Determinants of the Price of Housing in the Province of Alicante (Spain): Analysis Using Quantile Regression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review of the Literature
3. Materials and Methods
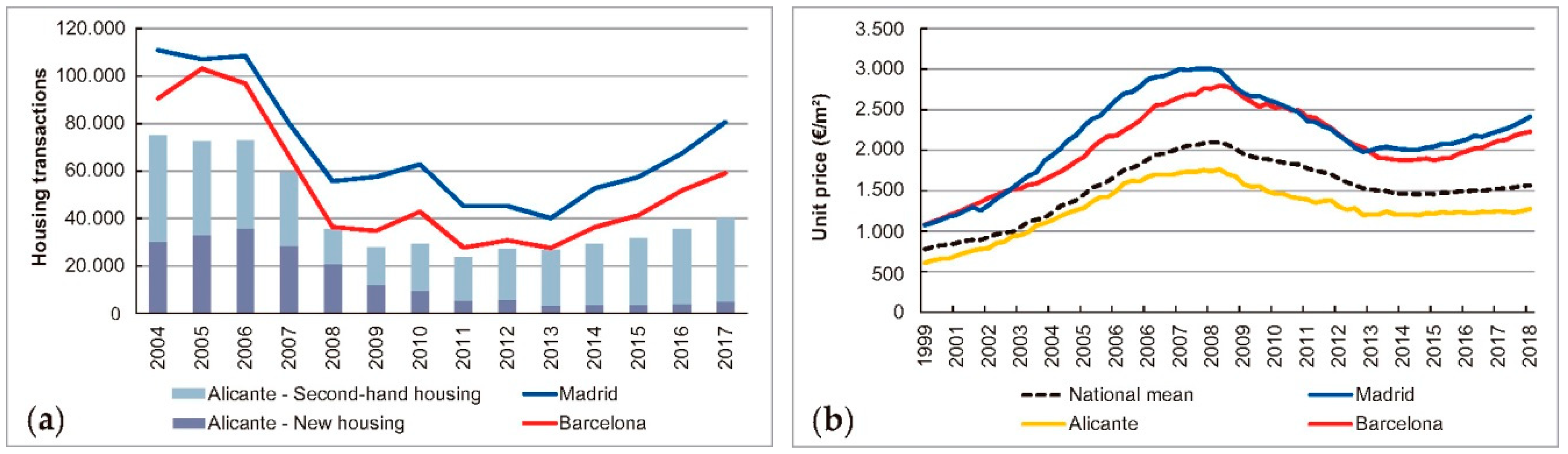
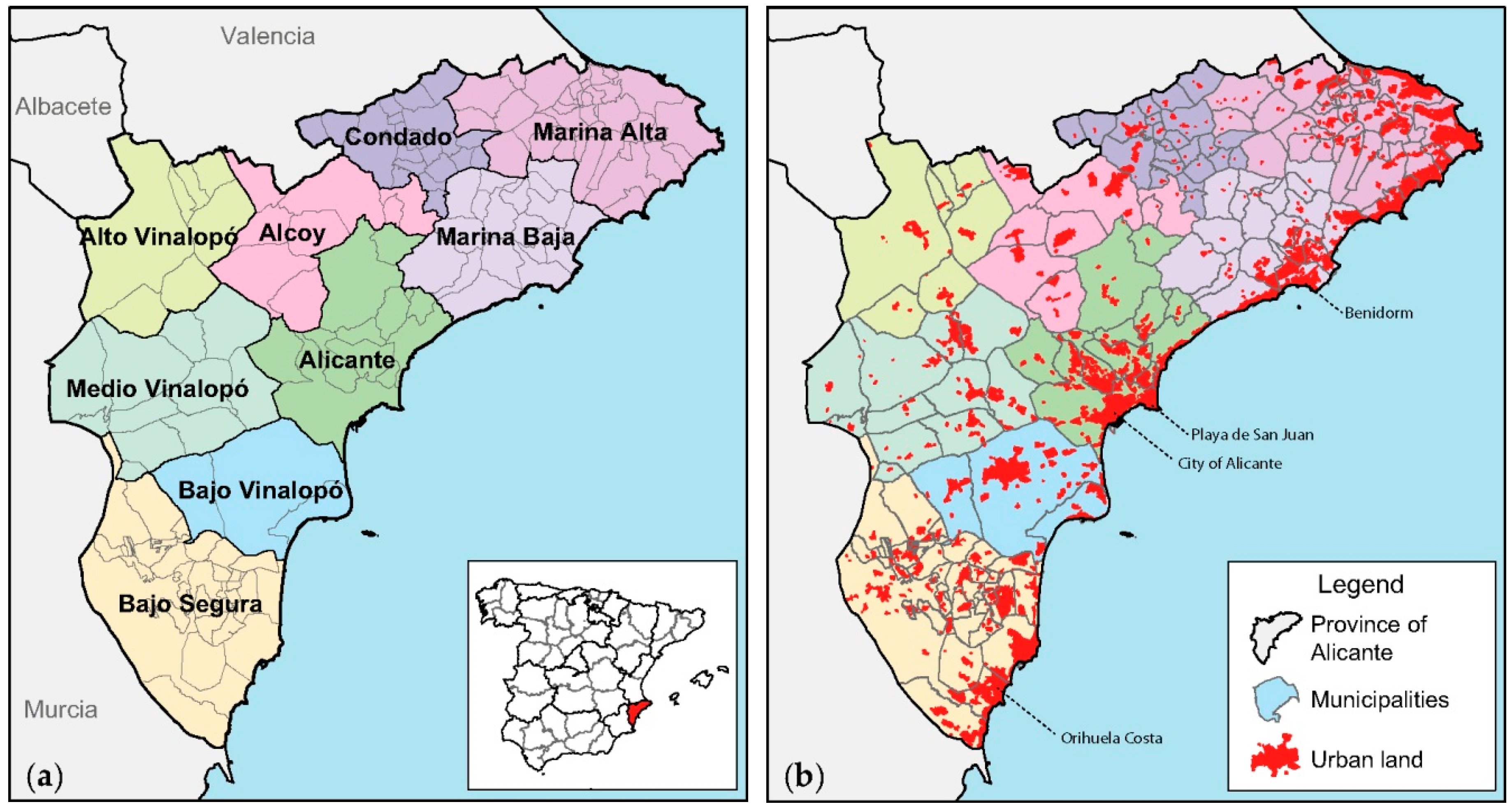
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Methodology
3.3. The Sources of Information
3.4. Data
4. Results
4.1. OLS Hedonic Price Models
4.2 Quantile Regression
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- The characteristics of the dwelling and the building have great importance in determining the price, followed by the characteristics of the neighbourhood and the location.
- Characteristics of dwellings and buildings, such as the surface area, age, housing typology (duplex, penthouse, or studio flat), the availability of garage slot or an elevator, have different effects on the price depending on the quantile.
- Location characteristics also show that there are two distinct markets, the coast and the inland areas.
- Neighbourhood characteristics show that certain segments of the population are willing to pay more for a home: people with university studies and foreigners. The latter are persons with sufficient economic resources; therefore, this population segment is mainly from Europe.
