1. Introduction
The emergence of social media has changed the way in which companies communicate with their customers, which has allowed them more direct and faster contact using advertising or marketing strategies [
1]. In addition, the cost of using social media for advertising is much lower than traditional methods of publicity [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. Aside from the lower cost of advertising, social media is used to promote transparency, efficiency, and openness by many governments [
7] and organizations [
4,
8]. Through social media, companies promote new products and services, announce offers, easily learn the tastes and preferences of their customers, and relate directly with them [
9,
10]. Therefore, correct use of social media can help companies to attract new customers and turn interested people into potential customers in a meaningful way. Because of the above, in addition to many other reasons, there is no doubt about the beneficial role of social media in business [
2,
11,
12,
13].
Social media can also serve as a tool to promote sustainability [
4,
14]. The concept of sustainability has evolved during recent decades, and today it is a popular term that is used in different contexts. The meaning of sustainability is strongly dependent on the context in which it is applied and on whether its use is based on a social, economic, or ecological perspective [
15,
16,
17]. Most of the interpretations of sustainable development in these three areas agree that a company’s policies and actions to achieve economic growth must respect the environment and also be socially equitable [
16]. Currently, sustainability issues are considered strategic topics to address to ensure the success and operability of an organization, and already represent a determining factor for investors in assessing the profitability of sustainable enterprises. For this reason, companies are increasingly trying to be sustainable [
18,
19,
20].
In Spain, many researchers [
16,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25] have studied the sustainability of companies in different sectors, but there are no studies on the impact of social media marketing on the environmental sustainability of companies that operate in the food and beverage services sector. Considering that the food and beverage services sector in Spain presents a great force for reducing the unemployment rate and increasing economic growth, the question is whether the companies that are operating in this sector are sustainable from the point of view of their customers and whether they promote environmental sustainability through social media, since, as we have seen above, social media is key for companies to communicate with their customers.
Bearing all these ideas in mind, the main objectives of this research paper were to analyze the impact of social media in promoting environmental sustainability in food and beverage services, specifically in restaurants, and whether these companies promote sustainability through social media for the conservation and maintenance of the environment. In order to achieve these objectives, a survey was designed and the responses were statistically analyzed. Consequently, the social media marketing of these companies is an explanatory variable related to their environmental sustainability. The main results show that social media marketing used by food and beverage service companies promotes environmental sustainability and shows its importance to their customers. This research is an important contribution to the literature on this subject because there are no empirical studies about the impact of social media marketing on the environmental sustainability of the food and beverage sector in Spain.
The paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 contains a review of the literature on social media marketing and sustainability.
Section 3 presents the hypotheses for this research project.
Section 4 briefly describes the data analysis.
Section 5 further discusses the empirical data analysis from the findings. The final sections are devoted to the discussion and conclusion of this study.
3. Hypothesis Development
As discussed in
Section 2, social media is one of the tools that brings together businesses and their consumers and therefore it is a key factor in the development of companies. Through social media, companies promote their marketing, which allows them to have a lower cost and be more efficient [
9,
13]. Companies use this tool not only to reduce the costs and increase their efficiency, but also to promote their image, corporate social responsibility, and environmental sustainability, among others.
Analyzing the existing literature on the social media influence on sustainability in general, we can see that there are a few studies on this important topic [
7,
14,
44], but there are no studies analyzing the situation of the food and beverage sector and environmental sustainability through social media. For this reason, in this research paper, our main objective was to analyze the impact of social media marketing in the environmental sustainability in food and beverage service companies in Spain, specifically in restaurants, by considering customers’ trust, perceived value, continuance intention, and satisfaction achieved with the company that promotes environmental sustainability for the conservation and maintenance of the environment through social networks.
