | 5.0 (38) | 9.42 (0.06) | |
| Senior high school | 9.2 (70) | 7.1 (54) | |||
| Junior College | 7.7 (59) | 10.7 (82) | |||
| Bachelor’s degree | 22.6 (173) | 20.4 (156) | |||
| Master’s degree or above | 7.3 (56) | 4.8 (37) | |||
| Income (RMB, per month) | <2000 | 16.6 (127) | 13.1 (99) | 20.59 (0.00) | |
| 2000 < 4000 | 8.1 (62) | 12.2 (93) | |||
| 4000 < 6000 | 16.8 (128) | 17.1 (131) | |||
| 6000 < 8000 | 7.7 (59) | 4.8 (37) | |||
| <8000 | 2.7 (21) | 0.90 (7) | |||
| Variables | Gender Comparison for Mean | Gender-Wise Correlations | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males (N = 397) | Females (N = 367) | Total (N = 764) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 1 PRS | 0.26 (0.65) | −0.20 (0.60) | 0.00 (1.00) | - | 0.16 * | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.17 * | 0.11 |
| 2 IP | 3.81 (0.58) | 3.61 (0.67) | 3.70 (0.63) | 0.19 * | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.64 * | 0.63 * | |
| 3 TP | 3.56 (0.76) | 3.40 (0.74) | 3.46 (0.77) | 0.23 * | 0.12 | 0.67 * | 0.19 * | 0.72 * | |
| 4 EP | 3.69 (0.72) | 3.77 (0.72) | 3.72 (0.72) | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.67 * | 0.36 * | 0.27 * | |
| 5 SpP | 3.57 (0.75) | 3.65 (0.63) | 3.61 (0.71) | 0.29 * | 0.64 * | 0.19 * | 0.36 * | 0.17 * | |
| 6 SuP | 3.26 (0.64) | 3.16 (0.70) | 3.19 (0.67) | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.17 * | |
| Study Variables | Items | Factor Loading | α | CFI | GFI | AGFI | SRMR | RMSEA | 95%CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS Participation (RSP) | 3 | 0.68–0.72 | 0.85 | 146.50 (33) | 4.45 | 0.910 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.040 | 0.05 | (0.059, 0.071) |
| PRS | 29 | 0.81–0.90 | 0.82 | 394.97 (94) | 4.20 | 0.953 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.034 | 0.06 | (0.052, 0.061) |
| IP | 9 | 0.75–0.88 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| TP | 5 | 0.55–0.81 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| EP | 4 | 0.56–0.77 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SpP | 6 | 0.67–0.83 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SuP | 5 | 0.75–0.84 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SEM for males (Model 1) | - | - | - | 617.50 (307) | 2.00 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.041 | 0.037 | (0.035, 0.038) |
| SEM for females (Model 2) | - | - | - | 599.11 (183) | 3.27 | 0.99 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.05 | 0.04 | (0.041, 0.063) |
| Variables | Male% (N) | Female% (N) | x2 (p) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS participation | Frequency (times/week) | 0–2 | 35.76 (142) | 30.24 (111) | 6.20 (0.04) |
| 3–4 | 43.57 (173) | 41.96 (154) | |||
| >4 | 20.65 (82) | 27.79 (102) | |||
| Duration | 30–59 min/time | 48.86 (194) | 35.42 (130) | 10.46 (0.00) | |
| 60–89 min/time | 21.91 (87) | 35.96 (132) | |||
| 90–119 min/time | 20.65 (82) | 19.34 (71) | |||
| ≥120 min/time | 8.64 (34) | 9.26 (34) | |||
| Intensity of RS | Low-intensity | 53.90 (214) | 64.30 (236) | 9.35 (0.00) | |
| Moderate-intensity | 34.50 (137) | 25.06 (92) | |||
| High-intensity | 11.58 (46) | 10.62 (39) | |||
| Total Sample | Males | Females | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 764) | (N = 397) | (N = 367) | |||
| Variables | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | t-value | d |
| PERCEPTION OF RS | 3.55 (0.61) | 3.58 (0.63) | 3.52 (0.58) | 1.05 | 0.05 |
| Industry perception | 3.70 (0.63) | 3.81 (0.58) | 3.61 (0.67) | 3.92 *** | 0.39 |
| Develop sports brand | 3.77 (0.64) | 3.95 (0.59) | 3.61 (0.76) | ||
| Skill training | 3.64 (0.58) | 3.72 (0.60) | 3.55 (0.77) | ||
| Sports media | 3.71 (0.32) | 3.85 (0.54) | 3.57 (0.58) | ||