- Finally, the market characteristics suggest that, in the province of Alicante, there is an ample second residence and rental housing market, which carries a rise in the sale price of properties as a consequence.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Model 1 OLS | Model 2 OLS | Model 3 OLS | Model 4 OLS | Model 5 OLS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | A_flat | Reference | ||||
| A_penthouse | 0.009 | 0.032 | 0.039 | 0.046 | 0.050 | |
| A_duplex | −0.009 | 0.024 | 0.023 | 0.016 | 0.012 | |
| A_studio_flat | −0.038 | −0.050 | −0.052 | −0.062 | −0.062 | |
| A_age | −0.111 | 0.022 | 0.010 | −0.004 | −0.013 | |
| A_area_m2 | 0.266 | 0.300 | 0.317 | 0.302 | 0.317 | |
| A_bathrooms | 0.319 | 0.209 | 0.224 | 0.216 | 0.221 | |
| A_floor | 0.155 | 0.054 | 0.020 | 0.016 | 0.007 | |
| A_terrace | 0.199 | 0.098 | 0.059 | 0.044 | 0.035 | |
| A_good_condition | Reference | |||||
| A_new_construction | 0.028 | 0.015 | 0.027 | 0.024 | 0.026 | |
| A_state_to_reform | −0.144 | −0.096 | −0.087 | −0.085 | −0.083 | |
| B | B_parking | 0.139 | 0.129 | 0.123 | 0.117 | |
| B_elevator | 0.210 | 0.181 | 0.178 | 0.171 | ||
| B_pool | 0.257 | 0.172 | 0.114 | 0.099 | ||
| C | C_Alicante | Reference | ||||
| C_Marina_Alta | 0.071 | 0.041 | 0.031 | |||
| C_Marina_Baja | 0.079 | 0.107 | 0.078 | |||
| C_Bajo_Vinalopo | 0.024 | 0.056 | 0.017 | |||
| C_Bajo_Segura | −0.075 | −0.090 | −0.129 | |||
| C_Condado | −0.011 | −0.009 | −0.016 | |||
| C_Alcoy | −0.050 | −0.045 | −0.060 | |||
| C_Alto_Vinalopo | −0.026 | −0.013 | −0.024 | |||
| C_Medio_Vinalopo | −0.057 | −0.040 | −0.054 | |||
| C_coastalregion | 0.232 | 0.149 | 0.095 | |||
| D | D_elderly | 0.111 | 0.091 | |||
| D_foreigners | 0.085 | 0.039 | ||||
| D_no_studies | −0.079 | −0.076 | ||||
| D_university | 0.182 | 0.163 | ||||
| E | E_secondary_dwelling | 0.136 | ||||
| E_rented_dwelling | 0.036 |

| Unstandardised Coefficients | Std Coef. | 95.0% CI for B | Collinearity Statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | Beta | t | Sig. | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Tolerance | VIF | ||
| (Intercept) | 10.010 | 0.012 | 802.6 | 0.000 | 9.986 | 10.035 | ||||
| A | A_flat | Reference | ||||||||
| A_penthouse | 0.116 | 0.007 | 0.050 | 16.3 | 0.000 | 0.102 | 0.130 | 0.90 | 1.11 | |
| A_duplex | 0.040 | 0.010 | 0.012 | 4.0 | 0.000 | 0.020 | 0.059 | 0.88 | 1.13 | |
| A_studio_flat | −0.309 | 0.015 | −0.062 | −21.1 | 0.000 | −0.338 | −0.280 | 0.96 | 1.04 | |
| A_age | −0.001 | 0.0002 | −0.013 | −3.5 | 0.001 | −0.001 | 0.000 | 0.63 | 1.59 | |
| A_area_m2 | 0.006 | 0.0001 | 0.317 | 80.3 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.54 | 1.86 | |
| A_bathrooms | 0.236 | 0.004 | 0.221 | 56.4 | 0.000 | 0.228 | 0.244 | 0.55 | 1.83 | |
| A_floor | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 2.0 | 0.041 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.81 | 1.24 | |
| A_terrace | 0.041 | 0.004 | 0.035 | 10.8 | 0.000 | 0.034 | 0.049 | 0.81 | 1.23 | |
| A_good_condition | Reference | |||||||||
| A_new_construction | 0.177 | 0.020 | 0.026 | 8.8 | 0.000 | 0.138 | 0.216 | 0.98 | 1.02 | |
| A_state_to_reform | −0.218 | 0.008 | −0.083 | -28.0 | 0.000 | −0.234 | −0.203 | 0.95 | 1.05 | |
| B | B_parking | 0.142 | 0.004 | 0.117 | 34.7 | 0.000 | 0.134 | 0.150 | 0.74 | 1.36 |
| B_elevator | 0.231 | 0.005 | 0.171 | 51.2 | 0.000 | 0.222 | 0.240 | 0.75 | 1.33 | |
| B_pool | 0.119 | 0.005 | 0.099 | 26.5 | 0.000 | 0.110 | 0.128 | 0.59 | 1.68 | |
| C | C_Alicante | Reference | ||||||||
| C_Marina_Alta | 0.058 | 0.007 | 0.031 | 8.4 | 0.000 | 0.045 | 0.072 | 0.61 | 1.64 | |
| C_Marina_Baja | 0.143 | 0.007 | 0.078 | 20.6 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 0.157 | 0.59 | 1.69 | |
| C_Bajo_Vinalopo | 0.030 | 0.007 | 0.017 | 4.5 | 0.000 | 0.017 | 0.044 | 0.59 | 1.71 | |
| C_Bajo_Segura | −0.186 | 0.007 | −0.129 | −27.7 | 0.000 | −0.199 | −0.173 | 0.39 | 2.59 | |
| C_Condado | −0.146 | 0.028 | −0.016 | −5.3 | 0.000 | −0.200 | −0.092 | 0.95 | 1.05 | |
| C_Alcoy | −0.221 | 0.012 | −0.060 | −18.5 | 0.000 | −0.245 | −0.198 | 0.78 | 1.28 | |
| C_Alto_Vinalopo | −0.144 | 0.018 | −0.024 | −7.8 | 0.000 | −0.180 | −0.108 | 0.90 | 1.11 | |
| C_Medio_Vinalopo | −0.202 | 0.012 | −0.054 | −16.7 | 0.000 | −0.226 | −0.179 | 0.79 | 1.27 | |
| C_coastalregion | 0.129 | 0.006 | 0.095 | 22.0 | 0.000 | 0.118 | 0.141 | 0.45 | 2.23 | |
| D | D_elderly | 0.282 | 0.012 | 0.091 | 23.6 | 0.000 | 0.259 | 0.306 | 0.56 | 1.80 |
| D_foreigners | 0.108 | 0.014 | 0.039 | 7.6 | 0.000 | 0.080 | 0.136 | 0.32 | 3.09 | |
| D_no_studies | −0.874 | 0.045 | −0.076 | −19.6 | 0.000 | −0.962 | −0.786 | 0.56 | 1.79 | |
| D_university | 0.996 | 0.024 | 0.163 | 42.2 | 0.000 | 0.950 | 1.043 | 0.56 | 1.79 | |
| E | E_secondary_dwelling | 0.321 | 0.010 | 0.136 | 31.6 | 0.000 | 0.301 | 0.341 | 0.45 | 2.20 |
| E_rented_dwelling | 0.201 | 0.021 | 0.036 | 9.4 | 0.000 | 0.159 | 0.244 | 0.57 | 1.76 | |
| Unstandardised Coefficients | Std Coef. | 95.0% CI for B | Collinearity Statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | Beta | t | Sig. | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Tolerance | VIF | ||
| (Intercept) | 10.073 | 0.015 | 671.6 | 10.044 | 10.102 | |||||
| A | A_flat | Reference | ||||||||
| A_penthouse | 0.122 | 0.008 | 0.052 | 15.0 | 0.000 | 0.106 | 0.138 | 0.90 | 1.11 | |
| A_duplex | 0.042 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 4.2 | 0.000 | 0.022 | 0.061 | 0.87 | 1.15 | |
| A_studio_flat | −0.335 | 0.026 | −0.068 | −12.9 | 0.000 | −0.386 | −0.284 | 0.98 | 1.02 | |
| A_age | −0.001 | 0.0002 | −0.015 | −3.5 | 0.001 | −0.001 | 0.000 | 0.61 | 1.63 | |
| A_area_m2 | 0.006 | 0.0001 | 0.308 | 65.3 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.53 | 1.88 | |
| A_bathrooms | 0.237 | 0.005 | 0.221 | 49.2 | 0.000 | 0.227 | 0.246 | 0.54 | 1.85 | |
| A_floor | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 2.8 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.81 | 1.23 | |
| A_terrace | 0.042 | 0.004 | 0.036 | 9.8 | 0.000 | 0.034 | 0.051 | 0.82 | 1.22 | |
| A_good_condition | Reference | |||||||||
| A_new_construction | 0.230 | 0.023 | 0.034 | 9.8 | 0.000 | 0.184 | 0.276 | 0.98 | 1.02 | |
| A_state_to_reform | −0.228 | 0.009 | −0.087 | −24.8 | 0.000 | −0.246 | −0.210 | 0.95 | 1.06 | |
| B | B_parking | 0.138 | 0.005 | 0.114 | 30.7 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 0.147 | 0.72 | 1.38 |
| B_elevator | 0.226 | 0.006 | 0.167 | 38.5 | 0.000 | 0.215 | 0.238 | 0.79 | 1.26 | |
| B_pool | 0.117 | 0.005 | 0.098 | 23.4 | 0.000 | 0.107 | 0.127 | 0.58 | 1.73 | |
| C | C_Alicante | Reference | ||||||||
| C_Marina_Alta | 0.055 | 0.008 | 0.030 | 7.0 | 0.000 | 0.040 | 0.071 | 0.59 | 1.68 | |
| C_Marina_Baja | 0.126 | 0.008 | 0.068 | 16.1 | 0.000 | 0.110 | 0.141 | 0.56 | 1.79 | |