In order to achieve the stated objective, variables such as perceived value, continuity intention, trust, and satisfaction must be analyzed in order to measure environmental sustainability through social media. These four variables have been studied in depth separately [
54,
55,
56,
57,
58] and jointly [
7,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63] by several researchers. The conclusions of these studies indicated the importance of these variables for the growth of a company’s productivity, financial performance, solvency, or short- and long-term risk reduction. This means that if the companies want to be stable and increase the productive capacity or profitability, they have to have customers that trust them and are satisfied with the products/services/politics of the company. Fornell et al.’s [
57] study considered a satisfied customer as an economic asset for the company with high returns and low risk. For all that, we can say that for companies, their customers’ satisfaction, continuance intention, trust, and perceived value are important factors. At the same time, consumers are increasingly demanding regarding the quality of products and services and want to know more about the business and political actions of the company [
64,
65,
66,
67]. Studies along these lines have shown that when consumers choose, they give preference to companies that respect environmental sustainability [
68,
69]. All this indicates that there can be a positive and direct relationship between the variables described above and environmental sustainability. Each of these variables and their possible relationships are studied below.
A study carried out by Chen and Lin [
7] indicates that perceived value is one of the key measures for the marketing of companies. Through perceived value, it is possible to detect consumers’ preferences or purchase intentions, taking into account the multiple components of value, the impact of roles and perceptions, and the importance of competition [
58]. In order to measure the consumers’ perceived value, the five theoretical types of value must be taken into account: functional value (FV), which measures an offering’s ability to fulfil its function; social value (SV), which represents the benefits derived through inter-personal/group interactions; emotional value (EMV), which accounts for benefits obtained from an offering’s ability to arouse feelings and/or affective states; epistemic value (EPV), which refers to benefits derived through an offering’s ability to arouse curiosity, provide novelty, or satisfy a desire for knowledge; and conditional value (CV), which represents the benefits derived in a specific situational context [
70]. The questions for measuring perceived value were included in the questionnaire. Preliminary studies show that the perceived value of the customers leads to positive behavior in terms of continuance intention [
7,
62]. The term continuance intention or repurchase intention is intended as the intention to continue purchasing specified goods or services from the same business, taking into account customers current situation and circumstances [