| Internet consulting | 3.67 (0.57) | 3.77 (0.71) | 3.58 (0.72) | ||
| Development industry | 3.47 (0.65) | 3.53 (0.51) | 3.41 (0.56) | ||
| Quality of service | 4.02 (0.72) | 4.26 (0.59) | 3.78 (0.65) | ||
| Insurance market | 3.78 (0.76) | 3.85 (0.57) | 3.71 (0.66) | ||
| Stimulate consumption | 3.81 (0.69) | 3.86 (0.50) | 3.76 (0.69) | ||
| Scientific management | 3.56 (0.73) | 3.53 (0.62) | 3.60 (0.65) | ||
| Type perception | 3.46 (0.77) | 3.56 (0.76) | 3.40 (0.74) | 2.72 *** | 0.27 |
| Walking | 3.44 (0.79) | 3.44 (0.73) | 3.44 (0.75) | ||
| Yoga or square dancing | 3.42 (0.73) | 3.46 (0.74) | 3.39 (0.72) | ||
| Tai chi or jogging | 3.45 (0.78) | 3.57 (0.74) | 3.33 (0.73) | ||
| Playing ball sports | 3.55 (0.79) | 3.70 (0.79) | 3.40 (0.70) | ||
| Running or cycling | 3.56 (0.78) | 3.64 (0.78) | 3.48 (0.79) | ||
| Experience perception | 3.72 (0.72) | 3.69 (0.72) | 3.77 (0.72) | 1.07 | 0.07 |
| Funny of sports participation | 3.82 (0.73) | 3.80 (0.76) | 3.84 (0.70) | ||
| Enhance one’s inner self | 3.73 (0.57) | 3.77 (0.64) | 3.69 (0.69) | ||
| Realize the value of life | 3.60 (0.83) | 3.54 (0.69) | 3.67 (0.77) | ||
| Positive psychological effect | 3.78 (0.74) | 3.64 (0.77) | 3.93 (0.72) | ||
| Space perception | 3.61 (0.71) | 3.57 (0.75) | 3.65 (0.63) | 1.81 ** | 0.18 |
| Community sports space | 3.63 (0.65) | 3.67 (0.79) | 3.58 (0.50) | ||
| Roadside | 3.50 (0.77) | 3.47 (0.74) | 3.53 (0.70) | ||
| Urban greenway | 3.65 (0.60) | 3.70 (0.79) | 3.60 (0.61) | ||
| Parks | 3.66 (0.73) | 3.54 (0.70) | 3.78 (0.66) | ||
| Residences surrounding | 3.59 (0.73) | 3.46 (0.71) | 3.71 (0.65) | ||
| Sports stadiums | 3.68 (0.78) | 3.61 (0.76) | 3.74 (0.68) | ||
| Support perception | 3.19 (0.67) | 3.26 (0.64) | 3.16 (0.70) | 1.89 ** | 0.19 |
| Integrate into the local plan | 3.21 (0.68) | 3.27 (0.66) | 3.15 (0.70) | ||
| Invest in community events | 3.12 (0.74) | 3.16 (0.73) | 3.07 (0.76) | ||
| The government provides funds and support | 3.33 (0.55) | 3.38 (0.59) | 3.29 (0.72) | ||
| Introduce social capital | 3.21 (0.68) | 3.25 (0.62) | 3.17 (0.64) | ||
| Supervising private organizations | 3.18 (0.70) | 3.26 (0.62) | 3.10 (0.68) | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, X.; Kayani, S.; Wang, J.; Imran, M.; Zagalaz Sánchez, M.L.; Amador Jesús, L.S.; Qurban, H. A Study on the Relationship between Urban Residents’ Perception of Recreational Sports and Their Participation in Recreational Sports: Based on Gender Differences. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5466. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195466
Zou X, Kayani S, Wang J, Imran M, Zagalaz Sánchez ML, Amador Jesús LS, Qurban H. A Study on the Relationship between Urban Residents’ Perception of Recreational Sports and Their Participation in Recreational Sports: Based on Gender Differences. Sustainability. 2019; 11(19):5466. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195466
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Xuefang, Sumaira Kayani, Jin Wang, Muhammad Imran, María Luisa Zagalaz Sánchez, Lara Sánchez Amador Jesús, and Haroona Qurban. 2019. "A Study on the Relationship between Urban Residents’ Perception of Recreational Sports and Their Participation in Recreational Sports: Based on Gender Differences" Sustainability 11, no. 19: 5466. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195466
APA StyleZou, X., Kayani, S., Wang, J., Imran, M., Zagalaz Sánchez, M. L., Amador Jesús, L. S., & Qurban, H. (2019). A Study on the Relationship between Urban Residents’ Perception of Recreational Sports and Their Participation in Recreational Sports: Based on Gender Differences. Sustainability, 11(19), 5466. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195466