| C_Bajo_Vinalopo | 0.010 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 1.3 | 0.184 | −0.005 | 0.025 | 0.56 | 1.78 | |
| C_Bajo_Segura | −0.220 | 0.008 | −0.152 | −28.4 | 0.000 | −0.235 | −0.205 | 0.38 | 2.64 | |
| C_Condado | −0.168 | 0.058 | −0.018 | −2.9 | 0.004 | −0.281 | −0.055 | 0.99 | 1.02 | |
| C_Alcoy | −0.224 | 0.016 | −0.061 | −14.2 | 0.000 | −0.255 | −0.193 | 0.81 | 1.23 | |
| C_Alto_Vinalopo | −0.128 | 0.036 | −0.021 | -3.5 | 0.000 | −0.199 | −0.057 | 0.96 | 1.04 | |
| C_Medio_Vinalopo | −0.224 | 0.019 | −0.060 | −11.8 | 0.000 | −0.261 | −0.187 | 0.87 | 1.15 | |
| C_coastalregion | 0.086 | 0.007 | 0.063 | 12.3 | 0.000 | 0.072 | 0.100 | 0.50 | 2.01 | |
| D | D_elderly | 0.282 | 0.015 | 0.091 | 19.4 | 0.000 | 0.254 | 0.311 | 0.52 | 1.92 |
| D_foreigners | 0.122 | 0.017 | 0.044 | 7.3 | 0.000 | 0.089 | 0.154 | 0.31 | 3.21 | |
| D_no_studies | −0.927 | 0.052 | −0.080 | −17.8 | 0.000 | −1.029 | −0.825 | 0.57 | 1.75 | |
| D_university | 0.991 | 0.027 | 0.162 | 36.9 | 0.000 | 0.938 | 1.043 | 0.60 | 1.68 | |
| E | E_secondary_dwelling | 0.323 | 0.012 | 0.137 | 27.5 | 0.000 | 0.300 | 0.346 | 0.47 | 2.15 |
| E_rented_dwelling | 0.184 | 0.024 | 0.033 | 7.7 | 0.000 | 0.137 | 0.231 | 0.54 | 1.86 | |
References
- INE, Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Encuesta de condiciones de vida: Hogares por régimen de tenencia de la vivienda y CCAA. Available online: http://www.ine.es/jaxiT3/Tabla.htm?t=4566&L=0 (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- Taltavull de la Paz, P. Construcción y vivienda en España, 1965–1995: Dos modelos de comportamiento del mercado inmobiliario. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Alicante, Facultad de Ciencias Económicas, Alicante, Spain, 1996. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10045/4074 (accessed on 6 March 2018).
- Keynes, J.M. Teoría general de la ocupación, el interés y el dinero; Fondo de Cultura Económica: México, Mexico, 1943; p. 356. ISBN 978-968-16-6841-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Fomento. Transacciones inmobiliarias (compraventa). Available online: https://www.fomento.gob.es/be2/?nivel=2&orden=34000000 (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Sirmans, G.S.; Macpherson, D.A.; Zietz, E.N. The composition of hedonic pricing models. J. Real Estate Lit. 2005, 13, 3–43. Available online: http://aresjournals.org/doi/abs/10.5555/reli.13.1.j03673877172w0w2 (accessed on 9 June 2018).
- Court, A.T. Hedonic price indexes with automotive examples. In The Dinamics of Automovile Demand; General Motors Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1939; pp. 99–117. [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, K.J. A new approach to consumer theory. J. Political Econ. 1966, 74, 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, R.G.; Henning, J.A. The determinants of residential property values with special reference to air pollution. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1967, 49, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, S. Hedonic prices and implicit markets: Product differentiation in pure competition. J. Political Econ. 1974, 82, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.B.; Rosen, K.T.; Fallis, G. Recent developments in economic models of housing markets. J. Econ. Lit. 1988, 26, 29–64. [Google Scholar]
- Brounen, D.; Kok, N. On the economics of energy labels in the housing market. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2011, 62, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Igbinosa, S.O. Determinants of Residential Property Value in Nigeria—A Neural Network Approach. Int. Multidiscip. J. Ethiop. 2011, 5, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selím, S. Determinants of House Prices in Turkey: A Hedonic Regression Model. Doğuş Üniversitesi Dergisi 2008, 9, 65–76. Available online: http://journal.dogus.edu.tr/index.php/duj/article/view/80 (accessed on 3 August 2018).
- Galvis, L.A.; Carrillo, B. Un índice de precios espacial para la vivienda urbana en colombia: Una aplicación con métodos de emparejamiento. Revista de Economía del Rosario 2013, 16, 25–59. Available online: http://www.urosario.edu.co/economia/documentos/v16_n1Galvis_Carrillo/ (accessed on 9 October 2018).
- Chasco Yrigoyen, C.; Sánchez Reyes, B. Externalidades ambientales y precio de la vivienda en Madrid: Un análisis con regresión cuantílica espacial. Revista Galega de Economía 2012, 21, 1–21. Available online: http://www.usc.es/econo/RGE/Vol21_2/castelan/bt4c.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2018).
- Ferreira Vaz, A.J. La dimensión de la subjetividad en la formación del valor inmobiliario: Aplicación del método de análisis de ecuaciones estructurales al mercado residencial de Lisboa. Doctoral thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2013. Available online: http://oa.upm.es/15577/ (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Hyland, M.; Lyons, R.C.; Lyons, S. The value of domestic building energy efficiency—Evidence from Ireland. Energy Econ. 2013, 40, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayar, R.; Demir, D. Hedonic estimation of housing market prices in Turkey. Erciyes Univ. J. Fac. Econ. Adm. Sci. 2014, 0, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerst, F.; McAllister, P.; Nanda, A.; Wyatt, P. Energy performance ratings and house prices in Wales: An empirical study. Energy Policy 2016, 92, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahirovich-Herbert, V.; Gibler, K.M. The effect of new residential construction on housing prices. J. Hous. Econ. 2014, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasco Yrigoyen, C.; Gallo, J.L. The impact of objective and subjective measures of air quality and noise on house prices: A multilevel approach for downtown Madrid. Econ. Geogr. 2013, 89, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Durán, L. Análisis del impacto de los aspectos relativos a la localización en el precio de la vivienda a través de técnicas de soft computing. Una aplicación a la ciudad de Valencia. Doctoral thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2016. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10251/63253 (accessed on 15 February 2018).
- Baudry, M.; Guengant, A.; Larribeau, S.; Leprince, M. Formation des prix immobiliers et consentements à payer pour une amélioration de l’environnement urbain: l’exemple rennais. Revue d’Économie Régionale & Urbaine 2009, 2, 369–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Pozo, A. Determinantes del precio de la vivienda usada en málaga una aplicación de la metodología hedónica. Revista de estudios regionales 2008, 82, 135–158. Available online: http://www.revistaestudiosregionales.com/documentos/articulos/pdf1043.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2018).