55,
71]. One of the advantages of continuance intention is that it reduce costs for businesses, as it is much more expensive to seek new customers than keep old ones [
72]. A study undertaken by Shao, Guo, and Ge [
62] has shown that perceived value from the company play a more significant role in facilitating customer satisfaction and continuance intention. Another study carried out by Chen and Lin [
7] has found that perceived value by users positively and significantly influence the continuance intention. This means that there is a positive relationship between perceived value and continuance intention. From here, the objective of Hypothesis 1 is to see whether the perceived value by customers influences the continuance intention toward the company, which means the use of goods and services of the company in future.
Therefore, the following hypothesis between the perceived value and continuance intention is proposed:
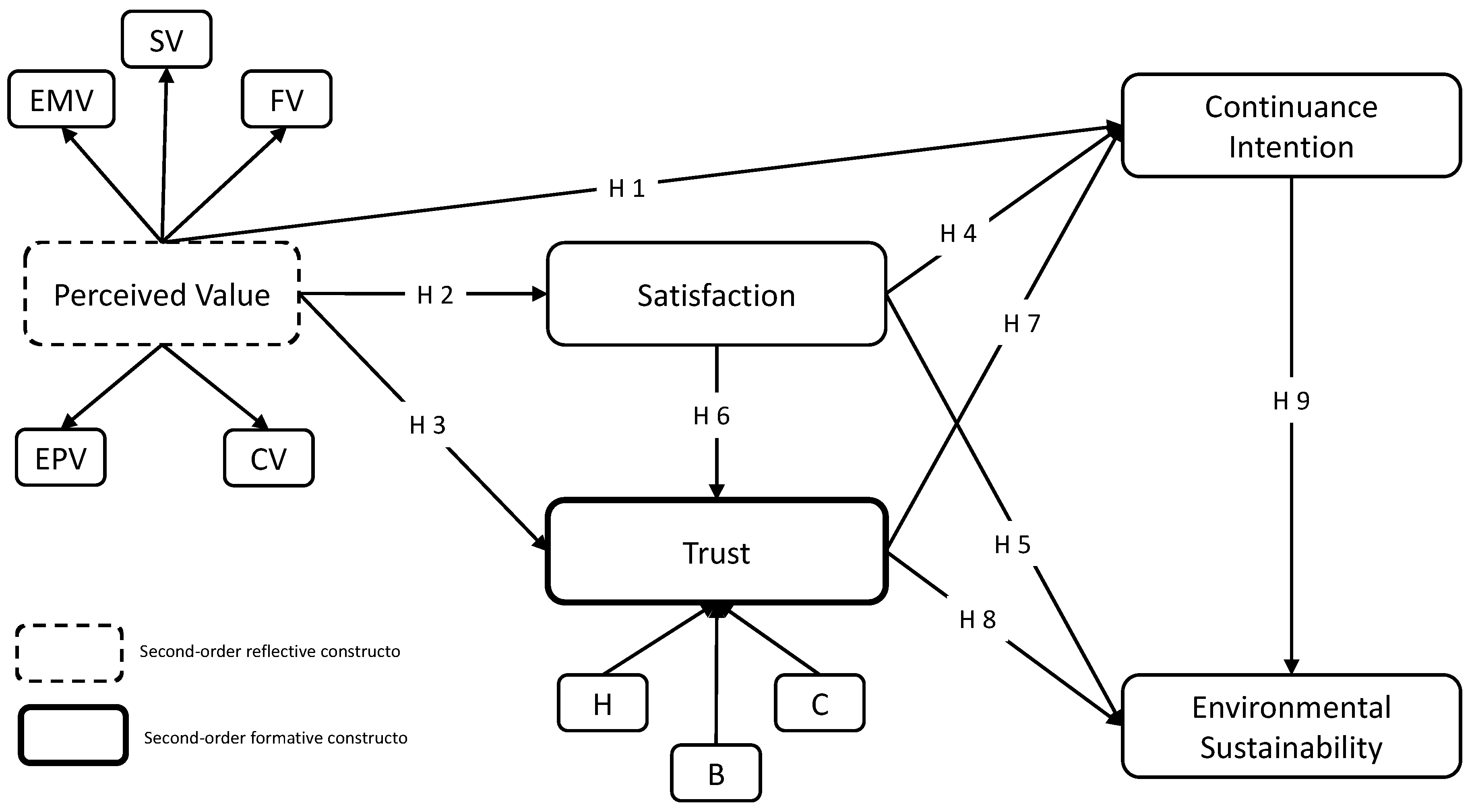
Hypothesis H1. Perceived value by customers has a positive influence on their continuance intention toward the company.
Many studies in marketing have determined that perceived value is an antecedent to customer’s satisfaction [
63,
70,
73]. This is defined as customers’ post-consumption evaluation that is dependent on the perceived quality and value [
73]; in other words, it is a process of evaluation between what was received and what was expected by consumers [
74]. Customer satisfaction has long attracted the interests of many researchers because of its significance in influencing post-purchase behavior [
75]. Different researchers have studied the relationship between customer satisfaction and perceived value [
63,
70,
76,
77]. According to these studies, there is evidence that perceived value is a significant determinant of satisfaction. Because of this, the objective of Hypothesis 2 is to determine whether perceived value of a business by consumers has a positive relationship with customer satisfaction.
Therefore, the following hypothesis between the perceived value and satisfaction is proposed:
Hypothesis H2. Perceived value has a positive influence on the satisfaction of customers.
For companies, it is not an easy task to retain the attention of their customers and to keep them satisfied. To do this, they need to improve customer loyalty through maximizing their trust toward the company and its services and goods [
78]. Trust is considered as one of the most important variables toward building a stable relationship between the company and its customers [
79,
80]. A study conducted in Spain by Ponte, Carvajal-Trujillo, and Escobar-Rodríguez [
81] has proved that online purchase intention is influenced by perceived value and trust. Also, this study shows that trust has a positive influence on perceived value. Another study carried out by García [
82] has shown the positive relationship between perceived value and trust. For this reason, the objective of Hypothesis 3 was to determine whether perceived value toward a business by consumers has a positive relationship with customer trust generated by the company.