- Humaran Nahed, I.; Roca Cladera, J. Hacia una medida integrada del factor de localización en la valoración residencial: El caso de Mazatlán. ACE: Arquitectura, Ciudad y Entorno 2010, 13, 185–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagner, A. Determinantes del precio de viviendas en la región metropolitana de Chile. El Trimestre Económico 2011, 78, 813–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohl, M.T.; Michels, W.; Oelgemöller, J. Determinanten von Wohnimmobilienpreisen: Das Beispiel der Stadt Münster. Jahrbuch für Regionalwissenschaft 2012, 32, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandt, S.; Maennig, W. The impact of rail access on condominium prices in Hamburg. Transportation 2012, 39, 997–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemo, C.; Raya, J.M. Change in the distribution of house prices across Spanish cities. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2012, 42, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, T.K.; Feuerschütte, S.; Kiefer, M.; an de Meulen, P.; Micheli, M.; Schmidt, T.; Wilke, L.-H. Ein hedonischer Immobilienpreisindex auf Basis von Internetdaten: 2007–2011. AStA Wirtschafts- und Sozialstatistisches Archiv 2013, 7, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaya, A.; Atan, M. Determination of the factors that affect house prices in Turkey by using Hedonic Pricing Model. J. Bus. Econ. Financ. 2014, 3, 313–327. Available online: http://dergipark.gov.tr/jbef/issue/32410/360453 (accessed on 3 August 2018).
- Wen, H.; Bu, X.; Qin, Z. Spatial effect of lake landscape on housing price: A case study of the West Lake in Hangzhou, China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, L. Housing market differentiation: The cases of Yenimahalle and Çankaya in Ankara. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2015, 19, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch Osuna, J.M. Sistema de valuación masiva de inmuebles para tasaciones. Contexto. Revista de la Facultad de Arquitectura de la Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León 2016, X, 51–63. Available online: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=353647474005 (accessed on 25 June 2018).
- Van Dijk, D.; Siber, R.; Brouwer, R.; Logar, I.; Sanadgol, D. Valuing water resources in Switzerland using a hedonic price model. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 3510–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano Monserrate, M.A. Formación de los precios de alquiler de viviendas en Machala (Ecuador): Análisis mediante el método de precios hedónicos. Cuadernos de Economía 2016, 39, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, B.; Watkins, C. Defining spatial housing submarkets: Exploring the case for expert delineated boundaries. Urban Stud. 2017, 54, 1446–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara Pulido, J.A.; Estrada Díaz, G.; Zentella Gómez, J.C.; Guevara Sanginés, A. Los costos de la expansión urbana: Aproximación a partir de un modelo de precios hedónicos en la Zona Metropolitana del Valle de México. Estudios demográficos y urbanos 2017, 32, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, D.; Park, C.; Kim, H.; Jung, T.; Kim, S. Park accessibility impacts housing prices in Seoul. Sustainability 2017, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, L. School district, education quality, and housing price: Evidence from a natural experiment in Hangzhou, China. Cities 2017, 66, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, J. Exploring Determinants of Housing Prices in Beijing: An Enhanced Hedonic Regression with Open Access POI Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, H. Have housing prices gone with the smelly wind? Big data analysis on landfill in Hong Kong. Sustainability 2018, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama Santos, F.A.d. Determinación de las cualidades de valor en la valoración de bienes inmuebles. La influencia del nivel socioeconómico en la valoración de la vivienda. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2017. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10251/90526 (accessed on 6 March 2018).
- Landajo, M.; Bilbao, C.; Bilbao, A. Nonparametric neural network modeling of hedonic prices in the housing market. Empir. Econ. 2012, 42, 987–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez Tabales, J.M.; Caridad y Ocerin, J.M.; Ceular Villamandos, N.; Rey Carmona, F.J. Obtención de precios implícitos para atributos determinantes en la valoración de una vivienda. Revista Internacional Administración Finanzas 2012, 5, 41–54. Available online: https://www.theibfr.com/download/riaf/2012-riaf/riaf-v5n3-2012/RIAF-V5N3-2012-3.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Núñez Tabales, J.M.; Caridad y Ocerin, J.M.; Rey Carmona, F.J. Artificial Neural Networks for predicting real estate prices. Revista de métodos cuantitativos para la economía y la empresa 2013, 15, 29–44. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10433/363 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Wen, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, L. Spatial effect of river landscape on housing price: An empirical study on the Grand Canal in Hangzhou, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 63, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetler, K.M.; Venn, T.J.; Calkin, D.E. The effects of wildfire and environmental amenities on property values in northwest Montana, USA. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, J.C.; Velásquez, H.; Agudelo, J. Infraestructura pública y precios de vivienda: Una aplicación de regresión geográficamente ponderada en el contexto de precios hedónicos. Ecos de Economía 2011, 15, 95–122. Available online: http://publicaciones.eafit.edu.co/index.php/ecos-economia/article/view/480 (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Moreno Murrieta, R.E.; Alvarado Lagunas, E. El entorno social y su impacto en el precio de la vivienda: Un análisis de precios hedónicos en el Área Metropolitana de Monterrey. Trayectorias. Revista de ciencias sociales 2011, 14, 131–147. Available online: http://trayectorias.uanl.mx/33y34/pdf/7_ramsas_elias.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2018).
- Fernández Durán, L.; Llorca Ponce, A.; Valero Cubas, S.; Botti Navarro, V.J. Incidencia de la localización en el precio de la vivienda a través de un modelo de red neuronal artificial. Una aplicación a la ciudad de Valencia. Catastro 2012, 74, 7–25. Available online: http://www.catastro.meh.es/documentos/publicaciones/ct/ct74/1.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- McGreal, W.S.; Taltavull de la Paz, P. Implicit house prices: Variation over time and space in Spain. Urban Stud. 2013, 50, 2024–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Goodman, A.C. Relationship between urban land price and housing price: Evidence from 21 provincial capitals in China. Habitat Int. 2013, 40, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey Carmona, F.J. Alternativas determinantes en valoración de inmuebles urbanos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Cordoba, Andalusia, Spain, 2014. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10396/12473 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Quispe Villafuerte, A. Una aplicación del modelo de precios hedónicos al mercado de viviendas de Lima Metropolitana. Revista de Economía y Derecho 2012, 9, 85–121. Available online: https://revistas.upc.edu.pe/index.php/economia/article/view/161 (accessed on 9 October 2018).
- De Ayala, A.; Galarraga, I.; Spadaro, J.V. The price of energy efficiency in the Spanish housing market. Energy Policy 2016, 94, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmolejo Duarte, C. La incidencia de la calificación energética sobre los valores residenciales: Un análisis para el mercado plurifamiliar en Barcelona. Informes de la Construcción 2016, 68, e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez Tabales, J.M.; Rey Carmona, F.J.; Caridad y Ocerin, J.M. Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques to analyze the determinants attributes in housing prices. Intel. Artif. 2016, 19, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas del Rosal, J.C. Métodos de valoración urbana. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Córdoba, Andalusia, Spain, 2017. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10396/15417 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Zhang, L.; Yi, Y. Quantile house price indices in Beijing. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2017, 63, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebula, R.J. The hedonic pricing model applied to the housing market of the city of Savannah and its Savannah historic Landmark district. Rev. Reg. Stud. 2009, 39, 9–22. Available online: http://journal.srsa.org/ojs/index.php/RRS/article/view/182 (accessed on 3 August 2018).
- Ezebilo, E. Evaluation of House Rent Prices and Their Affordability in Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea. Buildings 2017, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-G.; Zhang, X.-L.; Wu, W.-P. Application of fuzzy neural network for real estate prediction. In Advances in Neural Networks—ISNN 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1187–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Bonifaci, P.; Copiello, S. Price premium for buildings energy efficiency: Empirical findings from a hedonic model. Valori e Valutazioni 2015, 14, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Keskin, B.; Dunning, R.; Watkins, C. Modelling the impact of earthquake activity on real estate values: A multi-level approach. J. Eur. Real Estate Res. 2017, 10, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmolejo Duarte, C. La incidencia de la percepción del ruido ambiental sobre la formación espacial de los valores residenciales: Un análisis para barcelona. Revista de la Construcción 2008, 7, 4–19. Available online: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=127612580001 (accessed on 9 June 2018).
- Agnew, K.; Lyons, R.C. The impact of employment on housing prices: Detailed evidence from FDI in Ireland. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2018, 70, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch Osuna, J.M.; Soto Canales, K.; Garza Mendiola, R. Valuación de la calidad urbano-ambiental. Una modelación hedónica: San Nicolás de los Garza, México. Estudios Demográficos y Urbanos 2013, 28, 383–428. Available online: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=31230010004 (accessed on 9 October 2018). [CrossRef]
- Malpezzi, S. Hedonic Pricing Models: A Selective and Applied Review. In Housing Economics and Public Policy; O’Sullivan, T., Gibb, K., Eds.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kain, J.F.; Quigley, J.M. Housing Markets and Racial Discrimination: A Microeconomic Analysis; National Bureau of Economic Research: New York, NY, USA, 1975; p. 393. ISBN 0-870-14270-4. Available online: http://www.nber.org/books/kain75-1 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Freeman, A.M.; Herriges, J.A.; Kling, C.L. The Measurement of Environmental and Resource Values, 3rd ed.; RFF Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 479. ISBN 978-0-415-50157-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zietz, J.; Zietz, E.N.; Sirmans, G.S. Determinants of house prices: A quantile regression approach. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2008, 37, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.; Bassett, G. Regression Quantiles. Econometrica 1978, 46, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R. Quantile Regression; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 349. ISBN 978-0-521-84573-1. [Google Scholar]
- Buchinsky, M. Recent Advances in Quantile Regression Models: A Practical Guideline for Empirical Research. J. Hum. Resour. 1998, 33, 88–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R. R Package ‘quantreg’. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=quantreg (accessed on 3 September 2018).
- Barrodale, I.; Roberts, F.D.K. Solution of an overdetermined system of equations in the l1 norm [F4]. Commun. ACM 1974, 17, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.; d’Orey, V. Remark AS R92: A Remark on Algorithm AS 229: Computing Dual Regression Quantiles and Regression Rank Scores. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 1994, 43, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.W.; D’Orey, V. Algorithm AS 229: Computing Regression Quantiles. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 1987, 36, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.; Machado, J.A.F. Goodness of Fit and Related Inference Processes for Quantile Regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 1296–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEC, Sede electrónica del Catastro Inmobiliario. Información alfanumérica y cartografía vectorial. Available online: https://www.sedecatastro.gob.es/ (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- INE, Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Censo de Población y vivienda de 2011. Available online: https://www.ine.es/censos2011_datos/cen11_datos_resultados.htm (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- Limsombunchai, V.; Gan, C.; Lee, M. House price prediction: Hedonic price model vs. Artificial neural network. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2004, 1, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, C.; Nishimura, K.G.; Watanabe, T. House prices from magazines, realtors, and the land registry. BIS Pap. 2012, 64, 29–38. Available online: https://www.bis.org/publ/bppdf/bispap64f.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2018).
- Mora García, R.T. Modelo explicativo de las variables intervinientes en la calidad del entorno construido de las ciudades. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Alicante, Alicante, Spain, 2016. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10045/65829 (accessed on 15 February 2018).
- Zheng, S.; Kahn, M.E. Land and residential property markets in a booming economy: New evidence from beijing. J. Urban Econ. 2008, 63, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, A.; Hoesli, M.; Bender, A. Environmental variables and real estate prices. Urban Stud. 2001, 38, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinbaum, D.; Kupper, L.; Nizam, A.; Rosenberg, E. Applied Regression Analysis and Other Multivariable Methods, 5th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; p. 1072. ISBN 978-1-285-05108-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Simonoff, J.S. Handbook of Regression Analysis; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; p. 240. ISBN 978-0-470-88716-5. [Google Scholar]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning: With Applications in R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 426. ISBN 978-1-4614-7137-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, R.H.; Merenda, P.F.; Gold, R.Z. Introduction to Bivariate and Multivariate Analysis; Scott, Foresman and Company: Glenview, IL, USA, 1980; p. 444. ISBN 9780673150998. [Google Scholar]
- Grömping, U. R Package ‘Relaimpo’. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=relaimpo (accessed on 3 September 2018).
- Grömping, U. Relative Importance for Linear Regression in R: The Package Relaimpo. J. Stat. Softw. 2006, 17, 27. Available online: https://www.jstatsoft.org/v017/i01 (accessed on 3 September 2018). [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.W.; Lebreton, J.M. History and use of relative importance indices in organizational research. Organ. Res. Methods 2004, 7, 238–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.-C.; Wang, X. Hedonic house prices and spatial quantile regression. J. Hous. Econ. 2012, 21, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Category | Characteristics | References |
|---|---|---|
| Dwelling characteristics (A) | Dwelling typology | [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24] |