Therefore, the following hypothesis between the perceived value and trust is proposed:
Hypothesis H3. Perceived value has a positive influence on trust generated by the company in the customer.
Another important variable of this study is customer satisfaction toward the company. Satisfaction is the degree to which goods and services provided by the company meet a customer’s expectations; it is a highly personal assessment that is greatly influenced by individual expectations [
56]. Therefore, for the business strategy, it is a key factor that differentiates a company from competitors on the market and has a direct influence on the profitability generated by the company [
83]. A study conducted by Chiu et al. [
84] has shown that the repurchase intention of goods and services is determined by satisfaction. A positive correlation between satisfaction and continuance intention has been found [
7,
84]. From here, the objective of Hypothesis 4 was to determine whether the satisfaction of the company’s customers influences their continuance intention purchase of products and services from that company.
Therefore, the following hypothesis between the satisfaction and continuance intention is proposed:
Hypothesis H4. Satisfaction of the customers has a positive influence on continuance intention.
As it was mentioned before, environmental sustainability is a key factor for the companies to create green products, be competitive in the market, maximize profits, maintain employee loyalty, and be attractive to their customers [
39,
85,
86]. Nowadays, consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental, social, and economic implications of their consumption habits; for this reason, consumers demand that companies to be aware of their actions since the company’s activities have a significant impact on the environment and generally on the society [
86]. Research carried out about environmental management in Spain has shown that environmental management practices have positive effects on financial performance, market success, and customer and employee satisfaction [
87]. Taking into account the literature analyzed on customer satisfaction and environmental sustainability, it can be seen that there are no studies that analyze the direct relationship of these two variables. With this in mind, the objective of Hypothesis 5 was to determine whether the satisfaction achieved by customers is linked with the environmental sustainability.
Therefore, the following hypothesis between customer satisfaction and environmental sustainability is proposed:
Hypothesis H5. Satisfaction of the customers generated by the company has a positive influence on environmental sustainability.
The following hypothesis studies the relation between a customer’s satisfaction and trust. A study carried out in Spain about travel agencies has proved that the more satisfied a customer is in their relationship with the travel agency, the more trust they place in it [
54]. Further studies in marketing has also been found to show that customer satisfaction has a positive impact on customer trust [
88,
89]. Because of this, the objective of Hypothesis 6 was to analyze whether the satisfaction achieved by customers is related with trust, where if the customers are satisfied, this generates the trust they have for that company and its actions.
Therefore, the following hypothesis between the satisfaction and trust is proposed:
Hypothesis H6. Satisfaction of the customers generated by the company has a positive influence on trust.
Customer trust has been studied extensively by marketing and management researchers over the last three decades [
80,
90,
91,
92,
93]. Companies that gain the trust of their customers are more likely to expand, grow, and improve their profitability [
94]. The relationship between trust and continuance intention has been studied, where the positive relationship between these two variables has been shown [
95,
96]. From here, the objective of Hypothesis 7 was to determine whether customer trust is positively related to the intention to continue of the customer or user of this company.
Therefore, the following hypothesis between the trust and continuance intention is proposed:
Hypothesis H7. Customer trust has a positive influence on their continuance intention toward the company.
For companies, building customer trust is a complex process that involves technology and business practices, as well as movement from initial trust formation to continuous trust development [
80]. Users who trust companies are more loyal, satisfied, and intend to continue buying the same products and services [
78,
79,
80,
96]. Therefore, trust plays an important role in customers’ purchase decisions. In the same way, sustainability contributes to the decisions of customers [
68,
97] since they are aware of the results of their decisions. Even though the two variables are essential for consumers when making decisions about products or services, there are no studies that show the direct relationship of these two variables. For this reason, the objective of Hypothesis 8 was to determine whether customer trust is positively related to environmental sustainability. This means that if a customer trusts the company and its actions, this will have an impact on sustainability.
Therefore, the following hypothesis between the trust and environmental sustainability is proposed:
Hypothesis H8. Customer trust has a positive influence on environmental sustainability.