| Age of the dwelling | [12,16,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] | |
| Dwelling surface area | [11,13,15,16,18,20,21,22,23,24,26,27,28,29,30,31,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,41,42,43,44,45,46,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] | |
| Number of bedrooms | [11,13,14,17,19,20,21,23,24,28,31,34,41,50,56,61,62,63] | |
| Number of bathrooms | [14,20,23,24,31,38,49,55,57,61,64] | |
| Floor of the dwelling | [15,21,24,27,37,38,39,42,55,56,57,60,61] | |
| Terrace | [23,28,31,52,61] | |
| Wardrobe | [24,43,59] | |
| State of conservation | [11,16,22,23,24,28,30,34,59] | |
| Features of the building (B) | Garage slot | [13,16,18,23,24,28,31,38,44,45,46,49,54,55,58,59,61,64] |
| Elevator | [13,16,22,23,24,29,31,43,52,57,59] | |
| Swimming pool in the building | [13,18,22,31,54,57,58,59,60,61] | |
| Characteristics of the location (C) | Location within the territory or the city | [13,16,24,31,35,36,38,39,41,44,45,46,48,54,56,58,61,62,64,65] |
| Proximity to the coast | [24,25,48,66] | |
| Characteristics of the neighbourhood (D) | Age of the population | [15,28] |
| Number of Foreigners | [15,22,23,28,42,51,67] | |
| Level of studies | [15,21,25,50,57,67,68] | |
| Market, occupation and sale characteristics (E) | Price | In all studies this is the dependent variable |
| Use of the dwelling | [34,52,56] | |
| Housing tenure | [19] |
| Category | Characteristics | Unit | Description of the Variable | Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwelling characteristics (A) | A_flat | dummy | Indicates whether the property has this typology: Flat or apartment, penthouse, duplex, studio flat | YES |
| A_penthouse | ||||
| A_duplex | ||||
| A_studio_flat | ||||
| A_age | numerical | Age of the building (years) Number of years that have passed since it was built | ||
| A_area_m2 | Built dwelling surface (sqm) Gross square meters of the dwelling | |||
| A_bedrooms | Number of bedrooms in the dwelling | NO | ||
| A_bathrooms | Number of bathrooms | YES | ||
| A_floor | Floor the dwelling was located on within the building | |||
| A_terrace | dummy | Availability of terrace | ||
| A_wardrobe | Availability of built-in wardrobes | NO | ||
| A_good_condition | Classification that the seller assigns to the state of the dwelling, such as “good” | YES | ||
| A_new_construction | Newly build housing that can be: a project, under construction, or less than 3 years old | |||
| A_state_to_reform | Requires refurbishment | |||
| Features of the building (B) | B_parking | dummy | Availability of garage slot | YES |
| B_elevator | Availability of elevator | |||
| B_pool | Availability of swimming pool | |||
| Characteristics of the location (C) | C_Alicante | dummy | Identifier of the comarca: Alicante, Marina Alta, Marina Baja, Bajo Vinalopó, Bajo Segura, El Condado, Alcoy, Alto Vinalopó and Medio Vinalopó | YES |
| C_Marina_Alta | ||||
| C_Marina_Baja | ||||
| C_Bajo_Vinalopo | ||||
| C_Bajo_Segura | ||||
| C_Condado | ||||
| C_Alcoy | ||||
| C_Alto_Vinalopo | ||||
| C_Medio_Vinalopo | ||||
| C_coastalregion | Identification of property location within a coastal region | |||
| C_coastal_dist_km | numerical | Distance (km) from the property to the coast | NO | |
| Characteristics of the neighbourhood (D) | D_elderly | numerical | Ratio of dependant elderly | YES |
| D_foreigners | Ratio of foreign population | |||
| D_no_studies | Ratio of population without education | |||
| D_university | Ratio of the population with university studies | |||
| D_students | Ratio of the population with primary and secondary studies | NO | ||
| Market, occupation and sale characteristics (E) | E_price | numerical | The property price offered by the seller (in Euro) | Dependent variable |
| E_vacant_dwelling | numerical | Ratio of empty dwellings | NO | |
| E_main_dwelling | Ratio of main dwellings | |||
| E_secondary_dwelling | Ratio of second dwellings | YES | ||
| E_rented_dwelling | Ratio of housing for rent | |||
| E_mortgaged_dwelling | Ratio of mortgaged housing | NO | ||
| E_home_ownership | Home ownership ratio |
| Cat. | Continuous Variables | Dummies Variables | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Mean | SD | Min. | Max. | Coding. | Freq. | Percent. | |
| Dwelling (A) | A_flat | 30,140 | 88.3 | |||||
| A_penthouse | 2328 | 6.8 | ||||||
| A_duplex | 1179 | 3.5 | ||||||
| A_studio_flat | 491 | 1.4 | ||||||
| A_age | 31.2 | 11.3 | 1.0 | 93.1 | ||||
| A_area_m2 | 95.3 | 31.8 | 20.0 | 249.0 | ||||
| A_bedrooms | 2.6 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 5.0 | ||||
| A_bathrooms | 1.6 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 4.0 | ||||
| A_floor | 2.9 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 20.0 | ||||
| A_terrace | No Terrace With Terrace | 14,932 19,206 | 43.7 56.3 | |||||
| A_wardrobe | No wardrobe Wardrobe | 12,743 21,395 | 37.3 62.7 | |||||
| A_good_condition | 32,069 | 93.9 | ||||||
| A_new_construction | 255 | 0.8 | ||||||
| A_state_to_reform | 1814 | 5.3 | ||||||
| Building (B) | B_parking | No garage With garage | 21,055 13,083 | 61.7 38.3 | ||||
| B_elevator | No elevator With elevator | 8715 25,423 | 25.5 74.5 | |||||
| B_pool | No pool With pool | 20,296 13,842 | 59.5 40.5 | |||||
| Location (C) | C_Alicante | 12,674 | 37.1 | |||||
| C_Marina_Alta | 3833 | 11.2 | ||||||
| C_Marina_Baja | 3938 | 11.5 | ||||||
| C_Bajo_Vinalopo | 4276 | 12.5 | ||||||
| C_Bajo_Segura | 7165 | 21.0 | ||||||
| C_Condado | 137 | 0.4 | ||||||
| C_Alcoy | 905 | 2.7 | ||||||
| C_Alto_Vinalopo | 327 | 1.0 | ||||||
| C_Medio_Vinalopo | 883 | 2.6 | ||||||
| C_coastalregion | Non-coastal Coastal | 8636 25,502 | 25.3 74.7 | |||||
| C_coastal_dist_km | 5.78 | 10.37 | 0.00 | 54.90 | ||||
| Neighbourhood (D) | D_elderly | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 1.05 | |||
| D_foreigners | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.93 | ||||
| D_no_studies | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.37 | ||||
| D_university | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.54 | ||||
| D_students | 0.61 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.86 | ||||