Today, consumers are increasingly informed and have the tools necessary to evaluate the purchase of a product or service, so their decisions regarding whether to continue to buy the same products and services depends on the perceived factors of the company. Studies conducted by Chen [
68] and Mendleson and Polonsky [
69] have shown that consumers are in favor of companies that practice environmental sustainability. In addition, customers that are satisfied with the activities developed by the company are more willing to continue purchasing from the company [
7,
62]. In our study, we tested whether companies’ social networks users that have the intention to continue purchasing the company’s products and services influences environmental sustainability. From here, the objective of Hypothesis 9 was to determine whether there is a positive correlation between customer’s intention to continue to use goods and services of the company and environmental sustainability.
Therefore, the following hypothesis between the continuance intention and environmental sustainability is proposed:
Hypothesis H9. Customer’s continuance intention in the company has a positive influence on environmental sustainability.
According to the empirical studies consulted, the proposed hypothesis should be positive. Based on the hypotheses discussed above, we proposed the following research model (
Figure 1). The proposed research model for this study is a new model since there have been no researchers that study the relationship of variables such as customer trust, satisfaction, and continuance intention with environmental sustainability. An empirical study on customer experience and perceived value on sustainable social relationship in blogs using the same variables was carried out by Chen and Lin [
7]. Therefore, the factors and items of that study have been adapted to build our research model.
7. Discussion
The results obtained in the study on social media in restaurants show the direct and indirect influence exerted by variables, such as trust, perceived value, or continuity intention, on environmental sustainability. It should be noted that few studies have analyzed the influence that these variables have on environmental sustainability, and specifically, they are practically non-existent when they focus of the study of these variables is the service sector, as well as on studies that measure these relationships in social media. After a revision of the literature, one of the main problems was to develop this study., because of the scarcity of the academic works on this topic.
Variables as important as perceived value, continuance intention, or satisfaction, which serve to measure the level of influence the organization exerts on its interest groups, have received very little analyses in terms of one of the major communication channels, namely social media. For this reason, it is important to point out that although direct and positive hypotheses have been established in this study, these have been proposed with an exploratory character, which allows us to see whether there is an influence of the proposed variables on environmental sustainability, taking into account the influence that publications in restaurants’ social media have had.
The results obtained show very relevant data that should be taken into account for communication strategies regarding the social media of restaurants. First of all, it can be seen that the majority of users surveyed were between 31–45 years old, where a large part has undertaken university studies and have social profiles on Facebook and Instagram.
As for the relationships studied, the perceived value by followers through social media has a direct and positive influence on the continuance intention toward following the restaurant in its social media. This relationship has been extensively studied [
7,
62] and has a very high influence. Likewise, the influence of perceived value on satisfaction and trust, two of the most important variables of relational marketing, is also direct and positive [
141], and these influences were shown clearly and meaningfully.
In the analysis of user satisfaction and their influences, it should be noted that two of the three relationships studied were rejected. It was not demonstrated that the influence of user satisfaction on environmental sustainability was significant; on the contrary, it was demonstrated that their satisfaction has a direct and positive influence on the confidence they have in the restaurant, supporting the majority of the studies analyzed in the bibliography [
88,
89]. One of the results to emphasize within the research is the non-direct and positive influence of the satisfaction on the intention of continuity, although the relation, if it is significant, the analysis shows that the influence was the inverse one, where the continuance intention influences the satisfaction of the users.
Regarding trust, the two relationships raised were confirmed, where trust directly and positively influenced the intention of continuity, and trust significantly directly and positively influenced environmental sustainability.
Finally, continuance intention also directly and positively influenced environmental sustainability.
In this study, it was found that the influence of the company on users was relevant and that organizations could significantly influence their users such that they had a greater awareness of environmental sustainability through publications on their social media, where Facebook and Instagram were the platforms used most by users.
Another relevant finding were the results obtained from the environmental sustainability and satisfaction relationship, where the results indicated that there was no direct and positive relationship since the relationship was not significant.