| Market, etc (E) | price | 131,039 | 80,061 | 15,000 | 610,000 | |||
| price_ln | 11.61 | 0.59 | 9.62 | 13.32 | ||||
| E_vacant_dwelling | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.68 | ||||
| E_main_dwelling | 0.57 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 1.00 | ||||
| E_secondary_dwelling | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.84 | ||||
| E_rented_dwelling | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.53 | ||||
| E_mortgaged_dwelling | 0.39 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.96 | ||||
| E_home_ownership | 0.42 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.83 | ||||
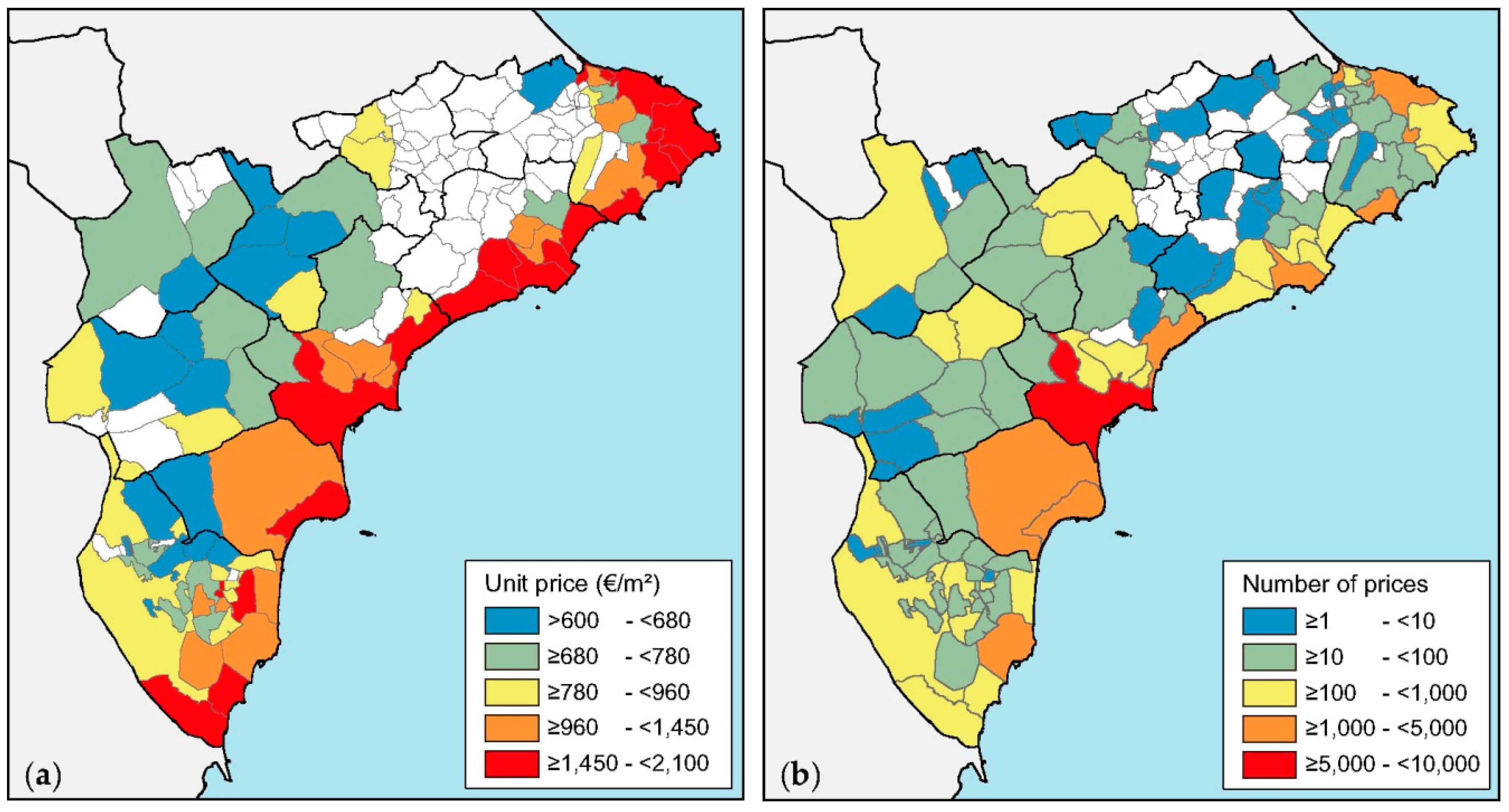
| Zone | N (%) | Average Price € (SD) | Unit Price €/m2 (SD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of Alicante | 34,138 (100%) | 131,039 (80,060) | 1390 (687) | |
| Coastal area | Marina Alta | 3833 (11.2%) | 162,816 (88,418) | 1754 (741) |
| Marina Baja | 3938 (11.5%) | 155,244 (83,295) | 1829 (692) | |
| Alicante | 12,674 (37.1%) | 149,077 (85,498) | 1427 (667) | |
| Bajo Vinalopó | 4276 (12.5%) | 111,428 (63,235) | 1157 (575) | |
| Bajo Segura | 7165 (21.0%) | 98,323 (54,090) | 1239 (544) | |
| Inland area | Condado | 137 (0.4%) | 86,903 (49,904) | 807 (334) |
| Alcoy | 905 (2.7%) | 75,502 (44,883) | 734 (337) | |
| Alto Vinalopó | 327 (1.0%) | 75,402 (42,474) | 711 (341) | |
| Medio Vinalopó | 883 (2.6%) | 71,042 (37,342) | 695 (323) |
| Total by Typology | Without /with Elevator | Average Price € (SD) | Unit Price €/m2 (SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typology | N (%) | %/% | no elevator | with elevator | no elevator | with elevator |
| flat | 30,140 (88.3%) | 25.0/75.0 | 81,650 (54,609) | 142,257 (77,293) | 967 (596) | 1505 (664) |
| penthouse | 2328 (6.8%) | 15.8/84.2 | 115,169 (76,454) | 185,014 (98,239) | 1270 (684) | 1634 (674) |
| duplex | 1179 (3.5%) | 59.5/40.5 | 151,423 (69,715) | 204,958 (90,011) | 1360 (536) | 1625 (634) |
| studio flat | 491 (1.4%) | 21.0/79.0 | 64,933 (39,548) | 69,876 (50,707) | 1347 (541) | 1569 (650) |
| Total | 34,138 (100%) | 25.5/74.5 | 88,484 (60,265) | 145,626 (80,798) | 1016 (608) | 1518 (665) |
| Characteristics | Model 1 OLS | Model 2 OLS | Model 3 OLS | Model 4 OLS | Model 5 OLS | Model 6 OLS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 10.574 *** (0.011) | 10.205 *** (0.011) | 10.056 *** (0.013) | 9.961 *** (0.013) | 10.010 *** (0.012) | 9.849 *** (0.154) | |
| A | A_flat | Reference | |||||
| A_penthouse | 0.021 * (0.010) | 0.074 *** (0.009) | 0.091 *** (0.008) | 0.107 *** (0.007) | 0.116 *** (0.007) | 0.119 *** (0.007) | |
| A_duplex | −0.028 * (0.013) | 0.076 *** (0.012) | 0.073 *** (0.011) | 0.050 *** (0.010) | 0.040 *** (0.010) | 0.036 *** (0.010) | |
| A_studio_flat | −0.187 *** (0.020) | −0.246 *** (0.018) | −0.259 *** (0.016) | −0.309 *** (0.015) | −0.309 *** (0.015) | −0.315 *** (0.014) | |
| A_age | −0.006 *** (0.0002) | 0.001 *** (0.0002) | 0.001 ** (0.0002) | −0.0002 (0.0002) | −0.001 *** (0.0002) | −0.0003 (0.0002) | |
| A_area_m2 | 0.005 *** (0.0001) | 0.006 *** (0.0001) | 0.006 *** (0.0001) | 0.006 *** (0.0001) | 0.006 *** (0.0001) | 0.006 *** (0.0001) | |
| A_bathrooms | 0.342 *** (0.006) | 0.224 *** (0.005) | 0.239 *** (0.005) | 0.231 *** (0.004) | 0.236 *** (0.004) | 0.233 *** (0.004) | |
| A_floor | 0.037 *** (0.001) | 0.013 *** (0.001) | 0.005 *** (0.001) | 0.004 *** (0.001) | 0.002 * (0.001) | 0.002 ** (0.001) | |
| A_terrace | 0.236 *** (0.005) | 0.117 *** (0.005) | 0.070 *** (0.004) | 0.052 *** (0.004) | 0.041 *** (0.004) | 0.037 *** (0.004) | |
| A_good_condition | Reference | ||||||
| A_new_construction | 0.194 *** (0.028) | 0.105 *** (0.025) | 0.186 *** (0.022) | 0.166 *** (0.020) | 0.177 *** (0.020) | 0.163 *** (0.020) | |
| A_state_to_reform | −0.379 *** (0.011) | −0.251 *** (0.010) | −0.229 *** (0.009) | −0.223 *** (0.008) | −0.218 *** (0.008) | −0.217 *** (0.008) | |
| B | B_parking | 0.168 *** (0.005) | 0.156 *** (0.004) | 0.149 *** (0.004) | 0.142 *** (0.004) | 0.133 *** (0.004) | |
| B_elevator | 0.284 *** (0.005) | 0.244 *** (0.005) | 0.241 *** (0.005) | 0.231 *** (0.005) | 0.232 *** (0.004) | ||
| B_pool | 0.308 *** (0.005) | 0.207 *** (0.005) | 0.137 *** (0.004) | 0.119 *** (0.005) | 0.124 *** (0.004) | ||
| C | C_Alicante | Reference | |||||
| C_Marina_Alta | 0.132 *** (0.007) | 0.076 *** (0.007) | 0.058 *** (0.007) | ||||
| C_Marina_Baja | 0.146 *** (0.007) | 0.197 *** (0.007) | 0.143 *** (0.007) | ||||
| C_Bajo_Vinalopo | 0.043 *** (0.007) | 0.099 *** (0.006) | 0.030 *** (0.007) | ||||
| C_Bajo_Segura | −0.108 *** (0.006) | −0.130 *** (0.007) | −0.186 *** (0.007) | ||||
| C_Condado | −0.098 ** (0.030) | −0.082 ** (0.028) | −0.146 *** (0.028) | ||||
| C_Alcoy | −0.182 *** (0.013) | −0.166 *** (0.012) | −0.221 *** (0.012) | ||||
| C_Alto_Vinalopo | −0.156 *** (0.020) | −0.078 *** (0.019) | −0.144 *** (0.018) | ||||
| C_Medio_Vinalopo | −0.213 *** (0.013) | −0.149 *** (0.012) | −0.202 *** (0.012) | ||||
| C_coastalregion | 0.315 *** (0.006) | 0.202 *** (0.005) | 0.129 *** (0.006) | 0.068 *** (0.010) | |||
| D | D_elderly | 0.343 *** (0.011) | 0.282 *** (0.012) | 0.244 *** (0.012) | |||
| D_foreigners | 0.238 *** (0.013) | 0.108 *** (0.014) | −0.038 * (0.016) | ||||
| D_no_studies | −0.910 *** (0.045) | −0.874 *** (0.045) | −0.722 *** (0.046) | ||||
| D_university | 1.112 *** (0.024) | 0.996 *** (0.024) | 1.021 *** (0.024) | ||||
| E | E_secondary_dwelling | 0.321 *** (0.010) | 0.335 *** (0.012) | ||||
| E_rented_dwelling | 0.201 *** (0.021) | 0.195 *** (0.023) | |||||
| Spatial fixed effects | No | No | Yes (by comarcas) | Yes (by comarcas) | Yes (by comarcas) | Yes (by municipality) |
| Statistics | Model 1 OLS | Model 2 OLS | Model 3 OLS | Model 4 OLS | Model 5 OLS | Model 6 OLS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.440 | 0.568 | 0.654 | 0.706 | 0.715 | 0.731 | |
| adj. R2 | 0.439 | 0.568 | 0.654 | 0.706 | 0.715 | 0.730 | |
| Std. Error | 0.441 | 0.387 | 0.347 | 0.320 | 0.315 | 0.306 | |
| F (sig.) | 2676.7 (p < 0.001) | 3449.9 (p < 0.001) | 2935.0 (p < 0.001) | 3154.3 (p < 0.001) | 3054.7 (p < 0.001) | 732.5 (p < 0.001) |
| Characteristics | Model 7 QR 10 | Model 8 QR 25 | Model 9 QR 50 | Model 10 QR 75 | Model 11 QR 90 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 9.736 *** (0.019) | 9.905 *** (0.016) | 10.073 *** (0.015) | 10.205 *** (0.016) | 10.241 *** (0.023) | |
| A | A_flat | Reference | ||||
| A_penthouse | 0.089 *** (0.012) | 0.102 *** (0.009) | 0.122 *** (0.008) | 0.136 *** (0.009) | 0.126 *** (0.012) | |
| A_duplex | 0.060 *** (0.010) | 0.078 *** (0.013) | 0.042 *** (0.010) | 0.020 (0.014) | 0.016 (0.017) | |
| A_studio_flat | −0.416 *** (0.022) | −0.392 *** (0.022) | −0.335 *** (0.026) | −0.239 *** (0.019) | −0.160 *** (0.031) | |
| A_age | −0.003 *** (0.0003) | −0.002 *** (0.0002) | −0.001 *** (0.0002) | 0.0004 (0.0003) | 0.003 *** (0.0003) | |
| A_area_m2 | 0.005 *** (0.0001) | 0.005 *** (0.0001) | 0.006 *** (0.0001) | 0.006 *** (0.0001) | 0.007 *** (0.0001) | |
| A_bathrooms | 0.236 *** (0.006) | 0.232 *** (0.005) | 0.237 *** (0.005) | 0.235 *** (0.006) | 0.229 *** (0.008) | |
| A_floor | 0.0001 (0.001) | 0.001 (0.001) | 0.002 ** (0.001) | 0.004 *** (0.001) | 0.007 *** (0.001) | |
| A_terrace | 0.056 *** (0.005) | 0.044 *** (0.005) | 0.042 *** (0.004) | 0.038 *** (0.005) | 0.023 *** (0.007) | |
| A_good_condition | Reference | |||||
| A_new_construction | 0.130 ** (0.045) | 0.141 *** (0.042) | 0.230 *** (0.023) | 0.220 *** (0.020) | 0.181 ** (0.069) | |
| A_state_to_reform | −0.245 *** (0.011) | −0.221 *** (0.010) | −0.228 *** (0.009) | −0.226 *** (0.012) | −0.204 *** (0.020) | |
| B | B_parking | 0.159 *** (0.006) | 0.158 *** (0.005) | 0.138 *** (0.005) | 0.124 *** (0.005) | 0.121 *** (0.007) |
| B_elevator | 0.293 *** (0.007) | 0.268 *** (0.006) | 0.226 *** (0.006) | 0.180 *** (0.006) | 0.161 *** (0.008) | |
| B_pool | 0.129 *** (0.006) | 0.120 *** (0.005) | 0.117 *** (0.005) | 0.118 *** (0.006) | 0.126 *** (0.008) | |
| C | C_Alicante | Reference | ||||
| C_Marina_Alta | 0.042 *** (0.011) | 0.048 *** (0.009) | 0.055 *** (0.008) | 0.067 *** (0.009) | 0.097 *** (0.011) | |
| C_Marina_Baja | 0.126 *** (0.009) | 0.115 *** (0.009) | 0.126 *** (0.008) | 0.147 *** (0.009) | 0.177 *** (0.012) | |
| C_Bajo_Vinalopo | 0.065 *** (0.011) | 0.029 *** (0.009) | 0.010 (0.008) | 0.001 (0.008) | 0.045 *** (0.013) | |
| C_Bajo_Segura | −0.194 *** (0.010) | −0.211 *** (0.008) | −0.220 *** (0.008) | −0.196 *** (0.009) | −0.135 *** (0.012) | |
| C_Condado | −0.070 (0.056) | −0.156 *** (0.046) | −0.168 ** (0.058) | −0.178 *** (0.038) | −0.189 *** (0.045) | |
| C_Alcoy | −0.211 *** (0.016) | −0.233 *** (0.021) | −0.224 *** (0.016) | −0.240 *** (0.012) | −0.233 *** (0.020) | |
| C_Alto_Vinalopo | −0.173 *** (0.038) | −0.134 *** (0.035) | −0.128 *** (0.036) | −0.123 *** (0.024) | −0.139 *** (0.019) | |
| C_Medio_Vinalopo | −0.249 *** (0.033) | −0.230 *** (0.018) | −0.224 *** (0.019) | −0.190 *** (0.018) | −0.148 *** (0.026) | |
| C_coastalregion | 0.195 *** (0.009) | 0.131 *** (0.007) | 0.086 *** (0.007) | 0.081 *** (0.007) | 0.104 *** (0.010) | |
| D | D_elderly | 0.340 *** (0.017) | 0.299 *** (0.015) | 0.282 *** (0.015) | 0.255 *** (0.016) | 0.246 *** (0.022) |
| D_foreigners | 0.050 * (0.020) | 0.098 *** (0.018) | 0.122 *** (0.017) | 0.127 *** (0.020) | 0.123 *** (0.026) | |
| D_no_studies | −1.131 *** (0.071) | −1.015 *** (0.055) | −0.927 *** (0.052) | −0.792 *** (0.060) | −0.697 *** (0.085) | |
| D_university | 0.811 *** (0.033) | 0.946 *** (0.029) | 0.991 *** (0.027) | 1.031 *** (0.030) | 1.107 *** (0.044) | |
| E | E_secondary_dwelling | 0.205 *** (0.014) | 0.259 *** (0.013) | 0.323 *** (0.012) | 0.381 *** (0.014) | 0.392 *** (0.018) |
| E_rented_dwelling | 0.150 *** (0.032) | 0.183 *** (0.027) | 0.184 *** (0.024) | 0.189 *** (0.029) | 0.262 *** (0.041) |
| Statistics | Model 7 QR 0.10 | Model 8 QR 0.25 | Model 9 QR 0.50 | Model 10 QR 0.75 | Model 11 QR 0.90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pseudo-R1 | 0.504 | 0.494 | 0.478 | 0.457 | 0.442 |
| The Regression Coefficient Increases with Increasing Price | The Regression Coefficient Remains Constant with Increasing Price | The Regression Coefficient Decreases with Increasing Price | Coefficients in Central Area Constant but with Different Extremes | Different Behaviour between High and Low Prices | The Regression Coefficient Does not Show a Definite or Constant Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| A_penthouse A_studio_flat A_age A_area_m2 C_Marina_Alta C_Marina_Baja C_Medio_Vinalopo D_no_studies D_university E_secondary_dwelling | A_bathrooms B_pool C_Condado C_Alcoy C_Alto_Vinalopo | B_parking B_elevator D_elderly | A_floor A_terrace A_state_to_reform E_rented_dwelling | C_coastalregion C_Bajo_Vinalopo C_Bajo_Segura | A_duplex A_new_construction D_foreigners |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mora-Garcia, R.-T.; Cespedes-Lopez, M.-F.; Perez-Sanchez, V.R.; Marti, P.; Perez-Sanchez, J.-C. Determinants of the Price of Housing in the Province of Alicante (Spain): Analysis Using Quantile Regression. Sustainability 2019, 11, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020437
Mora-Garcia R-T, Cespedes-Lopez M-F, Perez-Sanchez VR, Marti P, Perez-Sanchez J-C. Determinants of the Price of Housing in the Province of Alicante (Spain): Analysis Using Quantile Regression. Sustainability. 2019; 11(2):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020437
Chicago/Turabian StyleMora-Garcia, Raul-Tomas, Maria-Francisca Cespedes-Lopez, V. Raul Perez-Sanchez, Pablo Marti, and Juan-Carlos Perez-Sanchez. 2019. "Determinants of the Price of Housing in the Province of Alicante (Spain): Analysis Using Quantile Regression" Sustainability 11, no. 2: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020437
APA StyleMora-Garcia, R.-T., Cespedes-Lopez, M.-F., Perez-Sanchez, V. R., Marti, P., & Perez-Sanchez, J.-C. (2019). Determinants of the Price of Housing in the Province of Alicante (Spain): Analysis Using Quantile Regression. Sustainability, 11(2), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020437