8. Conclusions
The importance of this study focuses on the relevance of environmental sustainability today for society as a whole and specifically for companies. For this reason, this analysis focused on the services sector, one of the most important sectors for Spain, and specifically on the food and beverage sector. The food and beverage sector is the most accessible to all types of users and the one with the greatest possibility of influencing society. Therefore, it was studied whether restaurants through their social media influenced their followers and thus improved environmental sustainability.
In this study, several conclusions were reached that helped the decision-making of restaurant managers and community managers to plan communication strategies through social media since environmental sustainability has become one of the main concerns of the population.
One of the main objectives that organizations have in their strategies is to keep their followers. This study concludes that a follower who had a high level of perceived value will almost entirely intend to continue having a relationship with the organization. Similarly, a follower who appreciated the value in restaurant social media posts, a follower who is satisfied will build confidence in the company. This means that if an organization wants to increase the levels of satisfaction, trust, and continuance intention, it must generate publications that create value for its followers. Therefore, Hypotheses H1, H2, and H3 were validated.
In terms of satisfaction, it can be seen in the study that a restaurant that had satisfied its followers using social media will generate trust in the followers toward it but will not influence environmental sustainability directly. It was also concluded in this study that satisfaction did not influence the continuance intention. Therefore, Hypotheses H4 and H5 were not validated and Hypothesis H6 was accepted.
Regarding trust, it should be noted that users who had optimal levels of trust in the restaurant were followers who intended to continue following the restaurant, just as a follower with trust was a follower who would positively influence the restaurant’s environmental sustainability campaigns. Hypotheses H7 and H8 were therefore validated.
Finally, a follower who intended to continue following the restaurant on social media was a follower who to some extent saw positive environmental sustainability campaigns and collaborated with them. Hypothesis H9 was therefore validated.
It should be noted that if the company wants to carry out environmental sustainability campaigns through the social media of restaurants, it is important that managers enhance the confidence of followers toward the restaurant as this will have a decisive influence on the success of the campaign.
This study has some main implications for food and beverage company managers: First, managers of these companies must pay more attention to the values that are passed on to their customers since there was a positive relationship between customers’ perceived value from the company and the variables like continuance intention, trust, and satisfaction. Therefore, if companies had customers who trusted them, were satisfied with the service and goods, and planned to continue buying products and services from the company, this will lower the possibility that the company will have problems in the future. Second, if managers of food and beverage companies want to carry out environmental sustainability campaigns through the social media of restaurants, it is important to enhance the confidence of followers toward the restaurant as this will have a decisive influence on the success of the campaign. Finally, managers of food and beverage companies should know that to be sustainable is the duty of all citizens and if they participate to make their consumers aware of it, they will participate and protect the environment for future generations.
However, these implications cannot be generalized since previous studies have shown that there are different cultural differences that influence on customers’ behaviors, motivation, emotion, or evaluation choice among others [
142,
143,
144], and therefore, the results can vary depending on the country.
As in all studies, this paper is not short of limitations. Our main limitations are in the size, sample, and number of studies consulted previously. Another of the limitations could be the methodology used for this study. According to Hair et al. [
110], there are disadvantages when using the PLS-SEM technique. One of the disadvantages to using PLS-SEM is that it focuses on maximizing partial model structures, which means that it first optimizes the measurement model parameters and then, in a second step, estimates the path coefficients in the structural model. Another limitation to use PLS-SEM for theory testing and confirmation is that there is no adequate global measure of the goodness of a model fit. Finally, these researchers point out that the PLS-SEM parameter estimates are not optimal regarding bias and consistency. Despite the limitations, our study can be considered a first step in the study of restaurant social media on environmental sustainability.
Related to future research on this topic, it would be interesting to analyze the impact of social networks on environmental sustainability using samples collected from all regions of Spain. Also comparison of the result of Spain to one or several countries taking into account the variables of cultural differences would also be useful. In future studies, we will try to study different sectors, not only the food and beverage sector, as well as modifying the background variables of environmental sustainability. In addition, it would be interesting to use a different methodology, such as the Q methodology; with this tool we could quantify qualitative answers for customers and it will allow us to detect blind spots.